OCR A 5.1.3 Acids, Bases and Buffers
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
Arrhenius acid
releases H+ ion in aqueous solution
Arrhenius base
releases OH- ions in aqueous solution
Bronsted-Lowry acid
proton doner
Bronsted-Lowry base
proton acceptor
alkali
water soluble bases
-NaOH
-KOH
-Ca(OH)2
-NH3
-(aq) state symbol
bases
metal oxides/carbonates
(s) state symbol
chloric acid(VII)
HClO4
conjugate acid base pair
NH3 + H2O —> NH4+ + OH-
B2 A1 A2 B1
NH3 / NH4+
H2O / OH-
-linked by transfer of proton
conjugate acid
any species that has gained a proton
conjugate base
any species that has lost a proton
polyprotic acids
donate more than 1 proton
monoprotic
1 mole of monoprotic acid will produce 1 mole of H+ ions
eg: HNO3
diprotic
1 mole of diprotic acid will produce 2 moles of H+ ions
H2SO4
triprotic
1 mole of triprotic acid will produce 3 moles of H+ ions
H3PO4
acid base reaction
-form pH neutral salts
-made from metal from base and non metal from acid
-H+ ions from acid react w/ OH- ions from alkalis to make water
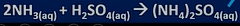
ammonia reaction with acid
-makes ammonia salts
-no water
metal + acid
-salt+ hydrogen




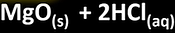



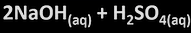
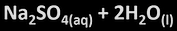




weak acid dissociation
-eg: CH3COOH & other carboxylic acids
-backward reaction favoured; less H+ produced
-only small amount of weak acid dissociates; assume [HA]start = [HA]equilibrium
-dissociation of acid is more than dissociation of water in the sol; assume [H+] = [A-]
![<p>-eg: CH<sub>3</sub>COOH & other carboxylic acids</p><p>-backward reaction favoured; less H+ produced</p><p>-only small amount of weak acid dissociates; assume [HA]<sub>start</sub> = [HA]<sub>equilibrium</sub> </p><p>-dissociation of acid is more than dissociation of water in the sol; assume [H<sup>+</sup>] = [A<sup>-</sup>]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/99402f1d-8dda-4da5-9811-ccbfde30ca3c.png)
strong acid dissociation
-eg: HCl. H2SO4, HNO3
-forward reaction favoured, more H+ produced

how does diprotic strong acid dissociate
-H2SO4 → H+ + HSO4- (first dissociation is strong acid)
-HSO4- → H+ + SO42- (second dissociation is weak acid)
calculate [H+]
strong base dissociation
-eg: NaOH, KOH
-forward reaction favoured; more OH- produced

weak base dissociation
-NH3
-backwards reaction favoured, less OH- produced
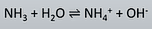
ionic product of water
-water exists in equilibria with its ions; water doesn’t just contain H2O molecules
-water dissociates weakly into H3O + OH-; assume that conc of water is constant

Kw
-same in sol at given temp
-value of 10-14 mol2dm-6
-value changes if temperature changes
Kw in pure water
-[H+] = [OH-]
-Kw = [H+]2
ph
-logarithmic scale that measures conc of H+ ions in solution
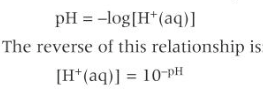
pH of strong acid
HCl —> H+ + Cl-
[strong acid] = [H+]
this only true for monobasic acid
pH of diprotic strong acid
[strong acid] = 2[H+]
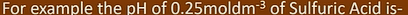

pH of base
-dissociate fully; produce 1 OH- ion every base molecule
-[base] = [OH-]
![<p>-dissociate fully; produce 1 OH- ion every base molecule</p><p>-[base] = [OH-]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/9ab5220b-2253-4673-9637-53d8749646ec.png)

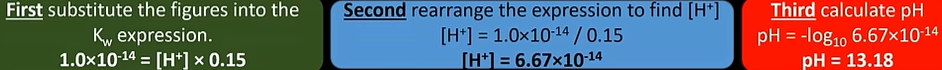
pKa
—logKa
-used for weak acid
-higher the value, weaker the acid

Ka
-acid dissociation constant
-higher the value, less weaker
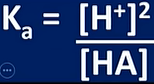
pH of weak acid
-HA(aq) ←> H+(aq) + A-(aq)
-we assume only small amount of weak acid dissociates:
-units; moldm-3

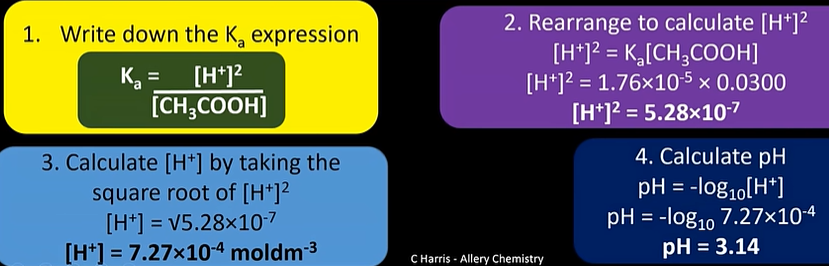


how to measure pH experimentally
-using pH meter but calibrate before
-place in distilled water; shld read 7, if not adjust
-place in standard sol pH 4 and 10; if not show correct pH adjust
-rinse w/ distilled water between each pH sol
titration
-acid/base of known conc in burette
-base/acid unknown conc, known vol in conical flask w/ indicator
-add chemical in burette to conical flask until indicator changes colour (end-point)
-add drop by drop near this point
-read how much of chemical in burette added (bottom of meniscus, eye level)
-record to 2dp till u get concordant results (within 0.1)
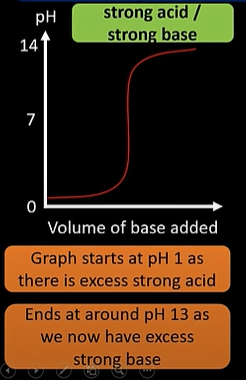
strong acid/ strong base titration curve
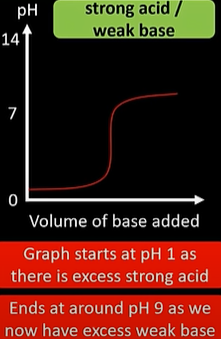
strong acid/ weak base titration curve
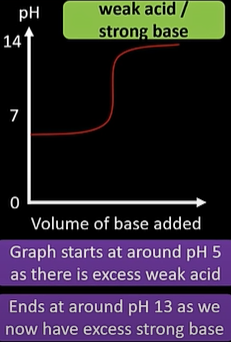
weak acid/ strong base titration curve
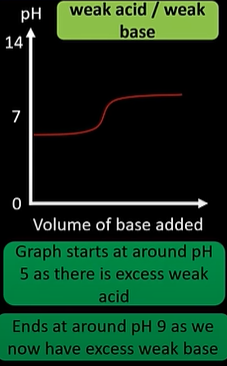
weak acid/ weak base titration curve
equivalence point
-when the vol of 1 sol exactly reacts w/ vol of other sol
-sols have exactly reacted with each other using matching stoichiometry
-assume [H+] = [OH-]
-centre of vertical section of curve
how to choose suitable indicator
-must entirely change colour within vertical part of titration curve
-weak acid/ weak base titration; no indicator suitable


Buffer
-chemical that resists the change in pH when small amounts of acid/base added
-2 types; acidic, base
making buffer
mixture of:
-excess weak acid & conjugate base/ salt
-weak base & conjugate acid
-weak acid & salt
-partial neutralization of excess weak acid by strong alkali (mix both as acid is in excess it partially neutralized by strong alkali to make salt, sol left with weak acid and salt)
buffer solution equilibrium equation
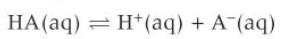
what happens when you add acid to buffer solution
-[H+] increases
-H+ reacts w/ conjugate base A-
-POE shifts left
-most of H+ ions removed
-[HA] increases
what happens when you add alkali to buffer solution
-[OH-] increases
-OH- reacts with H+ to make H2O
-HA dissociates to restore H+ ions
-[H+] increase
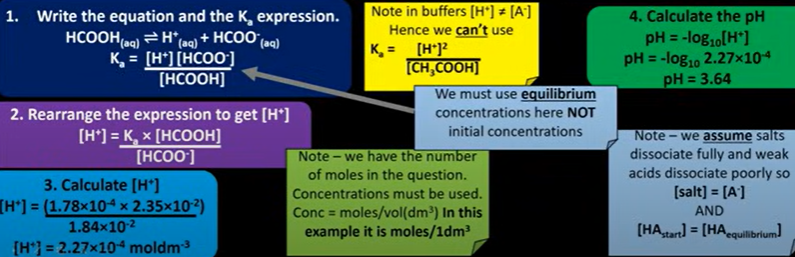
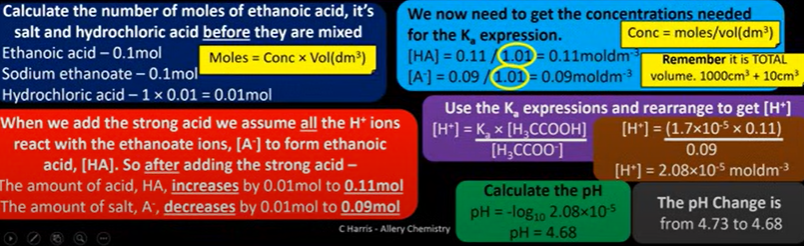
find pH of buffer solution
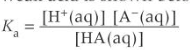


what happens when pH of blood below 7.35
acidosis:
-fatigue
-shortness of breath
-shock
-death
what happens when pH of blood above 7.45
alkalosis:
-muscle spasms
-light headedness
-nausea
buffer system in body
-carbonic acid-hydrogencarbonate buffer system
-H2CO3 + HCO3-
what happens when acid added to blood
-[H+] increases
-H+ reacts w/ HCO3-
-POE shifts left
-[H2CO3] increases
![<p>-[H+] increases</p><p>-H+ reacts w/ HCO<sub>3</sub><sup>-</sup></p><p>-POE shifts left</p><p>-[H<sub>2</sub>CO<sub>3</sub>] increases </p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/e4234a46-95bf-42c3-83f0-61379a5a0d35.png)
what happens when alkali added to blood
-[OH-] increases
-OH- reacts with H+ to make H2O
-H2CO3 dissociates to restore H+ ions
-[H+] increase