Astronomy Exam 2
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
electromagnetic radiation
an electric and magnetic disturbance that transports energy at the speed of light c
wavelength (λ)
the distance between the peaks of a wave
nanometers
Nanometers are a unit of measurement equal to one billionth of a meter, used to measure wavelengths of light
Frequency (v)
the number of waves that pass a stationary point in 1 second
photon
packet of light waves that can act as a particle or as a wave. The energy carried by a photon is proportional to its frequency and inversely proportional to its wavelength.
spectrum
display of light that is viewed or recorded after being sorted in order of wavelength or frequency
complete electromagnetic spectrum
gamma-rays, X-rays, ultraviolet (UV) radiation at the higher frequencies, and infrared (IR) radiation, microwaves, and radio waves at the lower frequencies
atmospheric windows
specific wavelength ranges in the electromagnetic spectrum where Earth's atmosphere allows certain types of radiation, like visible light and radio waves, to pass through with minimal absorption.
Refracting telescopes
Use a primary lens to bend and focus light onto an image
Reflecting telescopes
Easier to build than refracting/ use a primary mirror to focus the light. Is not affected by chromatic aberration
eyepiece
Magnifies the image produced by the telescope’s primary lens or mirror
focal lengths
The distance between the lens and the image sensor when the subject is in focus.
chromatic aberration
causes refracting telescopes to not bring all colors to the same focus, resulting in color fringes around the images
achromatic lens
corrects for chromatic aberration
optical telescopes
reflecting telescopes:
use lenses or mirrors to gather and focus light from distant objects
radio telescopes
reflecting telescopes:
are astronomical instruments that detect radio waves from space.
light-gathering power
The telescopes ability to collect light, most important feature
Resolving power
the ability of a telescope to reveal fine detail and is expressed by the equation
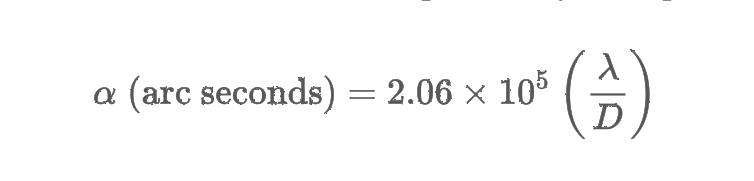
Diffraction fringes
caused by the interaction of light waves with the telescope’s apertures, limit the amount of detail that can be seen
Magnifying power
the ability of a telescope to make an object look bigger, least important
Mountains for observatories
The air on top of a mountain is relatively steady, and the seeing is better
Observatories are located far from cities to avoid light pollution
reflecting telescope focuses
light first comes to a focus at the prime focus, but a secondary mirror can direct light to other locations such as the Cassegrain focus. The Newtonian focus and Schmidt-Cassegrain focus are other focus locations used in some smaller telescopes
sidereal drive
Because Earth rotates, telescopes must have this to stay pointed at celestial objects
Spectrographs
using prisms or a grating spread light out according to wavelength to form a spectrum, revealing hundreds of spectral lines produced by atoms and molecules in the object being studied
comparison spectrum
contains lines of known wavelengths allows astronomers to measure the precise wavelengths of individual spectral lines produced by an astronomical object
Cosmic rays
are not electromagnetic radiation; they are subatomic particles such as electrons and protons traveling at nearly the speed of light, arriving from mostly unknown cosmic sources
Atom
Contains a nucleus surrounded by a cloud of electrons
nucleus
made up of one or more positively charged protons and, except for hydrogen, uncharged neutrons
isotopes
Atoms of the same element (that is, having the same number of protons) with different numbers of neutrons
ion
an atom that has lost or gained an electron through ionization
Coulomb force
The force that allows electrons in an atom are attracted to the nucleus
excited atom
an electron is raised to a higher orbit by a collision between atoms or the absorption of a photon having the proper energy
thermal energy
The sum of the agitation of the particles in an object, heat is the flow
blackbody radiation
Collisions among the particles in a hot, dense object accelerate electrons and cause the emission of this
Stefan-Boltzmann law
states that the hotter an object, the more total energy the blackbody radiates
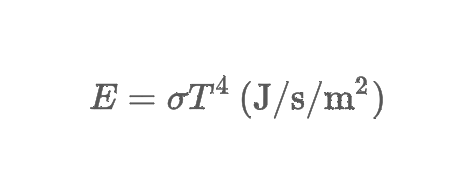
Wien’s law
quantifies the relationship between a blackbody’s temperature and the wavelength of maximum intensity
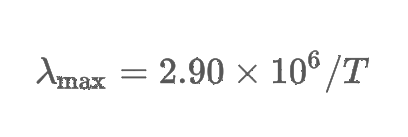
Kirchhoff’s 1st law
a hot solid, liquid, or dense gas emits electromagnetic radiation at all wavelengths and produces a continuous spectrum
Kirchhoff’s 2nd law
an excited, low-density gas produces an emission spectrum containing emission lines
Kirchhoff’s 3rd law
a light source viewed through a low-density, cool gas produces an absorption spectrum containing absorption lines
Doppler effect
The change in wavelength of radiation- red receding, blue moving towards
Balmer series
Spectral lines in the visible and near-ultraviolet spectrum of hydrogen produced by transitions whose lowest orbit is the second.
Radial velocity
the part of its velocity directed toward or away from Earth, what the doppler effect reveals
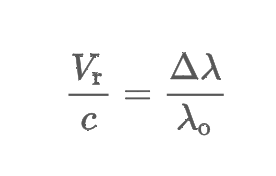
granulation
The fine structure visible on the solar surface caused by rising currents of hot gas and sinking currents of cool gas below the surface.
helioseismology
The study of the interior of the Sun by the analysis of its modes of vibration.
magnetic carpet
The widely distributed, low-level magnetic field extending up through the Sun’s visible surface
Maunder butterfly diagram
A graph showing the latitude of sunspots versus time; first plotted by W. W. Maunder in 1904.
solar constant
A measure of the energy output of the Sun; the total solar energy striking 1 m2 just above Earth’s atmosphere in 1 second.
proton–proton chain
A series of three nuclear reactions that build a helium atom by adding together protons; the main energy source in the Sun.
neutrino
A neutral, massless atomic particle that travels at or nearly at the speed of light.
Photosphere
the innermost layer of the Sun's atmosphere, emitting visible light. It is the region where energy is transferred from the Sun's core to the outer atmosphere