PSYC 3040 Q3
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
Real Movement
An object is really moving
Apparent Movement
A stationary object is appearing in different positions, creating illusion of movement
Induced Movement
The movement of one object gives illusion that another object is moving
Movement after effect
When you look at something moving for a while, afterwards things will still appear to be moving
Freeze response
Because moving objects tend to capture attention more, animals developed a freeze response to not get caught
Kinetic Depth Effect
Movement of a 2D object’s shadow can change into perception of a 3D object
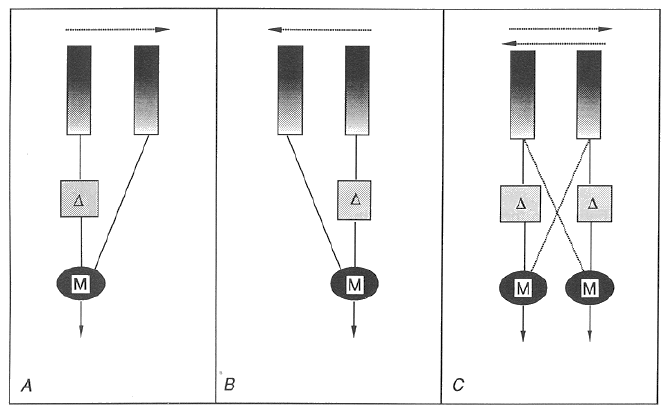
Reinhardt Detector
Used to detect motion
Two receptors , one is delayed, when they both reach at same time there is motion
Corollary Discharge signal
A copy of the eye movement is sent to visual cortex so it can tell when things are actually moving
Motor Signal
Signal sent to eyes to move eye muscles
Image Displacement Signal
Something is moving across the retina
What combination of Corollary Discharge and Image Displacement signal indicates motion?
Either only Corollary Discharge OR only Image Displacement, but not both
Evidence for corollary discharge theory
If we stare at stationary dot, and then move our eyes when we see afterimage, we perceive motion
What area of the visual pathway is responsive for motion detection)
Medial Temporal (MT) Cortex (also called V5)
Biological Motion
Placing lights on specific points of a person make it very easy to tell what is happening
Where is biological motion processed in the brain?
superior temporal sulcus (STS)
______ ________ is Inability to perceive a change in scene
Change Blindness
Examples of Change Blindness
Artificial Displays, Realistic Images, Mud splash, Continuity errors, change blindness
Inattentional Blindness
Failure to perceive unexpected objects.
Inattentional blindness vs Inattentional amnesia
Inattentional Blindness: failure to perceive stimulus
Inattentional amnesia: perceived stimulus but forgot
_______ moiton masks ______ motion in magic
Big; small
Where does action happen when pickpocketing/magic
It happens where the performer is not looking
We don’t mutlitask, we ______ between tasks
switch
If tasks are demanding what can be seen?
Performance dips
Which attention is called top-down attention
Endogenous attention
Which attention is called bottom-up attention?
Exogenous attention
paying attention to things that are different is called _____ attention
Exogenous
Visual salience
areas of stimuli that attract attention due to their properties
Feature search comes under which attention?
Exogenous
Which attention is known as “slow and serial”
Endogenous
which attention is “fully parallel”?
Exogenous
Conjunction and spatial search is associated with which attention?
Endogenous
Rank each search, from 1-3 with 1 being fast and 3 being slow, with the time taken to identify the object: Spatial Search; Feature Search; Conjunction Search
Feature Search
Conjunction Search
Spatial Search
Overt vs Covert attention
Overt: Involves looking directly at the object
Covert: attention without looking
Unattended objects are processed _______
slowly
Who’s study serves as evidence for mis-binding
Triesman & schmidt study
What happens in “preattentive stage” in the context of Feature Integration Theory
pre-attentive stage: feature of object are separated
What happens in the “Focused attention stage” in the context of Feature Integration Theory
features are bound into a coherent perception
In Dichotic listening task, people seem not to be processing the ______ stream?
ignored
What are some exceptions in the Dichotic listening task?
Hearing one’s own name, cuss words, intrusions
Shadowed and unshadowed
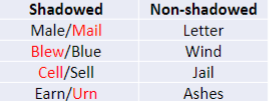
paying attention to things that are relevant is called _____ attention
endogenous
Unattended objects receive ________ processing
shallower
What are the 3 disorders of neglect
Hemispatial neglect, Extinction, Balint syndrome
Define Neglect
The inability to attend to or respond to stimuli in the contralesional visual field
Which side is usually neglected for people with visual neglect?
Left side
How can neglect be diagnosed?
Line cancellation task, Line bisection task, Copying pictures, objects, Drawing objects
What causes neglect?
Lesion in the right parietal lobe
Why is neglect usually on the left?
Due to the asymmetric attention in the brain.
PS: Left lobe controls attention to the right whereas right lobe controls attention to both sides.
The inability to perceive a stimulus in the presence of another is called
extinction
What causes neglect?
Lesion to right parietal lobe
Symptoms of Balin’t syndome
hard to reach out and touch/grab object (spatial localization ability)
very little eye movement, tend to stare straight
Behaves as if can only see one object at a time.
What causes balin’t syndrome?
Lesion to both sides of the brain.