THIS IS A MISTAKE, IGNORE
1/293
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
294 Terms
A nurse is assessing a child who has a rotavirus infection. Which of the following findings should the nurse expect?
Select all that apply.
a
Fever
b
Vomiting
c
Watery stools
d
Bloody stools
e
Confusion
a Fever
b Vomiting
c Watery stools
Confusion is a manifestation of Salmonella
Bloody stools are a manifestation of E. coli.
A nurse is teaching a group of parents about Salmonella. Which of the following information should the nurse include in the teaching?
Select all that apply.
a
Incubation period is nonspecific.
b
It is a bacterial infection.
c
Bloody diarrhea is common.
d
Transmission can be from house pets.
e
Antibiotics are used for treatment.
b It is a bacterial infection.
c Bloody diarrhea is common.
d Transmission can be from house pets.
The incubation period of Salmonella is 6 to 72 hr.
Salmonella is a bacterial infection. Antibiotics are not prescribed unless complications occur.
A nurse is teaching a group of caregivers about E. coli. Which of the following information should the nurse include in the teaching?
Select all that apply.
a
Severe abdominal cramping occurs.
b
Watery diarrhea is present for more than 5 days.
c
It can lead to hemolytic uremic syndrome.
d
It is a foodborne pathogen.
e
Antibiotics are given for treatment.
a Severe abdominal cramping occurs.
c It can lead to hemolytic uremic syndrome.
d It is a foodborne pathogen
A nurse is caring for a child who is suspected to have Enterobius vermicularis. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
a
Perform a tape test.
b
Collect stool specimen for culture.
c
Test the stool for occult blood.
d
Initiate IV fluids
a Perform a tape test.
Stool cultures are obtained to diagnose Salmonella or C. difficile infection
A manifestation of E. coli is bloody stools.
A nurse is caring for a child who has had watery diarrhea for the past 3 days. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
a
Offer chicken broth.
b
Initiate oral rehydration therapy.
c
Start hypertonic IV solution.
d
Keep NPO until the diarrhea subsides.
b Initiate oral rehydration therapy.
Isotonic IV solutions are recommended for children who experience severe dehydration.
Chicken broth is avoided for children who have diarrhea because of its increased sodium and inadequate carbohydrates.
Children who experience diarrhea are at risk for dehydration. Keeping them NPO is contraindicated.
A nurse is caring for an infant who has just returned from the PACU following cleft lip and palate repair. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
a
Remove the packing in the mouth.
b
Place the infant in a side-lying position.
c
Offer a pacifier with sucrose.
d
Assess the mouth with a tongue blade.
Submit
b Place the infant in a side-lying position.
The nurse should place the infant in a side-lying position to facilitate drainage and prevent aspiration.
The packing in the mouth should stay in place for 2 to 3 days
Objects in the mouth could injure the surgical site and should be avoided.
A nurse is teaching a parent of an infant who has gastrointestinal reflux disease. Which of the following should the nurse include in the teaching?
Select all that apply.
a
Offer frequent feedings.
b
Thicken formula with rice cereal.
c
Use a bottle with a one-way valve.
d
Position infant upright after feedings
e
Use a wide-based nipple for feedings.
a Offer frequent feedings.
b Thicken formula with rice cereal.
d Position infant upright after feedings
A bottle with a one-way valve and wide-based nipple is used for an infant who has cleft lip and palate.
A nurse is caring for a child who has Hirschsprung’s disease. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
a
Encourage a high-fiber, low-protein, low-calorie diet.
b
Prepare the family for surgery.
c
Place an NG tube for decompression.
d
Initiate bed rest.
b Prepare the family for surgery.
A client who has Meckel’s diverticulum is placed on bed rest to prevent further bleeding.
A client who has Hirschsprung’s disease is managed nutritionally. Placing an NG tube for decompression is not an appropriate action for the nurse to take.
A client who has Hirschsprung’s disease is encouraged to eat a low-fiber, high-protein, high-calorie diet.
A nurse is planning care for a 10-month-old infant who is 8 hr postoperative following cleft palate repair. Which of the following interventions should the nurse include in the infant's plan of care?
Feed the infant with a spoon for 48 hr.
Apply and release elbow restraints every hour.
Keep the infant supine.
Suction the mouth with an oral suction tube.
Apply and release elbow restraints every hour.
A nurse is caring for a 6-week-old infant who has a pyloric stenosis. Which of the following clinical manifestations should the nurse expect?
Red currant jelly stools
Distended neck veins
Projectile vomiting
Ridged abdomen
Projectile vomiting
A nurse is providing teaching to a parent of a child who has Hirschsprung disease is scheduled for initial surgery. Which of the following statements by the parent indicates an understanding of the teaching
"I'm glad that my child's ostomy is only temporary."
"I'm glad my child will have normal bowel movements now."
"I want to learn how to use my child's feeding tube as soon as possible."
"I want to learn how to empty my child's urinary catheter bag."
"I'm glad that my child's ostomy is only temporary."
A nurse is caring for an infant who has inadequate motility of part of the intestine resulting in a mechanical obstruction. The nurse should identify this finding as a manifestation of which of the following disorders?
Encopresis
Enterocolitis
Pyloric stenosis
Hirschsprung's disease
Hirschsprung's disease
A nurse is caring for an infant who has gastroesophageal reflux. The nurse should recognize that which of the following findings are associated with this condition?
Vomiting
cyanosis or apnea during crying
Weight loss
Respiratory issues, including wheezing
increased urine output
fever
Vomiting
cyanosis or apnea during crying
Respiratory issues, including wheezing
A nurse is admitting a 6-month-old infant who has dehydration. Which of the following amounts of urinary output should indicate to the nurse that the treatment has corrected the fluid imbalance?
0.5 mL/kg/hr
1-3 mL/kg/hr
7.5 mL/kg/hr
15 mL/kg/hr
1-3 mL/kg/hr
A nurse is admitting an infant who has severe dehydration from acute gastroenteritis. Which of the following findings should the nurse expect?
Bulging anterior fontanel
Bradypnea
13% weight loss
Capillary refill 3 seconds
13% weight loss
A nurse is caring for an infant who has gastroesophageal reflux. The nurse should place the infant in which of the following positions following feedings?
Place the infant in a prone position.
Place the infant in an infant seat.
Place the infant on his left side.
Place the infant on his right side.
Place the infant in an infant seat.
The provider has ordered an IV fluid bolus. The amount should be calculated using which of the following equations.
A. 5 mL/kg
B. 10 mL/kg
C. 20 mL/kg
D. 30 mL/kg
C. 20 mL/kg
When administering an IV fluid bolus for pediatric patients, the standard formula is 20 mL/kg of isotonic fluids (e.g., normal saline or lactated Ringer’s).
This bolus is typically given over 30 to 60 minutes in cases of dehydration or shock.
Exceptions:
Neonates and preterm infants may receive 10 mL/kg due to their immature cardiovascular system.
Patients with cardiac conditions may require lower volumes and slower administration.
An E. Coli infection could lead to what complication?
A. Constipation
B. Glomerulonephritis
C. Beta hemolytic strep
D. Hemolytic uremic syndrome
D. Hemolytic uremic syndrome
Foods to avoid during an episode of diarrhea include
A. milk
B. apples
C. apple juice
D. rice
C. apple juice
High in fructose and sorbitol, which can pull water into the intestines and worsen diarrhea.
Can cause osmotic diarrhea, making symptoms persist.
Rice → A part of the BRAT diet (Bananas, Rice, Applesauce, Toast), which helps bind stools.
Apples → Whole apples are high in fiber, but applesauce (low in fiber) is recommended for mild diarrhea.
Postoperative care for cleft lip and palate repair includes all of the following EXCEPT
A. keep infant pain free to decrease crying
B. positioning infant on stomach to facilitate drainage
C. avoid items that can be placed into mouth (pacifier, straw, spoon, etc)
D. apply elbow restraints to keep infant from injuring surgical site
B. positioning infant on stomach to facilitate drainage
A classic sign of pyloric stenosis is
A. weight gain
B. palpation of an olive shaped mass
C. scaphoid abdomen
D. need to change formula type
B. palpation of an olive shaped mass
A bowel condition that affects the entire GI tract is
A. Appendicitis
B. Celiac disease
C. Ulcerative colitis
D. Crohn disease
D. Crohn disease
Cardiac arrythmias can be associated with eating disorders where significant weight loss has been achieved.
A. True B. False
A. True
Crohn’s S/S
Anxiety
n/v/d
Slight fever
Appendicitis S/S
n/v/d
Rebound tenderness
Recent viral illness
Slight fever
Umbilical pain and guarding
GI Virus S/S
n/v/d
Slight fever
A nurse is providing education to parents of a toddler at a well-child checkup. Which of the following statements should the nurse include when discussing the prevention of food aversion or neophobia in young children?
Restrict the toddler's diet to familiar foods to prevent negative food associations.
Take away the toddler's favorite toy when they refuse to try new foods.
Introduce new foods to the toddler's diet frequently and encourage tasting.
Discourage the toddler from expressing dislikes to prevent negative food associations.
Introduce new foods to the toddler's diet frequently and encourage tasting.
Exposure to a variety of foods helps toddlers develop a diverse palate and reduces the likelihood of developing aversions to certain foods. Encouraging tasting, even if the toddler initially shows resistance, promotes acceptance over time.
A school nurse is caring for a 6-year-old child who has been experiencing constipation. The nurse is explaining to a nursing student that children who have constipation are at an increased risk of psychosocial problems. Which of the following factors contribute to this risk? (Select all that apply.)
Longer duration of illness
Older age of onset
Lack of interest in extracurricular activities
Fecal incontinence
Living in rural areas
Fecal incontinence is correct. Fecal incontinence with constipation can be emotionally distressing and may contribute to psychosocial problems in affected children.
Living in rural areas is correct. Children living in rural areas may face challenges accessing health care resources promptly, potentially leading to a longer duration of constipation and an increased risk of psychosocial problems.
Longer duration of illness is correct. A longer duration of constipation can lead to prolonged discomfort and distress, contributing to psychosocial problems in affected children.
Older age of onset is correct. Older children who have constipation may be more aware of their symptoms, leading to increased embarrassment and a higher risk of psychosocial problems.
Lack of interest in extracurricular activities is incorrect. While constipation may lead to social isolation, the lack of interest itself is not a direct factor that leads to psychosocial problems for children who have constipation.
A nurse is caring for a child who has been newly diagnosed with anorexia nervosa. The parents ask the nurse to tell them more about the condition. Which of the following responses should the nurse include?
"Anorexia nervosa is considered an indication of rebellion."
"Anorexia nervosa is learned from others, such as friends or influencers."
"Anorexia nervosa can lead to rigid patterns of eating."
"Anorexia nervosa distorts the way a person's self-image but does not impact physical activity."
"Anorexia nervosa can lead to rigid patterns of eating."
Anorexia nervosa can lead to rigid patterns of eating as a result of disruptions in the brain's neurotransmitters, and other functions of the brain.
A nurse is caring for an infant who has celiac disease. The parents ask the nurse for clarification after the provider explained the pathophysiology to them. Which of the following answers should the nurse provide for the parents?
"Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder resulting from an intolerance to gluten."
"Celiac disease results from developing negative attitudes towards food and eating."
"Celiac disease occurs when the intestine telescopes within itself."
"Celiac disease results in the leaking of fecal matter from the rectum."
"Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder resulting from an intolerance to gluten."
Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder characterized by an intolerance to gluten. The body is unable to breakdown gluten, causing an accumulation in the body, which can disrupt the villi and absorption of nutrients.
Developing negative attitudes towards foods and eating relates more to eating disorders and not celiac disease.
The intestine telescoping within itself relates to intussusception and not celiac disease.
Leaking of fecal matter from the rectum relates to encopresis and not celiac disease.
A nurse is caring for an infant who has a cleft lip and cleft palate. Which of the following communication techniques is therapeutic for infants?
Speak loudly and clearly to capture the infant's attention.
Maintain a friendly expression and use a soft, calm voice.
Use a firm touch to stimulate the infant's response.
Avoid responding to the infant's nonverbal cues to prevent overstimulation.
Maintain a friendly expression and use a soft, calm voice.
A nurse is providing education with the parents of a child who has constipation. The provider has prescribed polyethylene glycol (PEG). Which of the following instructions should the nurse include?
"Expect a bowel movement within a few hours after giving polyethylene glycol."
"Give polyethylene glycol only when the child appears visibly uncomfortable due to constipation."
"Give polyethylene glycol with food to enhance its effectiveness."
"Notify your provider if your child experiences abdominal distension."
"Notify your provider if your child experiences abdominal distension."
Polyethylene glycol (PEG) is an osmotic laxative that softens stool by drawing water into the intestines, making bowel movements easier.
Adverse effects include flatulence, nausea, stomach, diarrhea, abdominal swelling, rectal hemorrhage, electrolyte imbalance, dehydration, and metabolic acidosis. Adverse effects should be reported to the child's provider.
A child may have a bowel movement within a few hours of taking PEG, but it often takes more time and immediate results should not be expected. Providing accurate expectations helps prevent unnecessary concerns and interventions.
PEG can be given in a glass of water, coffee, or hot chocolate. The child should not eat for 2 hr before taking PEG.
PEG is often prescribed for regular use, regardless of the child's current discomfort level. Waiting until the child is visibly uncomfortable may result in inadequate prevention of constipation, as the medication is more effective when used consistently.
A nurse is providing education for the parents of a newborn who has a cleft palate. The parents express concern about when and how the cleft palate occurred. Which of the following responses by the nurse is correct?
"Cleft palate is when the esophagus does not develop properly during the sixth week of pregnancy."
"Cleft palate occurs due to an increase in amniotic fluid during the first twelve weeks of pregnancy."
"Cleft palate occurs due to a deficiency of folic acid in the second trimester of pregnancy."
"Cleft palate is the incomplete fusion of the roof of the mouth during the sixth or seventh week of gestation."
"Cleft palate is the incomplete fusion of the roof of the mouth during the sixth or seventh week of gestation."
While folic acid is important for neural tube development, cleft palate is primarily caused by the incomplete fusion of the palatal shelves, not a deficiency in folic acid.
A nurse is caring for a 1-year-old child who has a history of diarrhea for the past two days. The child is alert, oriented, and has had one wet diaper in the last 6 hr. Which of the following actions is most appropriate for encouraging hydration in this situation?
Providing electrolyte drinks through a syringe
Introducing frozen banana slices to encourage the 1-year-old child to eat
Offering the child a choice between a yellow or orange popsicle
Offering apple juice in a bottle or sippy cup
Providing electrolyte drinks through a syringe
Since the child is alert, oriented, and has had a wet diaper, they are either experiencing mild or no dehydration. Offering oral rehydration is an appropriate option. In situations where a 1-year-old child may be unwilling to drink fluids, providing electrolyte drinks through a syringe can help enhance oral rehydration.
A sugary popsicle is not the best choice. Older children may do well with frozen electrolyte popsicles that are not sugary, but they may not be the best choice for a 1-year-old child.
A nurse is providing education for the parents of an infant who has pyloric stenosis. Which of the following statements by the parents indicates they understand the underlying cause of pyloric stenosis?
"The pylorus is not producing enough stomach acid, leading to vomiting."
"There is a blockage in the intestines, causing the food to come back up."
"The muscles around the pylorus have become too thick, causing a blockage that leads to vomiting."
"An overproduction of digestive enzymes in the stomach causes vomiting."
"The muscles around the pylorus have become too thick, causing a blockage that leads to vomiting."
Pyloric stenosis is characterized by the thickening of the muscles around the pylorus, leading to a narrowing of the passage between the stomach and the small intestine which causes vomiting.
A nurse is collaborating with a nursing student in caring for a 3-year-old toddler who has a new onset of feeding issues. Which of the following statements should the nurse give when the student asks about the leading causes of feeding issues in toddlers?
"Feeding issues in toddlers are commonly due to an underlying congenital defect."
"Feeding issues in toddlers are commonly due to fear of certain foods."
"Feeding issues in toddlers are commonly due to cognitive delay."
"Feeding issues in toddlers are commonly due to oral motor skills."
"Feeding issues in toddlers are commonly due to fear of certain foods."
Food neophobia is a common cause of feeding issues for toddlers and preschoolers.
An emergency department nurse is caring for a 2-year-old toddler who has dehydration due to diarrhea and no past medical history. The toddler presents with lethargy and has not had any urine output in the last 12 hr. Which of the following treatments should the nurse expect the provider to prescribe?
Oral rehydration solution (ORS) at a rate of 200 mL/5 kg of body weight
IV bolus of 20 mL/kg of 0.9% sodium chloride (normal saline) over 10 to 20 min
IV bolus of 10 mL/kg of 0.9% sodium chloride (normal saline) over 10 to 20 min
Maintenance IV fluid rate of dextrose 5% in 0.9% sodium chloride (normal saline) with 20 mEq of potassium
IV bolus of 20 mL/kg of 0.9% sodium chloride (normal saline) over 10 to 20 min
ORS at this dose may be appropriate for a toddler who has mild or moderate dehydration but not for a toddler who has manifestations of severe dehydration who is lethargic and has had no urine output for over 12 hr
Maintenance fluid may be appropriate for a toddler who has mild or moderate dehydration but not for a toddler who has manifestations of severe dehydration who is lethargic and has had no urine output for over 12 hr. In addition, the nurse should not give potassium until the toddler has had at least one urinary output.
The nurse is providing education for the parents of a 2-month-old infant who has gastroesophageal reflux (GER). Which of the following responses should the nurse give to clarify the pathophysiology?
GER occurs when muscle at the bottom of the infant's food pipe is weak, causing milk or formula to flow back up.
GER is a condition where the muscle at the outlet of the stomach thickens, causing milk and formula to flow back up.
GER is a condition where the stomach lining is inflamed, causing milk and formula to flow back up.
GER is a condition where the upper intestines develop sores, causing milk and formula to flow back up.
GER occurs when muscle at the bottom of the infant's food pipe is weak, causing milk or formula to flow back up.
An underdeveloped or weak lower esophageal sphincter, causes milk or formula to flow back up from the stomach into the esophagus, causing spit-up. This clarifies the pathophysiology in easy-to-understand terminology.
Pyloric stenosis, rather than GER, is a condition in which the muscle at the outlet of the stomach thickens, leading to projectile vomiting.
Gastritis, rather than GER, is described as inflammation of the stomach lining which can cause symptoms such as heartburn and regurgitation.
Sores that develop on the lining of the stomach or upper part of the small intestine describes a condition such as peptic ulcers rather than GER.
A nurse is caring for a 4-year-old preschooler who is vomiting. Which of the following statements indicates the guardian understands the most common underlying cause of vomiting in children?
"My child is most likely vomiting because of a food allergy."
"My child is most likely vomiting due to the stomach bug their friend had."
"My child is most likely vomiting because they ate too much candy today."
"My child is most likely vomiting due to stress about starting preschool."
"My child is most likely vomiting due to the stomach bug their friend had."
Gastrointestinal infections, often caused by viruses, are a common cause of vomiting in children. The guardian's mention of a stomach bug and recent contact with a sick friend aligns with this common cause.
A nurse is caring for a newborn who has a cleft lip. Which of the following statements by the parents indicates a need for further teaching regarding the management of a cleft lip?
"We should use a special bottle with a squeezable nipple to control the flow of milk."
"We can gently clean the infant's mouth with a soft cloth after feedings."
"We should start dental care early, even before the infant gets teeth."
"We should wait to see a speech therapist until our child is speaking."
"We should wait to see a speech therapist until our child is speaking."
Delaying support may lead to difficulties in speech development.
A nurse is conducting a home visit for a 9-month-old infant who has failure to thrive (FTT). The infant's parent has a full-time job and attends graduate school. The parent suspects the infant may have a malabsorption disorder. Which of the following psychosocial risk factors should the nurse identify as a likely contributing factor to the infant's FTT?
Parent education
Underlying medical condition
Time scarcity
Infant's age
Time scarcity
Time scarcity can lead to inconsistent feeding schedules, which can contribute to FTT as regular nourishment is crucial for an infant's growth and development. If the work hours of the parents are erratic, it may interfere with consistent feeding times, thereby impacting the infant's nutritional intake.
A nurse on a pediatric unit is caring for a group of clients who have gastrointestinal disorders. Review the images of each disorder and place the expected findings for each disorder with the correct image.
Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis
Intussusception
Hirschsprung’s disease
Foul-smelling, ribbon like stools
Sausage shaped abdominal mass
Constant hunger
Failure to pass meconium within 48 hours after birth
Sudden, episodic abdominal pain
Projective vomiting
Bilious vomiting
Red, currant-jelly like stools
Olive shaped mass in the RUQ of the abdomen
Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis
Constant hunger
Projective vomiting
Olive shaped mass in the RUQ of the abdomen
Intussusception
Sausage shaped abdominal mass
Sudden, episodic abdominal pain
Red, currant-jelly like stools
Hirschsprung’s disease
Foul-smelling, ribbon like stools
Bilious vomiting
Failure to pass meconium within 48 hours after birth
A nurse is caring for a 2-month-old infant who is postoperative following surgical repair of a cleft lip. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Encourage the parents to hold and rock the infant.
Offer the infant a pacifier.
Administer ibuprofen as needed for pain.
Position the infant on her abdomen.
Encourage the parents to hold and rock the infant.
A nurse is caring for a child who is admitted with suspected acute appendicitis. Which of the following manifestations should indicate to the nurse that the child's appendix is perforated?
Sudden decrease in abdominal pain
Absent Rovsing's sign
Flaccid abdomen
Low-grade fever
Sudden decrease in abdominal pain
A nurse is caring for a child who has acute gastroenteritis but is able to tolerate oral fluids. The nurse should anticipate providing which of the following types of fluid?
Broth
Water
Diluted apple juice
Oral rehydration solution
Oral rehydration solution
A nurse is caring for a 6-month-old infant who has a prescription for clear liquids by mouth after a repair of an intussusception. Which of the following fluids should the nurse select for the infant?
Oral electrolyte solution
Half-strength infant formula
Half-strength orange juice
Sterile water
Oral electrolyte solution
A nurse is providing teaching to a parent of a child who has celiac disease. The nurse should include which of the following food choices for this child?
Barley
Rye
Rice
Wheat
Rice
Google Doc
https://docs.google.com/document/d/1G1PvPO66xwCWuTunzX2h9lqziSuee2hlpSge-HUKDOk/edit?usp=sharing
Mild Dehydration
Normal vitals (behavior, mucous membranes, pulse, BP).
Capillary refill > 2 sec.
Some thirst.
Oral rehydration therapy (ORT) is preferred.
50 mL/kg ORS over 4 hours
Replace diarrhea losses: 10 mL/kg per stool.
Mild Dehydration %
3-5%
Oral rehydration therapy (ORT) is preferred.
50 mL/kg ORS over 4 hours
Replace diarrhea losses: 10 mL/kg per stool.
Moderate Dehydration
Capillary refill 2 - 4 sec.
Irritability, increased thirst.
Slightly increased pulse (BP is normal or orthostatic).
Dry mucous membranes, decreased tears, poor skin turgor.
Mild tachypnea (faster breathing).
Normal to sunken anterior fontanel in infants.
Oral rehydration therapy (ORT) is preferred.
100 mL/kg ORS over 4 hours.
Replace diarrhea losses: 10 mL/kg per stool.
Moderate Dehydration %
6-9%
Oral rehydration therapy (ORT) is preferred.
100 mL/kg ORS over 4 hours.
Replace diarrhea losses: 10 mL/kg per stool.
Severe Dehydration (Emergency)
Capillary refill > 4 sec.
Tachycardia + orthostatic BP drop (risk for shock).
Extreme thirst.
Very dry mucous membranes + tented skin.
Hyperpnea (deep, rapid breathing).
No tears, sunken eyeballs.
Sunken anterior fontanel.
Oliguria or anuria (low or no urine output).
IV fluid therapy is required.
20 mL/kg isotonic IV bolus (Normal Saline or Lactated Ringer’s).
Monitor for signs of increased intracranial pressure.
Do not add potassium until kidney function is confirmed.
Severe Dehydration (Emergency) %
>10%
IV fluid therapy is required.
20 mL/kg isotonic IV bolus (Normal Saline or Lactated Ringer’s).
Monitor for signs of increased intracranial pressure.
Do not add potassium until kidney function is confirmed.
Acute Diarrhea Causes (self resolves in 14 days)
Infection (bacteria, virus, parasites), antibiotic use, foodborne illnesses.
Fatigue, malaise, poor appetite, weight loss, abdominal pain.
Monitor for dehydration signs.
Chronic Diarrhea Causes
Malabsorption syndrome, food allergies, inflammatory bowel disease.
Fatigue, malaise, poor appetite, weight loss, abdominal pain.
Monitor for dehydration signs.
Rotavirus (Acute Diarrhea)
Most common in children under 5
Dx: Stool sample
Fever, watery foul-smelling green diarrhea (5-7 days), vomiting (2 days)
Transmission: Fecal-oral route, 48-hour incubation
Focus on fluid replacement
Norovirus (Acute Diarrhea)
Dx: Stool sample
Severe vomiting, diarrhea, fever, myalgia
Transmission: Contaminated food, water, surfaces
Focus on fluid replacement
Salmonella vs Shigella (Acute Diarrhea)
Bloody diarrhea, fever, abdominal cramping
Raw/undercooked eggs, poultry, pet reptiles
Avoid antimotility agents
Avoid antibiotics (increases toxin release)
Bloody diarrhea, fever, abdominal cramping
Fecal-oral route, contaminated food/water
Avoid antimotility agents
Use antibiotics (Azithromycin or Ciprofloxacin)
E. Coli (Acute Diarrhea)
Watery to bloody diarrhea (1-2 days) and cramping
Contaminated food/water
Avoid antibiotics & antimotility agents (risk of hemolytic uremic syndrome)
Clostridium difficile (Acute Diarrhea)
Watery diarrhea, leukocytosis, fever
Overgrowth after antibiotic use
Metronidazole or Vancomycin
Giardia intestinalis (Acute Diarrhea)
Malodorous, pale, greasy stools, abdominal cramping
Contaminated food/water, pets
Dx: Stool test
Metronidazole, Tinidazole
Enterobius vermicularis (Pinworms)
Perianal itching, irritability, restlessness
Ingestion or inhalation of eggs
Dx: Tape Test
Mebendazole, Albendazole, Pyrantel pamoate
Tape Test (4 steps)
(For Enterobius vermicularis - Pinworms)
Apply transparent tape over the child’s anus at bedtime, preferably when they are asleep.
Remove tape before the child wakes up, ideally before toileting or bathing.
Bring the specimen to the lab for microscopic evaluation.
Practice good hand hygiene during and after the procedure.
Umbilical Hernia
Common, resolves on its own
S/S
Soft, visible bulge or protrusion around the umbilicus (belly button)
Typically painless
Possible discomfort, pain, aching, a distended abdomen, vomiting, fussiness, fever, or redness
Treatment:
Self-limiting or surgery (if beyond age 2-4)
Inguinal Hernia
Risk of strangulation
S/S
Visible bulge or swelling in the groin area.
May be more pronounced when crying, straining, coughing, or passing stool.
In male infants, the hernia may extend into the scrotum.
For female clients, it may appear in the labia majora.
Possible discomfort, pain, aching, a distended abdomen, vomiting, fussiness, fever, or redness
Treatment:
External palpation or surgery
Diaphragmatic Hernia (CDH)
Abdominal organs move into the chest cavity.
Life-threatening and requires surgery
S/S
Severe respiratory distress at birth.
Absent breath sounds on affected side.
Scaphoid abdomen (sunken).
Treatment:
Immediate surgery, ECMO, ICU care.
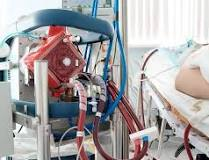
ECMO (Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation)
A machine that takes over heart and lung function when a patient's organs don't work on their own
Cleft Lip & Cleft Palate Patho
Occurs during first trimester when the lip and/or palate fail to fuse.
Can be unilateral (one side) or bilateral (both sides).
More common in males (cleft lip) and females (cleft palate).
Isolated Cleft Lip Feeding
Encourage breastfeeding.
Use a wide-based nipple for bottle feeding.
Squeeze infant’s cheeks together during feeding.
Cleft Palate (or both) Feeding
Feed in an upright position.
Use a one-way valve bottle and specialty nipple.
Burp frequently to reduce air swallowing.
Use syringe feeding if needed.
Cleft Lip Interventions
Cheiloplasty → Performed at 2-3 months
Additional surgeries may be needed for speech and aesthetic improvements.
Postoperative Care:
Pain control to prevent excessive crying (risk of incision rupture).
Monitor surgical site for crusting, bleeding, infection.
No pacifiers, spoons, or objects in the mouth.
Position on the back or side to protect repair.
Use elbow restraints to prevent touching the surgical site.
Cleft Palate Interventions
Palatoplasty → Performed at 6-12 months
Additional surgeries may be needed for speech and aesthetic improvements
Postoperative Care:
Pain control to prevent excessive crying (risk of incision rupture).
Monitor surgical site for crusting, bleeding, infection.
No pacifiers, spoons, or objects in the mouth.
Place in side-lying position to prevent aspiration.
Use elbow restraints to prevent touching the surgical site.
GER
Gastric contents reflux into the esophagus
Common in infants, resolves by 1 year
GER & GERD MAIN S/S (Infants)
Spitting up or forceful vomiting
Blood in vomit
Apnea or respiratory distress
Arching of the back (Sandifer's syndrome)
Failure to thrive
Irritability, excessive crying
GER & GERD MAIN S/S (Children)
Heartburn
Chronic cough
Noncardiac chest pain
Abdominal pain
Difficulty swallowing
GER & GERD Interventions
Small, frequent feedings.
Thicken formula
1 tsp–1 tbsp rice cereal per 1 oz formula.
Avoid triggering foods (caffeine, citrus, peppermint, fried/spicy foods).
Keep child upright after meals.
Infants sleep supine (not prone, side-lying, or upright).
Medications
Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs): Omeprazole, esomeprazole, pantoprazole, rabeprazole.
H2-Receptor Antagonists: Cimetidine, famotidine.
Nissen Fundoplication
Laparoscopic surgery where the top of the stomach (fundus) is wrapped around the esophagus.
GERD
Gastric contents reflux into the esophagus
Tissue damage occurs due to chronic reflux.
Hirschsprung
Absence of ganglion cells in parts of the colon → Decreased peristalsis → Mechanical obstruction
Found on rectal biopsy
Hirschsprung S/S (NBN)
No meconium within 24-48 hours.
Bile-stained vomiting
Abdominal distention
Poor feeding
Hirschsprung S/S (Infant)
Diarrhea alternating with vomiting
Failure to thrive
Chronic constipation
Vomiting
Hirschsprung S/S (Children)
Foul-smelling, ribbon-like stool
Visible peristalsis
Palpable fecal mass
Undernourished, anemic appearance
Abdominal distention
Severe constipation
Hirschsprung Interventions
Watch for enterocolitis (life-threatening bowel infection)
High-protein, high-calorie, low-fiber diet
May require TPN
Foley catheter care
Refer to specialists as needed
Monitor for dehydration signs (low urine output, dry mouth, lethargy)
Therapeutic Procedures
Surgical removal of the affected bowel section
Risk of short bowel syndrome
Nutritional deficiencies, chronic diarrhea
Temporary colostomy may be needed
Lifelong dietary modifications may be required.
Intussusception
Telescoping of bowel leads to venous obstruction & ischemia.
Most common cause of bowel obstruction
Infants 3 months to 6 years
Intussusception S/S
Child screams & draws knees to chest during pain episodes
RUQ Sausage-shaped mass
Red currant jelly stools (blood & mucus mixed)
Fever
Vomiting
Tender, distended abdomen
Sudden, episodic abdominal pain
Intussusception Interventions
Stabilization before procedure:
IV fluids to prevent dehydration.
Nasogastric (NG) tube for decompression if needed.
Therapeutic Procedures
Air Enema:
May be done with or without contrast.
Performed by a radiologist.
Hydrostatic Enema:
Guided by ultrasound.
No radiation exposure.
Surgery if unsuccessful or if bowel is necrotic.
Hypertrophic Pyloric Stenosis
Muscle at the stomach exit thickens, leading to gastric outlet obstruction.
Typically occurs within the first few weeks of life.
Hypertrophic Pyloric Stenosis S/S
Projectile, non-bilious vomiting
May contain blood
Metabolic alkalosis
RUQ Olive-shaped mass
Visible peristaltic waves moving left to right
Constant hunger due to poor gastric emptying.
Dehydration
Pallor, cool lips, dry skin/mucous membranes.
Decreased skin turgor, sunken eyes, thirst.
Decreased urine output (concentrated urine).
Rapid pulse due to dehydration.
Hypertrophic Pyloric Stenosis Interventions
NPO, IV fluids, NG tube decompression
Therapeutic Procedure
Pyloromyotomy (laparoscopic surgery for obstruction).
Reintroduce feeds slowly:
Clear liquids within 4-6 hours post-op.
Breast milk/formula within 24 hours as tolerated.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
Ulcerative colitis (affects the colon).
Crohn’s disease (affects any GI part, patchy lesions).
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) S/S
Weight loss
Bloody diarrhea
Fever
Anemia
Malabsorption
Abdominal pain, diarrhea, cramping, fatiguew
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) Interventions
Medications
Anti-inflammatory drugs: Sulfasalazine, corticosteroids.
Immunosuppressants: Methotrexate, azathioprine.
High-protein, low-fat diet
NPO during exacerbations → Total parenteral nutrition (TPN)
Appendicitis
Inflammation of the vermiform due to obstruction of the lumen.
Risk Factors
Most cases occur around 10 years old.
Appendicitis S/S
Periumbilical pain → RLQ pain (McBurney’s point).
Nausea, vomiting, fever, diarrhea, etc.
If rupture occurs:
Initial pain relief → Peritonitis → Shock.
Appendicitis Interventions
NPO, IV fluids, NG tube decompression.
Antibiotics
Therapeutic Procedures
(Laparoscopic or Open Surgery)
Keep NPO status (nothing by mouth) until bowel function returns.
Administer IV fluids and antibiotics post op
Provide wound irrigation and drain care if open surgery was performed.
Monitor for peritonitis, indicated by:
Fever, tachycardia, chills, pallor
Sudden relief of pain, followed by severe pain
Rigid abdomen, distension, rapid shallow breathing
Avoid heat on the abdomen (can worsen inflammation).
No enemas or laxatives (may cause rupture)
Celiac Disease
Autoimmune intolerance to gluten (wheat, barley, rye) damages villi
Includes oats (manufactured with gluten products)
Leads to malabsorption & GI inflammation.
Celiac Disease S/S
Steatorrhea
Bloating
Anemia
Weight loss
Muscle wasting
Celiac Disease Interventions
Lifelong gluten-free diet
Pediatric Eating Disorders
Anorexia nervosa: Self-starvation, extreme weight loss.
Bulimia nervosa: Binge eating followed by purging.
Binge Eating Disorder: Recurrent overeating without purging.
Screen adolescents annually (ages 9-18)
Treatment: Nutrition therapy, psychotherapy, possible hospitalization.
Screen adolescents annually (ages 9-18)
Pediatric Eating Disorders
Anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa, binge eating disorder