EGHS APUSH Full Study Set
1/601
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
602 Terms
Conservatism/New Right
A belief that limited government insures order competitive markets and personal opportunity. A view traditionally held by the Republican Party.
Moral Majority
A movement begun in the early 1980's among religious conservatives that supported primarily conservative Republicans opposed to abortion, communism and liberalism.
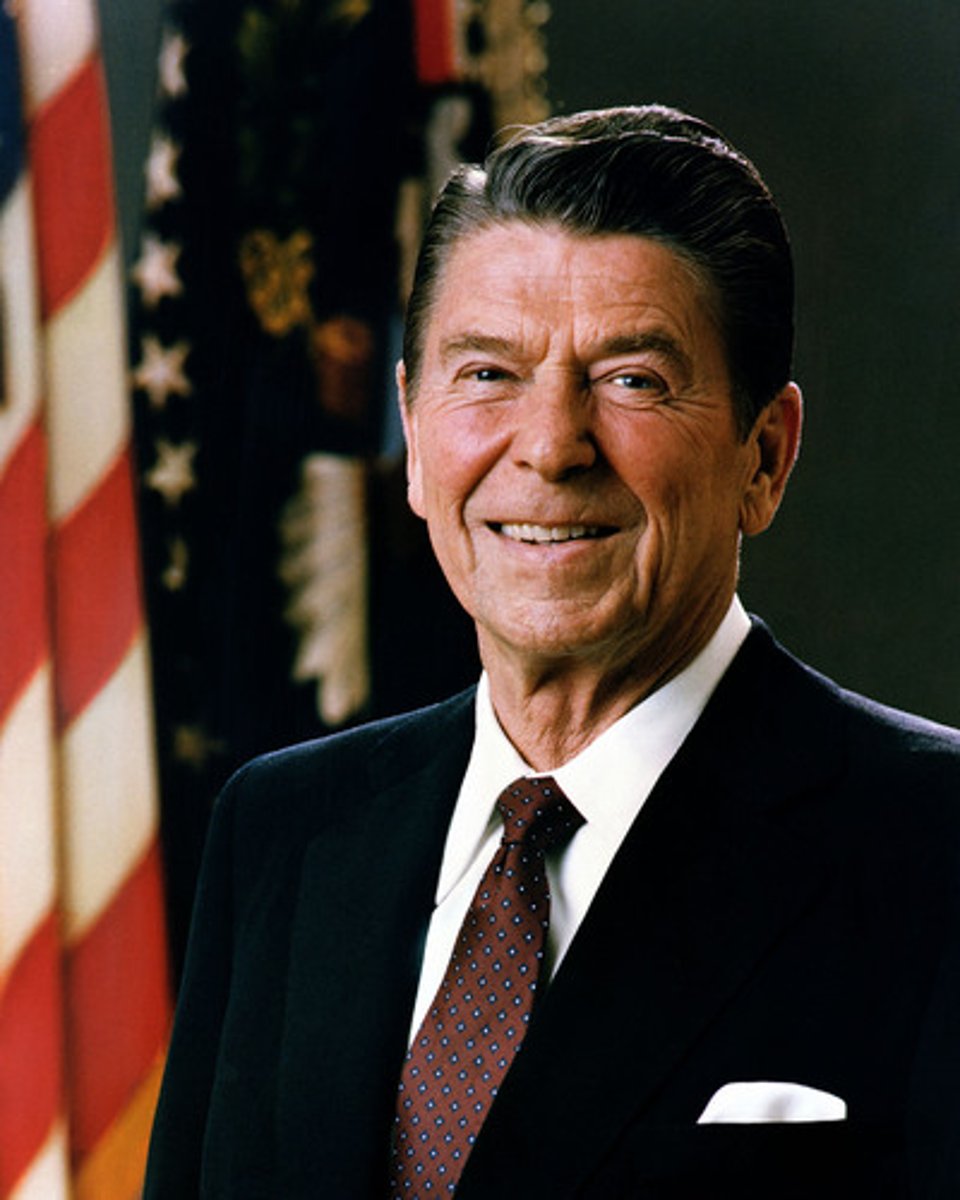
Ronald Reagan
first elected president in 1980 and elected again in 1984. Iran released hostages on his Inauguration Day in 1980. While president, he developed Reagannomics, the trickle down effect of government incentives. He cut out many welfare and public works programs. He proposed the Strategic Defense Initiative. His meetings with Gorbachev aided in ending the Cold War. He was also responsible for the Iran-contra Affair.

Supply-Side Economics (Reaganomics)
Economic policies of President Ronald Reagan, which focused on budget and tax cuts in order to increase private investment and defense spending. Social welfare programs and government regulation were also cut.
Yuppies
Term for "young urban professionals" of the 1980s who flaunted their wealth through conspicuous consumer spending
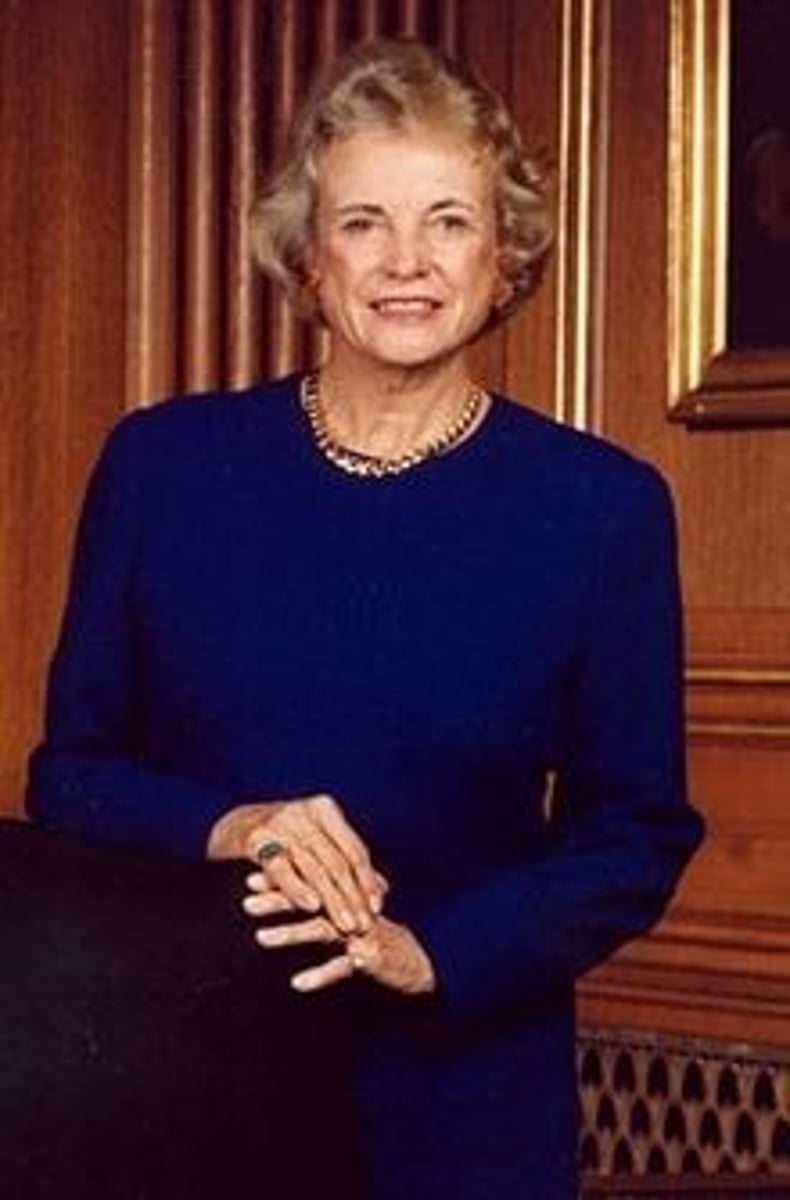
Sandra Day O'Connor
First female Justice of the US Supreme Court; appointed by Reagan

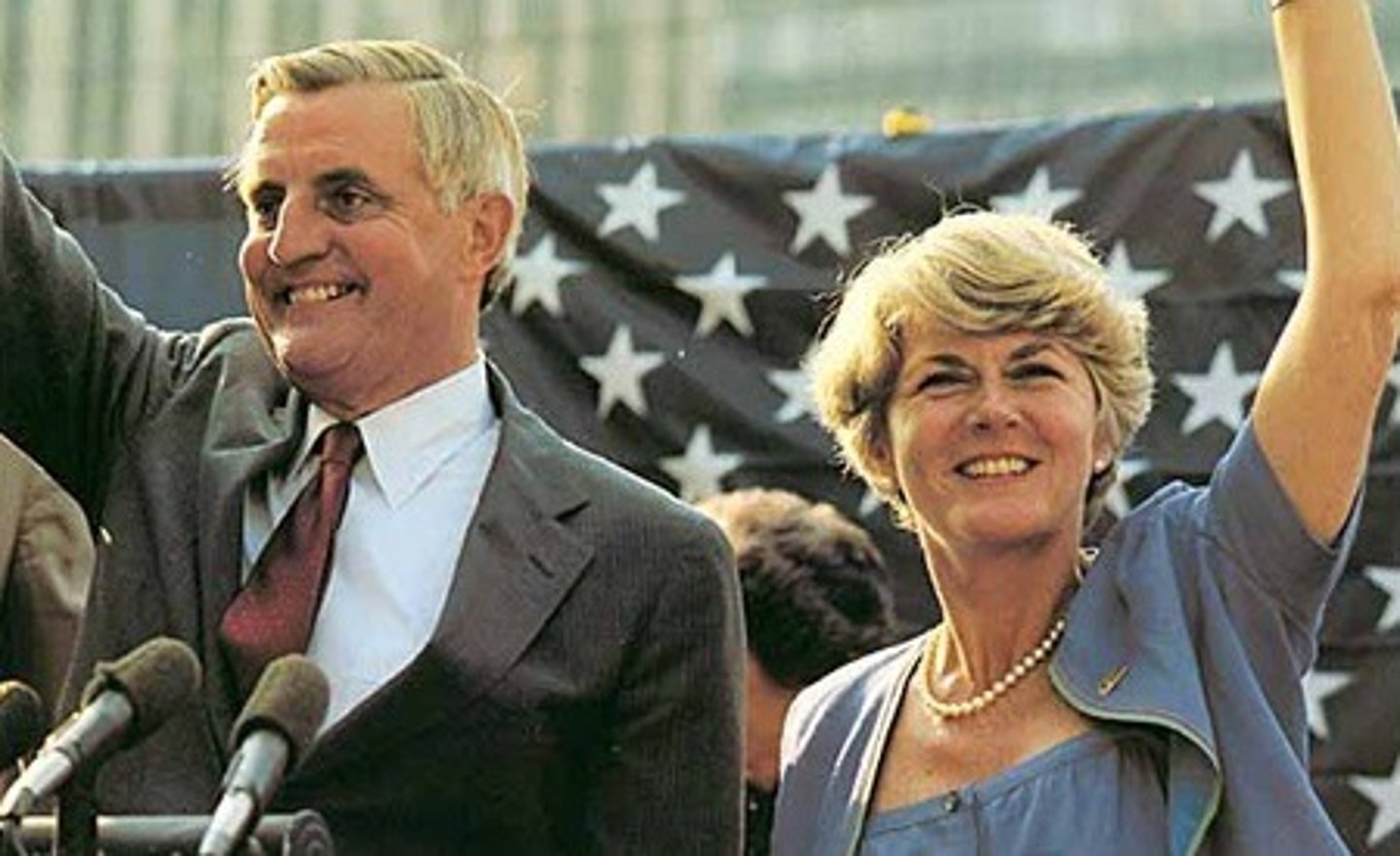
Geraldine Ferraro
The Democratic nominee for Vice President in 1984, first female candidate for a major party

Evil Empire
Ronald Reagan's description of Soviet Union because of his fierce anti-communist views and the USSR's history of violation of human rights and aggression.
Strategic Defense Initiative (SDI)
Popularly known as "Star Wars," President Reagan's SDI proposed the construction of an elaborate computer-controlled, anti-missile defense system capable of destroying enemy missiles in outer spaced. Critics claimed that SDI could never be perfected; some praise it as precipitating the downfall of the Soviet Union.
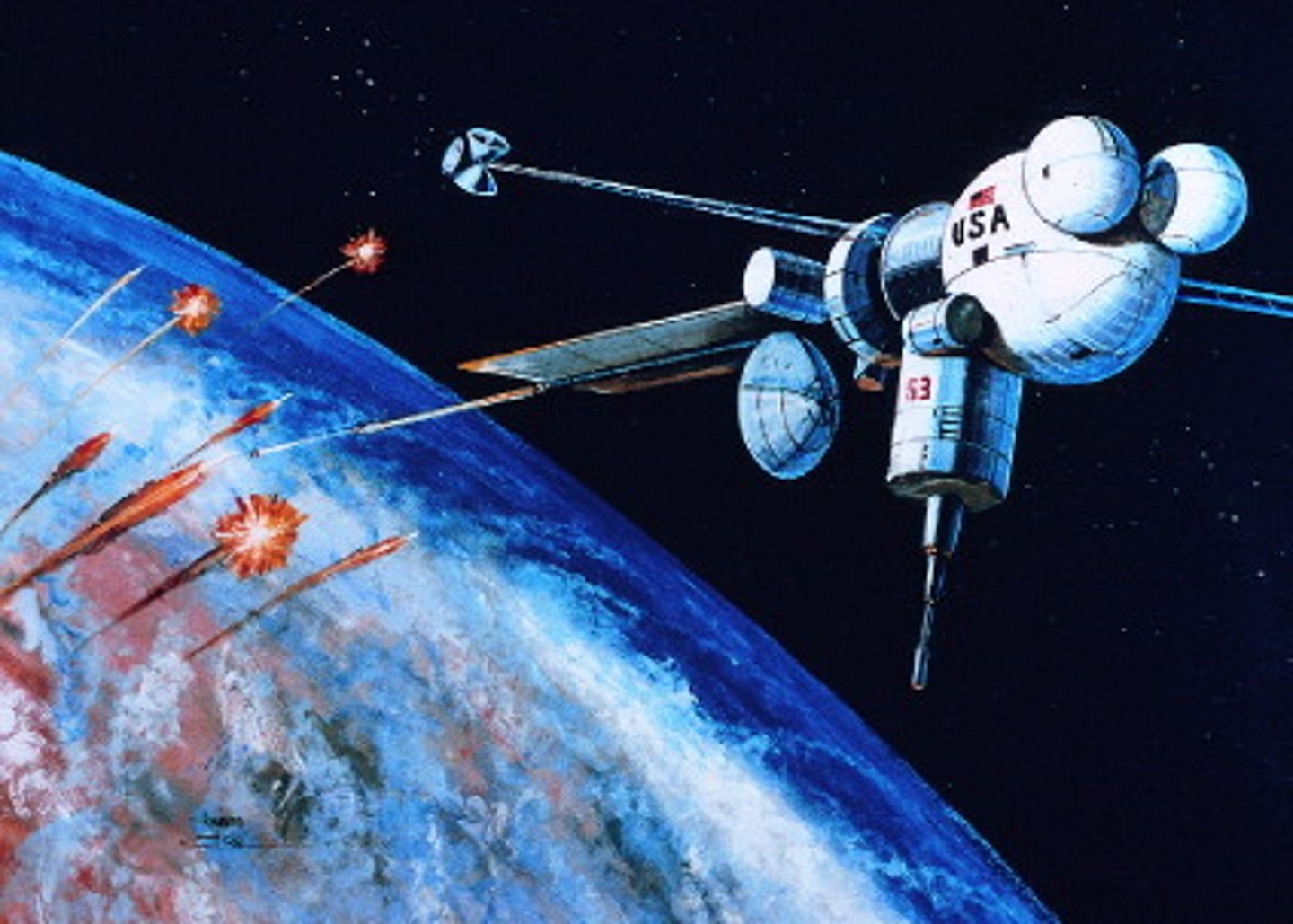
Iran-Contra Scandal
A major scandal of Reagan's second term that involved shipping arms to Iran to free hostages and diverting the money from the sale of these weapons to the Contra rebels in Nicaragua who were fighting a pro-communist government.
Mikhail Gorbachev
Last Soviet Premier whose foreign policy brought an end to the Cold War and whose domestic policy introduced major social and economic reforms to the former Soviet Union

Glasnost and Perestroika
Two reform movements in Russia. Glasnost was meant to provide opportunities to share new ideas. Perestroika was intended to give businesses more freedom for innovation and competition
George H.W. Bush
Reagan's Vice President, 41st president, approval rating aided by success in the Persian Gulf War, hurt by the recession and "Read my lip. No new taxes" pledge that he broke; lost 1992 election to Clinton
"Was just another Reagan with all the same idea"

Saddam Hussein
President of Iraq from 1979 to 2003. Waged war on Iran in 1980-1988. In 1990 he ordered an invasion of Kuwait but was defeated by United States and its allies in the Gulf War (1991). Defeated by US led invasion in 2003.

Operation Desert Storm / Persian Gulf War
Known as the first Gulf War, US led UN forces launched an attack to remove invading Iraqi forces from Kuwait in August, 1990 in order to prevent Iraq from dominating oil reserves in the Middle East.
Clarence Thomas
2nd African American US Supreme Court justice; conservative, appointed by President George H. W. Bush

Americans with Disabilities Act
Passed by Congress in 1991, this act banned discrimination against the mentally and physically disabled in employment and mandated easy access to all public and commercial buildings.
Bill Clinton
1992 and 1996; Democrat; Don't Ask Don't Tell policy implemented by Congress, NAFTA, Family and Medical Leave Act; Whitewater controversy, Lewinsky scandal (impeached and acquitted), Travelgate controversy, first balanced budget since 1960s

H. Ross Perot
Billionaire Texas businessman, best remembered for running for President in 1992 and 1996 under Independent Party banner; best 3rd party showing since 1912

"Don't Ask, Don't Tell"
Clinton managed to gain support for a compromise measure under which homosexual servicemen and servicewomen could remain in the military if they did not openly declare their sexual orientation
Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA)
U.S act that provides employees with up to 12 weeks of unpaid leave to care for family members or because of a serious health condition of the employee.
NAFTA
North American Free Trade Agreement; allows open trade with US, Mexico, and Canada.
Personal Responsibility and Work Opportunity Act
1996 federal law that transferred responsibility for welfare programs from the federal level to the state level and placed a five-year lifetime limit on payment of benefits to any given recipient
Immigration Reform and Control Act of 1986
Passed by Reagan, it was an update of the 1965 Immigration Act and outlawed the hiring of undocumented immigrants, but offered legal status to aliens who had lived in the U.S. for five years. Debates over immigration policy persisted, however, as did efforts to tighten U.S. border controls.
Bush v. Gore
5-4 US Supreme Court decision that declared that Florida vote recount violated equal protection clause (some votes would be examined more closely than others); ended Gore's challenge to 2000 election results.
George W. Bush
43rd president of the US (2000, 2004) who began a campaign toward energy self-sufficiency and against terrorism in 2001; No Child Left Behind Act; USA Patriot Act

No Child Left Behind
Signed into law in 2002. NCLB addresses accountability of school personnel for student achievement with the expectation that every child will demonstrate proficiency in Reading, Math, and Science. Criticized for increasing testing and having unobtainable goals.
War on Terrorism
Response to 9/11, US would actively fight terrorism throughout the world; took US into Iraq and Afghanistan
Osama Bin Laden / Al-Qaeda
Saudi Militant who heads the terrorist group, al Qaeda, is responsible for 9/11 and other terrorist attacks.

September 11, 2001 attacks
Terrorist attack by the Al Qaeda network; hijacked four commercial airliners and crashed them into the Pentagon the World Trade Center in Manhattan, and a field in Pennsylvania.
USA Patriot Act (2001)
Legislation passed shortly after the terrorist attacks of September 11, 2001, that granted broad surveillance and detention authority to the government.
Department of Homeland Security
Cabinet department created after the 9/11 terrorist attacks to coordinate domestic security efforts
Axis of Evil
A group of nations accused by the George W. Bush administration of sponsoring terrorism and threatening to develop weapons of mass destruction
Operation Iraqi Freedom (2003)
Operation where U.S. troops invaded Iraq looking for weapons of mass destruction, though none were ever found; Saddam Hussein's forces collapsed, Baghdad fell
Barack Obama
2008; Democrat; first African American president of the US, Affordable Care Act; Gulf of Mexico oil spill disaster; huge stimulus package to combat the Great Recession, removing troops from Iraq, strengthened numbers in Afghanistan; repeal of Don't Ask Don't Tell; New Start treaty with Russia
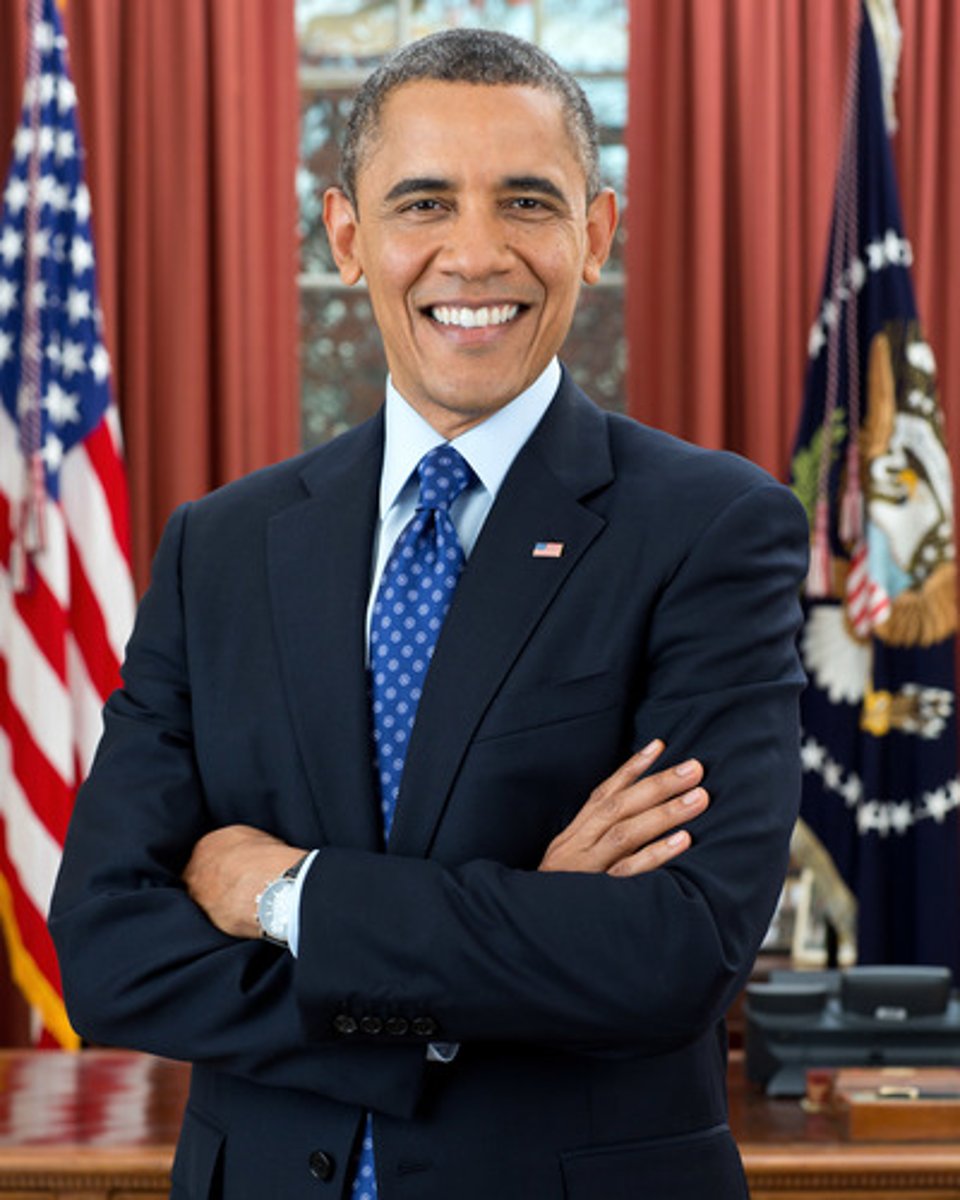

The Great Recession
Severe economic downturn that lasted from late 2007 through mid-2009 with unemployment at 10%, many bank foreclosures on property, and businesses failing or being bailed out by taxpayers
Affordable Care Act (Obamacare)
A health care reform act that reduced the uninsured population via expanded Medicaid eligibility and a reworking of the individual insurance marketplace. The Obama administration's signature legislation.
Tea Party
A Conservative political movement beginning in 2009 that opposes government spending and taxes
Defense of Marriage Act (DOMA)
1996, Declares that states are not obligated to recognize any same sex marriages that might be legally sanctioned in other states, defined marriage and spouse in heterosexual terms for federal law
Arab Spring
A revolutionary wave of protests and demonstrations overtaking dictators in the Middle East (2011), fuel largely by social media
ISIS
Islamic State in Iraq and Syria and is an extremist militant group that rules by Salafi law, and has established a terror state in the Middle East.
Midnight Judges
Nickname given to the group of federal judges appointed by John Adams the night before he left office.
Marbury v. Madison
Supreme Court case involving the Midnight Judges that established the power of Judicial Review
Judicial Review
Allows the Supreme Court to determine the constitutionality of laws
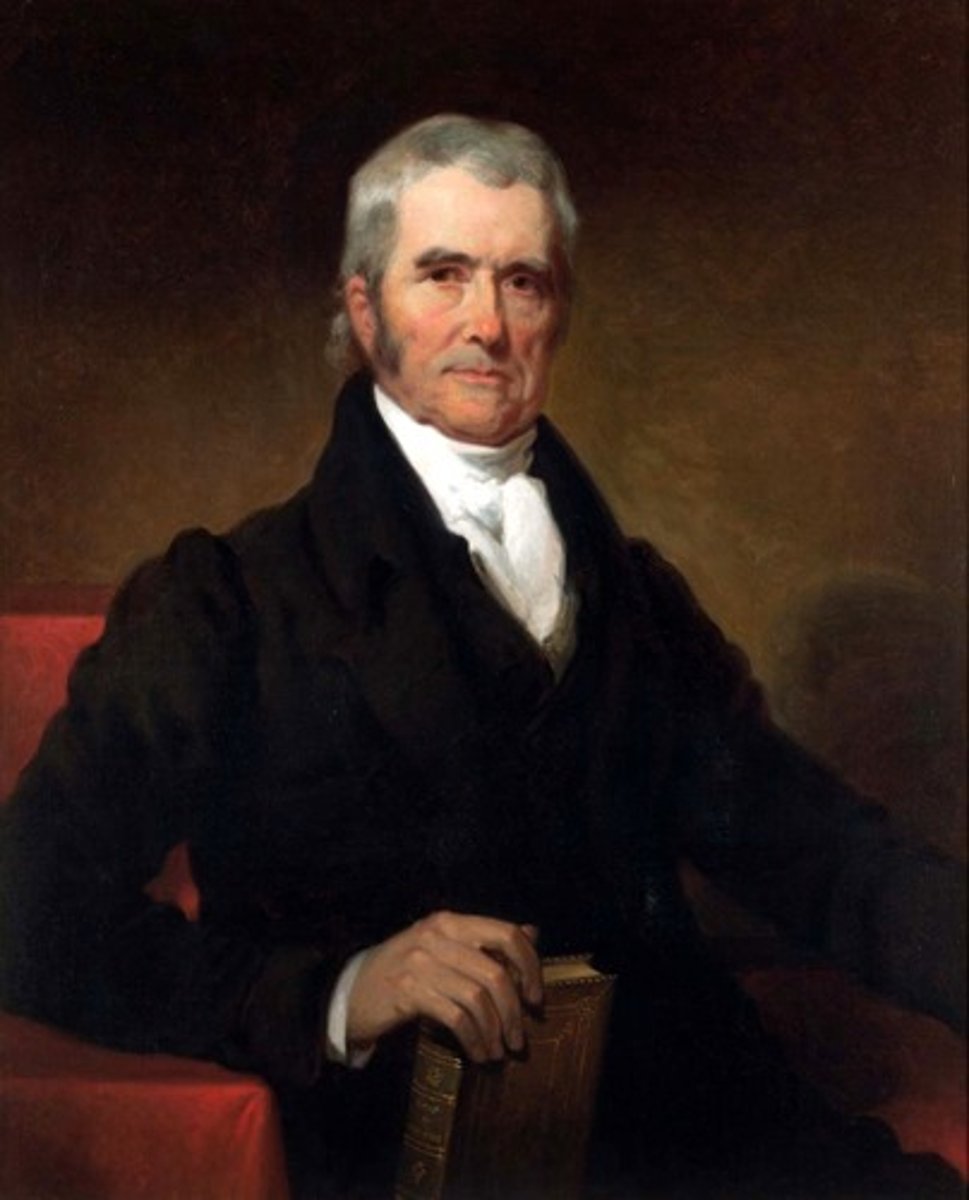
John Marshall
Chief Justice of the Supreme Court appointed by John Adams

Louisiana Purchase
Territory in western United States purchased from France in 1803 for $15 million; nearly doubled the size of the United States
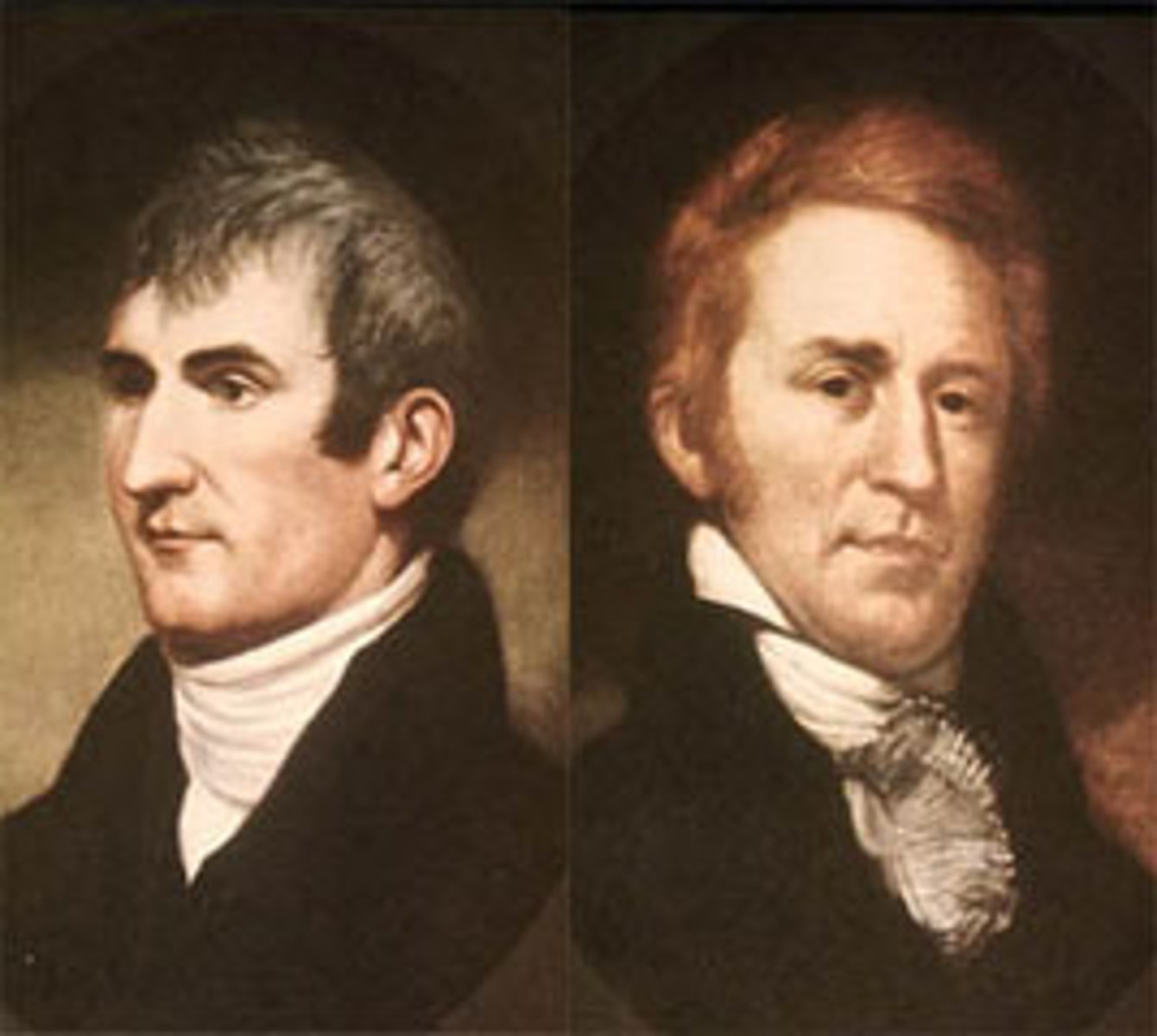
Lewis and Clark Expedition
An expedition sent by Thomas Jefferson to explore the northwestern territories of the United States, identify new plants and animals, locate Native American tribes, map the terrain, and find a route to the Pacific Ocean

Barbary Pirates
North Africans who attacked American ships and tried to ransom American sailors during Thomas Jefferson's presidency
Embargo Act of 1807
Act passed by Congress and President Jefferson prohibiting American ships from leaving for any foreign port
Battle of Tippecanoe
1811 battle in which Tecumseh and the Prophet's tribes are crushed by General Harrison when they try to unite multiple tribes for self-defense
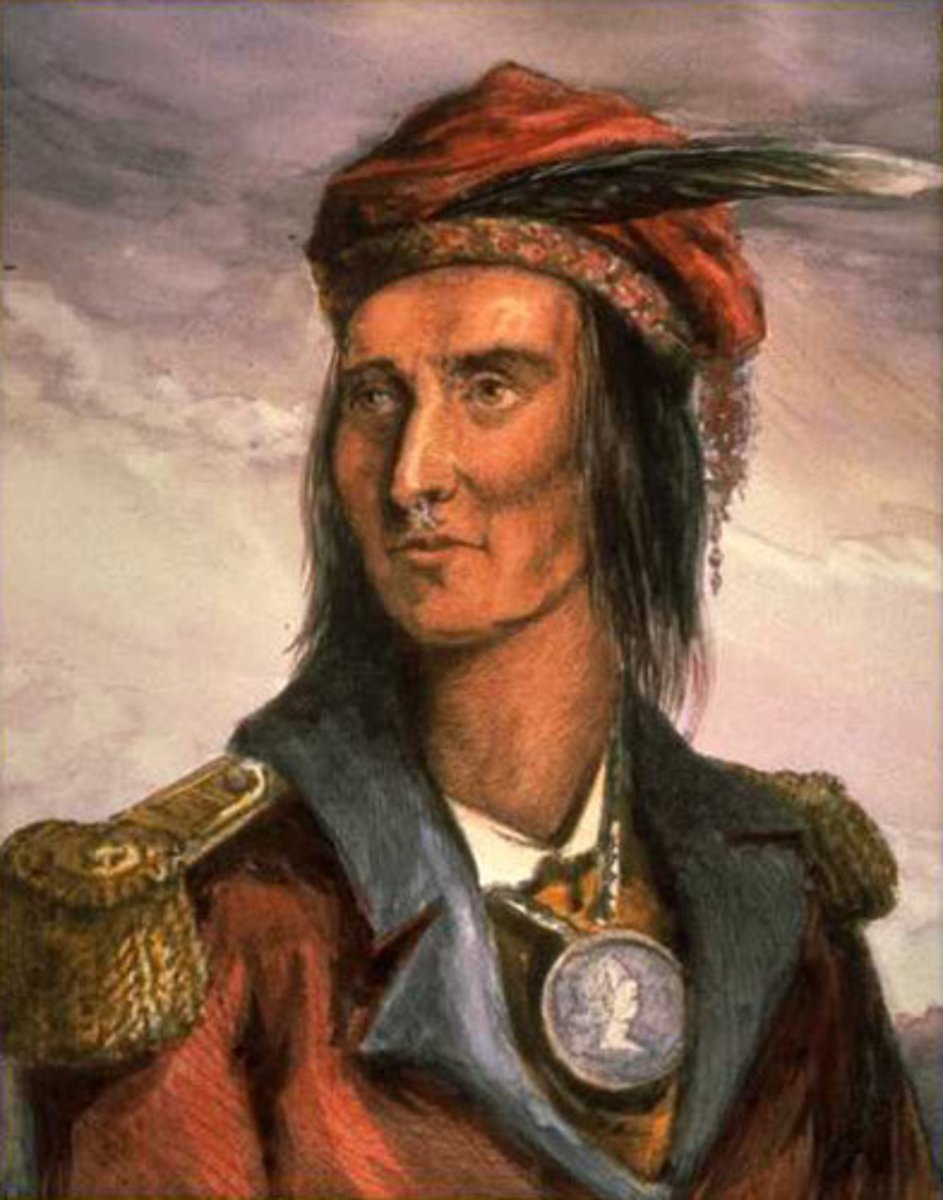
Tecumseh
a famous chief of the Shawnee who tried to unite Indian tribes against increasing white settlement (1768-1813)

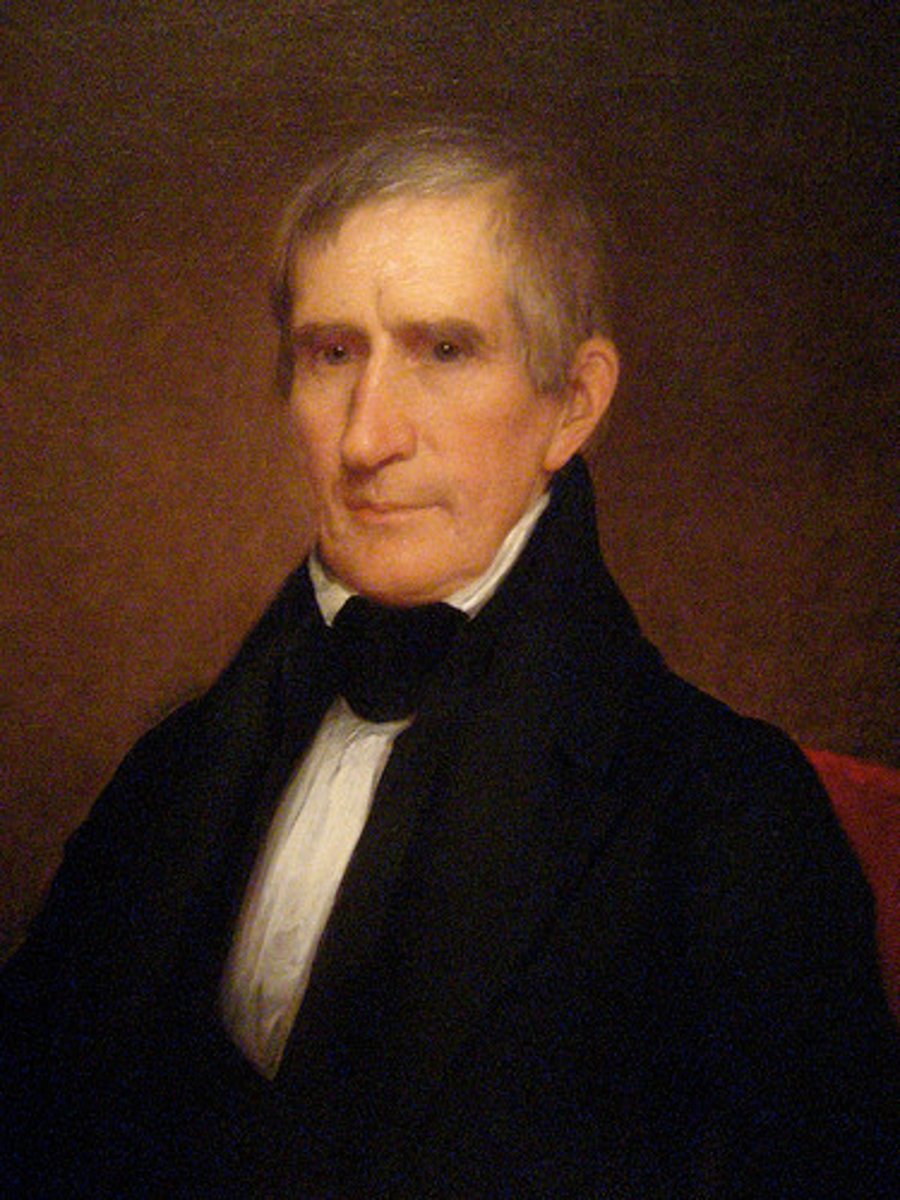
William Henry Harrison
An American military leader, politician, the ninth President of the United States, and the first President to die in office. His death created a brief Constitutional crisis, but ultimately resolved many questions about presidential succession left unanswered by the Constitution until passage of the 25th Amendment. Led US forces in the Battle of Tippecanoe.

War of 1812
War between the U.S. and Great Britain caused by England's use of impressment, inciting the Native Americans, and the refusal of Red Coats to leave the United States; ended with a renewed sense of American nationalism
War Hawks
Southern and Westerners during Madison's presidency who pressed for war with Britain
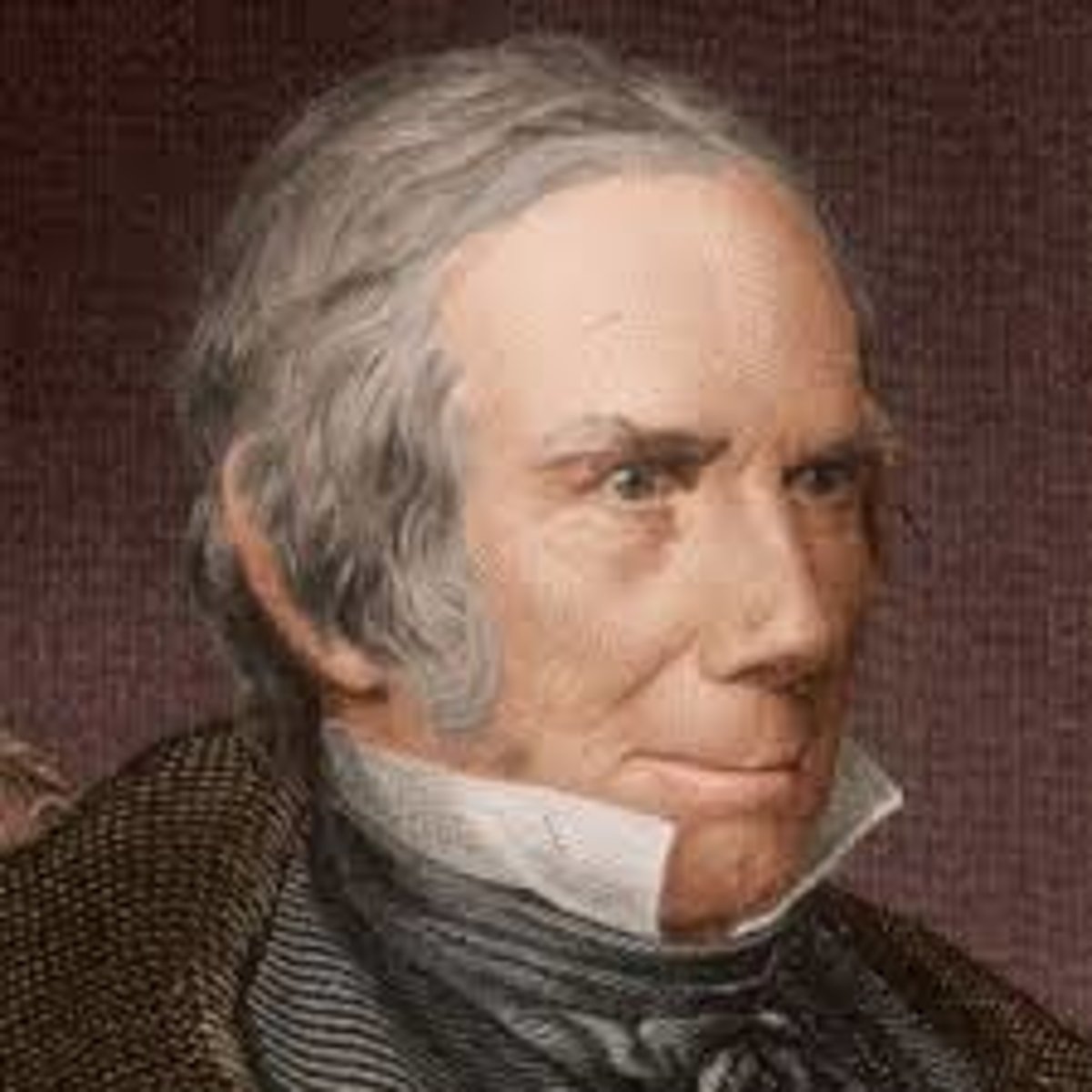
Henry Clay
A northern American politician. He developed the American System as well as negotiated numerous compromises, ran for president five times and was a War Hawk during the War of 1812

Impressment
British practice of taking American sailors and forcing them into military service
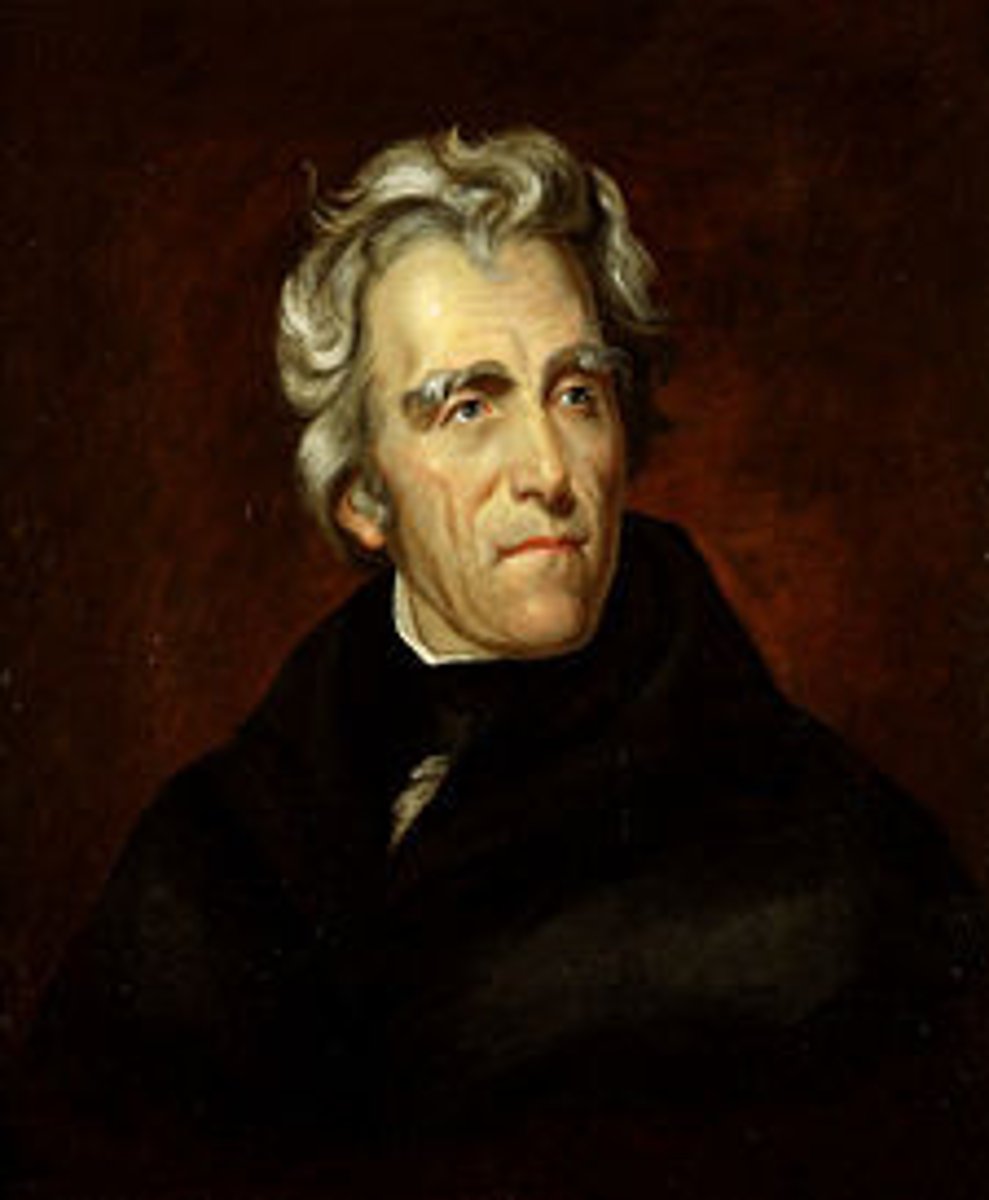
Andrew Jackson
The seventh President of the United States (1829-1837), who as a general in the War of 1812 defeated the British at New Orleans (1815). As president he opposed the Bank of America, objected to the right of individual states to nullify disagreeable federal laws, and increased the presidential powers.

Battle of New Orleans
A battle in 1815 between American and British troops for control of the Mississippi River, ending in an American victory; was won after the treaty was signed
Hartford Convention
Meeting of Federalists near the end of the War of 1812 in which the party listed it's complaints against the ruling Republican Party. These actions were largely viewed as traitorous to the country and lost the Federalist much influence
Treaty of Ghent
Treaty that ended the War of 1812 and maintained prewar conditions (antebellum status quo)
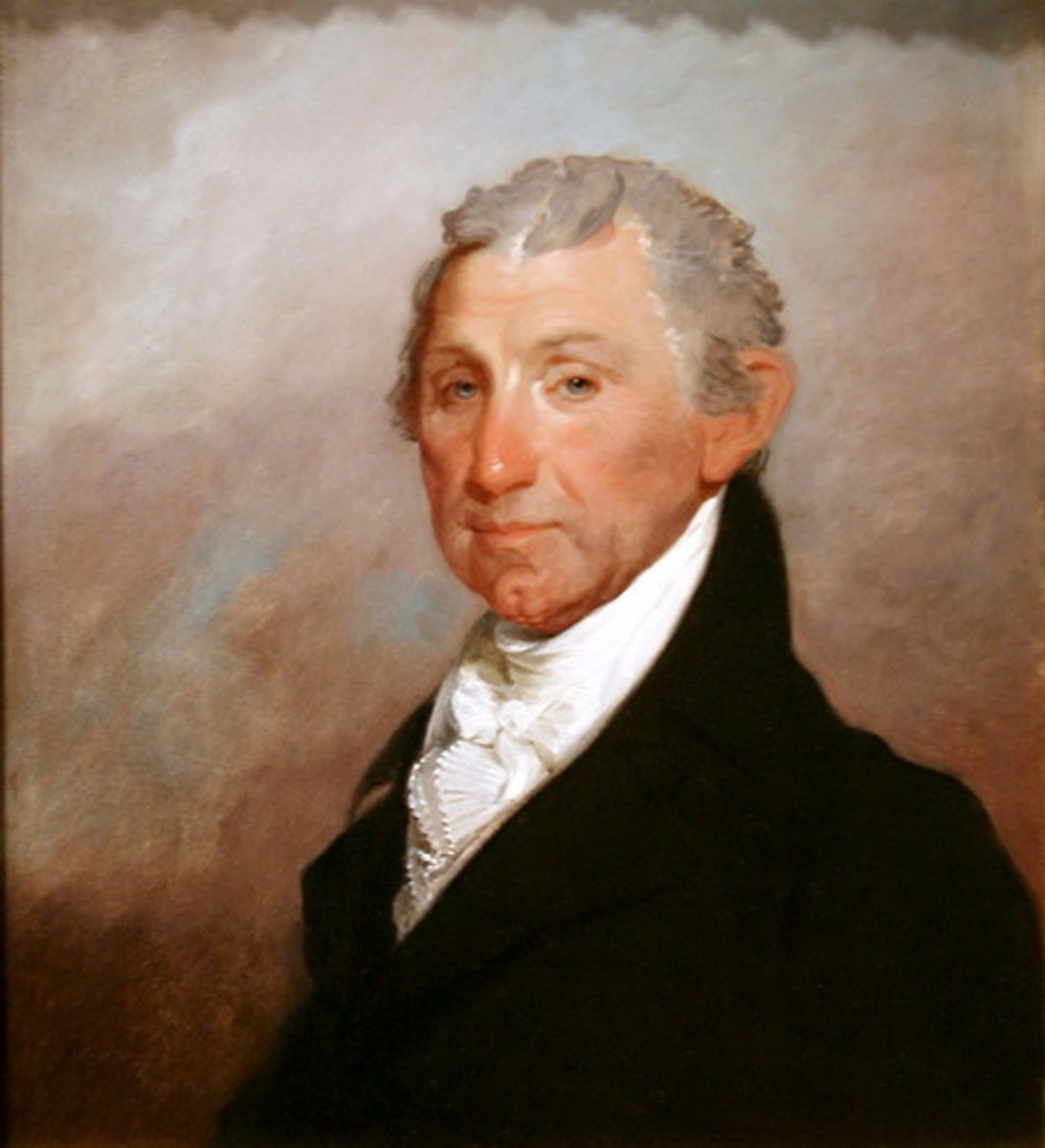
James Monroe
The 5th President of the United States (1817-1825); His administration was marked by the Era of Good Feelings, the acquisition of Florida, the Missouri Compromise, and the profession of the Monroe Doctrine

Era of Good Feelings
A name for President Monroe's two terms, a period of strong nationalism, economic growth, and territorial expansion. Since the Federalist party dissolved after the War of 1812, there was only one political party and few partisan conflicts.
Missouri Compromise
An agreement in 1820 between pro-slavery and anti-slavery factions in the United States concerning the extension of slavery into new territories; Missouri joined the union as a slave state, Maine joined as a free state, and slavery was prohibited in all other areas north of the 36-30 line.
Adam-Onis Treaty (1819)
Treaty in which Spain cedes all of Florida to the U.S. but in return U.S. would give up claims to Texas
Monroe Doctrine
A statement of foreign policy which proclaimed that Europe should not interfere in affairs within the United States or in the development of other countries in the Western Hemisphere.
American System
Economic program advanced by Henry Clay that included support for a national bank, high tariffs, and internal improvements; emphasized strong role for the federal government in the economy.
Corrupt Bargain
Refers to the claim from the supporters of Andrew Jackson that John Quincy Adams and Henry Clay had worked out a deal to ensure that Adams was elected president by the House of Representatives in 1824.
Market Revolution
Drastic changes in transportation (canals, RRs), communication (telegraph), and the production of goods (more in factories as opposed to houses) that occurred in the early 1800s.
National Road
A federally funded road, stretching from Cumberland, Maryland, to Vandalia, Illinois
Robert Fulton
American inventor who designed the first commercially successful steamboat
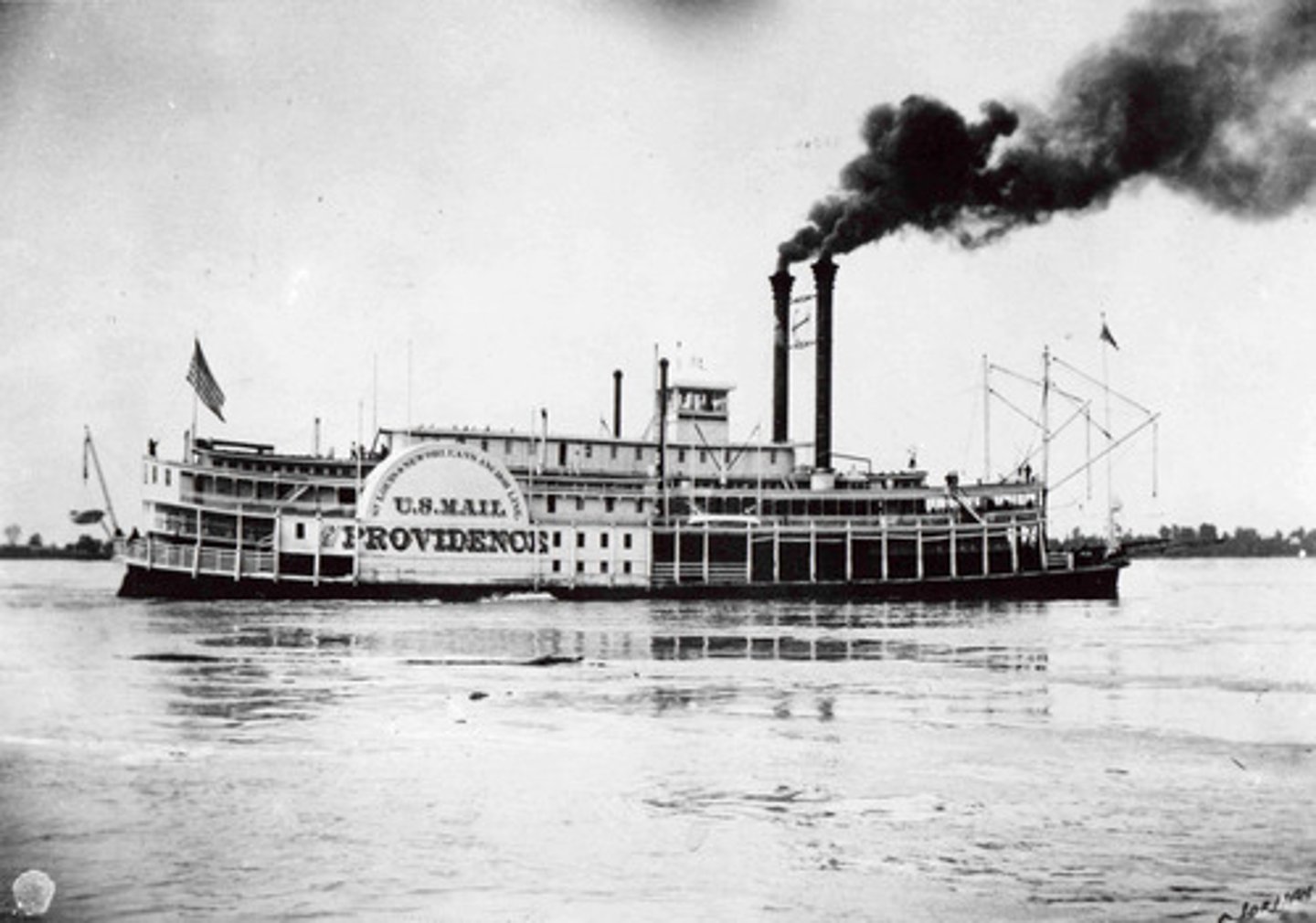

Erie Canal
An artificial waterway connecting the Hudson River at Albany with Lake Erie at Buffalo, New York
Samuel Slater
"Father of the Factory System" in America who escaped Britain with the memorized plans for textile machinery
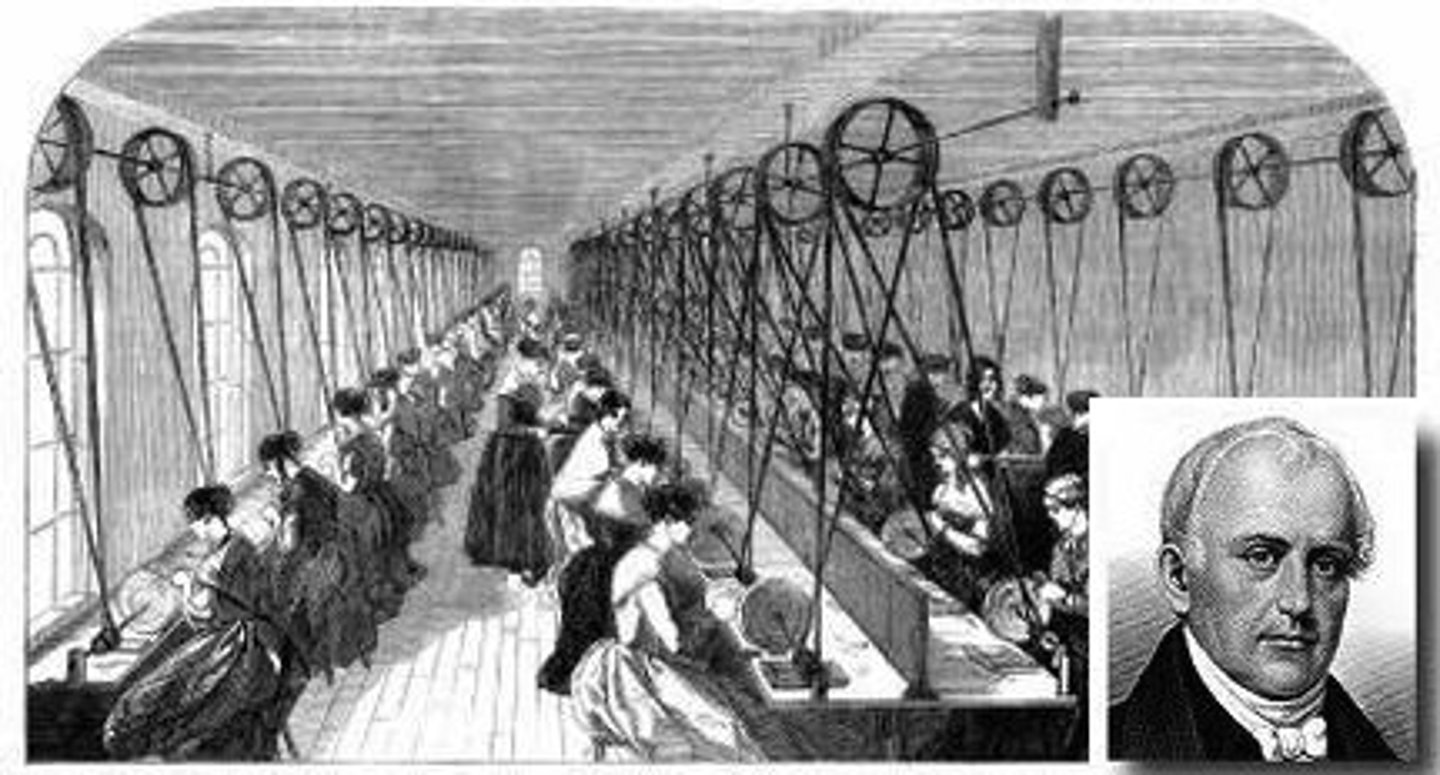
Lowell System
The use of water powered textile mills that employed young unmarried women in the 1800's
Spoils System
A system of public employment based on rewarding party loyalists and friends.
Democratic Party
One of the two major U.S political party;founded in 1828 by Andrew Jackson to support a decentralized government and state's rights
Whigs
Political Party led by Henry Clay; Favored the national bank, the American System and a strong legislative branch
Indian Removal Act
Passed in 1830, authorized Andrew Jackson to negotiate land-exchange treaties with tribes living east of the Mississippi. The treaties enacted under this act's provisions paved the way for the reluctant—and often forcible—emigration of tens of thousands of American Indians to the West.
Worcester v Georgia
Supreme Court ruling that the Cherokee nation was a distinct community in which the laws of Georgia had no force
Trail of Tears
The forced removal of Cherokees and other eastern tribes to lands west of the Mississippi River; 25% of the Natives died en route
Tariff of Abominations
Tariff passed by Congress in 1828 that favored manufacturing in the North and was hated by the South
Nullification
A state's refusal to recognize an act of Congress that it considers unconstitutional
Force Bill
Bill that authorized the use of the military against belligerent states when South Carolina nullified the Tariff of Abominations
Pet Banks
State banks where Andrew Jackson placed deposits removed from the federal National Bank.
Panic of 1837
When Jackson was president, many state banks received government money that had been withdrawn from the Bank of the U.S. These banks issued paper money and financed wild speculation, especially in federal lands. Jackson issued the Specie Circular to force the payment for federal lands with gold or silver. Many state banks collapsed as a result causing a panic. The Bank of the U.S. failed, cotton prices fell, businesses went bankrupt, and there was widespread unemployment and distress.
Log Cabin and Hard Cider Campaign
Term for the 1840 presidential campaign when William Henry Harrison, the Whig candidate tried to portray his down-home heritage and attack Martin Van Buren as an aristocrat
Mormons
Church founded by Joseph Smith in 1830 with headquarters in Salt Lake City, Utah; moved from IL to UT
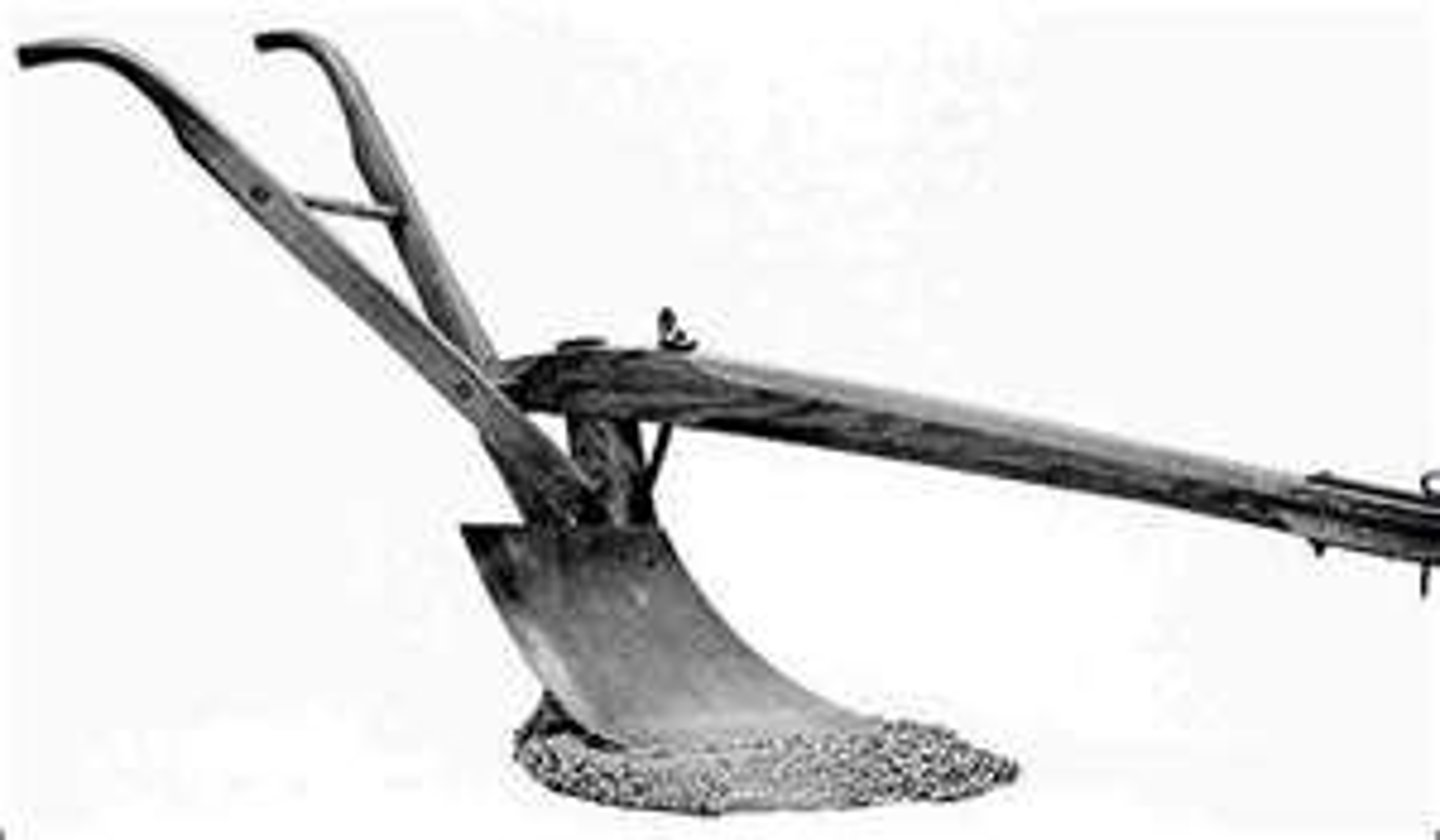
John Deere
American blacksmith responsible for inventing the steel plow which made plowing farmland in the west easier

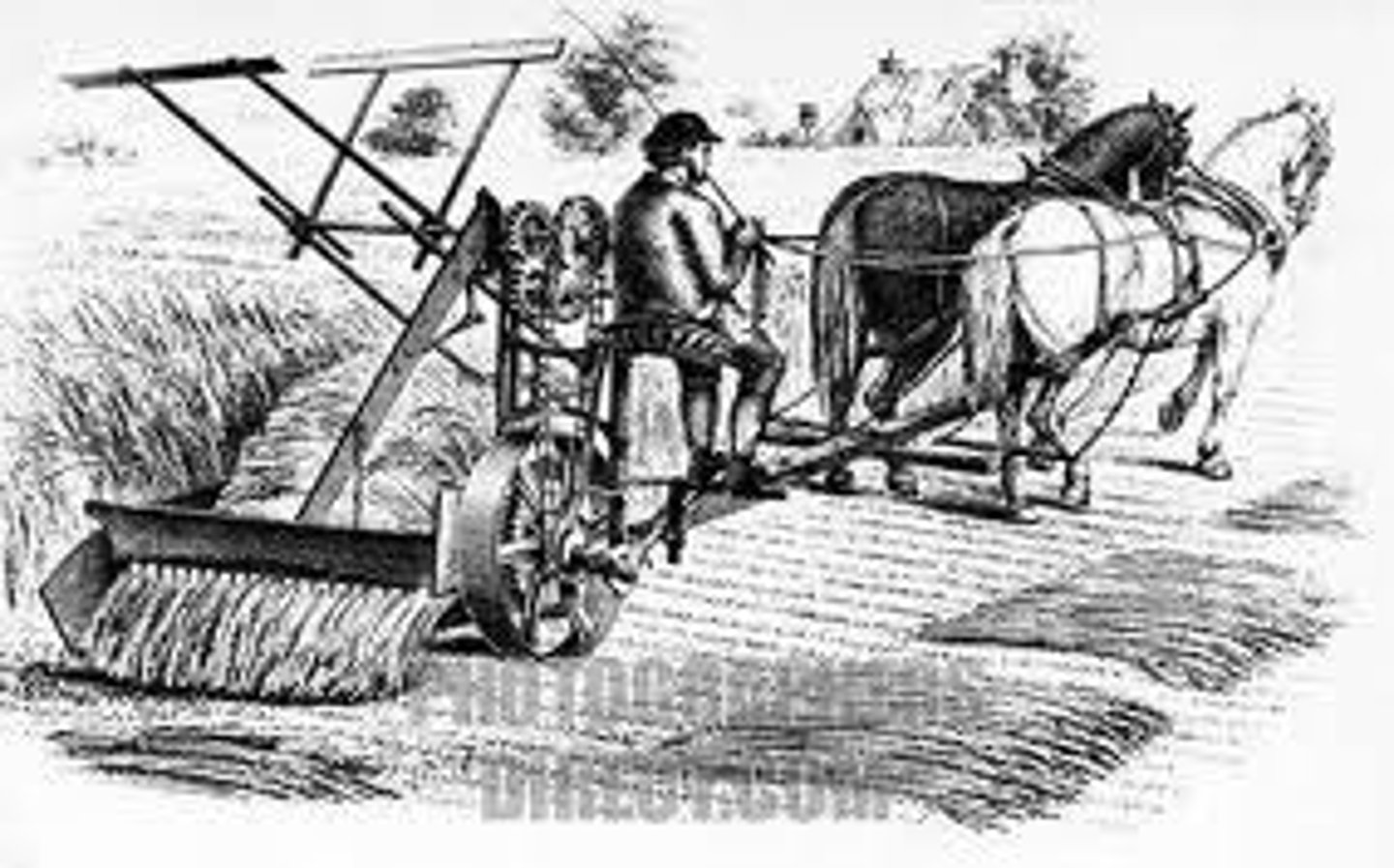
Cyrus McCormick
Inventor of the mechanical reaper that replaced scythes as the preferred method of cutting crops for harvest

Horace Mann
United States educator who introduced reforms that significantly altered the system of public education
Normal Schools
Teacher-training schools
Second Great Awakening
A second religious fervor that swept the nation in the early 1800s. It also had an effect on moral movements such as prison reform, the temperance movement, and abolition
Temperance
Abstinence from alcoholic drink
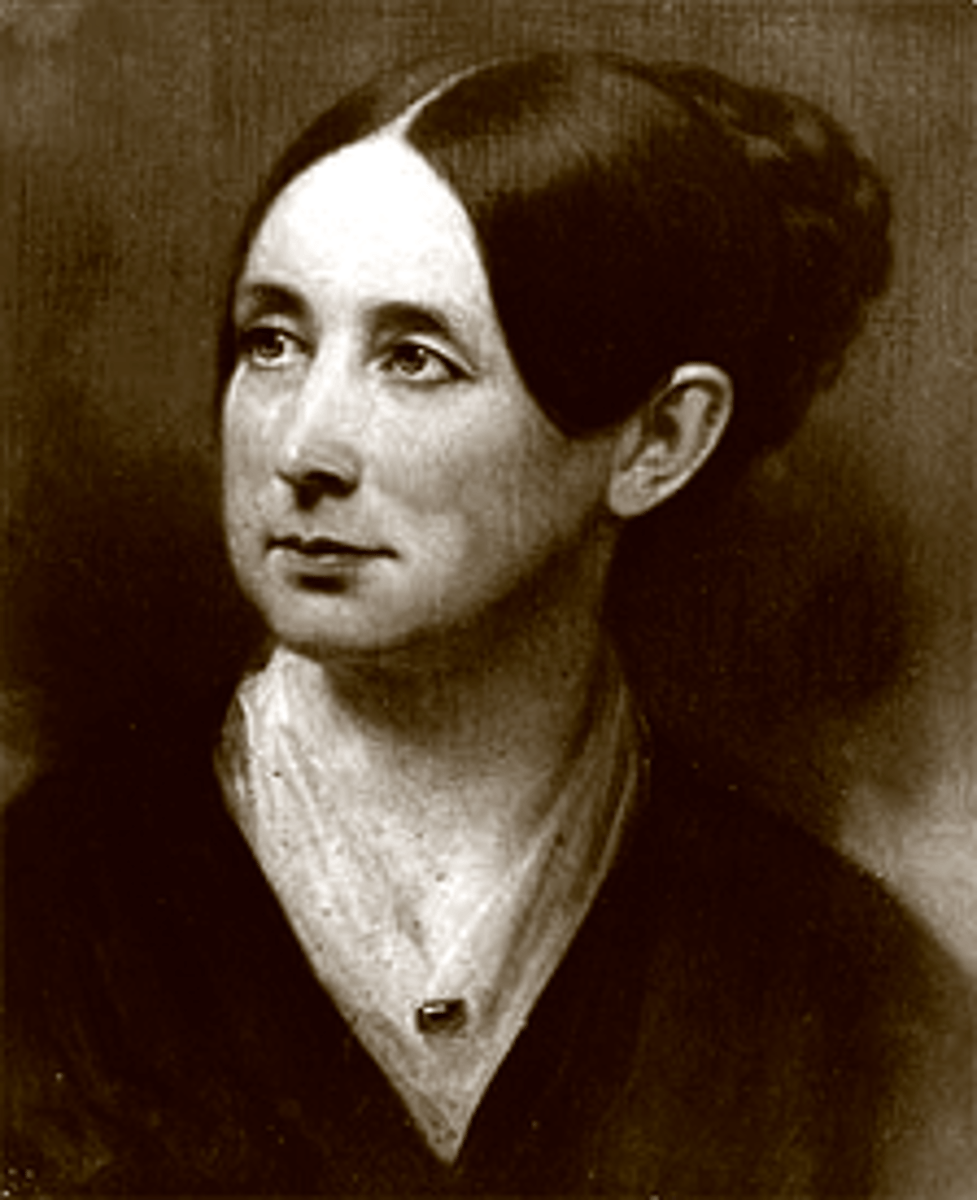
Dorthea Dix
Dedicated to improving conditions for the mentally ill and prisoners

American Colonization Society
Formed in 1817, it purchased a tract of land in Liberia and returned free Blacks to Africa.
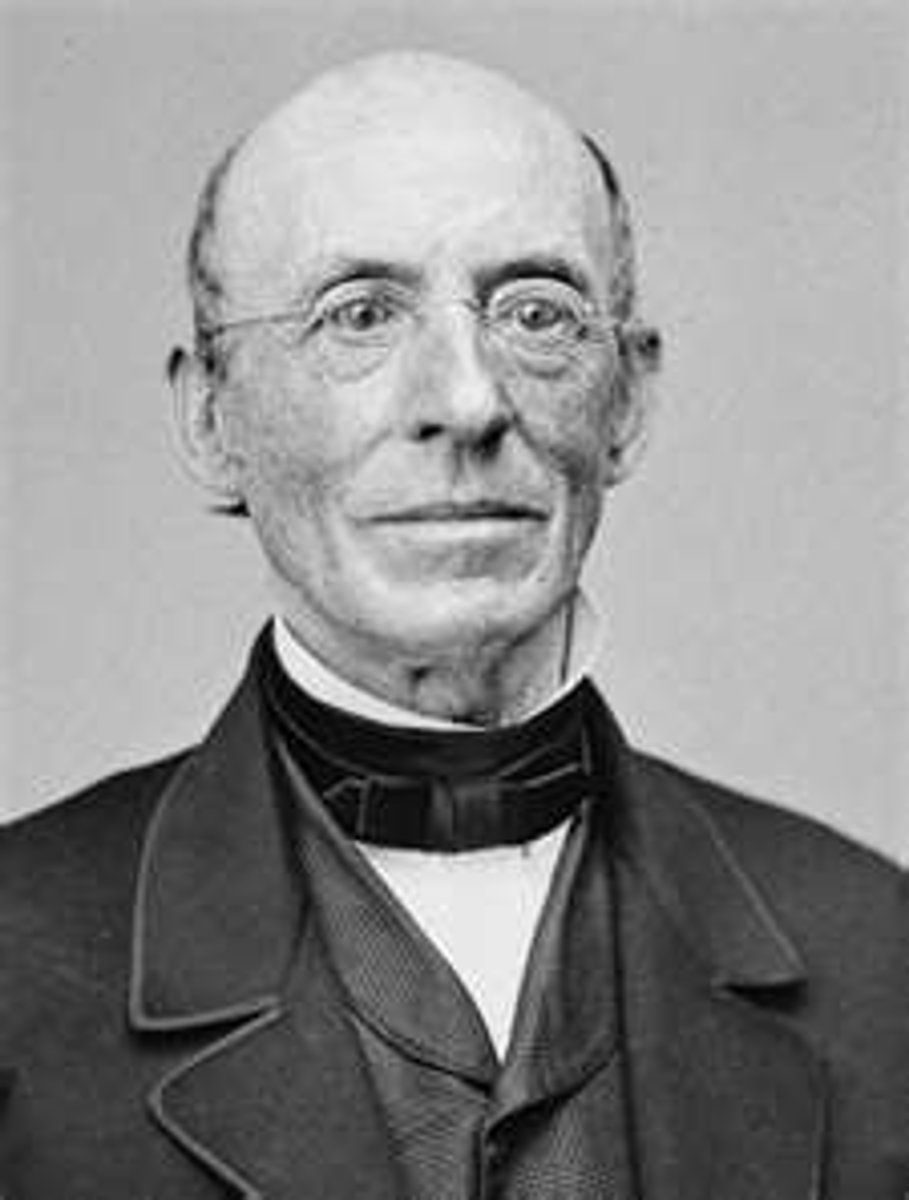
William Lloyd Garrison
Prominent American abolitionist, journalist and social reformer. Editor of radical abolitionist newspaper "The Liberator," and one of the founders of the American Anti-Slavery Society.

Abolition
Movement to end slavery
Hudson River School of Art
Landscape painters, inspired by the earth's natural beauty; achieved fame by painting romantic landscapes.
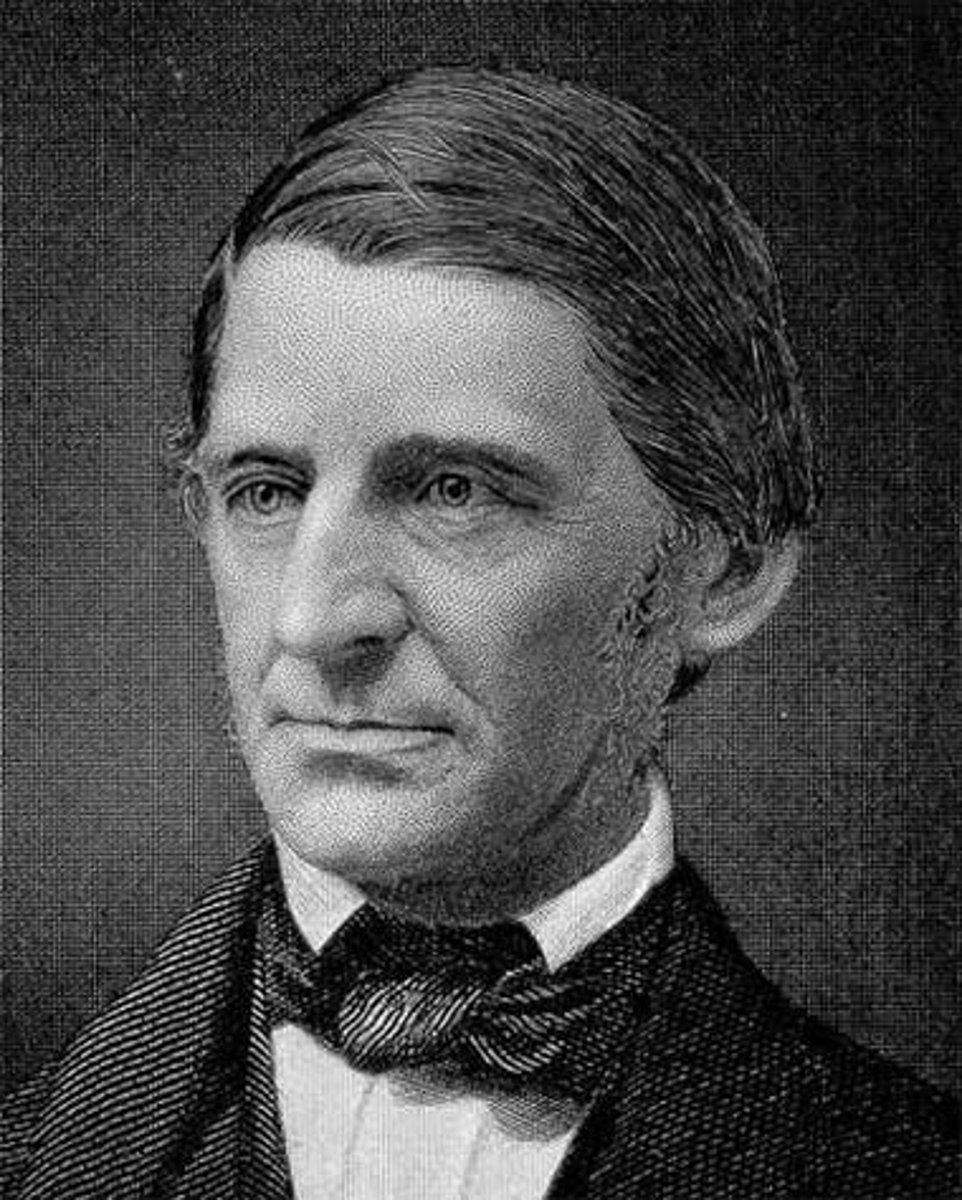
Ralph Waldo Emerson
American transcendentalist who was against slavery and stressed self-reliance, optimism, self-improvement, self-confidence, and freedom.

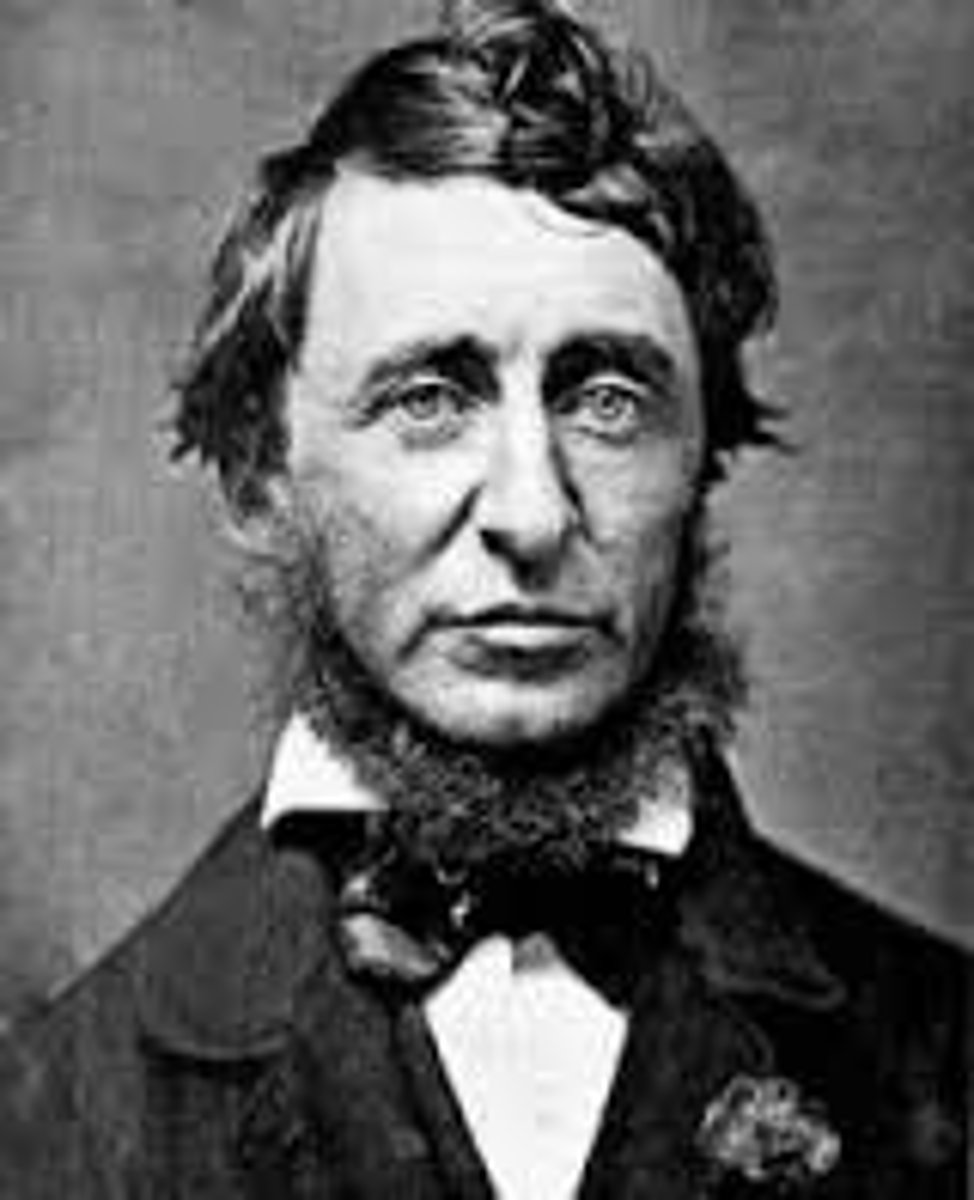
Henry David Thoreau
American transcendentalist who was against a government that supported slavery. He wrote down his beliefs in Walden. He started the movement of civil-disobedience when he refused to pay the toll-tax to support him Mexican War.

Transcendentalism
A nineteenth-century movement which held that every individual can reach ultimate truths through spiritual intuition, which transcends reason and sensory experience.