BOT 14 - 2 - Bryophytes: Non-vascular Plants
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
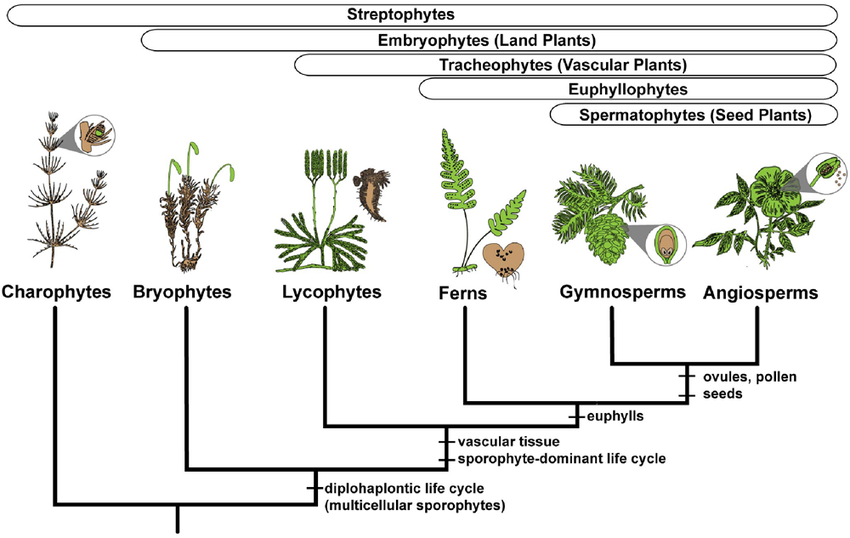
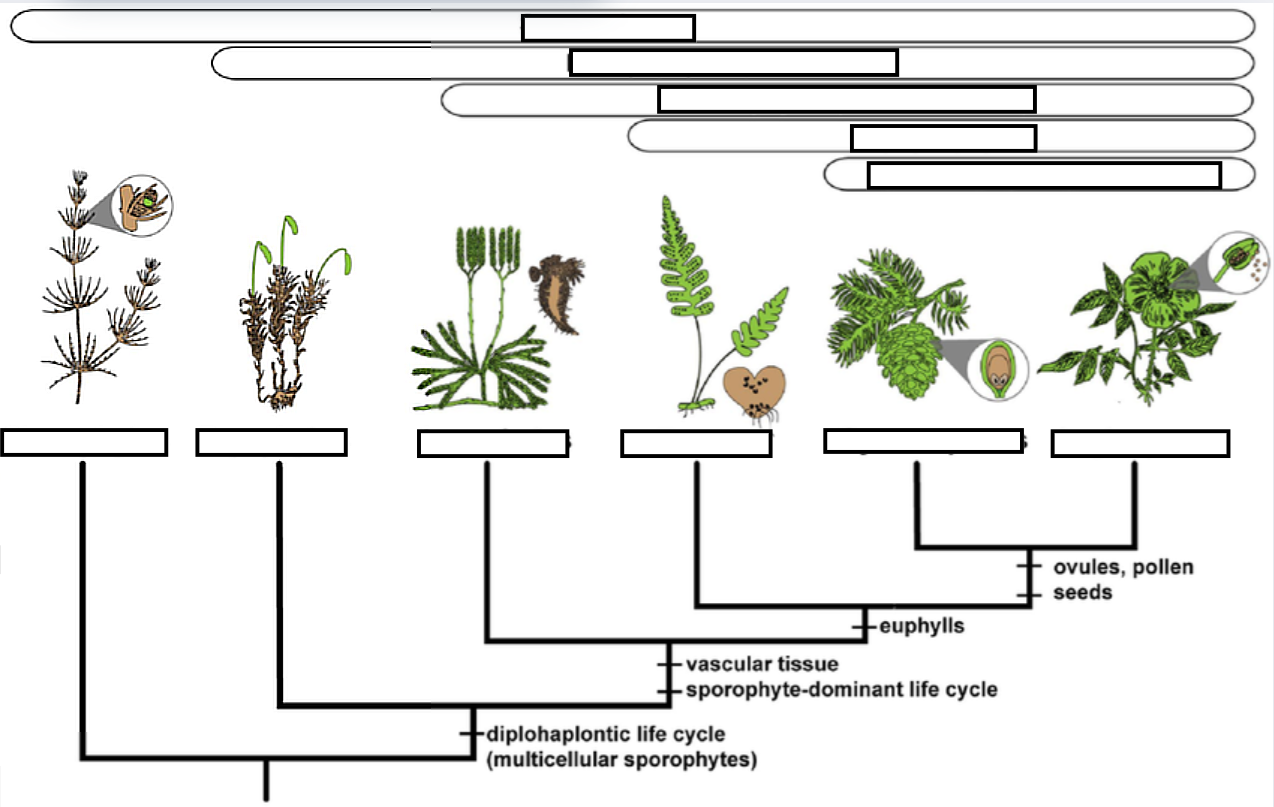

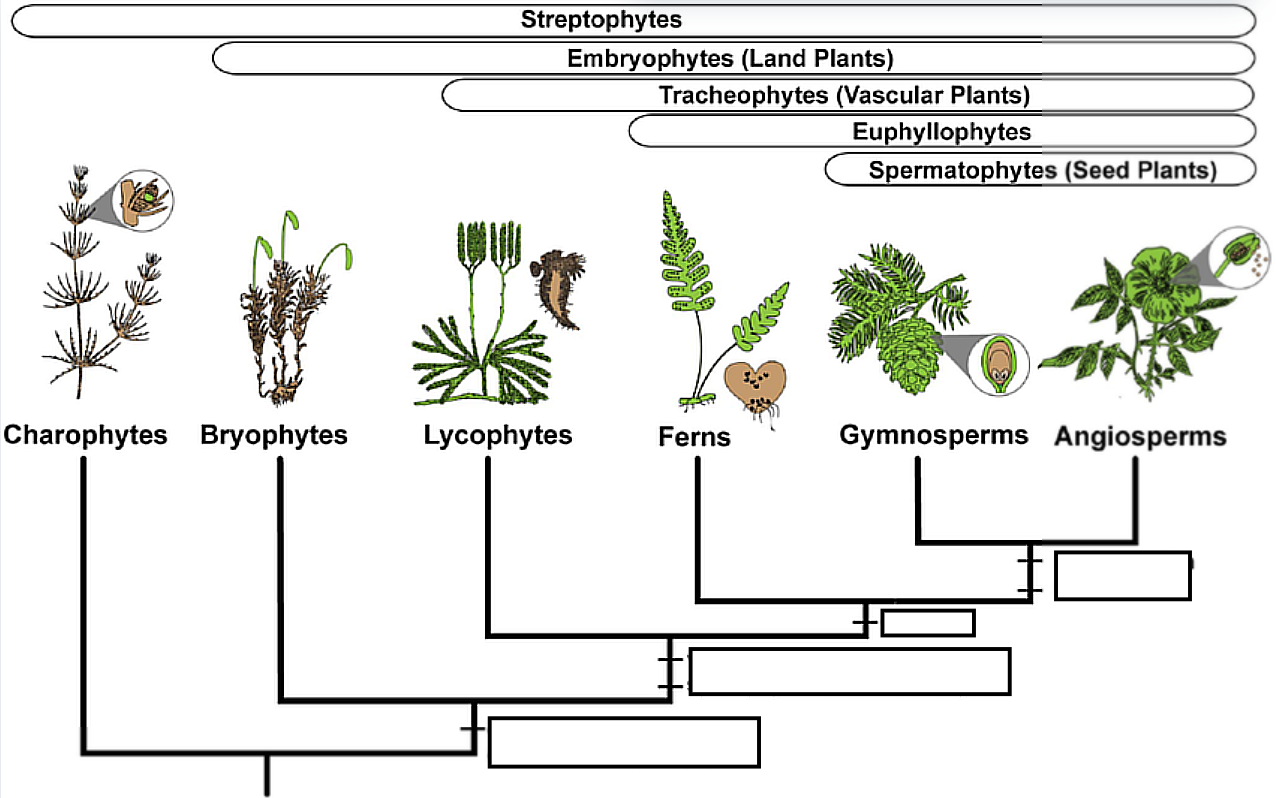
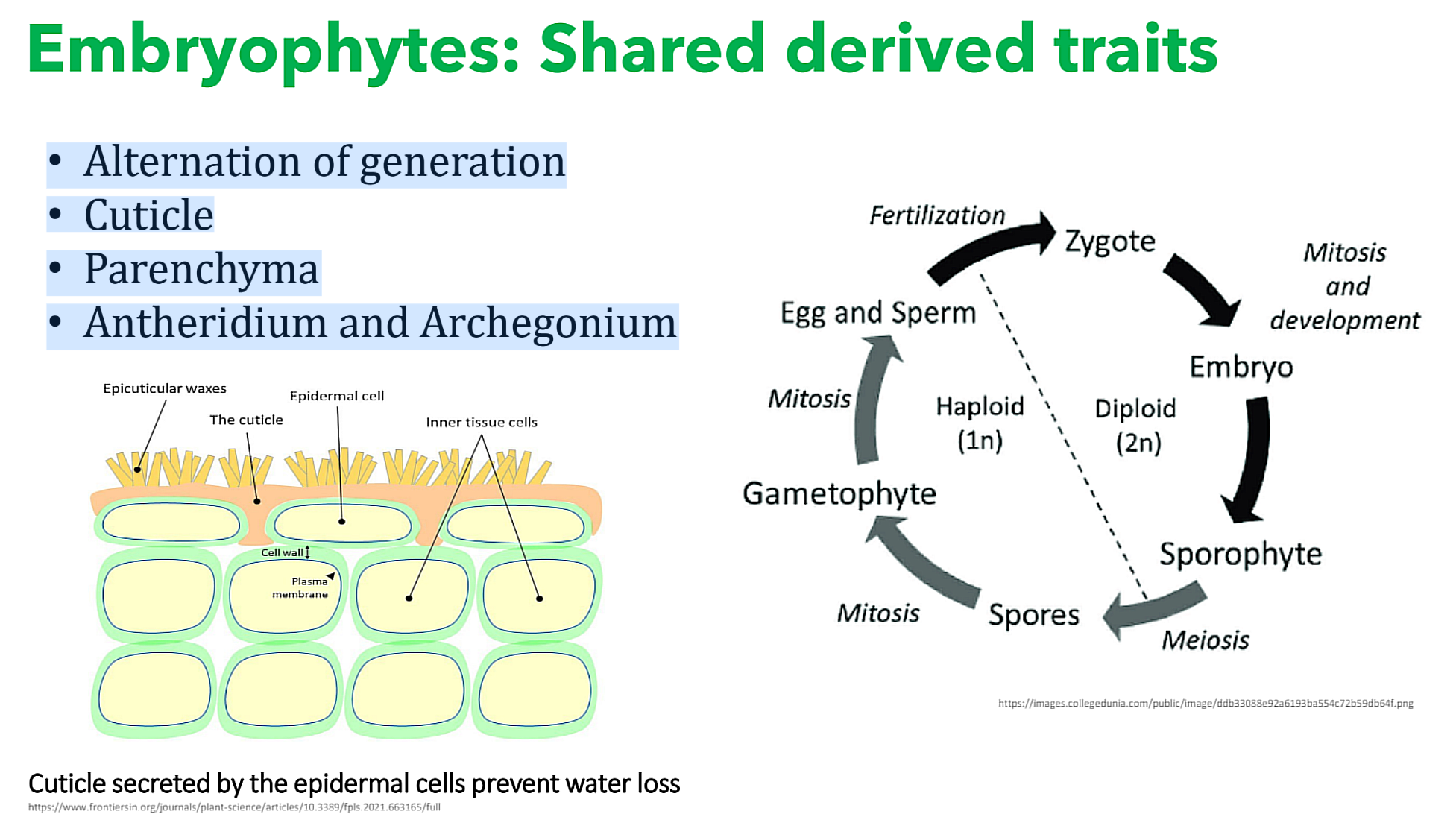
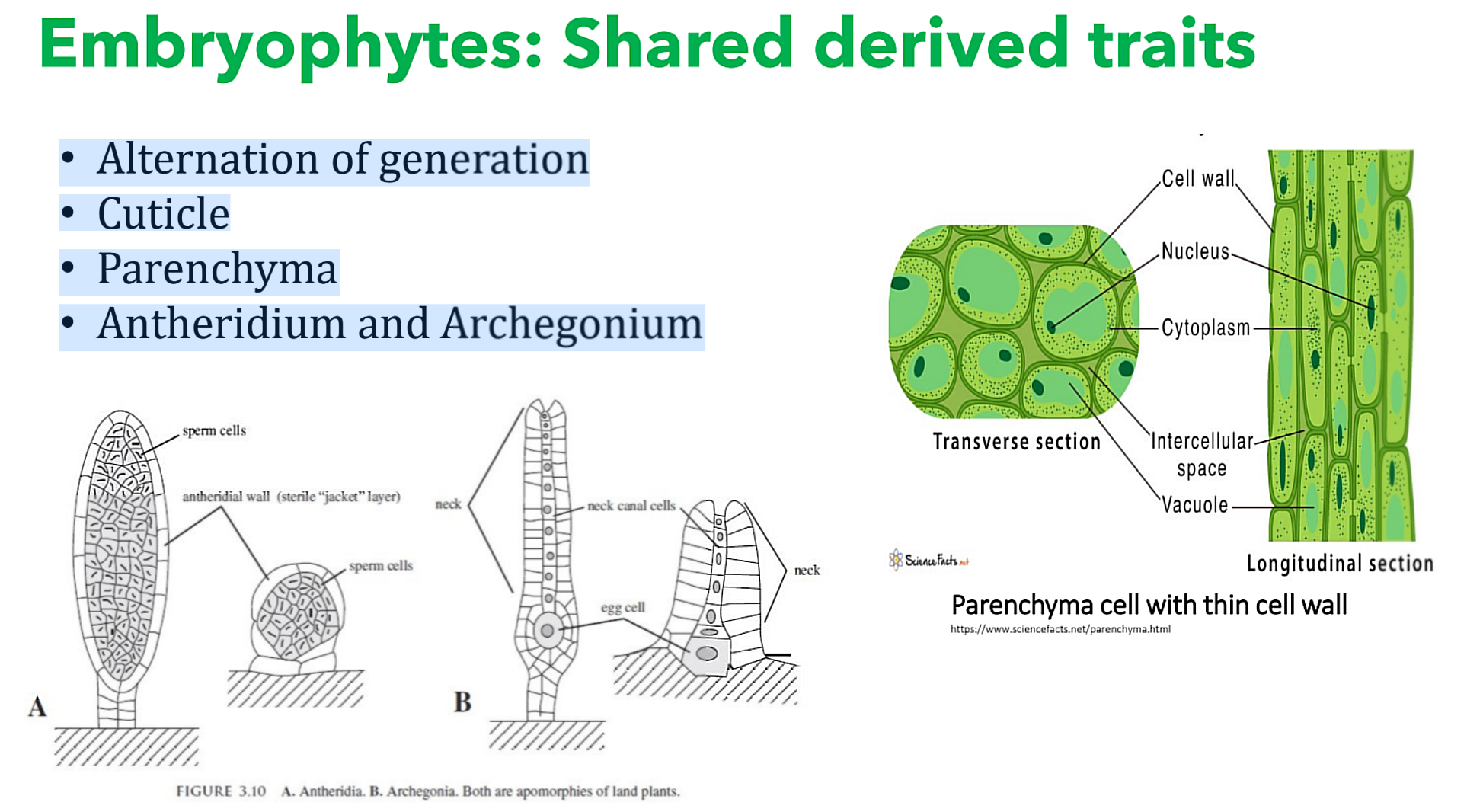
What are the Embryophytes: Shared derived traits?
• Small size
• Dominant gametophyte generation
• Lack of vascular tissues
• Rhizoids for anchorage
• Dependence on water for reproduction
What are all the Common Features of Bryophytes?
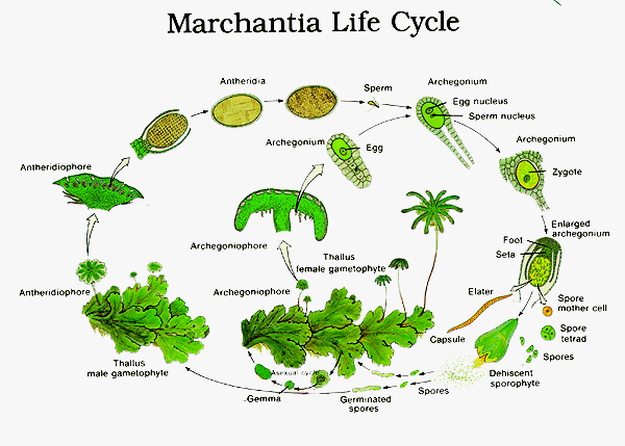
Marchantiophyta (6,000 species); Gametophyte (n)
Haploid
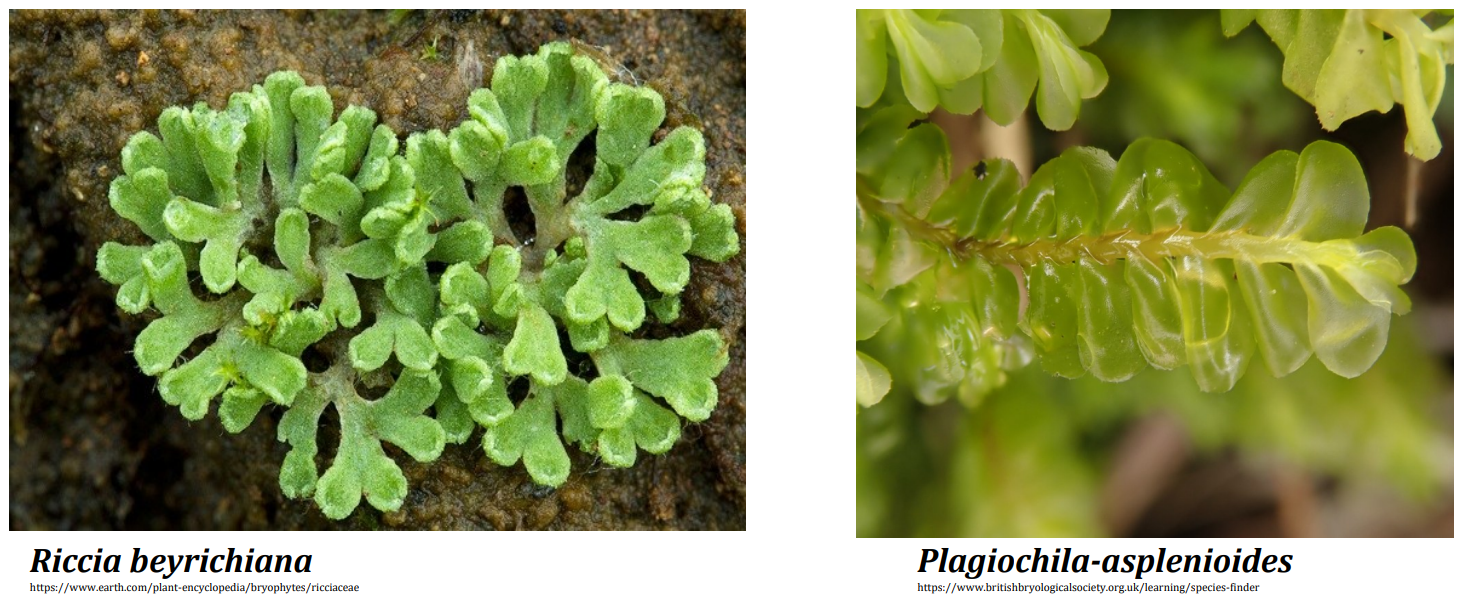
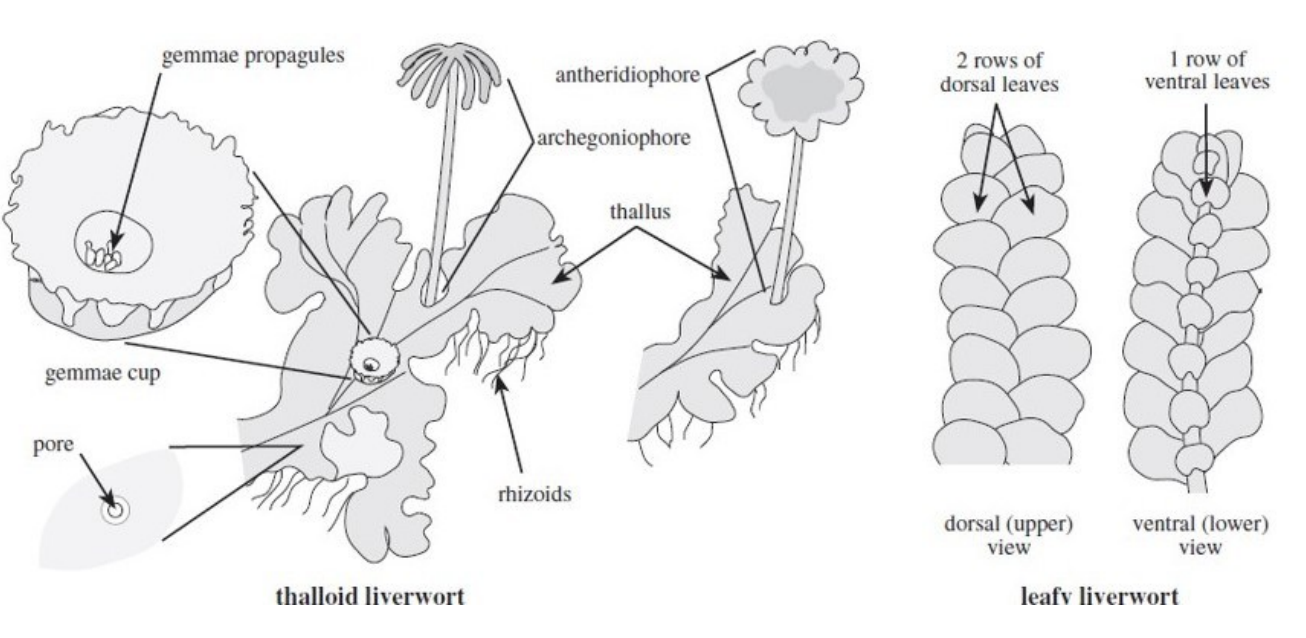

Division _______________________
Which generation?
- the free-living generation with both thalloid and leafy members
- what is its ploidy level?
Marchantiophyta (6,000 species), Anthocerotophyta (100 species); Gametophyte (n)
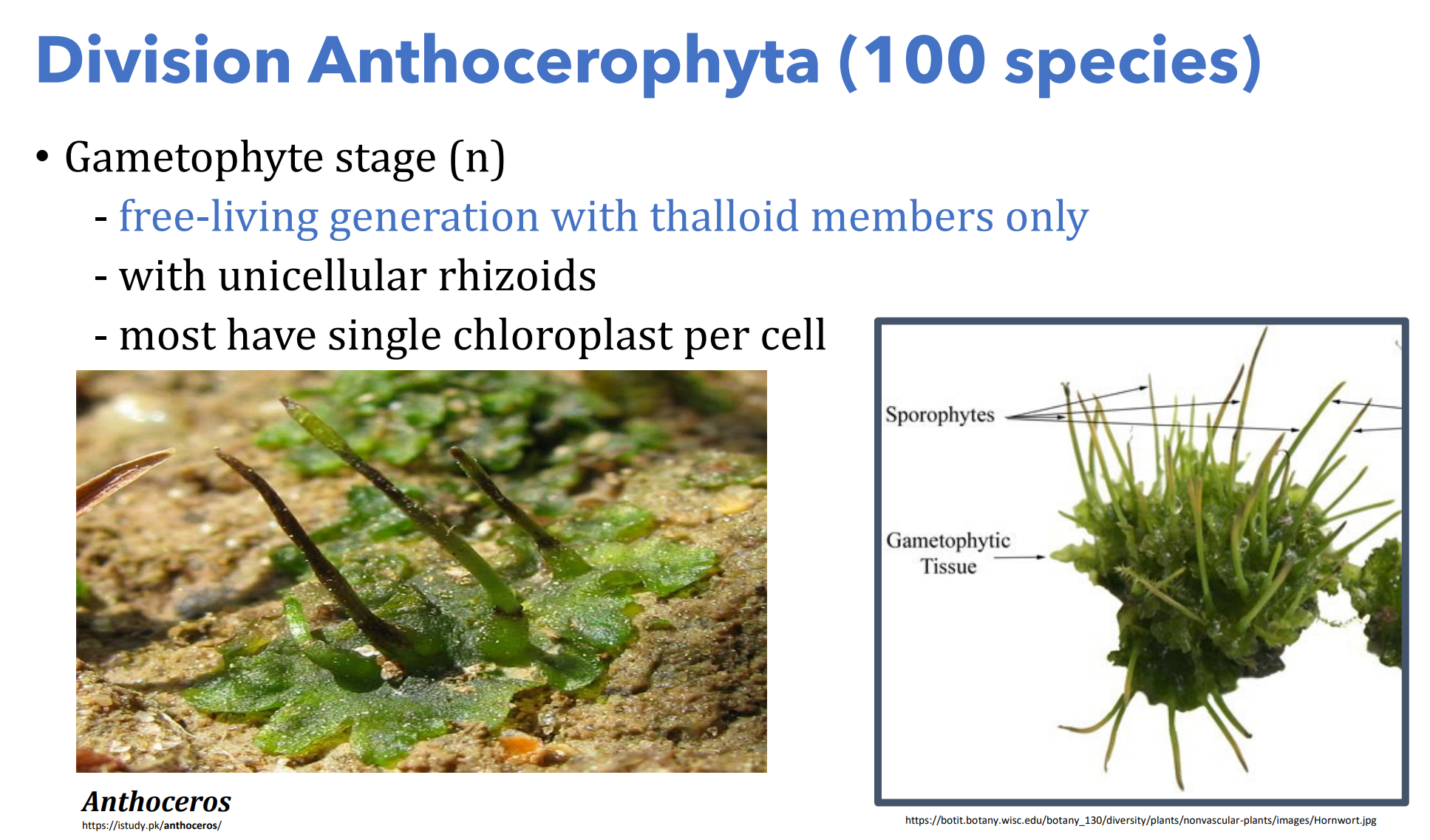
Division _______________________
Which generation?
- with unicellular rhizoids
Marchantiophyta (6,000 species); Gametophyte (n)
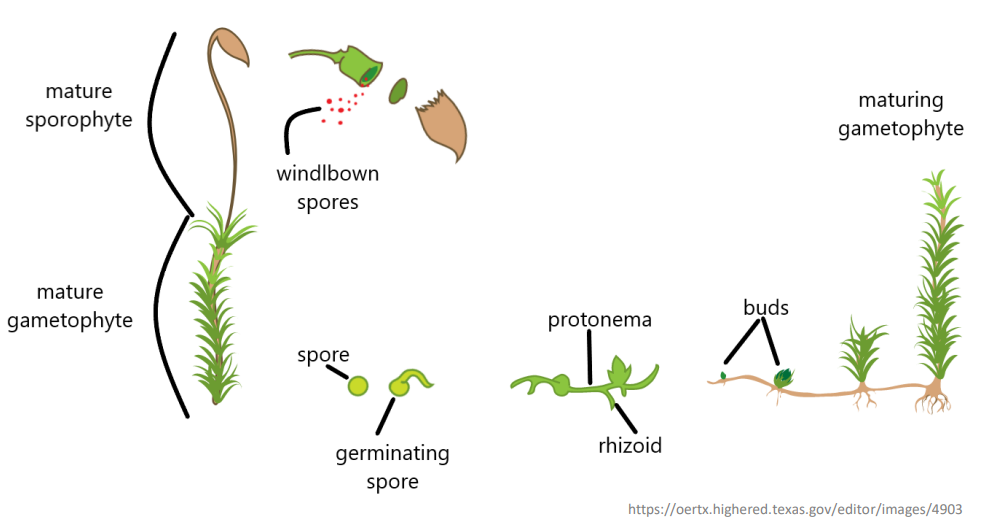
Division _______________________
Which generation?
- begins as a protonema stage in some genera
Marchantiophyta (6,000 species); Gametophyte (n)
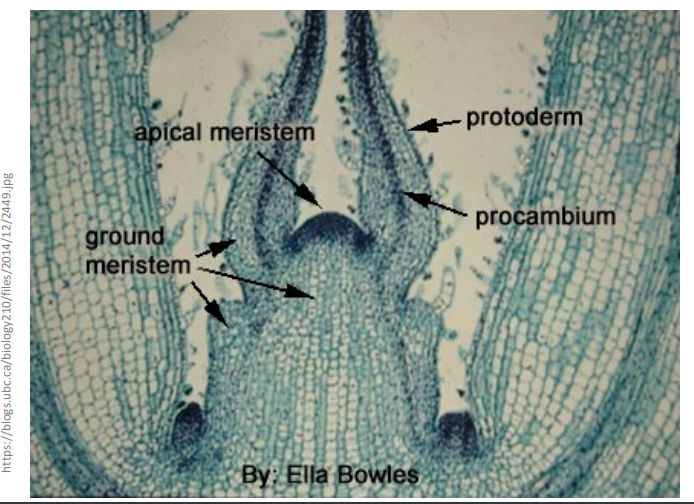
Division _______________________
Which generation?
- vertical growth is from apical meristem
Marchantiophyta (6,000 species), Bryophyta (9,500 species), Anthocerotophyta (100 species); Sporophyte (2n)
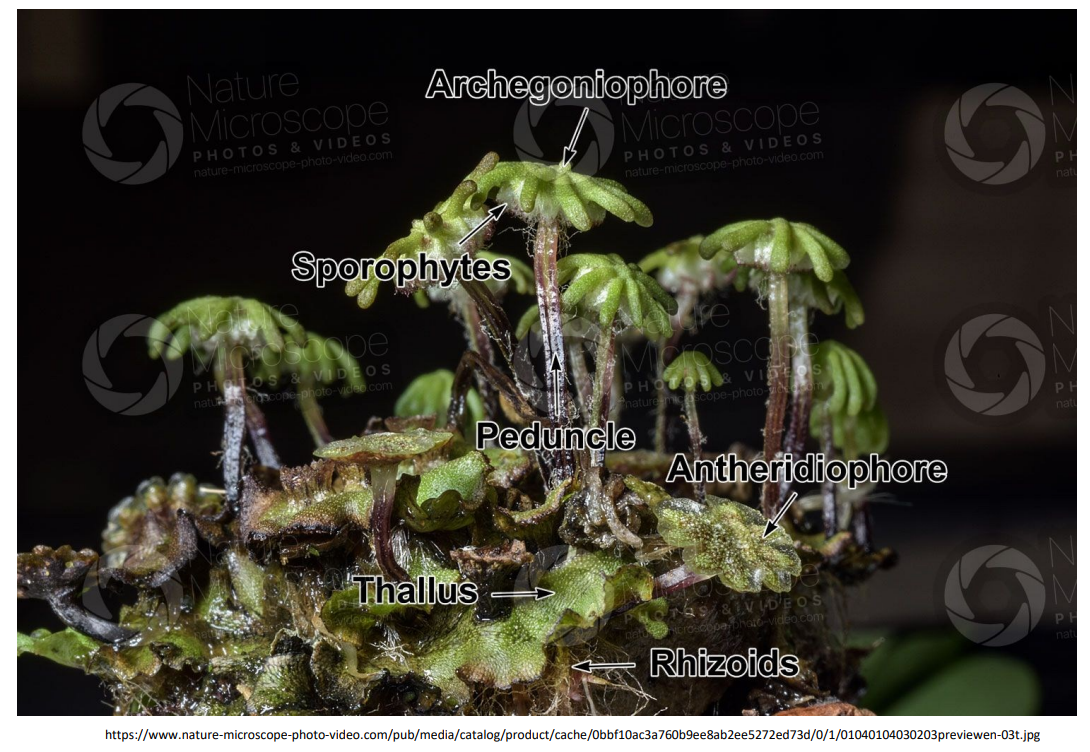

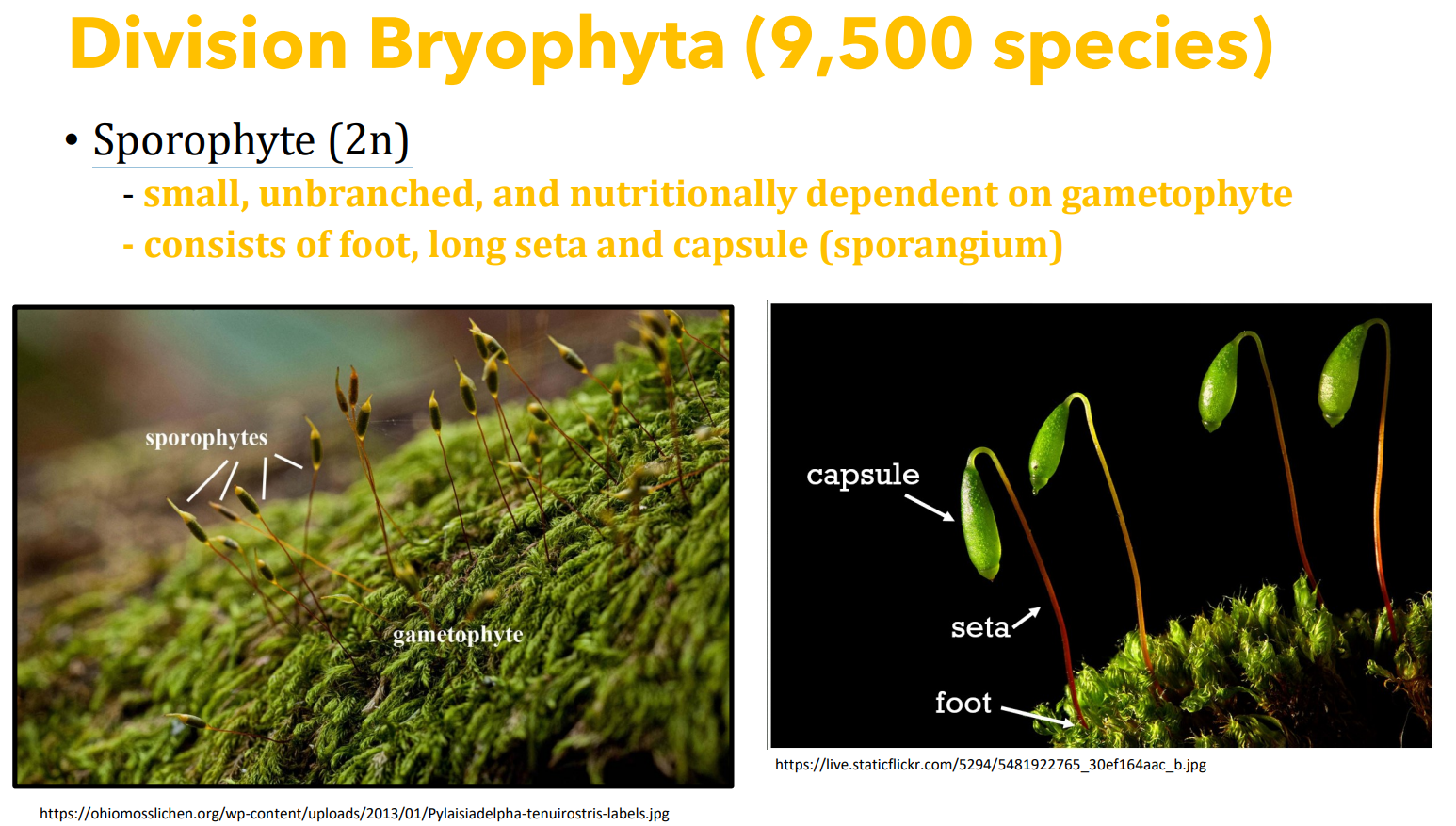
Division _______________________
Which generation?
- small, unbranched, and nutritionally dependent on counterpart generation
Marchantiophyta (6,000 species), Bryophyta (9,500 species); Sporophyte (2n)
sporangium

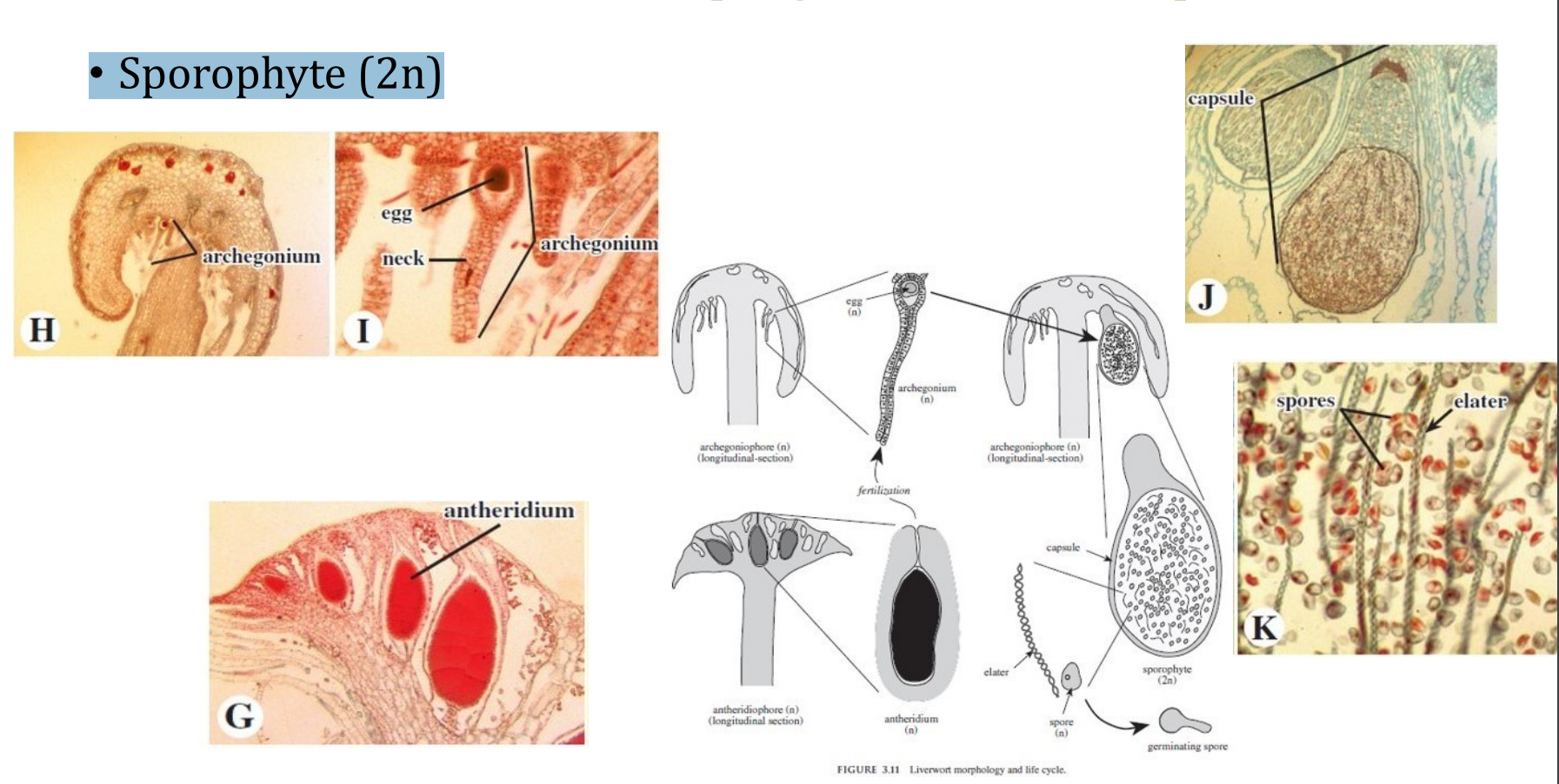
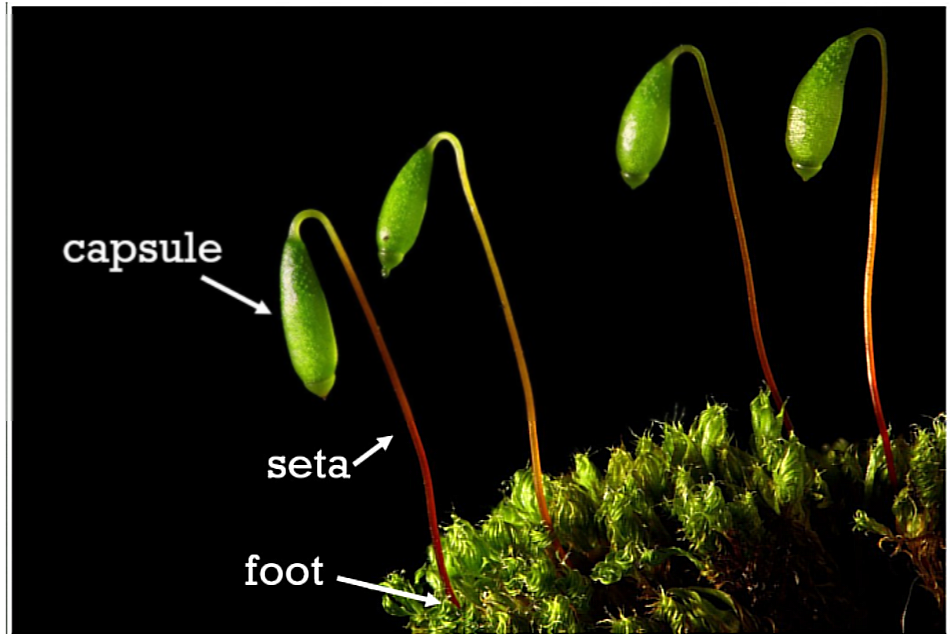
Division _______________________
Which generation?
- consists of a foot, seta and capsule (___________)
Marchantiophyta (6,000 species); Sporophyte (2n)

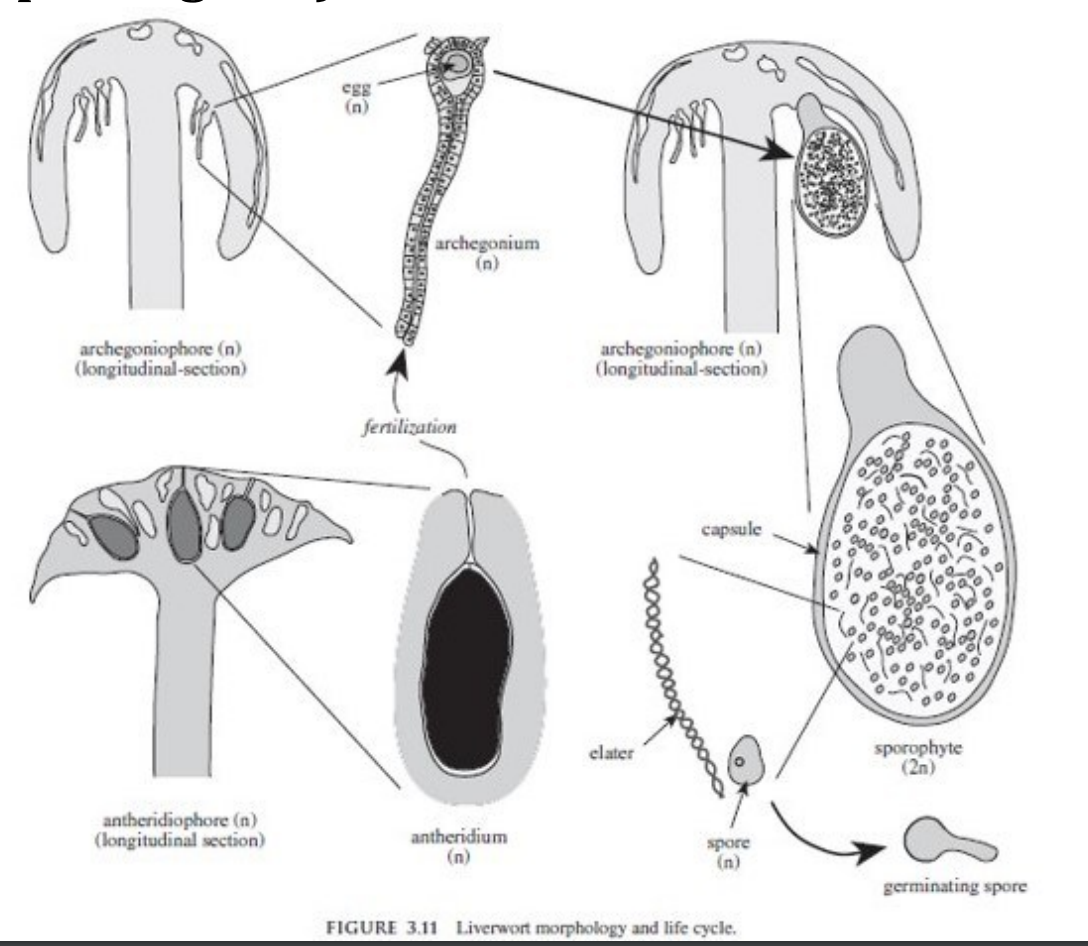

Division _______________________
Which generation?
- lacks stomata
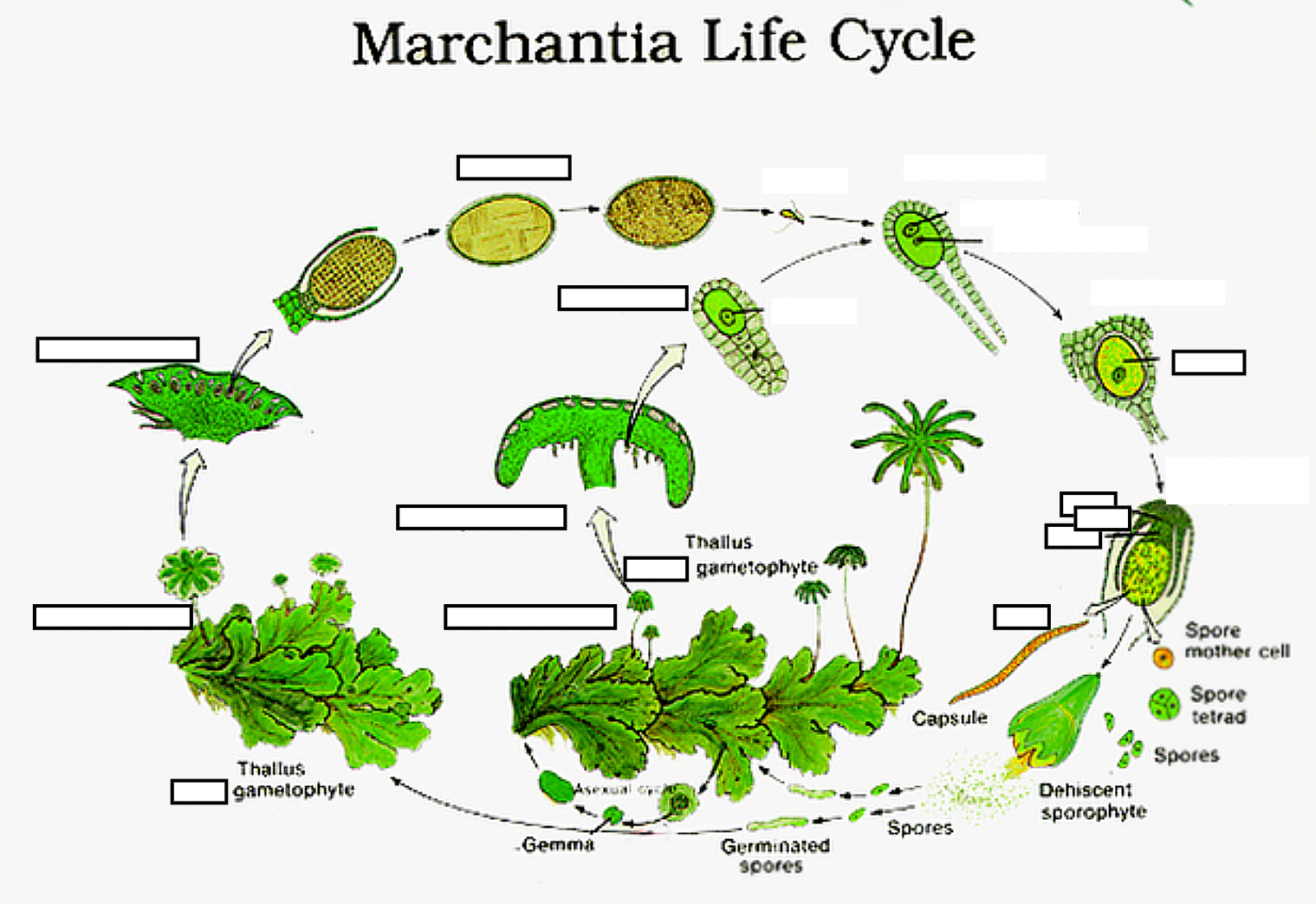
Bryophyta (9,500 species); Gametophyte (n)


Division _______________________
Which generation?
- free-living generation with leafy members only
Bryophyta (9,500 species); Gametophyte (n)


Division _______________________
Which generation?
- with multicellular rhizoids
Bryophyta (9,500 species), Division Marchantiophyta (6,000 species); Gametophyte (n)
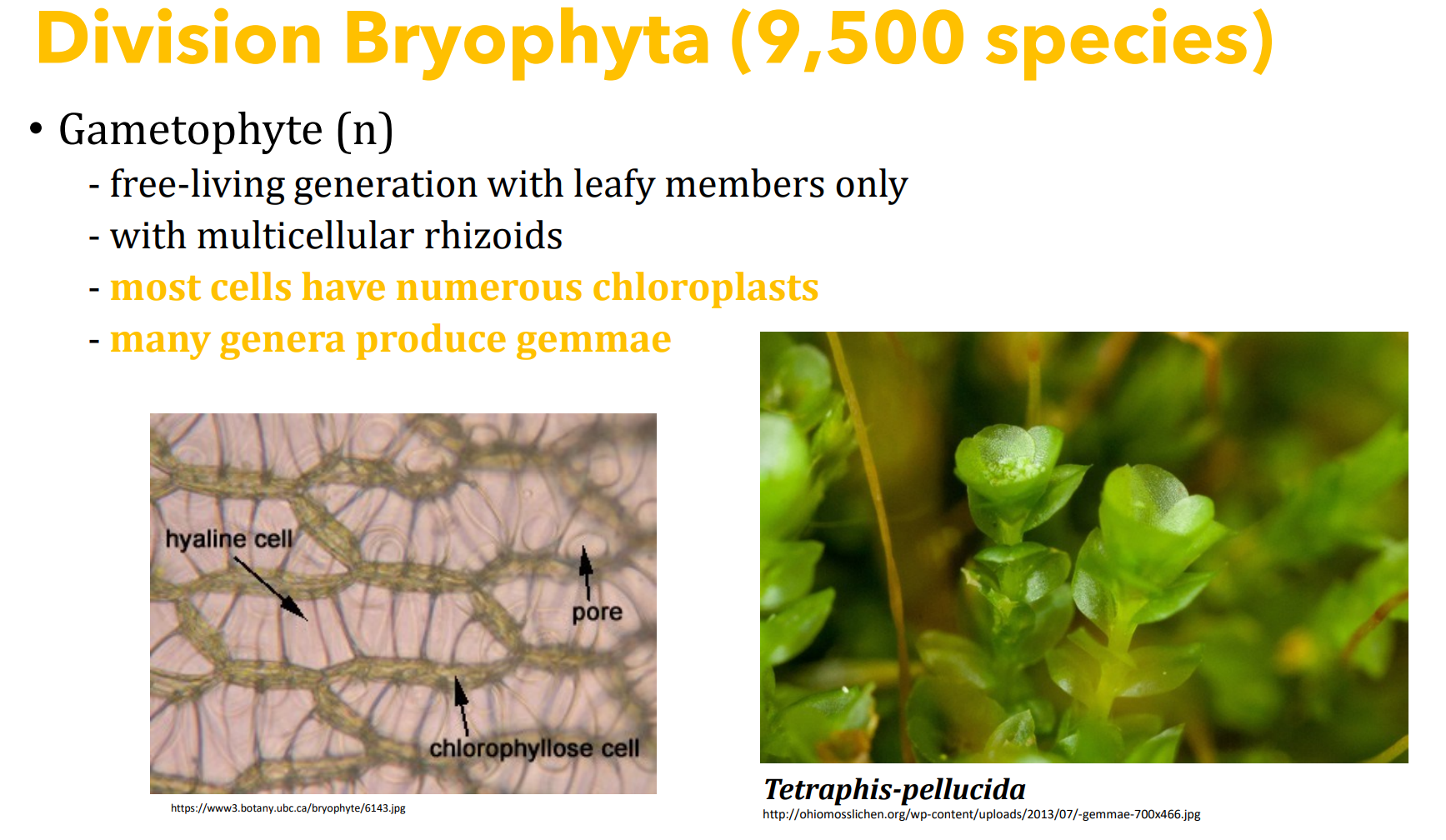

Division _______________________
Which generation?
- most cells have numerous chloroplasts
- many genera produce gemmae
Bryophyta (9,500 species); Gametophyte (n)
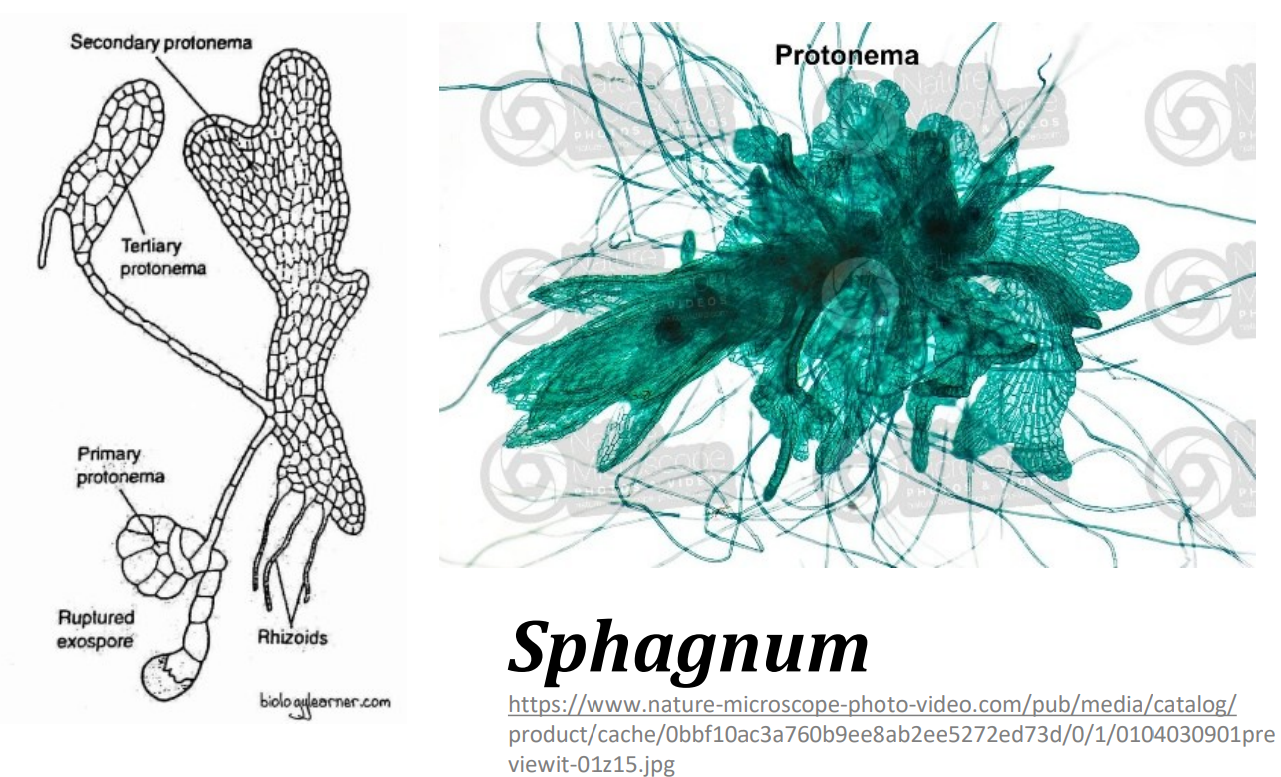
Division _______________________
Which generation?
- protonema stage growth by marginal meristem followed by further growth from an apical meristem in Sphagnum
Bryophyta (9,500 species); Gametophyte (n)
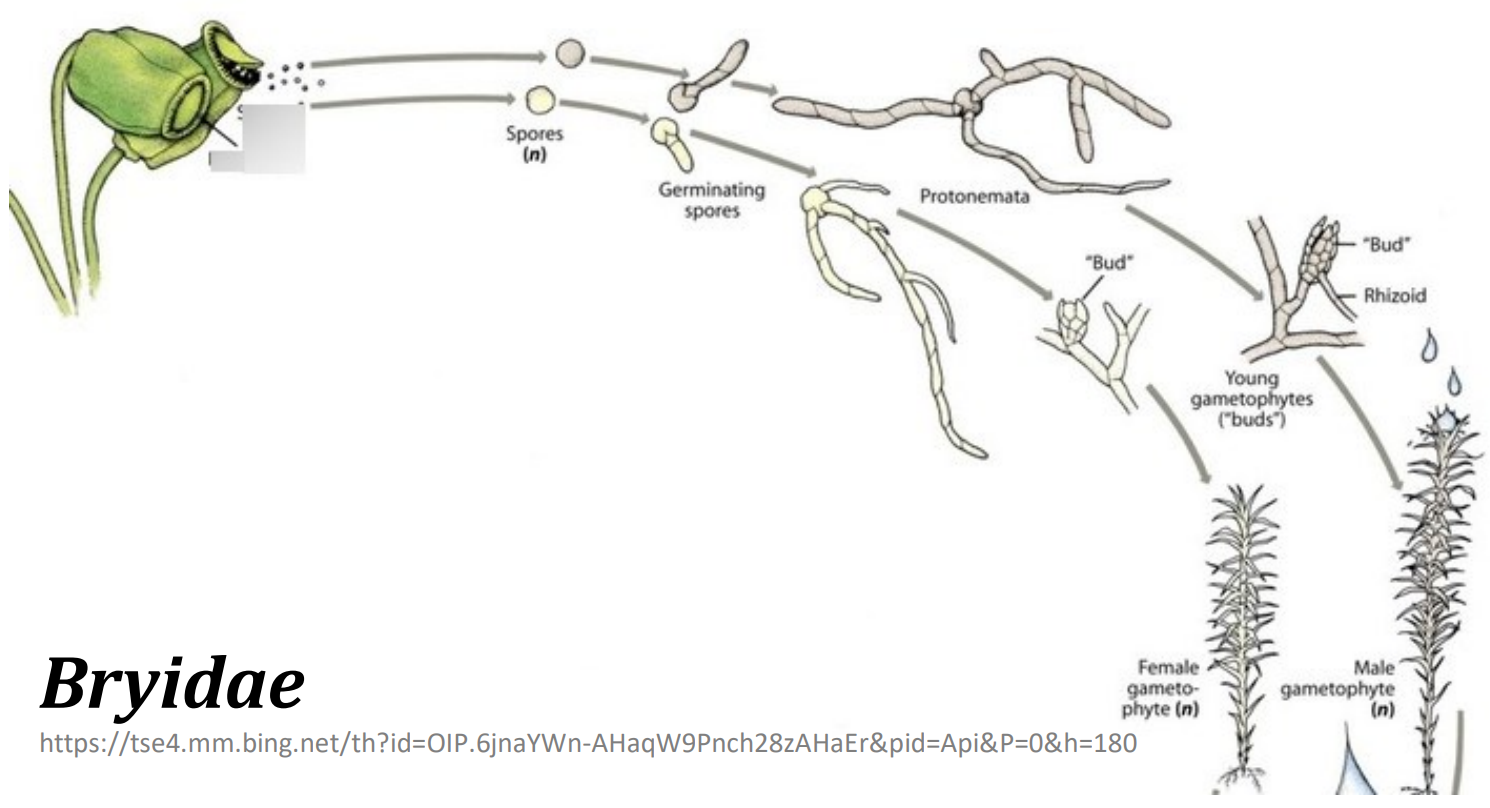
Division _______________________
Which generation?
- protonema stage growth by apical meristem only in Bryidae
Bryophyta (9,500 species); Sporophyte (2n); leptoids; hydroids

Division _______________________
Which generation?
- some species have _________ (food transport) and non-lignified _________ (water transport)
- some genera with stomata
Anthocerotophyta (100 species); Gametophyte (n)

Division _______________________
Which generation?
- free-living generation with thalloid members only
Anthocerotophyta (100 species); Gametophyte (n)

Division _______________________
Which generation?
- most have single chloroplast per cell
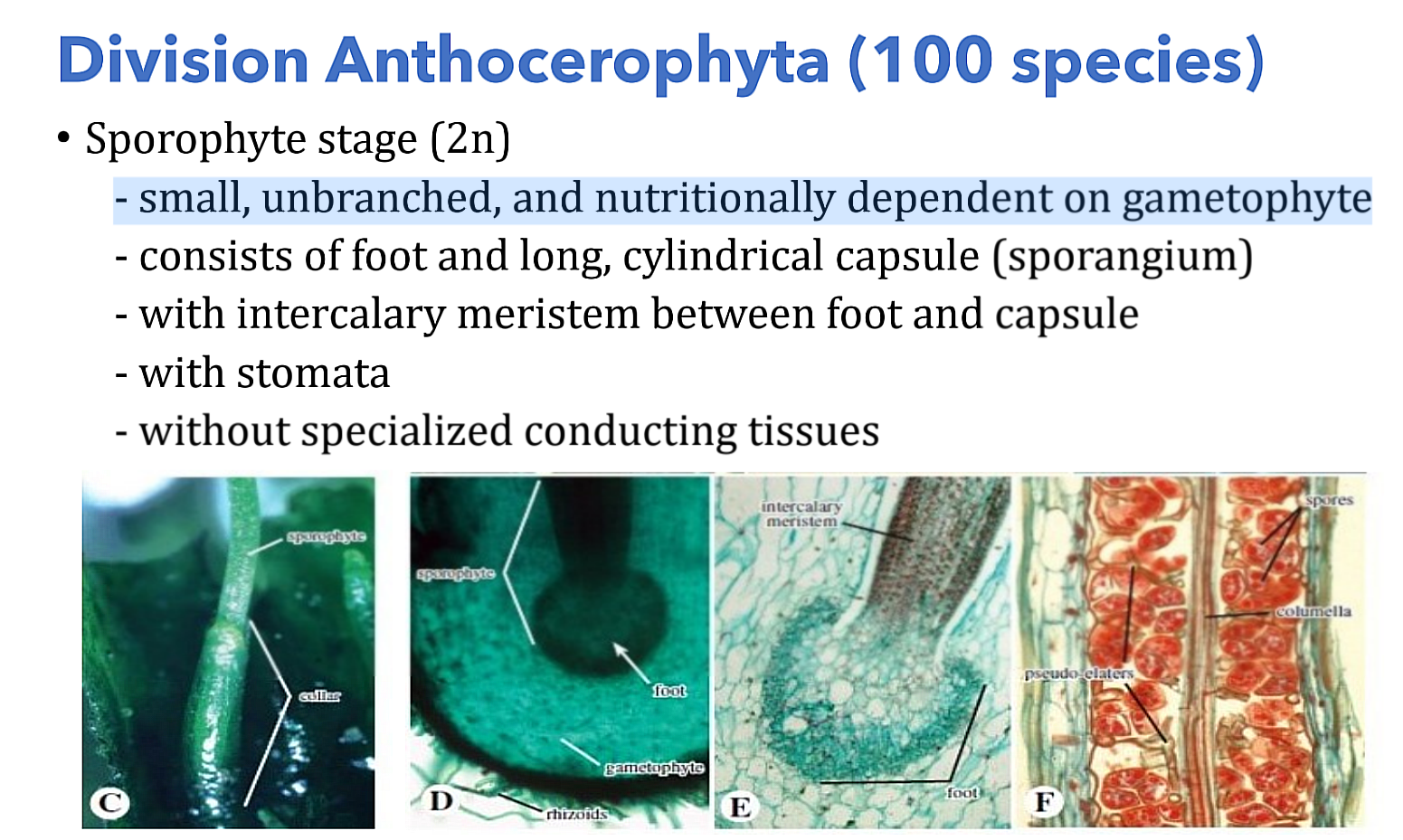
Anthocerotophyta (100 species); Sporophyte (2n); sporangium
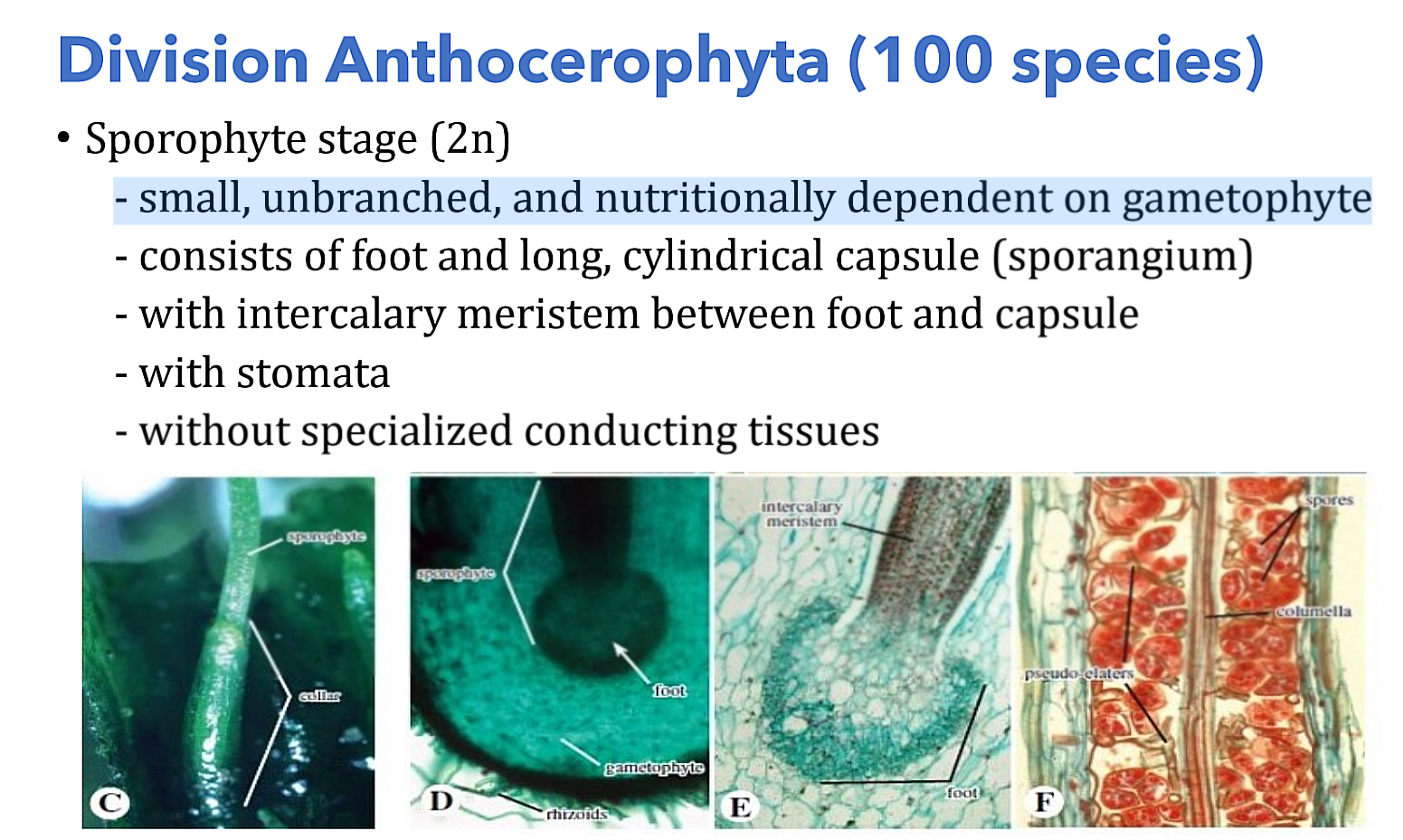
Division _______________________
Which generation?
- consists of foot and long, cylindrical capsule (___________)
Anthocerotophyta (100 species); Sporophyte (2n)
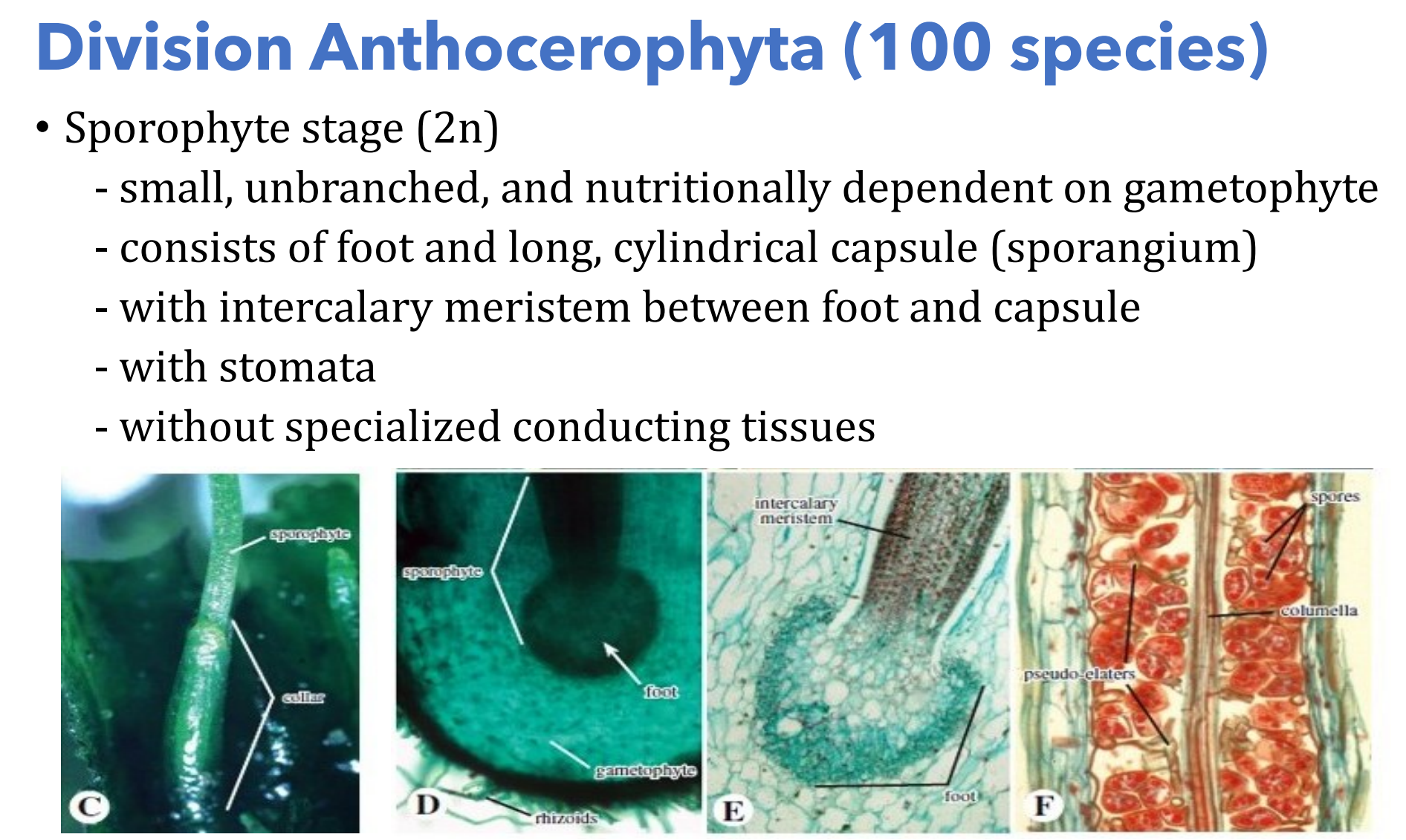
Division _______________________
Which generation?
- with intercalary meristem between foot and capsule
Anthocerotophyta (100 species); Sporophyte (2n)

Division _______________________
Which generation?
- with stomata
Anthocerotophyta (100 species); Sporophyte (2n)

Division _______________________
Which generation?
- without specialized conducting tissues
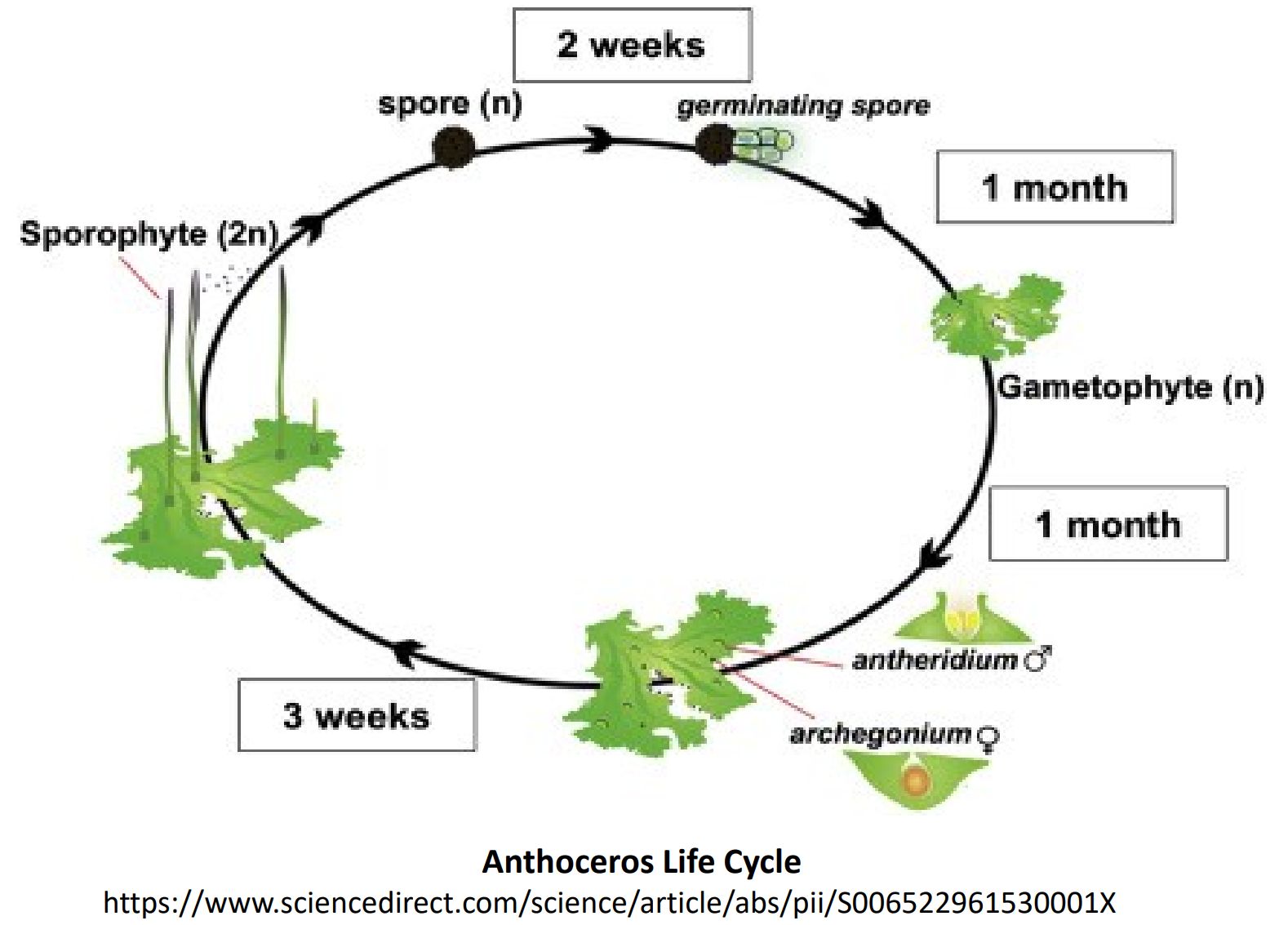

Bryophytes are pioneer species that contributes to the formation of soil for new plants to grow on.
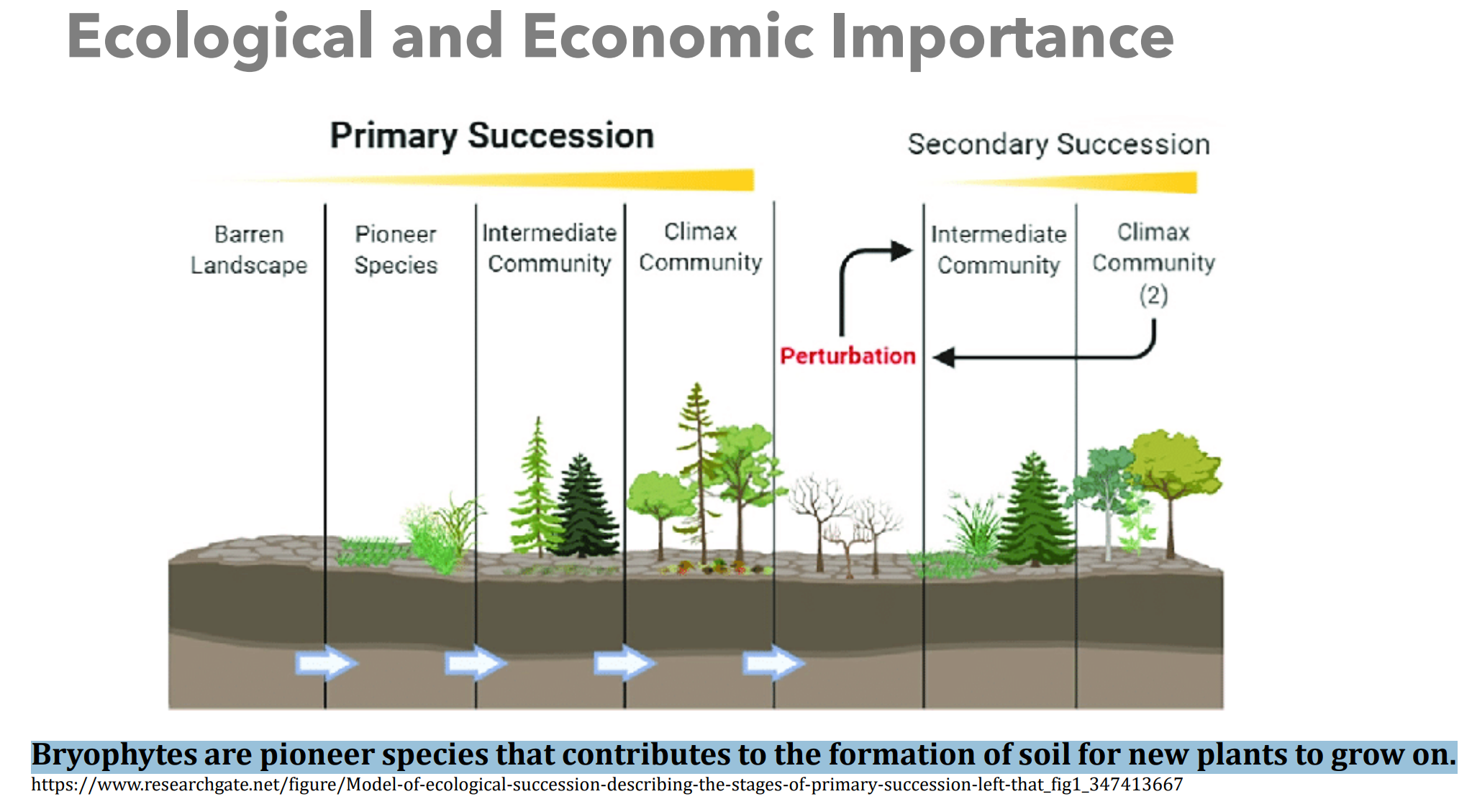
Ecological and Economic Importance
Why are bryophytes ecologically important?
Production of peat moss and a source of medically significant bioactive compounds.


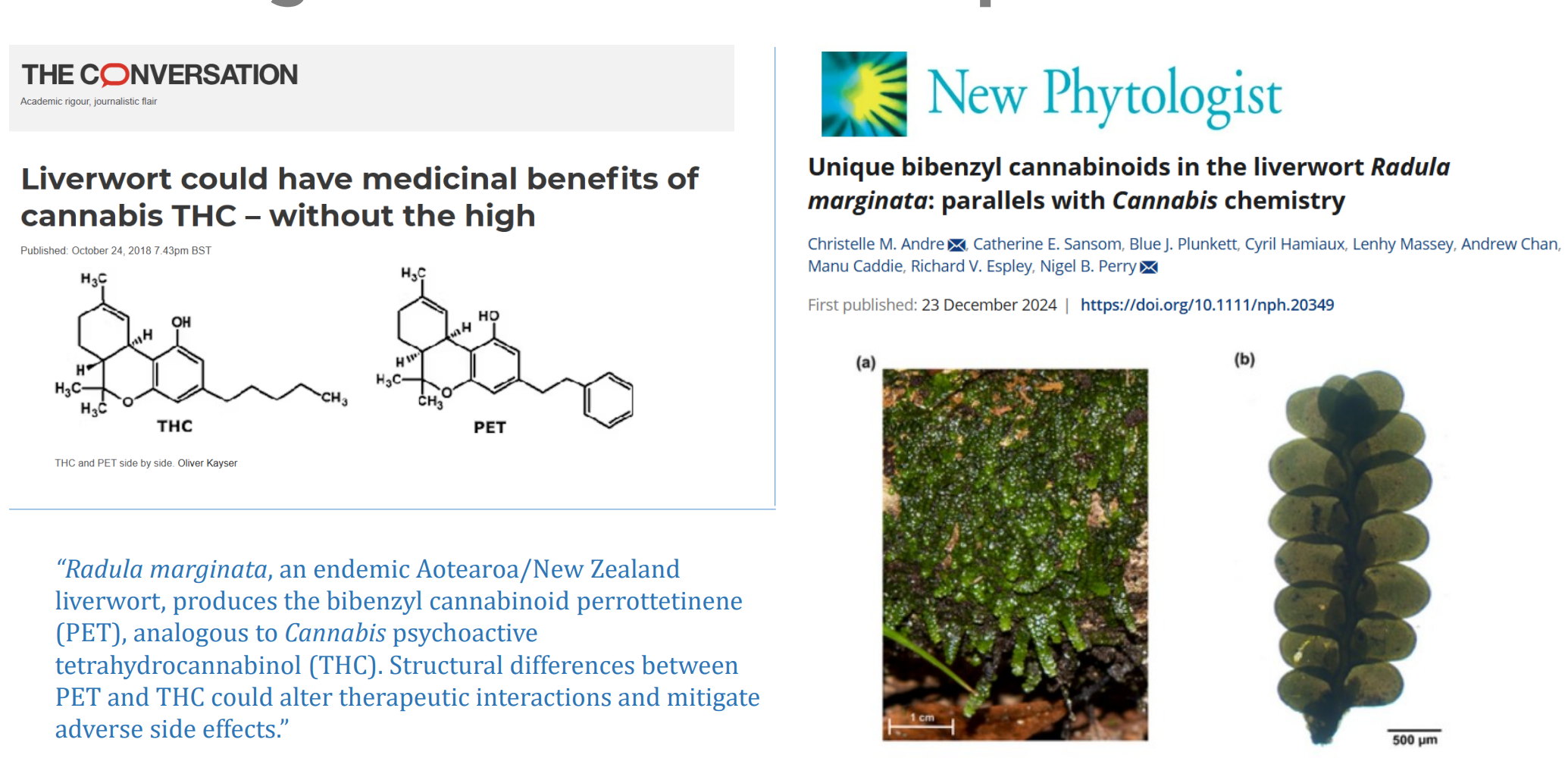
Ecological and Economic Importance
What are examples of bryophytes’ Economic importance?