mendelian inheritance study guide
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Who is Gregor Mendel and what is his contribution to genetics?
father of modern genetics" who discovered the fundamental laws of inheritance through his experiments with pea plants. He established that traits are passed from parents to offspring in predictable ways,
What model organism did Mendel use in his experiments (common and scientific name)? What are the characteristics of this species that made them suitable for Mendel’s experiments?
common- pea plants
sci name= Pisum sativum
good things about it: avail in several varieties (which varied in height and apperance) and the ease of making crosses
What is the difference between the blending and the particulate theories of inheritance?
blending theory of inheritance assumed that the characteristics of the parents were blended together in the offspring to produce an intermediate appearance. basically saying that there is a mix of traits and the baby is the average of the mix
With Mendel's particulate theory of inheritance, hereditary units of the parents were shuffled to produce new combinations in the offspring. states that discrete particles or genes are passed from parents to offspring. Genes that come from father and mother are independently expressed in offspring without merging or blending. Moreover, genes are passed from generation to generation
How did Mendel’s results differ from the understanding of heredity back in the 1700 and 1800’s?
Mendel’s results differed from the prior understanding of heredity because he showed that traits are passed down as discrete, particulate units (genes) that do not blend, but instead segregate and are inherited independently
What is a cross, hybridization and a hybrid?
cross and hybridization= s the ACT of breeding two distinct indivs with diff characteristics
offspring are HYBRIDS
ex= white purple plant and a white flower plant is a hybridization and the offspring from them are hybrids
What is the difference between cross-fertilization and self-fertilization?
cross fert= when you make two different particular plants cross by putting pollen from plant A onto the stigma of plant B
Pea plants have flowers with both, the male and the female parts, describe the experimental procedure conducted in order to prevent self-fertilization. Describe how cross-fertilization is conducted.
first, the prevention of self fert was done by Mendel prying open immature flowers and removing the anthers before they made pollen.
cross fert process: 1) removed anthers from purple flower. 2) used paintbrush to transfer pollen from anthers of white flower to the stigma of purple flower 3) cross poll happens
describe the laws of segreg and indep assort
laws of segregate= the genes SEGREGATE AKA SEPERATE. each gamete gets one aL.
laws of indep assort= no one can influence me. the aL for one gene seperate independently of the aL for another gene as long as the genes are diff chroms or far apart. helps have rnadom combos on the chrom
what is simple mend inherit
what types of aL play a role here
simple mend inherit=inherit controlled by a single gene with two aL. for ex, color of flower in pea plants is controlled by a single gene
two aL types: Dom and recess
what are mutant aL
how cmmon are they in pops
HUH
an aL that shows a DNA seq change (cuz of mutation)
common:
dom vs recess meaning
dom= it will show even if only one copy is present
recess= it will only be expressed and shown if two copies care present
what is a punnet sq
shows the possible combo of aL for a genetic cross
genoT vs phenoT vs phenoT ratio vs genoT ratio
geno= organism’s full heriditary information that is the unique DNA seq
pheno= an org’s actual observed properties that can be seen based on what the genotype is showing
genoT ratio= the proportional distribution of diff gene combos
phenoT ratio= what is the freq of diff observable traits in offspring
homo vs hetero org
having two identical aL for a gene = homo
hetero= two different aL for the same gene
true breeding line def
just means that through self pollination (a lot of it), they will all be homozygous for a specific trait- resulting in babies that have the same phenos has the parents.
when to use product rule vs binomial expansion vs multinomial expansion vs simple probability HUH
simple probability= likelihood of a single event occuring. so what is the chance of Event B happening out of all the total possibilities. just use the punnet square and no formulas
binomial= likelihood of seeing the prob of diff combos of offspring aka how many will show a certain trait. valid for things like, what is the prob of 3 out of 5 kids being affected. wont just talk about a single child.
product= this is where order matters. will be like- prob of getting affected kid first, then no affected second
mono vs dihybrid (single vs double factor crosses)
mono/single factor cross= examining one trait controlled by one gene
dihybrid/double factor= two traits controlled by two genes. for example, we could look at both seed shape and seed color. it would look like RrYy.
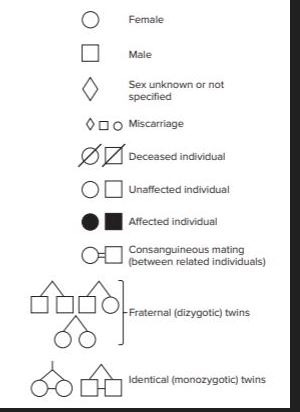
what is a ped chart
useful why
family tree diagram that shows how a trait is passed from on gen to next.
useful= powerful because they help you figure out mode of inheritance
what is msud
causes at genetic, cell and org level
symps
treatment
Dom or recess
what: meta disorder where body cant break down leucine, isoleucine and valine. which leads to urine smelling like sweet maple syrup
cause: by changes in one of the genes aka bckdha, bckdhb and dbt. this can lead to decreased activity of bckad enzymes that break down isoleucine, leucine and valine in proteins. when its not there, accumulation of these AA and their byproducts lead to interference with NTs, energy production in neurons, metabolic acidosis.
symp: tired, poor feeding, seizures, abnormal mvmts, brain swelling
tx: protein restricted diet, hemofiltration , thiamine supplementation, liver transplant
recess
why are rare genetic diseases common in comms such as Amish
ancestors are a small group of founders. any recessive mutation became more common in later generations. plus the people tend to marry within the community which increases chance of two carriers of the same recess aL having kids. basically the small pop and closed gene pool did this
wht is a carrier
person who carries one copy of a mutated gene for an inherited disease but wont have the D themselves.
phenoT will even say unaffected
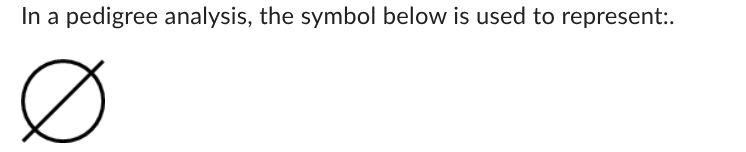
dead F

carrier man
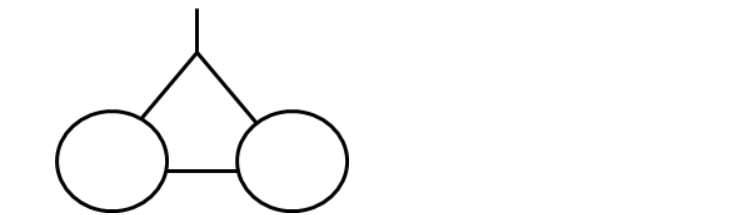
twins

affected F
analyze pedigrees and see if ur good
yes