Radiology test 2
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
Emergency
An emergency is a serious unexpected event that demands immediate attention
Level 1 - Trauma Unit
Helicopter rescue, radiology, fluoroscopy, CT, MRI, nuclear medicine, angiography, sonography, neurologic care, highly trained support - surgeons, physicians
Level 2 - Trauma Unit
ED physicians 24 hr duty, trained nurses, radiology, surgicial, fluoroscopic, angiography, CT, MRI, patients can be transferred to level 1
Level 3 - Trauma Unit
Smaller community hospitals, ED physicians and radiology on call at night, can be transferred to level 2 or 1
Golden Hour
Stabilizing the trauma patient within the first hour after the accident
What three assessments are there for golden hour?
Cardiac, Respiratory, Vertebral Fracture
What imagining is primarily for trauma patients?
Primarily CT
Chest, pelvis, lateral cervical spine - radiology
STAT
30 mins
ASAP
2 hours
Routine
12 hours
Triage
process of identifying victims, initial examination and assigning priorities for futher care
-Cardiac
-Respiratory
-Vertebral Fracture
Emergency Code - RED
FIRE
Emergency Code - BLUE
Cardiac arrest, cessation of respiration
Emergency Code- ORANGE
Hazardous material spill
Emergency Code- GREY
Combative person
Emergency Code- Silver
Weapon or hostage
Emergency Code - AMBER
Infant/Child abduction
Emergency Code- YELLOW
Internal/External Disaster
Emergency Code- RAPID RESPONSE
Team response for deteriorating medical condition
Emergency Code- TRAUMA TEAM
Team response for trauma patients
Emergency Code- CLEAR
Resolved
Name some things on emergency carts (crash carts) ?
Board, Stethoscope, defibrillator, blood pressure, syringes or needles, chest compression
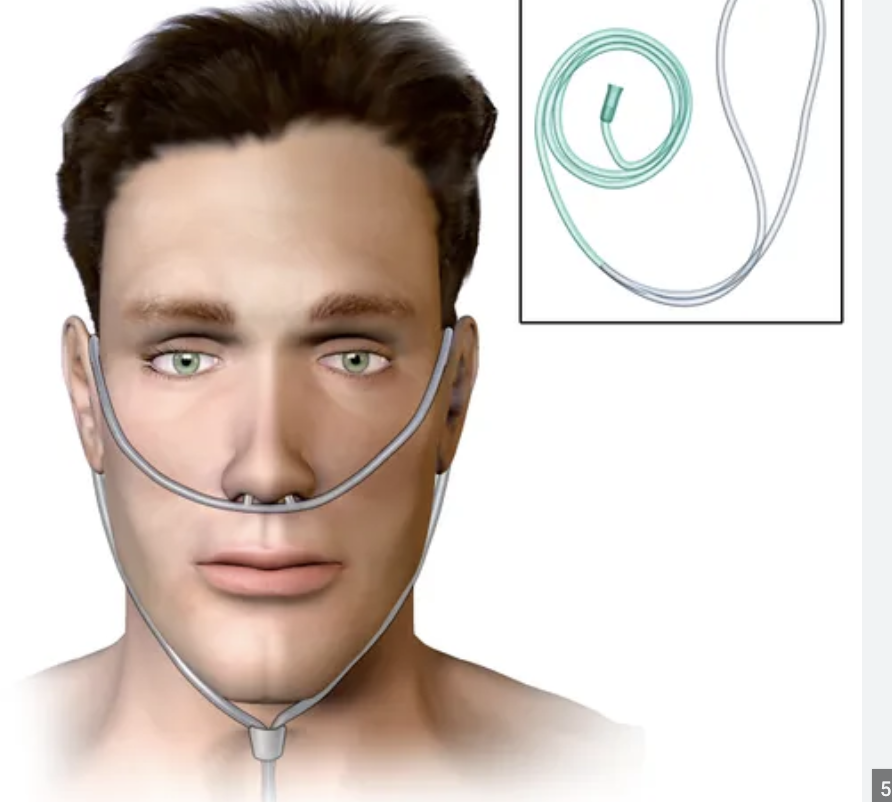
Nasal Cannula
Simple and most frequently used for long term oxygen administration
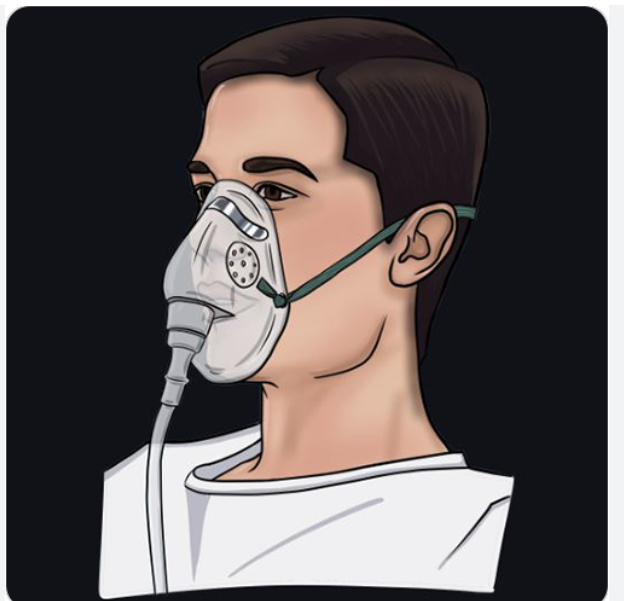
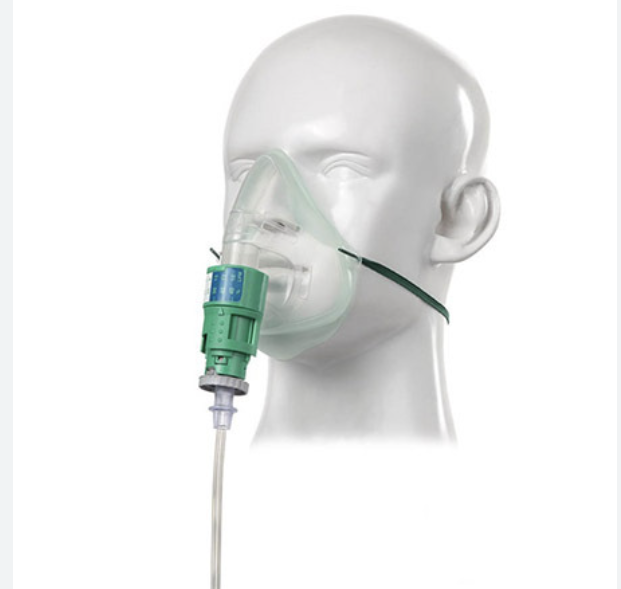
Simple face mask
Short term, uncomfortable, provide oxygen and humidity
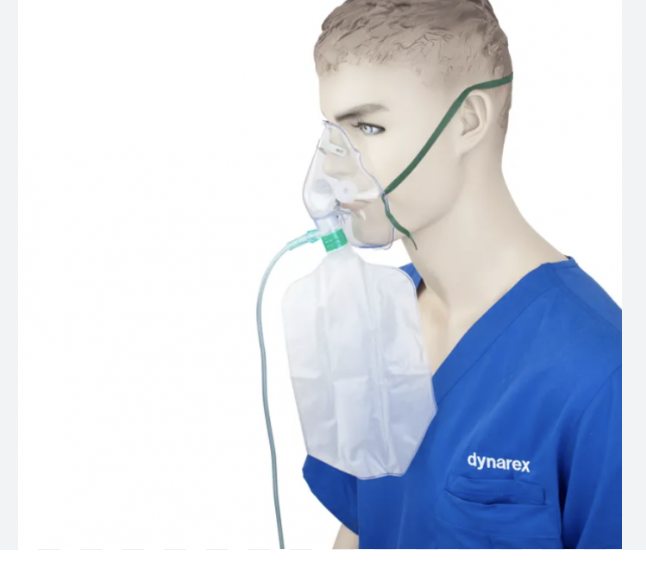
Non-rebreathing mask
Attached reservior bag, 100% oxygen
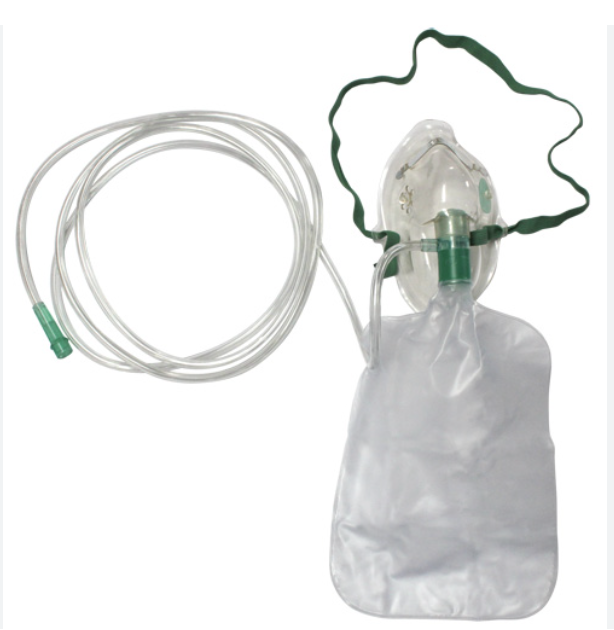
Partial rebreathing mask
Allows some exhaled air to enter the bag, oxygen = 40%-70%
High flow mask
Venturi mask, oxygen = 24%-60% for patients with COPD
Tent
Higher rate of humidity and oxygen, pediatric department for children
Used when kids need extra oxygen but aren’t ready for a nasal cannula or mask
Tracheostomy
opening in trachea and tube inserted which allows air to bypass nose and mouth
Intubation
ET tube (ETT), tube passed through oral cavity into trachea
Ventilator
Respiratory device, controls respiratory rate, volume of inspiration rate, and oxygen content
Moving 02 from tank to wall
Maintain flow rate
Check flow meter
Both valves must be turned on
Under no circumstances should oxygen be completed removed
Respiratory arrest
Breathing stops
Pulmonary Embolism
blood clot blocks one of the pulmonary arteries in your lungs
When is suction needed?
Mucous, blood, vomitus
All respiratory Emergencies
Respiratory arrest
Choking
Asthma
PE - Pulmonary embolism
Cardiac Emergencies
Cardiac Arrest
Myocardial infarction
Angina Pectoris
Angina Pectoris
Unable to supply heart with oxygen
Myocardial infarction (MI)
Heart Attack
Cardiac Arrest
Heart stopped beating
Contrecoup injury
Injury is on the opposite side of the blow
Levels of Consciousness
Alert + Conscious
Drowsy but responsive
unconscious but reactive to painful stimuli
comatose
Glasgow Coma scale
-To assess a persons LOC
Eyes, verbal, motor responses
highest number = 15
Chest injuries
Hemothorax (blood in pleural space) and Pneumothorax (air in pleural space)
Treatment = chest drainage (thoracentesis)
Types of shock
Hypovolemic
Neurogenic
Cardiogenic
Septic
Anaphylactic
Hypovolemic shock
Large amount of blood has been lost
Neurogenic shock
Injury to nervous system caused by head or spinal trauma
Cardiogenic Shock
Cardiac failure caused by interference with the heart function
Septic Shock
Massive infection
Anaphylactic Shock
Allergic reaction, contact with foreign substances which the individual has become sensitized
Diabetes Insipidus (DI)
Caused by kidney or pituitary disorder
polyuria + thirst
Fever, vomiting, and convulsions
Diabetes Mellitus (DM)
Type 1 - Autoimmune, under 25 years old, genetic environmental cause, Diabetic coma
Type 2- over 40 years old, low blood sugar, treated with hypoglycemic drugs
Cerebrovascular Accident (CVA)
Stroke
caused by hemmorrhage + occulusion
When blood flow to part of the brain is suddenly blocked or interrupted
FAST
BEFAST
Face, Arm, Speech, Time
Balance, Eyes, Face, Arm, Speech, Time
Used to spot warning signs of a stroke
Vertigo
Lightheaded + dizzy because the room will be spinnin
Syncope
Fainting
Orthostatic Hypotension
-A mild reduction in oxygen supply to the brain that occurs with changes in body position
-Standing up too fast, start to feel lightheaded when getting up
Epistaxis
Nosebleed
Sterile members in the OR
Surgeon
Surgical Assistant
PA
Scrub nurse
CST - Certified Surgical technologist
Non-sterile members in OR
Anesthesia provider
Circulator
Radiographer
3 key elements to have a fire
Fuel
Oxygen
Heat
-Most common is electrical
RACE
Rescue, Alarm, Contain, Extingush/Evacute
-What to do when there is a fire
PASS
Pull, Aim (at base), Squeeze, Sweep
-using a fire extinguisher
Ergonomics
Study of the human body in relation to the working environment for the purpose of preventing injuries
Body mechanics + 3 principles
Principles of proper body alignment, movement, + balance
Base of support
Center of gravity
Line of gravity
3 items used with stretcher transfers
Draw sheet
Slider Board
Sliding mats
Element of history
Onset
Duration
Location
Quality of pain
Aggravates
Alleviates
Subjective data
Patient feelings, Pain level, Attitude, Opinion of observer
Objective Data
Perceptible to senses, able to be measured, signs that can be seen,heard, felt
ex. Skin temp, pallor
Pallor
Refers to the color of skin
Pale, Cyanotic, jaundice
Diaphoretic
Cold sweat
Orthopnea
Difficult to breath lying flat
Name the vital signs
Temperature
Pulse
Respiratory rate
Blood pressure
Normal temperature
98.6 Degrees Fahrenheit (+ or - 1)
Normal Pulse
60-100 BPM
Normal respiration
12-20 BPM
Normal blood pressure
systolic = 95-119 mmHg
Diastolic = 60-79 mmHg
Temperature locations on body
Oral, Axillary, Rectal, Tympanic, Temporal
Hyperthermia
High body temp
Hypothermia
Low body temp
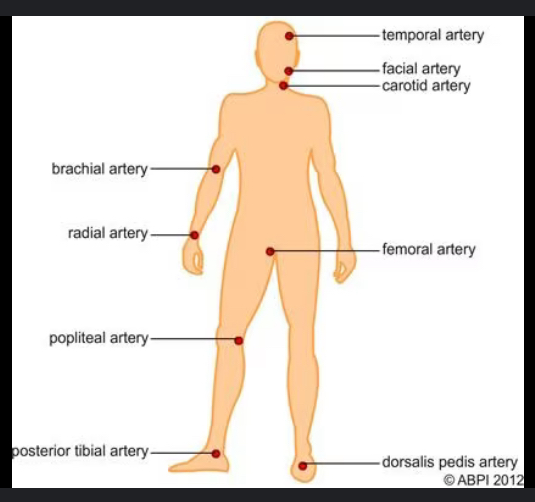
Pulse locations on body
Brachial, Radial, Posterior tibial, Temporal, Carotid, Apical, Femoral, Popliteal, Dorsalis pedis
Tachycardia
Heart rate is greater than 100 bpm
Bradycardia
Heart rate is less than 60 bpm
Bradypnea
Slow breathing
Tachypnea
Fast breathing
Dyspnea
Difficulty breathing
Hyperventilating
Breathing too fast and deep, oxygen-carbon balance is off
Hypertension
High blood pressure
Hypotension
Low blood pressure - results in shock
BUN
Blood Urea Nitrogen
Normal- 7-18 mg/dL
Creatine
Waste product
Normal- 0.6 - 1.3 mg/dL
Arterial catheters
Monitors cardiac activity, measures heart rate + blood pressure
Electrocardiogram
Measures electrical activity of the heart
displays on graph
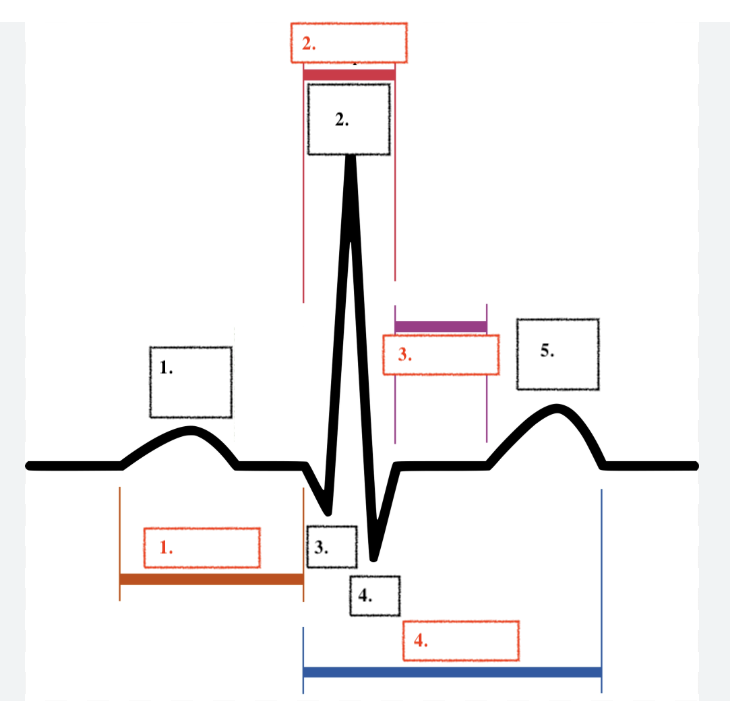
Label
P
R
Q
S
T
PR Segment
QRS Segment
ST Segment
QT Segment
Normal cardiac cycle
Atrial contraction/ventricular contraction and rest
P-R interval
P-R interval - beginning of de and re polization
atrial depolarization then ventricular depolarization
QRS interval
Ventricular contraction occurs because of depolarization
S-T interval
S-T ventricular contraction and recovery
Depolarization
electrical wave causing contraction of the chamber wall
Repolarization
an electrical recovery period