Chapter 11: DNA Replication
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
1
New cards
DNA replication relies on the __________ of DNA strands
complementarity
2
New cards
Parental and daughter DNA segments are interspersed in both strands following replication
dispersive model
3
New cards
Meselson and Stahl Experiment
1\. Add an access of 14N-containing compounds to the growth medium so all of the newly made DNA will contain 14N.
2\. Incubate the cells for various lengths of time.
3\. Lyse the cells by the addition of lysozyme and detergent, which disrupt the bacterial cell wall and cell membrane, respectively.
4\. Load a sample of the lysate onto a CsCl gradient.
5\. Centrifuge the gradients until the DNA molecules reach their equilibrium densities.
6\. DNA within the gradient can be observed under a UV light.
2\. Incubate the cells for various lengths of time.
3\. Lyse the cells by the addition of lysozyme and detergent, which disrupt the bacterial cell wall and cell membrane, respectively.
4\. Load a sample of the lysate onto a CsCl gradient.
5\. Centrifuge the gradients until the DNA molecules reach their equilibrium densities.
6\. DNA within the gradient can be observed under a UV light.
4
New cards
what did Meselson and Stahl see after 0’ 20’ and 40’
0’ 15N/15N band
20’ 14N/15N band
40’ 14N/14N band and 14N/15N band
20’ 14N/15N band
40’ 14N/14N band and 14N/15N band
5
New cards
Synthesis of DNA proceeds __________ around the bacterial chromosome
bidirectionally
6
New cards
DNA Polymerase III
main replication enzyme, synthesizes in 5' to 3' direction
\-Needs primer cuz it needs a free 3'OH end
\-Antiparallel to template strand
\-Gives rise to leading/lagging strand
7
New cards
removes RNA primers
DNA Polymerase I
8
New cards
single primer synthesized towards fork
leading strand
9
New cards
3' to 5', needs several primers away from fork as fork unwinds
lagging strand
10
New cards
The origin of replication in E. coli is termed _____
oriC
origin of Chromosomal replication
origin of Chromosomal replication
11
New cards
Three types of DNA sequences in oriC are functionally significant
• AT-rich region
• DnaA boxes
• GATC methylation sites
• DnaA boxes
• GATC methylation sites
12
New cards
events that occur at OriC region
1. DnaA proteins bind to DnaA boxes and to each other
1. Additional proteins bind to bend DNA
2. Strands separate at AT-rich region
2. DnaB/helicase binds to origin
3. DnaC assists
4. Helicase separates DNA bidirectionally creating 2 replication forks
13
New cards
1. Composed of six subunits
2. Travels along the DNA in the 5’ to 3’ direction
3. Uses energy from ATP
DnaB / Helicase
14
New cards
__________ are involved in regulating replication
• Need to ensure only one round of replication
• Need to ensure only one round of replication
GATC methylation sites
15
New cards
______________ methylates the A on both strands
• Immediately after replication, the daughter strand is not methylated
• Takes several minutes to become methylated
Initiation of replication only occurs efficiently on fully methylated DNA
• Second round initiation is blocked
• Immediately after replication, the daughter strand is not methylated
• Takes several minutes to become methylated
Initiation of replication only occurs efficiently on fully methylated DNA
• Second round initiation is blocked
DNA adenine methyltransferase (Dam)
16
New cards
DNA helicase separates the two DNA strands by breaking the hydrogen bonds between them
This generates _______ ahead of each replication fork, alleviated by______ through cutiing one of the strands ahead of the fork
This generates _______ ahead of each replication fork, alleviated by______ through cutiing one of the strands ahead of the fork
positive supercoiling
Topoisomerase II also called DNA gyrase
Topoisomerase II also called DNA gyrase
17
New cards
_____________- bind to the separated DNA strands to keep them apart
• Bases are exposed and can hydrogen bond with individual nucleotides
• Bases are exposed and can hydrogen bond with individual nucleotides
Single-strand binding proteins
18
New cards
short RNA strands start, or prime, DNA synthesis made by primase are …..in length
10-12 nucleotides
19
New cards
criteria of DNA polymerase
1. 5' to 3'
2. Needs a free 3' OH (RNA primer provides it at the end)
3. New strands are antiparallel to template strand
20
New cards
DNA pol I and III involved in _______
DNA pol II, IV and V are….
DNA pol II, IV and V are….
Normal replication
.DNA repair and replication of damaged DNA
.DNA repair and replication of damaged DNA
21
New cards
• Responsible for most of the DNA replication
• Composed of 10 different subunits
• The alpha subunit catalyzes PHOSPHODIESTER bond formation between adjacent nucleotides (DNA synthesis)
• The other 9 fulfill other functions
• The complex of all 10 subunits is referred to as the __***DNA pol III holoenzyme***__
• Composed of 10 different subunits
• The alpha subunit catalyzes PHOSPHODIESTER bond formation between adjacent nucleotides (DNA synthesis)
• The other 9 fulfill other functions
• The complex of all 10 subunits is referred to as the __***DNA pol III holoenzyme***__
DNA pol 3
22
New cards
• Composed of a single polypeptide
• Removes the RNA primers and replaces them with DNA
• Removes the RNA primers and replaces them with DNA
DNA pol 1
23
New cards
Subunit Composition of DNA polymerase III Holoenzyme
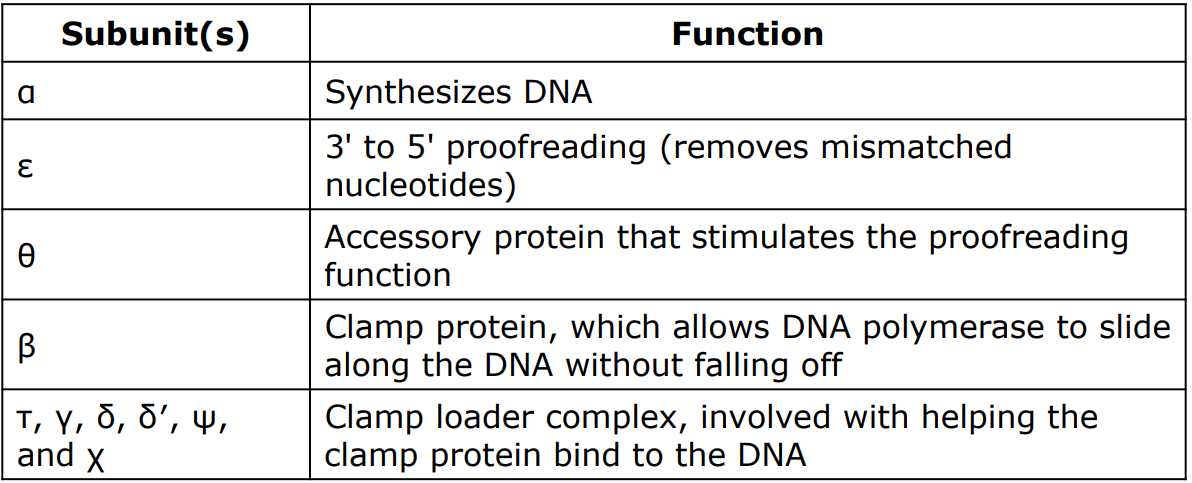
24
New cards
T/F: Bacterial DNA polymerases may vary in their subunit composition, HOWEVER ALL HAVE SIMILAR CATALYTIC SUBUNIT
true
25
New cards
how does DNA pol 1 remove RNA primers
It uses a 5’ to 3’ exonuclease activity to digest the RNA and 5’ to 3’ polymerase activity to replace it with DNA
26
New cards
_______ catalyzes the formation of a phosphodiester bond to connect DNA fragments
DNA ligase
27
New cards
DNA helicase and primase are physically bound to each other to form a complex called the ________
• This complex better coordinates the actions of helicase and primase
• This complex better coordinates the actions of helicase and primase
primosome
28
New cards
The primosome is physically associated with two DNA polymerase holoenzymes to form the __________
replisome
29
New cards
Two DNA pol III proteins act in concert to replicate both the leading and lagging strands
The two proteins form a_________ that moves as a unit toward the replication fork
The two proteins form a_________ that moves as a unit toward the replication fork
dimeric DNA polymerase
30
New cards
Upon completion of an Okazaki fragment, the enzyme releases the lagging template strand
The________ then reloads the polymerase at the next RNA primer
And another LOOP is formed
The________ then reloads the polymerase at the next RNA primer
And another LOOP is formed
clamp loader complex
31
New cards
On the opposite side of the chromosome to oriC is a pair of termination sequences called_______
__***ter sequences***__
32
New cards
The protein tus (________) binds to the ter sequences
tus bound to the ter sequences stops the movement of the replication forks
tus bound to the ter sequences stops the movement of the replication forks
termination utilization substance
33
New cards
T1 prevents the advancement of the fork moving__________
T2 prevents the advancement of the fork that is moving __________
T2 prevents the advancement of the fork that is moving __________
left to right (CCW)
right to left (CW)
right to left (CW)
34
New cards
• Intertwined circular molecules are termed _______
• These are separated by the action of _____
• These are separated by the action of _____
catenanes
topoisomerase 2
topoisomerase 2
35
New cards
The dna mutants fell into two groups when shifted to the non-permissive temperature
Some showed a rapid arrest
• These genes encoded enzymes needed for replication of the DNA
Other mutants completed their current round of replication but could not start another
• Encoded genes needed for initiation of replication
• These genes encoded enzymes needed for replication of the DNA
Other mutants completed their current round of replication but could not start another
• Encoded genes needed for initiation of replication
36
New cards
DNA polymerases catalyzes the formation of a covalent (ester) bond between the
Innermost phosphate group of the incoming deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate and 3’-OH of the sugar of the previous deoxynucleotide
37
New cards
In the process, the last two phosphates of the incoming nucleotide are released in the form of
pyrophosphate (PPi )
38
New cards
DNA polymerase III remains attached to the template as it is synthesizing the daughter strand, this is a _______ feature
processive
39
New cards
β subunit forms a dimer in the shape of a ring around template DNA
• It is termed the **clamp protein**
• Once bound, the β subunits can freely slide along______
• Promotes association of holoenzyme with DNA
• It is termed the **clamp protein**
• Once bound, the β subunits can freely slide along______
• Promotes association of holoenzyme with DNA
dsDNA
40
New cards
what 5 subunits make up the clamp loader?
τ, γ, δ, δ′, ψ, and χ
41
New cards
In the absence of the β subunit
• DNA pol III falls off the DNA template after about 10 nucleotides have been polymerized
• Its rate is ___________
In the presence of the β subunit
• DNA pol III stays on the DNA template long enough to polymerize up to 500,000 nucleotides
• Its rate is ______________
• DNA pol III falls off the DNA template after about 10 nucleotides have been polymerized
• Its rate is ___________
In the presence of the β subunit
• DNA pol III stays on the DNA template long enough to polymerize up to 500,000 nucleotides
• Its rate is ______________
\~ 20 nucleotides per second
\~ 750 nucleotides per second
\~ 750 nucleotides per second
42
New cards
reasons why fidelity is high
• Stability of base pairing
• Structure of the DNA polymerase active site
• Proofreading function of DNA polymerase
• Structure of the DNA polymerase active site
• Proofreading function of DNA polymerase
43
New cards
Configuration of the DNA polymerase active site
• Helix distortion caused by mispairing prevents incorrect nucleotide fitting properly in active site
known as….
• Helix distortion caused by mispairing prevents incorrect nucleotide fitting properly in active site
known as….
induced-fit phenomenon
44
New cards
• DNA polymerases use a____________ activity to digest the newly made strand until the mismatched nucleotide is removed
• DNA synthesis then resumes in the 5’ to 3’ direction
• DNA synthesis then resumes in the 5’ to 3’ direction
3’ to 5’ exonuclease
45
New cards
the only DNA pol with 5’ to 3’ exonuclease activity
DNA pol 1
46
New cards
Evidence for Multiple Origins of Replication
A pulse of radiolabeled nucleoside was taken up by cells and incorporated into newly made DNA strands.
Labeled areas were interspersed between non-labeled, indicating multiple regions had initiated replication
Labeled areas were interspersed between non-labeled, indicating multiple regions had initiated replication
47
New cards
Origins of replication in Saccharomyces cerevisiae are termed ARS elements (………..)
• They are about 50 bp in length
• They have a high percentage of A and T
• ARS consensus sequence (ACS)
• They are about 50 bp in length
• They have a high percentage of A and T
• ARS consensus sequence (ACS)
Autonomously Replicating Sequence
48
New cards
ACS
A T T T A T (A or G) T T T A
49
New cards
Eukaryotic Replication begins with assembly of the ____________
prereplication complex (preRC)
50
New cards
components of preRC
Origin recognition complex (ORC)
MCM Helicase
\--Binding of MCM completes DNA replication licensing
Cdc6
Cdc1
MCM Helicase
\--Binding of MCM completes DNA replication licensing
Cdc6
Cdc1
51
New cards
six-subunit complex that acts as the first initiator of eukaryotic DNA replication
ORC
52
New cards
eukaryotic replication steps
1. during G1 phase ORC binds to origin
2. Cdc6, Cdc1, & MCM helicase assemble onto origin to form preRC; MCM helicase binds to leading strand
1. during S phase, preRC is converted to an active replication site by phosphorylation via protein kinases ; Cdc6, Cdc1, and ORC are released, MCM helicase moves in 3’ to 5’ direction and DNA rep. proceeds bidirectionally Binding of MCM completes DNA replication licensing
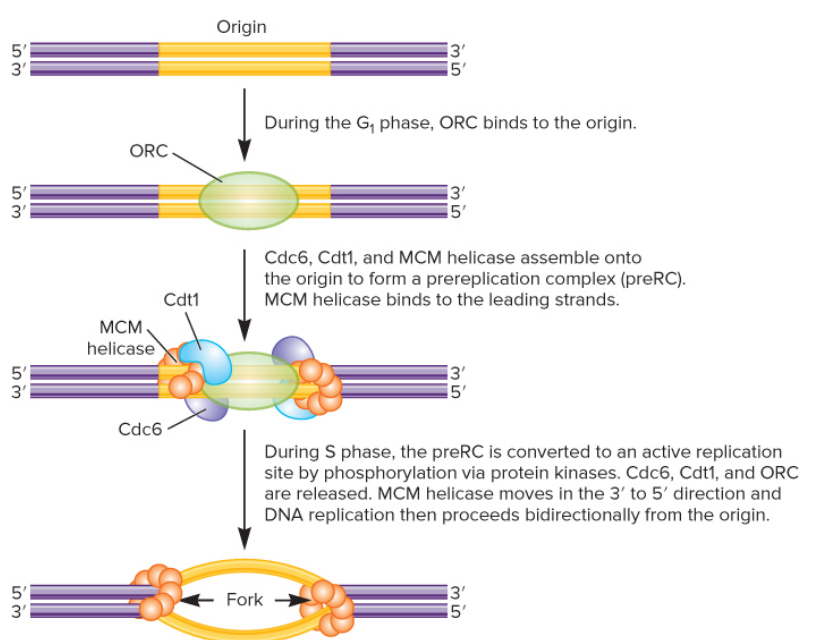
53
New cards
mammalian DNA polymerases (total over 12)
alpha (α), delta (δ), epsilon (ε) and gamma (γ) have the primary function of replicating DNA
α, δ and ε →
γ →
alpha (α), delta (δ), epsilon (ε) and gamma (γ) have the primary function of replicating DNA
α, δ and ε →
γ →
NUCLEAR DNA
MITOCHONRIAL DNA
MITOCHONRIAL DNA
54
New cards
______ is the only polymerase to associate with primase
DNA pol alpha
55
New cards
The DNA pol α/primase complex synthesizes a short RNA-DNA hybrid primer
10 RNA nucleotides followed by 20 to 30 DNA nucleotides
56
New cards
The exchange of DNA pol α for ε or δ is required for elongation of the leading and lagging strands. This is called _____________
polymerase switch
57
New cards
• DNA pol ε is used for the processive elongation of the --------
• DNA pol δ is used for the ----------
• DNA pol δ is used for the ----------
leading strand
lagging strands
lagging strands
58
New cards
DNA pol β is not involved in DNA replication
It plays a role in removal of incorrect bases from damaged DNA
59
New cards
• Involved in the replication of damaged DNA
• They can synthesize a complementary strand over the abnormal region
• They can synthesize a complementary strand over the abnormal region
translesion-replicating polymerases
60
New cards
Distinct from prokaryotic replication ________- runs into primer of adjacent Okazaki fragment
• Pushes portion of primer into short flap
• ___________ removes the primer
• Pushes portion of primer into short flap
• ___________ removes the primer
Polymerase δ
Flap endonuclease
Flap endonuclease
61
New cards
Long flaps are removed by __________--
DNA2 nuclease/helicase
62
New cards
Telomeric sequences consist of moderately repetitive tandem arrays
• Several guanine nucleotides
• Many thymine nucleotides
________ that is 12-16 nucleotides long
• Several guanine nucleotides
• Many thymine nucleotides
________ that is 12-16 nucleotides long
3’ overhang
63
New cards
At the_____- of linear chromosomes - the end of the strand cannot be replicated!
3’ ends
64
New cards
Telomerase contains protein and RNA…..
This allows the telomerase to bind to the 3’ overhang
This allows the telomerase to bind to the 3’ overhang
template
The RNA is complementary to the DNA sequence found in the telomeric repeat
The RNA is complementary to the DNA sequence found in the telomeric repeat
65
New cards
enzymatic action of telomerase
Step 1: binding
\--telomerase binds to 3’ overhang
Step 2: polymerization
\--telomerase synthesizes 6-nucleotide repeat
Step 3: translocation
\--telomerase moves 6 nucleotides to the R and makes another repeat
complementary strand is made by primase, DNA poly., ligase
These steps are repeated many times to lengthen one strand
\--telomerase binds to 3’ overhang
Step 2: polymerization
\--telomerase synthesizes 6-nucleotide repeat
Step 3: translocation
\--telomerase moves 6 nucleotides to the R and makes another repeat
complementary strand is made by primase, DNA poly., ligase
These steps are repeated many times to lengthen one strand
66
New cards
Cells become _________ when telomeres are short
senescent