Topic 3 (AQA Alevel Biology)
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
118 Terms
SIZE AND SURFACE AREA
-
What do cells exchange?
Intake of oxygen and nutrients
Excrete carbon dioxide and urea
Exchange heat to maintain temperature
Describe the SA:V for a smaller animal
High surface area to volume ratio
How do multicellular organisms exchange with the environment?
Using exchange organs and mass transport systems
Why can't multicellular organisms diffuse directly with the environment?
Some cells are deep within the body
Larger animals have low SA:V - it's difficult to exchange enough substances to supply the larger volume of the animal through the relatively small outer face
What affects heat exchange?
BODY SIZE:
Rate of heat loss depends on surface area
Animals with larger surface area loose heat more easily so have high metabolic rates to generate enough heat to stay warm
Animals with smaller surface area retain heat
SHAPE:
Compact shape Animals also have smaller surface area relative to their volume [Small SA:V] so that minimises heat loss
Animals with less compact shape have larger surface area relative to volume [large SA:V] so that increases heat loss
E.g- less compact=large ears or pointed nose
State some behavioural and psychological adaptations of an animal to assist exchange
Animals with high SA:V tend to lose more water as it evaporates from their surface
Some desert mammals have kidney structure adaptions so they produce less urine to compensate
Small mammals living in cold region eat large amount of high energy food to support their high metabolic rates
smaller mammals can have thicker fur to hibernate during winter
Larger organisms in hotter regions may find it hard to cool down
Elephants have large ears to increase SA so more heat can be lost
Hippos spend much of the day in water to help lose heat
GAS EXCHANGE
Name 2 major adaptations for Gas Exchange Surfaces
Large Surface Area
Thin [often 1 epithelial cell thick] to provide short diffusion path
also requires conc gradient
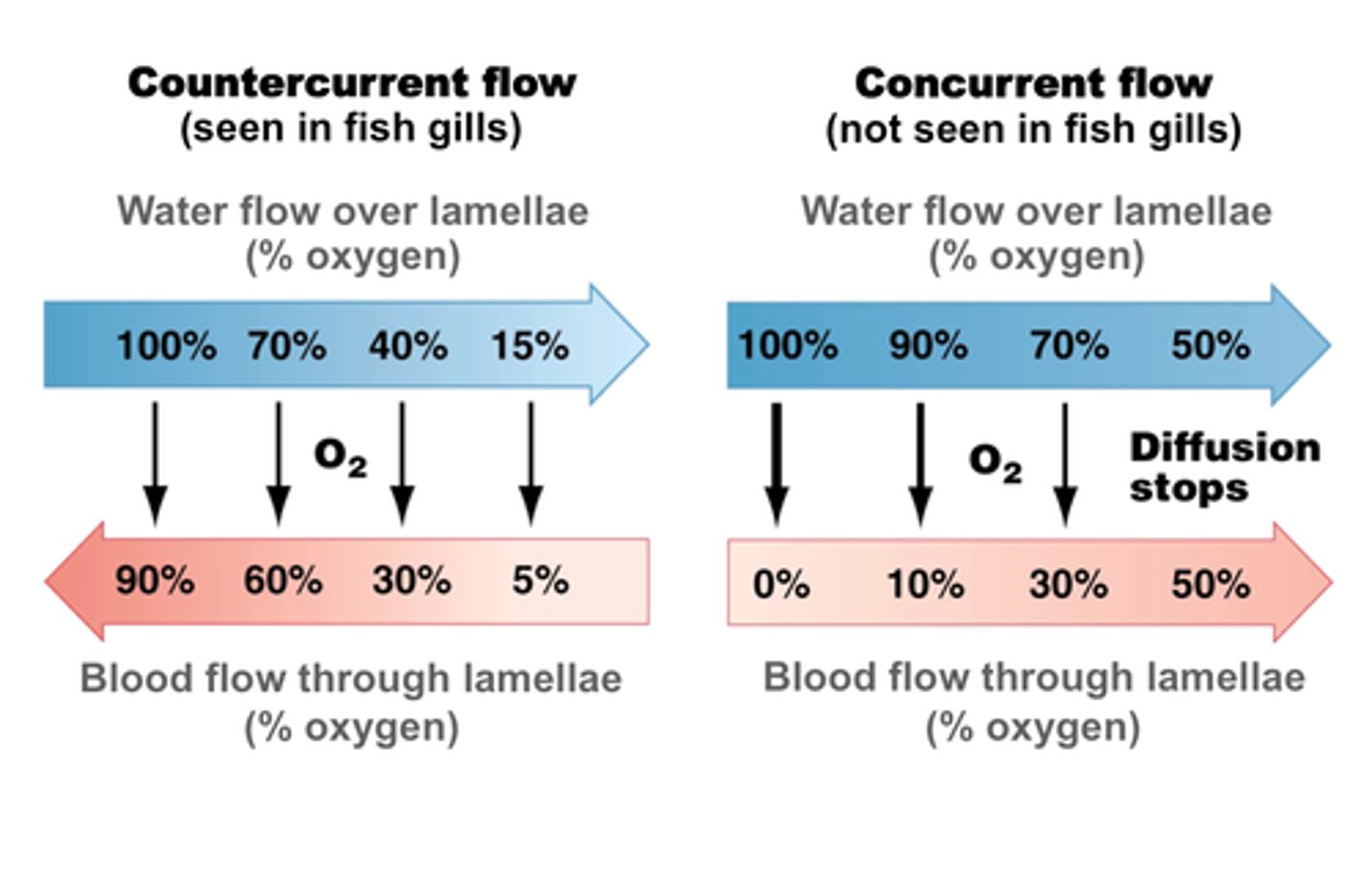
Describe the gas exchange system in a fish
COUNTER-CURRENT SYSTEM
low conc of oxygen in water than air
Water, containing oxygen, enters fish through mouth and passes out through the gills
Gill made of many thin plates called gill filaments
Gill filaments have large SA for gas exchange
Gill filament covered in smaller lamellae which increases SA further
Lamellae is made of thin surface layer of cells and is close to network of blood capillaries
So increased rate of exchange
Blood flows in opposite direction to water to maintain large conc gradient
Describe the exoskeleton of an insect
Composed of a hard fibrous material called chitin (for protection)
Covered by a lipid rich /waxy layer (to prevent water loss)
No lungs but a tracheal system
Describe the tracheal system of an insect
Consists of series of small holes in the exoskeleton called spiracles
These open to a network of fine tubes called tracheae (lined with rings of chitin)
Tracheae sub-divide into tubes of smaller diameter called tracheoles (unlined)
Tracheoles end at body cells
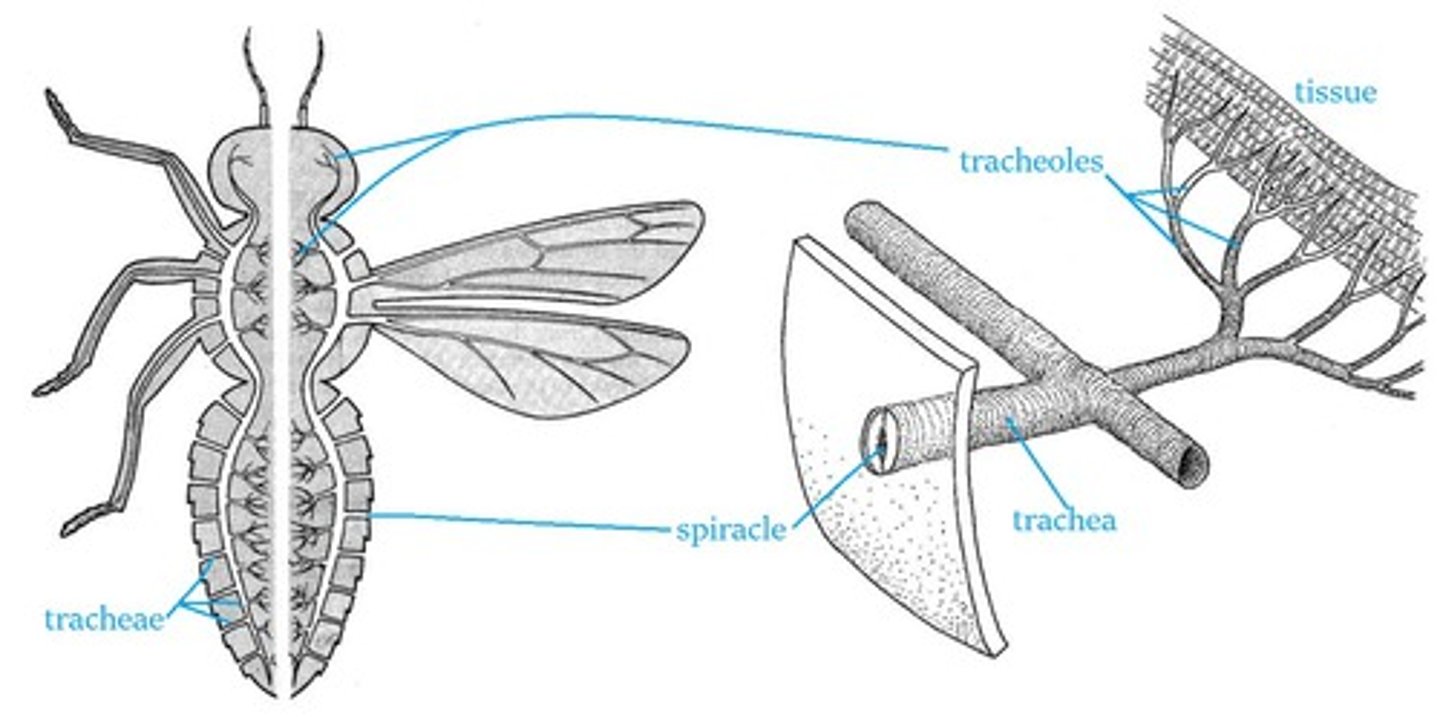
Name the adaptation of an insect for effective gas exchange
Gaseous exchange is carried out across the walls of the tracheoles by diffusion.
Very large number of fine tracheoles - large surface area
Walls of tracheoles are thin - short diffusion pathway
Use of oxygen and production of carbon dioxide sets up steep diffusion gradients
Walls made of chitin to withstand pressure
Hairs on surface to avoid dehydration on body surface
Name 3 ways an insect exchanges gas
Via a:
Diffusion gradient
Mass transport [abdominal pumping]
Trachioles filling with water during flight
Describe how a insect exchanges gas via a diffusion gradient
OXYGEN
Air moves inwards through spiracles [pores] pn insect's surface
Oxygen travels down a conc gradient towards body cells
Trachae branches into trachioles
Trachioles have thin, permeable walls and go to individual cells
So oxygen diffuses directly to respiring ells
Describe how an insect exchanges gas via mass movement [abdominal pumping]
CARBON DIOXIDE
Abdominal muscles contract to constrict trachiole
increase in pressure = acceleration of carbon dioxide because pressure gradient has steepened from high to low
Describe how an insect exchanges gas when flying
Anaerobic Respiration in insect
Anaerobic respiration produces lactic acid that dissolves in water which alters the water potential of the muscle cell
Lactic acid decreases water potential of muscle cells so water moves inwards via osmosis down the water potential gradient.
The end of the tracheoles decrease in volume as water travels from tracheole to muscle cells.
Decrease in volume draws air inwards down a pressure gradient
final diffusion pathway is gas rather than liquid
How do plants control water loss?
Plants's stomata surrounded by guard cells
if plant is dehydrates, guard cells lose water and become placid which closes pore
What is a xerophyte?
a plant adapted to reduce water loss (reduce transpiration) for life in a warm, dry or windy habitat
Describe the adaptation of a Xerophyte
Stomata in sunken pits-trap still moist air
Hairs-"
Curled leaves with stomata inside-protects stomata from windy conditions that increase rate of diffusion and evaporation
Reduced no. stomata-fewer places for water to escape
waxy cuticles-reduce evaporation
What is a halophyte?
salt-tolerant plant
GAS EXCHANGE IN HUMANS
Describe the path of oxygen from the air
Mouth+Nose > trachea > 2 bronchi > 1 bronchus > bronchioles > alveoli
What is ventilation?
movement of air in and out of the lungs
Consists of inspiration [breathing in] and expiration [breathing out]
What components control ventilation action?
Diaphragm
Internal and external intercostal muscles
Rib cage
Describe the process of inspiration
External intercostal muscles contract
Diaphragm contracts
Rib cage moves up and out
Diaphragm flattens, so volume of thoracic cavity increases
As volume of thoracic cavity increases, lung pressure decreases [to below atmospheric pressure]
Air flows down a pressure gradient
From high atmospheric pressure to low internal pressure inside thoracic cavity
So air flows inwards
ACTIVE PROCESS as it requires energy
Describe the process of expiration
External intercostal and diaphragm muscles relax
Rib cage moves downwards and inwards
Diaphragm curves
Volume of thoracic cavity decreases causing air pressure to increase [above atmospheric pressure]
Air flows out down the pressure gradient and out of the lungs
PASSIVE PROCESS as does not require energy
State the difference between forced expiration and normal expiration
Forced = ACTIVE
Normal = PASSIVE
Describe the process of forced expiration
External intercostal muscles relax AND internal intercostal muscles constrict [antagonistic intercostal muscle moemtn]
Rib cage pulled further down and in
Where does gas exchange happen in humans?
alveoli
State the adaptation of the alveoli
Large SA because there's a huge number of alveoli in the lungs
Surrounded by network of capillaries
Thin exchange surface- alveolar epithelium is 1 cell thick sos short diffusion path
Describe the path of oxygen in alveoli
Oxygen diffuses out of the alveoli
Across alveolar epithelium
Across capillary endothelium [type of epithelium]
Oxygen associates to haemoglobin in the blood
What is an endothelium?
A type of epithelium
THE EFFECTS OF LUNG DISEASE
What is tidal volume?
Volume of air in each breath
What is ventilation rate?
Number of breath per minutes
What is FEV1?
Forced expiatory volume is the maximum volume of air that can be breathed out in 1 second
What is FVC?
Forced vital capacity is the maximum volume of air it is possible to breathe forcefully out of the lungs after a really deep breath in
What is residual air?
Leftover air in lungs
Cant be expelled
How is a lung function test presented and how is the data colected?
A graph produced by spirometer
Name 4 diseases that affect the lungs
TB --> Pulmonary Tuberculosis
Fibrosis
Asthma
Emphesyma
Describe how TB affects the lungs
TB Bacteria triggers immune réponse
Immune system builds wall around bacteria on the region of lung that its situated on--> forms small, hard lump called TUBERCLES
Infected tissue within tubercle dies
so gaseous exchange surface is damaged and limited so the tidal volume decrease
Reduced tidal volume = less air inhaled with each breath so person breathes faster to compensate lack of oxygen
Ventilation rate increases
Symptoms: persistent cough
TB can cause fibrosis
Describe how fibrosis affects the lungs
Fibrosis is the formation of scar tissue
Scar tissue may be formed in response to an infection or the exposure to asbestos or dust
Scar tissue thicker and less elastic than normal lung tissue
Lungs ability to expand s reduced
Lungs cant hold as much air —> Tidal volume is reduced
—> FVC is also reduced
Reduction is rate of gaseous exchange as diffusion is slower across a thicker membrane
Faster ventilation rate to get enough air into lungs to oxygenate their blood
Symptoms: Shortness of breath, a dry cough, chest pain, fatigue and weakness
Describe how asthma affects the lungs
Airways become inflamed and irritated due to allergic reaction
Smooth muscle lining the bronchioles contracts and large mass of mucus is produced
Airways become constricted so breathing becomes difficult
Air flows in and out is reduced so less oxygen enters the alveoli to oxygenate blood
Reduced air flow = reduced FEV1
Symptoms: wheezing, tight chest, shortness of breath
DIGESTION AND ABSORPTION
Whta is digestion?
The breaking down of large biological molecules into smaller molecules to be able to move across membranes and be easy absorbed
What is amylase used for?
Break down of starch[polysaccharide] to maltose[disaccharide]
Involves hydrolysis of glycosidic bonds
Where is amylase produced?
salivary glands and pancreas
Where does amylase act?
mouth and small intestine
What enzymes hydrolyse disaccharides?
Membrane bound disaccharidases attached to the cell membrane of epithelial cells lining the ileum [final part of small intestine]
Breaks disaccharides into monosaccharides
Glucose + Glucose --> Maltose
Glucose + Fructose --> Sucrose
Glucose +. Galactose --> Lactose
Describe how lipids are broken down
Lipase made in pancreas to work in small intestine
HAEMAGLOBIN
What are haemoglobins?
A group of chemically similar molecules found in many different organisms that all complete the same function
What is haemoglobin composed of?
Protein with a quaternary structure-it's made of four polypeptide chains
What does each polypeptide chain in haemoglobin contain?
A haem group which contains an iron ion and gives the haemoglobin it's red colour
What is the role of haemoglobin?
To carry oxygen around the body
What is oxyhaemoglobin?
haemoglobin bound to oxygen
How many molecules of oxygen can each molecule of human haemoglobin carry?
4
Where does oxygen join and leave haemoglobin/oxyhaemoglobin?
Oxygen joins haemoglobin, in red blood cells, in the lungs
Oxygen leaves oxyhaemoglobin near the body cells
What is association/loading?
When an oxygen molecule joins to haemoglobin
What is dissociation/unloading?
When oxygen leaves oxyhaemoglobin
What does having an affinity for oxygen mean?
The tendency a molecule has to bind with oxygen
What does Haemoglobin's affinity for oxygen depend on?
The partial pressure of oxygen (pO2)
What is partial pressure of oxygen?
A measure of oxygen concentration
What is the relationship between haemoglobins affinity for oxygen and partial pressure of oxygen?
High pO2= Oxygen loads onto haemoglobin to form oxyhaemoglobin
Lower pO2= Oxyhaemoglobin unloads its oxygen
What happens to oxygen loading and unloading in the alveoli?
>HIGH oxygen concentration
>High pO2
>HIGH affinity
>Oxygen ASSOCIATES/LOADS
What happens to oxygen loading and unloading in the respiring tissue?
>LOW oxygen concentration
>LOW pO2
>LOW affinity
>Oxygen DISASSOCIATES/UNLOADS
What does a dissociation curve show?
how saturated the haemoglobin is with oxygen at any given partial pressure
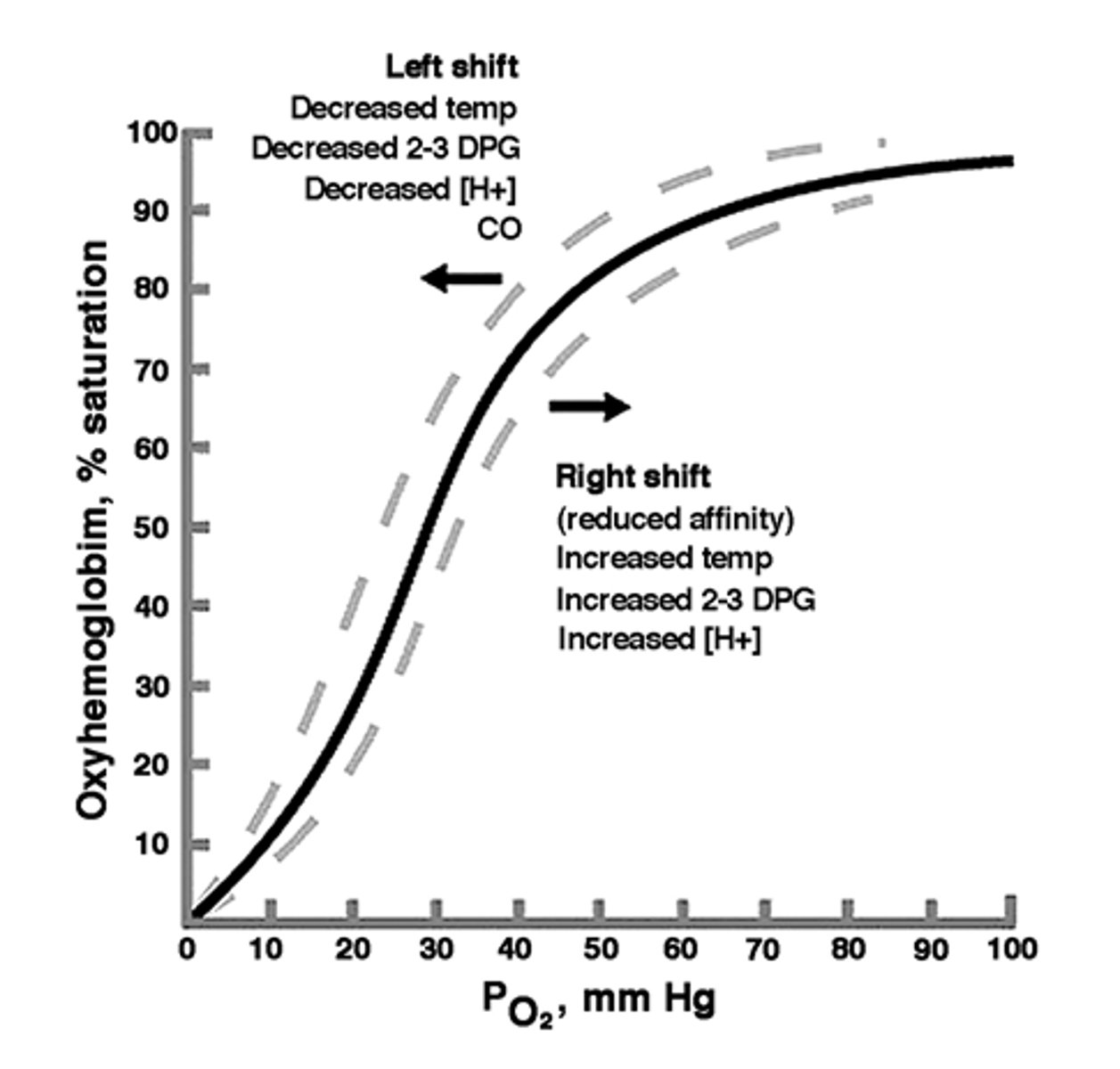
Why is the oxyhaemoglobin dissociation curve S shaped?
When haemoglobin combines to its first O2 molecule it changes shape to make it easier for more O2 to join, creating the steep part.
Once the haemoglobin gets more saturated it's hard for more oxygen to bin, creating the shallow part at the end
What is the partial pressure of carbon dioxide (pCO2)?
measure of concentration of CO2 in a cell
How does pCO2 effect the rate of unloading of O2 in respiration?
What is this called?
>When cells respire they produce CO2 raising pCO2 and increasing the rate of oxygen unloading because HIGHER pCO2= quicker unloading of O2
>The Bohr effect
How does high pCO2 affect the dissociation curve?
It shifts it right
What does it mean when the dissociation curve is more to the left or right?
Left= higher affinity for oxygen
Right= lower affinity for oxygen
What is a Lugworm's affinity for oxygen like?
>Lives in burrows beneath sand
>LOW oxygen concentration in environment
>HIGH affinity for oxygen
What is a Hawk's affinity for oxygen like?
>HIGH respiratory rate
>HIGH oxygen concentration in environment
>LOW affinity for oxygen
What is a Rat's affinity for oxygen like?
>High surface area to volume ratio
>So greater oxygen demmand
>LOW affinity for oxygen
What is Foetal haemoglobin's affinity for oxygen like?
>HIGH affinity for oxygen
>This means maternal haemoglobin will dissociate itself in the placenta and the foetal haemoglobin will load with oxygen.
What is Myoglobin's affinity for oxygen like?
>Red pigment in mammalian muscles.
>Higher affinity for O2 than Hb only releasing it at low partial pressure
THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
What is the mammalian circulatory system?
A mass transport system that carries raw materials and waste products around the body
What are the types of blood vessels?
Arteries, arterioles, veins, venules and capillaries
The pulmonary artery carries blood from..... and carries blood to..... ?
From= heart
To=Lungs
The pulmonary vein carries blood from..... and carries blood to..... ?
From= lungs
To= heart
The aorta carries blood from..... and carries blood to..... ?
From= heart
To= body
The vena cava carries blood from..... and carries blood to..... ?
From= body
To= heart
The renal artery carries blood from..... and carries blood to..... ?
From= body
To= kidneys
The renal vein carries blood from..... and carries blood to..... ?
From= kidneys
To= vena cava
What does blood transport?
Respiratory gases, products of digestion, metabolic wastes and hormones
How are the two circuits of the circulatory system different?
One takes blood from the heart to the lungs and back to the heart, and the other takes blood around the rest of the body. Meaning blood goes through the heart twice to complete one full circuit
Structure and function of arteries?
Carries oxygenated blood away from the heart (apart from pulmonary)
-Thick, muscular wall with elastic layer
>Able to withstand high pressure bursts of blood from the heart
-Medium sized lumen
>Encourages fast movement of blood around the body
Structure and function of arterioles?
Arteries divide into smaller vessels called arterioles which direct blood to areas that need it
-Contract to restrict blood flow and relax to allow full blood flow
>Gets blood to the areas that need it
-Circular muscle
>Directs blood to areas that need it
Structure and function of veins?
Carries deoxygenated blood back to the heart
-Thin, muscular wall
>Low pressure
-Valves
>Prevent backflow
-Large lumen
>Allows movement of large volumes of blood to the heart at normal pressure
Structure and function of capillaries?
Arterioles branch into capillaries which form networks called capillary beds
-Always close to cells in exchange tissues decreasing diffusion pathway
-Walls are one cell thick to decrease diffusion pathway
-Large number to increase surface area
>Exchange substances between capillaries and cells
What are venules?
Capillaries connect arterioles and venules at the capillary beds; venules are small blood vessels that connect to veins
What is tissue fluid?
The fluid that surrounds cells in tissues
What is tissue fluid made from?
Small molecules that leave the blood plasma, e.g. Oxygen, water, and nutrients
What does tissue fluid lack that blood contains?
It doesn't have red blood cells are big proteins as they're too large to be pushed out through the capillary walls
What do cells exchange with tissue fluid?
Cells take in oxygen and nutrients from tissue fluid and release metabolic waste into it
What is pressure filtration?
In capillary beds, small molecules are filtered out of the capillary under hydrostatic pressure forming tissue fluid
Why is fluid pushed out of the capillaries?
There is a greater hydrostatic pressure at the start of the capillary bed (nearest the arteries) than in the tissue fluid.