PRD 132: Porcelain Fused to Metal Restorations
1/123
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
124 Terms
847-016 bur
In PFM, we create a Shoulder margin with __
Shoulder chamfer
In PFM, there is a __ blend
Esthetic
In PFM, we have an ___ bevel
1%
Metal ceramic represent ___ of our crowns at pacific
cast metal
Metal ceramic restorations combine the strength and accuracy of __ with the esthetics of porcelain.
porcelain
Metal ceramic restorations combine the strength and accuracy of cast metal with the esthetics of __.
reliable
PFM is considered as __ restorations
cast metal
PFM consists of a __substructure
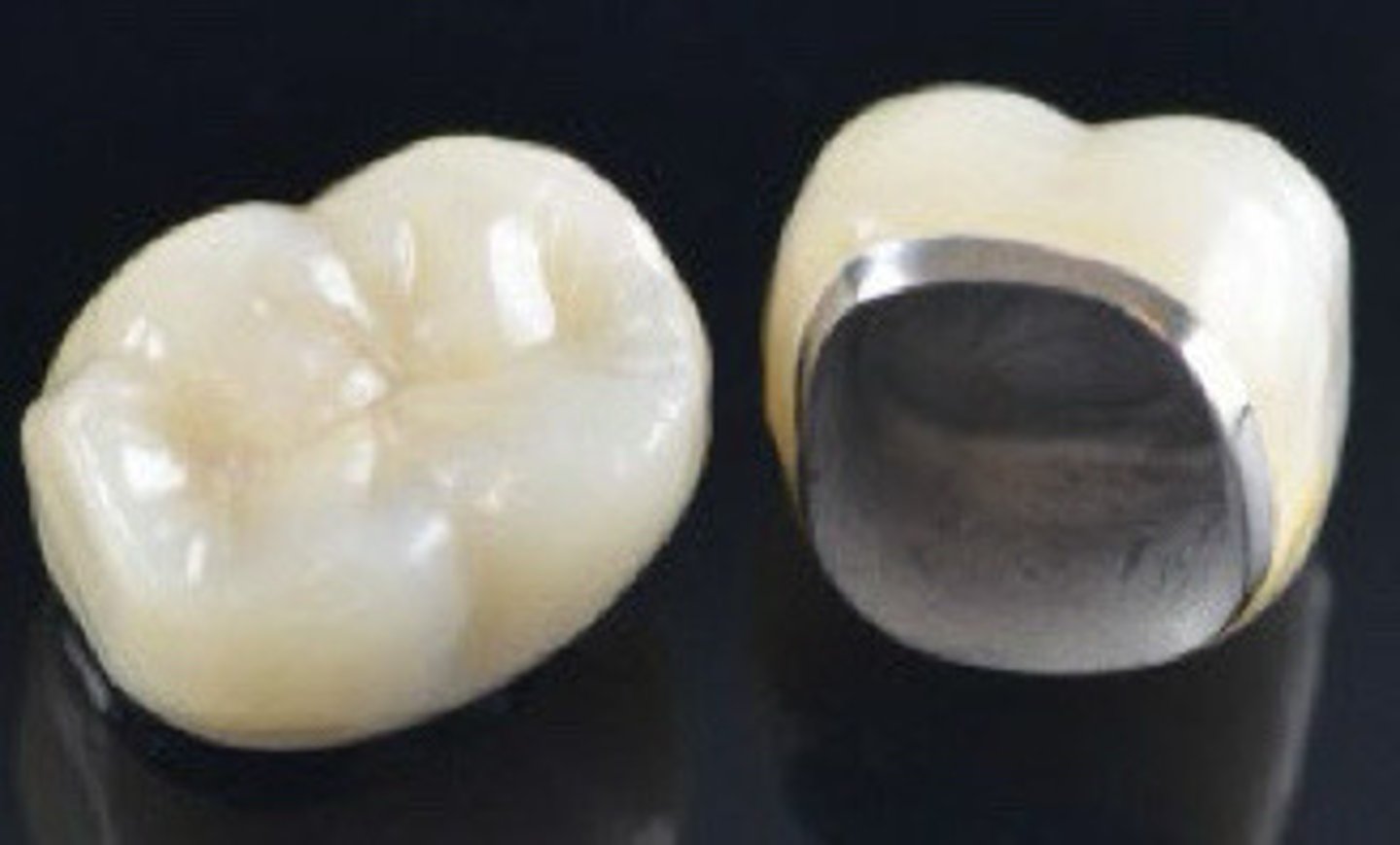
Veneered
covered with a thin coating of a fine material
veneered
PFM has Porcelain __ for esthetics
(veneer coverage can vary)
Aggressive
PFMs have __ preparation to mask metal
substructure
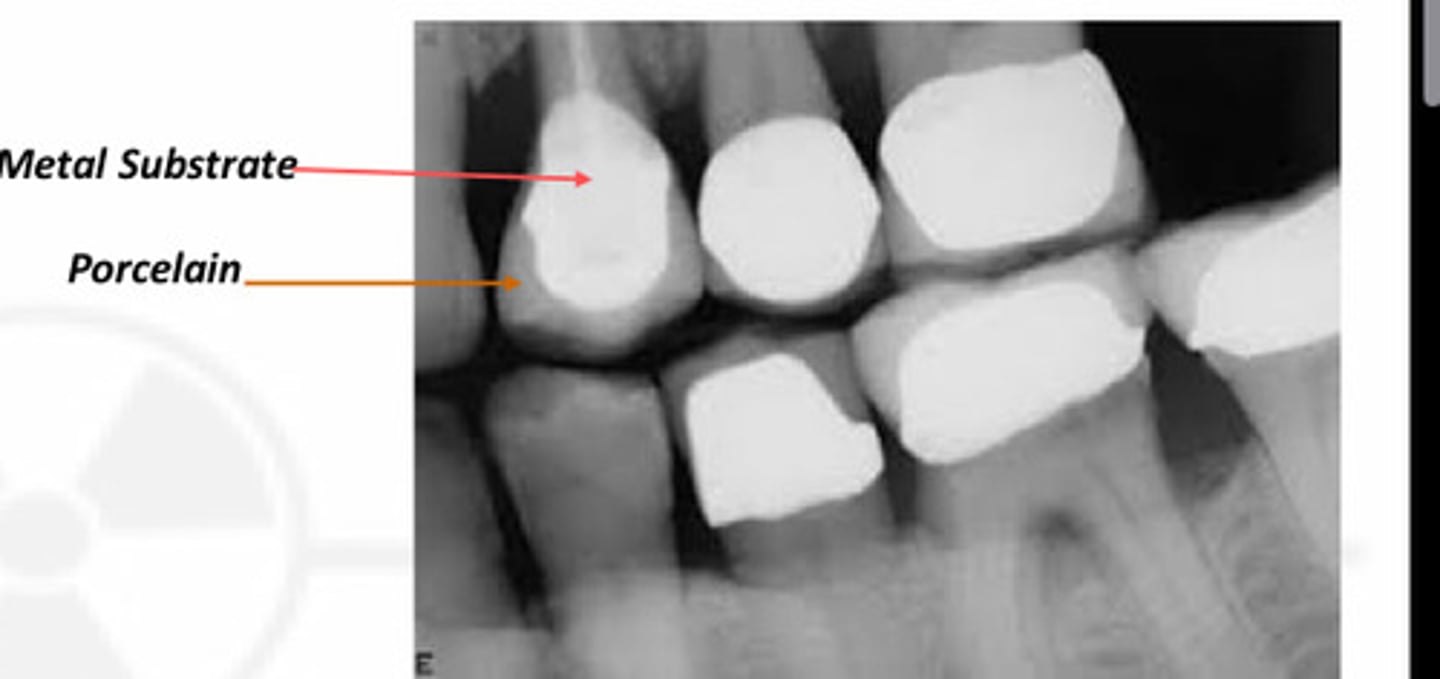
Metal substrate
__ looks brighter in radiograph than the overlying porcelain
Layered Zirconia (Bilithic)
PFM have Similar radiographic appearance to__
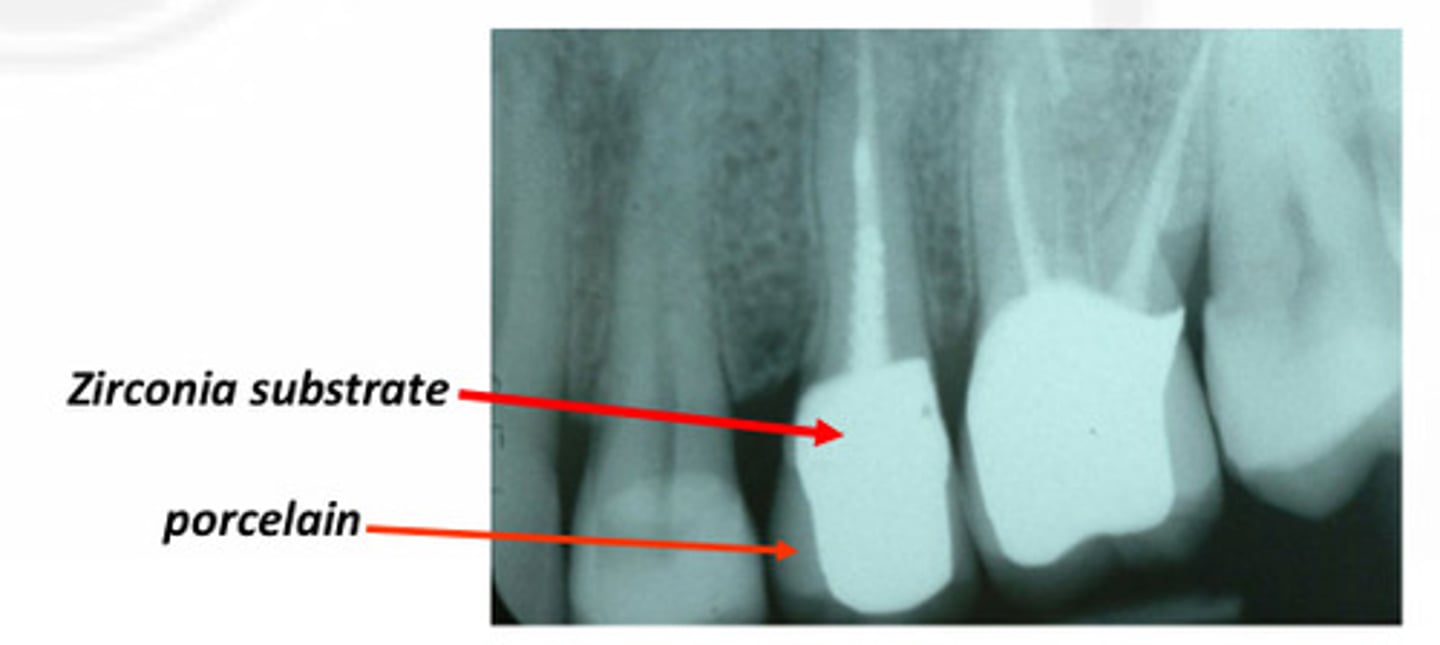
Zirconia
__ is radiographically as bright as other metal alloys
Long span fixed partial dentures
__ indications are used (due to strength at the connectors)
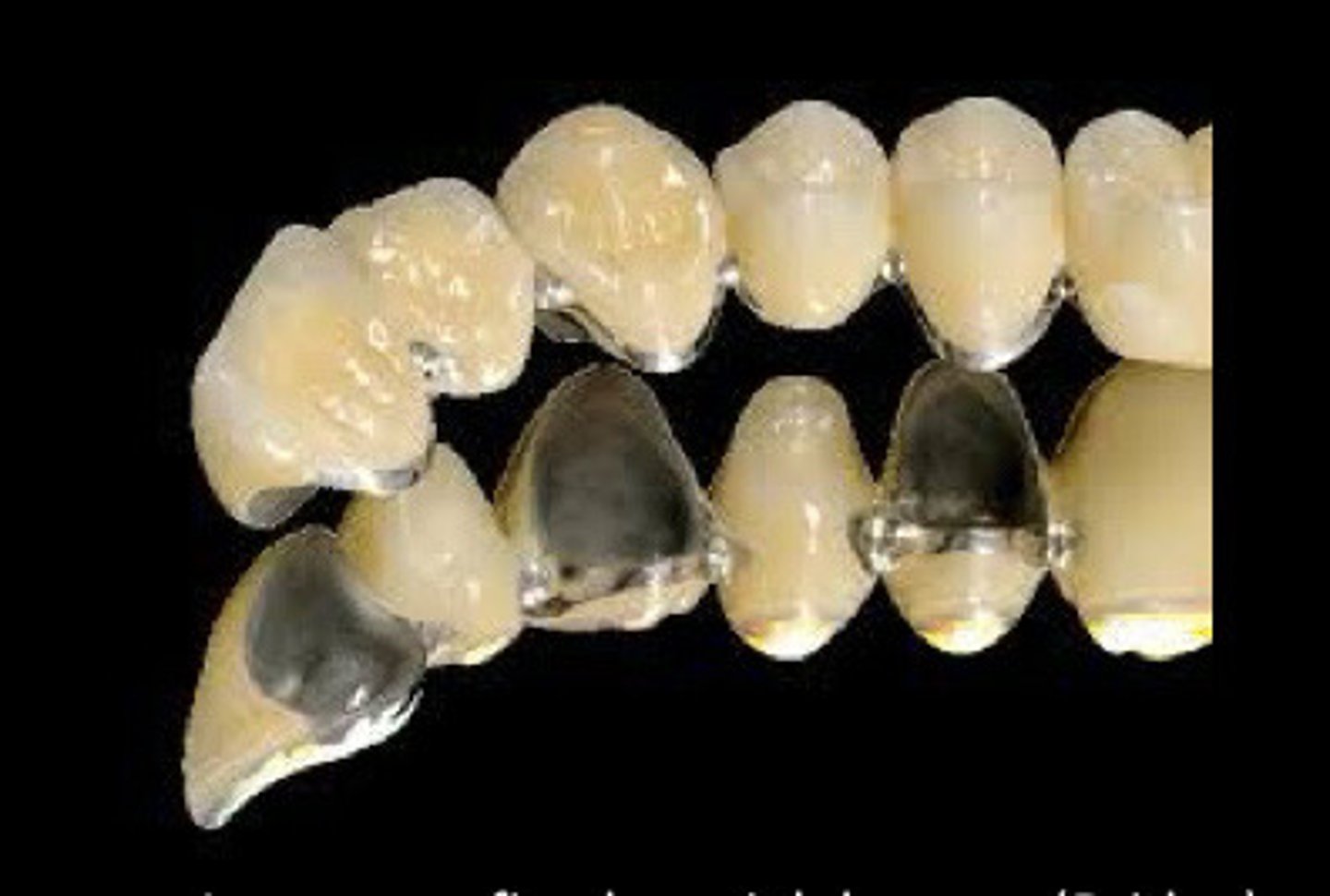
Structural
PFM has more __ strength than zirconia so the joining in long span don't break
survey crown
Abutment teeth for removable partial dentures indications (2nd year)
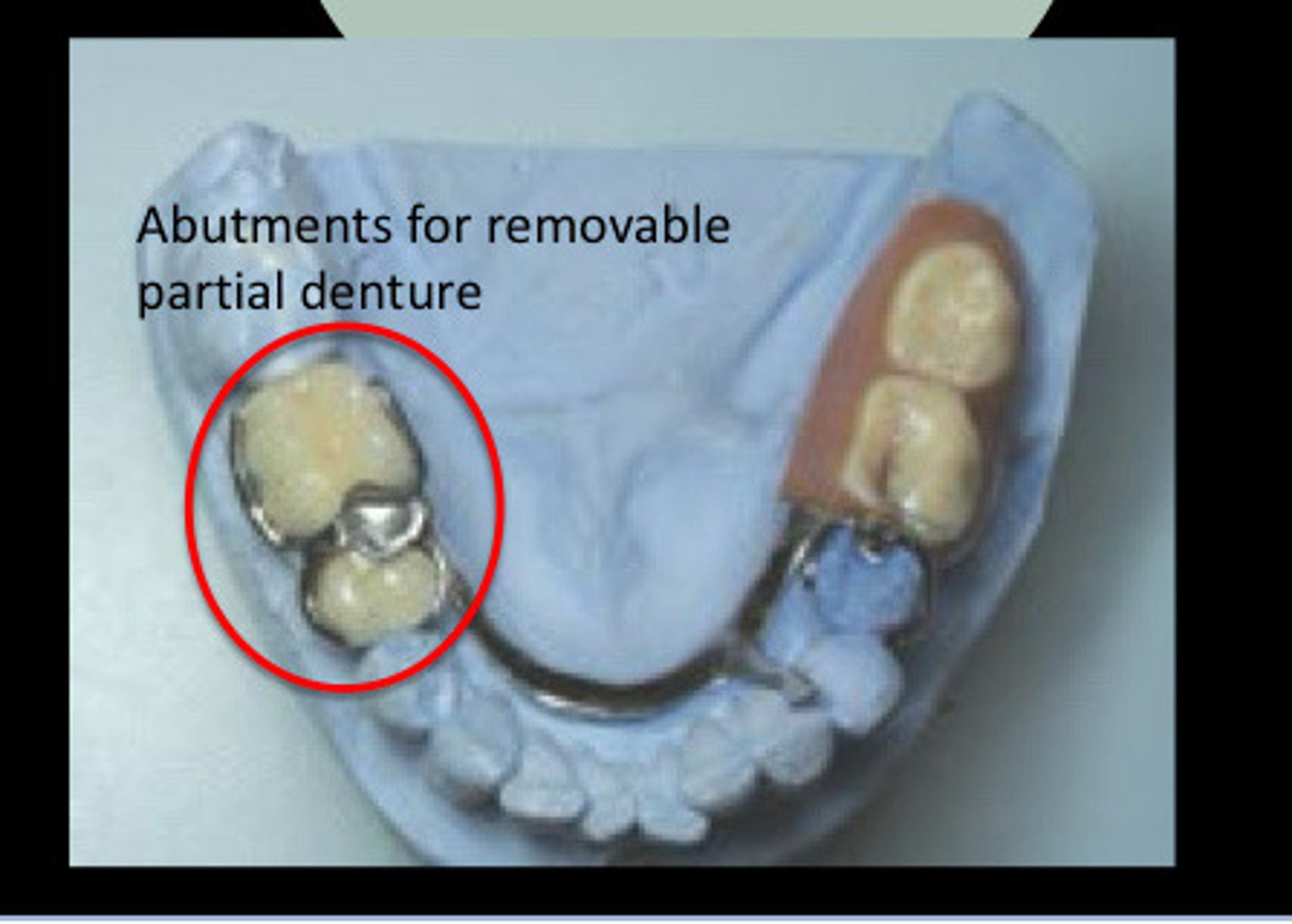
Survey crown
- a crown which is fabricated for use as an abutment tooth for a RPD
- guide planes are formed on the axial surfaces and should be no more than 2-3 mm in occlusal gingival height
periodontal disease
A major contraindication for PFM are patients with untreated __
large pulp
A major contraindication for PFM are young patients with __ chambers because prep is really aggressive
Secondary dentin
Dentin that forms after eruption and continues at a very slow rate throughout the life of the tooth (decreases size of pulp chamber
nickel and beryllium
A major contraindication for PFM is Bio-incompatibility: Some patients are allergic to certain metals such as __
Metal alloy
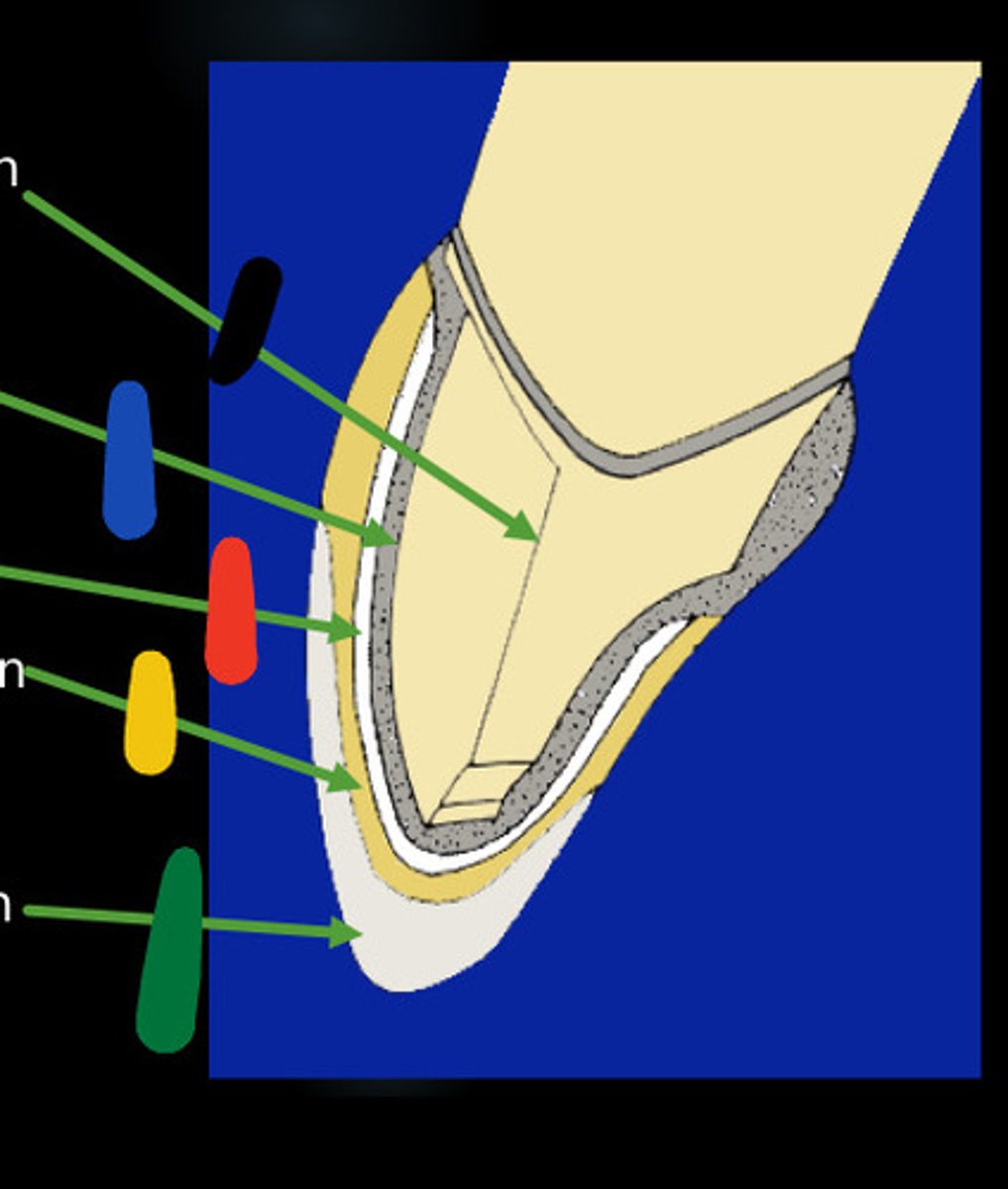
Black
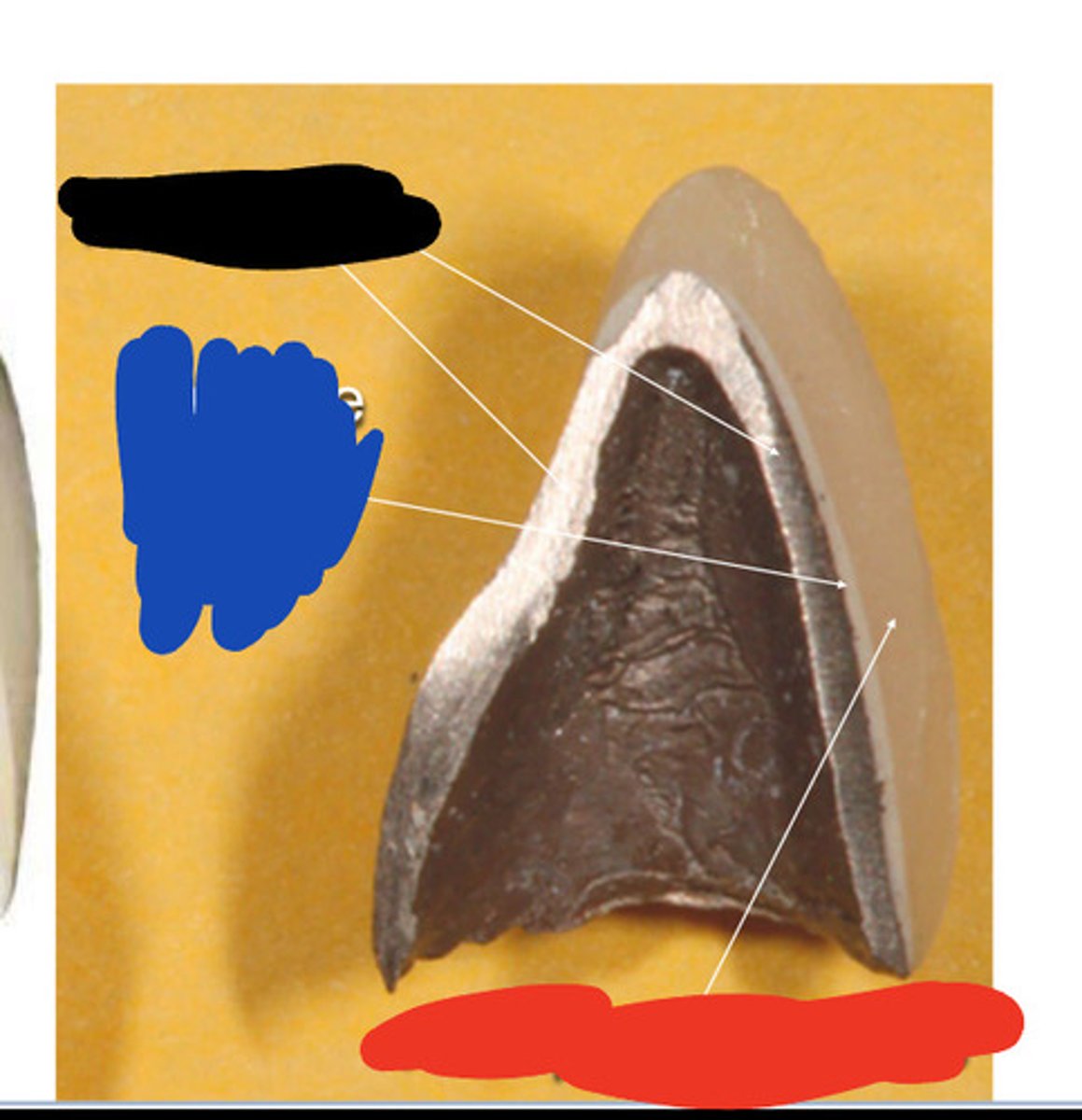
Opaque ceramic layer
Blue
Feldspathic ceramic
this type of silicate ceramic are the most esthetic and transulcent materials, used for veneers, can be leucite or porcelain, but have low mechanical strength (red)

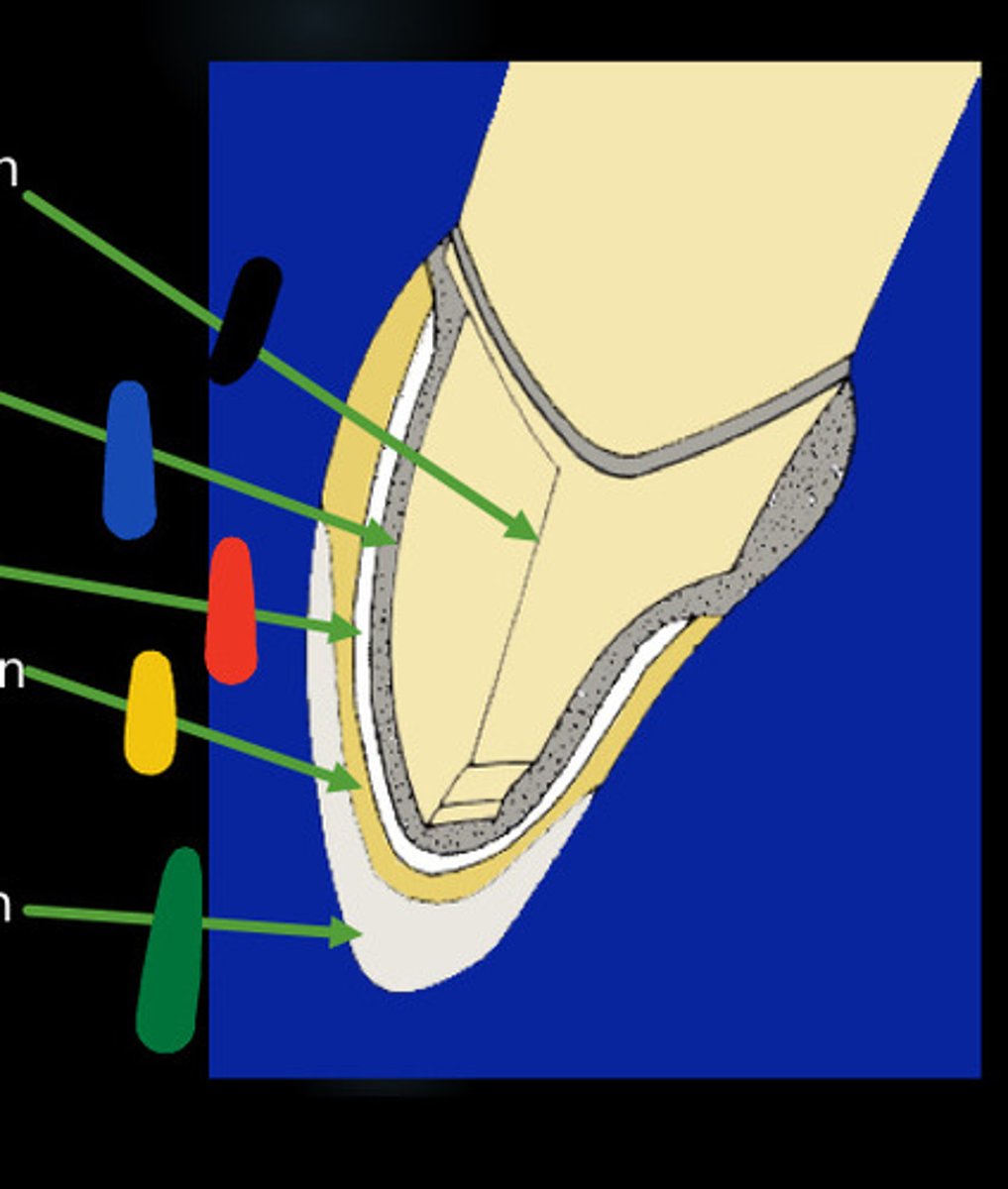
Metal coping
the innermost layer of the crown, onto which the ceramic will be fused
0.3-0.5mm
What is the width of metal coping
Opaquer
conceals the metal and develops bond between metal and porcelain
Body, incisal porcelain
for esthetics, together 0.8-1mm thick for an overall required thickness of 1.1-1.5mm on porcelain veneered surfaces
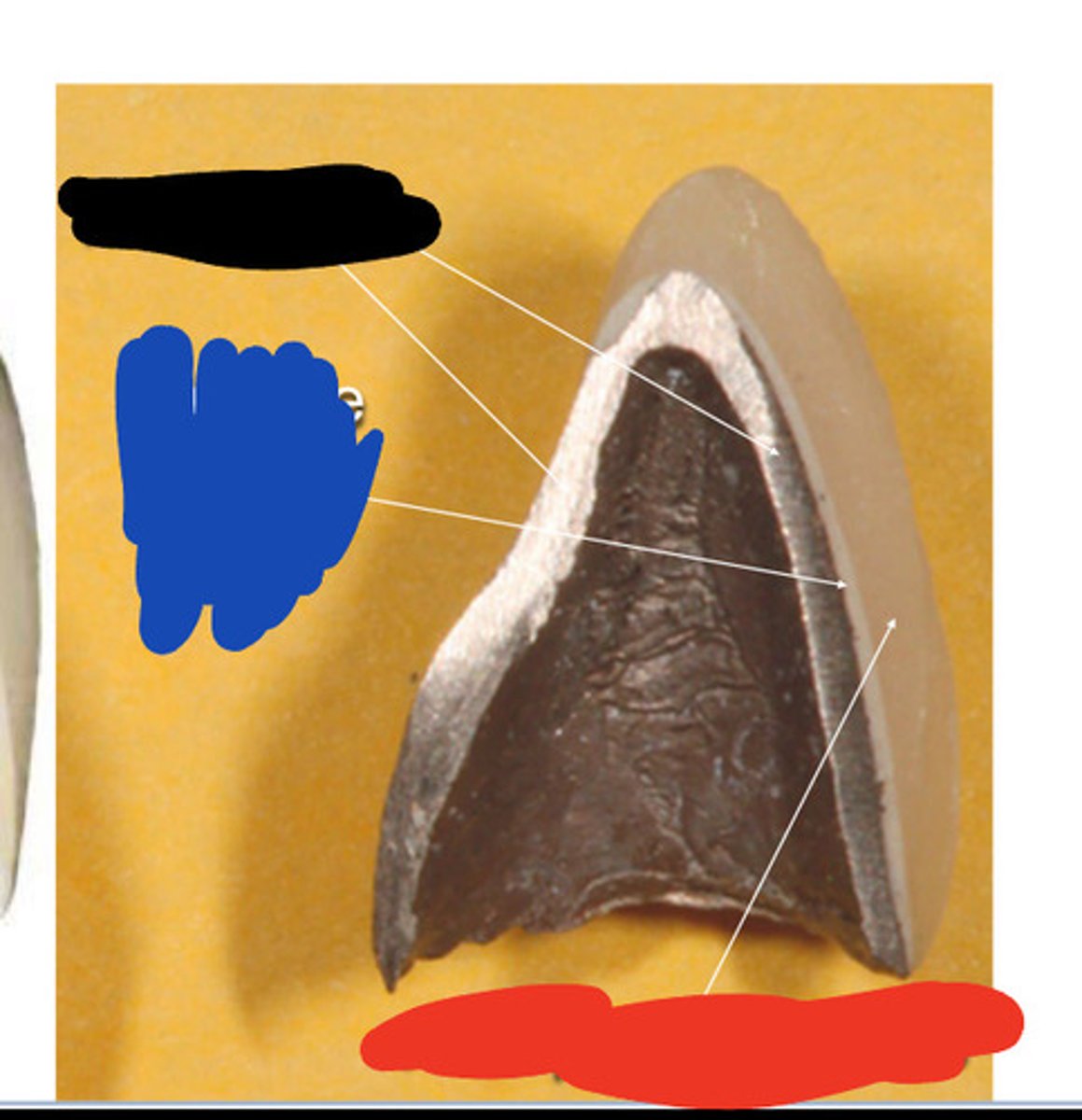
Prepared tooth
Black

Metal coping
Blue

Opaquer
Red
Body porcelain
This porcelain is placed and fired on the opaque layer. It provides some translucency and contains oxides that aid in shade matching (DENTIN, YELLOW)

Incisal porcelain
-This type of porcelain is more translucent than the above types. (ENAMEL, GREEN)
Metal porcelain
No function on the __ junction
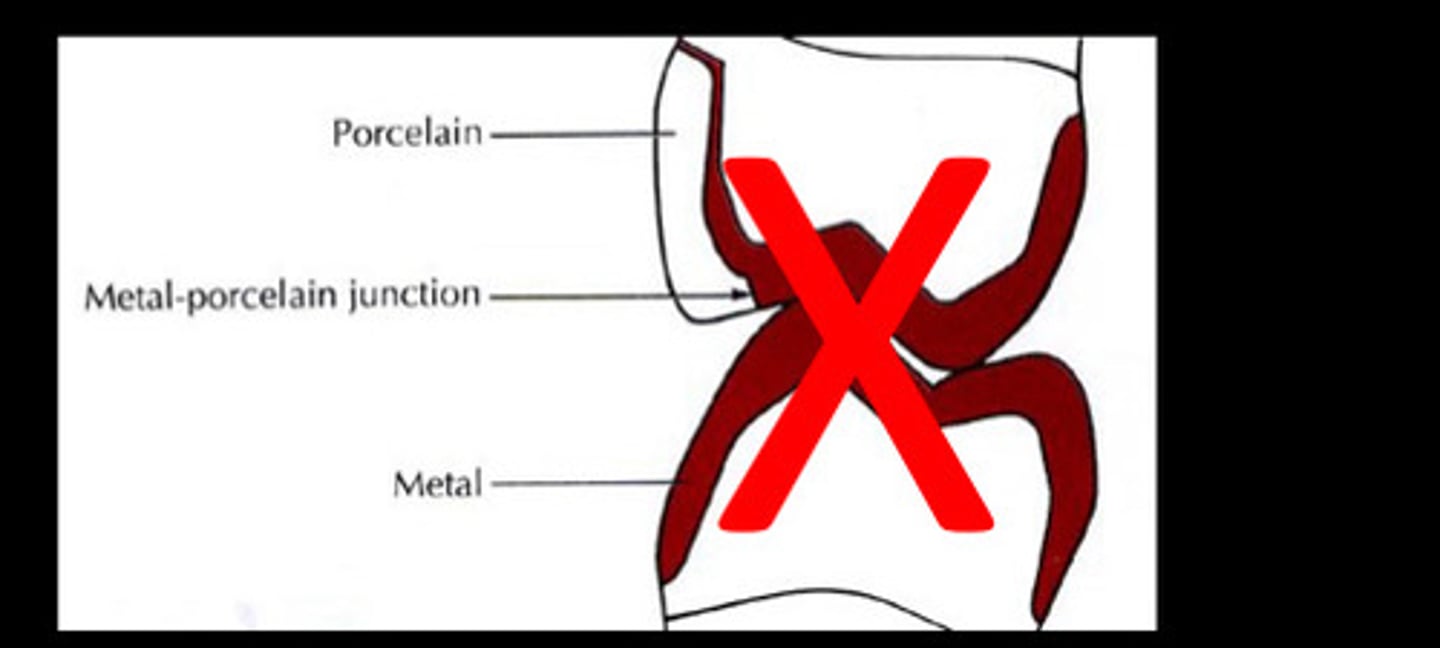
1.5 mm
Metal ceramic interface must be
ideally at least __ from all
centric occlusal contacts.
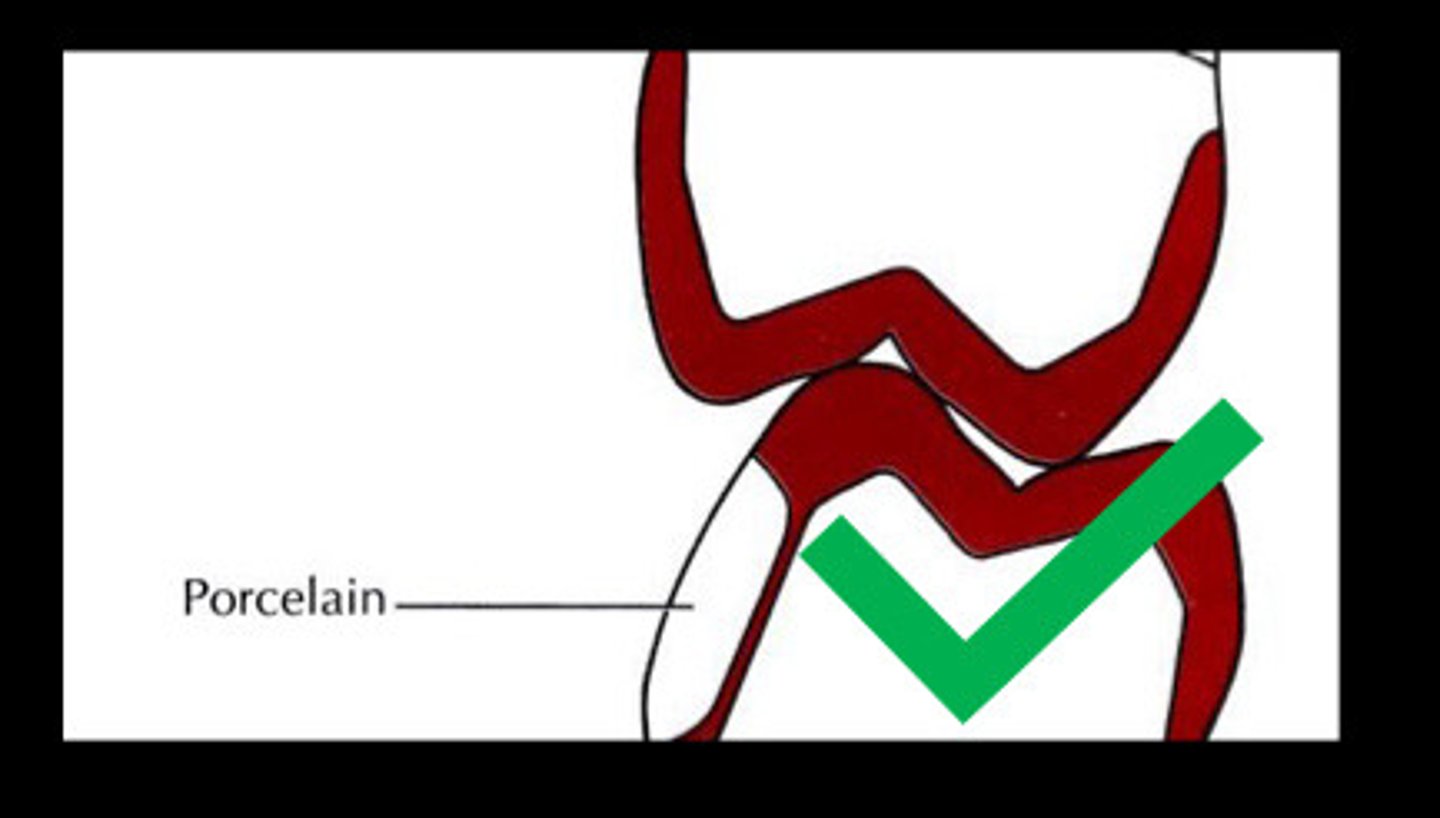
Porcelain
__ is stacked by hand (labor intensive)
surface glaze
The __ during an additional firing.
underlying body and opaque porcelain.
The perceived color of the restoration is significantly influenced by the color of the __
Gold, palladium, platinum
Noble metal casting alloys
Gold ***
Good corrosion resistance due to inherent nobility
Platinum
Increase melting point (which one?)
Nickel, cobalt, chromium, titanium
Base metal casting alloys
Principal elements
Nickel and cobalt are ___ of base metal alloys
greening
Chromium and titanium Oxidize rapidly and prevents diffusion of oxygen into underlying metal (protects it from corrosion) but these oxides could cause __ of porcelain.
Silver
Base metal may Also contain Silver, Copper and Gallium. ___ is not a noble metal (in dentistry) and could also cause greening of porcelain if present .
Oxide layer
__ that has been formed during casting should be
partially removed (either by acid or airborne particle
abrasion with aluminum oxide

Thin
We want the controlled oxide layer to be
surface irregularities
The controlled oxide layer create __ to help with mechanical bond besides chemical bond.
chemical bonding
Manufacturers incorporate small amounts of certain base
metals that form oxides to increase __ to the metal-ceramic adherence.
match
The linear coefficient of thermal expansion from the metal
and ceramic must closely __ to achieve a strong
interfacial bond.
"wetting"
__ the alloy surface by the porcelain slurry at the
firing temperature (the opaque layer)

Glass
Dental porcelains are chemically
Quartz, feldspar, other oxides
Dental porcelains include the following minerals
Tetragonal crystals
Dental porcelains are ___ dispensed in glassy matrix
below
Porcelain must have a firing temp well __ the melting range of the metal
thermal expansion
Porcelain must have a significantly high __ compatible with the metal
wax up
1) __ for metal coping
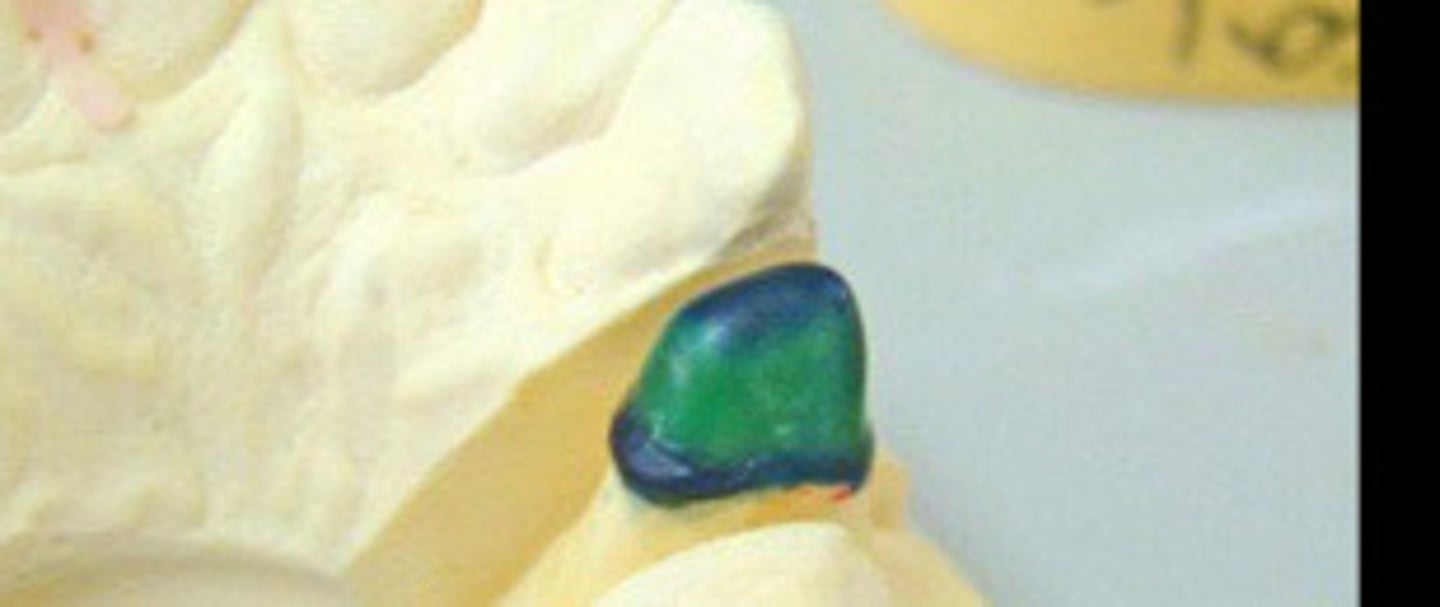

Cast
2) metal coping is

Opaque porcelain
3) __ is added on top of coping
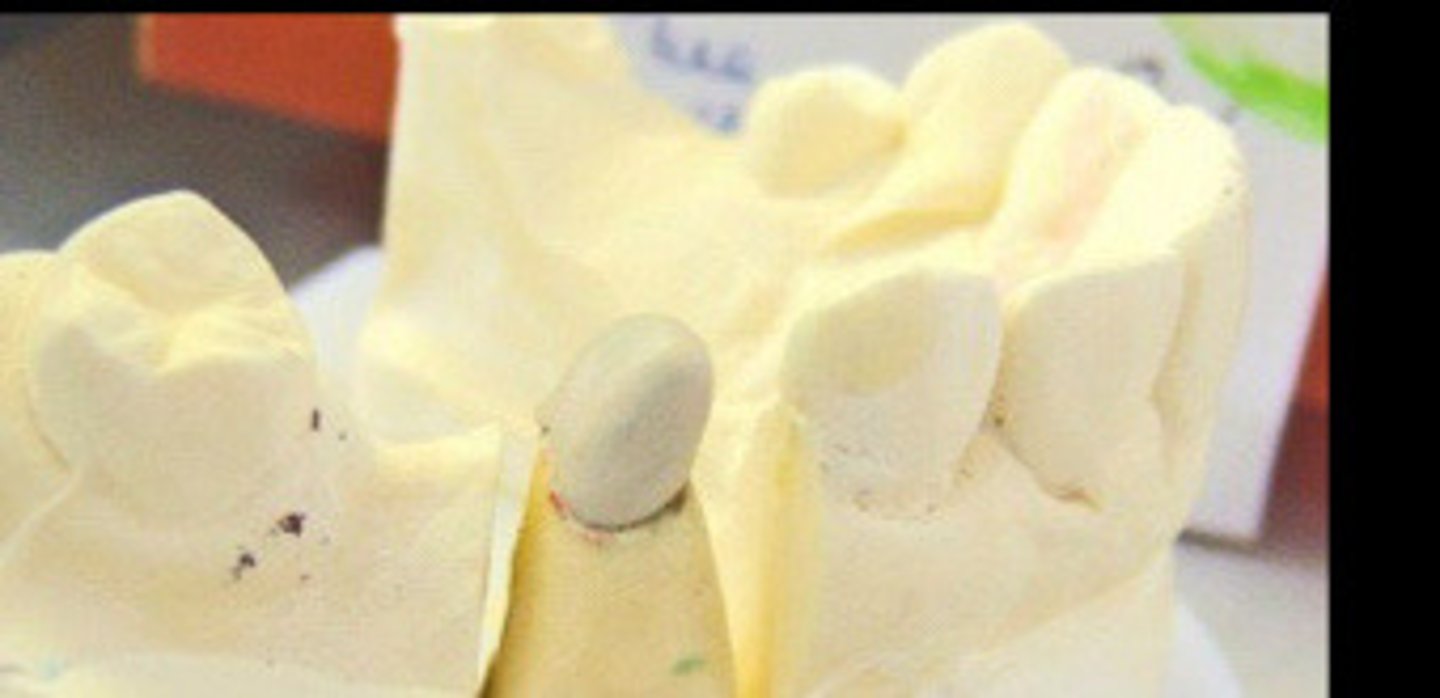
shades
4) porcelain __ are added

contours
5) after firing, __ corrected w/ burs

polished
6) after stain, glaze and final firing metal collar on lingual _
Adhesive failure
Between different materials
Cohesive failure
Between same material
Adhesive failure
If oxide layer was not formed between metal porcelain interface
Adhesive failure
If metal is contaminated in metal porcelain interface
Adhesive failure
If porcelain is contaminated in metal porcelain interface
Cohesive failure
If there are inclusions/voids in porcelain porcelain interface
Cohesive failure
If oxide layer too thick in metal oxide metal oxide interface
Cohesive failure ***
If metal has inclusion and voids in metal metal interface (highly unlikely)
Ceramic
PFM __ occlusal

3/4 metal
PFM __ occlusal
Metal
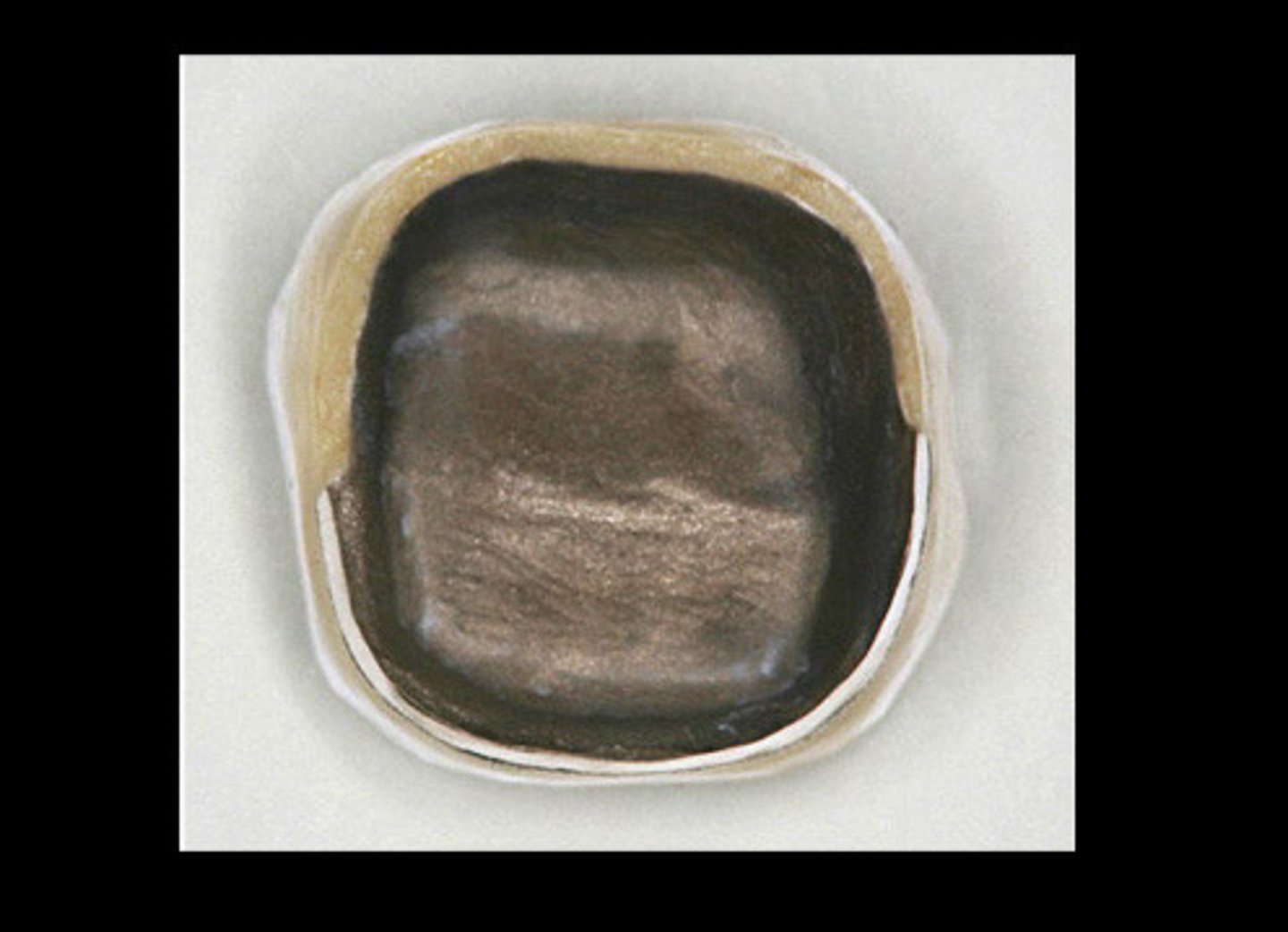
PFM __ occlusal

1.5mm
For metal occlusal - __ occlusal reduction
2.0mm
For porcelain occlusal - __ occlusal reduction
1.5-2.0mm
For combination occlusal - __ occlusal reduction for metal and porcelain areas respectively
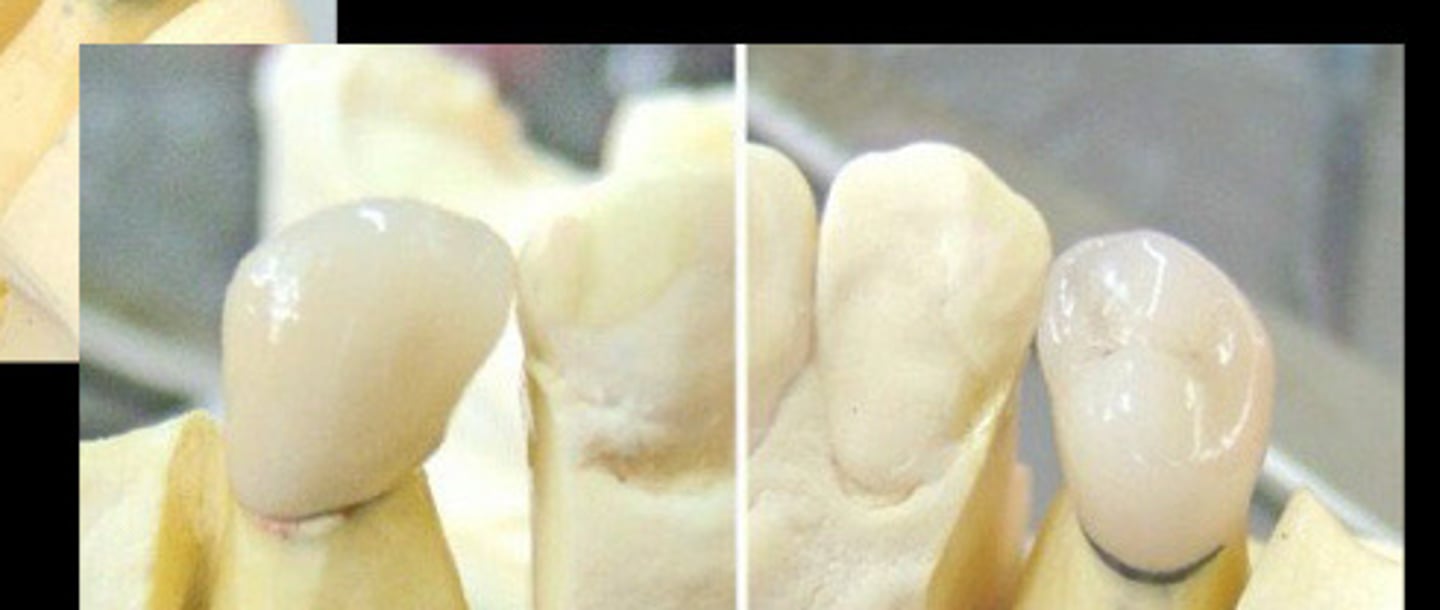
Disappearing metal margin
just a line of metal seeing on the cervical in PFM

Metal and porcelain
Disappearing metal margin is a combination of
Long bevel and heavy chamfer
Disappearing metal margin is created w/ __ burs
45-65 degrees***
The angle of buccal margin
Porcelain margin
the extension of ceramic material to the finish line of the preparation without visible metal substructure in the marginal area in PFM
Metal collar margin
Generally on the lingual in PFM
120 degrees
Margin design for disappearing metal margin have a __ sloped shoulder margin
posterior
Disappearing metal margin commonly used in the __ margin teeth
buccal
We are doing this type of disappearing metal margin teeth today on the __
90 degrees
Porcelain margin is __ shoulder margin
Shoulder
Porcelain margin is a 90 degree __ margin
Esthetics
We use porcelain margin when better esthetics are involved (we aren't doing this today)

Metal collar margin
Often on lingual
Porcelain
Today, the 4 PFM has a __ occlusal
Conservation of tooth structure
• Avoid weakening tooth structure
• Avoid damaging the pulp
buccal
Today, the 4 PFM has a sloped shoulder margin (__) (disappearing metal)

Rentention
Preventing the restoration from being dislodged by forces parallel to the path of insertion (or along the long axis of the tooth) (occlusal direction)
Lingual
Today, the 4 PFM has a chamfer margin on the
Resistance
Preventing the restoration from being dislodged by horizontal or oblique forces
Structural durability
Providing adequate reduction for material strength.
Marginal integrity
Providing proper finish line for close adaptation of material to minimize bacterial microleakage.
(providing seal)
Preservation of periodontium
Providing proper shape and contour to prevent plaque accumulation for optimal periodontal health
Esthetics
qualities focused on appreciation of beauty