Transcriptomics 1- what, why and how
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
What is the transcriptome?
The set of all RNA transcripts, including coding and non-coding, in an individual or a population of cells.
Draw the timeline of the Central Dogma of Molecular Biology.
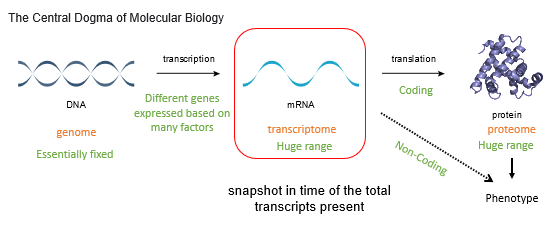
Name 6 environmental factors
Weather (esp plants)
Hormones
Diet
Drugs
Psycological (e.g., stress)
Experience, e.g., learning
What 4 processes do transcripts in a cell reflect on?
Transcription
Splicing
Nuclear export
Decay
3 reasons why we study the transcriptome?
What genes are expressed in which organism (evolution, gene function)
What genes are expressed in what cells (what makes a specific cell type, function, gene function).
What gene expression changes occur under certain conditions (loss/gain of function, environment, disease mechanism + biomarkers)
Name 5 types of RNA in a cell.
mRNA
rRNA
tRNA
noncoding RNA
sn/snoRNA
First, second and third most abundant RNA by mass?
rRNA
tRNA
mRNA
What is the most abundant RNA by number of molecules?
tRNA.
What 2 methods can sequence mRNA and ncRNA?
PolyA enrichment
rRNA depletion
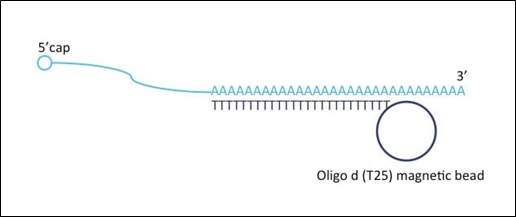
What happens during PolyA enrichment?
Oligo d (T25) magnetic bead moves along mRNA from 3’ to 5’ cap
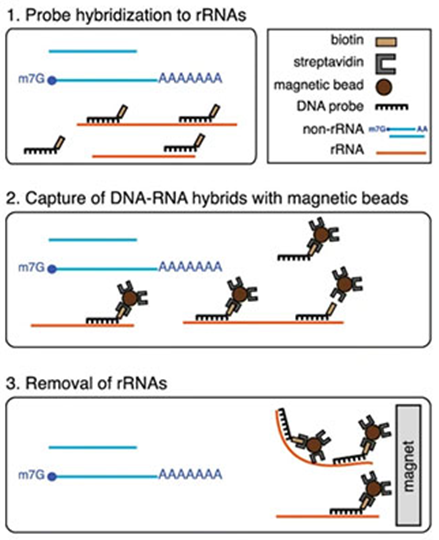
What happens during rRNA depletion? (3)
Probe hybridization to rRNAs
Capture of DNA-RNA hybrids with magnetic beads.
Removal of rRNAs.
How is sequence data for the transcriptome generated? (3)
Extract RNA, then remove the rRNA (or purify mRNA).
Fragment, reverse transcribe, add adapters, sequence.
Send for next-generation sequencing (high throughput sequencing).
What technology produces:
100-150 bp per end
300 bp per end
10kb
Illumina HiSeq
Illumina MiSeq
PacBio/ONT
What is sequencing depth?
The total number of reads obtained from a high-throughput sequencing run.
What is coverage?
The ratio of the total number of bases obtained by sequencing to the size of the genome.
What 3 things is identification of RNA molecules dependent on?
Length
Abundance
Number of sequence reads.
What are the 4 bulk RNA-seq current standards?
Average library insert size is 200 base pairs
2 or more replicates
Each replicate should have 30 million aligned reads
Replicate concordance
What does replicate concordance mean?
The gene level quantification should have a Spearman correlation of <0.9 between isogenic replicates and >0.8 between anisogenic replicates (replicates from different donors).
What is the single-cell isolation followed by RNA-seq specific standards?
Each replicate requires only 5 million aligned reads.
Name 3 adaptations to the technology to look at low abundance transcripts.
Pol II- associated RNA enrichment
Run-on RNA enrichment
Metabolic RNA labelling
How is a transcriptome generated with a reference genome?
Map the sequence data to the reference genome. Use splice aligning of DNA/pre-mRNA to produce spliced mRNA and RNA sequenced reads.
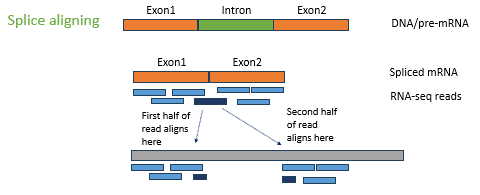
When generating the transcriptome with a reference genome, why are there sequence differences between reads and reference? (2)
Alternative splicing
SNPs or mutation
When generating a transcriptome without a reference genome, how do you assemble the sequence data? (2)
Overlap graphs OR
De Bruijn graphs
Role of overlap graphs? Is it memory intensive?
Simply align all the reads against each other to find overlap, and extend the reads to form transcripts.
Memory intensive.
Role of De Bruijn graphs? Is it memory intensive?
They identify all the k-mers (of length k) in the reads, and assemble these by searching for k-1 overlap. Less memory intensive.
How do you measure expression? (3)
Each sample is mapped back to the reference using aligners and Quasi-mappers
Identification of novel transcripts
Gene expression can be estimated by counting the number of reads that come from the gene after normalising for total read number
What are aligners?
They align reads and reports SNPs.
What are Quasi-Mappers?
Just gives counts per gene.
What is differential gene expression?
Difference in abundance of gene transcripts within a transcriptome
At 5% significance (P<0.05), how many are false positives?
1 in 20
What does FDR stand for?
False discovery rate
What is the q value?
FDR-corrected p value. Gives more confidence.