Option C - Ecology and Conservation
1/68
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
species
a group of organisms with similar characteristics , which can potentially interbreed and produce fertile offspring
populations
a group of organisms of the same species who live in the same area at the same time.
autotrophs
absorbs carbon dioxide, water, and inorganic nutrients such as nitrates from the abiotic environment and uses them to synthesize all the carbon compounds that they need [corn plant]
heterotrophs
cannot make all the carbon compounds that they need and instead obtain them from other organisms.
heterotrophs
many carbon compounds including proteins or starch must be digested by ____ before they can absorb and use them [wood mouse]
saprotrophs
obtain organic nutrients from dead organisms by external digestion. they secrete digestive enzymes into dead leaves or wood, dead animals and feces. [mostly bacteria and fungi]
saprotrophs, consumers, detritivores
three main modes of heterotrophic nutrition
consumers
feed on living organisms by ingestion, taking other organisms into their digestive system for digestion and absorption
detritivores
obtain organic nutrients from detritus by internal digestion. [honey bees]
detritus
dead material from living organisms and includes dead leaves or roots, parts of composing animals and feces.
community
a group of populations of different species living together and interacting with each other in an area.
food web
the complex network of feeding relationships in a community
abiotic environment
the non-living surroundings of a community
ecosystem
formed by communities by its interactions with the abiotic environment, these interactions include the transfers of chemical elements, between populations in the community and the abiotic environment as a part of nutrient recycling
mesocosm
demonstrates how ecosystem can have the potential to be sustainable over long periods of time. as long as nutrients are recycled, ecosystems can only require a supply of energy, usually in the form of light, to continue indefinitely.
Quadrat
a square sample area used in ecological research used to determine the presence of species in an area.
producers
organisms that make their own food. plants, algae, and some bacteria absorb light energy and convert it by photosynthesis into chemical energy in carbon compounds.
Biomass
this is lost so the energy content per gram of the tissues of each successive trophic level is not lower. this is lost when carbon dioxide produces is excreted. the removal of waste products of metabolism such as urea aslo causes the loss of ___.
energy
supplied to ecosystems in the form of light and converted to chemical energy by producers [autotrophs].
this cannot be recycled and is lost from ecosystems, but more light is received
Hydrogen carbonate ions [HCO3]
carbon is presented in this form in aquatic ecosystem and is formed when water and CO2 combine to form carbonic acid, which dissociates to produce _____ ions.
methane
this gas is produced naturally by a group of prokaryotes called methanogenic archdeans. They break down organic matter in anaerobic conditions and release it as a waste product.
accumulation of methane
this process happens in swamps, bogs and other sites where anaerobic conditions, so dead organic matter is not fully decomposed by saprotrophic bacteria and fungi.
limestone
a rock that consist mainly of calcium carbonate [CaCO3] and often consist of many fossils such as mollusks shells and skeletons of hard corals.
fossils
absorb CaCO3 and its shells, specifically shells of marine mollusks fall into the sea bed when they die and become part of a limestone rocks.
peat and coal
conditions are found in bogs and swamps, so partially decomposed plant matter accumulates to form thick deposits ____ and when its crushed and converted into _____.
oil and gas
slit is deposited on the bed of some shallow seas, together with remains of dead marine organisms. the slit on the sea bed was converted to shale, with compounds from the organic matter becoming ___ and ___ trapped in pores in the rock
25%
the radiation is predominantly short wavelengths and it is absorbed in the atmosphere by ___ with ozone layer absorbing much of the ultraviolet.
75%
__ of the solar radiation reaches the earths surface where most of it is absorbed and converted to heat. the surface of the earth re-emits radiation, but at much longer wavelengths, mostly infrared heat.
greenhouse effect
when 70% - 85% is trapped by gases in the atmosphere and re-emits the radiation and some of it passes back to the earths surface, causing global warming.
methane
causes more warming per molecule than CO2 but it is at a much lower concentration in the atmosphere so its impact on global warming is less.
CO2 and water vapor
the most significant greenhouse gases
ocean acidification
this is the result of the CO2 released by humans since the start of the industrial revolution dissolved in the oceans. this has caused the pH level to drop by 30% .
affect of ocean acidification on reef-building corals
with reduced carbonate concentrations in seawater not only can new calcium carbonate not be made for corals to absorb but also dissolves in existing corals, threatening the existence of all reef ecosystems.
transect
a method of sampling at regular positions across an ecosystem, to investigate whether the distribution of species is correlated with an abiotic variable
what happen if 2 species have similar ecological niche
compete in the overlapping parts of the niche, for example breeding sites or food sources
competitive exclusion principle
when one species inevitable prove to be superior competitor and will cause the other species to be lost from the ecosystem, occupying a niche.
fundemental niche
the niche that a specie could potentially occupy. other species prevent its competitor species from occupying parts of this niche by out-competing or by excluding it.
realized niche
the niche that is actually occupied by a specie
keystone species
has a disproportionate effect on the structure of an ecological community. the conservation of this species is essential for the overall conservation of the ecosystem.
herbivory
primary consumers that feed on plants or other producers; harms producers but reduces competition between producers.
predation
predators benefit as they feed on prey; predation affects numbers and behavior of prey.
parasitism
a parasite that lives on or in a host, obtaining food from the host and harming it
mutualism
different species living together in a close relationship, from which they both benefit.
mutualism between reef-building corals
corals that build reefs contain mutualistic photosynthetic algae called zooxanthellae
the coral provides the alga with a protective environment and holds it in position close to the water surface where photosynthesis occurs.
the zooxanthellae provide the coral with products of photosynthesis such as glucose, amino acids and oxygen.
food chain
a single sequence of organisms, each of which consumes the previous one in the chain.
most species of consumer eat a variety of other organisms, so are n many different food chains
gross production
the total amount of energy in food assimilated by an animal or in food made by photosynthesis in producers
net peoduction
the amount of energy converted to biomass in an organism.
feed conversion ratio (FCR)
the efficiency with which a species uses food
intake of food / net production of biomass
the higher the ratio, the higher the respiration rate of the species and the lower the percentage of ingested energy that is converted to biomass.
birds and mammals usually have high respiration rates because they maintain constant body temperature
closed ecosystem
an ecosystem that does not exchange nutrients with its surroundings
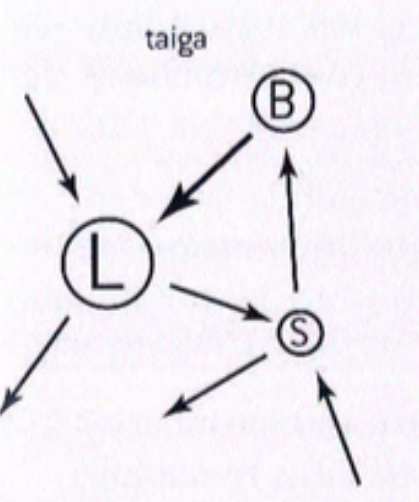
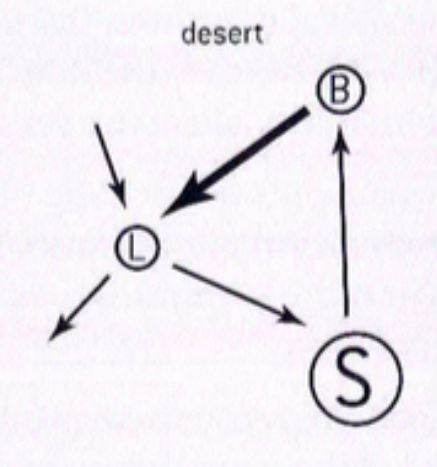
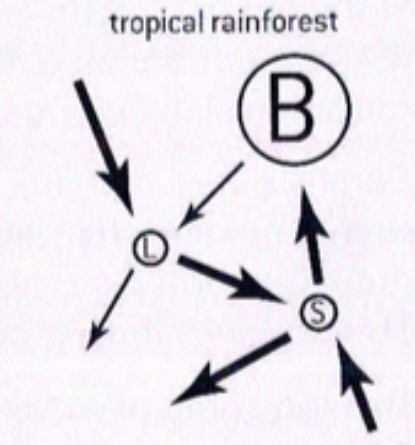
three main storage compartments in terrestrial ecosystem
biomass (living organisms)
litter (deaf organic matter)
soil
taiga
desert
tropical rainforest
nitrogen cycle
this results from the runoff from fields in lakes and rivers.
nitrogen oxides from vehicle exhausts dissolve in water in the atmosphere to form nitrates, which are deposited in rainwater
ecological succession
a series of changes to an ecosystem, caused by complex interactions between the community of living organisms and the abiotic environment
primary succession
starts in an area where living organisms have not previously existed, for example a new island, created by volcanic activity.
climax community
this causes ecological succession to stop due to the estable ecosystem developing with a group of organisms
climograph
shows the relationship between temperature, rainfall, and the type of stable ecosystem that is predicted to develop
alien species
a type of organism that humans have introduced to an area where it doesn’t naturally occur.
they are released either accidentally or deliberately into local ecosystems often become invasive because predators from their natural community that control their numbers have not been introduced.
they compete with epidemic species for food and habitat.
biomagnification
the concentration of pollutants in the tissues of organisms
it happens at each stage in the food chain, with higher trophic levels reaching toxic doses
some pollutants are absorbed into living organisms and accumulate because they are not efficiently excreted.
when a predator consumes prey that contains a pollutant, the level in the body of the predator rises and can reach levels much higher than those in the bodies of its prey.
edge factors
large unbroken areas of forest usually contain more species than a similar total area of fragmented forest.
ex situ
because of the loss of natural habitat or catastrophic populations declines, it forces conservationists to transfer threatened populations from their natural habitats to zoos, botanic gardens or wild refuges.
in situ
the ideal place to conserve a species in its own habitat.
many national parks and nature reserves have been established for his purpose
indicator species
this species needs particular environmental conditions
they shows what the conditions in an ecosystems are
lichen species vary in their tolerance of Sulphur dioxide so can be used to assess the concentration of this pollutant in an area.