muscular system
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
4 functions of our muscles
movement, maintain support, joint stability, and generates heat
3 types of muscle tissue
skeletal, cardiac, and smooth
skeletal muscle location
attached to bones by tendons
skeletal muscle shape
long, cylindrical, multinucleated, striations
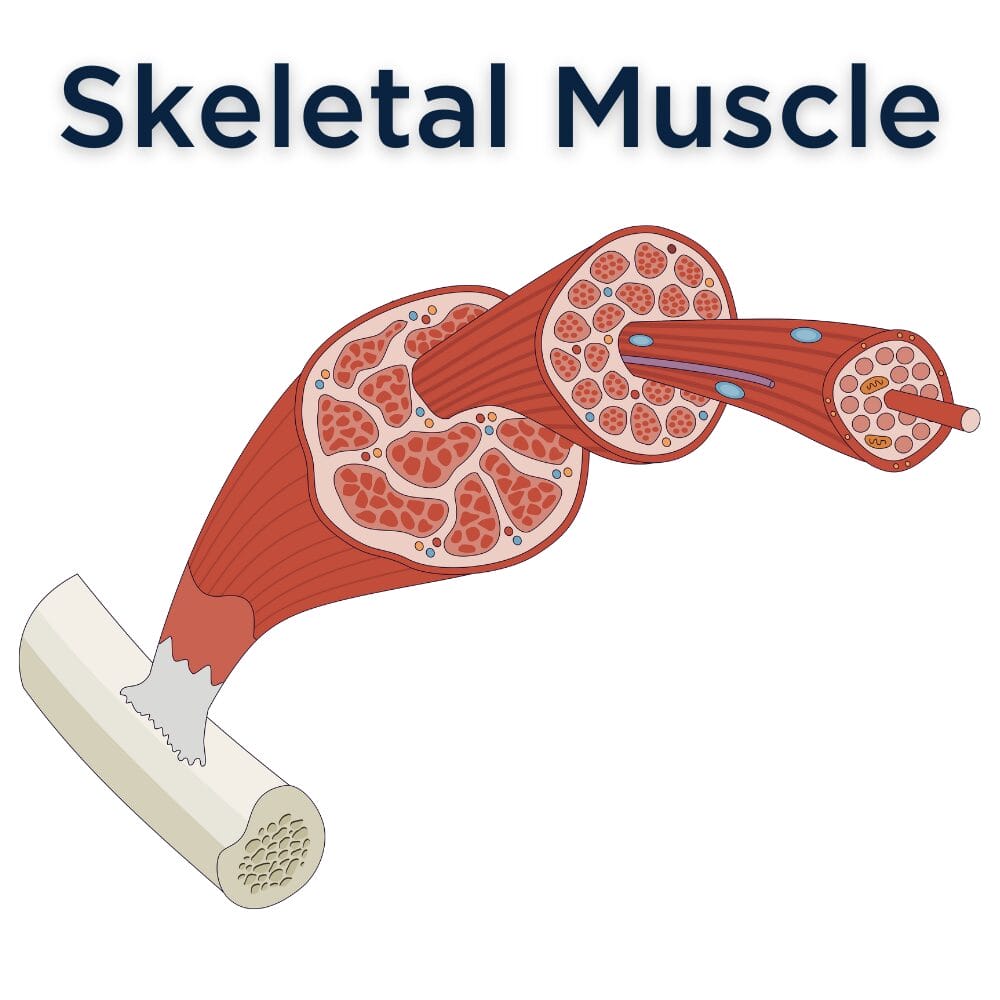
skeletal muscle regulation of contraction
voluntary
skeletal muscle speed of contraction
slow to fast
smooth muscle location
walls of hollow organs
smooth muscle shape
no striations, spindle-shaped cells, single nucleus
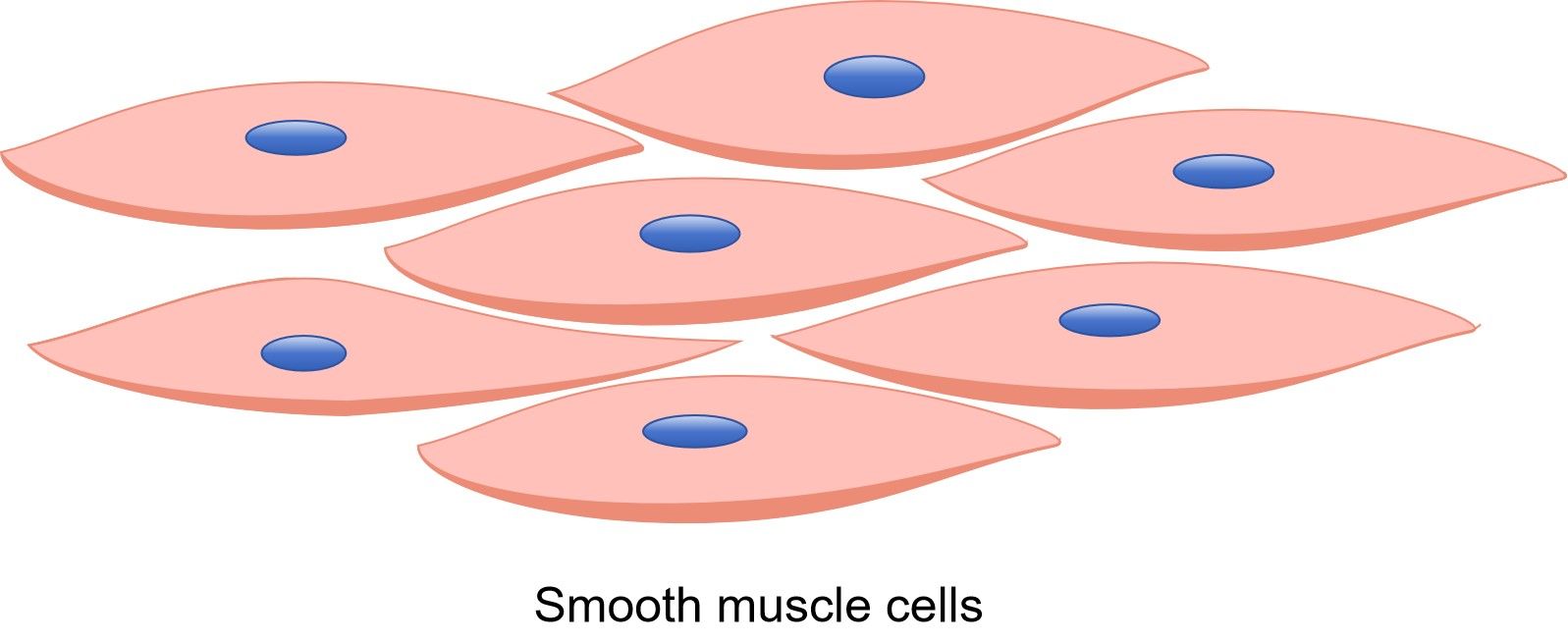
smooth muscle regulation of contraction
involuntary
smooth muscle speed of contraction
very slow
smooth muscle rhythm
in some
skeletal muscle rhythm
none
cardiac muscle location
only in the heart
cardiac muscle shape
striations, single nucleus, intercalated disc, branched shape
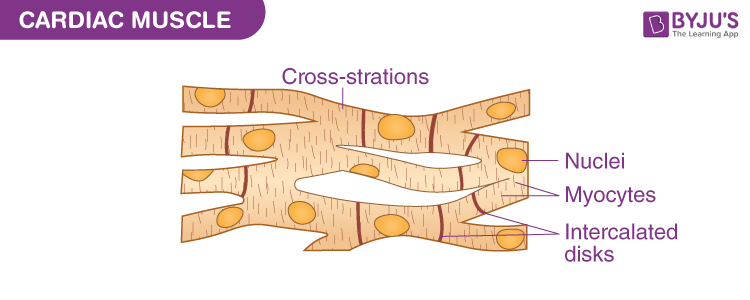
cardiac muscle regulation of contraction
involuntary
cardiac muscle speed of contraction
slow
cardiac muscle rhythm
always present
wrapping of the muscle fiber
endomysium
wrapping of the muscle fascicle
perimysium
wrapping of multiple fassicles
epimysium
sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) storage
claim
i band
light band
a band
dark bands
sarcomere
contractile unit of a muscle fiber
thick filaments
myosin filaments
thin filaments
actin filaments
myosin filament heads
cross bridges
the structure the actin filaments are anchored to at their endpoints
z-disc
region from one endpoint to another endpoint in the actin and myosin filaments
sarcomere
myofibril
chains of sarcomere
bare zone
has no actin filaments
properties of skeletal muscle activity
irritability and contractility
irritability
ability to receive and respond to stimuli
contractility
ability to shorten when an adequate stimuli is received
extensibility
ability to stretch
elasticity
ability to recoil
motor unit
a neuron and all the muscle fibers it stimulates
neuromuscular junction
site where nerve and muscle fibers meet
axonal terminal
the end of the motor neuron that meets in the neuromuscular junction
synaptic cleft
small gap between the muscle and nerve that is filled with interstitial fluid
nuerotransmitter in skeletal muscle
acetylcholine (ACh)
sliding filament theory
cross bridges on the myosin will attach to binding sites on actin filaments to move the filaments together (creating a contraction)
message sent (step 1 of sliding filament theory)
a message comes from the brain and travels through the spinal cord into a neuron which reaches the neuromuscular junction
neurotransmitter (step 2 of sliding filament theory)
acetylcholine is released into the synaptic cleft which then binds to the sarcolemma. this opens the sodium - potassium channels
depolarization (step 3 of sliding filament theory)
Na+ and K+ begin to move but more Na+ moves out than K+ moves in, creating an imbalance of charges which creates a electric current (action potential)
sarcoplasmic reticulum and calcium (step 4 of sliding filament theory)
the action potential moves across the sarcolemma and down the t-tubicles, which causes the SR to release calcium (Ca+). Ca+ binds with the troponin, changing the shape of the troponin and tropomyosin, revealing the actin binding sites.
myosin and actin (step 5 of sliding filament theory)
myosin releases inorganic phosphate and ADP which creates ATP. myosin can then change shape to bind to the actin binding sites. myosin and actin slide towards each other to create the contraction.
relaxation (step 6 of sliding filament theory)
ATP binds back to the myosin to detach and reposition the myosin from the actin. troponin covers back up the actin binding sites. Ca+ moves back into the SR and the sarcolemma is repolarized.
initial source of energy for muscle contraction
stored ATP
energy