Psychology Exam 1 Review
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Clinical Psychology
A branch of psychology that focuses on diagnosing and treating mental, emotional, and behavioral disorders.
Developmental Psychology
The study of how people grow and change throughout the lifespan.
Cognitive Psychology
The study of mental processes such as perception, memory, and problem-solving.
Social Psychology
The study of how individuals influence and are influenced by others.
Forensic Psychology
The application of psychology to legal issues and criminal investigations.
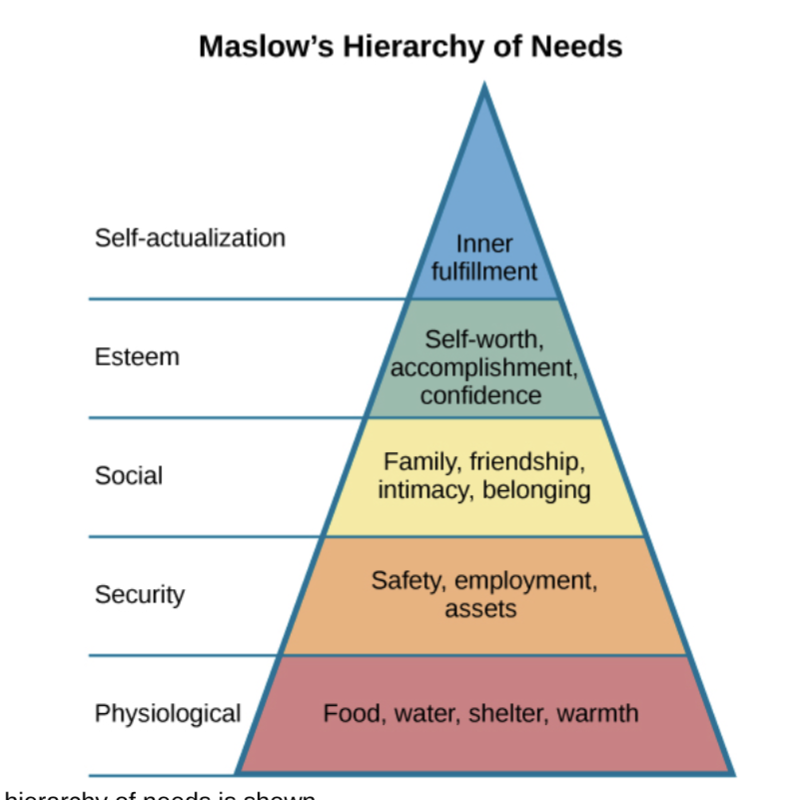
Physiological Needs
Basic requirements for human survival, such as food, water, and shelter.
Safety Needs
The need for security and protection from physical and emotional harm.
Love/Belonging Needs
The need for social interactions, relationships, and acceptance from others.
Esteem Needs
The need for self-esteem, respect from others, and recognition.
Self-Actualization
The realization of one’s potential, personal growth, and peak experiences.
Characteristics of a Self-Actualized Person
Realism, acceptance, problem-solving focus, autonomy, and continued growth.
Naturalistic Observation Research
Research method involving observation of subjects in their natural environment without interference.
Hypothesis Driven Experiments
Experiments testing specific predictions by manipulating variables.
Case Study Research
A detailed examination of an individual or small group.
Tuskegee Experiment
An unethical study on untreated syphilis in African American men that failed to inform participants of their diagnosis and did not provide proper treatment even after penicillin became available.
Dependent Variable
The outcome measured in an experiment.
Independent Variable
The variable manipulated in an experiment to observe effects on the dependent variable.
Correlation
A statistical relationship between two variables.
IRB (Institutional Review Board)
A committee that reviews research to ensure ethical standards are met.
Informed Consent
Participants' agreement to partake in research with full awareness of risks.
Peer Review
Evaluation of research by experts in the field before publication.
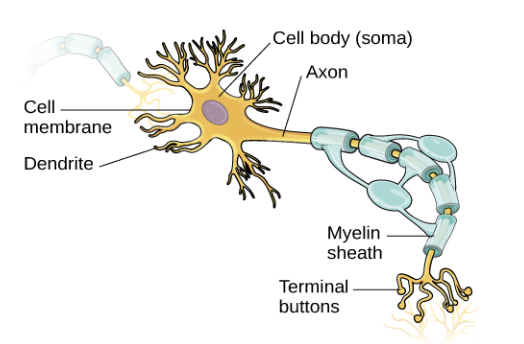
Neuron Structure
Includes dendrites, cell body, axon, and myelin sheath.
Synapse Structure
Composed of presynaptic terminal, synaptic cleft, and postsynaptic membrane.
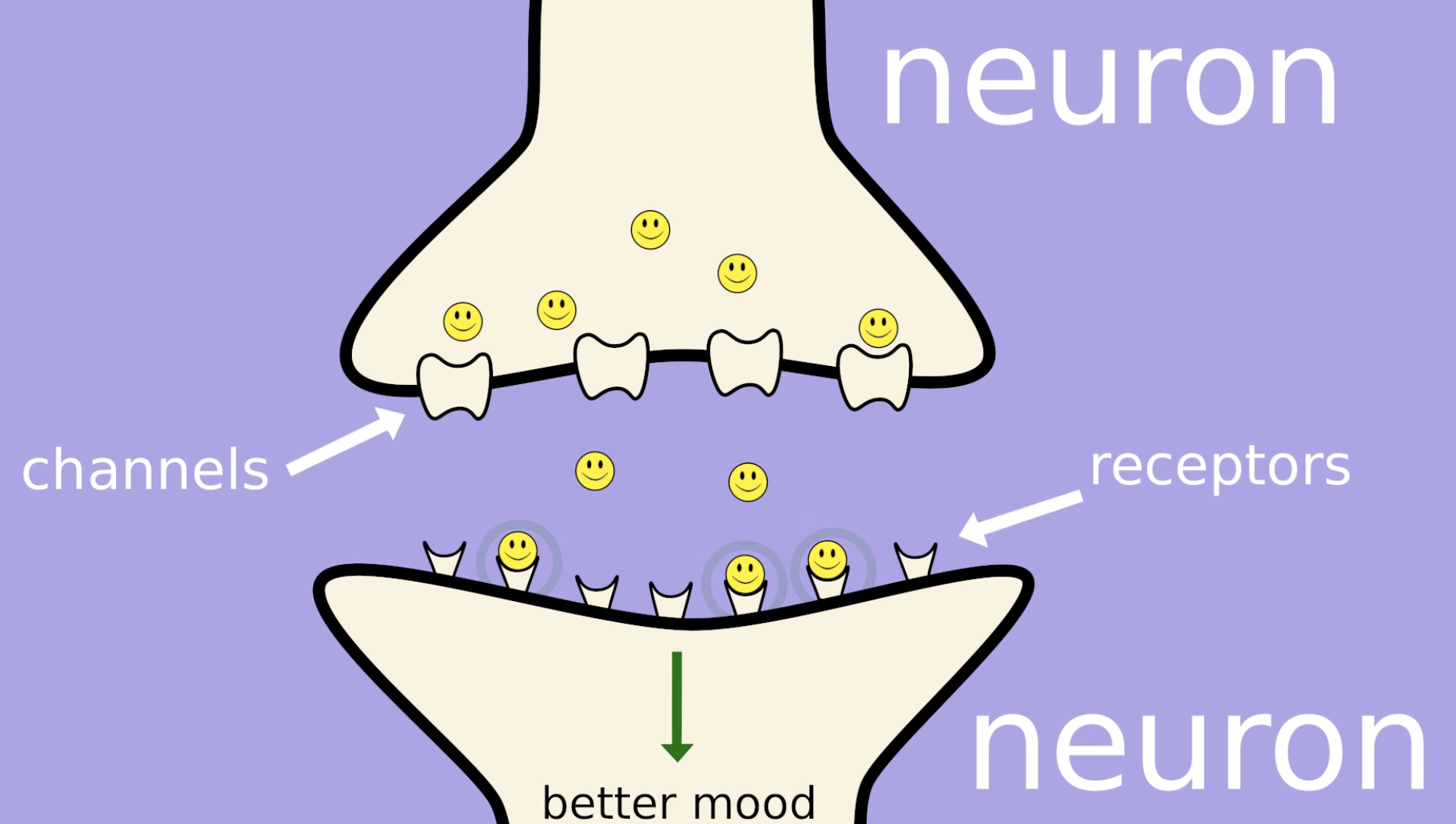
How do SSRIs act in the brain to treat depression?
SSRIs work by blocking the reuptake of serotonin in the brain, increasing the levels of serotonin available in the synaptic cleft, which helps improve mood and alleviate symptoms of depression.
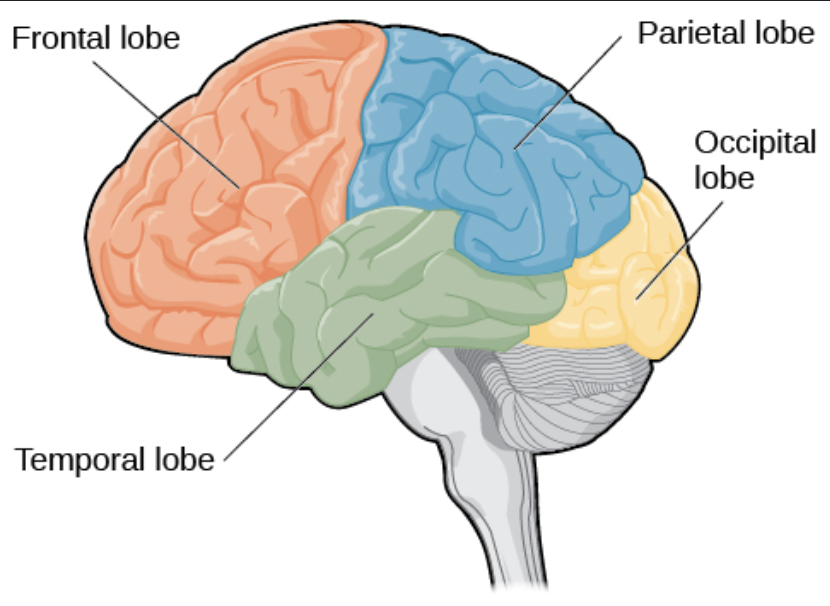
Frontal Lobe
Brain region responsible for decision-making and problem-solving.
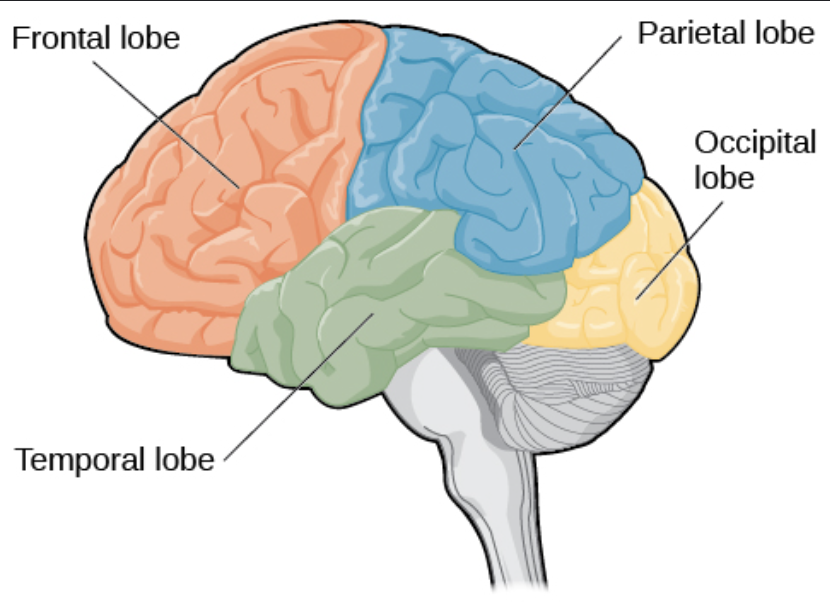
Parietal Lobe
Brain region involved in processing sensory information and spatial awareness.
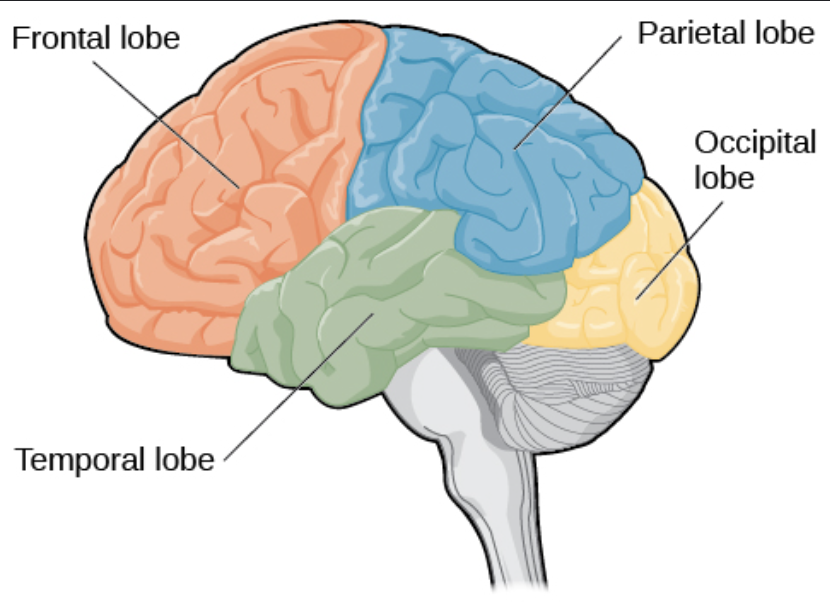
Temporal Lobe
The part of the brain responsible for processing sounds and managing memory.
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Pyramid
The levels include physiological needs, safety needs, love and belonging, esteem, and self-actualization, with higher needs becoming prominent only after lower needs are satisfied.
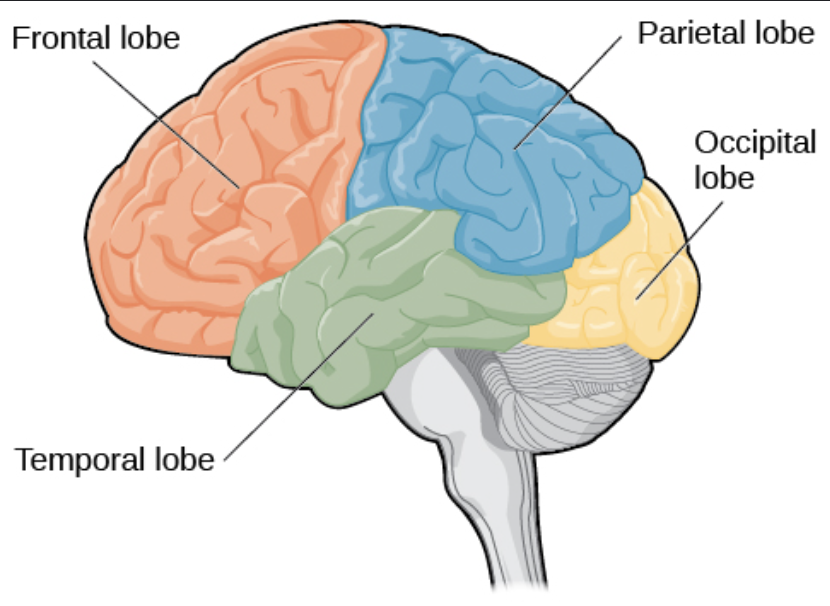
Occipital lobe
The region of the brain located at the back of the head, primarily responsible for visual processing and interpreting visual information.
Name 5 areas of psychology
Cognitive, Clinical, Developmental, Counseling, and Forensic Psychology
Synapse
The connection point between two neurons where they communicate with each other using chemicals called neurotransmitters.
What are the parts of a neuron
Dendrites, cell body (soma) , axon, axon terminals, and synapse.
Electrical Conductance and Action Potential
Electrical conductance is the movement of ions in and out of a neuron. An action potential is a quick change in the neuron's electrical state that allows it to send signals.
Chemical Neurotransmission
The process where neurotransmitters are released from one neuron, travel across the synapse, and bind to receptors on another neuron, allowing them to communicate.
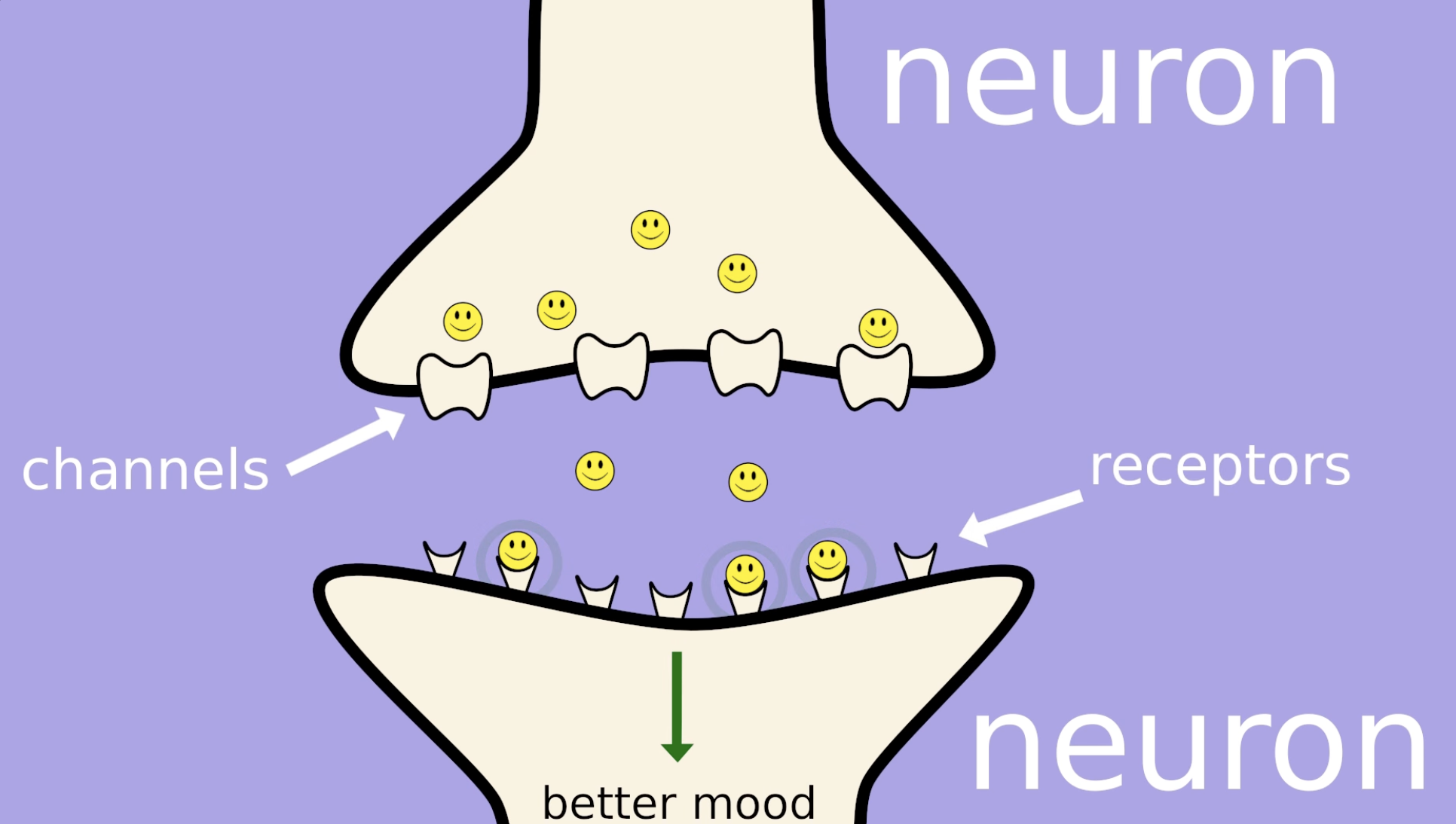
List at least 3 Neurotransmitters
Dopamine, serotonin, and adrenaline.
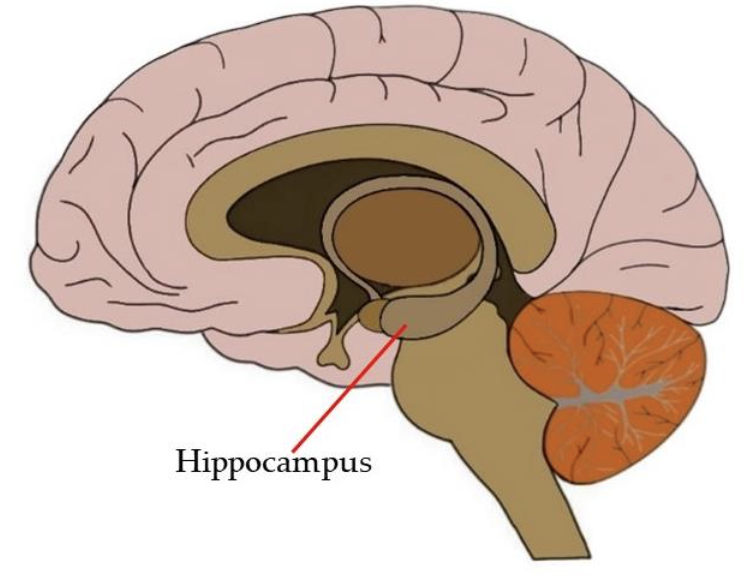
Hippocampus
A brain structure involved in memory formation and spatial navigation.
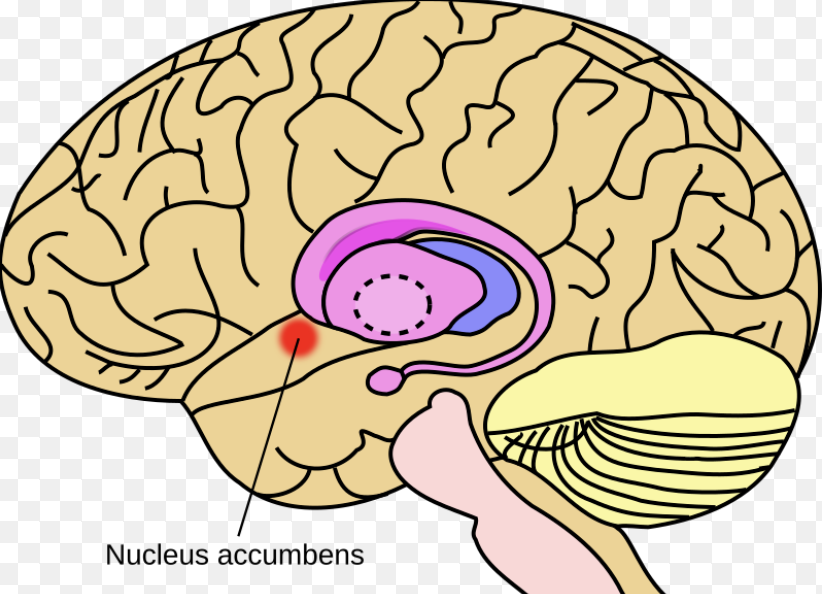
Amygdala & Nucleus Accumbens
Brain regions involved in emotion regulation and reward processing. The amygdala processes emotions like fear and pleasure, while the nucleus accumbens is crucial for the brain's reward circuit.
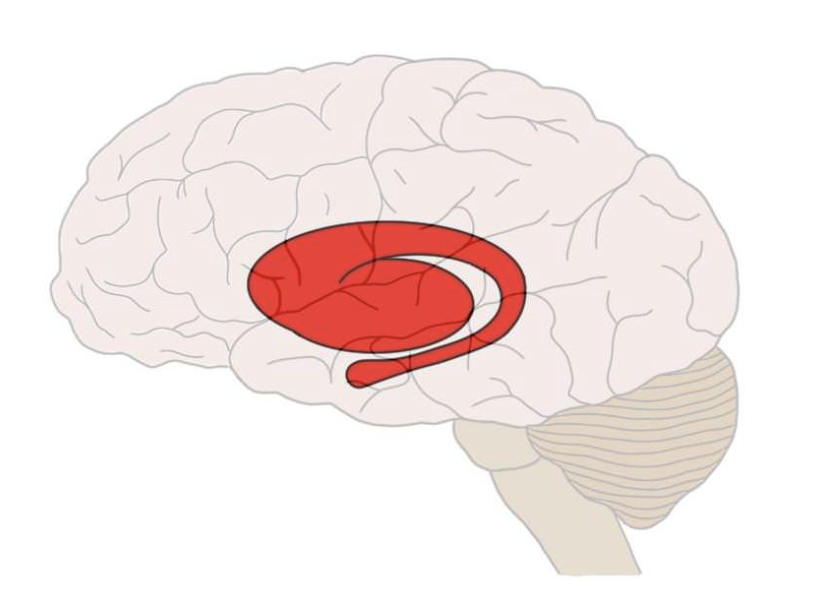
Striatum
A subcortical brain structure that plays a key role in the coordination of movement and is involved in reward processing and habit formation.
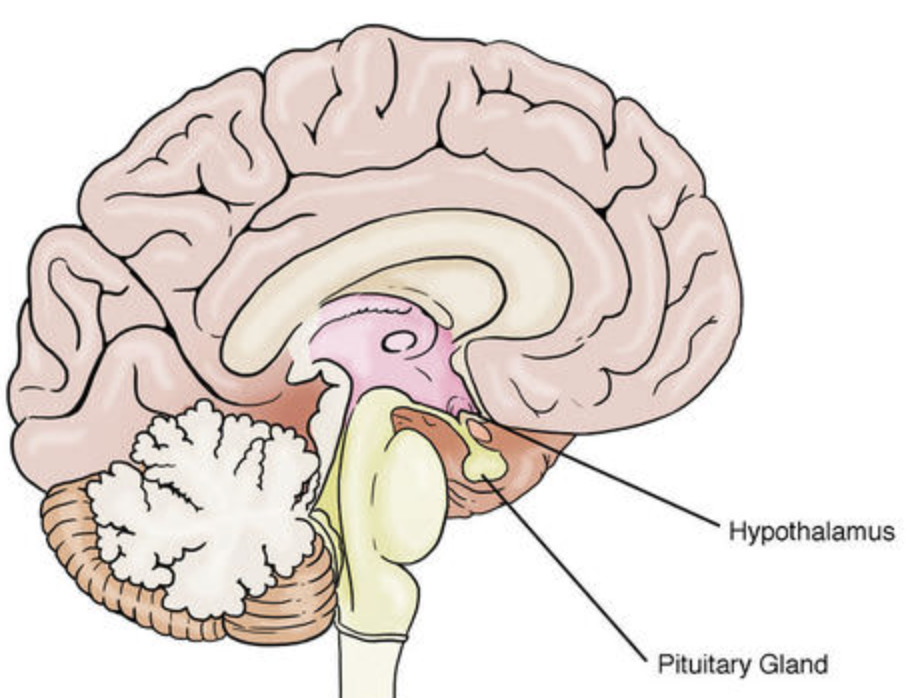
Hypothalamus
Controls basic bodily functions like hunger, thirst, temperature, and sleep.
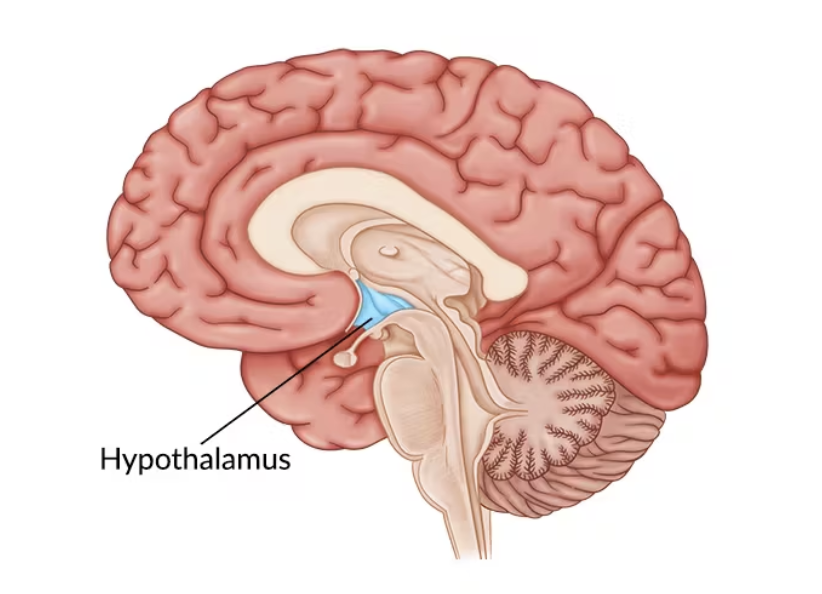
Pituitary gland
Regulates the functions of other endocrine glands and controls growth, metabolism, and reproduction.
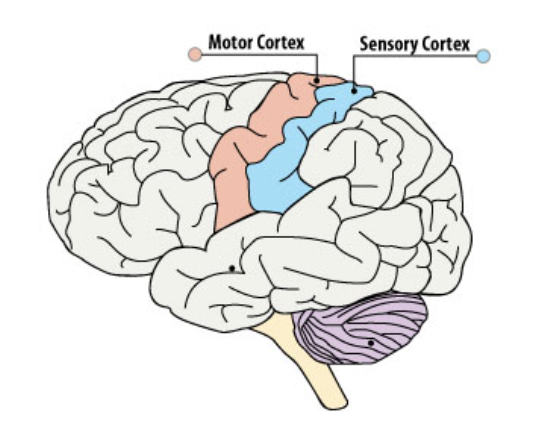
Sensorimotor Cortex
Processes sensory input and integrates it with motor functions for coordinated movement.
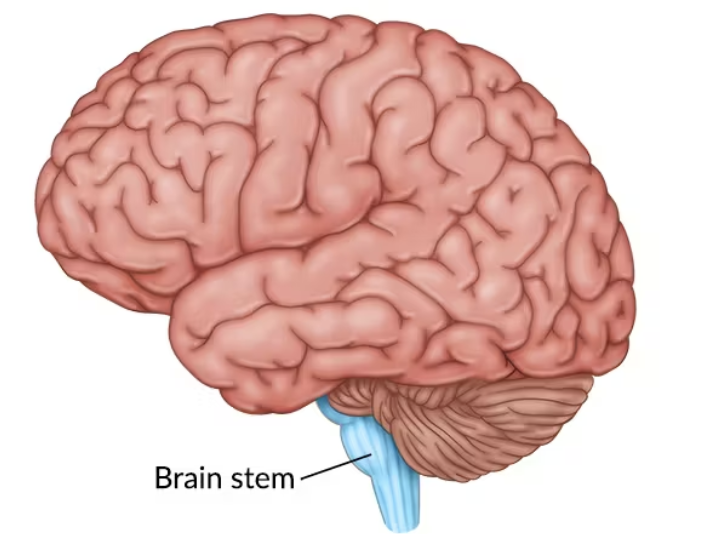
brain stem
Controls vital life functions such as breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure.