NSG 116: Quiz #1 Immunizations
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
What is immunity
the body's ability to protect itself from disease-causing organisms, like viruses, bacteria, and fungi
What causes serum sickness?
the body's immune system reacting to foreign proteins, typically found in medications or treatments like antivenoms. These proteins, often from animals like horses or rabbits, are recognized as harmful, triggering an immune response
Adults 60 or older
Varicella vaccine to prevent shingles
Adults 65 or older
Td booster every 10 years
Annual influenza vaccine (recommended for sept or Oct)
One time pneumococcal vaccine (2nd dose if it has been 5 years or more since the first dose)
Immunization of specific diseases when at risk with travel or occupation
Malaise
A general sense of being unwell
Born before 1956
One dose of MMR unless they have had the disease
Td booster is given every
10 years
Vaccine schedule: birth to 6 years
Hepatitis B (3 doses)
Rotavirus
D-Tap
HIB
PCV (pneumonia)
IPV (polio)
MMR
Varicella
How does the stomach acid assist the body
The low pH kills harmful bacteria
If you have an allergy to yeast you can not get
Hep B
Vaccines are contraindicated
Children less than one
The immunocompromised
Pregnant Women
Vaccine schedule: 11 to 16 yrs old
Meningitis vaccine (2 doses)
HPV
T-dap
At least 6 months or flu season
Annual yearly influenza vaccine
At least 12 months
MMR(live virus)
Varicella ( live virus)
T-dap vs D-tap vaccine
D-tap is for younger kids under 7
T-dap is for older kids and adults
What does a T-dap/ D-tap vaccine cover
Tdap and DTaP are both vaccines that protect against tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis, but they are used for different age groups.
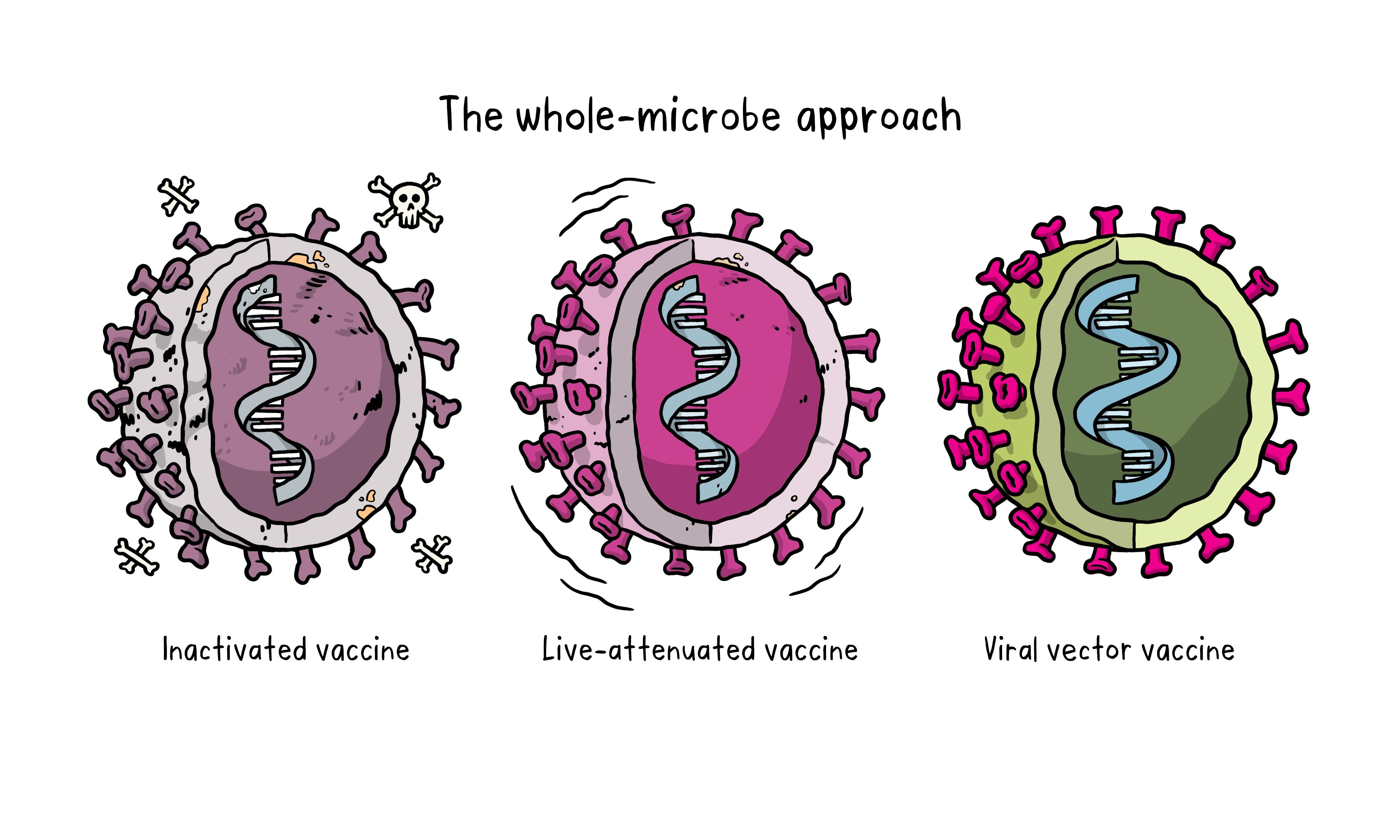
Attenuated (weakened) vaccines produce
Long lasting immunity similar to if you got the actual disease and made your own antibodies
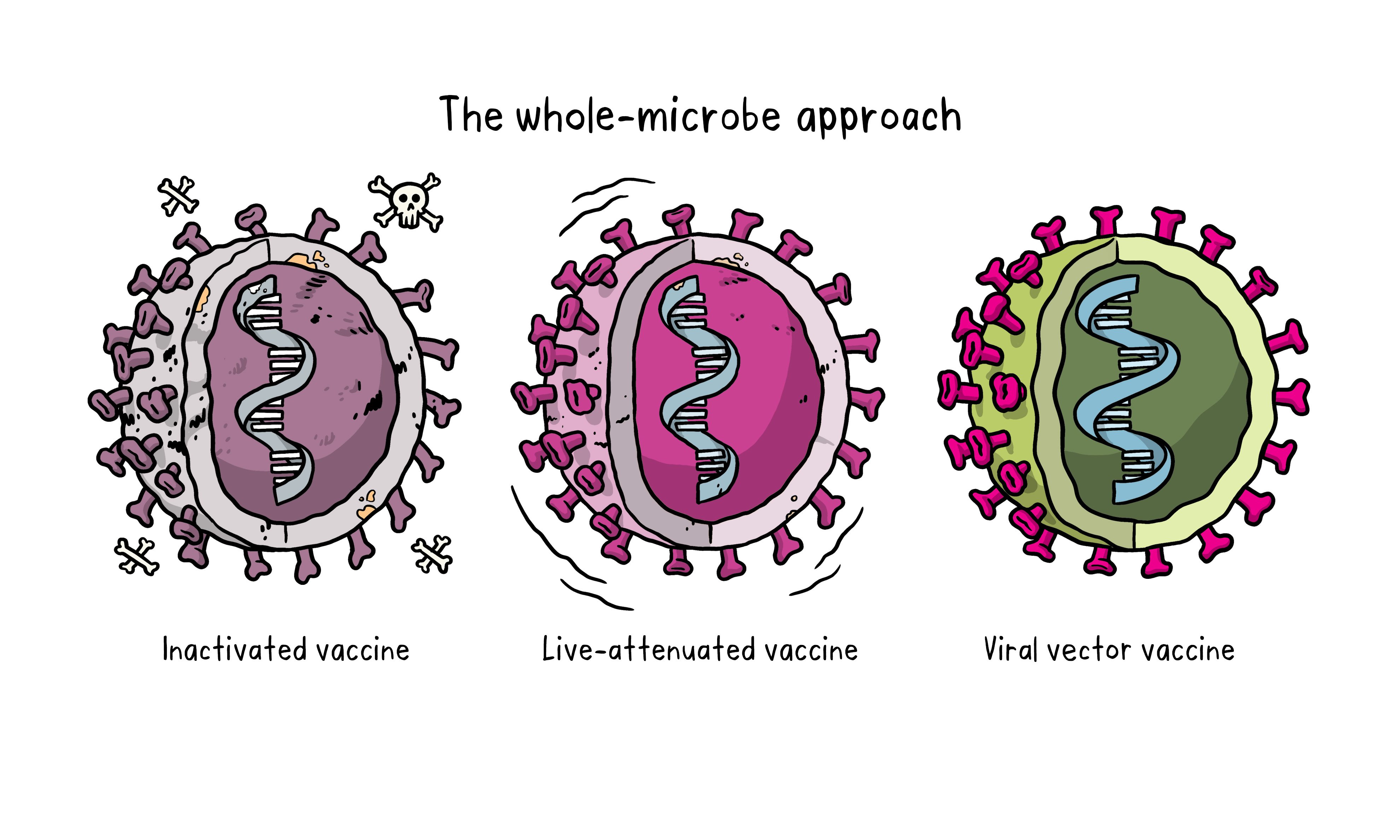
Attenuated vaccines
Microorganisms that have been weakened and are given to stimulate antibody production against the microorganisms prior to a natural infection
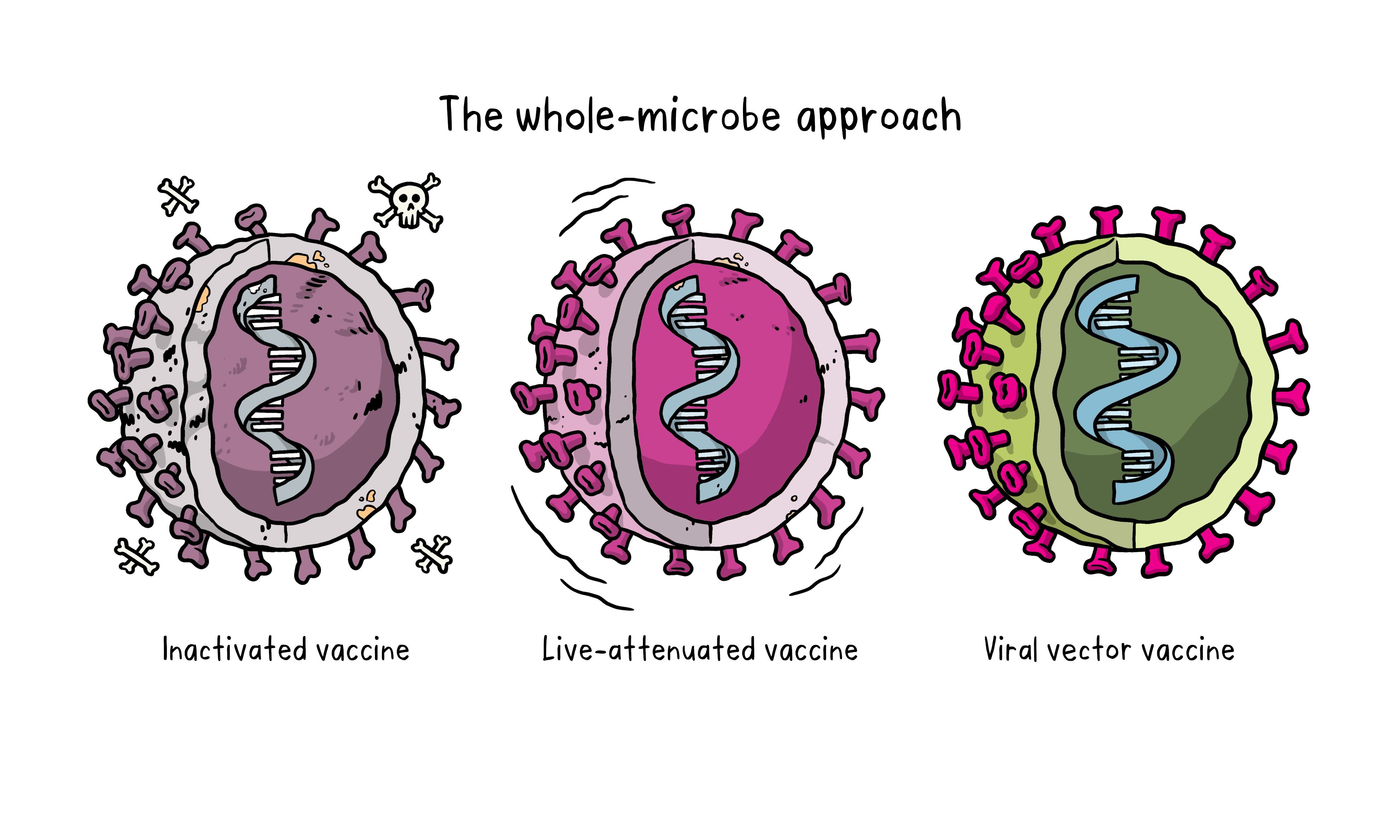
Inactivated vaccines
Microorganisms or components of microorganisms that have been killed to stimulate antibody’ production against the microorganism prior to a natural infection
Vaccines/immunizations involve bolstering a person’s immune system by
Inducing antibody formation which will provide active protection against a specific infectious disease
Vaccines are frequently called immunization’s because
They stimulate immunity
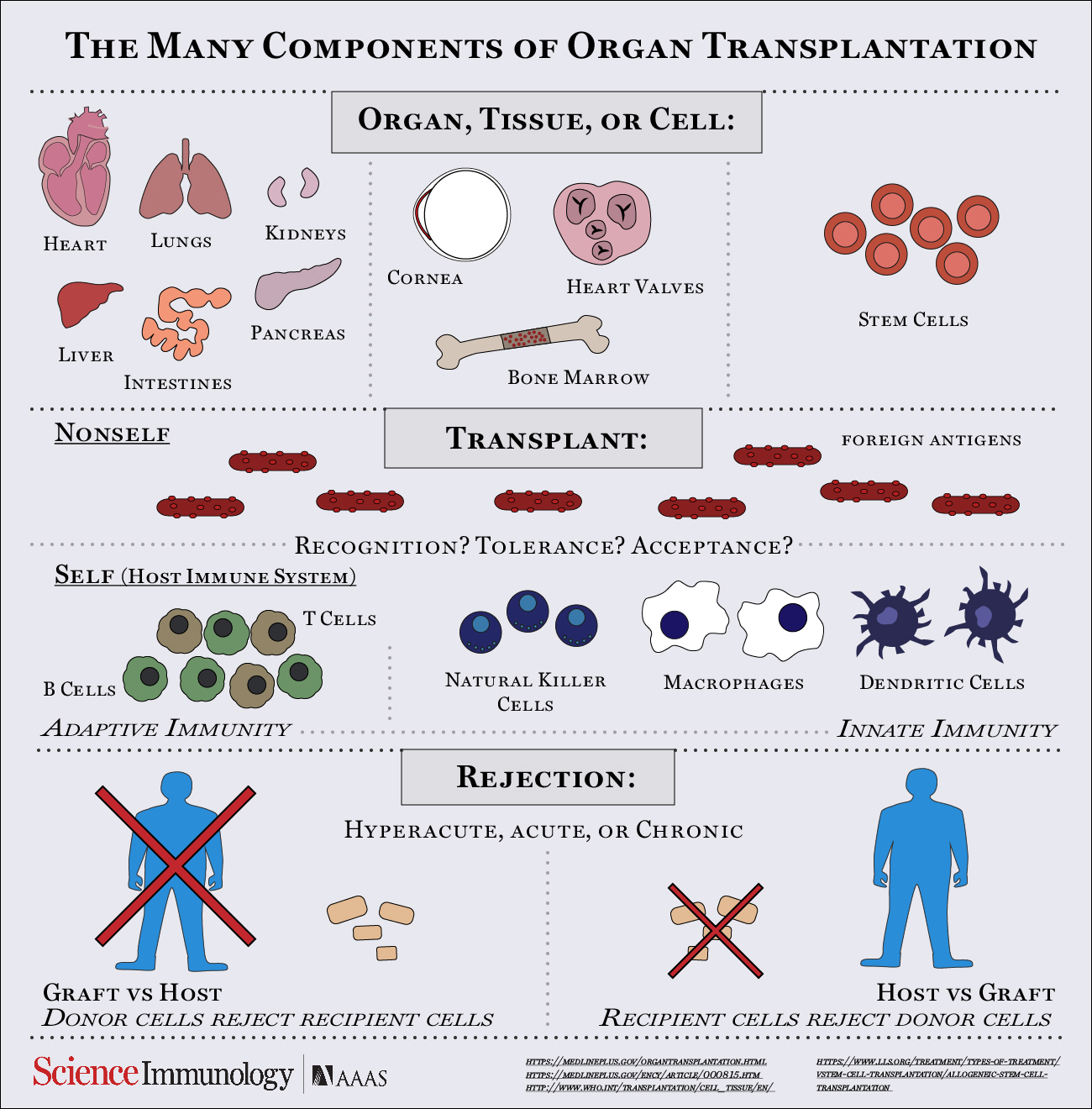
Immune concern with organ transplant therapy
The body can see the organ transplant as a foreign object and try to eliminate it, this is why patients take anti rejection drugs for the rest of their lives
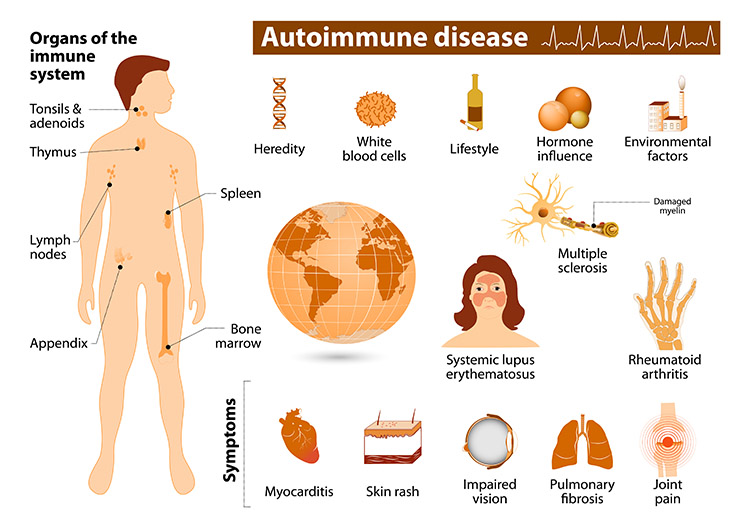
Examples of autoimmune diseases
Rheumatoid arthritis
Crohns disease
Psoriasis
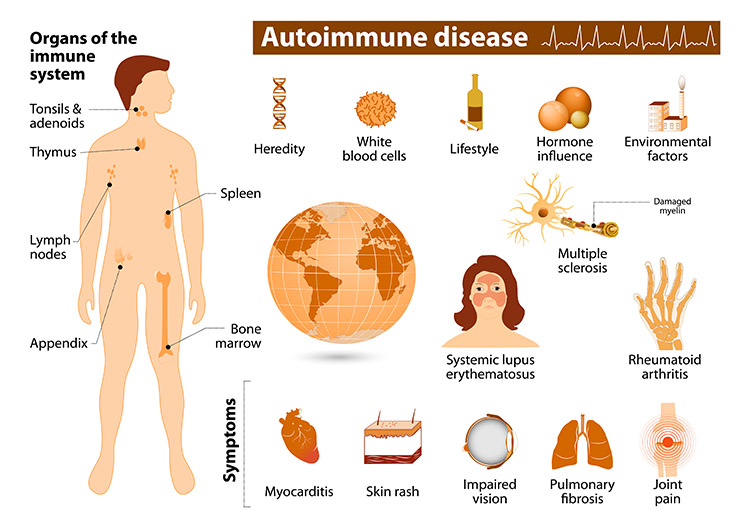
What are autoimmune diseases
When the person’s immune system loses the ability to determine the difference between self and non self
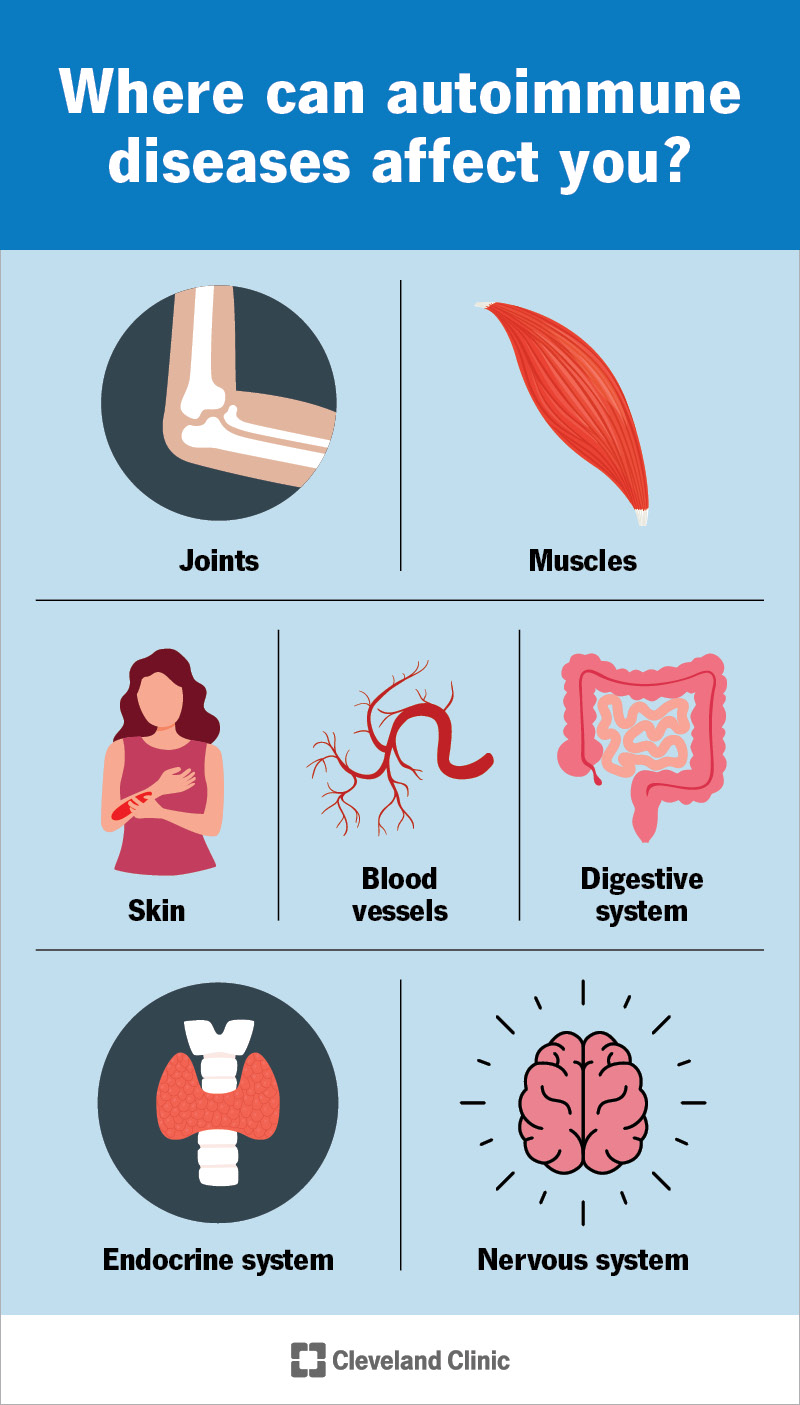
Where can autoimmune diseases effect you
Joints
Muscles
Skin
Blood vessels
Digestive System
Endocrine System
Nervous System

White blood cells (leukocytes) travel through the blood stream and into
Tissues to search and destroy invaders
White blood cells (WBCs) are part of
the body's immune system and are normally present in small numbers in urine.
, an increased number of WBCs in the urine can indicate an underlying medical condition.
Can immunocompromised patients have the flu vaccine
Yes the CDC recommends that they get an annual influenza vaccine
Immunocompromised people can’t take
Attenuated (live) vaccines
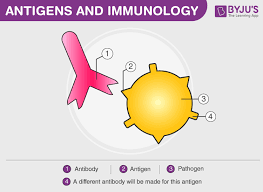
What are antigens
substances that trigger an immune response in the body.
typically proteins or carbohydrates found on the surface of cells, viruses, bacteria, or other foreign particles.
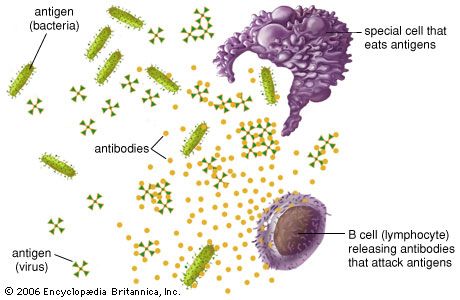
When the immune system encounters an antigen
it recognizes it as a potential threat and produces antibodies specifically designed to bind to and neutralize that antigen.
helps protect the body from infections, allergies, and other harmful substances.
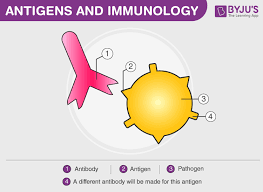
Examples of antigens:
parasites
viruses
bacteria
cancer cells
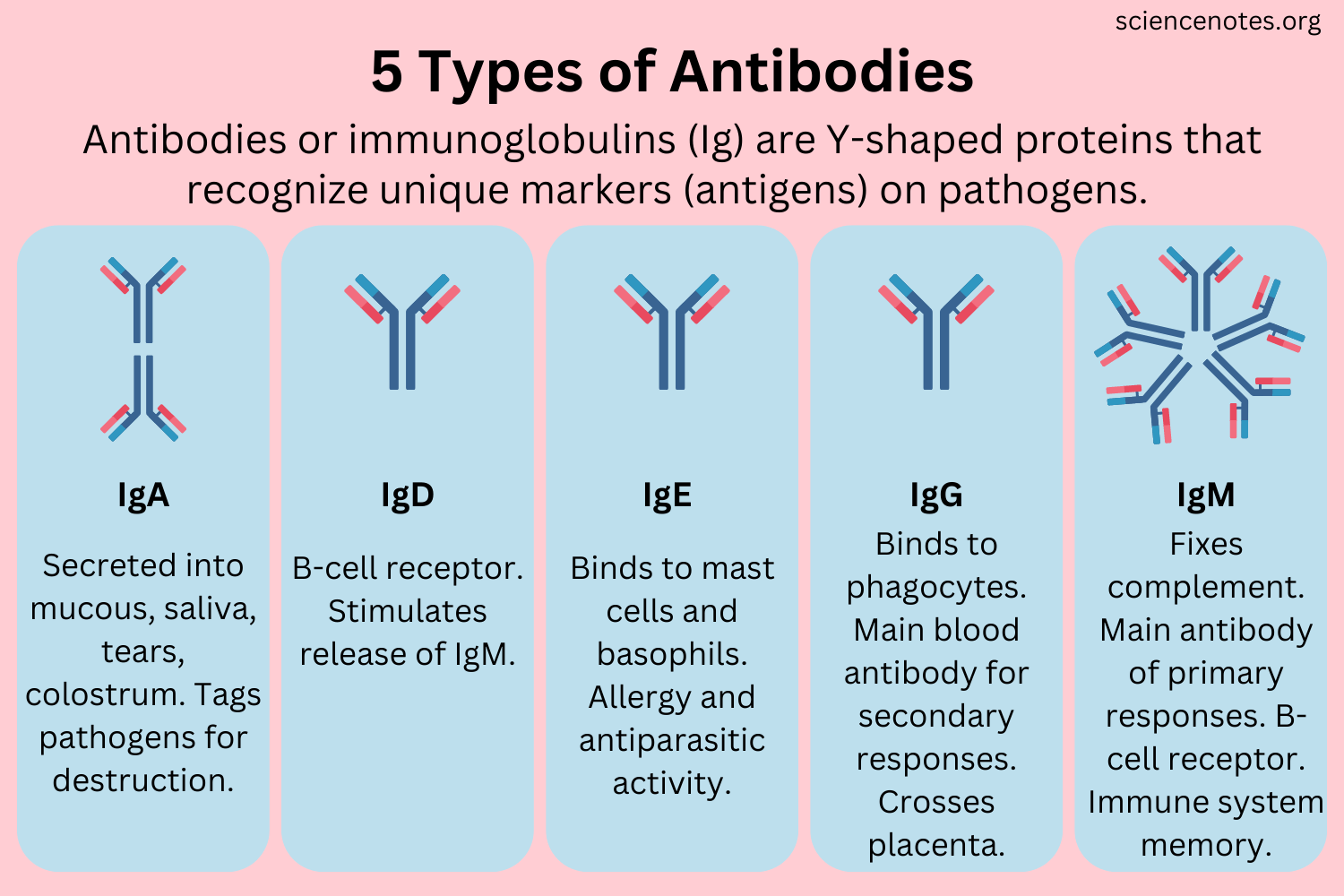
Example of immunoglobin
Immunoglobulins, also known as antibodies, are proteins in the blood and tissue fluids that help the body fight infection. Examples of the 5 antibodies immunoglobulins include IgA, IgG, IgM, IgD, and IgE
What are antibodies(immunoglobulin)
proteins that protect you when an unwanted substance enters your body.
Produced by your immune system,
bind to these unwanted substances in order to eliminate them from your system.
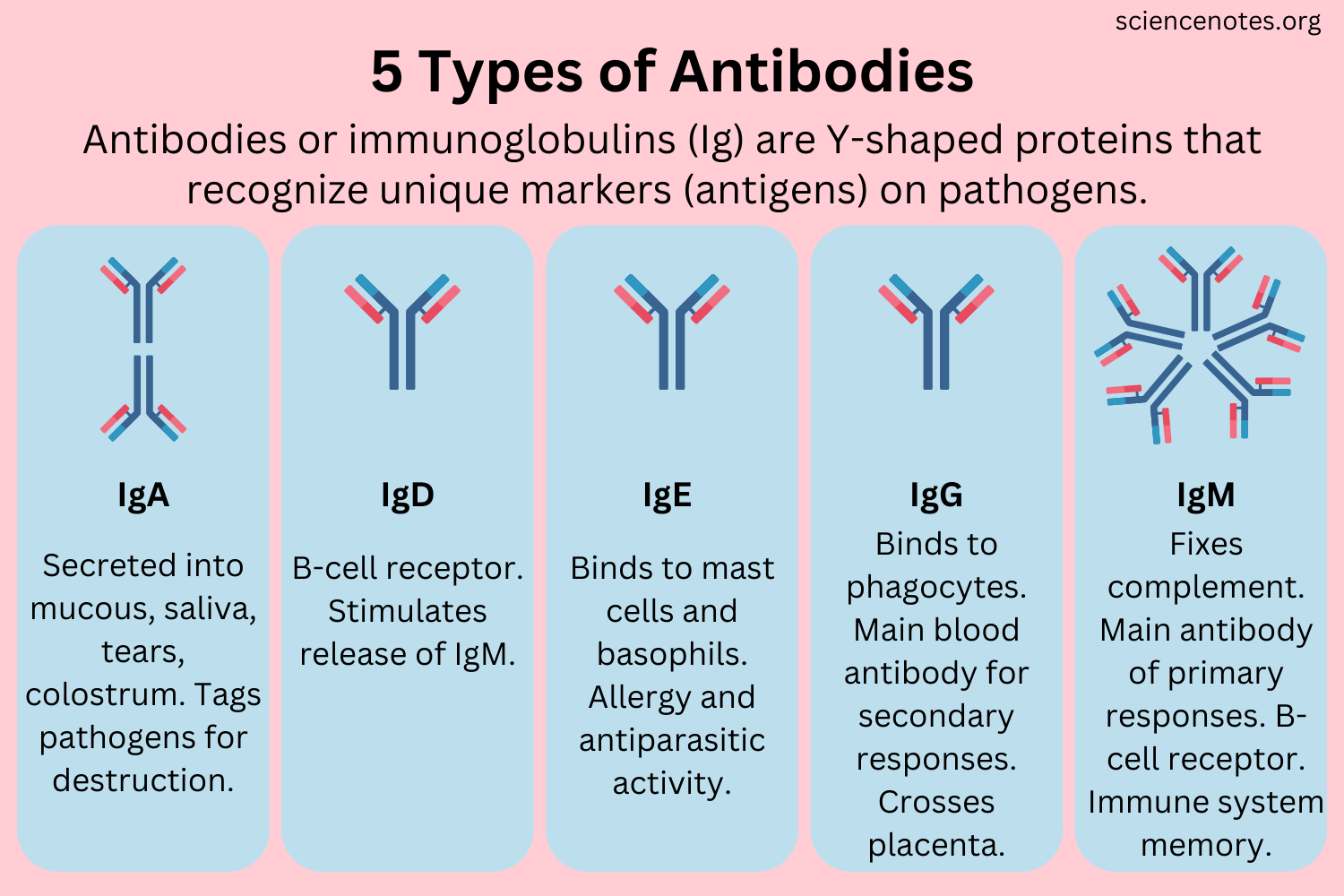
The 5 antibodies (immunoglobulin)
Examples of immunoglobulins include IgA, IgG, IgM, IgD, and IgE
What is immunoglobulin
Y shaped proteins produced by the B cell that recognize antigens on pathogens
also known as antibodies, are proteins in the blood and tissue fluids that help the body fight infection.
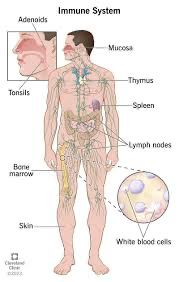
What is the immune system
a complex network of cells, tissues, and organs within the body that works to defend against infection and disease by identifying and destroying harmful invaders like bacteria, viruses, and parasites,
it remembers past invaders to respond more effectively if they return.
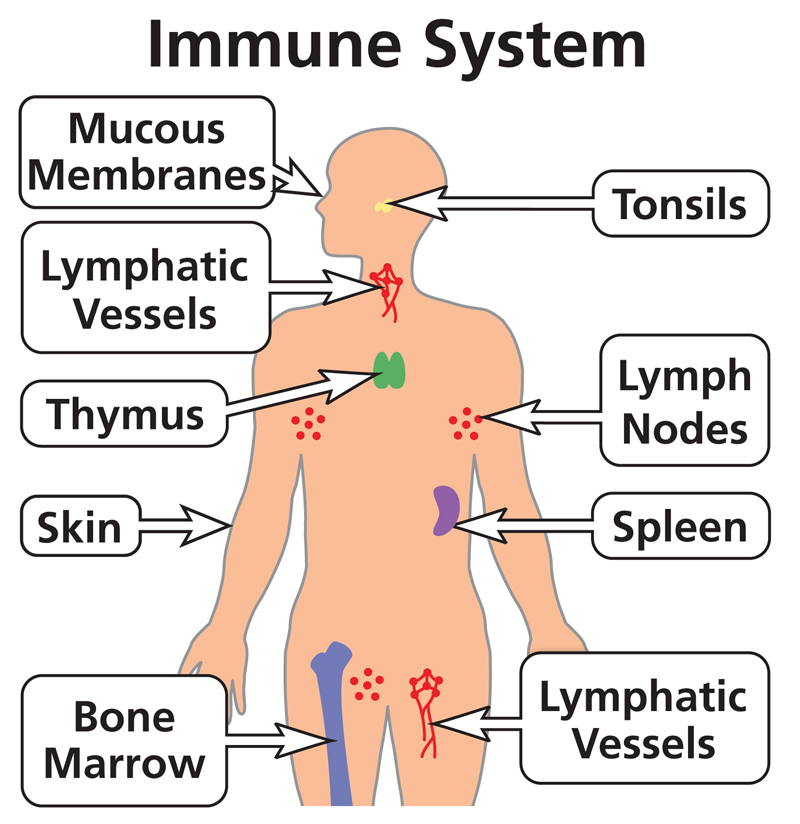
Barriers that assist the body in immunity
tears
saliva
skin
stomach acid
mucus lining
cells

How do tears assist the immune system
has antibacterial enzymes
How does the mucus lining help the immune system
the mucus lining traps dirt and microbes
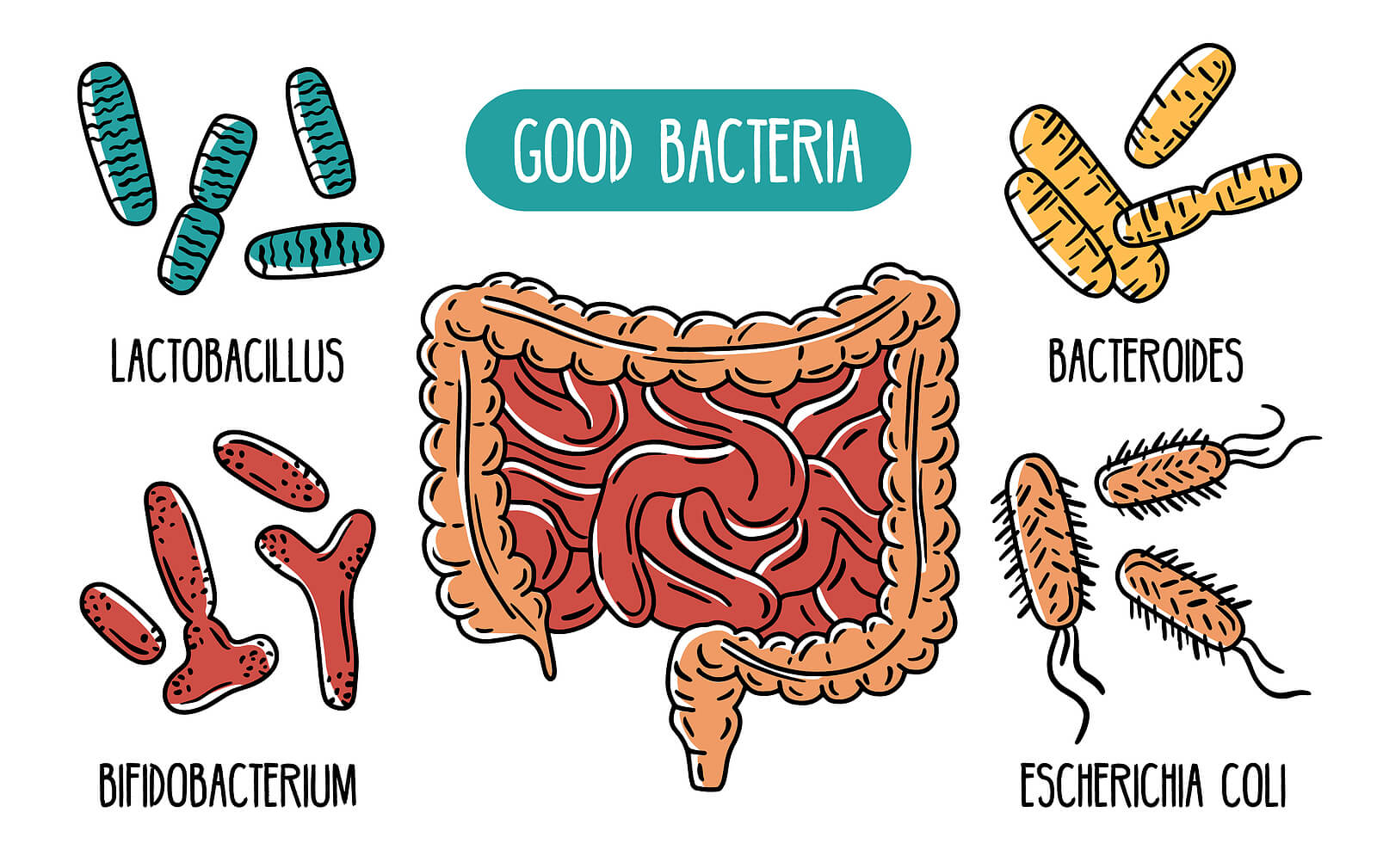
What is good gut bacteria
The gut microbiota, also known as gut flora or gut microbiome,
the community of microorganisms that live in the human digestive tract.
made up of bacteria, viruses, fungi, and protozoa, totaling over 100 trillion microorganisms in a 70 kg person.
The gut microbiota is an organ in itself, weighing around 200 grams, and containing 150–200 times more genes than all human cells combined.
How does stomach acid help the immune system
the low pH kills the harmful microbes
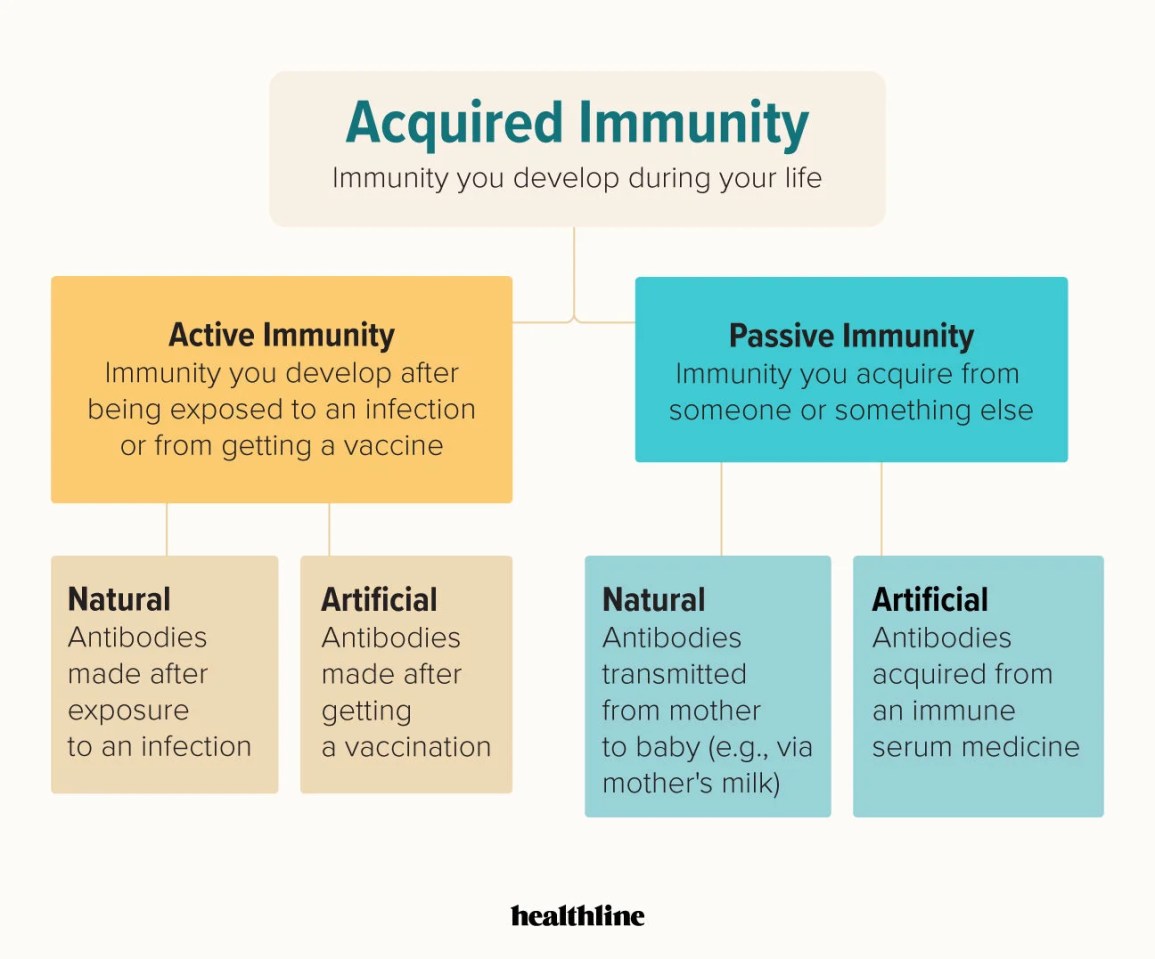
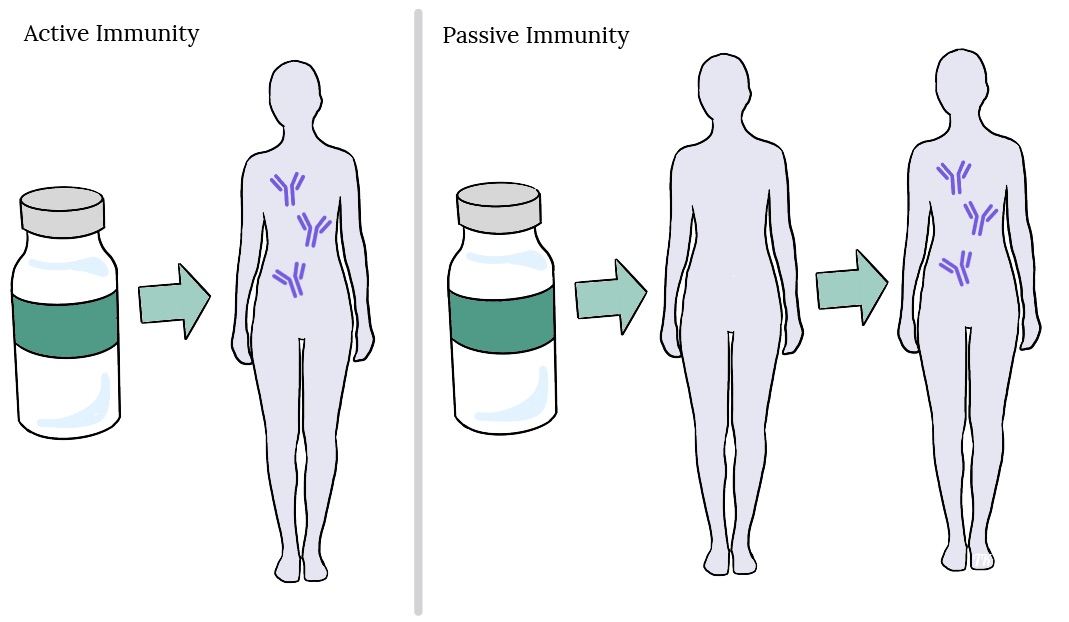
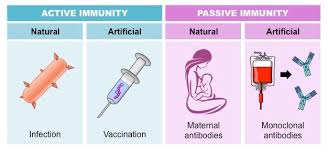
The two types of immunity
active immunity
passive immunity
How do you get active immunity
when your body's immune system produces antibodies to fight a disease. This can happen when you're exposed to a disease through natural infection or vaccination.
How do you get passive immunity
when a person receives antibodies from another person or animal, instead of producing them through their own immune system.
Passive immunity can be acquired naturally or artificially.
natural passive immunity
During pregnancy, a mother's antibodies pass through the placenta to the fetus.
Antibodies are passed from the mother to the infant through breast milk, especially in the first few days after birth.
How long does natural passive immunity last
Passive immunity provides immediate protection, but it's short-lived, lasting a few weeks to a few months.
The antibodies eventually break down and become nonfunctional.
Passive natural immunity is important because,
before a baby's immune system can produce its own antibodies, It can protect against diseases that a baby is exposed to during and after birth.
Passive immunity can be used to
treat people who have weakened immune systems or who are unable to respond to vaccines.
Artificial passive immunity
Antibody injections: A person can receive an injection of antibodies, such as immune globulin (IG), to provide immediate protection from a disease.
Donor serum: A person can receive antibodies from the serum of an immunized donor.
Monoclonal antibodies: A person can receive antibodies generated from cloned cell lines.
artificial passive immunity
(through blood transfusion)
artificial active immunity
(from vaccinations)
natural active immunity
(from infection)
What is a toxoid
a weakened bacterial toxin that has been chemically altered to lose the toxicity
The body's immune system produces antibodies that recognize and bind to the toxoid, creating immunity to the toxin.
What are toxoids used for
used to protect against diseases caused by toxins secreted by specific bacteria,( such as diphtheria and tetanus)
are usually given as a series of doses over time, and booster shots may be needed.
What are the types of vaccines
Vaccines can be live, attenuated(weakened), or killed.
What do vaccines do for the immune system?
They stimulate the body's immune system to produce antibodies that recognize and bind to the microorganism that causes disease.
Effects of immunization/toxoid
boosts immune system
induces antibody formation
reduces mortality risk
near eliminates disease
Agents for passive immunity
immune serum
Immune serum
provides passive immunity
is rapid acting to provide temporary immunity (1-3 months)
made from healthy donated plasma
What is the goal of immune serum
to prevent /decreased the incidence and severity of disease symptoms
Black Box warning for immune serum
thrombosis development
so give the minimum dose to at risk patients and hydrate frequently
Mild/ transient effects of immunization
soreness, swelling, fever, fussiness, tiredness, loss of appetite, and vomiting
These side effects usually go away on their own in a few days
Serious/ life threatening effects of vaccination
pneumonia, infection of the brain and/or spinal cord covering, or seizures that are often associated with fever.
What is a titer
Test that determines the amount of antibodies in a person’s blood
Why do we use titers
to measure the concentration of antibodies in a person's blood, essentially determining if they have immunity to a specific disease by checking if their body has produced antibodies against a particular pathogen
What can titers allow
healthcare providers to assess past infections, vaccination effectiveness, and decide if booster shots are needed based on their immune response
Immunization contraindications
conditions that increase the risk of a serious adverse reaction to a vaccine.
Vaccines should not be given to people with contraindications.
Women who are pregnant should generally not
not receive live vaccines
Examples of immunization contraindications
Severe allergic reaction: A previous severe allergic reaction to a vaccine or vaccine component, such as anaphylaxis
Severe immunodeficiency: A condition that severely weakens the immune system, such as HIV infection, leukemia, or cancer
Pregnancy: Women who are pregnant should generally not receive live vaccines
Acute illness: A moderate or severe illness, with or without fever
Recent blood transfusions: Receiving a blood product that contains antibodies within a certain time frame
History of encephalopathy: Having a brain injury within a certain time frame after receiving a pertussis-containing vaccine
Intussusception: A history of intussusception, which is a condition that affects the intestines
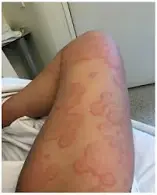
What is serum sickness
a reaction to proteins in antiserum derived from a non-human animal source
occurring 5–10 days after exposure
Symptoms often include a rash, joint pain, fever, and lymphadenopathy.
What are antivenins
also known as antivenom, is a medical treatment that neutralizes the toxins of a snake, spider, or insect bite
. It's an antibody therapy that's injected into a patient as soon as possible after the bite.
How are antivenins made
made by injecting a small amount of venom into an animal, such as a horse or sheep.
The animal's immune system produces antibodies to fight the venom.
The antibodies are harvested from the animal's blood and purified.
The purified antibodies are then concentrated into a pharmaceutical-grade antivenom.
The antivenom is injected into the patient to neutralize the venom.
White blood cells fight off
Pathogens
The lower the pH
The higher the acidity of the stomach acid
65 years old and up need these vaccines
Shingles vaccine
Pneumonia vaccine
Annual influenza vaccine
Vaccination information sheet
Vaccine Information Statements (VISs) are information sheets produced by the CDC that explain both the benefits and risks of a vaccine to vaccine recipients.
How often are tetenus boosters given
adults get a tetanus booster shot every 10 years. The booster can be a Tdap (tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis) or Td (tetanus, diphtheria) shot.
What does serum sickness cause
Edema of face,throat, tongue
Which can compromise airways
This is a emergency, patient should get to the hospital or call 911
Treatment for serum sickness
Treat the symptoms with antihistamines,NSAIDS,corticosteroids,topical, and medications
What is prophylaxis
is a medical term for preventive care or measures taken to prevent disease. It can also refer to treatments that prevent a condition from recurring.
Examples of prophylaxis
Vaccinations: Prevent the development of diseases
Health screenings: Help detect diseases early
Annual checkups: Help detect diseases early
Medications: Prevent the development of illnesses or the recurrence of conditions
Surgery: Prevent the development of conditions or the recurrence of conditions
Antibiotics: Prevent infections before or during certain surgeries or procedures
Hemostatic agents: Prevent bleeding in people with hemophilia
Older adults and vaccinations
COVID-19 vaccine: Protects against COVID-19
Seasonal flu (influenza) vaccine: Recommended for people of all ages every year
RSV (respiratory syncytial virus) vaccine: Protects against RSV
Td or Tdap (tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis) vaccine: A booster vaccine is needed every 10 years
Pneumococcal vaccines: Protects against pneumococcal disease, including infections in the lungs and bloodstream
Zoster (shingles) vaccine: Protects against shingles and complications related to shingles
Adults may require immunizations in certain circumstances
Exposure
Travel
Occupational
The nurses role is to
Assess/teach/administer/ evaluate for adverse effects
Vaccines containing allergens are
the yellow fever vaccine/some rabies vaccines contain significant amounts of egg protein
Most flu shots and the nasal spray flu vaccine are manufactured using egg-based technology.
Those with active cancer cannot get
live vaccine
If you have a fever
You can not get a vaccine
Cancer patients can’t get a vaccine
2 months before or after chemotherapy
Why is it important to ask for allergies
because it helps healthcare providers identify potential life-threatening reactions a patient might have to medications, foods, or environmental triggers, allowing them to make informed decisions about treatment plans
Vaccines during pregnancy
Flu
COVID
MMR 1 month before pregnancy
What is thrombosis
Blood clot
Age 60 or older
Varicella vaccine to prevent shingles
What is imunosuppression
Suppression of the body’s immune system and its ability to fight infections and other diseases
What are the agents for active immunity
Vaccines and toxoids
Immunocompromised people have reduced
Antibody response and may need higher or more frequent doses for adequate immunity
HIV positive patients cannot have
No live oral or viral vaccines because the bacteria or virus might reproduce and cause active infection
Serum sickness can compromise
Airways due to edema of throat and tounge