Species Diversity: Bacteria and Viruses
1/60
Earn XP
Description and Tags
SBI3U (Secours) - #2 hyperdoc
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Prokaryote
unicellular organism without nucleus and membrane-bound organelles
Bacteria are a _______ cell
prokaryotic
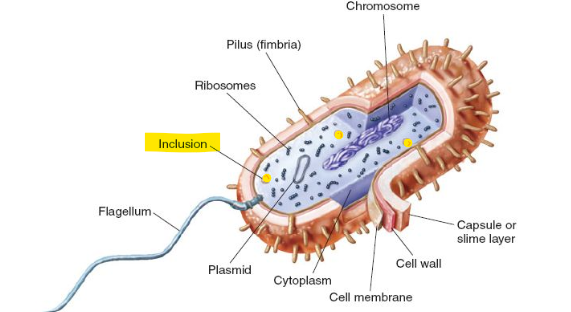
Pili
small hairs that help bacteria stick to other cells and surfaces, used for conjugation
Flagellum
type of tail that helps bacteria move
capsule/slime layer (3 functions)
sticky material
reduces water loss
resists temperature
blocks antibiotics and viruses
cell wall
mainly composed of peptidoglycan
chromosome
large chromosomal loop of DNA, necessary for the normal function of the cell
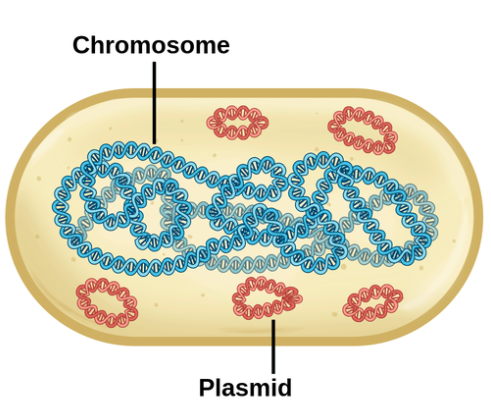
plasmid
small loop of DNA, can carry genes that produce antibody resistance
☆ responsible for mutations
Inclusions
particles of aggregated protein, important for metabolism and viral replication
4 important bacterium groups
proteobacteria (ancestors of mitochondria)
cyanobacteria (ancestors of chloroplasts)
gram-positive bacteria
gram-negative bacteria
Gram-Positive Bacteria
cell walls have thick layer of peptidoglycan which is dyed purple when gram-stained
more susceptible to antibiotics
many of them cause diseases
Gram-Negative Bacteria
cell walls have thin layer of peptidoglycan which is dyed pink when gram-stained
complex, double plasma layer blocks antibiotics
Bacteria can be classified by their 3 common ______. These are ________, _______, and ______.
shapes, coccus, bacilli, spirilla
Bacteria are also classified by dyeing the cell walls, in a process called ______________.
gram-staining
3 arrangements of cocci bacteria
coccus
diplococci
streptococci

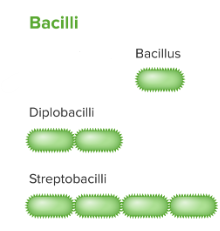
3 arrangements of bacilli bacteria
bacillus
diplobacilli
streptobacilli
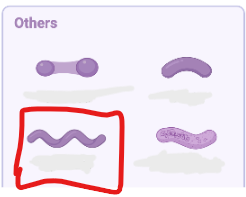
what kind of bacteria shape is this?
spirillum

Why have bacteria been successful? (3 reasons)
can live with or without oxygen
occupy all ecological niches
can form endospores
Obligate Aerobes
organisms that need oxygen to survive
Facultative Anaerobes
organisms that can survive either with or without oxygen
Obligatory Anaearobes
organisms that cannot live in the presence of oxygen
Provide 2 examples of ecological niches occupied by bacteria. (multiple answers)
1) producers
2) decomposers
Endospores
protective structure with a rigid wall
formed when a bacteria condenses chromosomes and other necessary survival components, wrapping them inside a rigid and resistant wall
other components will disappear, leaving a small endospore that can withstand extreme environments for a long time
3 types of bacteria reproduction
Binary Fission
Conjugation
Transformation
Binary fission is _____, around __ mins
quick, 20
Conjugation
sexual reproduction
2 cells share DNA when one cell copies a gene from a plasmid
transfer is initiated when pili attach
Transformation
complete strand of DNA is transferred from dead bacteria/the environment to a living bacteria
physical contact is not required
☆ can now become pathogenic
Pathogenic
disease-causing
Antibiotics
chemical compounds produced by certain strains of bacteria or fungi that kill bacteria
Antibiotics were discovered by ________ ________ by accident
Alexander Fleming
The first discovered antibiotic was _______ , which is a toxin from Penicilliun _____
penicillin, mould
Advantages of bacteria (6 points)
decomposers and producers, important in nitrogen and carbon cycles
develop mutualistic relationships (ex: produce vitamins in digestive system)
food (ex: yogurt, pickles)
Chemical manufacturing
Production of antibiotics
inside the body, they compete with other organisms
Besides diseases, how can bacteria be harmful?
create cavities
cause ulcers
Viruses belong to which kingdom?
NONE
Why are virsues non-living?
they need a host to reproduce, and they don’t have distinctive organelles
Bacteriophages
viruses that infect bacteria through a process called transduction
All viruses work by forcing the _____ _____ to make copies of themselves, resulting in an ______ because the host cell cannot make the ______ needed to carry out _____ functions.
host cell, infection, materials, normal
Pandemic vs Epidemic
Pandemic = global infection
Epidemic = local infection
Animal viruses are classified into two types:
DNA viruses and RNA viruses
DNA vs RNA
DNA = double stranded
RNA = single stranded
DNA virus examples
chicken pox, hep B, cold sores
RNA virus examples (more serious)
Measles, HIV (AIDS), Rabies
HIV vs AIDS
HIV is the virus, while AIDS is the late stage of the HIV infection
In animal cells, the _____ ______ enters the host
full virus
The 2 ways bacteriophages reproduce
Lytic Cycle
Lysogenic Cycle
Lytic Cycle
A replication process in viruses where the genetic material uses the host cell's structures to make new viruses
Lysogenic Cycle
A replication process in viruses where viral DNA enters the chromosome of the host cell. The virus can remain latent (provirus) and activate later by ordering the production of new viruses by the host cell.
Provirus
the viral DNA that is part of the host cell’s chromosome
In the _____ cycle, reproduction is fast
lytic
Binding/Attachment
1st stage of the lytic cycle
proteins on the virus’ surface attach to protein receptors on the surface of the host’s cell membrane
Entrance
2nd stage of the lytic cycle
the virus injects its genetic material (RNA or DNA) into the host cell, or the full virus enters
Replication
3rd stage of the lytic cycle
the host cell makes more proteins and DNA or RNA
Assembly
4th stage of the lytic cycle
new viral particles are assembled
Lysis
Final stage of the lytic cycle
The host cell bursts open and releases new viruses
How is the lysogenic cycle different and similar to the lytic cycle?
the host is not lysed immediately
the virus DNA is integrated into the bacteria’s chromosomes (as opposed to digesting the host’s DNA)
follows the same stages except for the dormancy stage
Lysogenic cycle dormancy stage
Formation of the provirus
Cell division + replication
Return to lytic cycle (replication, assembly, lysis)
Archaea
a group of not well understood prokaryotes
Why are archaea often called extremophiles? Provide 5 examples of extremophiles.
because of their ability to live in extreme environments
Methanogens (produce methane in hypoxic conditions)
Halophiles (survive in high concentrations of salt)
Extreme thermophiles (survive in high temp)
Psychrophiles (survive in low temp)
Acidophiles (survive in acidified environment)
Differences between bacteria and archaea
Bacteria | Archaea |
|---|---|
|
|
5 types of vectors (carriers of viruses)
Airborne (ex: common cold)
Contaminated food/water (ex: polio)
Infected animal bite (ex: rabies)
Sexual contact (ex: Herpes)
Contaminated blood or needles (ex: HIV)
What do bacteria use to move? (2 ways)
Using flagella and cilia
Some secrete a slime layer and ooze over surfaces