Lecture N: Translocation and Phloem
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
In dicots, where is phloem in relation to the xylem?
It is outside the xylem
Phloem vs. xylem contents
Phloem: contains lots of sucrose, amino acids, and potassium
Xylem: mostly contains water
Girdling
The practice of cutting off phloem from the outside of the tree to either kill it or increase yield
Phloem vs. xylem: positive pressure/tension, and does osmosis matter?
Phloem: under positive pressure, osmosis matters
Xylem: under tension, doesn’t have solute potential so osmosis doesn’t matter
Water will come out of the phloem if the stem is cut, but not the xylem
What cells make up the phloem? How do they compare to the xylem’s cells?
The phloem consists of sieve-tube elements and companion cells connected by plasmodesmata.
Unlike the xylem, the phloem is made up of living cells.
What are the 3 types of phloem loading?
Diffusion (passive symplastic)
Apoplastic loading (active apoplastic)
Polymer trapping (active symplastic)
What is the cellular direction of movement of phloem loading?
Mesophyll (M) —> Companion cell (CC) —> Sieve element (SE)
Phloem loading: diffusion
(passive symplastic)
Sucrose moves from high to low concentration, and there is no apparent accumulation of sucrose in veins
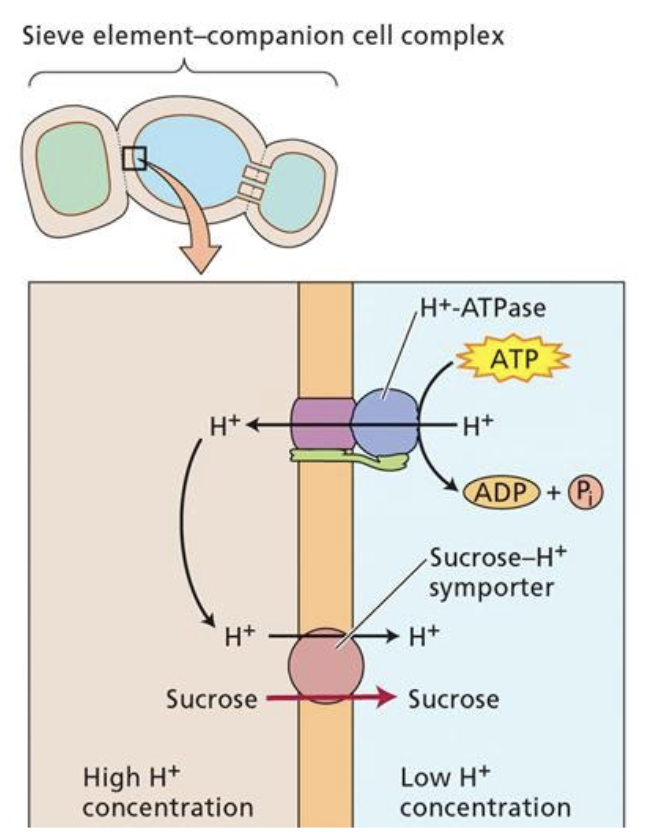
Phloem loading: apoplastic loading
(active apoplastic)
Using ATP to create a proton gradient, sucrose is unloaded into the cell wall (why it’s called apoplastic) then pumped into the companion cell along with H+ using a symporter. This causes sugars to be in high concentration in the veins
Phloem loading: polymer trapping
(active symplastic)
Sucrose is synthesized in the mesophyll cells and move into the CC/SE. Enzymes convert the sucrose to a sugar polymer that can’t move back to the M.
Source-sink in terms of sucrose concentration
Generally the source has the highest sucrose concentration and the sink has a much lower concentration.
Harvest index
Ratio of commercial or edible yield to total shoot yield
Companion cells
Connected to sieve elements through plasmodesmata, provide them with ATP
Sieve elements
Sieve-tube elements (angiosperms), sieve cells (gymnosperms)
Connected to each other by sieve plates and transport water and sugar
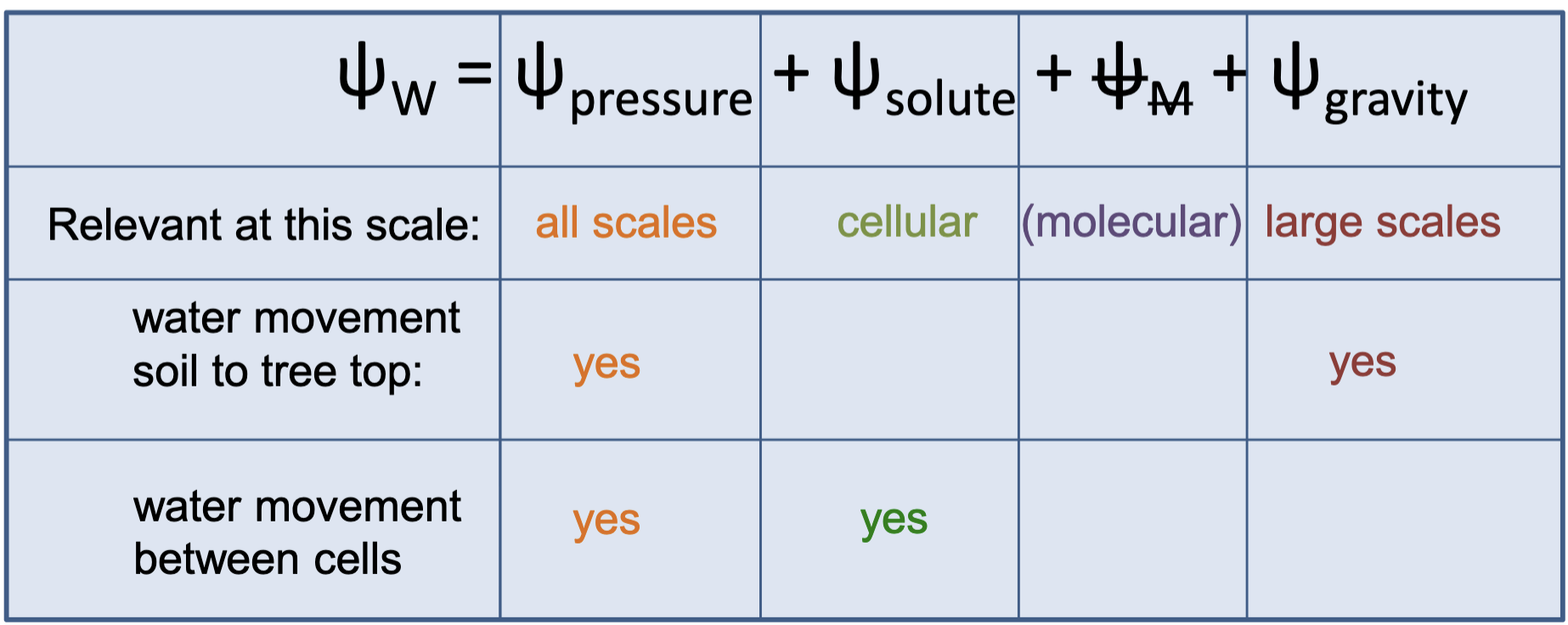
Scale of water movement: what matters? (imp)
When does pressure or solute potential matter?
Pressure potential drives movement of water over long distances and at the cellular level in the xylem and phloem
Solute potential only matters at the cellular level (specifically for phloem, not xylem)
Mass flow (important)
The movement of solute and solvent along a gradient of total pressure without a semipermeable membrane
Osmosis vs. mass flow: what is the main difference?
Osmosis is based on pressure and concentration of solvents, but mass flow is only dependent on pressure
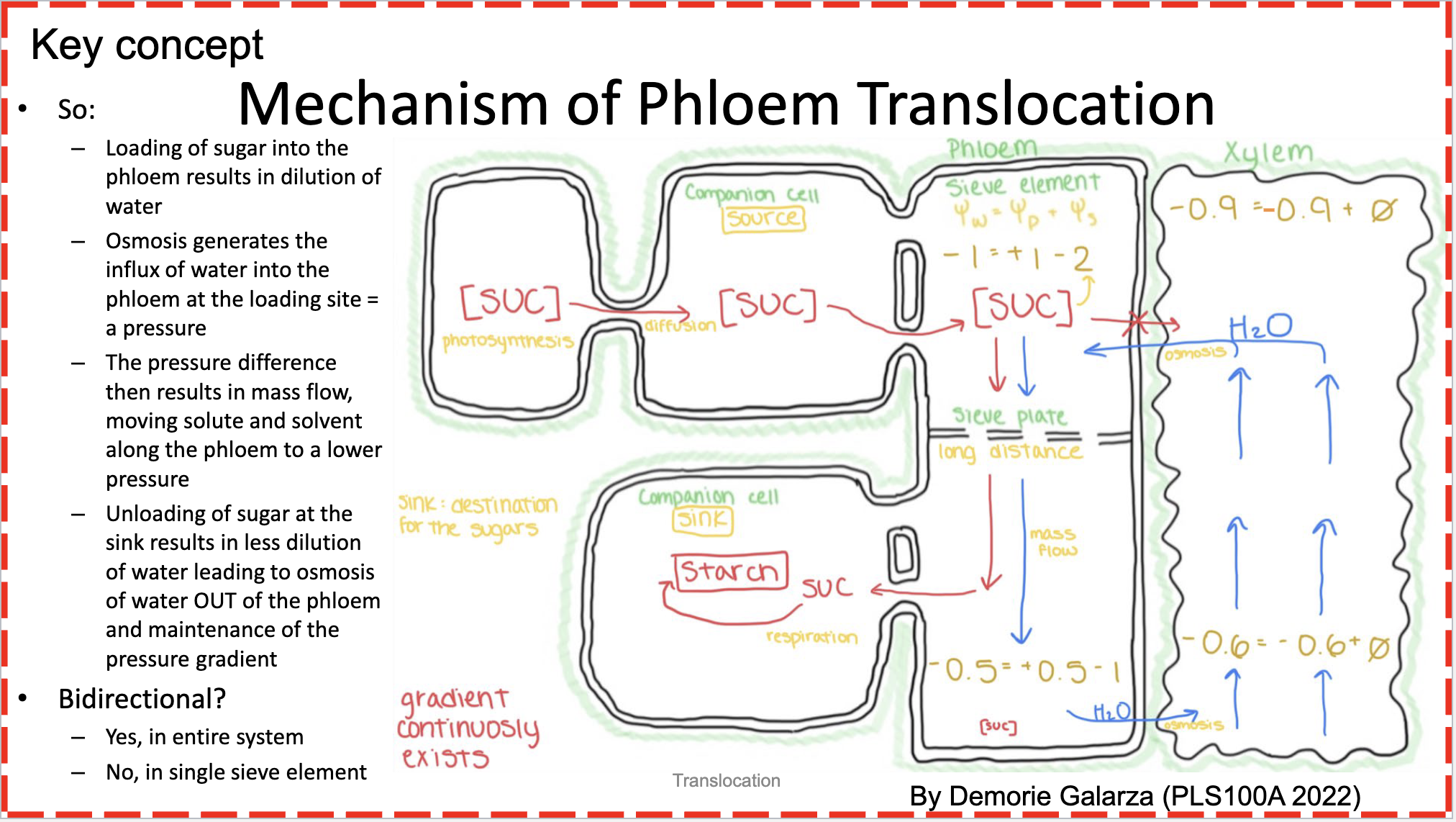
Mechanism of phloem translocation: how is sugar moved from the source to the sink?
Sucrose diffuses from the mesophyll cells (in a leaf) into the CC, then into the SE. The SE has a very negative solute potential from all of the sucrose, so water enters the SE from the xylem vessels through osmosis to create a positive pressure potential.
The sucrose is pushed a long distance down to the sink companion cell, where it is converted to starch which is a crystal and doesn’t contribute to solute potential. This leads the solute potential to decrease and water diffuses back into the xylem.
The whole process is cyclic.