JMU BIO 103 topic 9 mcmullen
1/140
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
141 Terms
green plants include
green algae, nonvascular plants, seedless vascular plants, gymnosperms + angiosperms (seed vascular plants)
chlorophyll b
in green plant synapomorphies primary photo-synthetic pigment
thylakoids
stacked in grana in the chloroplasts
starch
the food storage product in green plants (potato, bananas)
cellulose and hemicellulose
major cell wall components in green plant synapomorphies
Plasmodesmata
channels through cell walls in green plants that connect the cytoplasms of adjacent cells
Coleochaete
genus; sister to land plants
2 haploids
make a diploid zygote
diploid
2n
haploid
n
gametes
in land plants to complete a life cycle, ____ have to fuse together
Ulva
multicellular green algae
land plants include
nonvascular plants, seedless vascular plants, gymnosperms (seed vascular plants), angiosperms (seed vascular plants)
cuticle
land plants have an outer, waxy covering called
gametangia
land plants, each with an outer, sterile layer of protective cells that keeps them moist, and produces gametes
sporophyte
a diploid embryo that grows into a multicellular, _______ individual (generation)
non-vascular plants
liverworts, hornworts, mosses
wort
means plant or herb. In medieval times, it was thought that liverworts could be used against liver disease. That was because these plants were shaped somewhat like a human liver
Hornworts
mature sporangium splits open to release spores (sporophytes-release spores-next generation)
mosses
male and female gametes, have sporophytes above them
lignin
Mosses have hydroids and leptoids, which are cells that comprise tissues similar to xylem and phloem, except there is no _____ in the cell walls
stomata
are often present on the moss sporophytes
gametophyte
haploid generation in land plants
sporophyte
diploid generation in land plants
sporic meiosis
in land plants, an alternation of haploid and diploid generations occurs in organisms that exhibit
yes
is water necessary for fertilization?
gametophyte
is the sporophyte or gametophyte generation dominant in general plant life cycle?
1 or 2
how many types of spores are produced in general plant life cycle?
sporophyte capsule
where does meiosis occur in general plant life cycle?
gamatangia
A name for colony-forming algae
homospory
one type of spore is produced
Rhizoids
anchor gametophytes to substrate
peristem
cap on top
epigram
little layer of tissue that has to peel off
Organs
vascular plant roots, stems, leaves
vascular tissue system
xylem and phloem
Lignin
substance in vascular plants that makes cell walls rigid
vascular plants
have tissues made of cells that transport water and nutrients throughout the plant
seedless vascular plants
Plants that have vascular tissue but reproduce by spores (ferns, club mosses, and horsetails)
Cooksonia
(SV) first vascular plant, sporangia were round, became extinct by mid-Devonian period
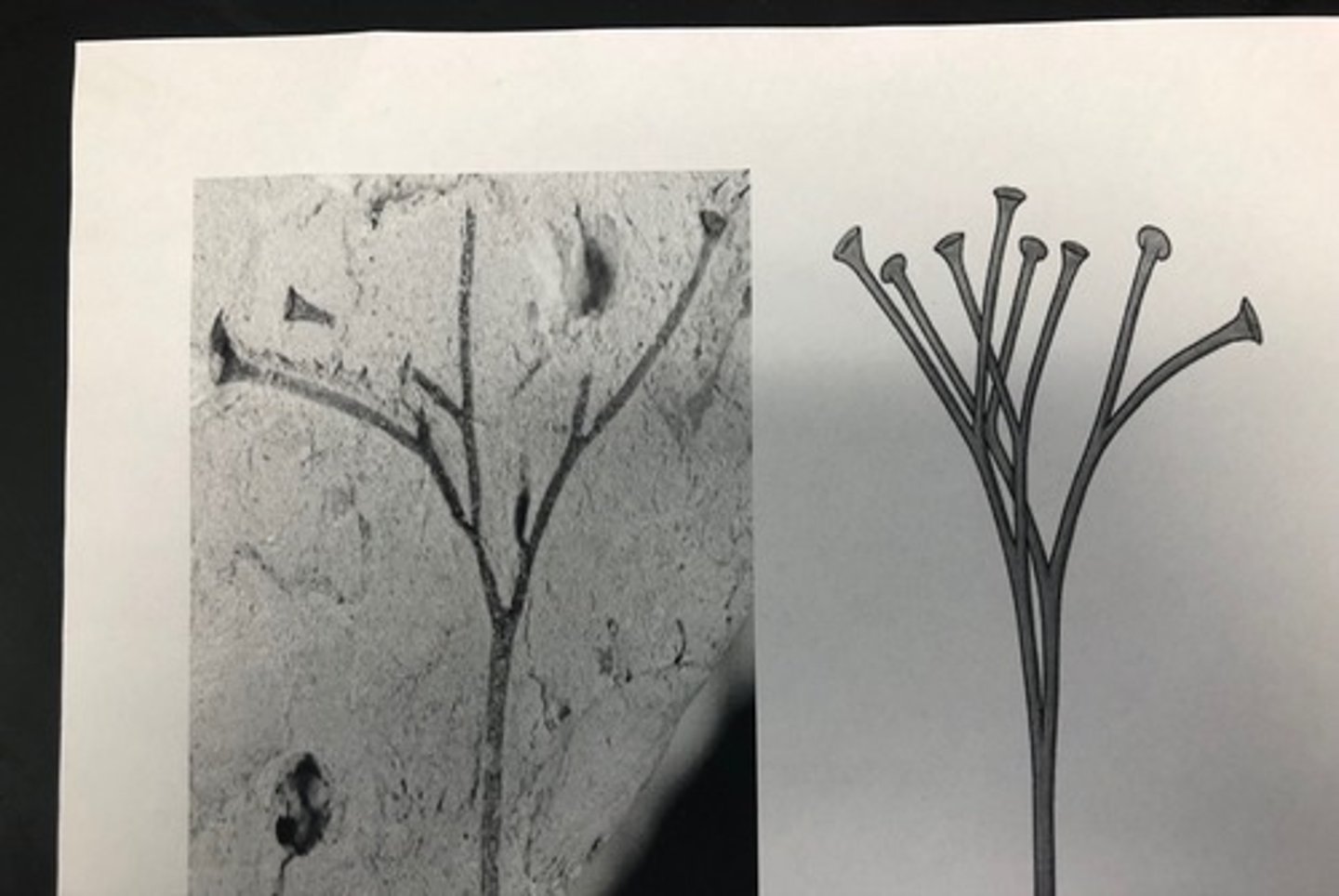
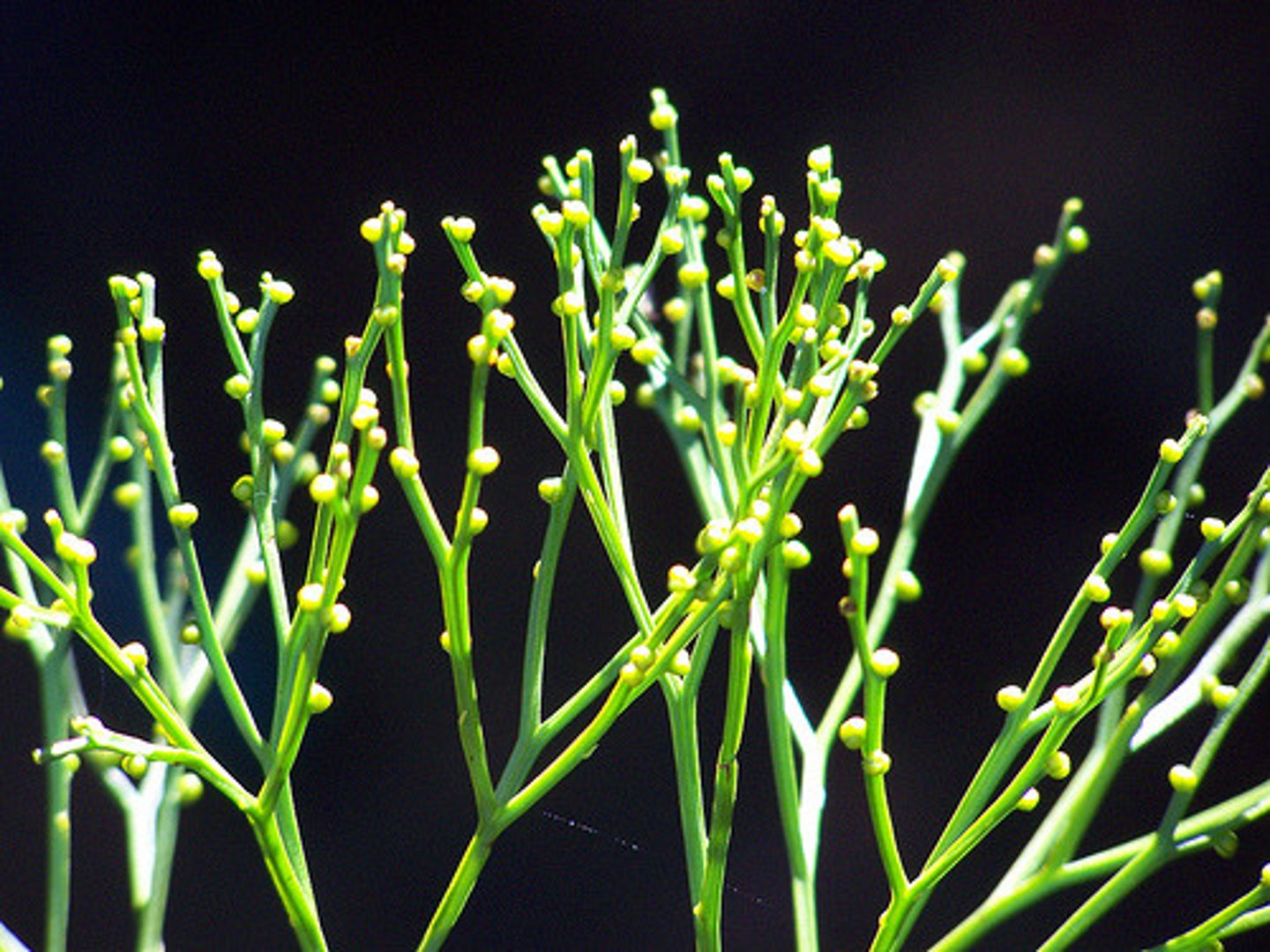
psilotum nudum "whisk fern"
(SV) enations look like little leaves

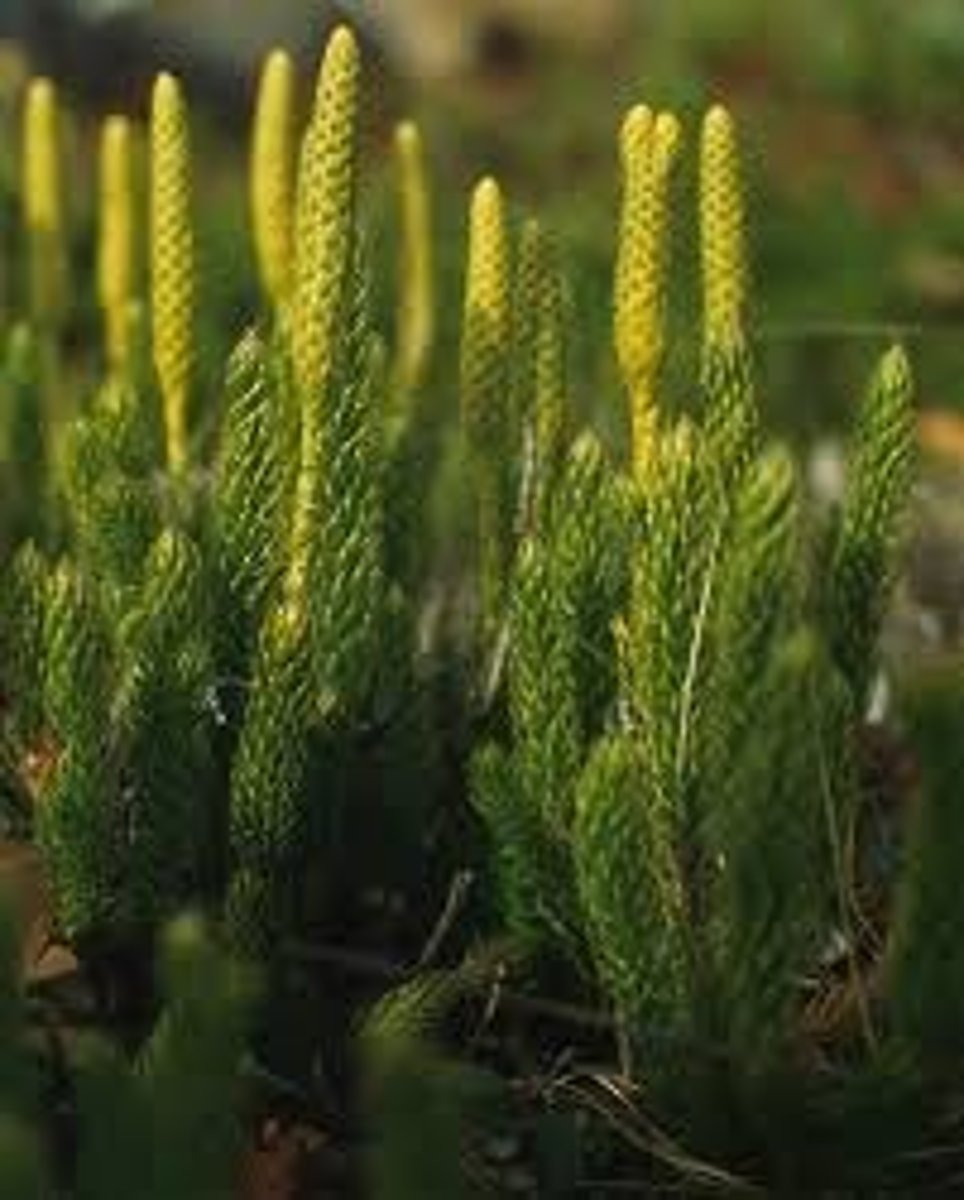
Lycopodium
(SV) club moss, spores are powdery/slippery (used for gloves, condoms)

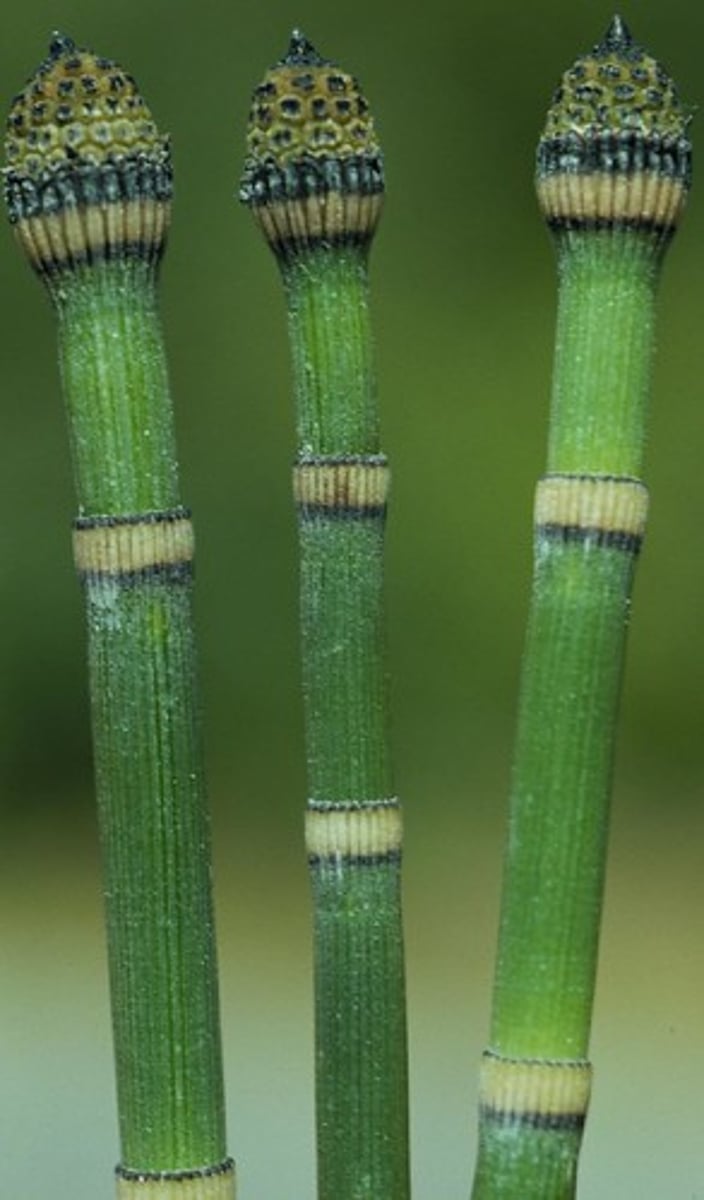
Equisetum
(SV) snake grass, horsetail, rough head used to clean dishes

strobili
collections of sporangia
Equisetum
spores with elaters
Polypodium
(SV) fern
sorus
cluster of sporangia on the underside of a fern frond
sporangia
meiosis occurs in the ___ of a fern
homospory
production of a single type of spore
sporophyte
in a fern the ______ generation is dominant
seed plants
plants that produce seeds for reproduction
seed
plant embryo and a food supply encased in a protective covering
pollen
A fine dust that contains the sperm of seed-producing plants
siphonogamy
fertilization using pollen tubes in seed plants
water
When pollen is present, ____ is not used for fertilization in seed plants
anatomy of a seed
embryo+ nutritive tissue+ seed coat
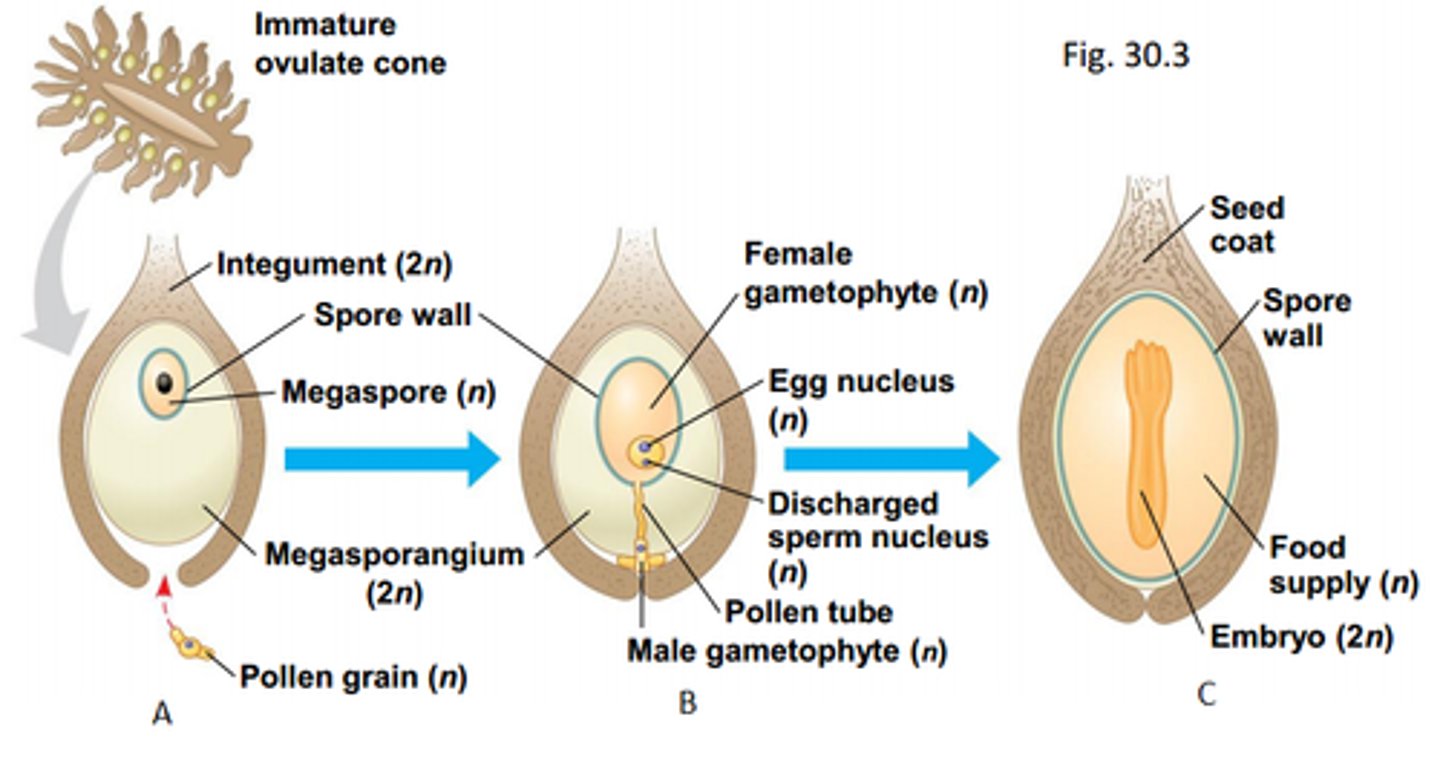
Gymnosperms
A plant that produces seeds that are exposed rather than seeds enclosed in fruits
Phylum Coniferophyta
(G) conifers (pines, firs, spruces, bald cypress; Pinus), appeared in at least 290 mya
Pinus
male cones, pollen grains
microspores
develop into male gametophytes
sporophyte
dominant generation in pine
ovule
female cones in pine
Megasporangia
produce megaspores that give rise to female gametophytes
gametangia
A reproductive organ that houses and protects the gametes of a plant
archegonium
structure that produces eggs, develops on the gametophyte
Heterospory
the production of two distinct types of spores by different structures
Spores
in gymnosperms, ___ are not released
Angiosperms
flowering plants that produce seeds in fruit
double fertilization in angiosperms
one sperm fertilizes the egg to form a zygote and one sperm combines with two polar nuclei to form the endosperm
microgametophyte
3-nucleate ____ in angiosperms
megagametophyte
8-nucleate _____ in angiosperms
eucalyptus tree
largest angiosperm
wolffia
smallest angiosperm
typical flowers
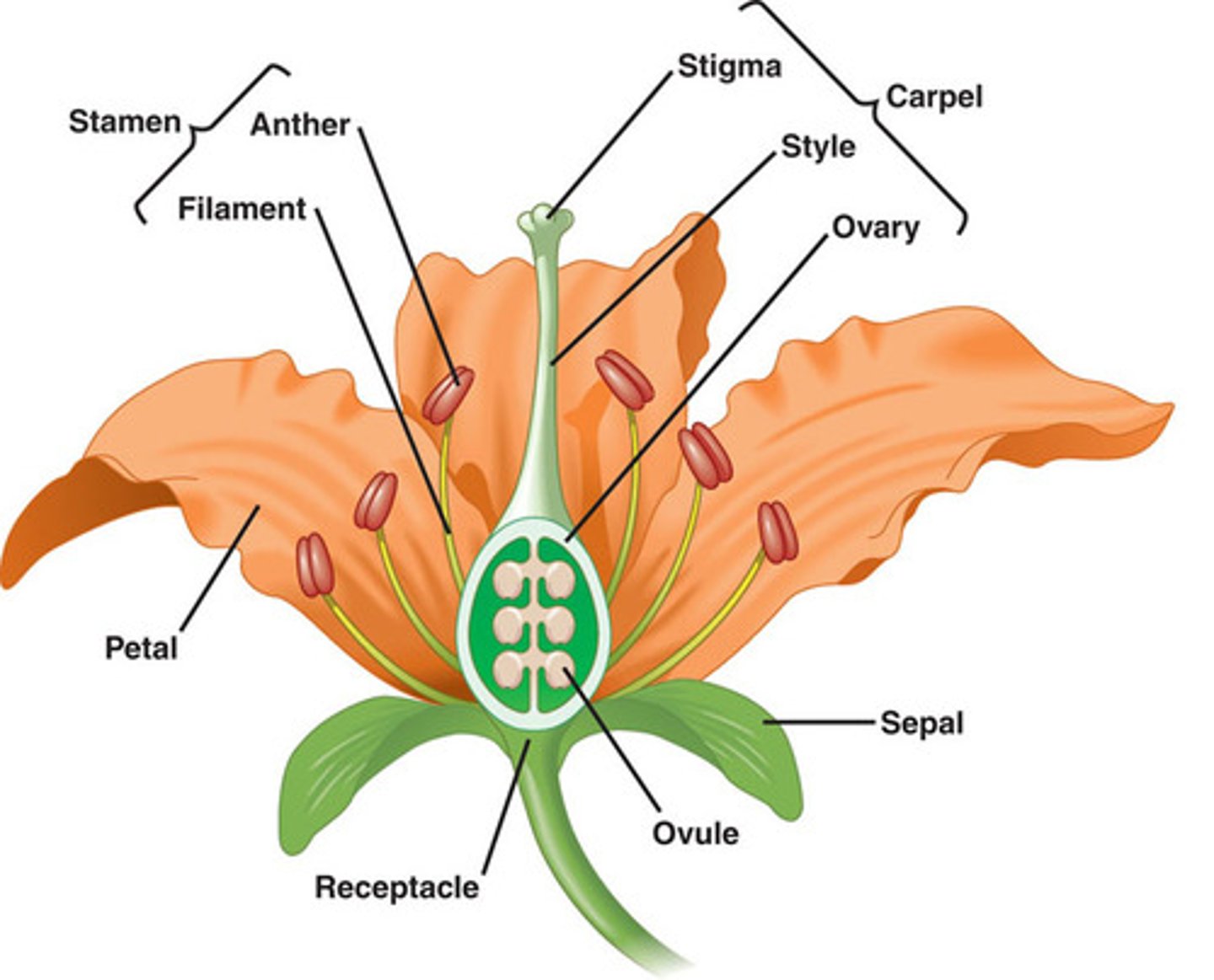
Sepals
comprise the calyx
Petals
make up the corolla
Anthers
contain pollen sacs in which male gametophytes are produced
Class Monocots
Named for their single seed leaves called cotyledons
multiples of 3
in monocots flower parts are in
parallel
in monocots leaf venation is

scattered
in monocots, stem vascular bundles are
ring
in monocots, xylem and phloem are in a
Monocots
coconut, rice, trillium
Class Dicots
Named for their two seed leaves (two cotyledons)
4 or 5
in dicots, flower parts are in multiples of
net
in dicots, leaf venation is

distinct ring
in dicots, stem vascular bundles are in a
xylem
root phloem between arms of
Dicots
cinquefoil, daisy, strawberry, poppy, cactus
inflorescence
A group of flowers tightly clustered together.
Panicle
compound raceme
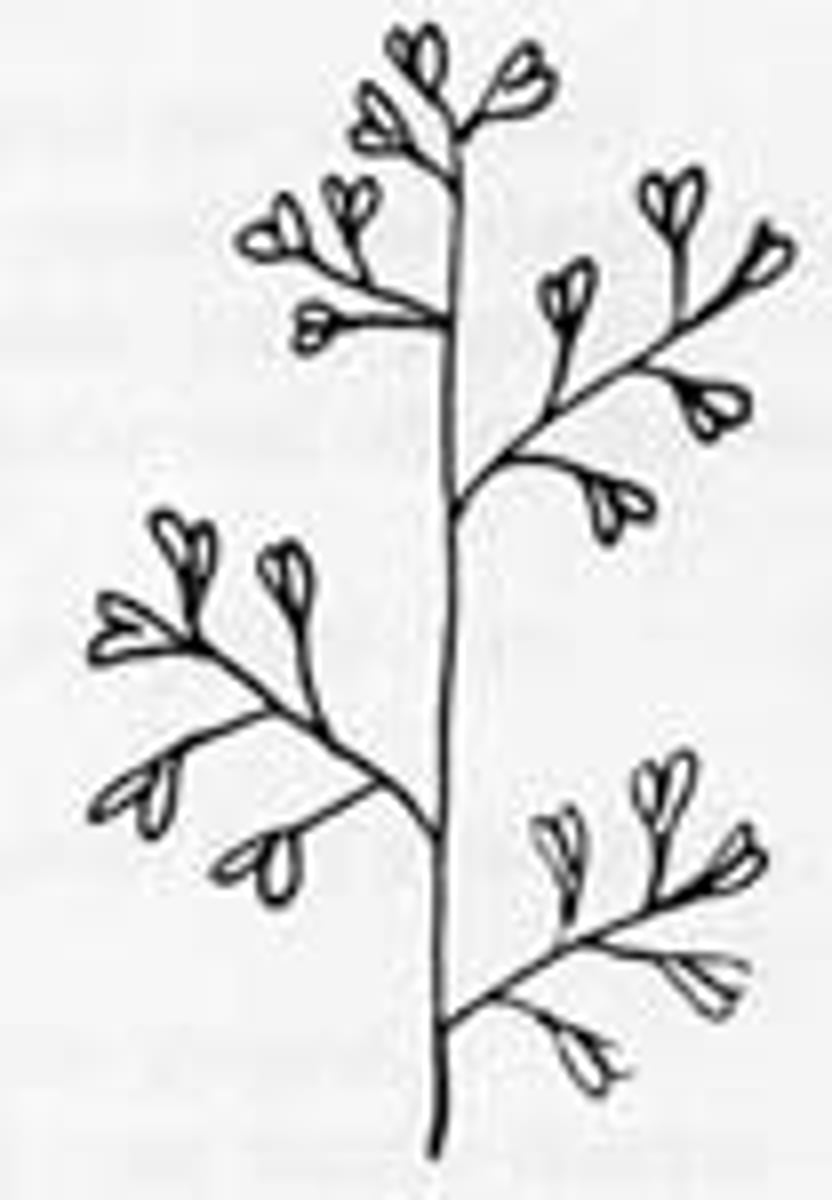
spike inflorescence
unbranched, elongated inflorescence with sessile flowers
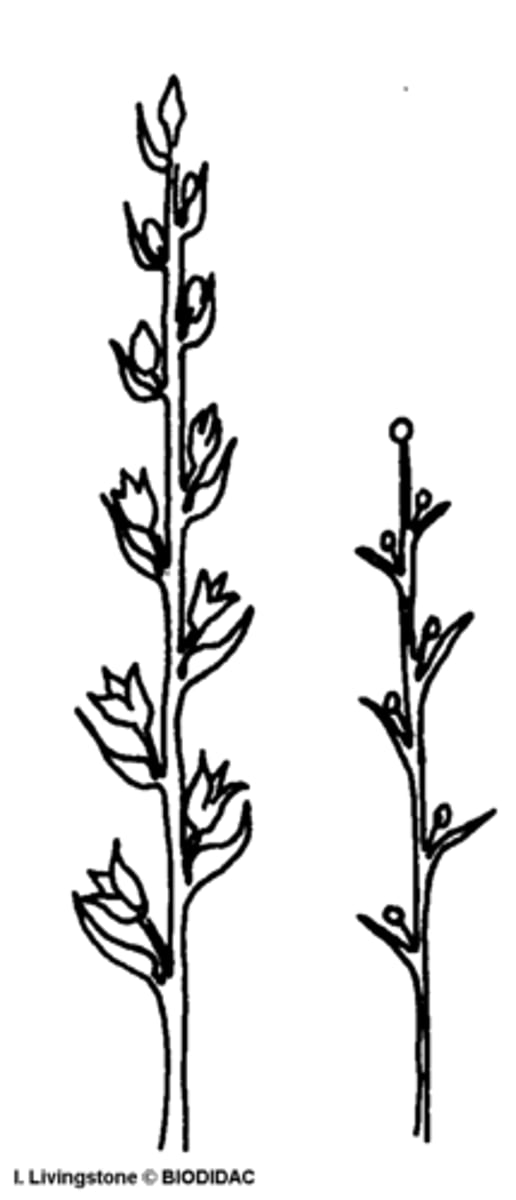
raceme inflorescence
unbranched, elongated inflorescence whose flowers have pedicels
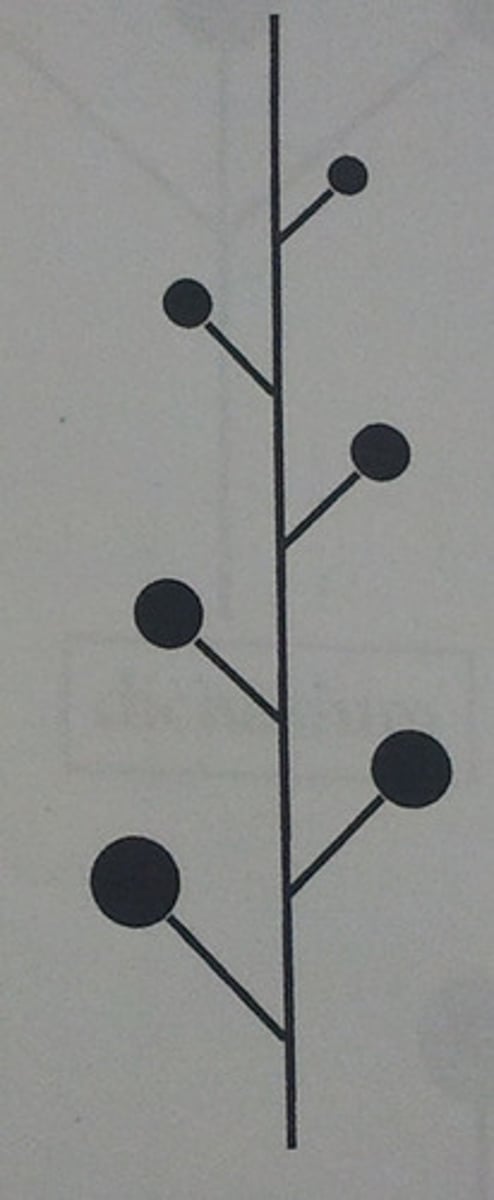
head inflorescence
dense cluster of sessile or sub sessile flowers (ray flowers, sunflowers)

catkin inflorescence
A dense spike or raceme of apetalous, imperfect flowers. It often falls as a single unit

microsporangia
will be grouped within the anther (meiosis)
megasporangia
will be within the ovary
oogamy
large non-motile egg, smaller motile sperm; animals and all land plants exhibit
isogamy
The production of equal-sized gametes.
sporophyte generation
is diploid