NBDHE( law and ethics)
1/1717
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
1718 Terms
Purpose of the DH Code of Ethics
To achieve high levels of ethical consciousness, decision making, and practice by members of a profession.
DH core values include:
Veracity
Autonomy
Beneficence
Justice
Non-maleficence
Confidentiality
Societal trust
Veracity
Truthfulness
Autonomy
-Deals with the PATIENT, not the practitioner.
-Right to privacy; freedom of choice
The patients have rights to informed consent, full disclosure, privacy, freedom of choice, etc.
Beneficence
-Do what benefits the patient (promotes their well-being)
-Example: Doing dental screening
Justice
Fairness
Non-Maleficence
Do no harm. Deals with the PRACTITIONER.
Example- providing protective eyewear to the patient
Confidentiality
The act of holding information in confidence, not to be released to unauthorized individuals
Societal Trust
Value patient trust.
Based on our actions and behavior.
Civil offense
-A crime against an INDIVIDUAL but not against society.
-Satisfaction is sought (usually money)
-Most dental cases fall under this category.
-Common lawsuits are dental injections, adverse drug reactions related to contraindications to medical history, or failure to diagnose
-Best way to avoid lawsuits is through documentation, charting, and communication
What is the best way to avoid lawsuits
Best way to avoid lawsuits is through documentation, charting, and communication
Civil Law: Contract Law
-2 main types: implied and expressed
-Involves the practitioner and patient
-Can involve termination of patients and abandonment of patients
Implied contract
An agreement made through inference by signs, inaction or silence
Expressed contract
A written or oral agreement in which all terms are explicitly stated
Abandonment in contracts
Dismissal of a patient without ample and proper notice
Civil Law: Tort Law
Wrongs against a person or property: damages can be sought by injured party.
Intentional Torts (civil law: torts) includes:
-Assault
-Battery
-Deceit/Misrepresentation
-Defamation
-Breach of confidentiality
-Invasion of property (patients body is the property)
Assault
-A type of intentional tort
-Intention to cause bodily harm WITHOUT actually doing it (threatening)
Battery
-A type of intentional tort
-Intention to cause bodily harm WITH touching them
Defamation
-A type of intentional tort
-Act of harming or ruining another's reputation
-2 types (libel and slander)
Libel
-A type of defamation (which is an intentional tort)
-WRITTEN defamation
-Think L=Library > Libel
Slander
-A type of defamation (which is an intentional tort)
-Verbal defamation
-Think S=Spoken > Slander
Unintentional Tort (Civil law: torts) includes:
Negligence and malpractice
Negligence
-Failure to do what a reasonable person would do
-Includes Standard of Care and duty
-Example: breaking instrument tip in periodontal pocket and neglecting to tell the patient
4 essential factors in negligence:
1. Acceptance of the patient by the provider
2. Breach of duty (harm does not have to happen to be a breach)
3. Causal relationship between the breach and damage
4. Damage or harm to the patient
2 main types of law
Civil and criminal
2 main branches off of civil law
Contract law and tort law
OSHA
Occupational Safety and Health Administration
-Responsible for developing universal/standard precaution protocols for employees to prevent them from contracting disease through blood and/or other body fluids
-Protects the employees
-Pertains to clinics and facilities
-Includes Blood-Borne Pathogens and MSDS
HIPAA
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996
-Maintains patient confidentiality
-All health care entities that electronically process, store, transmits or receives medical forms, claims, or remittances
-Office has to provide the patient a copy of HIPAA policy every 3 years
How frequently does a HIPAA form need to be signed?
Only one time unless..
1. Changes are made and the patient needs to add or remove an individual from a previous form
2. The government has made changes to HIPAA policy
CDC
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
-Recommends infection control protocol and conducts research to determine how diseases are transmitted
-Provides guidelines for disease prevention/transmission
-Located in Atlanta, GA
COBRA
Consolidated Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act
-Law to provide terminated employees or those who lose insurance coverage because of reduced work to be able to buy group insurance for themselves and their families (spouse and children) for a limited amount of time (for 18 months)
Informed Consent
-AUTONOMY
1. Presented in an understandable language
2. Nature and need of procedure
3. Benefits and risks of procedure
4. Prognosis
5. Alternatives to recommended procedure
6. Patient is allowed to ask questions
Malpractice
Professional negligence where harm results
To prove there must be:
1. Act of omission or commission
2. Failure to satisfy standard of care
3. Harm or injury to the patient
Statute of Limitations
-Time frame (limitation period) within which legal action must be taken
-Varies from state to state and the type of lawsuit
-Because dental lawsuits vary from state to state and type of offense, there is NO definite time for a universal statute of limitations
Dental records
-Documentation of complete data
-Additional information (radiographs, referrals, prescriptions, OHI, etc.)
Ownership:
-Dentist owns paper on which information is printed
-Patient owns information
-It is ok for dentist to charge reasonable fee to transfer records (even if there is a balance on the account)
Another term for the employer (dentist)
Respondent Superior
Statutory Law for Dental Professionals
-Licensure requirements, examination, and eligibility requirements
-Licensure by endorsement
-Approval of educational programs
-Examination and disciplinary authority
-Scope of practice
-Supervision requirements
-Continuing education requirements
Utilitarianism
The consequentialist principle that one should choose the course of action that creates the most good for the greatest number of people
Deontology
-The study of the nature of duty and obligation.
-Right or wrong regardless of the consequences.
-Kant's approach
Fat soluble vitamins
A- All
D- Dieters
E- Eat
K- Kilocalories
Infection control measures consist of:
-Regulated biohazard waste
-Safety Data Sheet (SDS)
-Personal protective equipment (PPE)
-Disinfectants
-Sterilization
Regulated biohazard waste
-Must be disposed of properly
-Examples include: sharps, items that drip of saturated blood and/or saliva, hard and soft tissues removed from the patient's mouth
Safety Data Sheet (SDS)
Sheet that provides information on the safe use of and hazards of chemicals, as well as emergency steps to take in the event chemicals are splashed, sprayed, or ingested
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Protective barrier that blocks exposure to a pathogen or a hazardous material.
-Mask (change when it becomes wet/moist and with every patient
-Examination gloves
-Protective eyewear
-Protective (impervious) clothing
PPE provides barriers to minimize exposure to:
1. Aerosol- invisible airborne particles; remain in air for awhile
2. Spatter- visible airborne particles of blood and/or saliva; drop quickly to a surface
3. Direct contact- occurs through direct touching of an infectious agent (blood, saliva)
4. Indirect contact- through a contaminated object (hand mirror)
Disinfectant purpose
Kill or inactivate MOST pathogenic microbes. However, NOT spores
Qualities of a disinfectant include:
-Rapid, broad spectrum antimicrobial (bactericidal, fungicidal, tuberculocidal, virucidal)
-Odorless, easy to use, fast acting, and economical
-Compatible to environment and surfaces
-Residual effect- continues to work after it is dried
-Non-toxic to touch or inhalation
-EPA registered
-Cleans and disinfects
Types of disinfecting agents
1. Chlorine-based compounds
2. Iodophors
3. Phenols (water or alcohol based)
4. Quaternary compounds
Chlorine-based compounds
Corrosive to metals
Strong odor
Iodophors
Can discolor some surfaces yellow
Phenols (water or alcohol based)
May leave a film or residue on surfaces
Quaternary Compounds
Not corrosive but have a lower kill spectrum; limited efficacy
Gluteraldehyde
-Should not be used as a surface disinfectant because of the toxic effects of the fumes
-Also, it is corrosive
-Immersion sterilant for 10 or more hours
Levels of surface disinfectants
1. High- used in surgical areas
2. Intermediate- used in dental offices; must kill TB organisms.
3. Low- generally used at home; not acceptable for use in a dental office.
Sterilization purpose
To kill ALL pathogenic microbes, including spores
Chemical sterilization (conditions, considerations & materials)
Conditions:
-Recommended minimum temperatures -273 F for 20 minutes with a pressure of kPa/25psi
Considerations:
-Ventilation is necessary
-May damage rubber and plastic items
-Spore test= Geobacillus (formerly Bacillus) stearothermophilus
Dry Heat Sterilization (conditions, considerations & materials)
Conditions:
-340 F for 1 hour
-or 320 F for 2 hours
Considerations:
-Recommended for metal instruments
-Avoid paper products
-May damage rubber and plastic items
-Not recommended for handpieces (think DRY HANDS)
-Spore test= Bacillus atrophaeus
Steam Sterilization (conditions, considerations & materials)
Conditions:
-Recommended minimum sterilization parameters are 250 F with 15 or 20 lbs. per square inch (psi) for 30 minutes
Considerations:
-Corrodes non-stainless (carbon) steel instruments
-Dulls instruments and burs
-Ok for SOME plastics (cotton rolls/gauze)
-Paper packages come out wet and tear
-Spore test= Geobacillus (formerly Bacillus) stearothermophilus
Preparation for sterilization
1. Clean instruments in ultrasonic cleaner > reduces risk of puncture wounds from manual scrubbing
2. Avoid overloading instruments in autoclave > place in a single layer (using cassettes helps prevent overloading)
3. Use proper ventilation
Sterilization packaging materials
-Cassettes and wraps
-Plastic/paper pouches
-Nylon clear tubing
-Paper
External indicators (on packaging materials or tape)
Color change indicates that the instruments have been heat processed (reached temp)
Biological Indicators (Spore Testing)
-Should be conducted weekly
-Determine if the sterilization cycle is reaching proper temperature, time, and pressure to kill ALL microorganisms
Spore test for chemical sterilization
Geobacillus stearothermophilus
Spore test for dry heat sterilization
Bacillus atrophaeus
Spore test for steam sterilization
Geobacillus stearothermophilus
G.V. Black Class I
Pits and fissures on lingual surfaces of anterior and on occlusal, buccal, and lingual surfaces of posterior teeth
G.V. Black Class II
Proximal surface of posterior teeth; commonly involves occlusal surfaces
G.V. Black Class III
Proximal surfaces of anterior teeth; does not involve the incisal edge
G.V. Black Class IV
Proximal surface of anterior teeth; involves the incisal edge
G.V. Black Class V
Cercial (gingival) 1/3 of the facial or lingual surfaces of any tooth. (Root caries)
G.V. Black Class VI
Incisal edge of anterior or cusp tips of posterior teeth
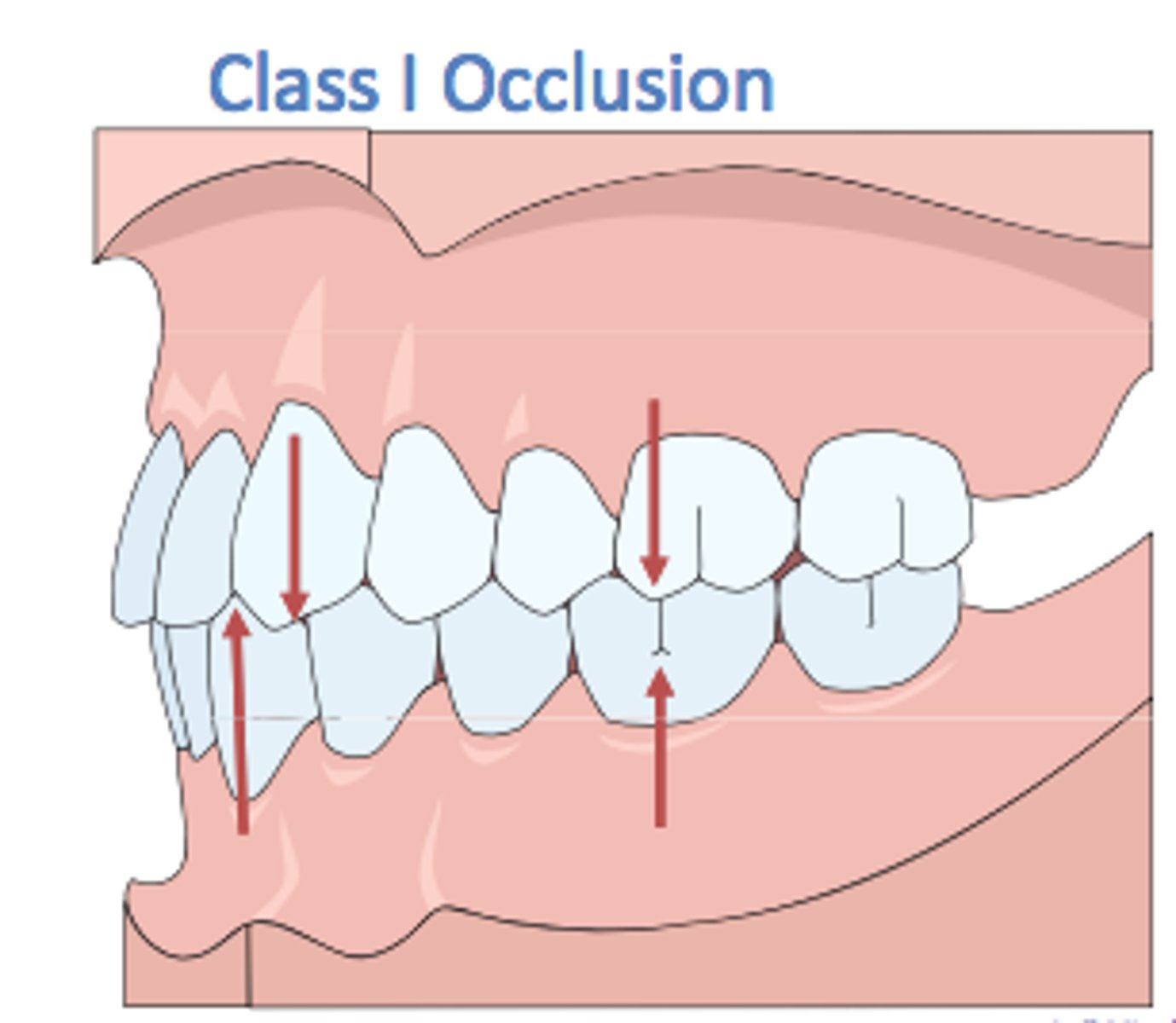
Class I Occlusion (describe and draw)
(Mesognathic) Normal
-Mesiobuccal cusp of the maxillary first molar is positioned in the buccal groove of the mandibular first molar.
-Maxillary canine occluded with the distal half of the mandibular canine and the mesial half of the mandibular first premolar
-Malposition of individual teeth or groups of teeth
Class II Occlusion (describe and draw)
(Retrognathic)
Molar Relationship: Buccal groove of the mandibular first permanent molar is distal go the mesiobuccal cusp of the maxillary first permanent molar by at least the width of a premolar.
Canine Relationship: Distal portion of the maxillary canine is mesial to the mesial portion of the mandibular canine by at lease the width of a premolar.
Division I-retruded mandible with one or more maxillary anterior teeth protruded facially.
Division II- retruded mandible with one or more maxillary anterior teeth inclined lingually.
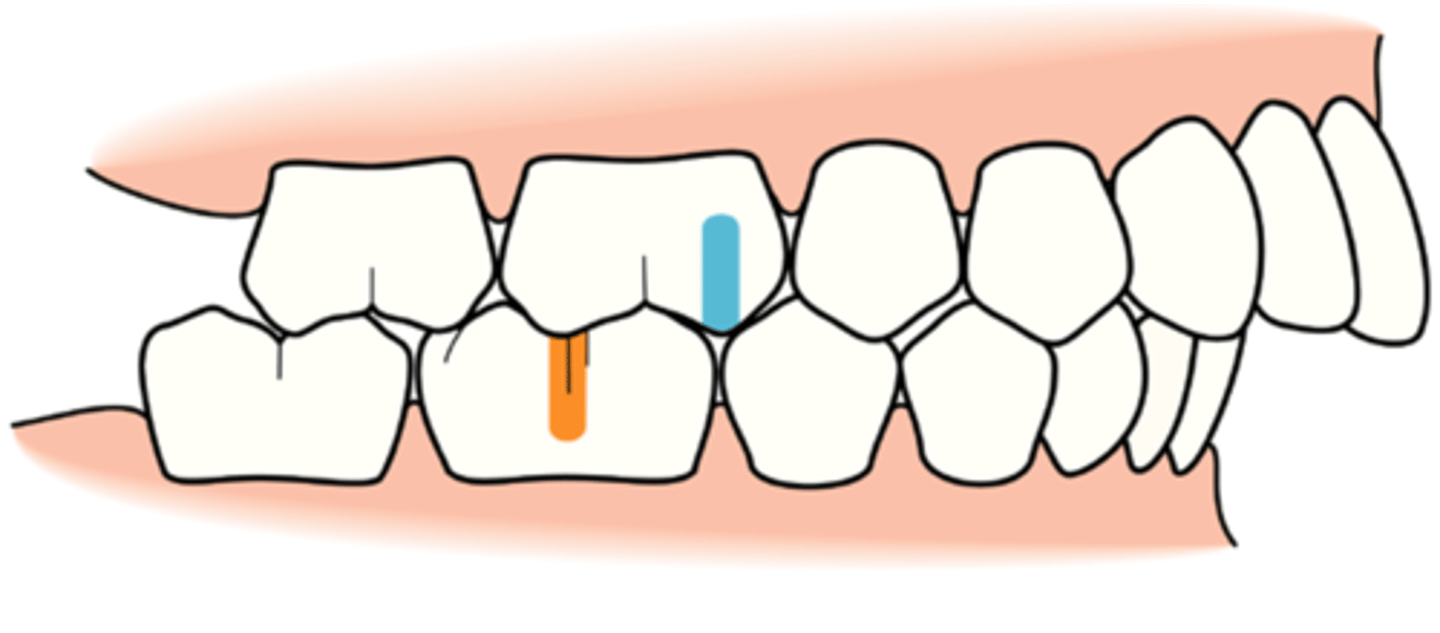
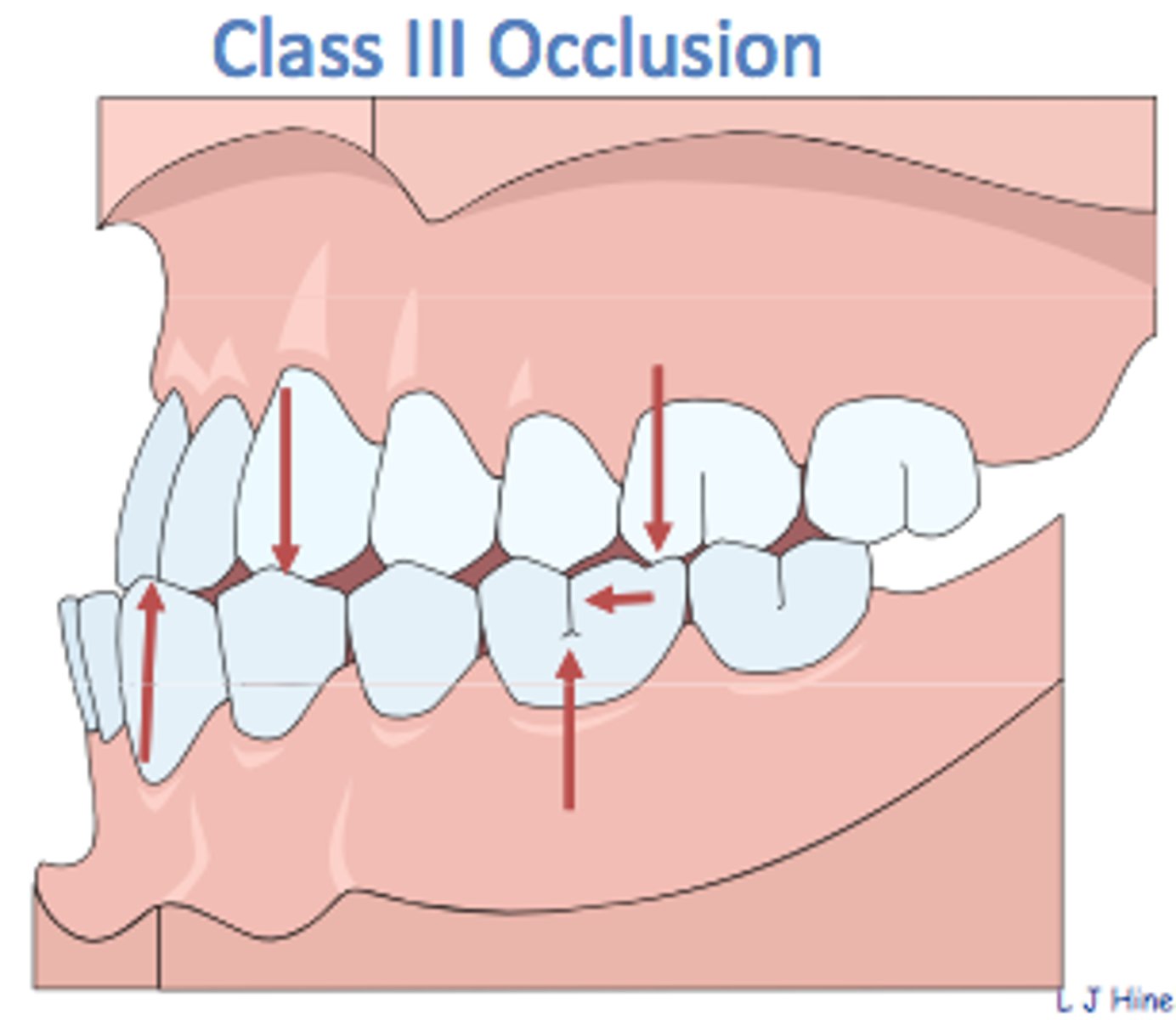
Class III Occlusion (describe and draw)
3=P (Prognathic)
Molar Relationship: Buccal groove of the mandibular first permanent molar is mesial to the mesiobuccal cusp of the maxillary first permanent molar by at least the width of a premolar
Canine Relationship: Mesial portion of the maxillary canine is distal to the distal surface of the mandibular canine by the width of a premolar
Malocclusion includes:
-Overbite
-Overjet
-Open-bite
-Cross-bite
-Midline shift (deviation)
-Edge-to-edge
-End-to-end - cusp-to-cusp
Overbite
Vertical overlap of the maxillary incisors to the mandibular incisors
Overjet
Horizontal distance between the lingual of the maxillary anterior incisors and the facial of the mandibular anterior incisors.
Openbite
Teeth not in occlusion between the maxillary and mandibular teeth or arch.
Crossbite
Maxillary teeth are positioned lingual to or totally facial to mandibular teeth.
Midline shift (deviation)
Midline of maxillary central incisors does NOT align with midline of mandibular central incisors
Edge-to-edge
Incisal edge to incisal edge of the maxillary anterior to mandibular anterior teeth
End-to-end - cusp-to-cusp
Relationship of the posterior teeth
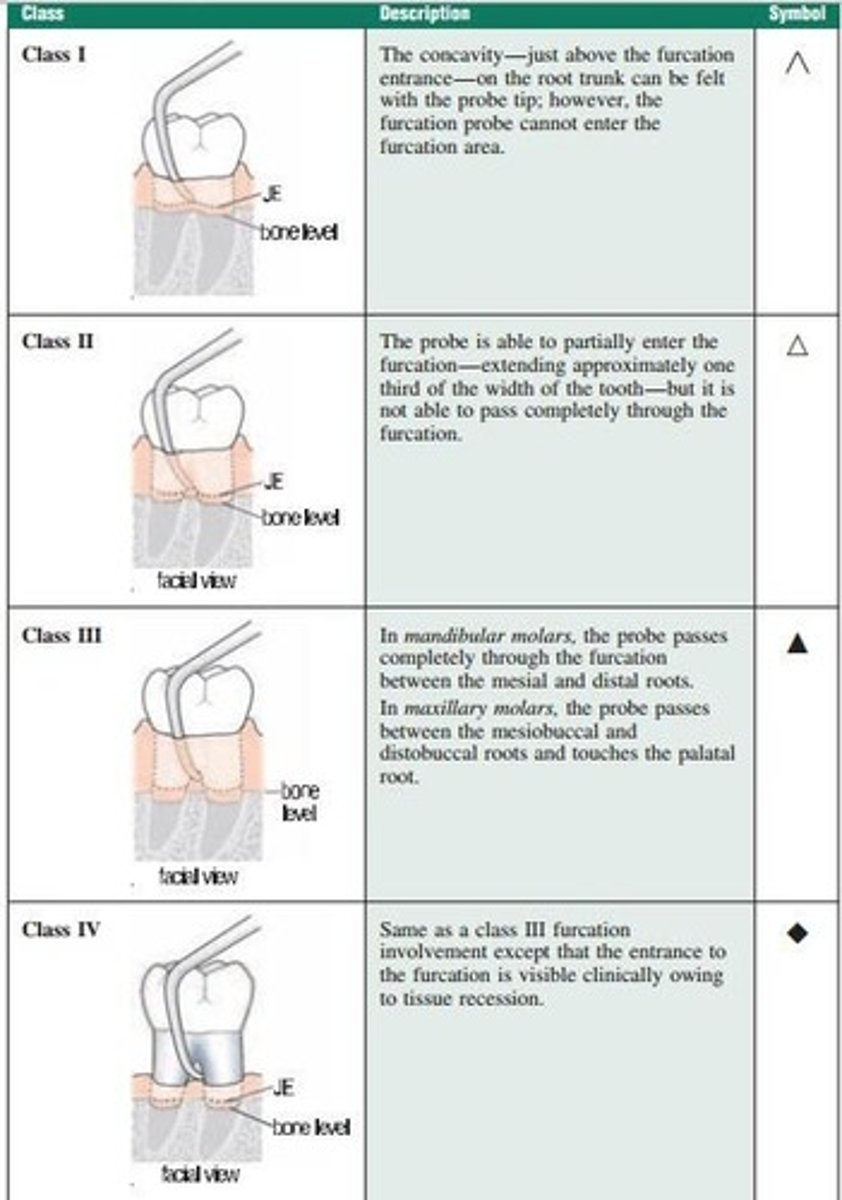
Class I Furcation
early evidence of bone loss; instrument can enter the depression leading to the furcation
Class II Furcation
Moderate bone loss; instrument can enter furcation, but cannot pass between the roots
Class III Furcation
Evidence of severe bone loss in between roots; instrument can pass through entire furca; tissue is covering furca
Class IV Furcation
Same as Class III with exposure resulting from gingival recession
Mobility- N
Normal
Mobility Class 1 or I
Involves slight horizontal mobility less than 1 mm
Mobility Class 2 or II
Involves moderate horizontal mobility; greater than 1mm- with no vertical displacement
Mobility Class 3 or III
Involves severe mobility with possible combined horizontal and vertical movement
Write furcation symbols Class I-IV
Calculus
Mineralized plaque; provides an irritant for the gingiva
Types of calculus and the nutrient source?
Supragingival- Nutrient source is saliva
Subgingival- Nutrient source is cervicular fluid and inflammatory exudate
Detecting calculus
Calculus-detecting explorers: posterior includes 11/12 and pigtail; anterior & cervical 1/3 of posterior teeth includes orban-type
Dry teeth with compressed air
Radiographs
Extrinsic stain
A stain that can be removed from tooth surfaces by polishing or scaling
Intrinsic stain (and causes)
Endogenous- not removable
Causes- pulpal necrosis, internal resorption, excessive systemic fluoride and/or tetracycline use during tooth development.
Origin of black-line stain
-Gram positive bacteria
-Typically located on cervical 1/3 of facials and linguals
Origin of brown stain
Associated with poor oral hygiene and/or drinking dark-colored beverages (coffee, tea, fruit juices and red wine)
Origin of dark brown and black stain
Associated with tobacco use
Origin of orange stain
-Chromogenic bacteria in plaque
-Associated with poor oral hygiene
-Typically located on anterior teeth