Theories of Personality in Psychology
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
Personality
the unique and relatively stable ways in which people think, feel, and behave.
Character
value judgments of a person's moral and ethical behavior.
Temperament
the enduring characteristics with which each person is born.
Psychoanalytic Perspective
a perspective in the study of personality that focuses on unconscious processes and childhood experiences.
Behavioristic Perspective
a perspective that emphasizes observable behaviors and the effects of learning and environment.
Humanistic Perspective
a perspective that emphasizes personal growth and the concept of self-actualization.
Trait Perspective
a perspective that focuses on the identification and measurement of personality traits.
Sigmund Freud
Founder of the psychoanalytic movement in psychology.
Preconscious Mind
level of the mind in which information is available but not currently conscious.
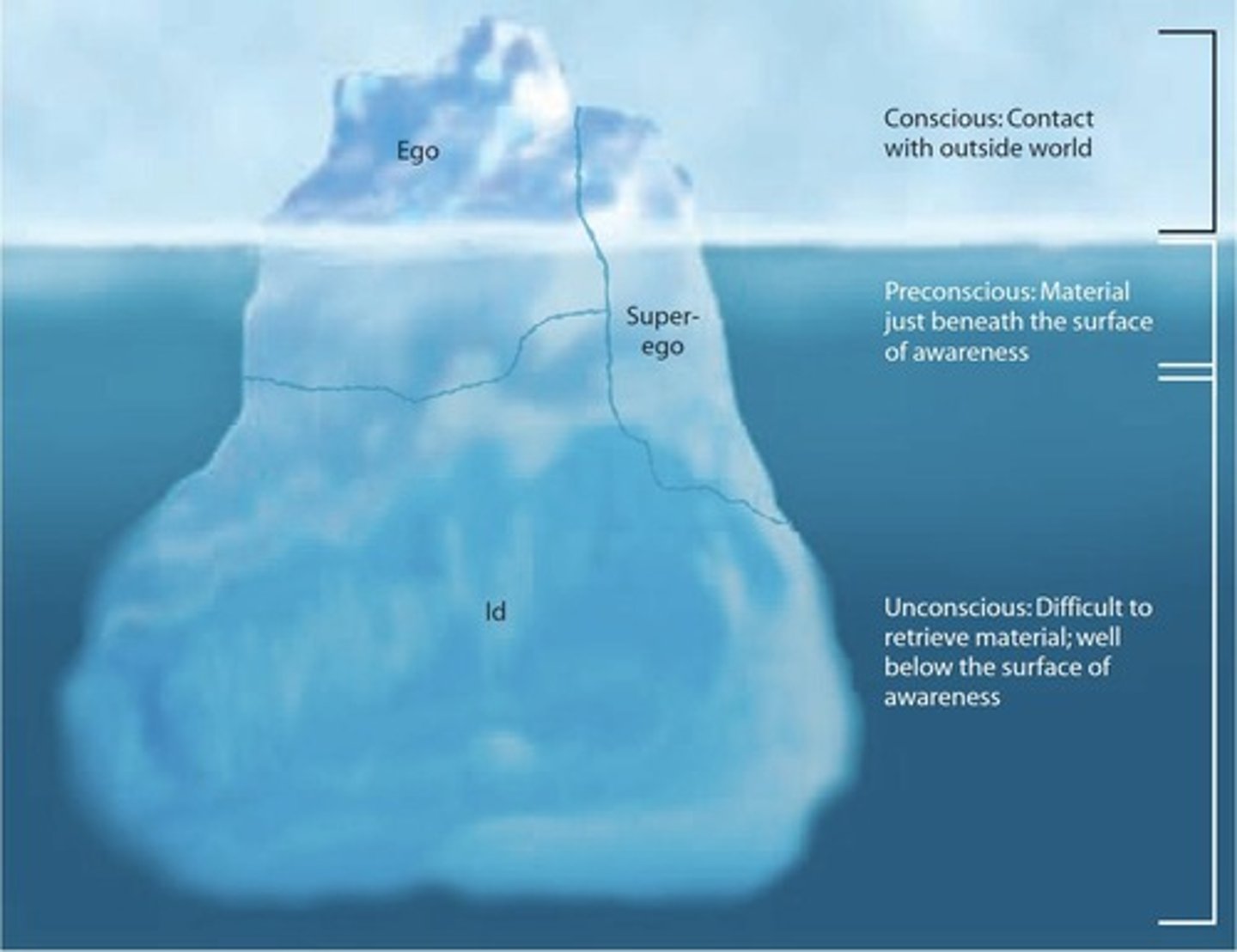
Conscious Mind
level of the mind that is aware of immediate surroundings and perceptions.
Unconscious Mind
level of the mind in which thoughts, feelings, memories, and other information are kept that are not easily or voluntarily brought into consciousness.
Id
part of the personality present at birth and completely unconscious.
Libido
the instinctual energy that may come into conflict with the demands of a society's standards for behavior.
Pleasure Principle
principle by which the id functions; the immediate satisfaction of needs without regard for the consequences.
Ego
part of the personality that develops out of a need to deal with reality, mostly conscious, rational, and logical.
Reality Principle
principle by which the ego functions; the satisfaction of the demands of the id only when negative consequences will not result.
Superego
part of the personality that acts as a moral center.
Ego Ideal
part of the superego that contains the standards for moral behavior.
Conscience
part of the superego that produces pride or guilt, depending on how well behavior matches or does not match the ego ideal.
Psychological Defense Mechanisms
unconscious distortions of a person's perception of reality that reduce stress and anxiety.
Denial
psychological defense mechanism in which the person refuses to acknowledge or recognize a threatening situation.
Repression
Psychological defense mechanism in which the person refuses to consciously remember a threatening or unacceptable event, instead pushing those events into the unconscious mind.
Rationalization
Psychological defense mechanism in which a person invents acceptable excuses for unacceptable behavior.
Projection
Psychological defense mechanism in which unacceptable or threatening impulses or feelings are seen as originating with someone else, usually the target of the impulses or feelings.
Reaction formation
Psychological defense mechanism in which a person forms an opposite emotional or behavioral reaction to the way he or she really feels to keep those true feelings hidden from self and others.
Displacement
Redirecting feelings from a threatening target to a less threatening one.
Regression
Psychological defense mechanism in which a person falls back on childlike patterns of responding in reaction to stressful situations.
Identification
Defense mechanism in which a person tries to become like someone else to deal with anxiety.
Compensation (substitution)
Defense mechanism in which a person makes up for inferiorities in one area by becoming superior in another area.
Sublimation
Channeling socially unacceptable impulses and urges into socially acceptable behavior.
Fixation
Disorder in which the person does not fully resolve the conflict in a particular psychosexual stage, resulting in personality traits and behavior associated with that earlier stage.
Psychosexual stages
Five stages of personality development proposed by Freud and tied to the sexual development of the child.
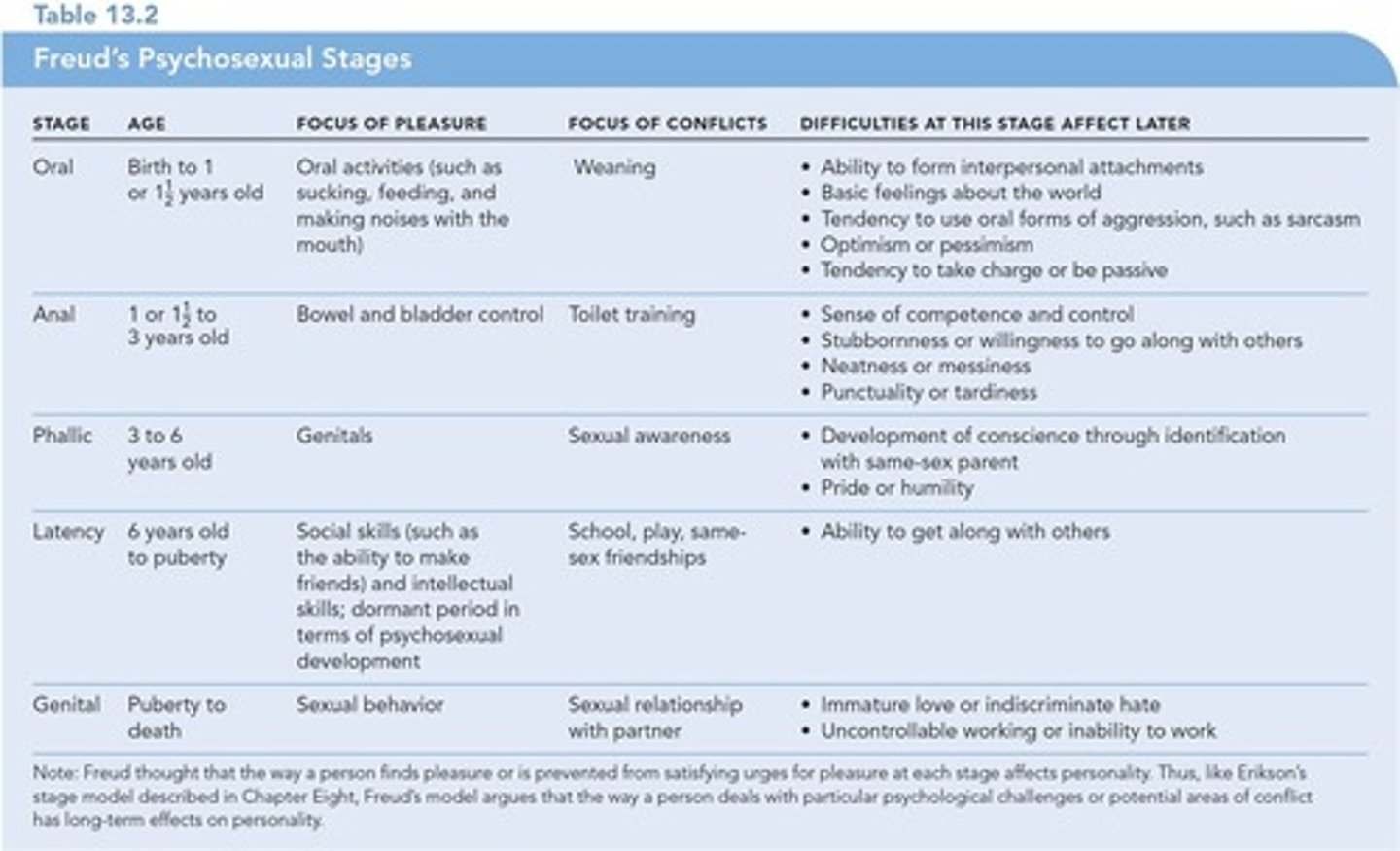
Oral stage
First stage occurring in the first year of life in which the mouth is the erogenous zone and weaning is the primary conflict.
Anal stage
Second stage occurring from about 1 to 3 years of age, in which the anus is the erogenous zone and toilet training is the source of conflict.
Anal expulsive personality
A person fixated in the anal stage who is messy, destructive, and hostile.
Anal retentive personality
A person fixated in the anal stage who is neat, fussy, stingy, and stubborn.
Phallic stage
Third stage occurring from about 3 to 6 years of age, in which the child discovers sexual feelings.
Oedipus complex
Situation occurring in the phallic stage in which a child develops a sexual attraction to the opposite-sex parent and jealousy of the same-sex parent.
Latency
Fourth stage occurring during the school years, in which the sexual feelings of the child are repressed while the child develops in other ways.
Genital
Sexual feelings reawaken with appropriate targets.
Psychoanalysis
Freud's term for both the theory of personality and the therapy based on it.
Neo-Freudians
Followers of Freud who developed their own competing theories of psychoanalysis.
Personal unconscious
Jung's name for the unconscious mind as described by Freud.
Collective unconscious
Jung's name for the memories shared by all members of the human species.
Archetypes
Jung's collective, universal human memories.
Feelings of inferiority
The driving force behind personality as proposed by Adler.
Birth order theory
Adler's theory that suggests birth order influences personality.
Basic anxiety
Anxiety created when a child is born into the bigger and more powerful world of older children and adults.
Neurotic personalities
Maladaptive ways of dealing with relationships in Horney's theory.
Theory based on social relationships
Erikson's theory that covers the entire life span.
Defense mechanisms
Psychological strategies used to cope with reality and maintain self-image.
Learned responses or habits
Behaviorists define personality as a set of these.
Habits
In behaviorism, sets of well-learned responses that have become automatic.
Social cognitive learning theorists
Theorists who emphasize the importance of both the influences of other people's behavior and of a person's own expectancies on learning.
Social cognitive view
Learning theory that includes cognitive processes such as anticipating, judging, memory, and imitation of models.
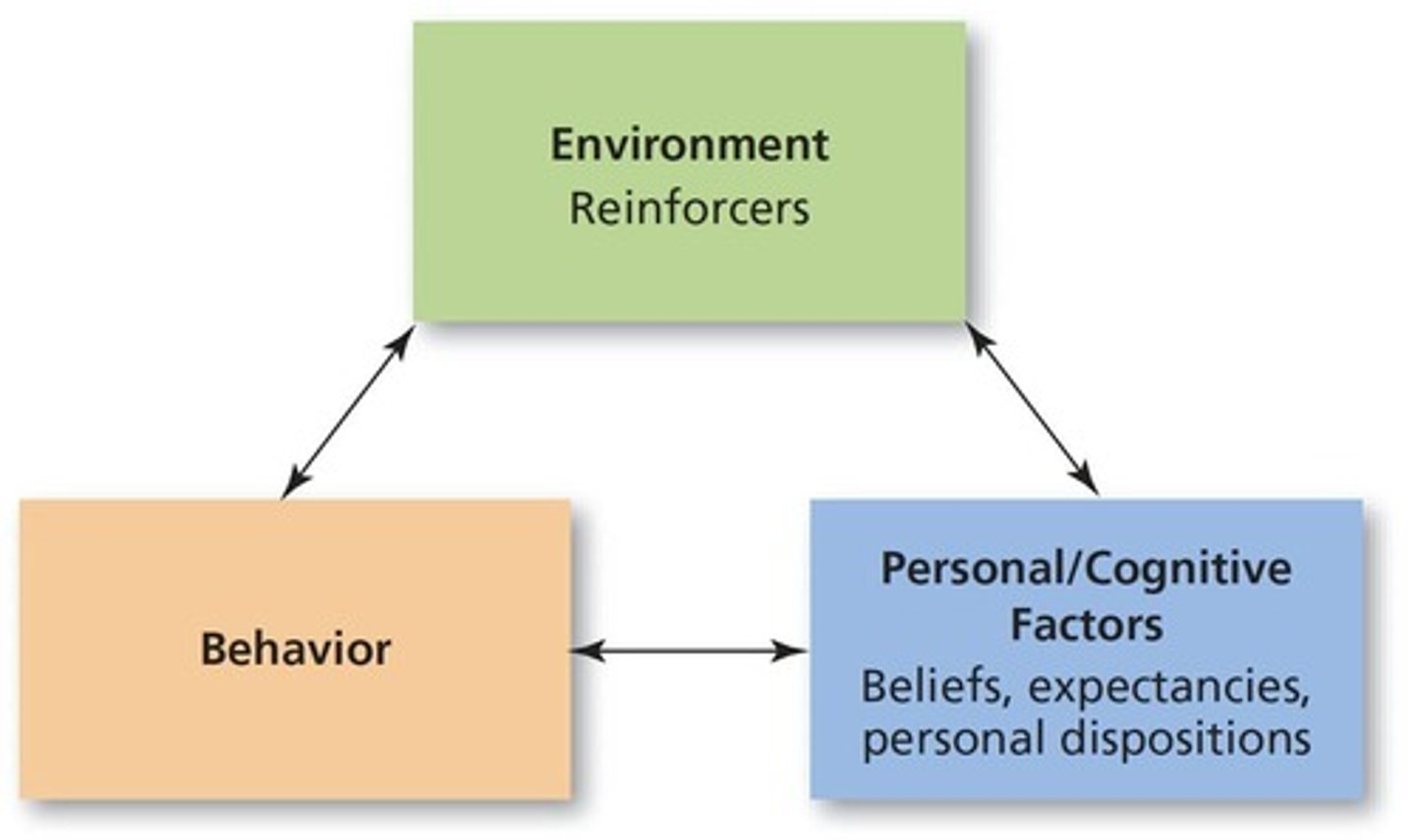
Reciprocal determinism
Bandura's explanation of how the factors of environment, personal characteristics, and behavior can interact to determine future behavior.
Self-efficacy
Individual's perception of how effective a behavior will be in any particular circumstance (NOT the same as self-esteem).
Humanistic perspective
The 'third force' in psychology that focuses on aspects of personality that make people uniquely human, such as subjective feelings and freedom of choice.
Self-actualizing tendency
The striving to fulfill one's innate capacities and capabilities.
Self-concept
The image of oneself that develops from interactions with important, significant people in one's life.
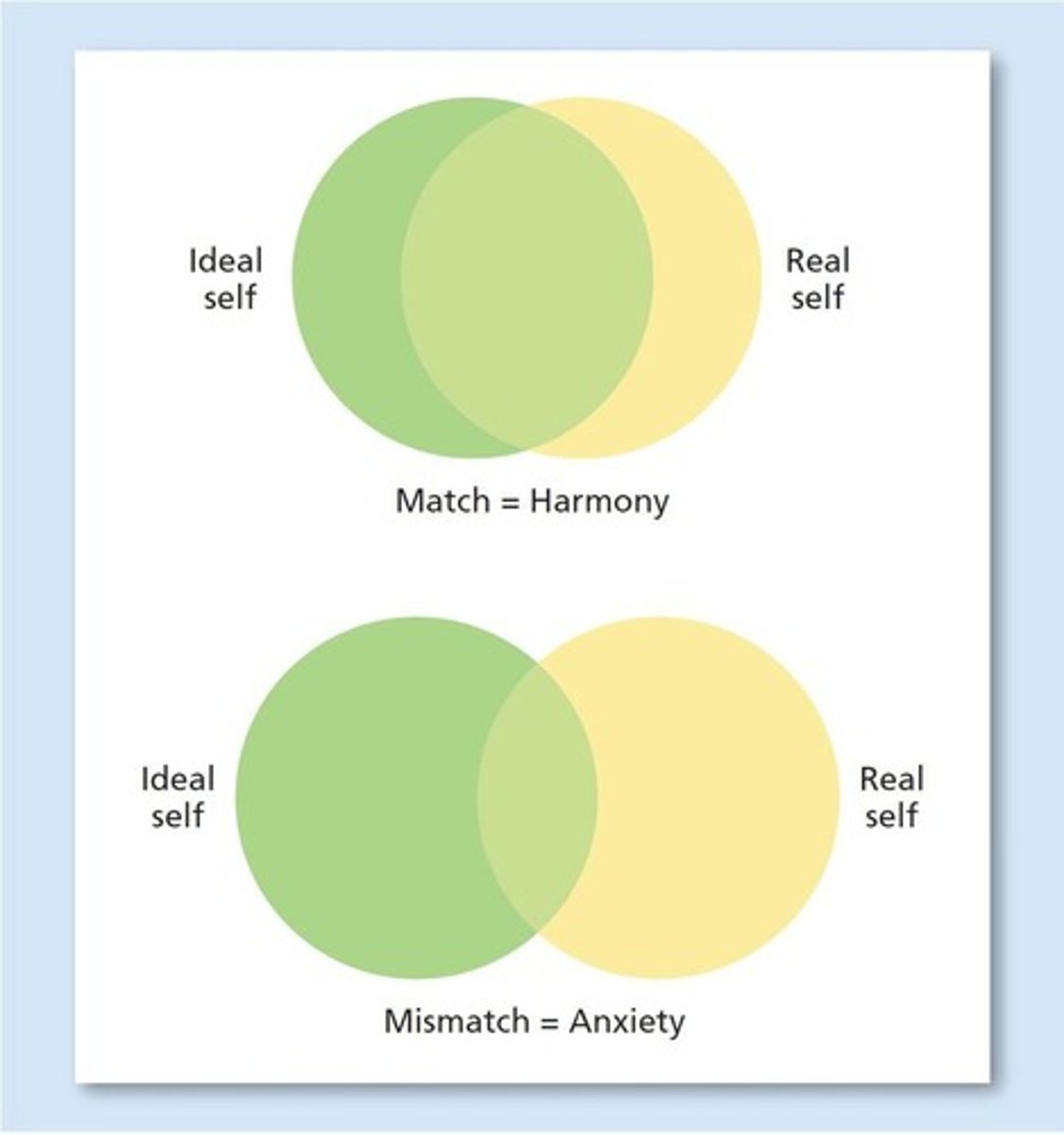
Real self
One's perception of actual characteristics, traits, and abilities.
Ideal self
One's perception of whom one should be or would like to be.
Positive regard
Warmth, affection, love, and respect that come from significant others in one's life.
Real Self
A person's actual perception of traits and abilities.
Ideal Self
The perception of what a person would like to be or thinks he or she should be.
Harmony and Contentment
Experiences when the ideal self and the real self are very similar.
Mismatch
Occurs when there is a discrepancy between the ideal self and the real self, leading to anxiety and neurotic behavior.
Unconditional Positive Regard
Positive regard that is given without conditions or strings attached.
Conditional Positive Regard
Positive regard that is given only when the person is doing what the providers of positive regard wish.
Fully Functioning Person
A person who is in touch with and trusting of the deepest, innermost urges and feelings.
Trait Theories
Theories that endeavor to describe the characteristics that make up human personality in an effort to predict future behavior.
Trait
A consistent, enduring way of thinking, feeling, or behaving.
Cattell's Factor Analysis
A method that reduced the number of traits to between 16 and 23.
Surface Traits
Aspects of personality that can easily be seen by other people in the outward actions of a person.
Source Traits
The more basic traits that underlie the surface traits, forming the core of personality.
Introversion
Dimension of personality in which people tend to withdraw from excessive stimulation.
Five-Factor Model (Big Five)
Model of personality traits that describes five basic trait dimensions.
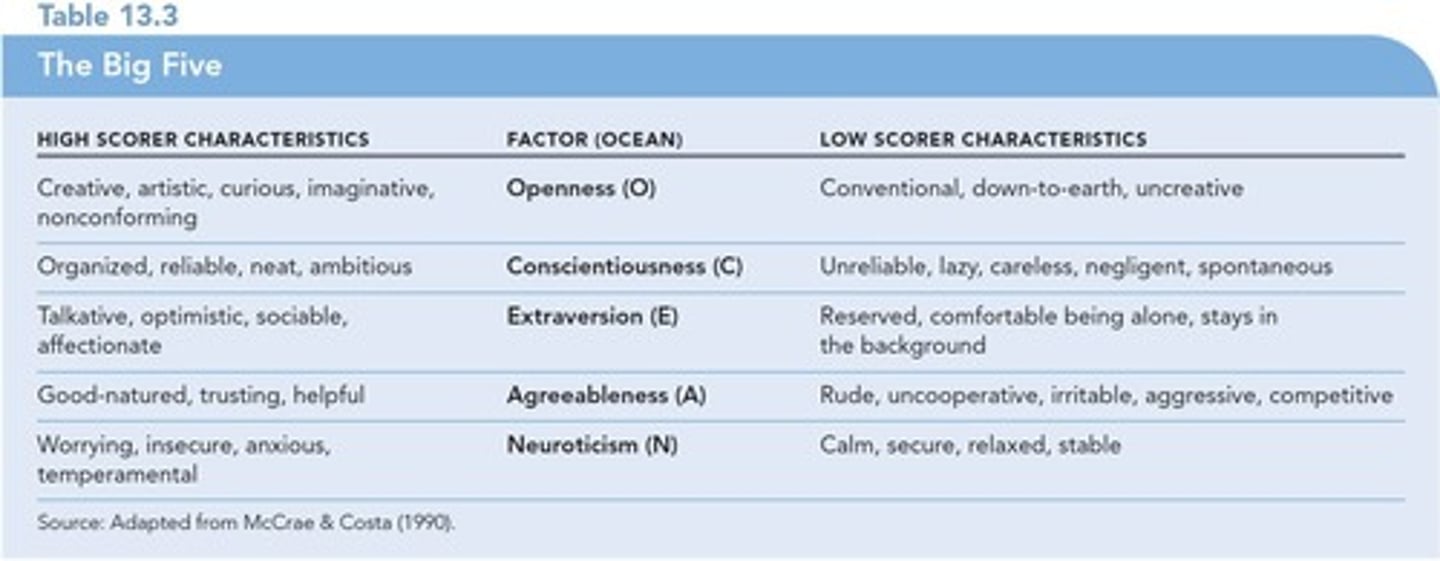
Openness
Willingness to try new things and be open to new experiences.
Conscientiousness
The care a person gives to organization and thoughtfulness of others; dependability.
Extraversion
Dimension of personality referring to one's need to be with other people.
Extraverts
People who are outgoing and sociable.
Introverts
People who prefer solitude and dislike being the center of attention.
Agreeableness
The emotional style of a person that may range from easygoing, friendly, and likeable to grumpy, crabby, and unpleasant.
Neuroticism
Degree of emotional instability or stability.
Trait-Situation Interaction
The assumption that the particular circumstances of any given situation will influence the way in which a trait is expressed.
Behavior Genetics
A field of study of the relationship between heredity and personality.
Twin and Adoption Studies
Research that has found support for a genetic influence on many personality traits.
Identical Twins
Twins that share 100% of their genes and have a correlation of about 50 percent in personality scores.
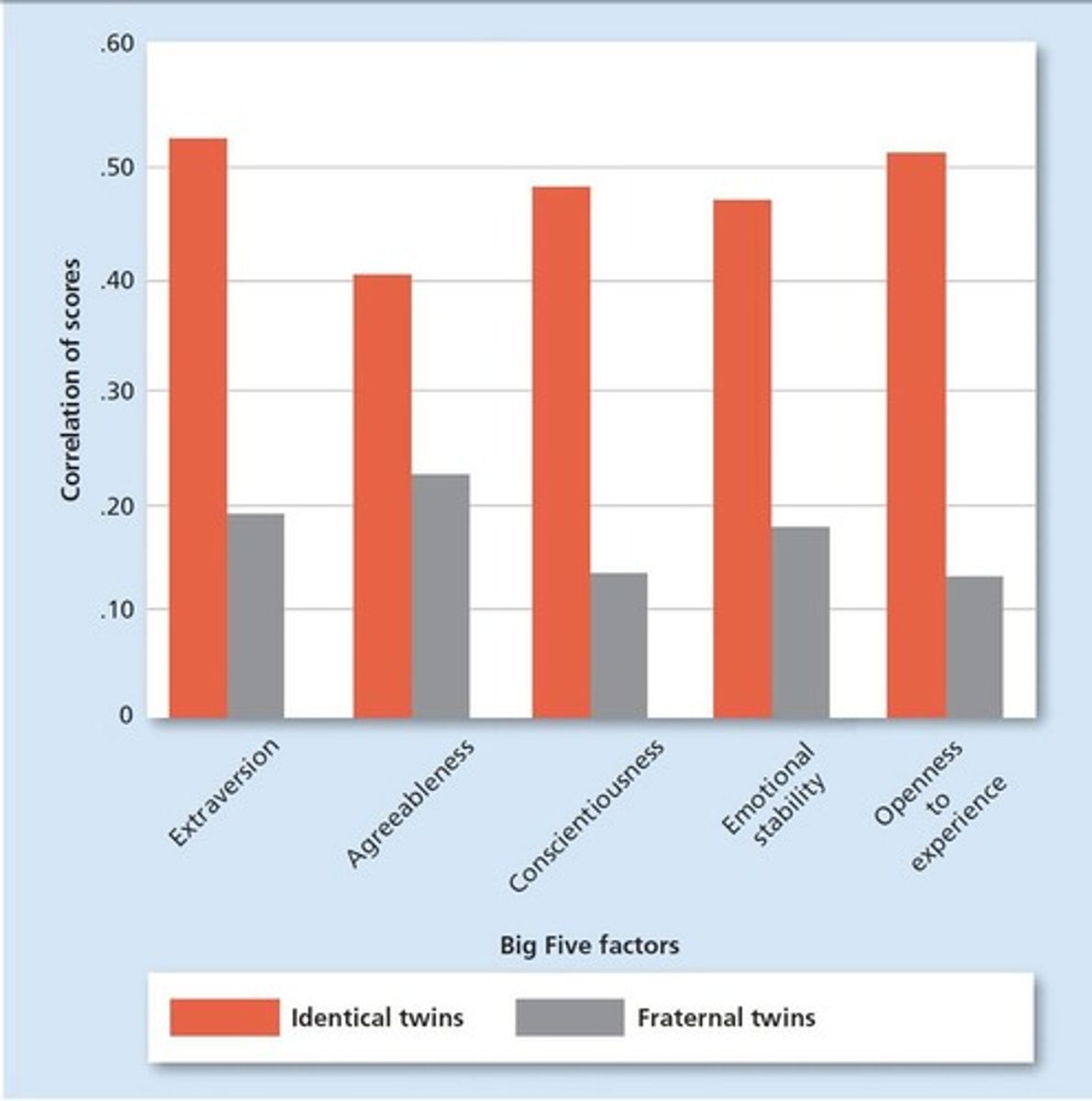
Fraternal Twins
Twins that share about 50% of their genes and have a correlation of only about 15 to 20 percent in personality scores.
Cultural Personality Dimensions
Four basic dimensions of personality along which cultures may vary: individualism/collectivism, power distance, masculinity/femininity, uncertainty avoidance.
Interview
Method of personality assessment in which the professional asks questions of the client and allows the client to answer, either in a structured or unstructured fashion.
Halo Effect
Tendency of an interviewer to allow positive characteristics of a client to influence the assessments of the client's behavior and statements.
projection
Defense mechanism involving placing, or 'projecting,' one's own unacceptable thoughts onto others.
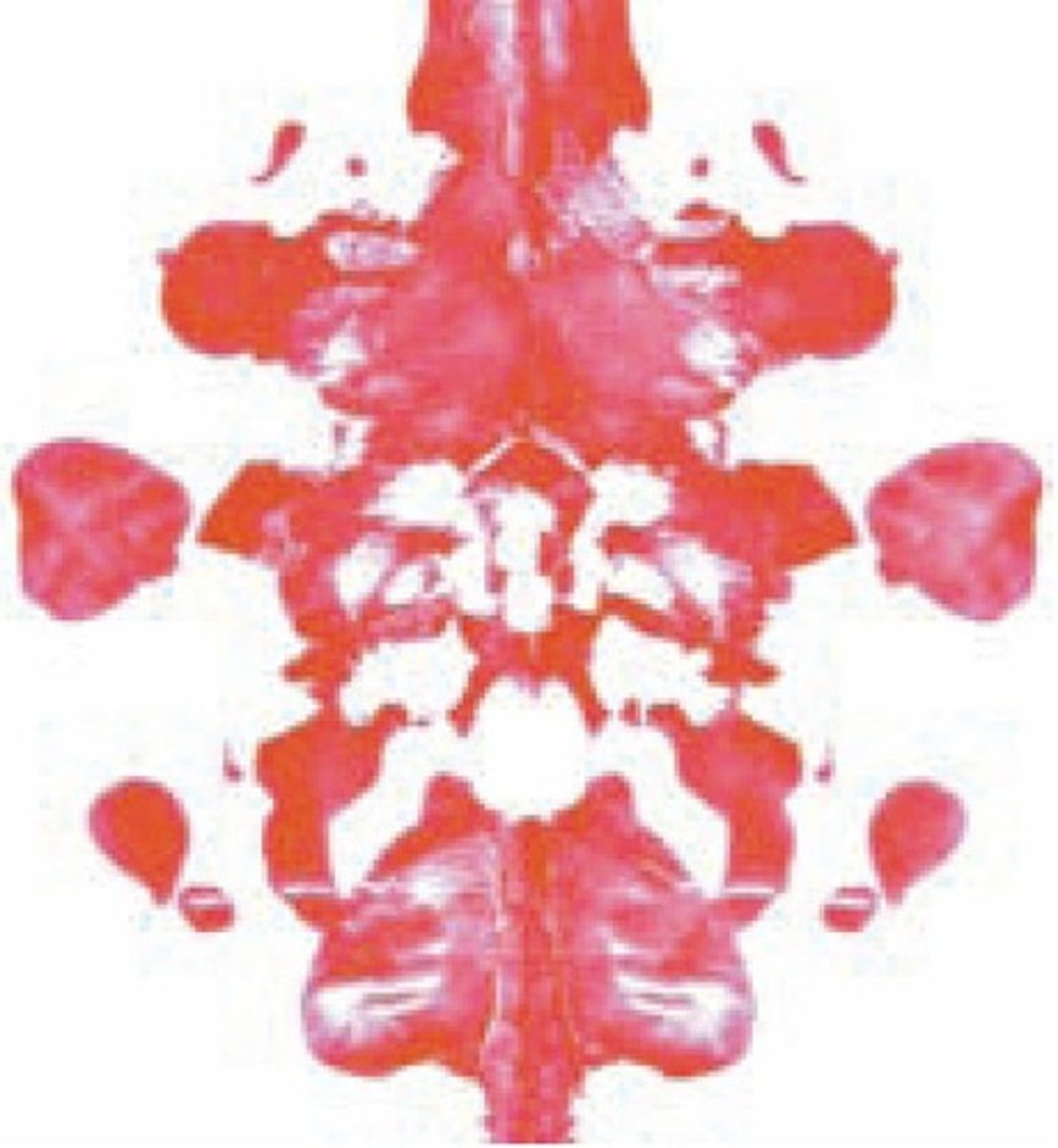
Projective Tests
Personality assessments that present ambiguous visual stimuli to the client and ask the client to respond with whatever comes to mind.
Rorschach Inkblot Test
Projective test that uses 10 inkblots as the ambiguous stimuli.
Thematic Apperception Test (TAT)
Projective test that uses 20 pictures of people in ambiguous situations as the visual stimuli.
Subjective Assessment
Concepts and impressions that are only valid within a particular person's perception and may be influenced by biases, prejudice, and personal experiences.
Direct Observation
Assessment in which the professional observes the client engaged in ordinary, day-to-day behavior in either a clinical or natural setting.
Rating Scale
Assessment in which a numerical value is assigned to specific behavior that is listed in the scale.
Frequency Count
Assessment in which the frequency of a particular behavior is counted.