Exam 2
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
109 Terms
Cellular Respiration
metabolic reactions convert food molecules into ATP
Metabolism
all of the chemical reactions occurring in the body
Metabolic Rates
the measure of a person’s energy use
Depends on speed and efficiency of different enzymes
Changes according to activity levels
Influenced by exercise, biological sex, and genetics
Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR)
the energy use of a resting, wakeful person
Average BMR: 70 cals/hr or 1680 cals/day
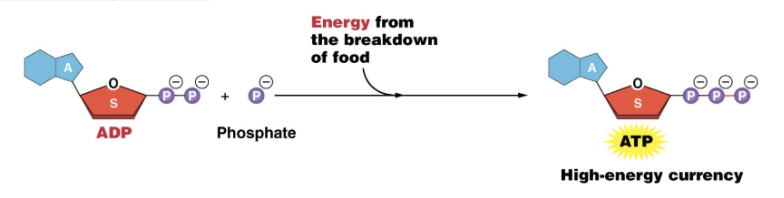
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
consists of adenine, a ribose sugar, and 3 negatively charged phosphate groups
Energy stored in chemical bonds of ATP
Phosphorylation
phosphate group is transferred (removed) from ATP to an enzyme to generate energy (ADP)
Energy is transferred
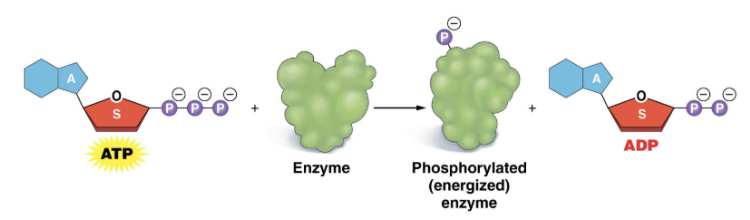
Regenerating ATP
cellular respiration replenishes ATP when used in the cell
Breathing and Cellular Respiration
Cellular respiration requires oxygen from breathing as part of the metabolic process; carbon dioxide waste is returned to the lungs
Aerobic Cellular Respiration
cells generate energy with oxygen
Occurs mostly in the mitochondria
Glucose (C6H12O6) + 6O2 → 6H2O + 6CO2
Simplified Equation: Glucose + oxygen = carbon dioxide + water
Anaerobic Respiration
cells generate energy without oxygen
Occurs during intense exercise: muscles run low on oxygen
ATP comes from glycolysis only
NAD+ level decrease
Muscle cells use fermentation to regenerate NAD+
Fermentation
microbes transform milk sugars into lactic acid
Yeast cells convert glucose to ethyl alcohol
Stages of Cellular Respiration
Glycolysis
Citric Acid Cycle
Electron Transport Chain and ATP Synthesis
Glycolysis
6-carbon glucose molecule is broken down into two 3-carbon pyruvic acid molecules
Occurs in cytosol
Doesn’t require oxygen
Spend 2 ATP, output 4 ATP: Produces 2 ATP
Glycolysis Steps
Empty taxicab (NAD+) picks up electrons and hydrogen ions (H+)
Becomes full taxicab (NADH) that carries electrons to final destination
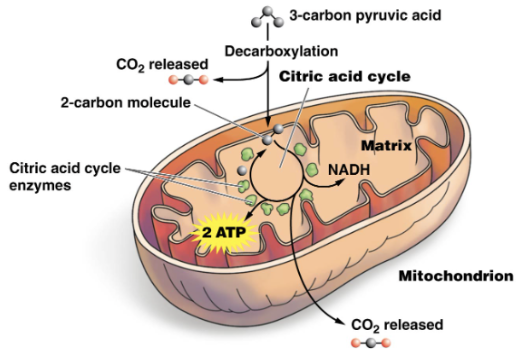
After Glycolysis:
Pyruvic acid loses a carbon dioxide (decarboxylated)
2-carbon fragment is metabolized inside mitochondrion
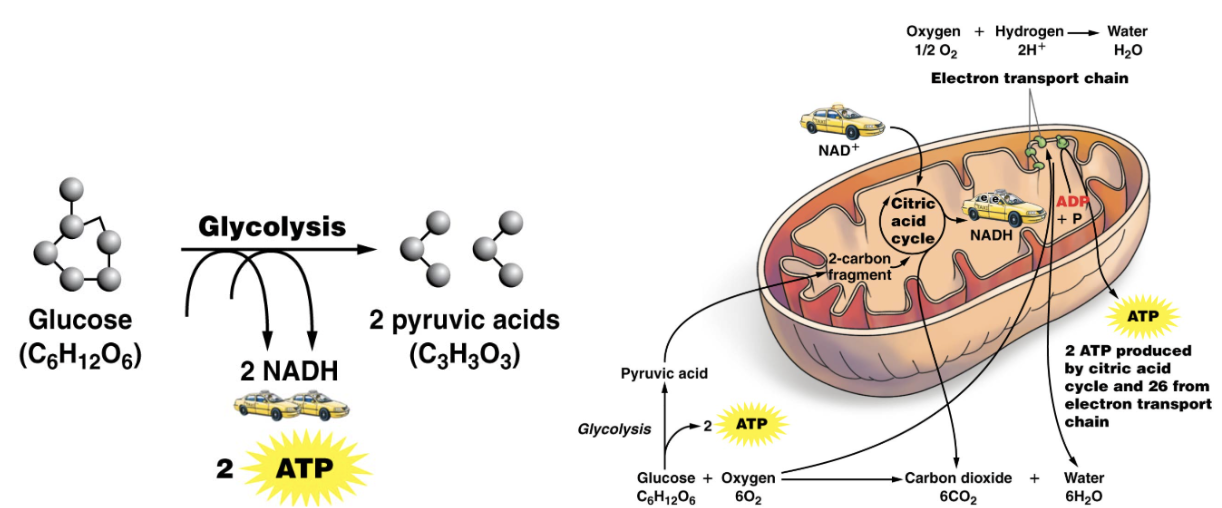
Citric Acid Cycle
series of enzyme-catalyzed reactions in the matrix of the mitochondria
Produces 2 ATP
Releases carbon dioxide and NADH
Electronic Transport Chain
series of proteins in the mitochondrion acting like a conveyor belt for electrons
Electron Transport Chain Steps
NADH drops off electrons and H+ ions
Electrons move through the chain
H+ concentration increases as the ions are moved into the intermembrane space
Charged H+ ions can’t diffuse across the membrane
Pass through ATP synthase protein channels
Sythesize 26 ATP molecules
Electrons eventually combine with oxygen to produce water
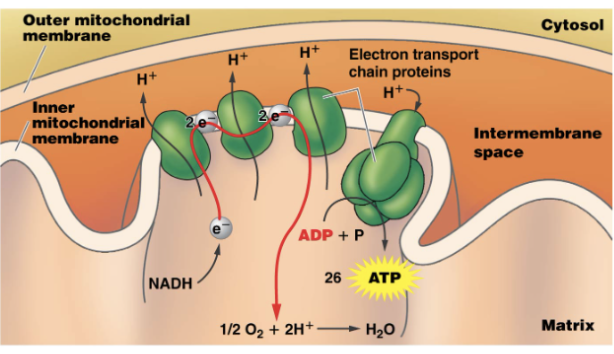
Results of the Electron Transport Chain
26 ATP
Water
Global Climate Change
local changes in average temperature, precipitation, and sea level
Relative to historical conditions
Global Warming
the progressive increase of Earth’s average temperature
Contributes to global climate change
Mostly attributed to human activities
What is the cause of Global Warming?
Increases in concentration of greenhouse gases:
Water vapor
Carbon dioxide (CO2)
Methane (CH4)
Ozone (O3)
The Greenhouse Effect
atmospheric greenhouse gases trap energy from the sun
The Greenhouse Effect and Bodies of Water
Bodies of water absorb heat energy and help maintain stable temperatures
Hydrogen bonds allow water to absorb and release heat
Bonds break and release as needed
Prevents large changes in temperature
Heat
the total amount of energy associated with movement of atoms and molecules
Temperature
measures the intensity of heat, how fast molecules move
Fossil Fuels
concentrated energy forms produced from the stored carbohydrates of ancient, buried organisms
Petroleum, coal, natural gas
What has the use of fossil fuels led to?
an increase in the levels of atmospheric carbon dioxide
Where is the scientific proof of the increase of fossil fuels in the atmosphere from?
ice cores
Photosynthesis
process that plants use to trap light energy
Uses light energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into sugar and oxygen
Opposite of respiration: the inputs of one are the outputs of the other
Chloroplasts
organelles where photosynthesis occurs
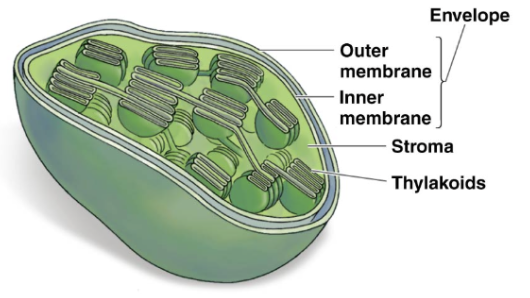
Chloroplast Envelope
inner and outer membranes of the chloroplast
Stroma
thick fluid in chloroplast
Thylakoids
disk-like membranous structures in chloroplasts
stacked in piles
Chlorophyll
covers surface of thylakoid membranes
Absorbs light energy from the sun: absorbs blue and red wavelengths, reflects green wavelengths
Photosynthesis Chemical Reaction
6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy → C6H12O6 + 6O2
Carbon + Water + Light → Glucose + Oxygen
Photosynthesis Steps
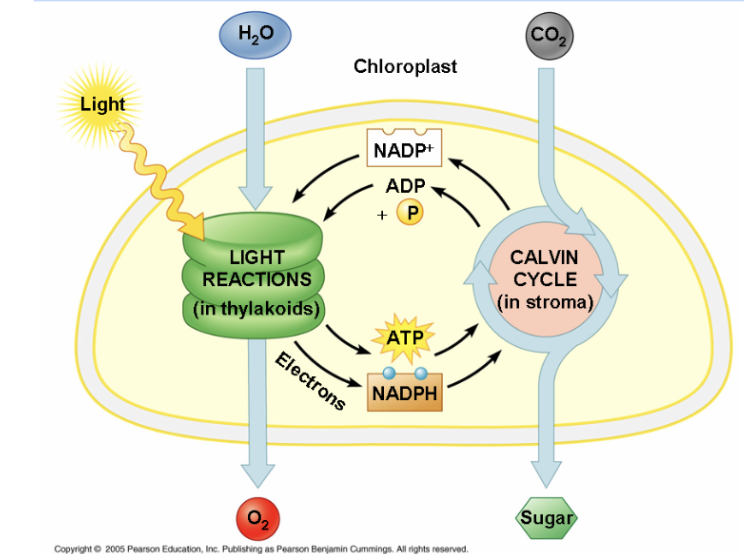
The Light Reactions
Calvin Cycle
Photosynthesis: The Light Reactions
sunlight excites chlorophyll electrons in thylakoid
Produces oxygen, ATP, and NADPH
Photosynthesis: The Light Reaction Steps
Light energy is absorbed by chlorophyll, which releases electrons to step 2
Electron transport chain pumps hydrogen ions into thylakoid
Water is split to provide replacement electrons to chlorophyll
Hydrogen ions power ATP production and combine with electrons to produce NADPH
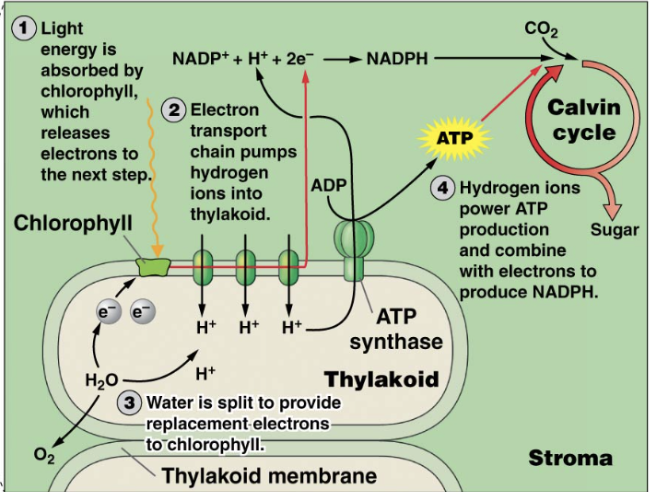
Photosynthesis: The Calvin Cycle
series of reactions that occur in the stroma
Produces glucose using ATP and NADPH
Photosynthesis: The Calvin Cycle Steps
Carbon Fixation
Reduction
Regeneration
The Calvin Cycle: Carbon Fixation
Carbon dioxide is added to RuBP (a 5 carbon sugar)
Result: The 6-carbon product is unstable, splits into two 3-carbon molecules of 3-PGA
The Calvin Cycle: Reduction
Energy from ATP and electrons from NADPH (both from the light-dependent reactions) convert 3-PGA into G3P (result)
The Calvin Cycle: Regeneration
Out of every 6 molecules of G3P, 5 are recycled to regenerate 3 molecules of RuBP
Remaining G3P used for glucose and carbs
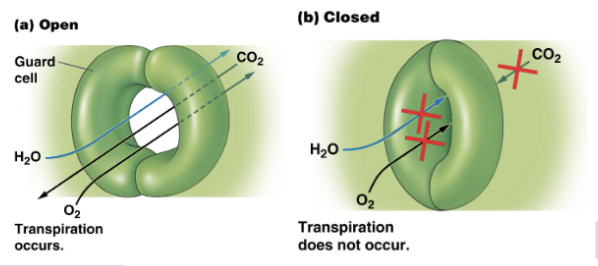
Stomata
openings in leaves for entrance of gases
Guard Cells
Regulate stomata openings
Transpiration
movement of water through a plant’s stomata
Stomata open: plenty of carbon dioxide, loss of water
Stomata closed: conserves water, limits photosynthesis
Photorespiration
series of reactions that counteract photosynthesis
Closed stomata limit carbon dioxide levels
Oxygen is used instead of carbon dioxide to react with RuBP
Plants will release carbon dioxide instead of oxygen
Tumors
unregulated cell division forming a lump of cells with no function
Benign Tumor
doesn’t affect surrounding tissues, not cancer
Malignant Tumor
invades surrounding tissues; cancerous
Metastasis
cells break away from a malignant tumor and start new cancers at distant locations
How do cancer cells travel through the body?
Through the circulatory and or lymphatic system
How are cancer cells different than normal cells?
Replicate when they shouldn’t
Invade surrounding tissues
Move to other locations in the body
Risk factors for cancer
Inherited through genes
Environmental exposures: carcinogens
Synergistic Risk Factors
enhance the activity of other carcinogens
Tobacco
Alcohol
Together, they have a greater cancer risk than either alone
How to decrease cancer risk
Don’t consume alcohol or tobacco
Low fat, high fiber diet
Exercise
Healthy weight
Types of Reproduction
Asexual
Sexual
Asexual Reproduction
one parent
Offspring are genetically identical to parent
Efficient: only need one parent
Sexual Reproduction
gametes combine from two parents
offspring are genetically different from one another and from the parents
Requires gametes made by meiosis
Increase variability by having 2 parents
Types of Genetic Materials
Genes
Chromosomes
Genes
section of DNA with instructions for building all cell proteins
What carries genes?
DNA
must be copied before cells divide
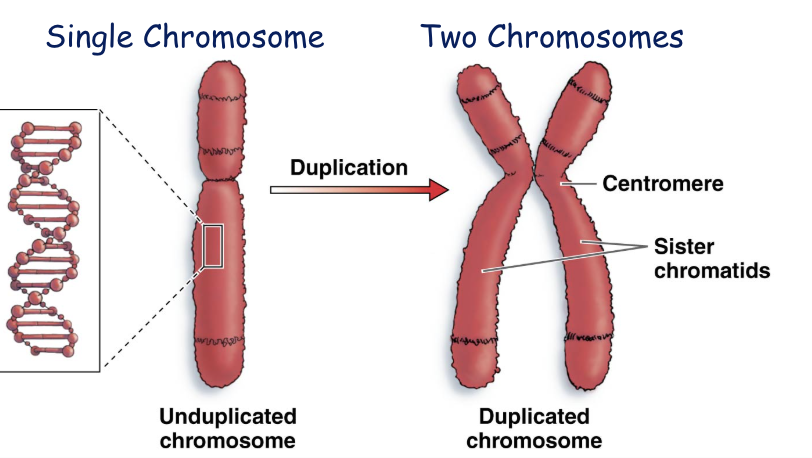
Chromosomes
made of DNA wrapped around proteins
In uncondensed, string-like form before cell division
Carry hundreds of genes
Sister chromatids: duplicated chromosomes, attached at the centromere
DNA Structure
double stranded
Sides of ladder: sugar-phosphate backbone
“Rungs” of ladder: nitrogen bases connected by hydrogen bonds
Adenine (A) pairs with thymine (T)
Cytosine (C) pairs with guanine (G)
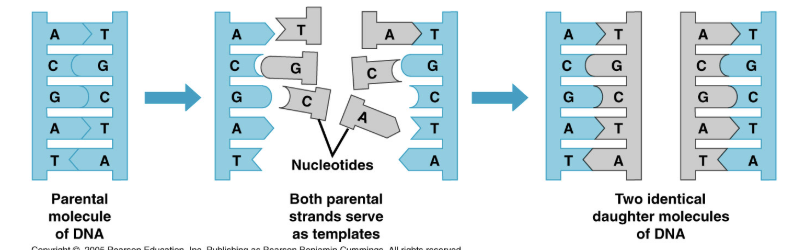
DNA Replication
Occurs before cell division
Begins by splitting helix in half down the middle
Semiconservative Replication: Newly formed DNA strand has one-half new daughter DNA and one-half conserved parental DNA
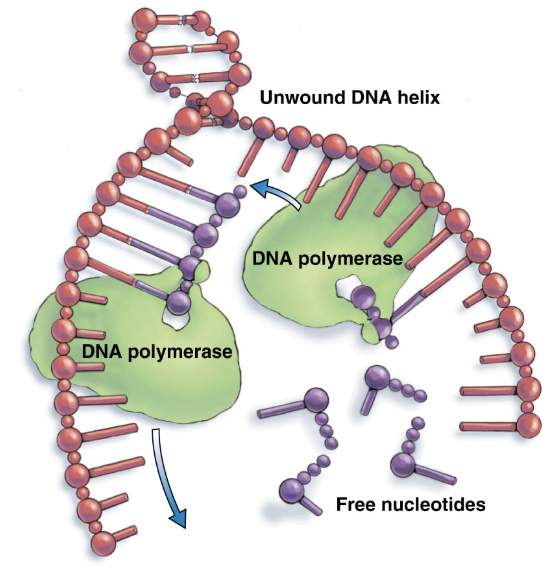
DNA polymerase
enzyme that replicates DNA
moves along the unwound DNA to form the new strands
Where does the cell cycle occur?
In all somatic (body cells)
NOT sexual reproduction cells
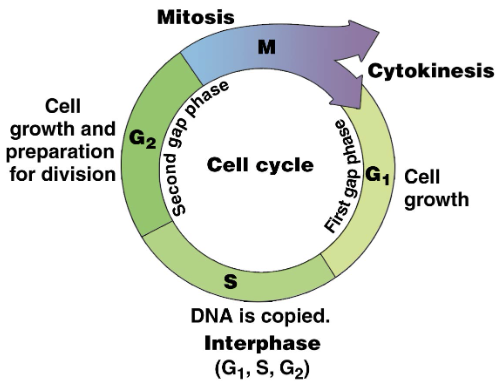
Cell Cycle Steps
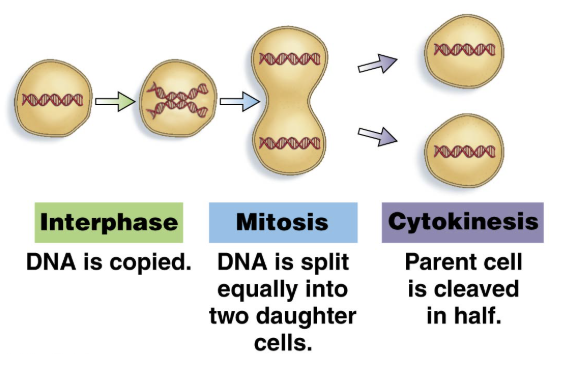
Interphase: DNA replicates
Mitosis: DNA separates
Cytokinesis: cells separate
Interphase Steps
G1: cell grows, organelles duplicate
S: DNA replicates
G2: cell makes proteins needed to complete mitosis
In what phase of the cell cycle do cells spend most of their time?
Interphase
Mitosis
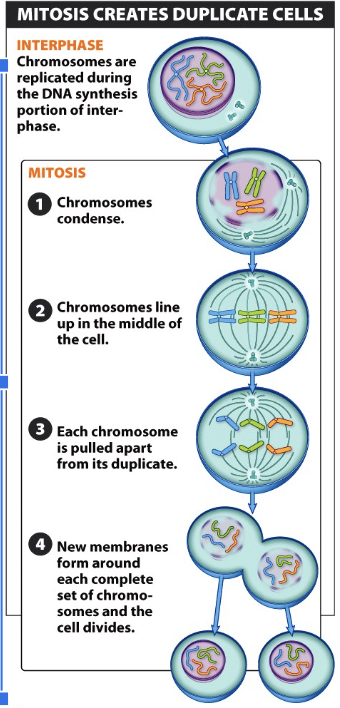
Movement of chromosomes from original eukaryotic parent cell into two genetically identical daughter cells
Cells spend about 10% of their time here
Stages of Mitosis
Prophase: plump
Metaphase: middle
Anaphase: apart
Telophase: the end
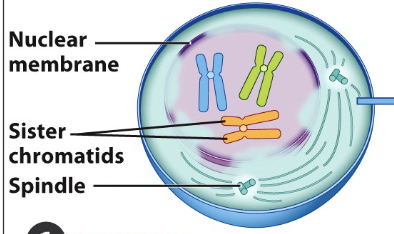
Mitosis: Prophase
Nuclear membrane breaks down
Sister chromatids/Chromosomes condense
Spindle begins to form
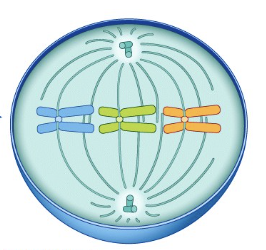
Mitosis: Metaphase
Chromosomes line up in MIDDLE of cell
Spindle fully formed
Chromosomes attach to spindle
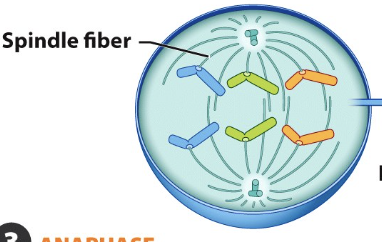
Mitosis: Anaphase
spindle contracts and pulls chromosomes APART to opposite sides of cell
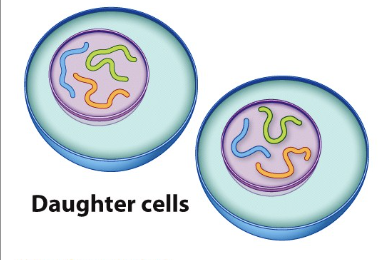
Mitosis: Telophase
nuclear membrane is reassembled and cell begins to split
Two individual nuclei
Each have same # of chromosomes as you started with
Is cytokinesis a part of mitosis?
NO!
Cytokinesis
cell splits into two independent cells
Cytoplasm and organelles duplicate and separate
Cytokinesis: cut
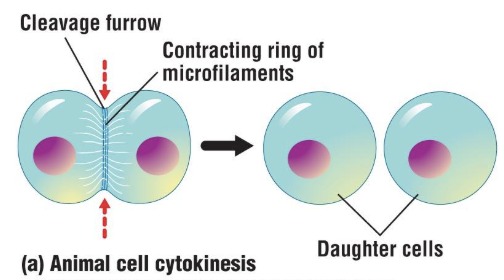
Cytokinesis in animal cells
Cell membrane forms at or near the place once occupied by the chromosomes
Contractile ring pinches the cell in two form the outside
Spot where is splits is called the cleavage furrow
Easier than in plant cells: animal cells have just a cell membrane, no cell wall
Cytokinesis in plant cells
Different than animal cells bc plant cells also have a cell wall, which is thicker than the cell membrane
Divide from outside in
Cell wall precursors collect at center of cell, forming a cell plate between the two plasma membranes
Cell Cycle Control
Normal cells pass checkpoints to determine if they are ready to proceed with cell division
Proteins determine condition of the cell
Three Checkpoints:
G1
G2
Metaphase
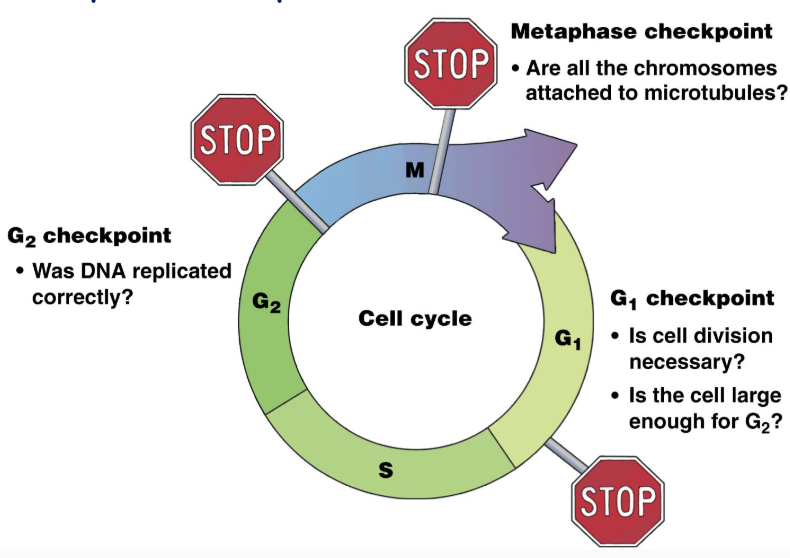
Cell Cycle Checkpoint: G1
Is cell division necessary
Is the cell large enough for G2?
Cell Cycle Checkpoint: G2
Was DNA replicated correctly?
Cell Cycle Checkpoint: Metaphase
Are all the chromosomes attached to microtubules?
Mutation
a change in sequence of DNA
May change the structure and function of the protein coded by the DNA
May be inherited or caused by carcinogens
Mutated tumor suppressor genes can increase the likelihood of cancer: protein fails to stop tumor growth
Proto-oncogenes
Genes that code for the cell cycle control proteins
Oncogenes
formed from mutated proto-oncogenes
Proteins no longer regulate cell division properly
Usually overstimulate cell division
Cancer
Usually related to changes in a cell’s DNA
Changes can be caused by substances from the environment or viruses
Changes affect growth factors and receptors for the growth factors
Biopsy
Surgical removal of cells or fluid for analysis
Fluid: typically a benign cyst
Solid mass of cells:
Benign tumors resemble other cells
Malignant tumors do not resemble other tissue cells from the same sample
Chemotherapy
chemicals that selectively kill dividing cells
Combo of different drugs used
Interrupts cell division in different ways
Helps prevent resistance to the drugs
Normal dividing cells are also killed (bone marrow, hair follicles, stomach lining)
Radiation Therapy
use of high-energy particles to destroy cancer cells
Damages DNA of cancer cells to prevent cell division
Usually for cancers close to the surface
After surgical removal of tumor
Meiosis
specialized form of cell division in gonads to produce gametes
Reduces number of chromosomes in each cell by one-half
Chromosomes come in homologous pairs: chromosomes that match each other that were in the egg and sperm that made you
Gamete gets one of each pair
Diploid Cells
have two copies of each chromosome
Haploid Cells
have one copy of each chromosome
Gametes, only in meiosis
Meiosis Cell Types
Adult form (diploid cells) —> Meiosis (haploid cells) —> Fertilization (diploid cells)
Meiosis: Homologous Chromosomes
one maternal and one paternal chromosome (from egg and sperm) that pair up with each other inside a cell during meiosis
Similar in size, shape, and gene order
Gametes
Specialized sex cells (egg, sperm)
produced by meiosis in the gonads (sex organs)
Haploid cells, with one set of the 23 chromosomes in humans
Fused Gametes
Form a diploid zygote
Occur during fertilization
Meiosis Process
Uses the DNA that was duplicated during interphase
Two Phases
Meiosis 1
Meiosis 2
Meiosis 1
Separating out the homologous chromosomes into two haploid cells