Alkenes
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Nomenclature for alkenes
Drop the “ane” from the end of the parent alkane and add the sufix “ene”. The position of the double bond in a carbon chain is indicated by prefixing the ending with the number of first C-atom involved in the double bond. ( C=C takes priority over other substituents and is the lowest number possible.)
What is E-Z isomerism
A type of stereoisomerism where atoms are rotated around a double bond depending on the isomerism displayed. (E stanbds for entgegnen, opposite in german is also called trans; Z stands for Zusammen, together in genrman called Cis.)
What is the definition of stereoisomerism
Moleccules that have the same molecualr formula, the same structual formula but different spatial arrangements of the bonds.
Cahn Ingold priority rules
1) Assign a priority to the 2 atoms bonded directly to each side of the bound bond
2) The atom with the higher atomic number is given the higher priority
3) If thea toms are the same then you look at the next atom in the group to assign a higher priority to.
4) If the 2 highest prioriy groups are either above or below the double bond it is the Z isomer and if they are across the double you have the E isomer.
What are pi bonds?
Pi bonds are a type of covalent bond that occurs when two atomic orbitals overlap sideways, involving the sharing of electrons in p orbitals. They are typically found in double and triple bonds, where one bond is a sigma bond and the other(s) are pi bond(s).
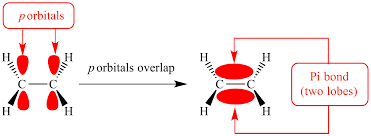
What are sigma bonds?
Sigma bonds are the strongest type of covalent chemical bond formed by the head-on overlapping of atomic orbitals. They can involve two s-orbitals, an s and a p-orbital, or two p-orbitals. Unlike pi bonds, which are formed from the side-to-side overlap of p-orbitals, sigma bonds allow for free rotation around the bond axis.
Why is the bond enthalpy of the pi bond is less than the sigma bond
Pi bonds take part in reaction more, it is less because the i bonds overlap sideways
What is an electrophile
An electrophile is a species that accepts an electron pair from a nucleophile to form a chemical bond. They are typically positively charged or electron-deficient atoms or molecules.
What are hybridized orbitals?
Hybridized orbitals are a mix of atomic orbitals to form new orbitals that are equal in energy, optimized for bonding in molecules. This is where the 2s, 2px and 2py orbital all have the same number of electrons
How do hybridized orbitals relate to sigma bonds?
Hybridized orbitals are involved in the formation of sigma bonds. A sigma bond occurs when these hybridized orbitals overlap head-on between two atoms, creating a strong covalent bond
How are sigma bonds made?
Sigma bonds are formed by the head-on overlap of atomic orbitals between two atoms. This can involve two s-orbitals, an s and a p-orbital, or two p-orbitals, resulting in a strong covalent bond due to the sharing of electrons.
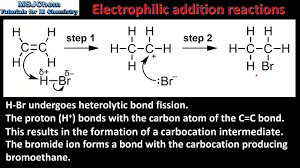
What intermediate do electrophillic addition reactions with alkenes use?
Carbocation
How does a alkene reaction with Br2 take place?
This reaction takes place in a non polar solvent such as CCl4. This is so the solvent is not attracted to the electron rich double bond. The high electron density of the double bond causes slight temporary polarisation of the bromine molecule, This acts as the test for alkenes as they change bromine water from red-brown to colourless.
How does electrophillica addition work?
Electrophilic addition is a reaction mechanism where an electrophile reacts with a nucleophile, typically involving the addition of an electrophile to the double bond of an alkene. This results in the formation of a carbocation intermediate, which can then react with a nucleophile to complete the addition.
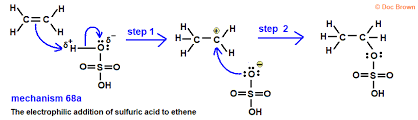
Electrophillic addition reaction with sulphuric acid
Alkenes are absored by cold concentrated sulphuric acid to form akyl hydrogen sulphates. Adding water and warming causes hydrolysis leading to the production of an alcohol
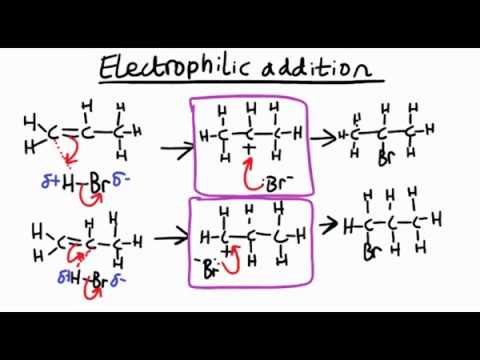
How does electrophillica addition work with unsymmetrical alkenes
If the alkene is unsymmetrical, such as propene and the molecule being added is also unsymmetrical, such as hydrogen bromide then 2 possible products could be formed
What polymers can be made via addition polymerisation
Poly (ethene), Poly (propene), Poly (phenylethene) ccalled polystyrene.
What does the non polar nature of monomers mean for polymers
Monomers are non polar and the C-C along with the C-H binds are fairly strong. Loner chains with fewer branches have stronger intermoleculr forces because they can pack close so they are stronger and more rigid with higher melting points.
How is high density polyethen made
It is made at low pressure (5 - 25 atm) and at 20 to 50oC in the presence if a catalyst (TiCl4)
How is low density polyethene made?
It is made at a higher pressure than low denisty polyethene (1000-2000 atm) and at 100-300oC
Monomer to polyymer
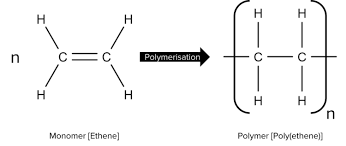
What happens to the intermolecular forces of a monomer onces it forms a polymer
There is more branching so intermolecular forces get weaker more specifically van deer waals forces.
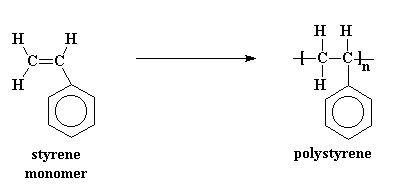
How is polystyrene made
Styrrene makes polystyrene via heating in the presence of benzoyl peroxide
What properties do polystyrene have
Polystyrene is a lightweight, rigid plastic known for its excellent insulation properties, ease of molding, and clarity. It is used in various applications including packaging, disposable cutlery, and insulation. It is also a thermosetting plastic
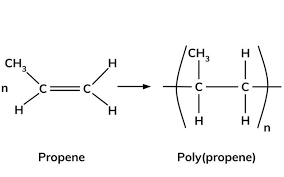
How is poly propene made
It is made via the separation of other plastics.
What properites does poly propene have
Polypropylene is a versatile, lightweight plastic known for its resistance to moisture, chemicals, and fatigue. It is commonly used in packaging, textiles, automotive parts, and consumer goods.
Ethene’s monomer name, monomer diagram, structure, polymer name, everyday name and uses
Its monomer name is ethene, its polymer name is polyethene, its everyday name is polythene and its uses are plastic bags
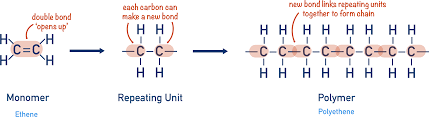
Propene’s monomer name, monomer diagram, structure, polymer name everyday name and uses
Its monomer name is propene, its polymer name is poly propene and its everyday name is also poply propene, it is used for plastic bowls
phenylethene monomer name, monomer diagram, structure, polymer name everyday name and uses
its monomer name is phenylethene or styrene, its polymer name is polystyrene its everyday name is styrene and it is used for packaging insulation
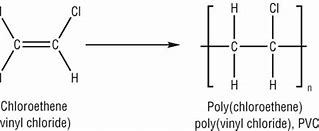
Chloroethene monomer name, monomer diagram, structure, polymer name everyday name and uses
also called vinyl chloride its monomer name is chloroethene, its polymer name is polyvinyl chloride / poly chloro ethene, its everyday name is PVC and it is used for water pipes and flooring.
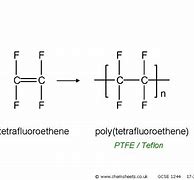
Tetrafluoroethene monomer name, monomer diagram, structure, polymer name everyday name and uses
tetrafluoroethene is its monomer name, its polymer name is polytetrafluoroethylene, commonly known as Teflon, used for non-stick cookware and seals.
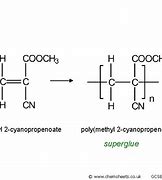
methyl 2 - cyanopropenoate monomer name, monomer diagram, structure, polymer name everyday name and uses
Methyl 2-cyanopropenoate is its monomer name, its polymer name is poly(methyl 2-cyanopropenoate), and it is used in coatings and adhesives and glue. Its every day name is super glue
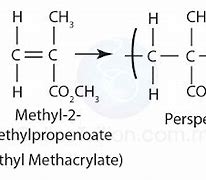
Methyl 2 methyl propenoate monomer name, monomer diagram, structure, polymer name everyday name and uses
Methyl 2-methylpropenoate is its monomer name, its polymer name is poly(methyl 2-methylpropenoate), and it is used in plastics windows, its every day name is perspex
What properties do addition polymers have and what property make vdwfs stronger
because the carbon chain is usually non polar they are very unreactive, the wekear intermolecular forces affect the properties of the [polymer. Longer chains with fewer branches have stronger van der waals forces making these polymers stronger, more rigid and having a higher melting point
Why do some poly alkenes have dipole dipole forces
Some addition polymers are polar, which means that there are stronger dipole-dipole forces between the chains, which makes the polymer hard but brittle.
Why does polystyrene haqve weak vdwfs and is flexible?
The benzene ring is a large branch so it is difficult for the polymer to pack closely so weaker VDWFs result in lower strength and flexibility.
What are plasticisers?
Additives that increase polymer flexibility by reducing intermolecular forces. They fit in between the polymer chains and push them apart weakening the intermolecular forces.