Questions I need to know before exam 3
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
State the first two laws of thermodynamics
all energy is set and fixed
energy is chaotic and creates disorder (entropy).
Explain how the laws of thermodynamics are related to metabolism
As entropy increases, the reaction reaches equilibrium.
Define metabolism
All reactions that transpire inside a cell, including those use and release energy, are the cell’s metabolism.
Identify a reactant, enzyme, and product in a metabolic pathway
A reactant would include Threonine, Deaminase, and
Differentiate between anabolic and catabolic pathways
Anabolic pathways requires an input of energy to synthesize complex molecules from simpler ones. Catabolic pathways involve degrading complex molecules into simpler ones.
Define free energy change (delta G)
The difference in the change of heat with the amount of entropy in a given system.
Describe the free energy change of spontaneous reactions
The free energy change is negative and gives off energy.
Identify the three kinds of "work" performed in cells that require energy input
Transportation, chemical, and mechanical
Explain why living beings never reach metabolic equilibrium
Reaching metabolic equilibrium means it the organism would die.
Differentiate between and define exergonic and endergonic reactions
An exergonic reaction is when energy is released from a molecule when it breaks. An endergonic reaction is when the energy is used to build a molecule.
Describe the role of ATP in coupling endergonic and exergonic reactions
ATP in coupling is when the energy from the exergonic reaction is used to create an endergonic reaction.
Define phosphorylation
Phosphorylation is when a phosphorus from a molecule (ATP) is used to assist another reaction.
Briefly explain how ATP functions as a sort of energy battery system in the cell- in what form is ATP when it has a higher energy state? In what form is the molecule when it has released energy?
The molecule ATP, has a phosphorus attached to the molecule, that is released and the energy used from the phorphus is transferred over.
Define enzyme
A large number of proteins that build up to become a catalyst for metabolism,
How do enzymes catalyze reactions?
The enzymes use a space called the active site that allows substrates to attach and act as a catalyst.
Explain why enzymes are useful even for spontaneous reactions that release energy
They are useful because the energy generated from the spontaneous reactions can be used for other reactions.
Describe how free energy change of a reactions (delta G) is or is not impacted by an enzyme
The free change of a reaction is impacted by the enzyme because it will release more energy.Active si
Define the various regions of an enzyme, using terms such as active site, substrate, enzyme-substrate complex, cofactors, and co-enzymes
active site is the area a substrate would bond too.
a substrate is a molecule that bonds to an enzyme to help speed up a reaction.
Enzyme-substrate complex is when the enzyme binds to the active site.
cofactors inorganic molecules
A coenzyme is an organic helper molecule, with basic atomic structure compromised of hydrogen and carbon
Identify factors that influence enzymes and the rate of reaction
factors that influence enzymes are temperature and pH
Differentiate between and identify competitive versus non-competitive inhibition (allosteric)
Competitive inhibitors block the active site of an enzyme to prevent further reactions. Non-competitive is similar, but instead of the active sight, it blocks off the active sight, it uses a different area called the allosteric site to block off the substrates.
Broadly describe feedback inhibition of enzymes
Feedback inhibition involves using a reaction product to regulate its own further production.
Explain why enzymes are often inhibited by their own products in a reaction or series of reactions
They are inhibited by their own products because the product can help recognize its own reactant and use it to encode the enzyme to stop.
Differentiate between the terms aerobic and anaerobic in relation to cellular respiration
Aerobic uses oxygen and anaerobic does not.
Distinguish between substrate-level phosphorylation and the work of ATP synthase.
Substrate-level phosphorylation receives its energy from the a chemical reaction while ATP synthase receives it from the hydrogen powered ions
Draw the mitochondria and label the outer membrane, intermembrane space, inner membrane, cristae, and matrix
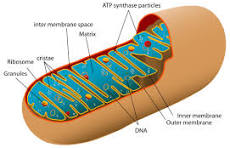
Differentiate between oxidation and reduction
Oxidation loses electrons.
Reduction increases electrons
Determine whether glucose is reduced or oxidized during cellular respiration, and explain why
Glucose is oxidized because it will be losing electrons as it is falling apart.
NAD+ and FAD are our electron carrier molecules during cellular respiration: Describe the cycle of oxidation/reduction of these molecules
Has NAD+ and FAD carries a proton, they reduce the proton during cycles of glycolysis, transformation, and the citric acid cycle, but they oxidize as they are carried into the ETC.
Describe the overall chemical reaction that occurs during each step of cellular respiration (what goes in—reactants—and what comes out—products)
Glycolysis- glucose to pyruvate.
Transformation-pyruvate to acetyl CoA, CO2, NADH
Citric acid cycle- acetyl CoA to 2H2O, CO2, 3NADH, FADH2, ATP
ETC- 34 ATP, H2O
Know where each step takes place within the cell
Glycolysis-cytoplasm
Citric acid cycle- mitochondria
ETC-mitochondria
Identify which steps of cellular respiration produce CO2 (and where the carbon in CO2 is “coming from”)
Pyruvate oxidation- carbon chain
Citric acid cycle- Isocitrate, Ketoglutarate
In what form is energy captured during each step?
Identify at which steps substrate-level phosphorylation (production of ATP) occurs
Identify at which steps NAD+ accepts electrons
Glycolysis, pyruvate, and Citric acid cycle
Substrate-level phosphorylation: pyruvate, Citric acid cycle, and ETC.
NAD+ accepts at pyruvate, Citric acid cycle, ETC.
Explain why the citric acid cycle is referred to as a cycle (continuous process of chemical reactions)
Its starts with Acetyl CoA and ends with Acetyl CoA.
During the breakdown of glucose via glycolysis, transition reaction, and citric acid cycle, electron carriers accept electrons—where are those electrons transported to? AKA, what and where is their final destination?
ETC
Identify which step of cellular respiration requires oxygen: What is the role of oxygen in cellular respiration?
ETC- its role is to produce water
Explain what the energy of captured electrons is directly used for in the mitochondria
Pump Hydrogen ions in the inner minchondria.
Describe the proton (H+) gradient generated by the electron transport chain in the mitochondria—indicate which side of the inner membrane has a higher concentration of H+ ions.
The proton gradient pumps out protons in the inner mitochondria from the mitochondrial matrix.
Describe the structure and function of the ETC, including where it is located and what it uses for “fuel”
The structure of an ETC is a series of electron transporters embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane. It uses Electrons from the NADH and FADH2 transporters to fuel the proton pump.
Describe the role of oxygen in the electron transport chain (and examine the chemical reaction that allows oxygen to fulfill its roles
Oxygen performs in the ETC by producing water.
Define chemiosmosis
Chemiosmosis is the process of converting free energy from the series of redox reactions to create ATP from the proton pump.
Describe the structure and function of ATP synthase, including where it is located, what it uses for “fuel”, how it generates a mechanical energy, and what it uses this kinetic/mechanical energy for.
ATP Synthase is located in the ETC where it uses a motor to pump to produce ATP. The fuel is the proton gradient. What does it use for the
Describe the regeneration of ATP from ADP and a phosphate groups
The ADP is regenerated from the ATP synthase that flows down the proton gradient.
Compare and contrast aerobic respiration with anaerobic respiration
aerobic involves the use of oxygen anaerobic doesn’t.
Provide an example of an electron acceptor that might be used during anaerobic respiration
Carbon dioxide
Contrast cellular respiration with fermentation
Fermentation is anaerobic while cellular respiration is aerobic.
Fermentation is a process that includes glycolysis plus an additional step in order to start over. Explain why the cell cannot simply repeat glycolysis many times, or in other words, explain the purpose of the additional step.
Glycolysis breaks down glucose to pyruvate converting NAD+ to NADH. However NADH is limited, so it needs the additional step of fermentation to convert the NAD+ to NADH.
Describe the overall chemical reaction that occurs during lactic acid fermentation
Pyruvic acid+NADH↔lactic acid+NAD+
Describe the overall chemical reaction that occurs during alcohol fermentation
pyruvic acid+H+→CO2+acetaldehyde+NADH+H+→ethanol+NAD+
Explain under what conditions a cell, such as a bacterium, might switch from aerobic cellular respiration to fermentation
When there is a lack of oxygen molecules.
Answer the "3 big picture questions"
What happens to carbon?
What happens to electrons?
Is ATP used or created?
Carbon gets turned into carbon dioxide
The electrons are transported through a redox reaction
ATP is created in the chemiosmosis step of the ETC.
Distinguish between phototroph and chemotroph
Phototroph uses light to create food. Chemotroph uses inorganic molecules
Distinguish between autotroph and heterotroph
be aware: the terms autotroph and phototroph are often confused online
Autotrophs are organisms that produce organic molecules from smaller inorganic compounds
heterotroph are organisms that consumes organic substances or other organisms for food
Determine where ( in which organelle) photosynthesis takes place in plants
Takes place in the leaves. specifically the middle layer called mesophyll.
What are the main reactants of photosynthesis
CO2 + H2O
What are the main products of photosynthesis
Sugar + Oxygen
Identify the big picture "goal" or purpose of each step (1. Light dependent reactions and 2. Calvin Cycle) in one sentence for each.
sun is absorbed by chlorophyll and that energy is stored in chemical energy.
converts CO2 to sugar
Define "electromagnetic spectrum" and describe the wavelength range of visible light
Electromagnetic spectrum is the range of all possible frequencies of radiation. The range for visible light is 700 nm and 400 nm
Define photon and its relation to energy.
A photon is a distinct packet of light energy.
It relates to energy as a photon can energize an electron from an atoms grounded state to its excited state.
Describe how pigments molecules determine the colors that our eyes perceive
Pigments reflect or transmit the wavelengths they cannot absorb, making them appear a mixture of the reflected or transmitted light colors.
Explain why purple-blue plants with pigments like anthocyanin are an example of an adaptation to low light conditions.
The pigmentation of an anthocyanin are adapted to low light because they can capture a broad wavelength of light.
Describe the role of the light harvesting complex in a photosystem
They pass energy from sunlight to the reaction venter in each photosystem.
Identify where the photosystems are physically located in the chloroplast (hint: which membrane?)
they are embedded in the thylakoid membrane
What is the primary role of the light-harvesting complex of the photosystem?
They pass energy from sunlight to the reaction center.
In the reaction-center complex of the photosystem, a special pair of chlorophyll a molecules are able to grab onto and "excite" electrons-- where do those electrons come from? Where do the electrons go after this step?
They come from water. They eventually go through the Electron transportation and reduced to NADPH which are then transported to the Calvin cycle.
Hydrogen ions are produced when chlorophyll a is reduced (as described above)-- the H+ form a gradient and want to flow out of the membrane-- what does the movement of these H+ ions allow the cell to generate?
ATP
Identify whether oxygen is oxidized or reduced in the light dependent reaction
oxygen is being reduced?
Determine which molecule is reduced at the end of the electron transport chain in the thylakoid
NADP+
What molecules from the light dependent reaction will go on to interact with molecules in the Calvin Cycle?
What carbon-containing molecule is the main reactant of this cycle (goes into the cycle)?
Identify whether energy in the form of ATP is used or produced during the Calvin Cycle. As such, determine whether the process is endergonic or exergonic
Is the electron carrier NADPH reduced or oxidized during the Calvin Cycle?
The final product of the Calvin Cycle, G3P, is used to make what important energy storage molecule in plants (p.s. the energy is stored in the chemical bonds)?
Define stomata
Identify the challenge that a very hot environment poses to plants (who breathe through stomata)
How does CAM photosynthesis help plants overcome that obstacle?