Physics laws learnt over time
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
Newton first law
An object remains at rest or in uniform motion in a straight line unless acted upon by a net external force.
Newton second law
The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass. ( F = ma)
Newton third law
For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. ( Fab = -Fab)
Conservation of Energy
Energy cannot be created or destroyed — it only changes from one form to another. The total energy in a closed system stays the same.
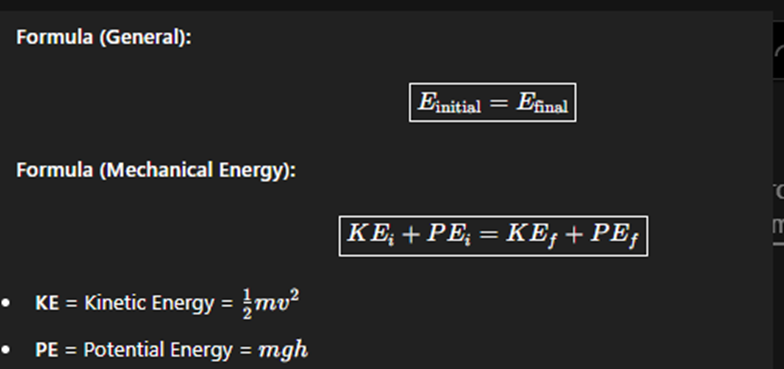
Law of Universal Gravitation
Every mass attracts every other mass with a force proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.

Work Energy theorem
The net work done on an object is equal to its change in kinetic energy.
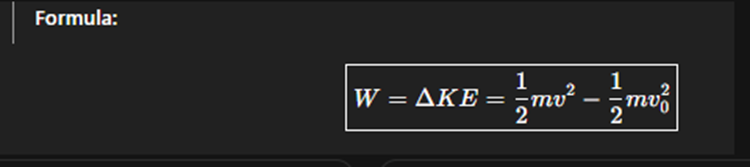
Work meaured in joules
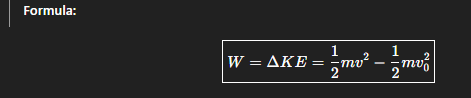
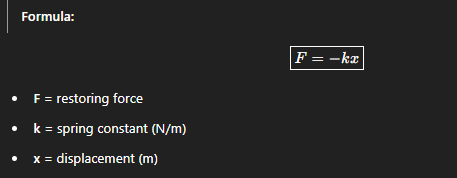
Hook’s Law (Springs)
The force needed to compress or stretch a spring is proportional to the displacement.
Momentum
Momentum is the quantity of motion an object has. It depends on an object’s mass and velocity.
Simple definition:
Momentum is how much motion an object has and how hard it is to stop it.( the greater the harder)

Impulse
Impulse is the change in momentum caused by a force acting over a period of time.

Law of conservation of Momentum
In a closed system with no external forces, the total momentum before a collision is equal to the total momentum after.
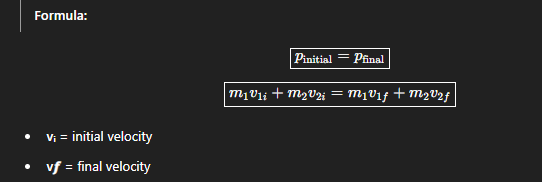
Mechanical Energy
The sum of kinetic and potential energy in a system.

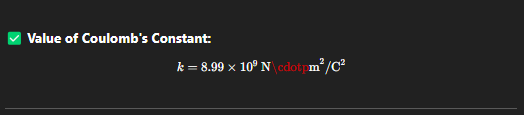
Coulomb constant
It tells us how strong the electric force is between two 1-coulomb charges that are 1 meter apart.
Coulomb's law
The electric force between two charges is directly proportional to the product of their charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. (Vector)
Simple Definition ( Coulomb’s Law tells us how strong the electric force is between two charges.)


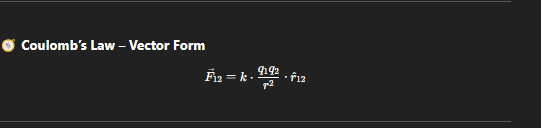
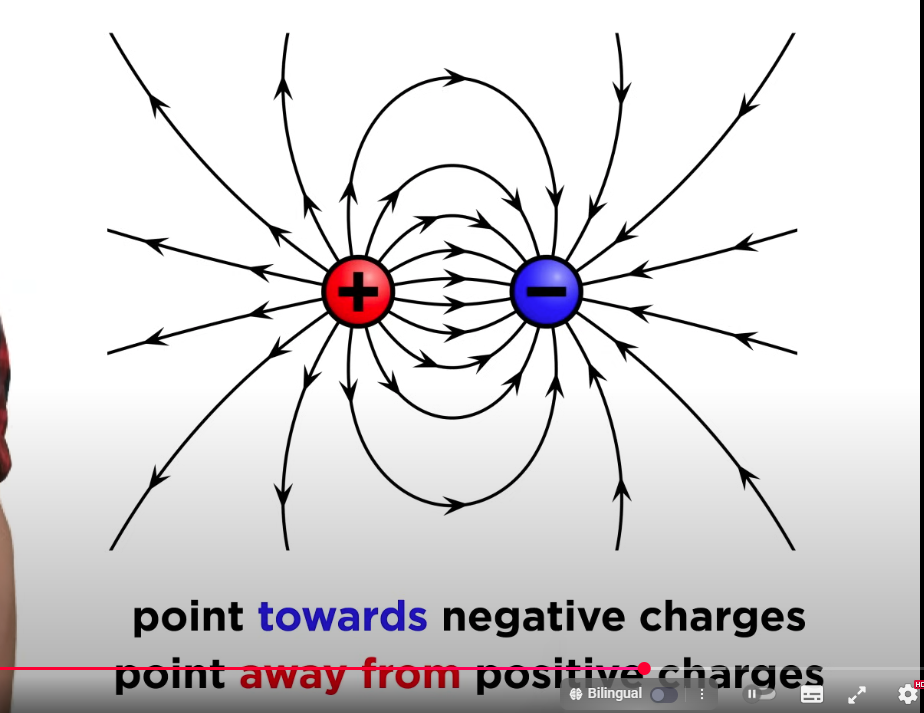
Electric field (Vector quantity)
The electric field is a region around a charged object where another charged object experiences a force.
It represents the force per unit charge exerted on a small positive test charge.
(Positive Charge goes away , negative charge goes towards)




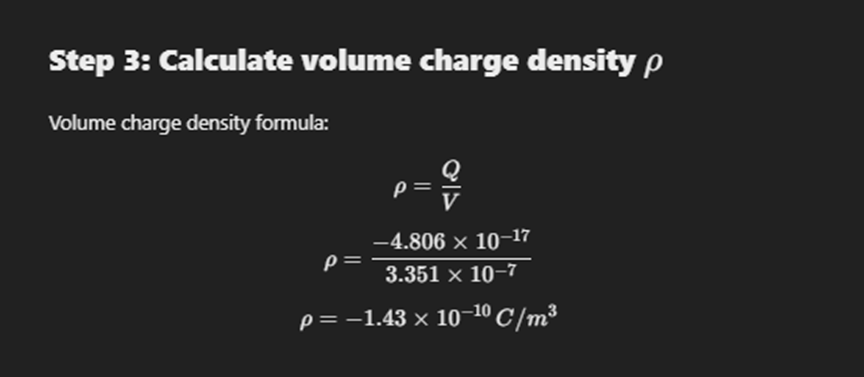
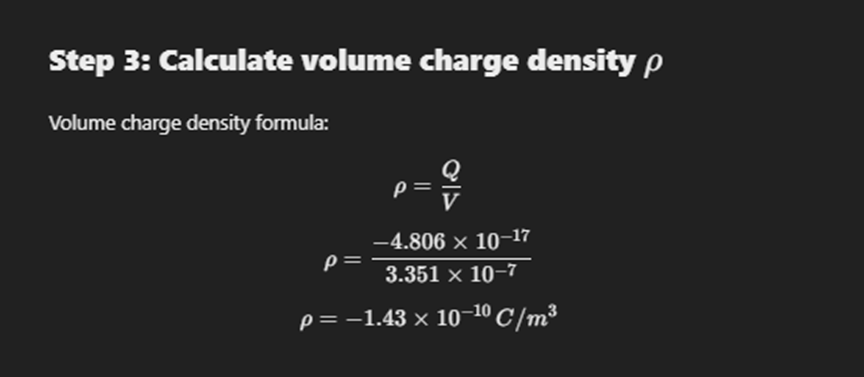




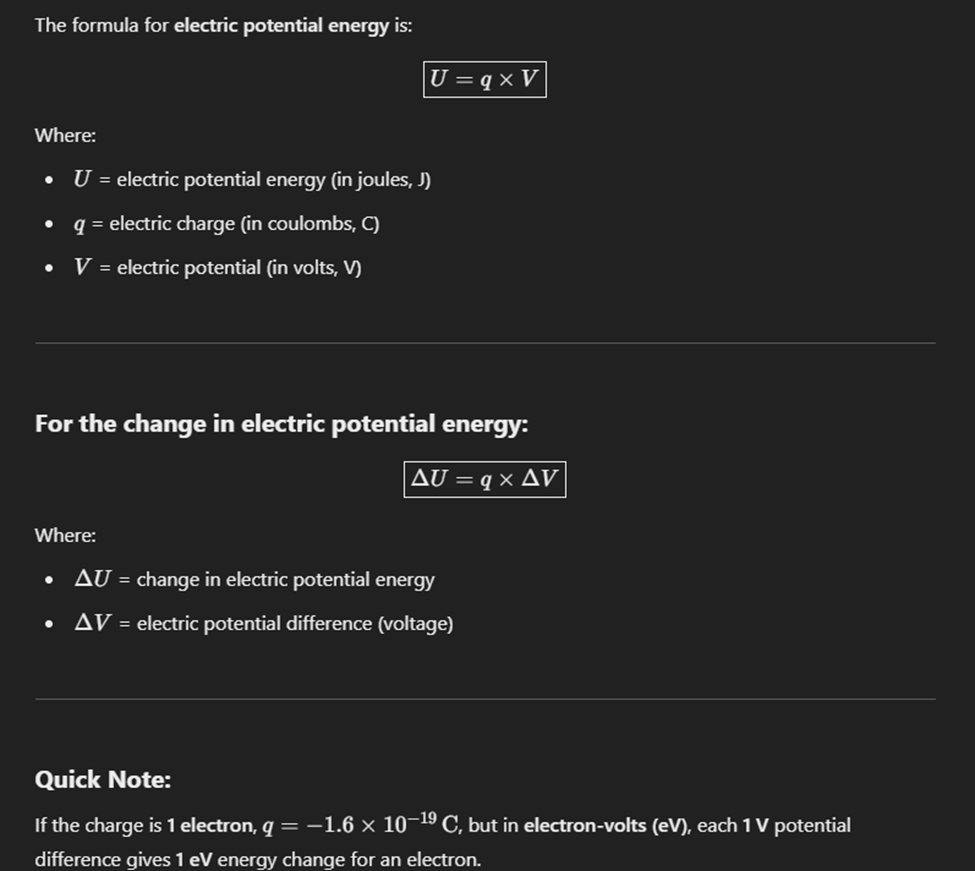
Electric Potential Energy(scalar)
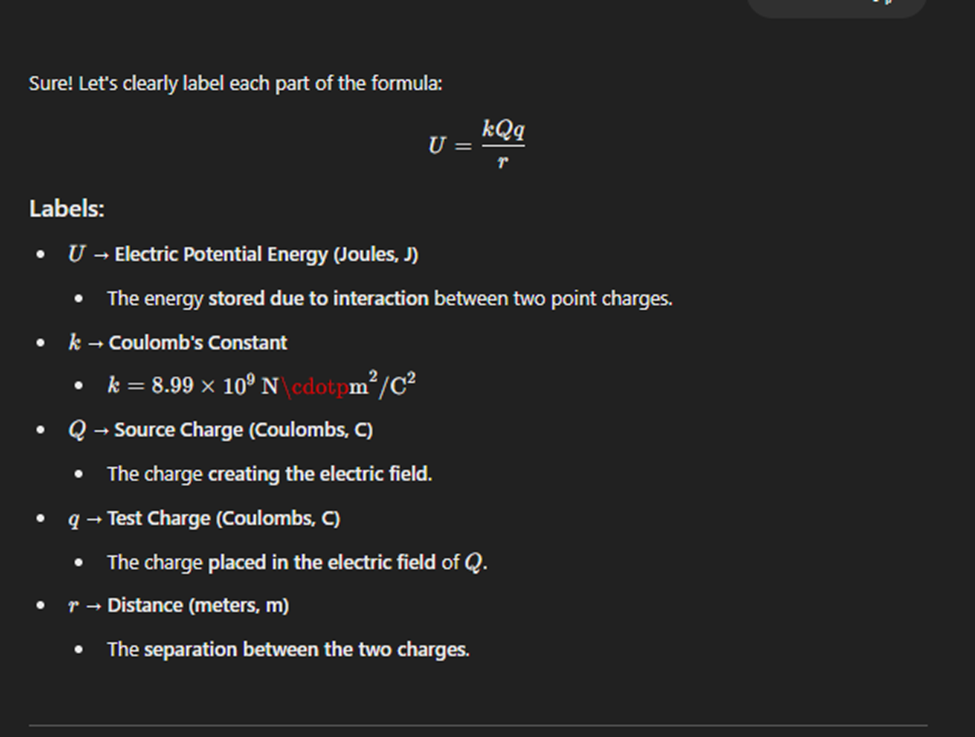
Electric potential at a point is the amount of electric potential energy per unit charge at that point in an electric field.
It tells us how much work is needed to move a charge to that point.

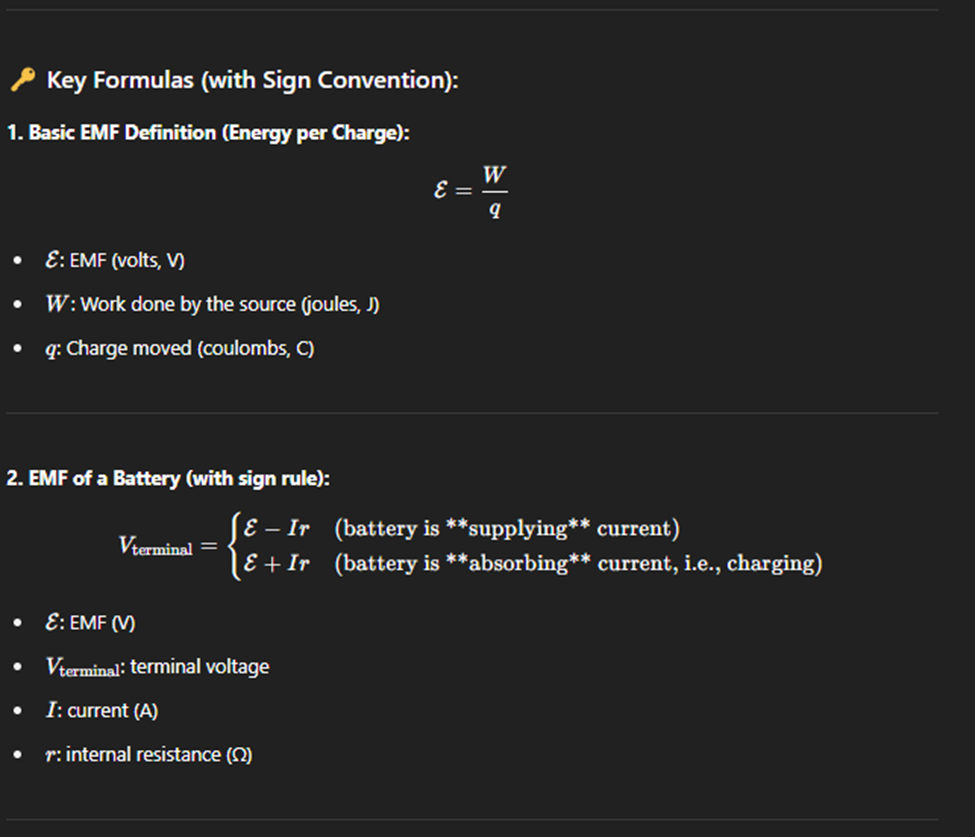
Electromotive Force (EMF)
Electromotive force (EMF) is the maximum potential difference a power source (like a battery or generator) can provide when no current is flowing (i.e., under open-circuit conditions).
Even though it’s called a “force,” EMF is actually a voltage.
If the battery is supplying
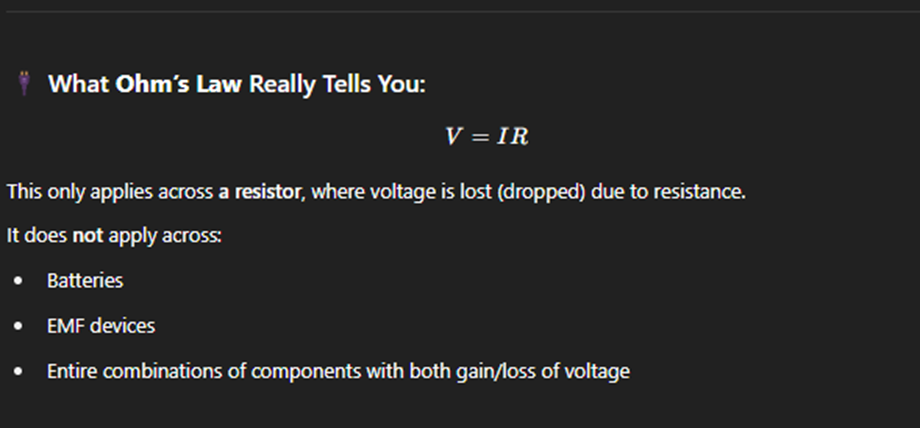
Ohm’s Law
Ohm’s Law states that the current (I) through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage (V) across the two points, provided the temperature remains constant.
This means:
The higher the voltage, the more current flows—as long as resistance stays the same.
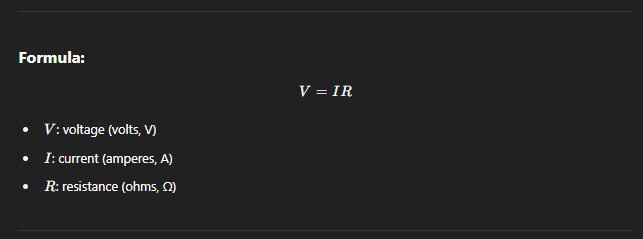
Law of Speed of Light in a Medium
The speed of light in a medium is governed by the refractive index of that medium. Light slows down when it enters a medium with a refractive index greater than 1. The higher the index, the slower the light

Law of Reflection
The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection, and both angles lie in the same plane as the normal to the surface.

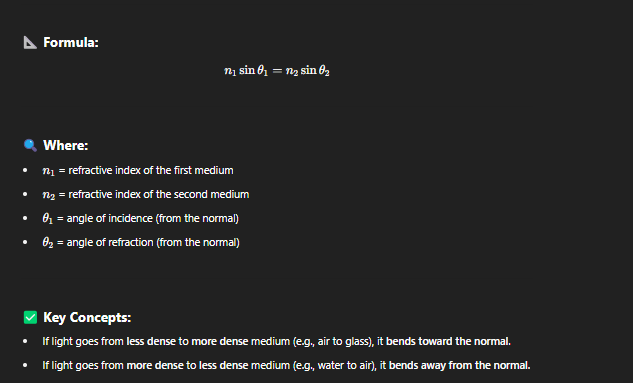
Snells Law
The ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is equal to the ratio of the indices of refraction of the two media.
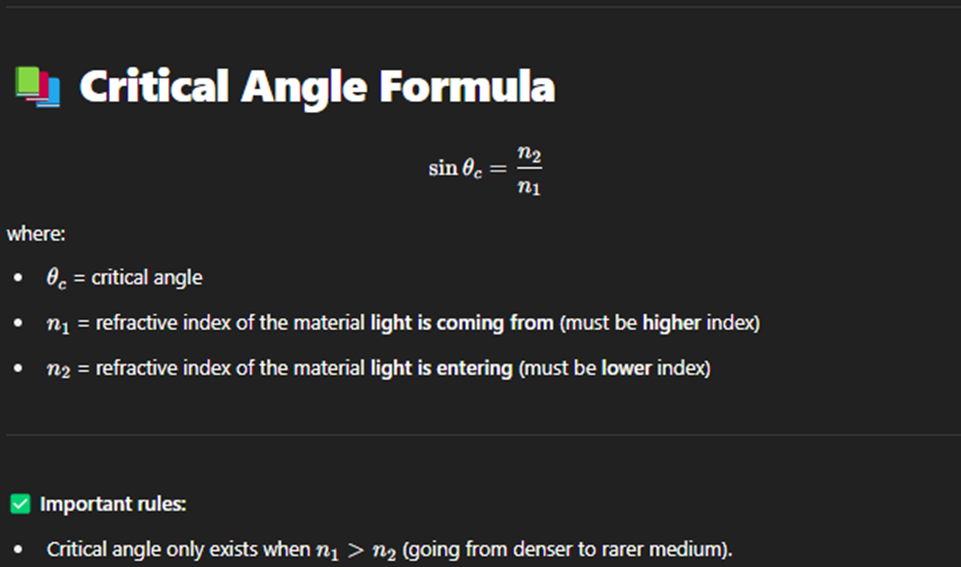
Critical Angle
Total internal refelction
The critical angle is the angle of incidence in a denser medium at which the refracted ray just grazes along the boundary.(When using the formula always use n1 as the larger refractive index).
Simple definition:
The critical angle is the smallest angle of incidence at which total internal reflection happens instead of refraction.
Total internal reflection: At θi>θc, Total Internal Reflection occurs (light reflects entirely back into the denser medium).
Constructive Interference
When two waves meet in phase (crests with crests, troughs with troughs), their amplitudes add together, resulting in a brighter or stronger wave.

Destructive Interference
When two waves meet out of phase (crest meets trough), their amplitudes cancel each other, resulting in a dimmer or completely cancelled wave.

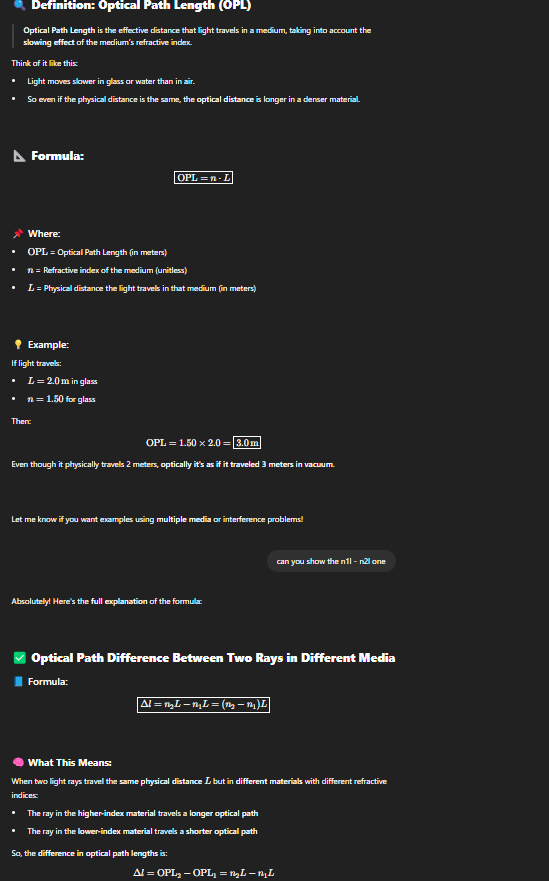
Optical Path Length (OPL)
Optical Path Length is the effective distance that light travels in a medium, taking into account the slowing effect of the medium’s refractive index.
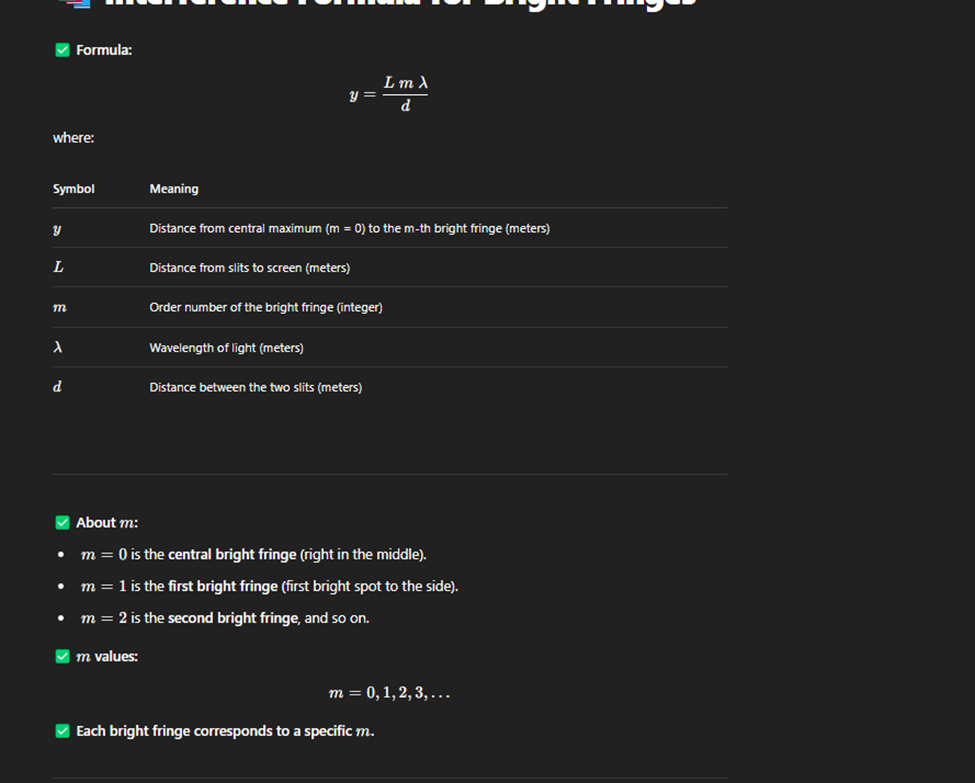
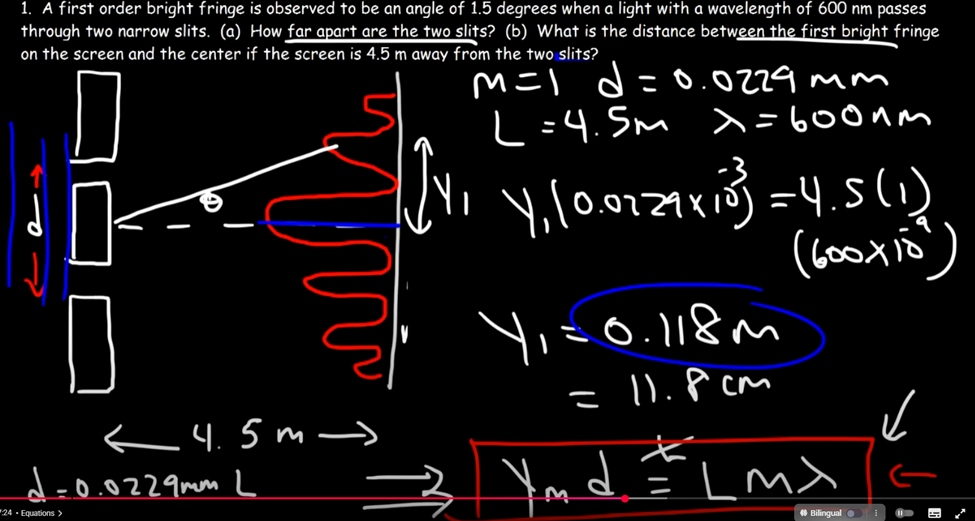
Double Split

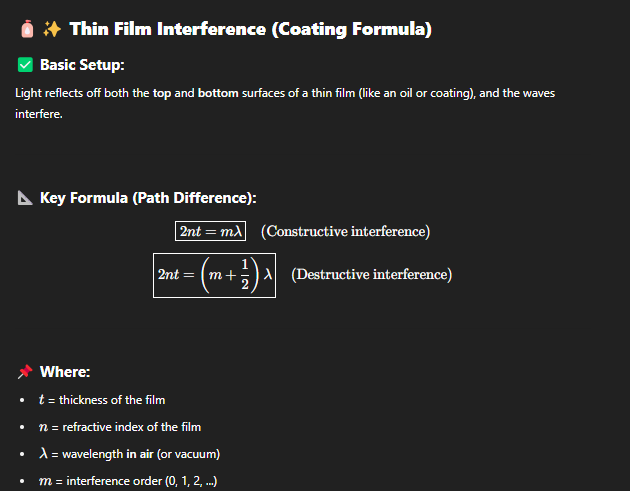
Coating Formla
n is the index of the coating,
If light reflects off a surface that’s thicker or slower (higher index), it flips — gets a λ/2\lambda/2λ/2 phase shift.
If it reflects off something thinner or faster (lower index), no flip — no phase shift.
when this happens constructive formula becomes destructive and vice versa
“Light of wavelength 624 nm is incident perpendicularly on a soap film (n = 1.33)
suspended in air. What are the (a) least and (b) second least thicknesses of the film for
which the reflections from the film undergo fully constructive interference?
“
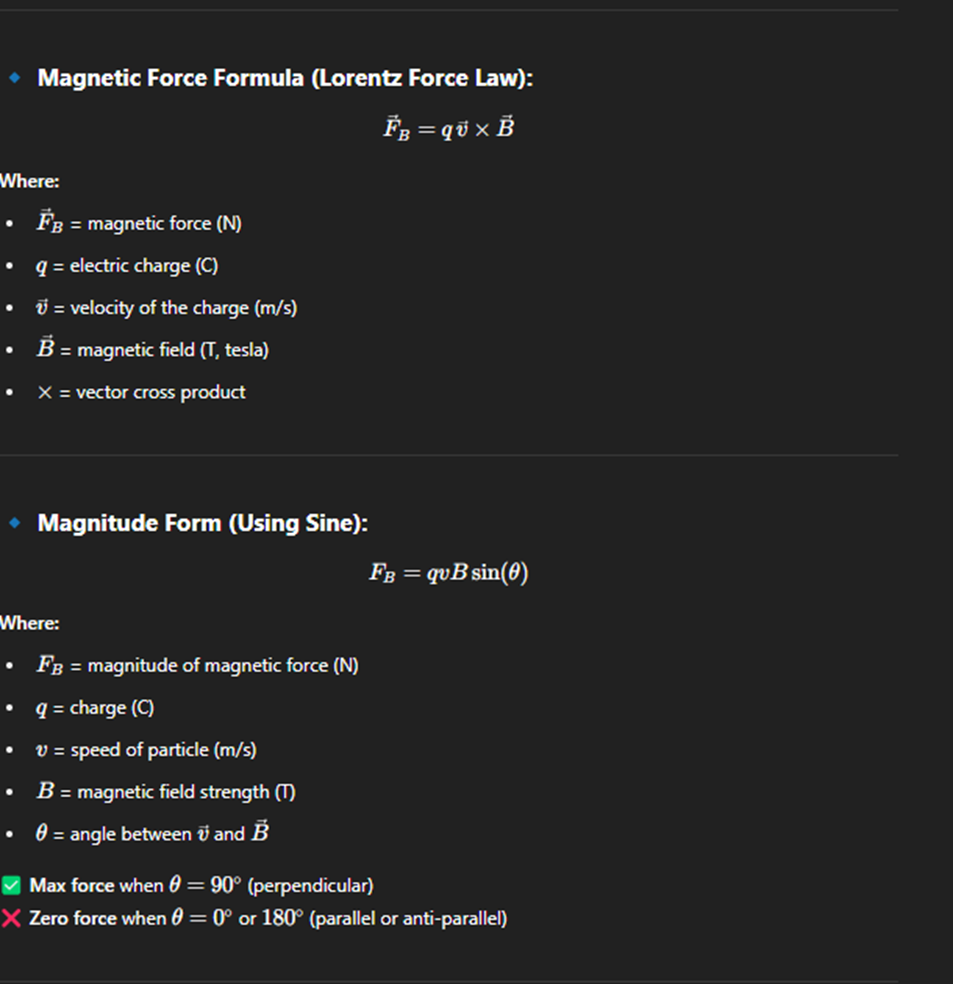
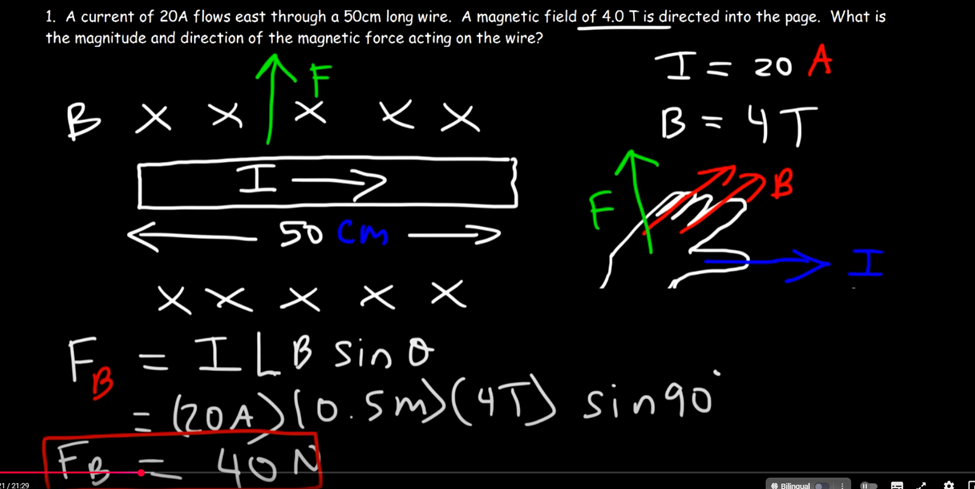
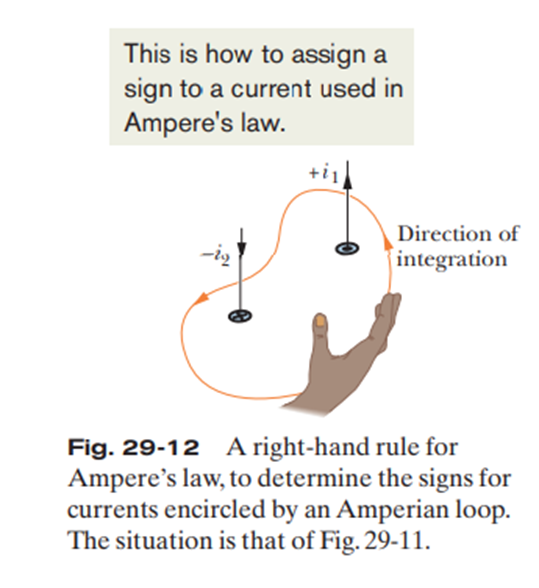
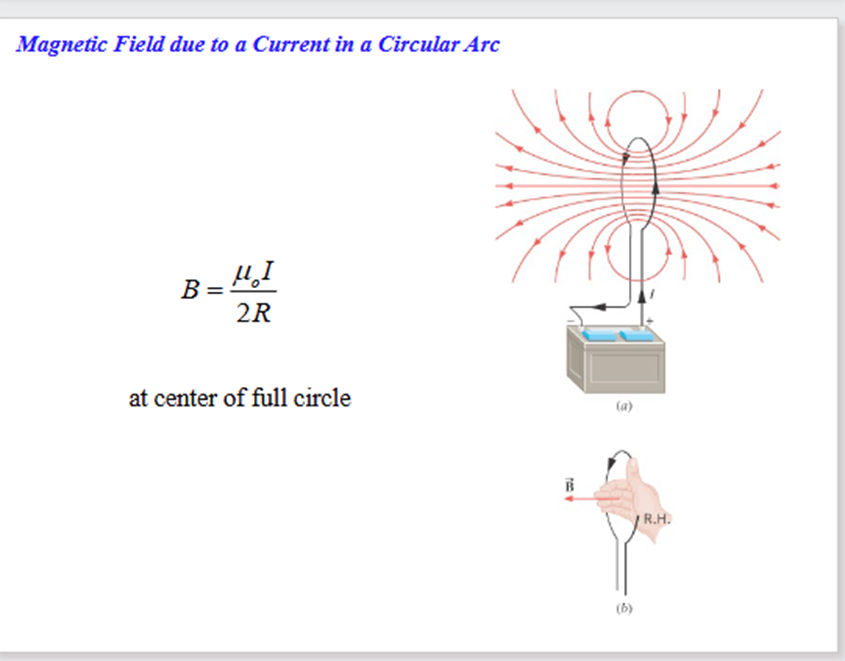
Magnetic Field Force
A region in witch moving charges experience a magnetic force.
(When circle B Goes out page, use the sin formula )

Magnetic Force on a current carrying wire
When a current flows through a wire in magnetic field, the wire experiences a magnetic force.


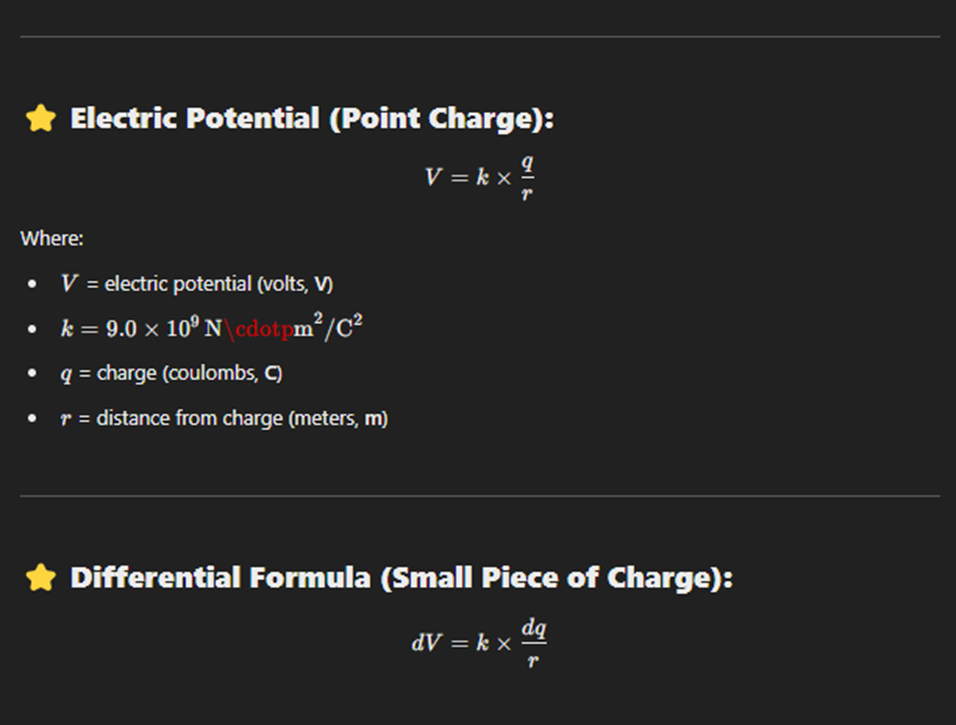
Potential Difference
Potential difference (also called voltage) is the amount of work done per unit charge to move a charge between two points in an electric field.
It tells you how much energy a charge gains or loses when moving between two points.

Cross Product
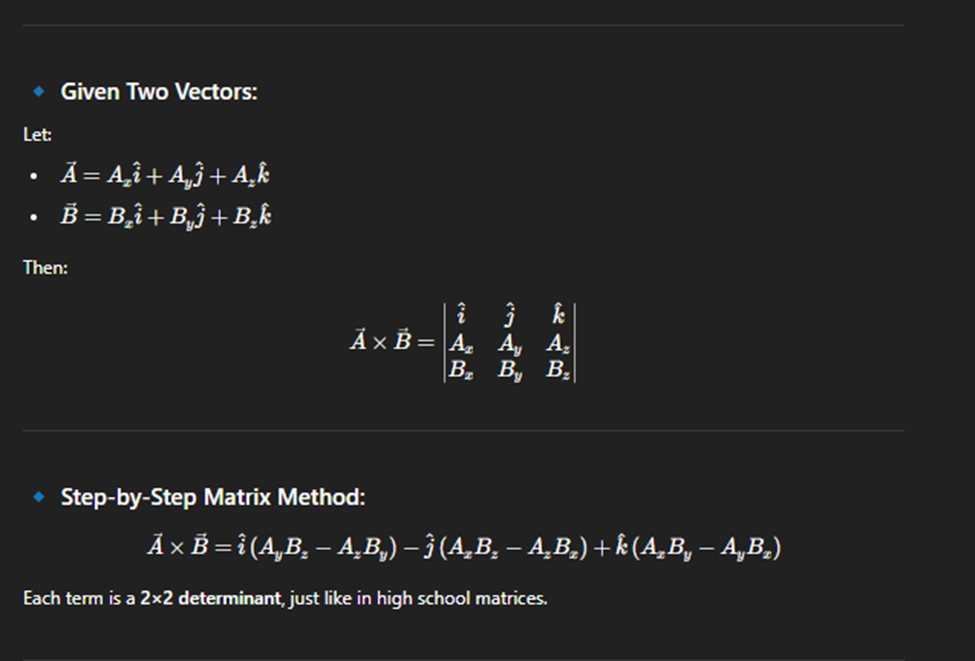

Put in the matrices
i : Remove that part from matrices and just do the other 2 sides
so just do the j and k. and cross look at example.
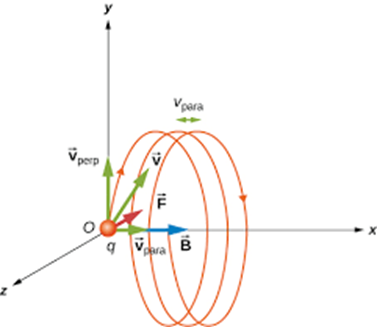
Helical Path
A helical path is the three-dimensional spiral motion of a charged particle when it moves through a uniform magnetic field at an angle (not perpendicular or parallel) to the field.
This path combines:
Circular motion (due to the perpendicular component of velocity to the magnetic field),
and linear motion (along the direction of the magnetic field).
Think of it like a spring-shaped or corkscrew-like path — spiraling forward.

Dot Product

Parallel and Series
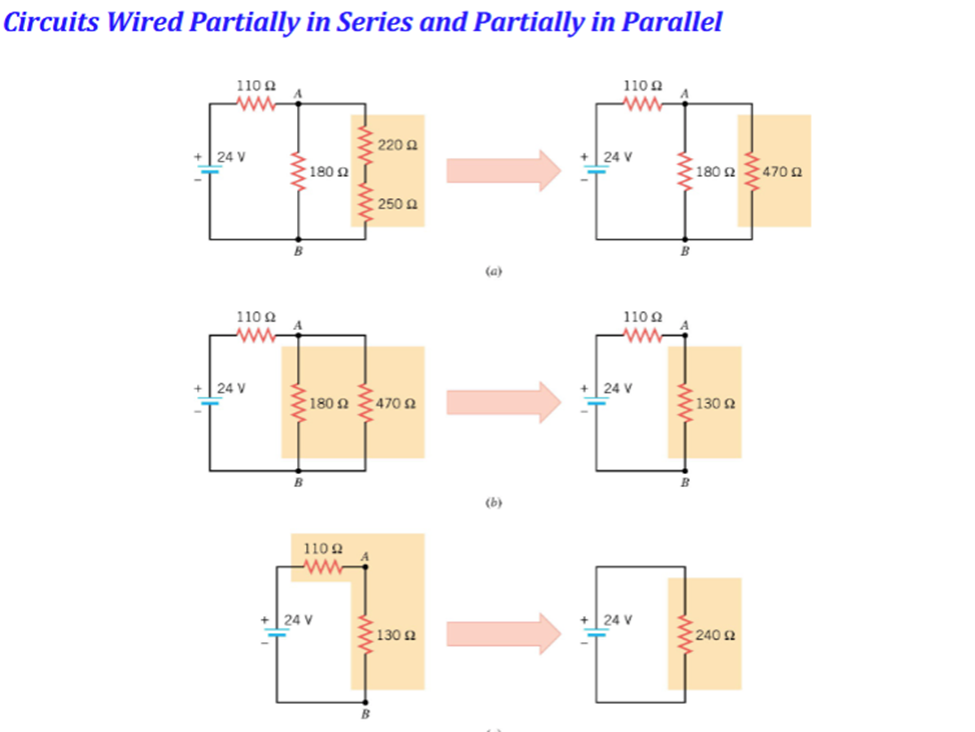
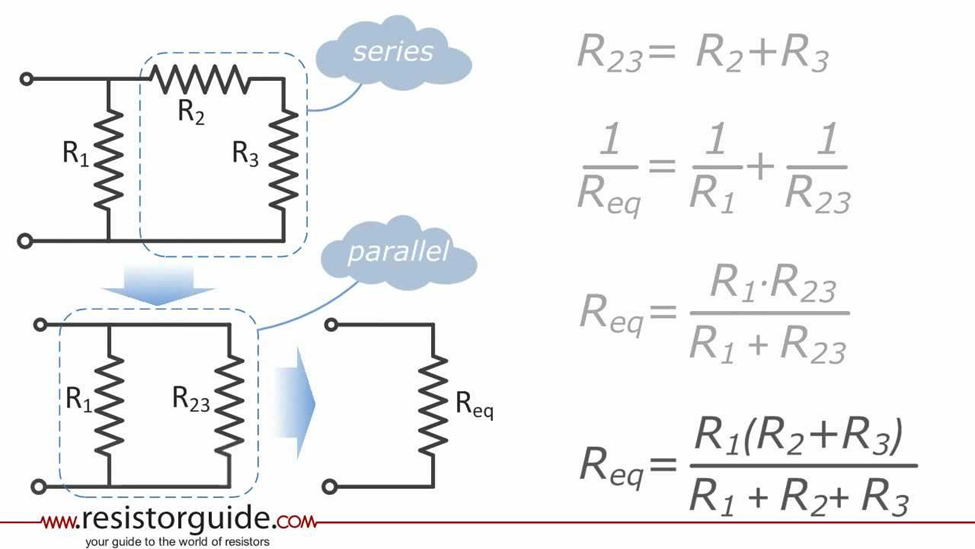
Adding In series:
Calculate new voltage (if you know the voltage in both before just add those together), but the current before is same after
Adding in parallel:
Voltage Before is same after (You cannot parallel connect two points that have different voltages without something bad happening.), Calculate the new current
Use Ohms law to calculate
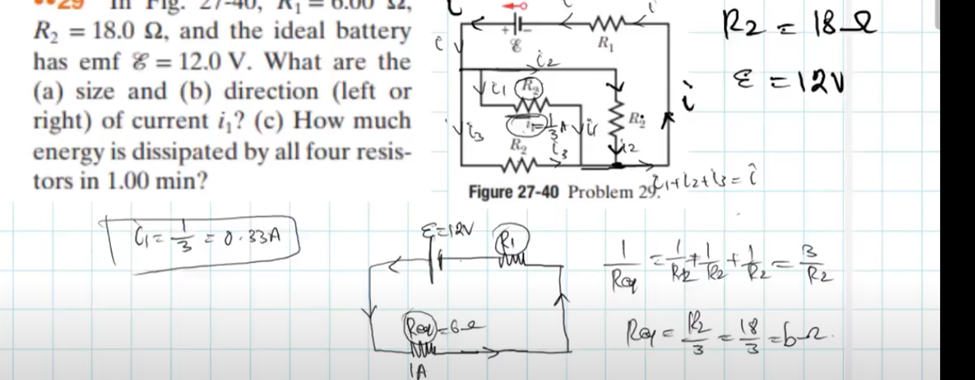
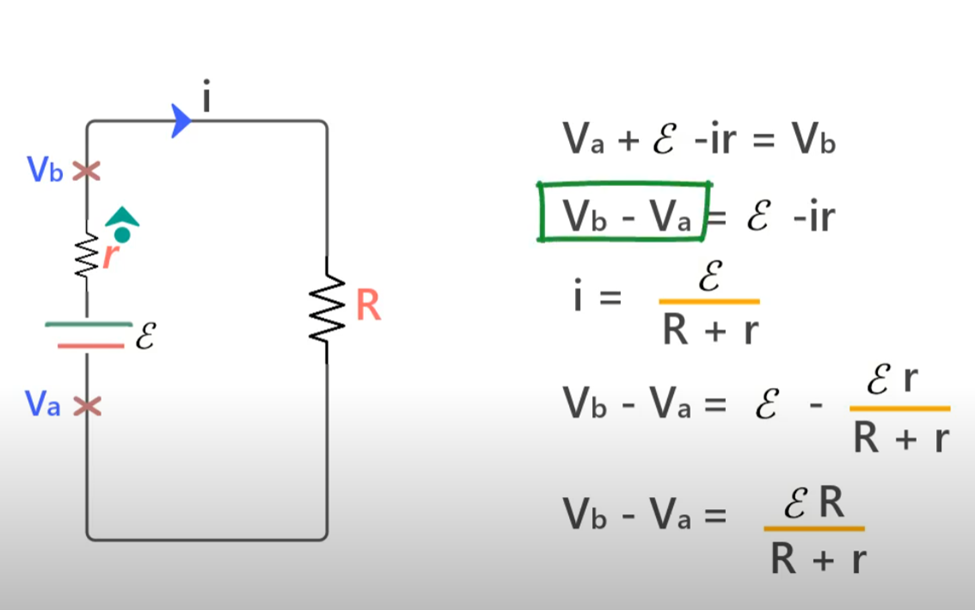
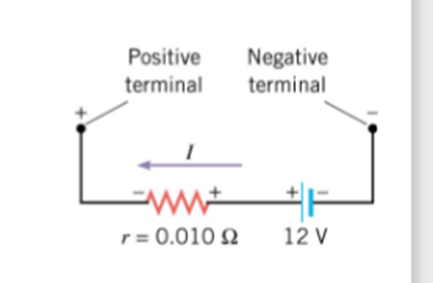
The circuit goes clockwise so yeah and just find a direct path to find potential difference 2 points.
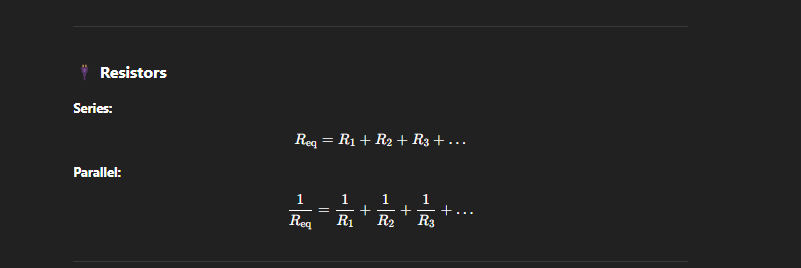
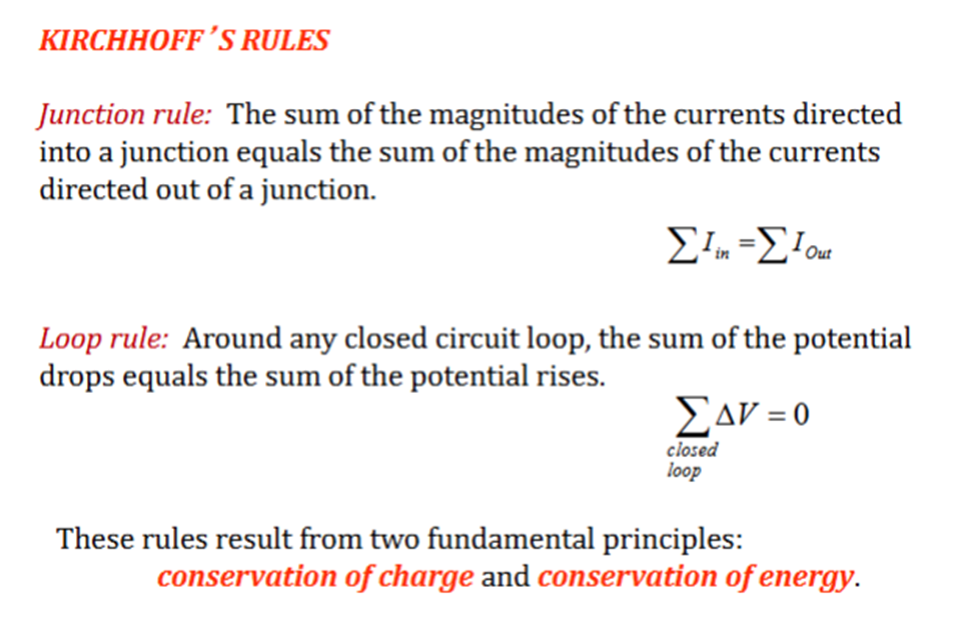
Kirkcoffs laws
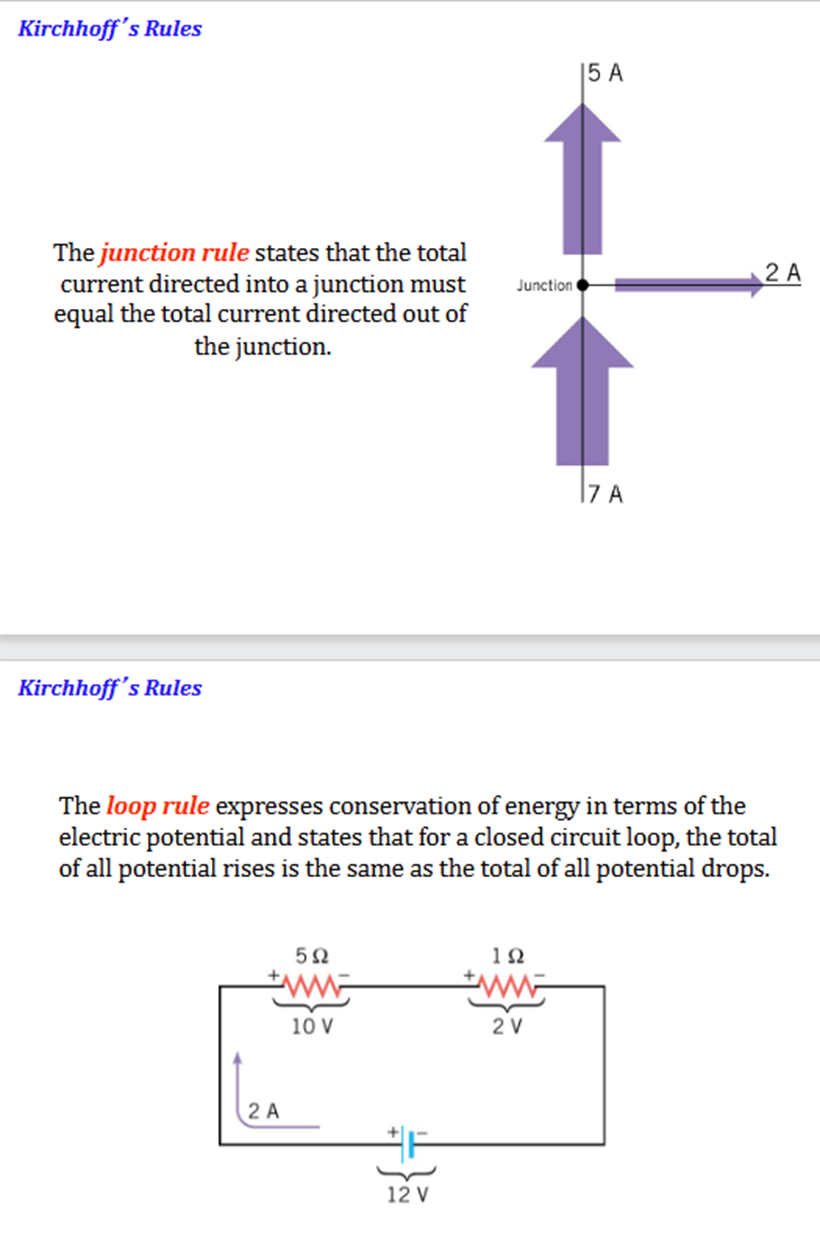
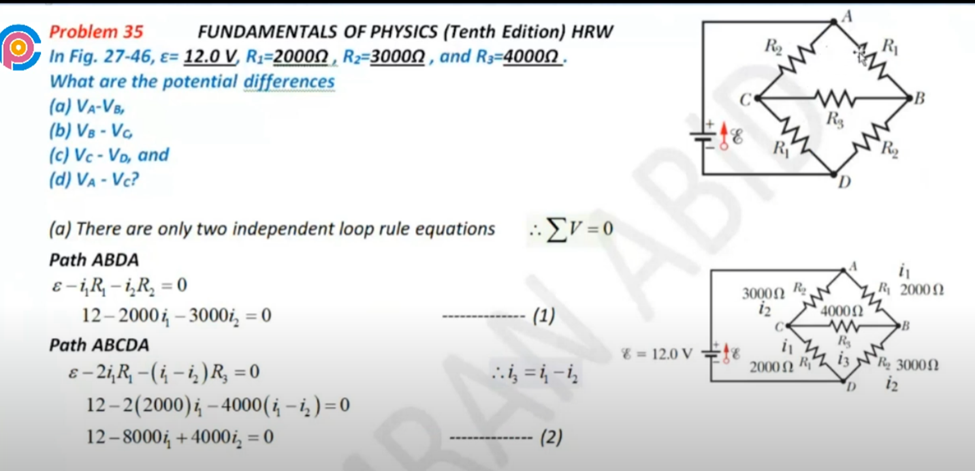
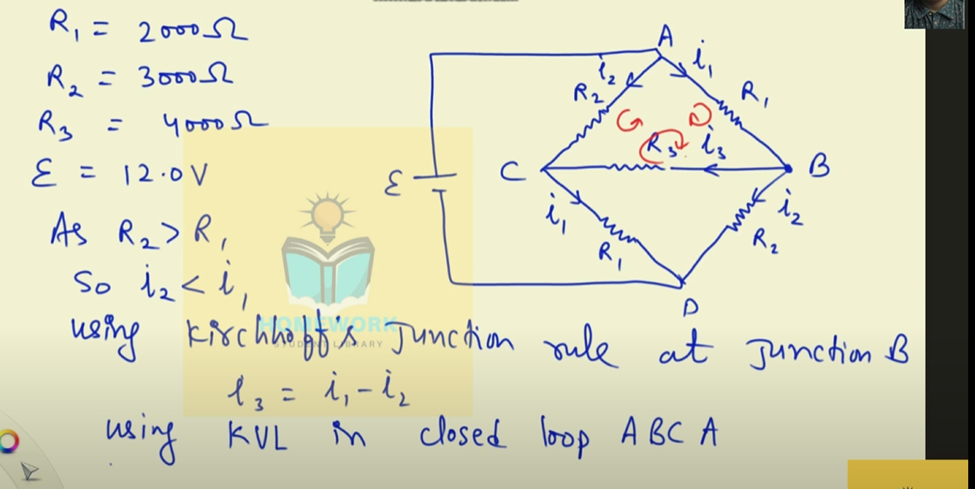
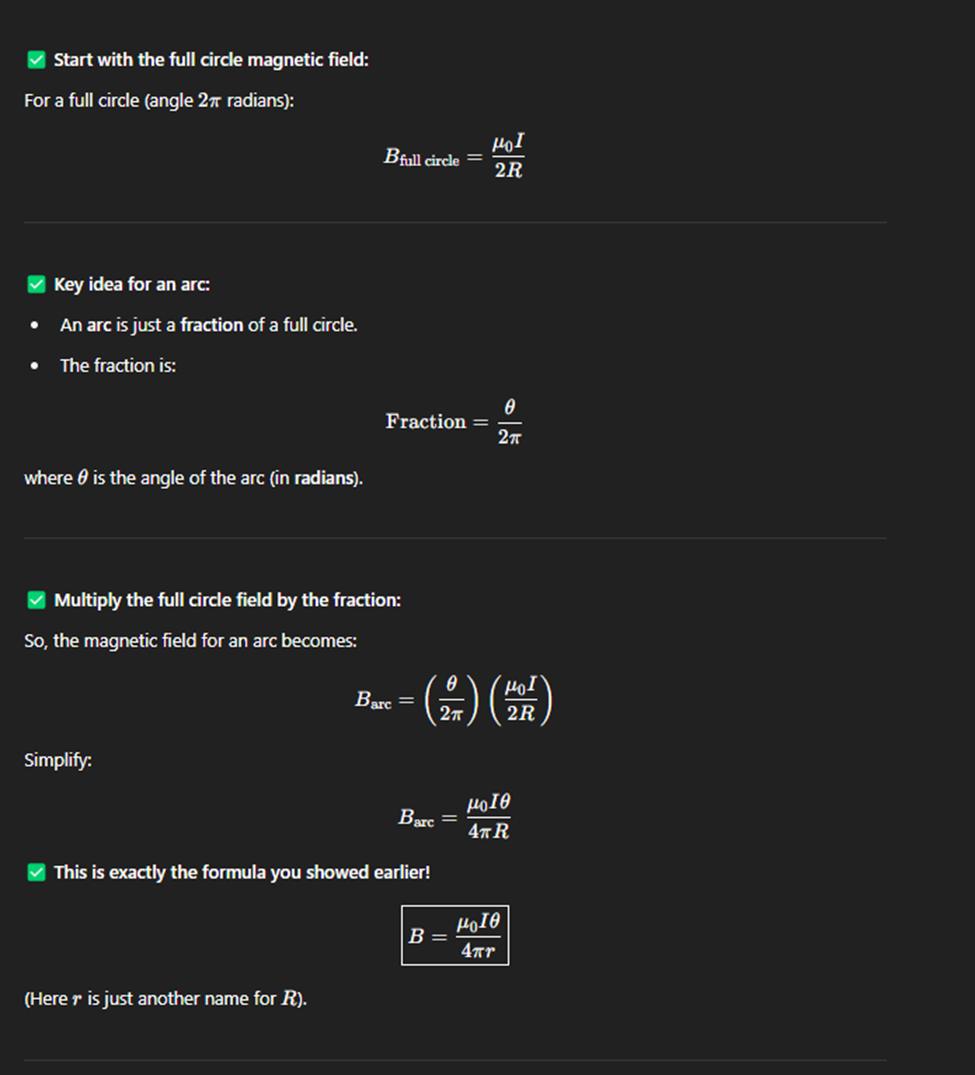
Bio Savart Law
The Biot–Savart Law describes the magnetic field produced at a point in space due to a small segment of current-carrying wire. It's fundamental in magnetostatics and is analogous to Coulomb's law in electrostatics.

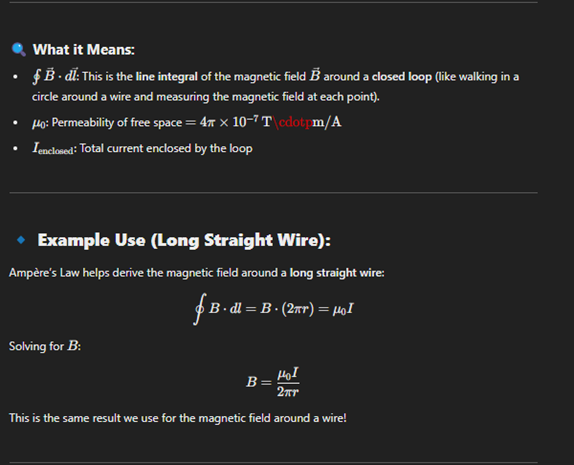
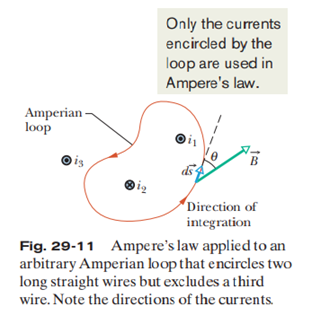
Ampère’s Law
Ampère’s Law says that the magnetic field around a closed loop is related to the total electric current passing through that loop.
Simplified Definition:
The more current flows through a wire or loop, the stronger the magnetic field it creates around it.



solenoid
A solenoid is a long coil of wire wound in the shape of a cylinder. When electric current passes through it, it creates a nearly uniform magnetic field inside the coil. Solenoids are commonly used in electromagnets, inductors, and valves.

Magnetic Flux
Magnetic flux is a measure of how much magnetic field passes through a given area.
(Think of it like the number of magnetic field lines going through a surface.)

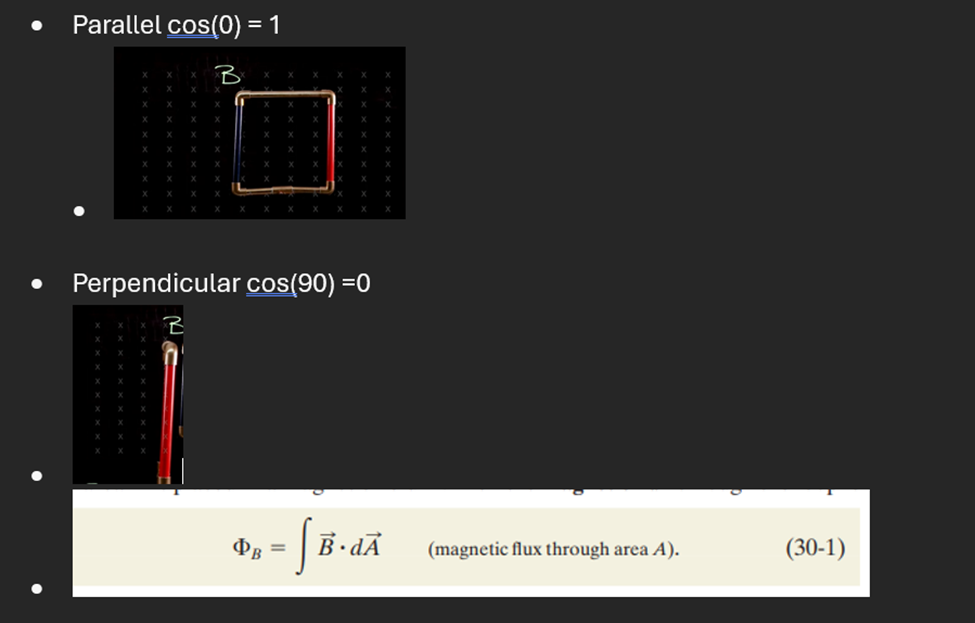
If above the horizontal do 90 – degree of horizontal


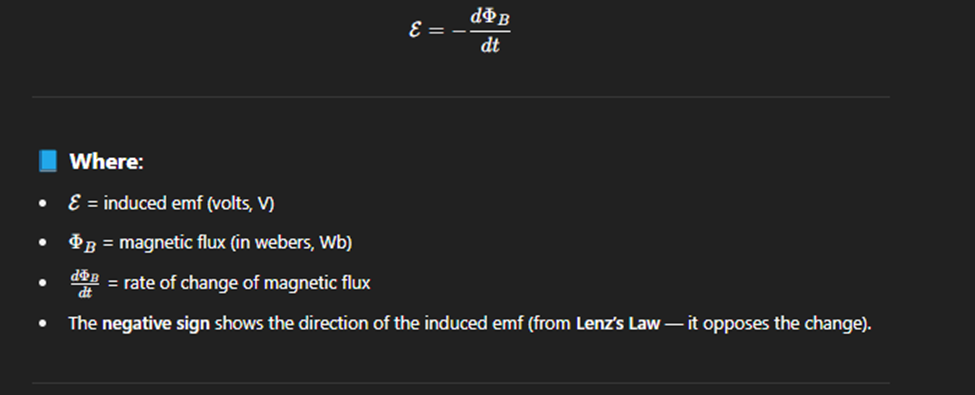
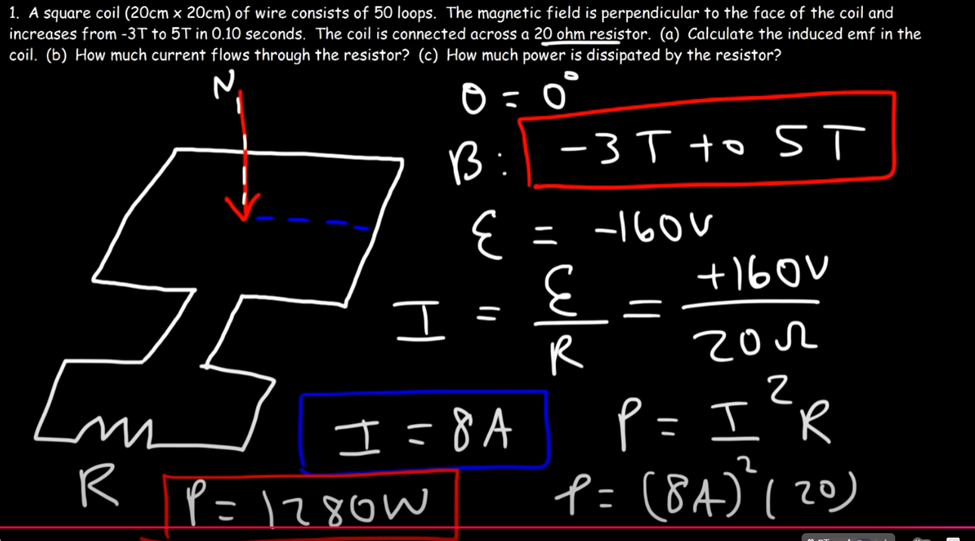
Faradays Law
Faraday's Law of Electromagnetic Induction states that a change in magnetic flux through a circuit induces an electromotive force (EMF) in the circuit.
· Simple Definition:
· If the magnetic field through a loop changes, it creates a voltage (EMF).
In other words:
· Changing magnetic field = Electricity generated




Lenz Law
· Lenz's Law states that the direction of the induced current (or EMF) is such that it opposes the change in magnetic flux that caused it.
· Simple Definition:
· When a magnetic field changes, the current it creates will act in a way that tries to stop that change.
The the magnetic field that acts because of lenz law is called the induced magnetic field
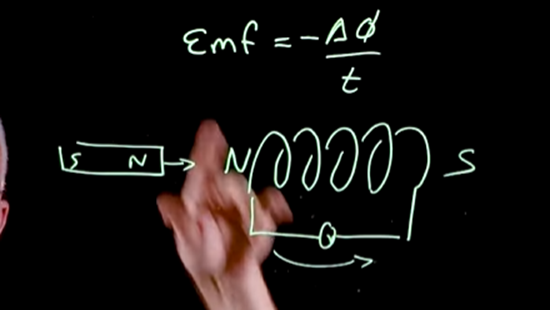
· As the magnet pushes in coil, it produces a north pole to oppose to magnet. If the magnet moves away the coil will produce a south pole, to bring the magnet closer. This is related to conservation of energy.
Capacitor
A capacitor is an electrical component that stores electric charge and energy in an electric field between two conductive plates separated by an insulating material (called a dielectric).
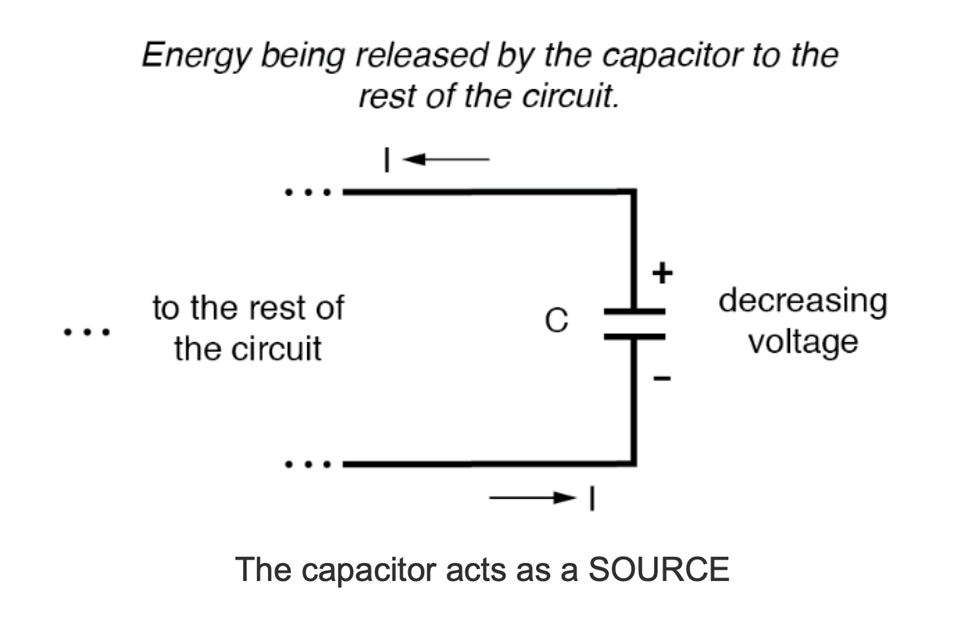

Resistor acts as a discharger
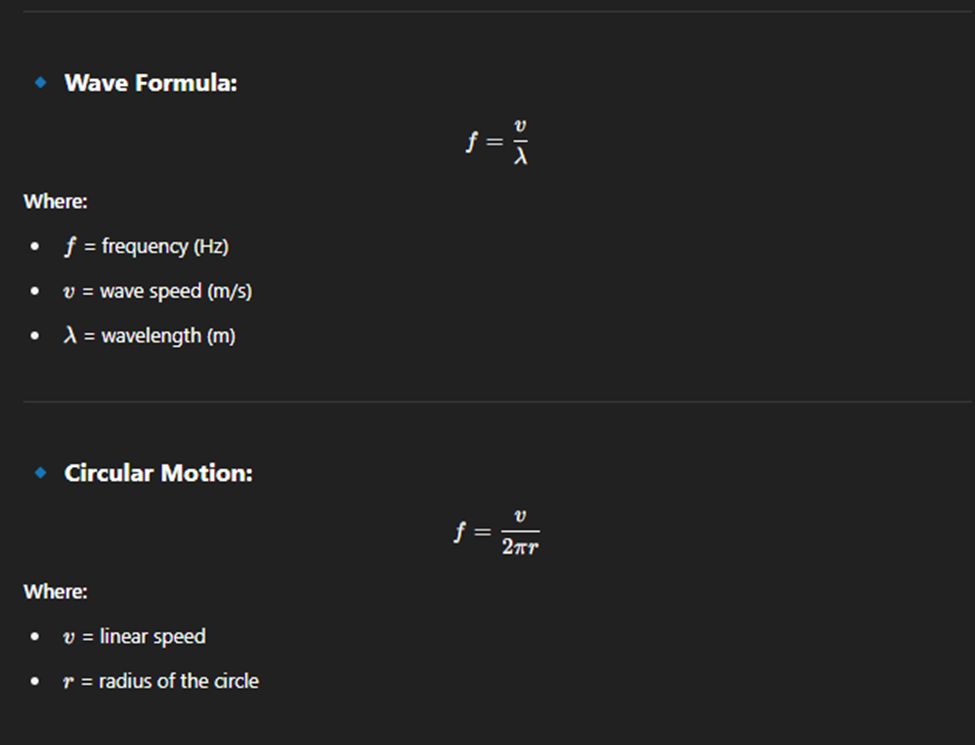
WaveLength
Angular Wave Number
Wavelength - distance between 2 consecutive points on a wave phase
Angular Wavenumber
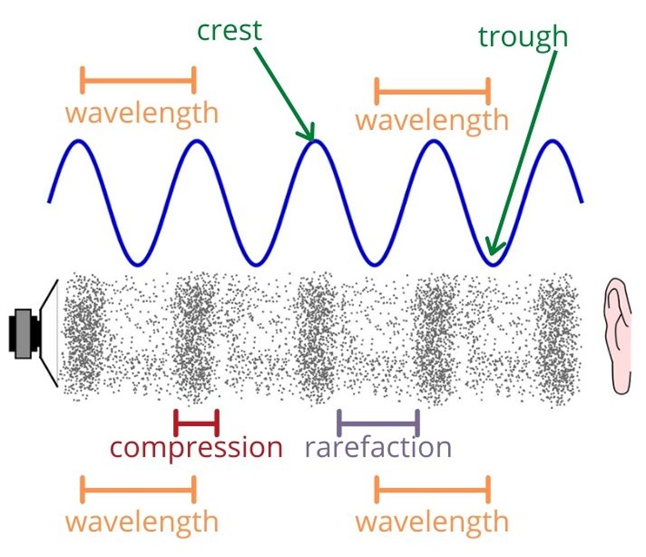

Period, Frequency
Period time complete one full wave cycle
Frequency Number of wave cycles in a second



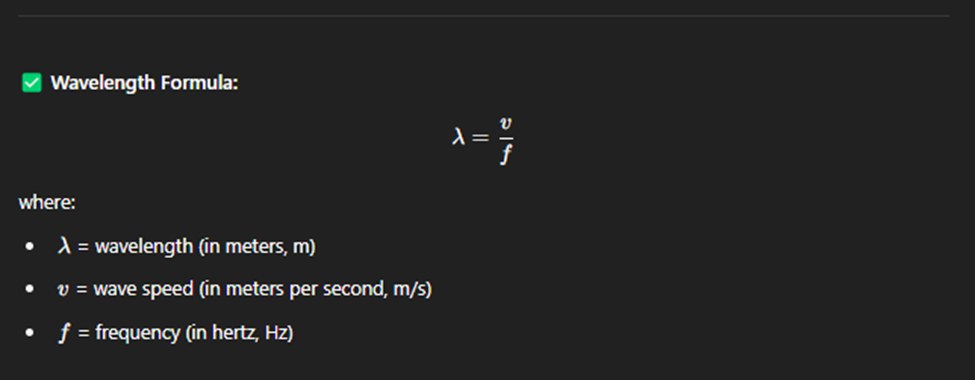
Angular Frequency, Angular Velocity
Angular Frequency - How quickly the wave oscillates
Angular Velocity - Measures how fast something rotates around a circle.

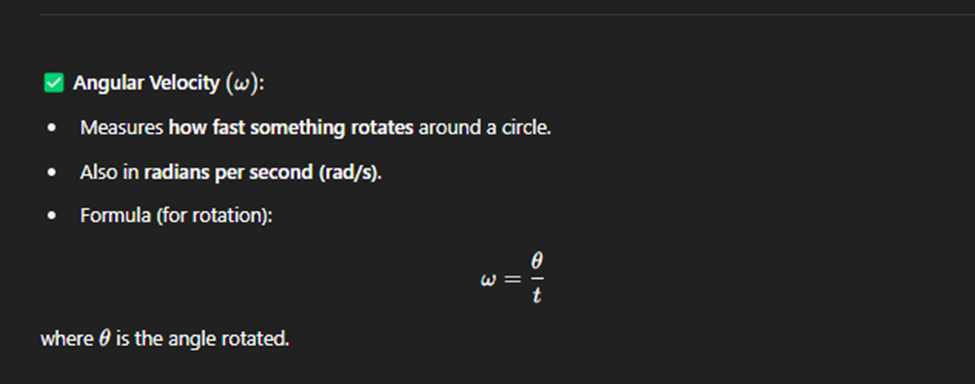
The Wave Function

Wave Speed


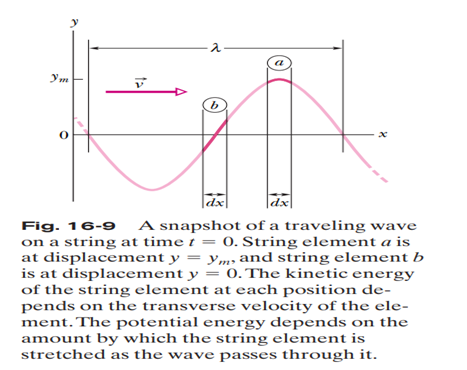
Points on a transverse wave

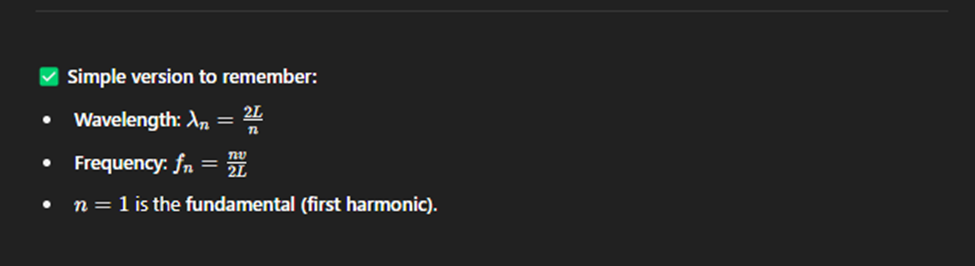
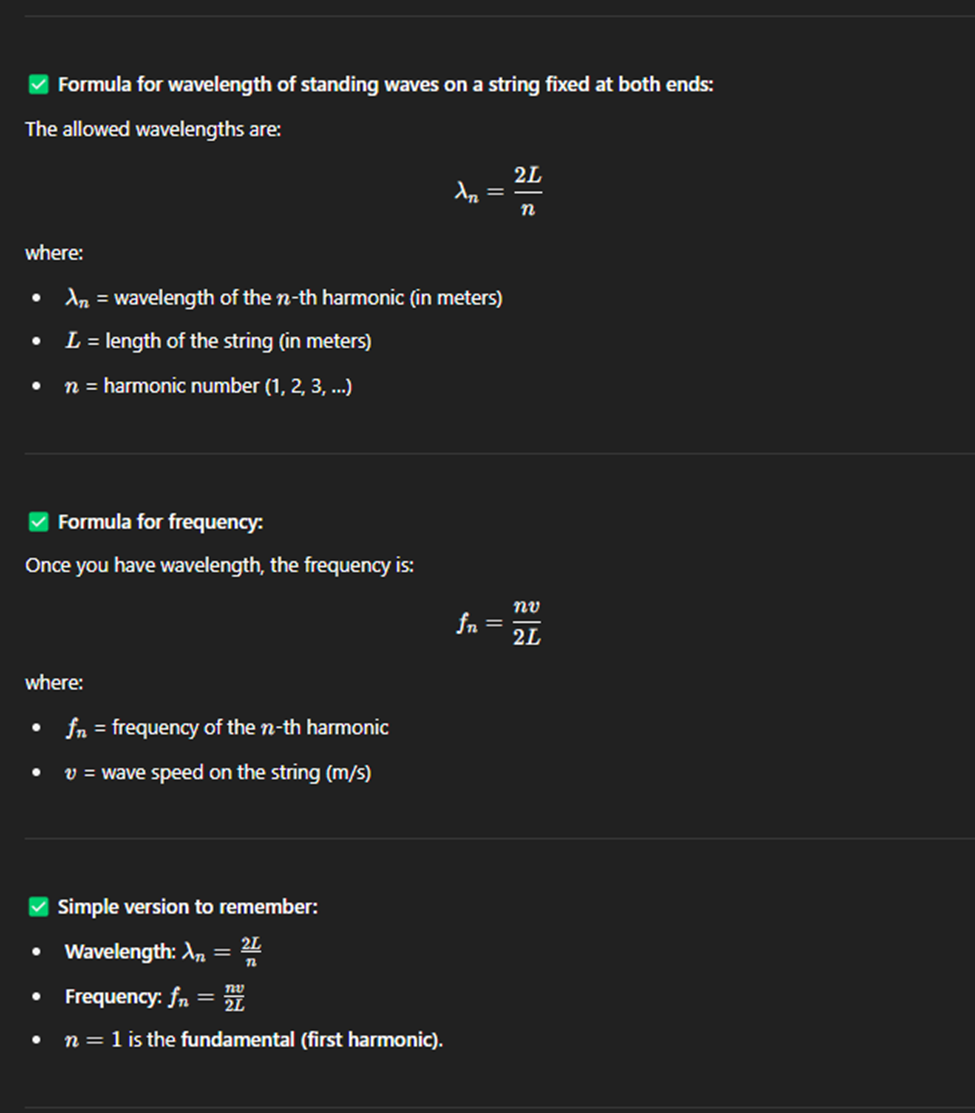
String Fixed at Both Ends
A string fixed at both ends means the ends of the string cannot move, and standing waves form along the string when it vibrates.
Only certain wave patterns (called harmonics) are allowed.

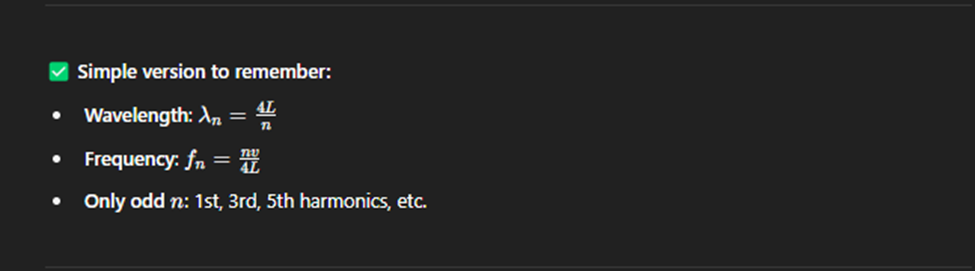
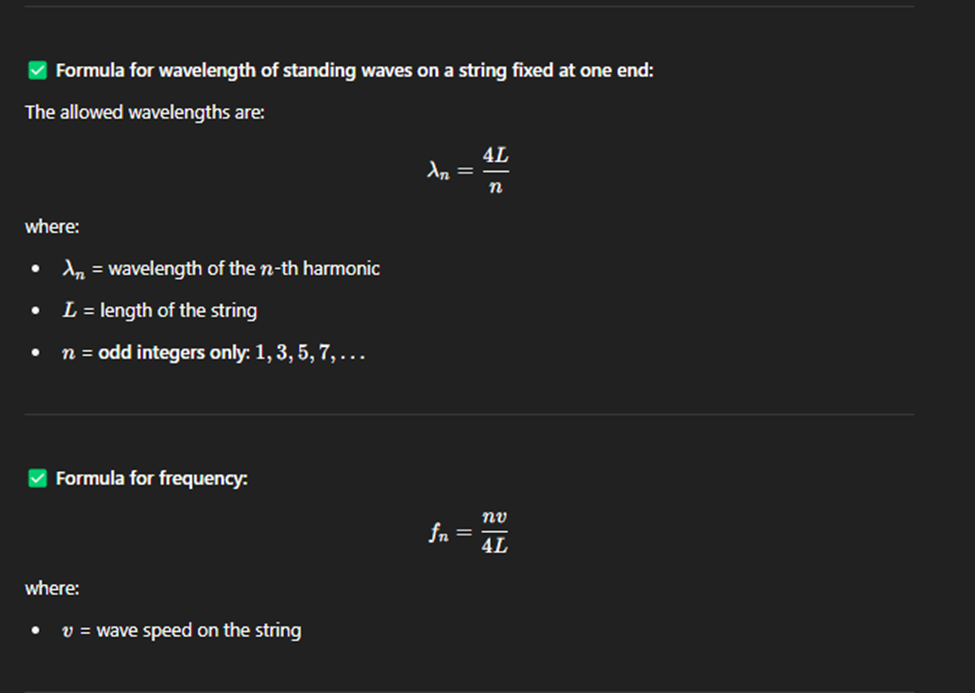
String Fixed at One End
A string fixed at one end and free at the other end means one end cannot move (node) and the other end is free to move (antinode).
This setup creates standing waves, but only odd harmonics are allowed.
Wave Inteference


Constructive louder sound, destructive lower sound
Sound Intnesity

Doppler Effect
The Doppler effect is the change in frequency or wavelength of a wave when the source or observer is moving.
In simple words:
If something moves toward you, the sound (or light) gets higher in pitch or frequency.
If it moves away from you, the sound gets lower.

Single Slit

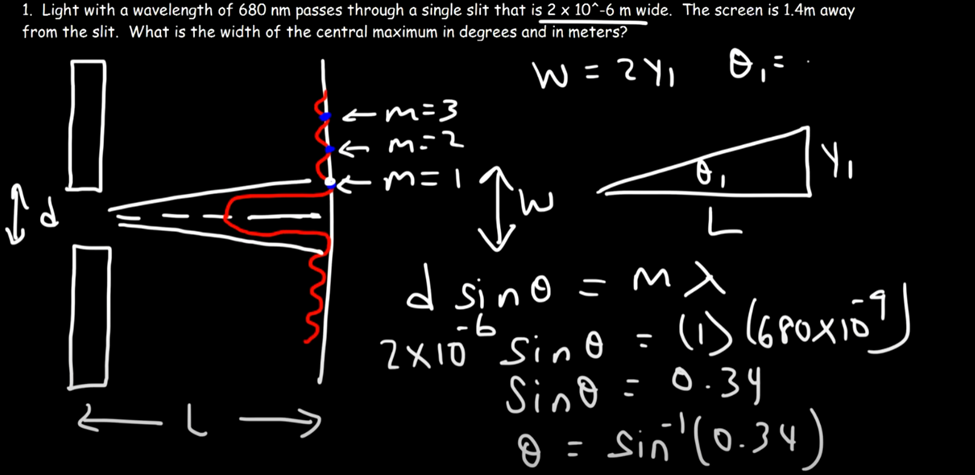


Diffraction Double Slidth

Diffraction Gratings



Real Image
✅ Real Image — Definition:
A real image is formed when light rays actually meet at a point after reflecting from a mirror or refracting through a lens.
✅ Key Properties of a Real Image:
The image can be projected onto a screen.
It is usually inverted (upside down).
Formed by converging light rays.
Created by concave mirrors or converging lenses when the object is outside the focal point.
Virtual Image
Virtual Image — Definition:
A virtual image is formed when light rays only appear to meet but do not actually meet after reflection or refraction.
✅ Key Properties of a Virtual Image:
The image cannot be projected onto a screen.
It is usually upright (right-side up).
Formed by diverging light rays.
Created by:
Plane mirrors (normal mirrors you use every day)
Convex mirrors
Converging lenses when the object is inside the focal point.
✅ Simple words:
A virtual image is an illusion made by light — it looks real, but light rays don’t actually come from where you see the image.
Sign Convention (Spherical and plane mirrors)
Virtual image mirrror opposite side
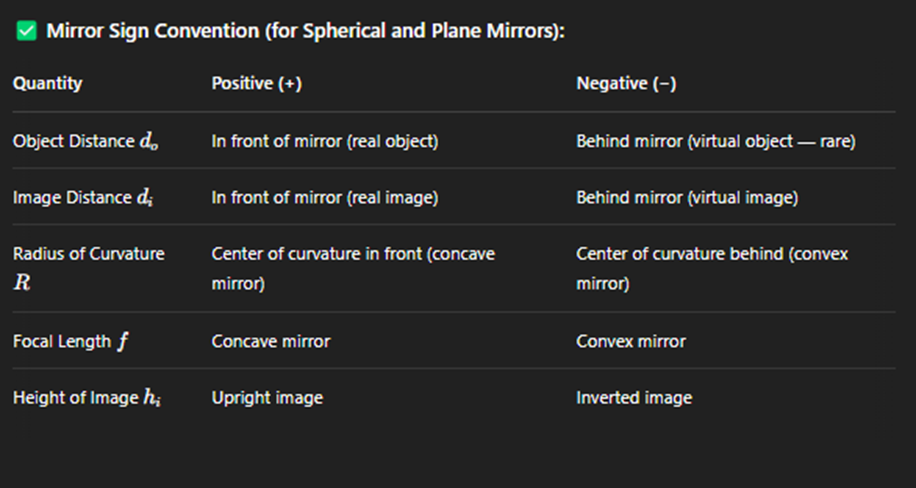
Sign Convention Lenes
Virtual image lens same side

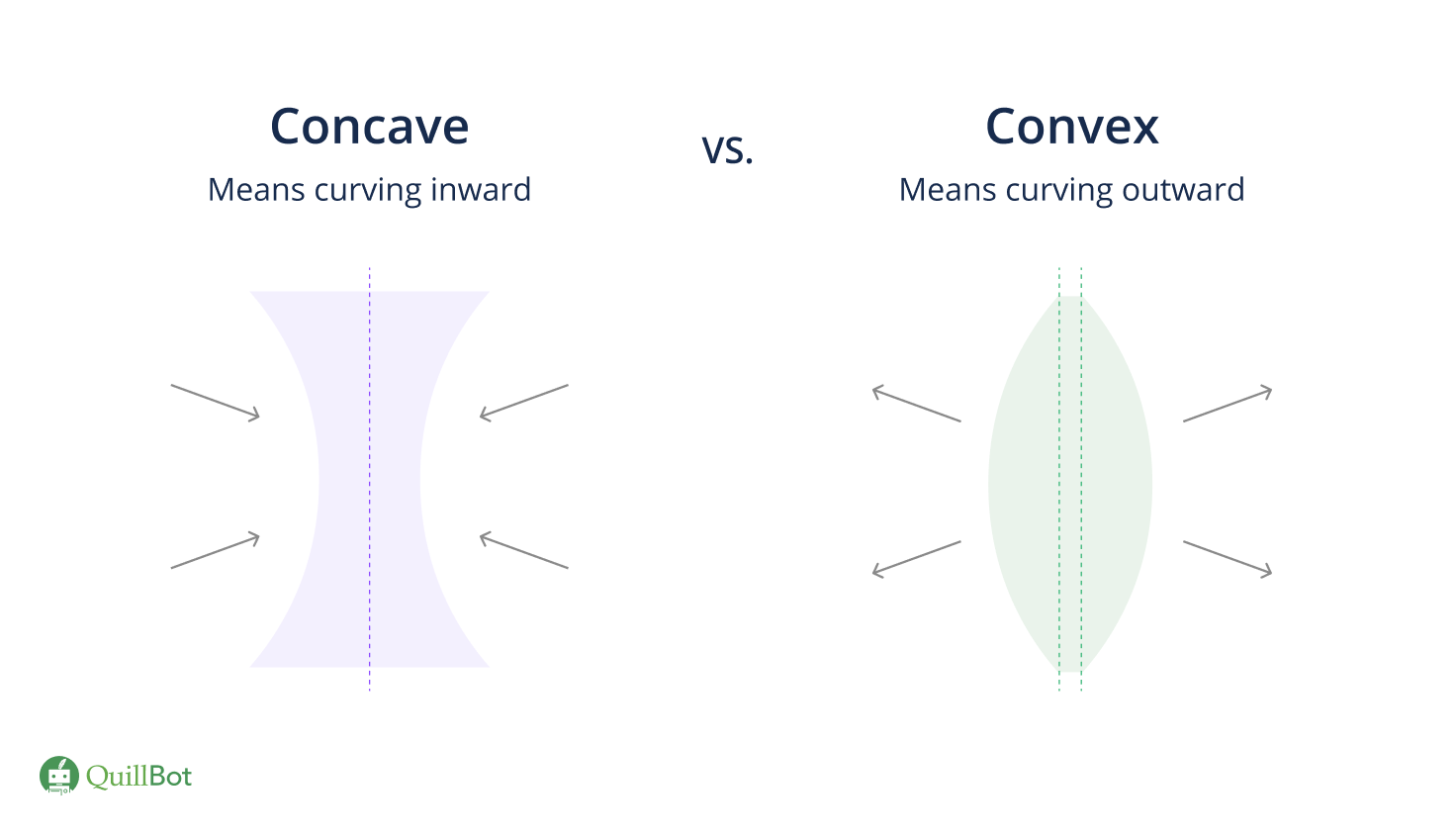
Concave and Convex
Concave (Diverging)
Convex (Converging)
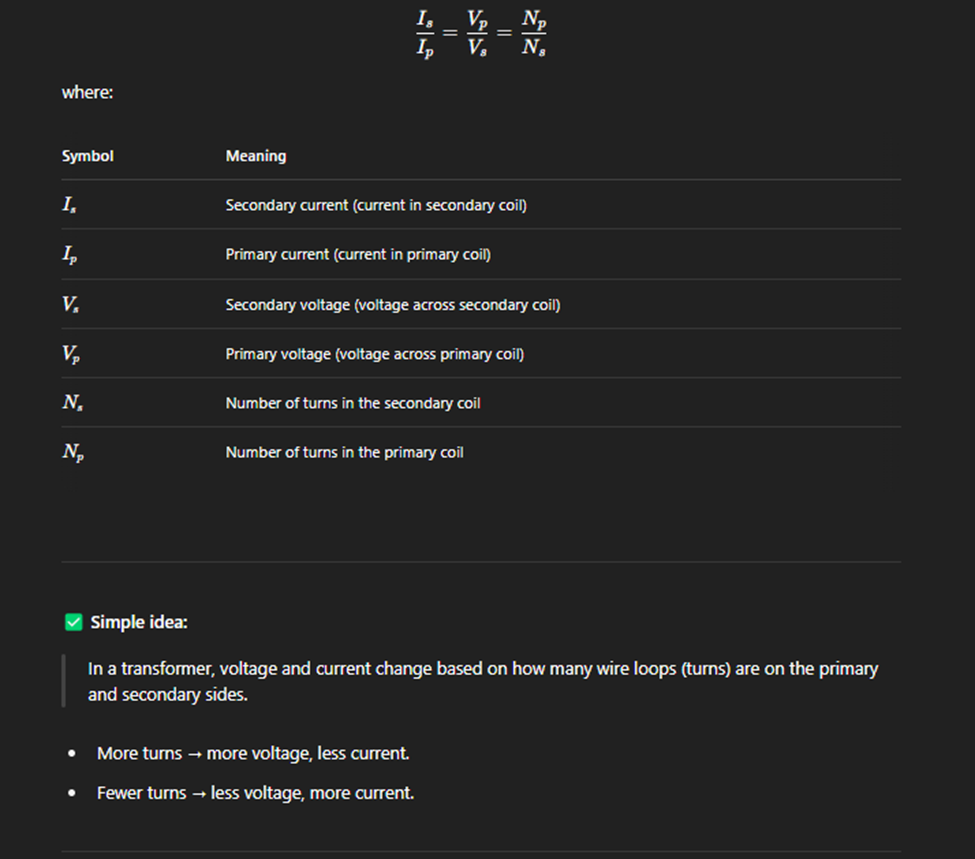
Transfomer
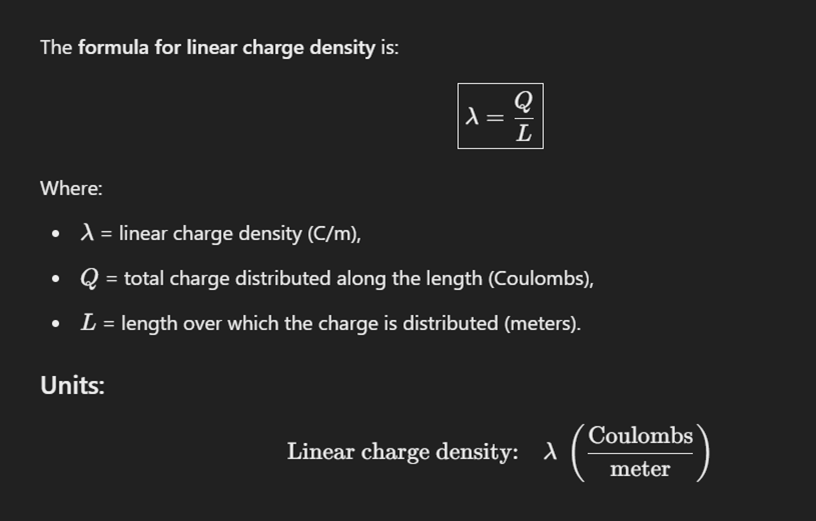
Linear Charge Density