Tooth Surface Loss - Monitoring and Management
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
What is abrasion?
physical wear by objects other than another tooth
eg tools like lewis
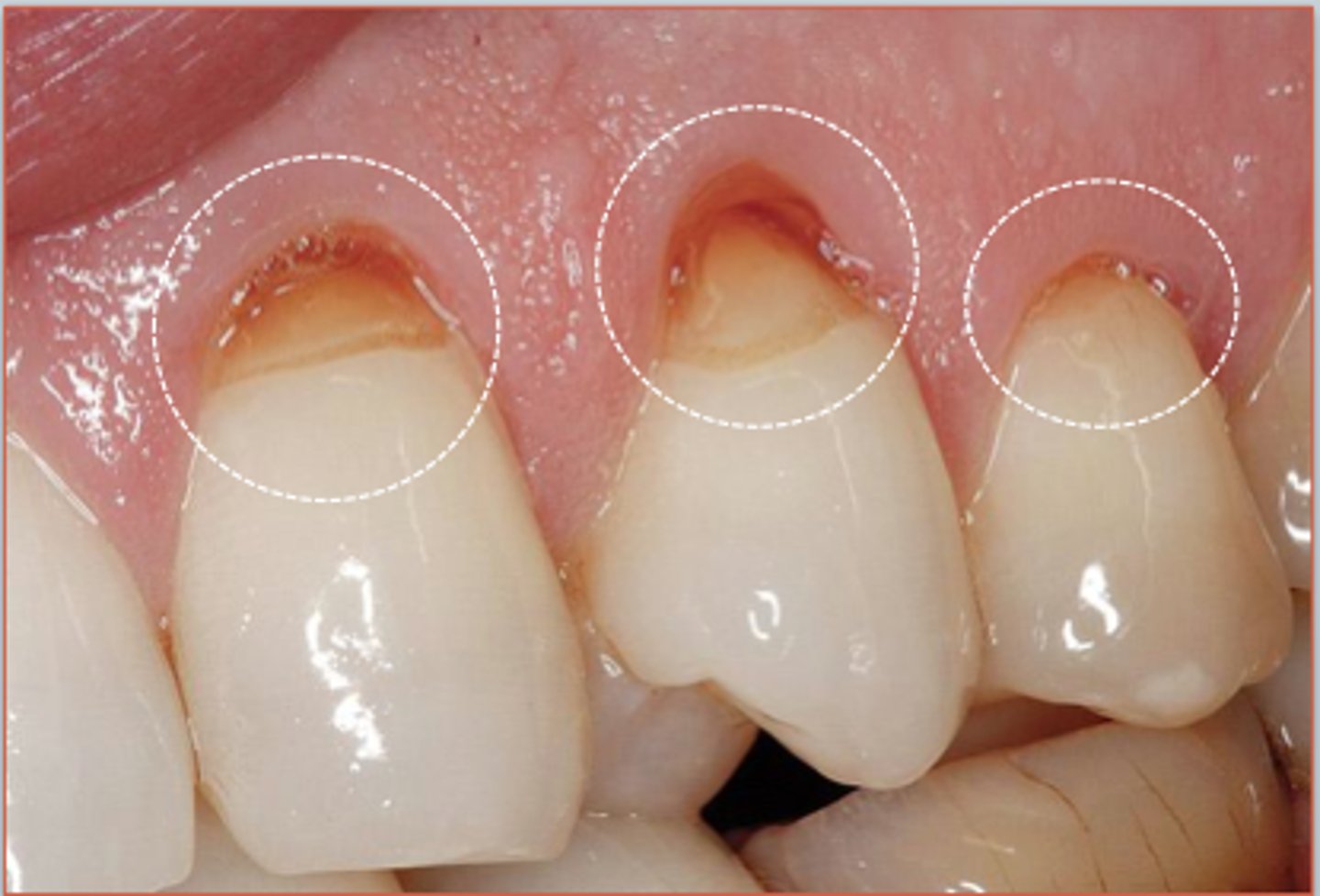
what is erosion
loss of enamel and dentine from chemical attack and not by bacteria eg vomiting
what happens to amalgam in erosion
enamel is more acid resistant than enamel and dentine so if erosion happens the tooth surface will be lost and amalgam is the same so it becomes higher than tooth - submargination
what is attrition
physical wear of one tooth surface against another tooth surface causing tissue loss on the contacting surfaces
what are the extrinsic risk factors of erosion
diet
enviornmental
meds
lifestyle
what are the environmental extrinsic risk factors
exposure to in inorganic agents
eg swimmers, wine tastersm fertiliser factory workers eg
why are acid containing drinks bad
2 main acids - citric and phosphoric
directly attack the tooth lattice and remove calcium
citrate annion has higher affinity for lattice than phosphate so can cause direct acid attack at ph 2
32% ca in saliva is complexed by citrate which reduces saliva saturation and buffer effect and encourages dissolution
what are the medication extrinsic risk factors
method of drug administration - frequency duration and inhalation/liquid
pH of meds
eg aspirin, iron tonics, HCL supplement, vit C, acidic salivary flow stimulants
what are the lifestyle extrinsic risk factors
behavioural eg excessive consumption if acidic foods
night time baby bottle feeding with acidic beverages
healthier lifestyles and dieting - vegetarians prone
strenous sporting activities - prone to acid reflux and reduced saliva
OH and tooth whitening
what are intrinsic factors
vomiting
regurgitation and reflux
rumination - regurgitation then chewing and swallowing it
what is the difference between vomiting and reflux/regurgitation
vomiting - forceful expulsion of stomach contents
reflux/regurgitation - lack of diaghramatic muscular contraction and small quantity ejected
what biological factors modifying the erosion process
saliva
tooth composition and structure - variation of tooth substance
dental anatomy and occlusion - prominent teeth get hit by acid and abrfaction can make it worse
soft tissue anatomy and physiological function - influences acid contact areas
what does saliva do
dilution and clearance of acid out the mouth
neutralising and buffering
maintenance of supersaturated state next to the tooth surface of ca and phosphate
acquired pellicle formation
why do teeth not grow
statherin protein stops ca and phosphate in saliva to precipitate on tooth surface
how do we prevent and treat tooth wear
diagnosis - IO and full history, photos, salivary tests, study models
inform and instruct on causes
oh advice
what do u need in a diet history
day of the week and weekend at least usually a whole week
and when and what they ate
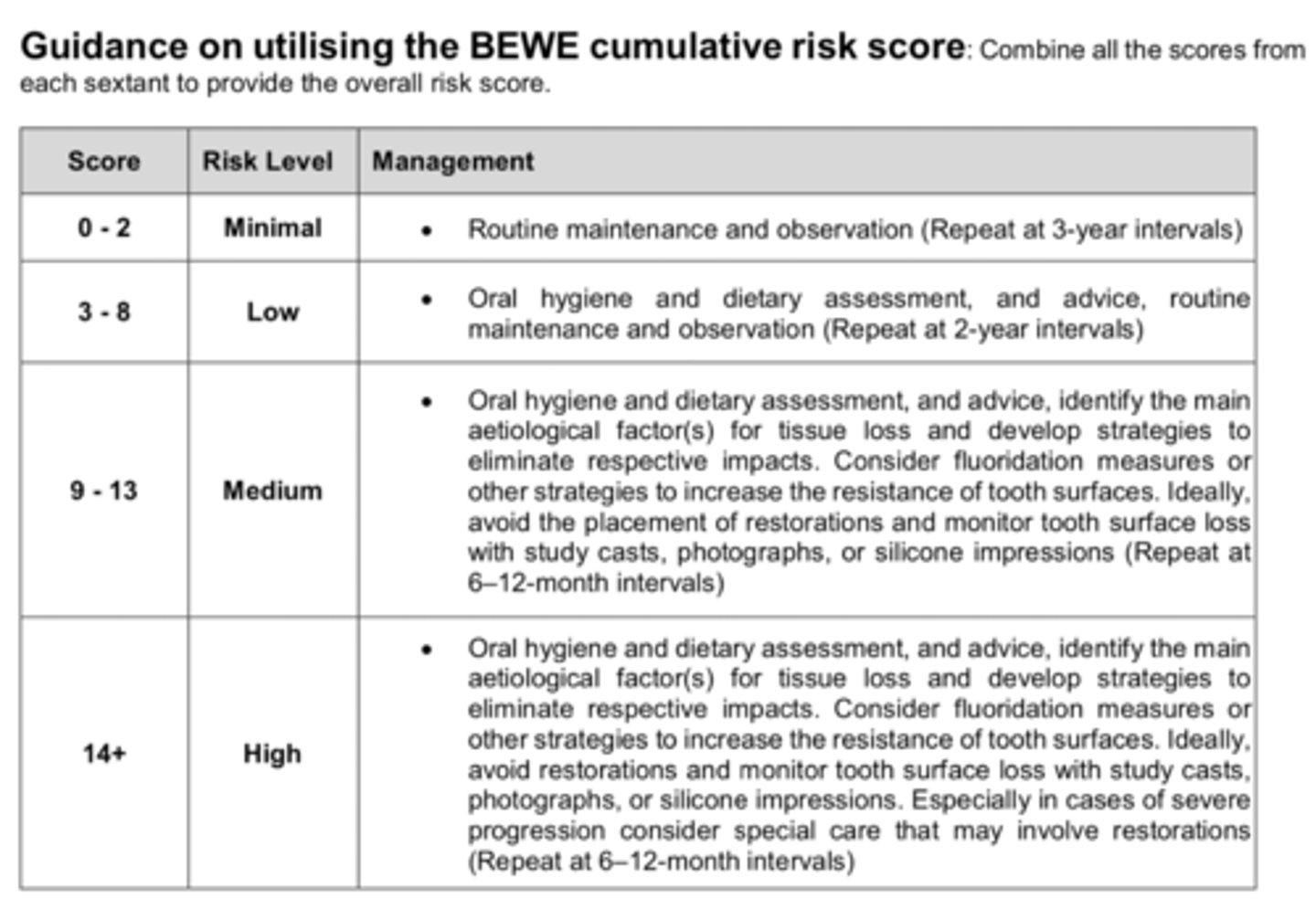
What is the BEWE?
basic errosive wear exam
highest score per sextant recorded and totalled
how do we treat tooth wear
arrest errosive process
make space for restorations
repair palatal loss with veneers
maintain/increase OVD
what is dahl appliance
creates space orthodontically and decreases no. of crowns required
removable co/cr splint with thick coverage of palatal anteriors and buccal retention