MAPS -- Ultimate Study Guide
1/220
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
221 Terms
Maritime Choke Points
Panama Canal, Bering Strait, Korea Strait, Malacca Strait, Hormuz Strait, Bab el Mandeb, Suez Canal, Bosporus Strait, Denmark Strait, Gibraltar Strait
Cyber Choke Points
Northern Virginia, Fortaleza, Bude, Djibouti, Mumbai, Singapore
Agricultural Production Areas
Mississippi Triangle, South American Soy Zone, North European Plains, Slavic Black Soil Region, Indo-Gangetic Plains, Eastern China, Southeast Asian Deltas
Mississippi Triangle
Soy, Corn (exporting)
South American Soy Zone
Soy, Corn (exporting)
North European Plains
Wheat
Slavic Black Soil Region
Wheat (exporting)
Indo-Gangetic Plains
Wheat, Rice
Eastern China
Rice
Southeast Asian Deltas
Corn, Wheat Rice (exporting rice)
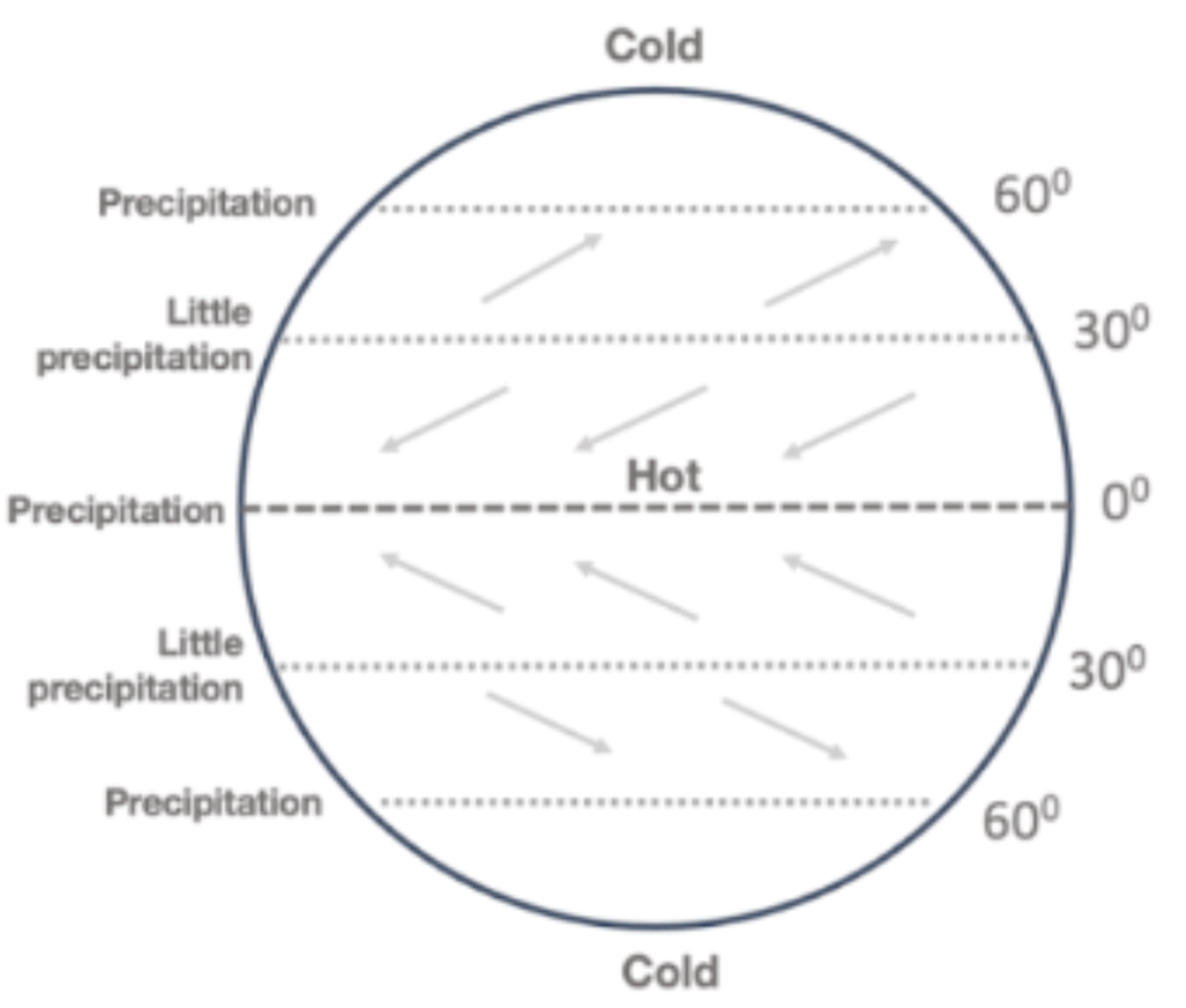
Global Wind, Precipitation and Temperature Patterns
Cold at poles; precipitation at 60N, 0, and 60S; little precipitation at 30N and 30S; Northeast winds, southwest winds, northwest winds, southeast winds.
Orographic Rainfall
Rain on one side of a mountain, arid rain shadow on the other.
Air cools when it rises over mountains and can’t hold as much moisture.
Exotic River
Rain generated in mountains forms a river that flows into an arid area.
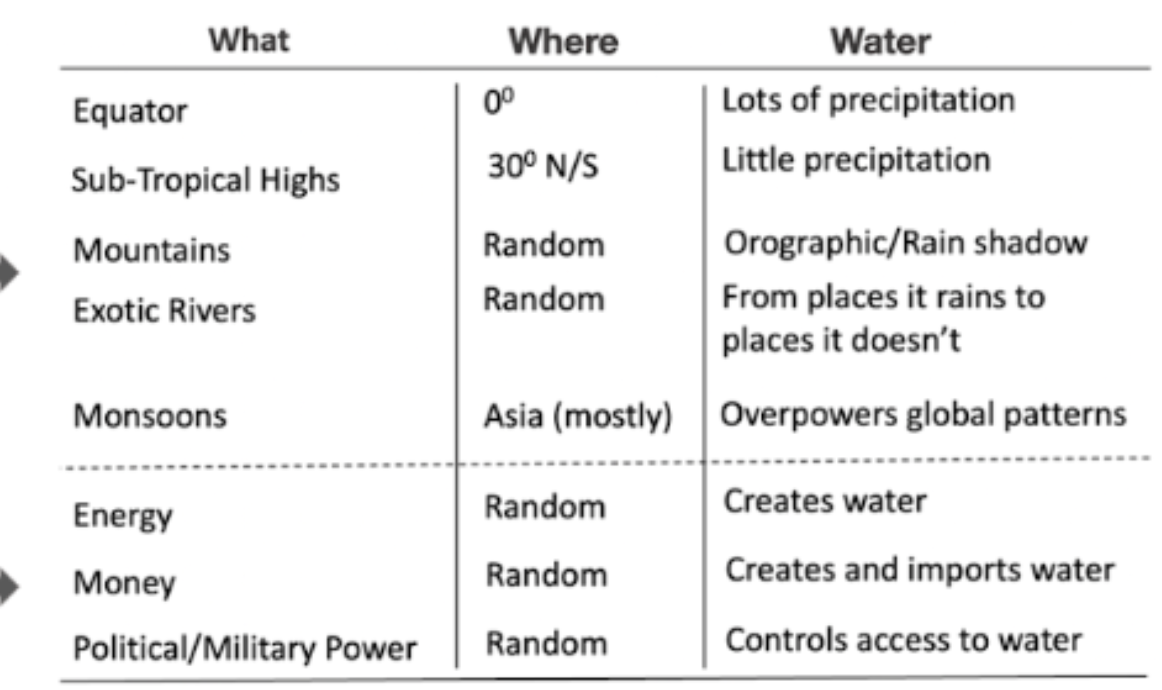
What/Where/Water
Lots of precipitation at Equator (0); little precipitation at sub-tropical highs (30N/S); Mountains have orographic rain and rain shadows; Asian monsoons overpower global patterns. Energy creates water; money creates and imports water; political and military power controls access to water.
Sahel
Divides Africa into pastorial/agricultural, Islam/Christianity, Equatorial/North Africa
Natural Border
A border made from a natural features, such as a river or a mountain range.
Resource Curse
Countries rich in natural resources are exploited and suffer economically.
Rentier State
State that gains its wealth from hosting foreign governments and businesses.
Berlin Conference
European colonial powers splitting Africa up into colonies — ignored natural borders and ethnic divides, focused on resource extraction.
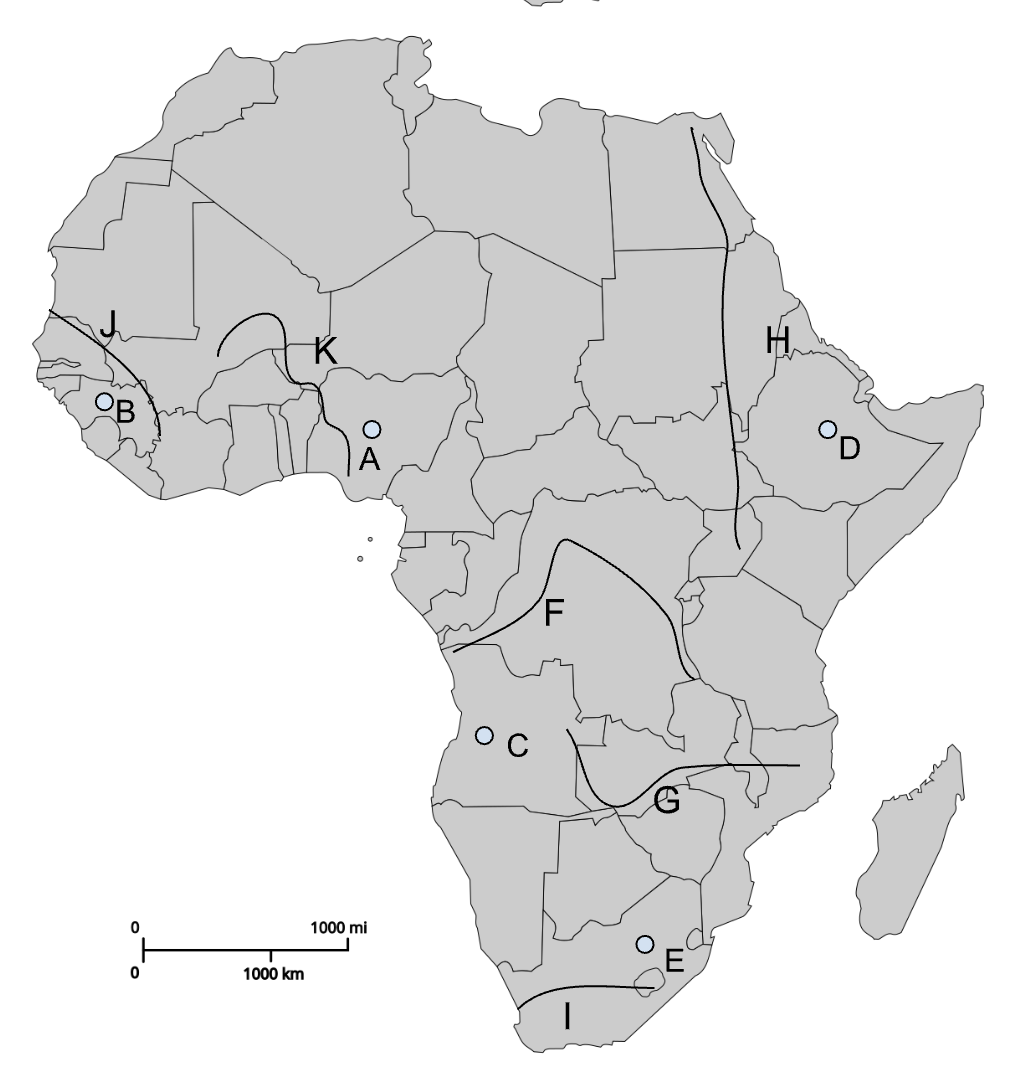
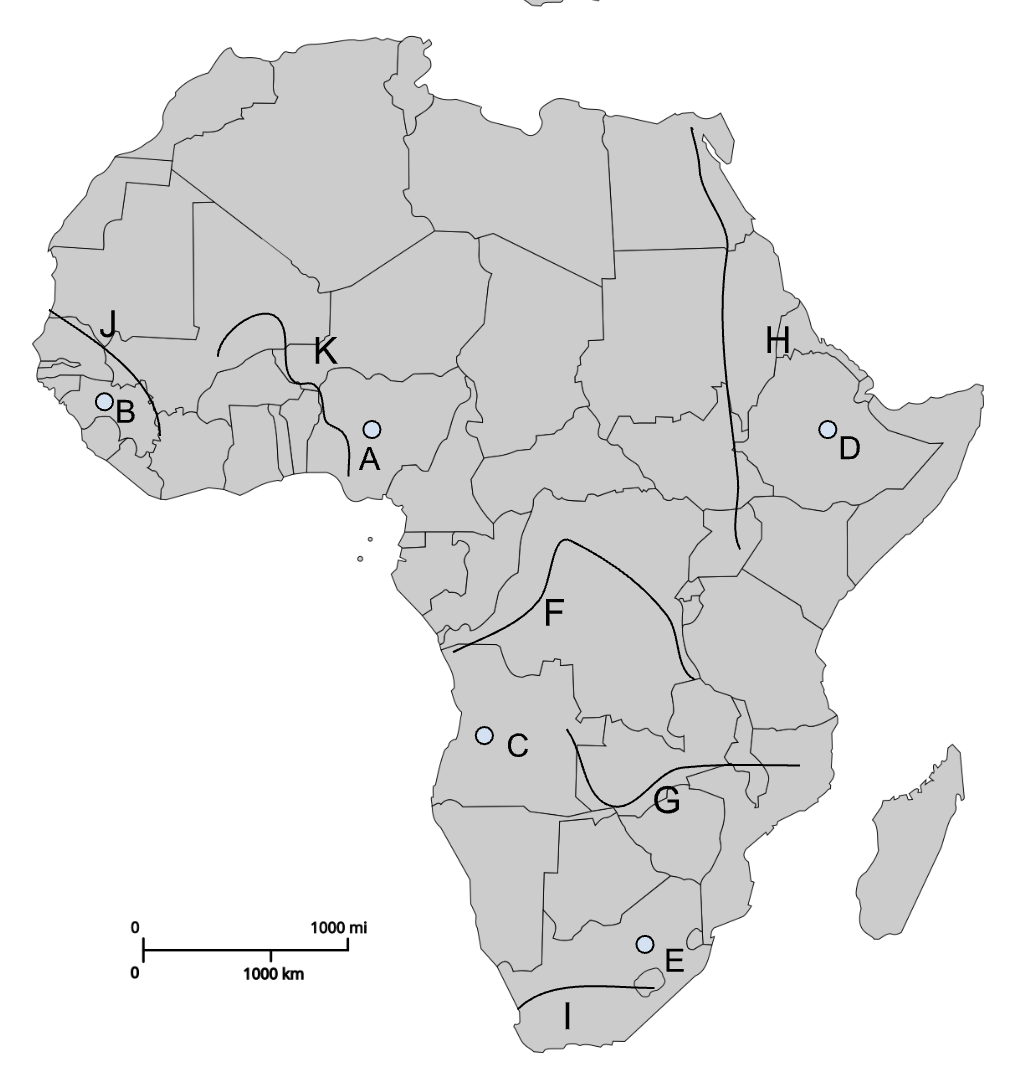
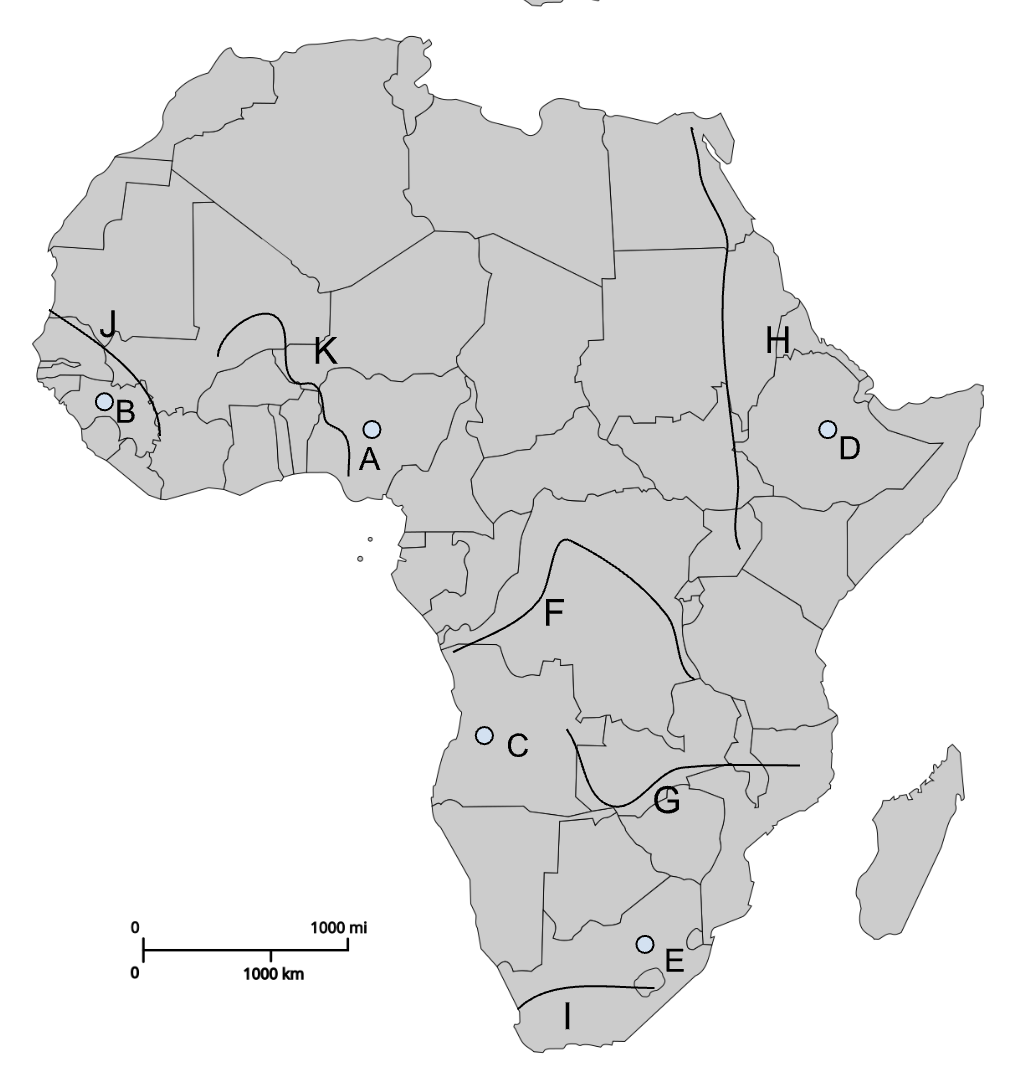
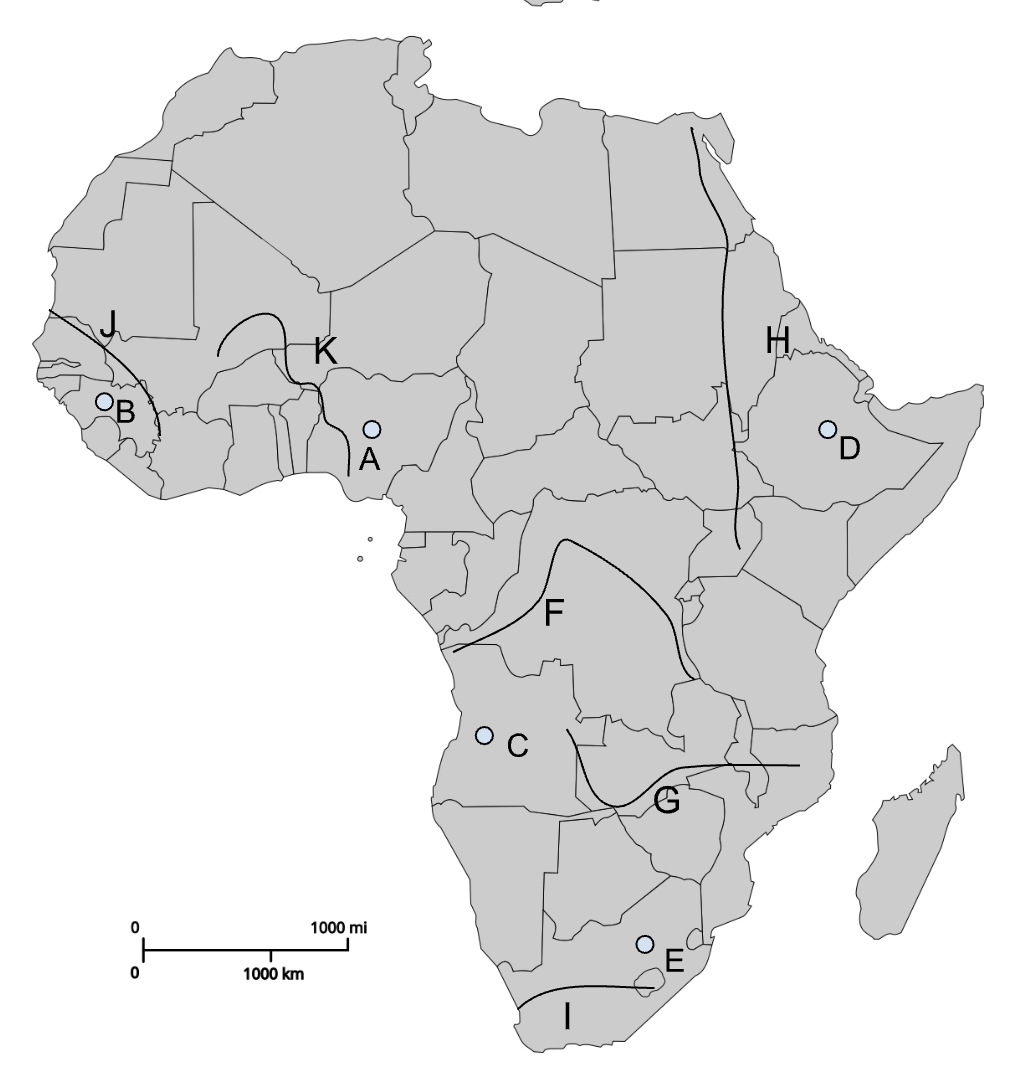
A
Jos Plateau
B
Fouta Djallon
C
Angolan Highlands
D
Ethiopian Highlands
E
Drakensberg Plateau
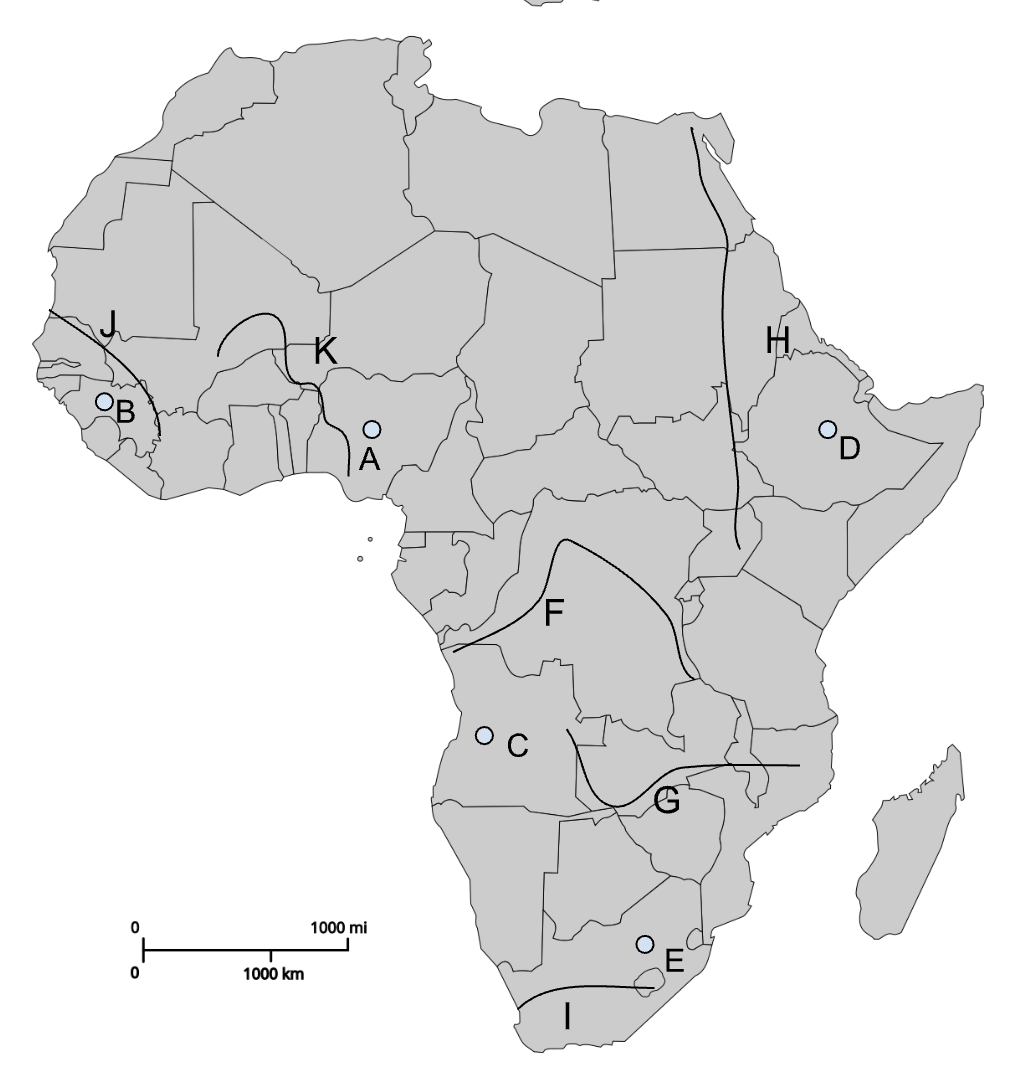
F
Congo River
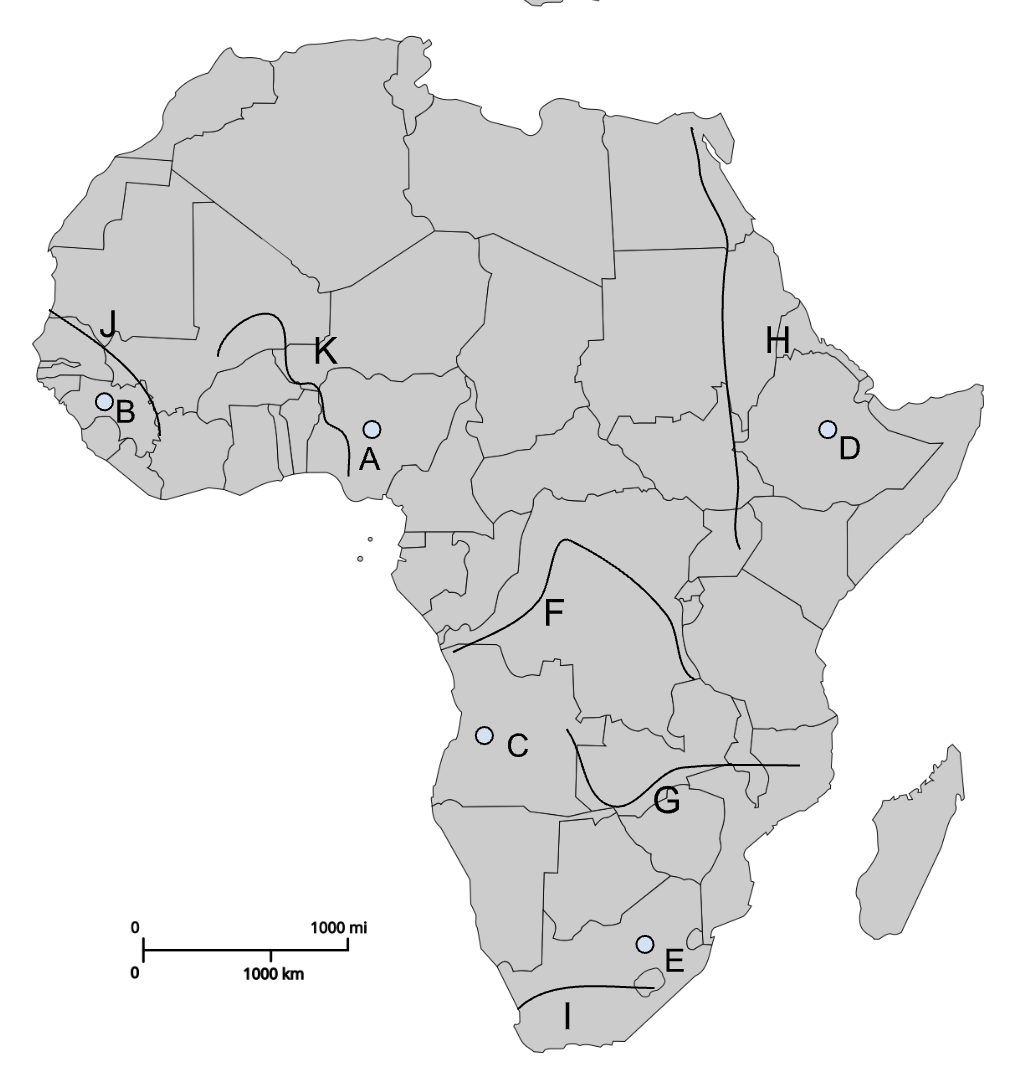
G
Zambezi River
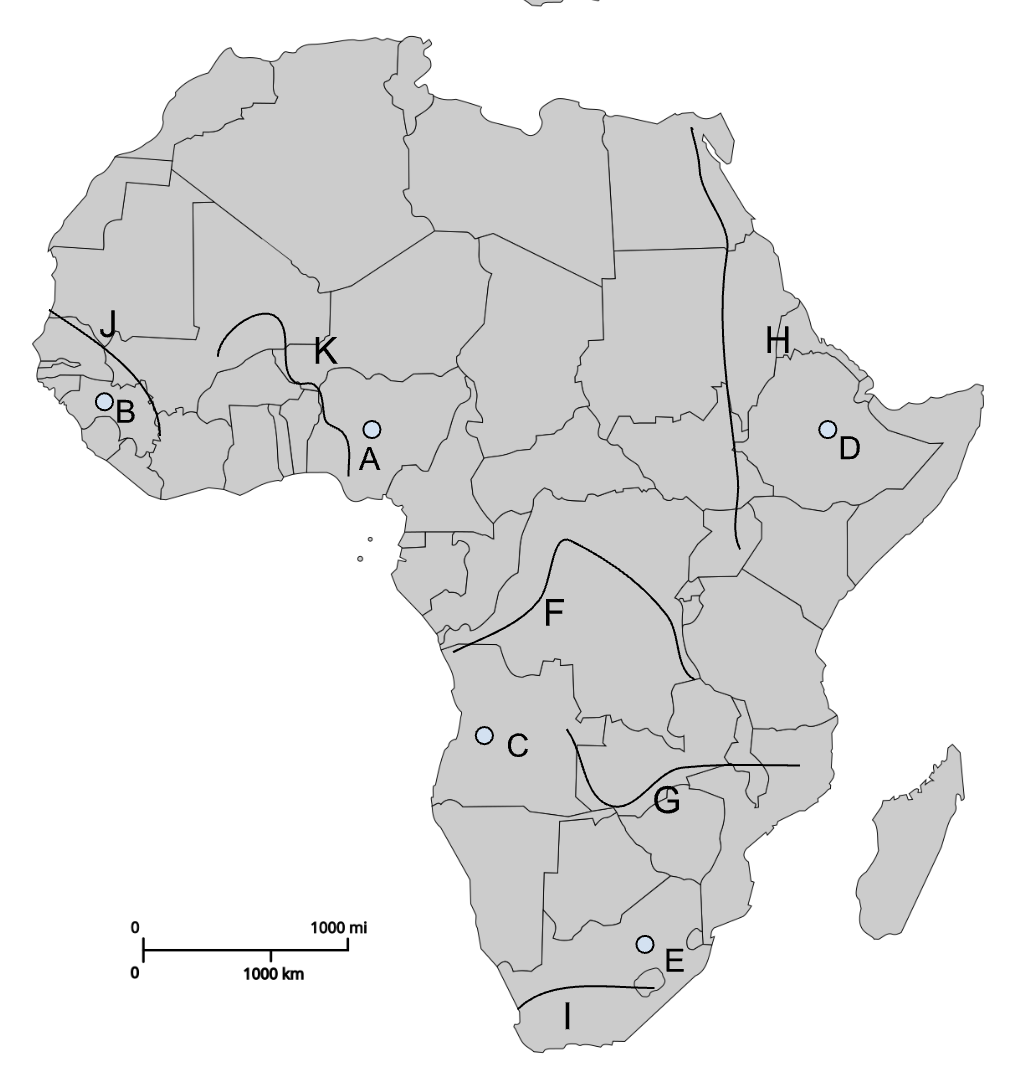
H
Nile River
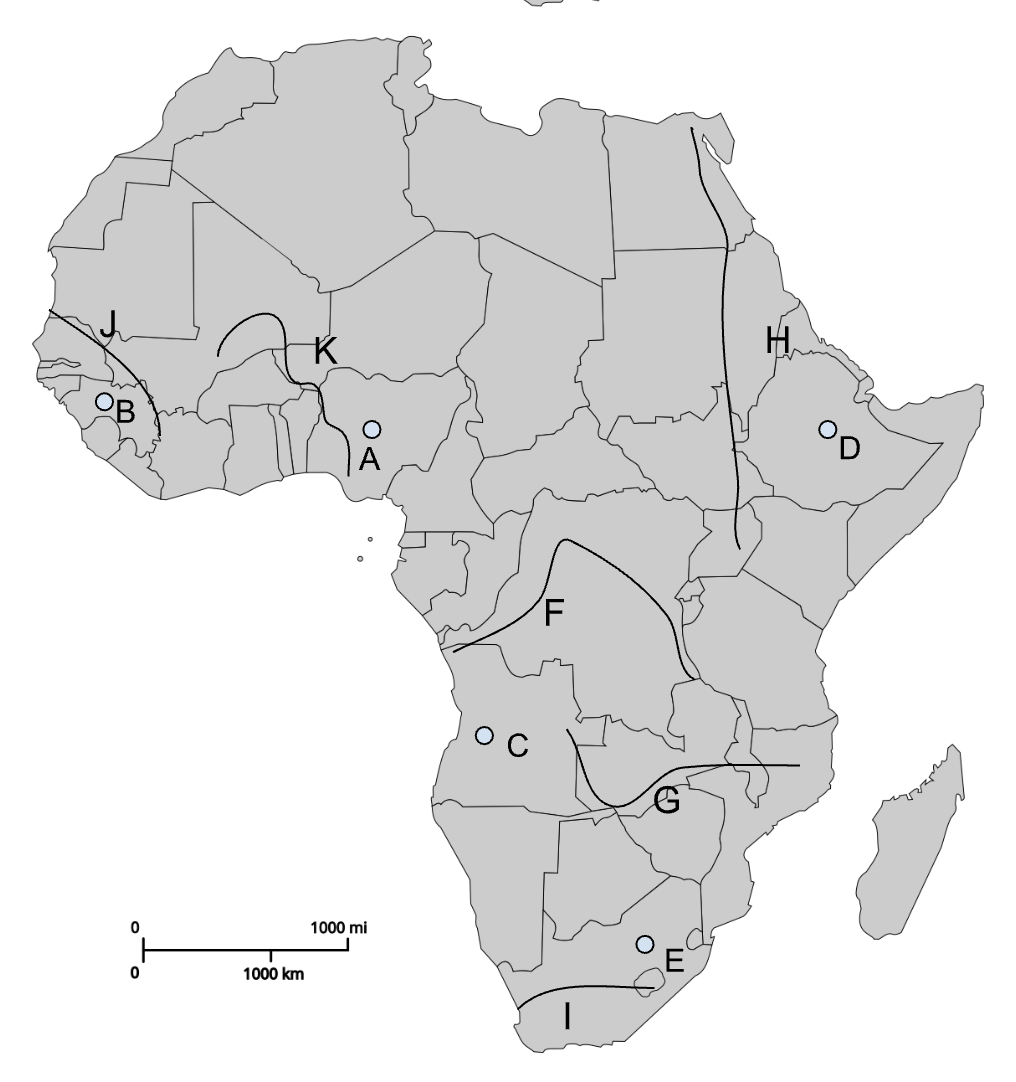
I
Orange River
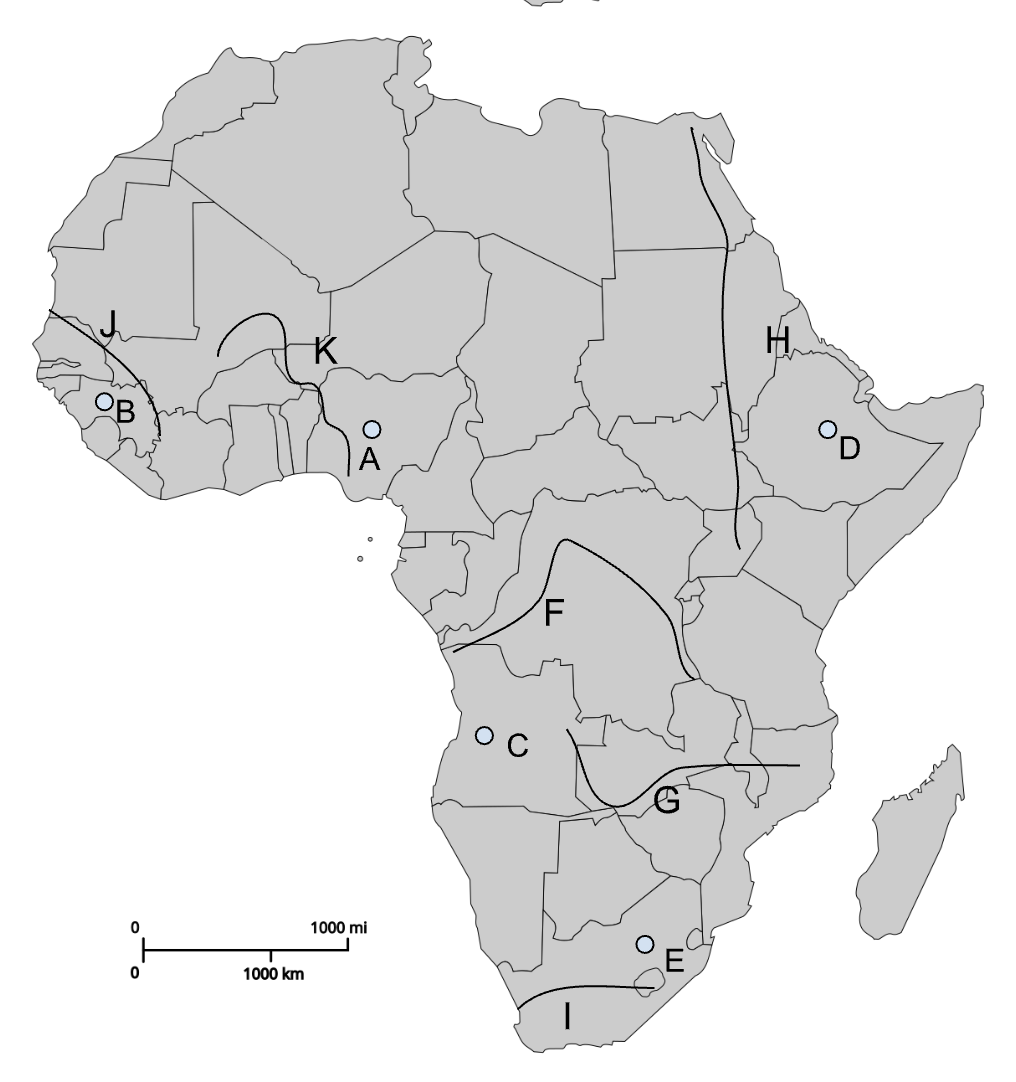
J
Senegal River
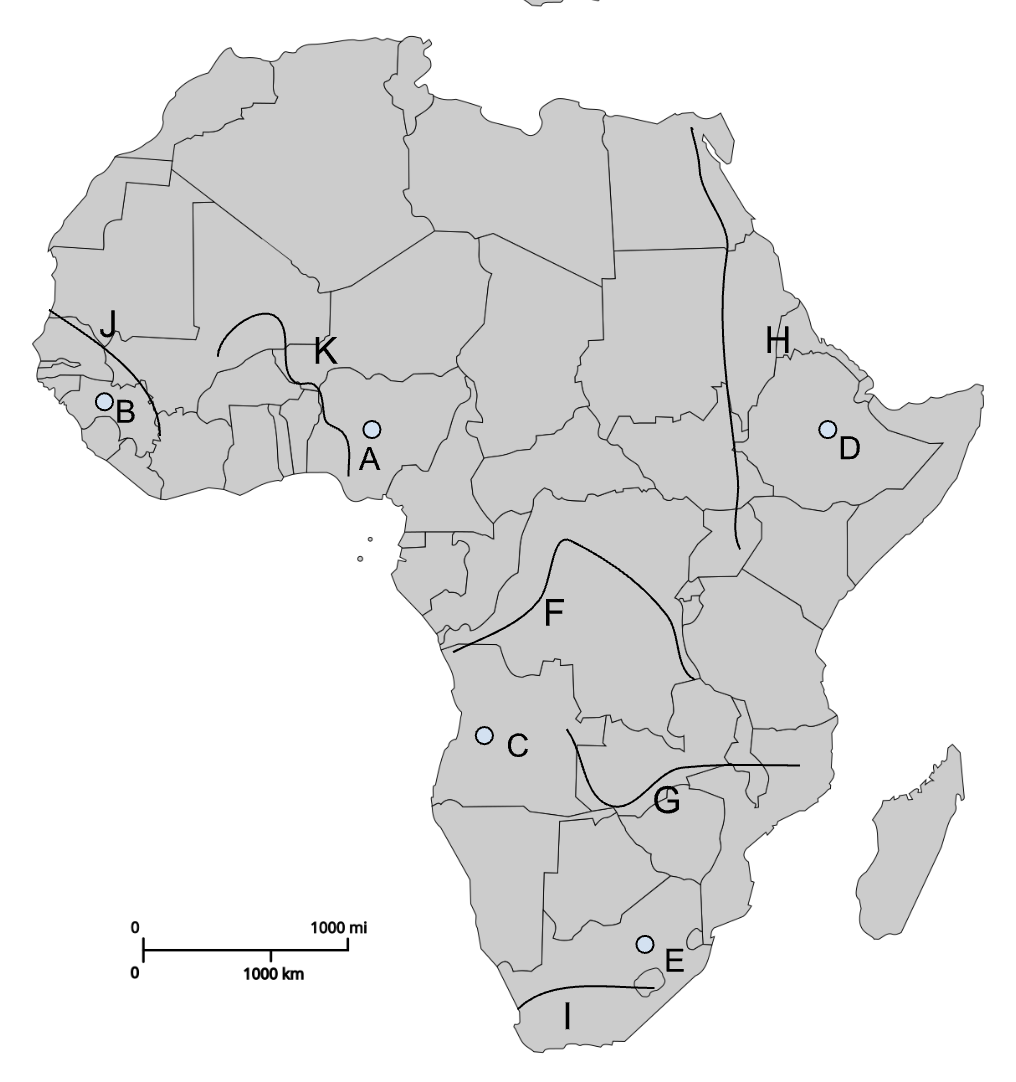
K
Niger River
States without tsetse fly
Kenya, Namibia South Africa
Allowed Colonial Settlement
Capitals: Nairobi, Windhoek, Pretoria, Bloemfontein, Cape Town
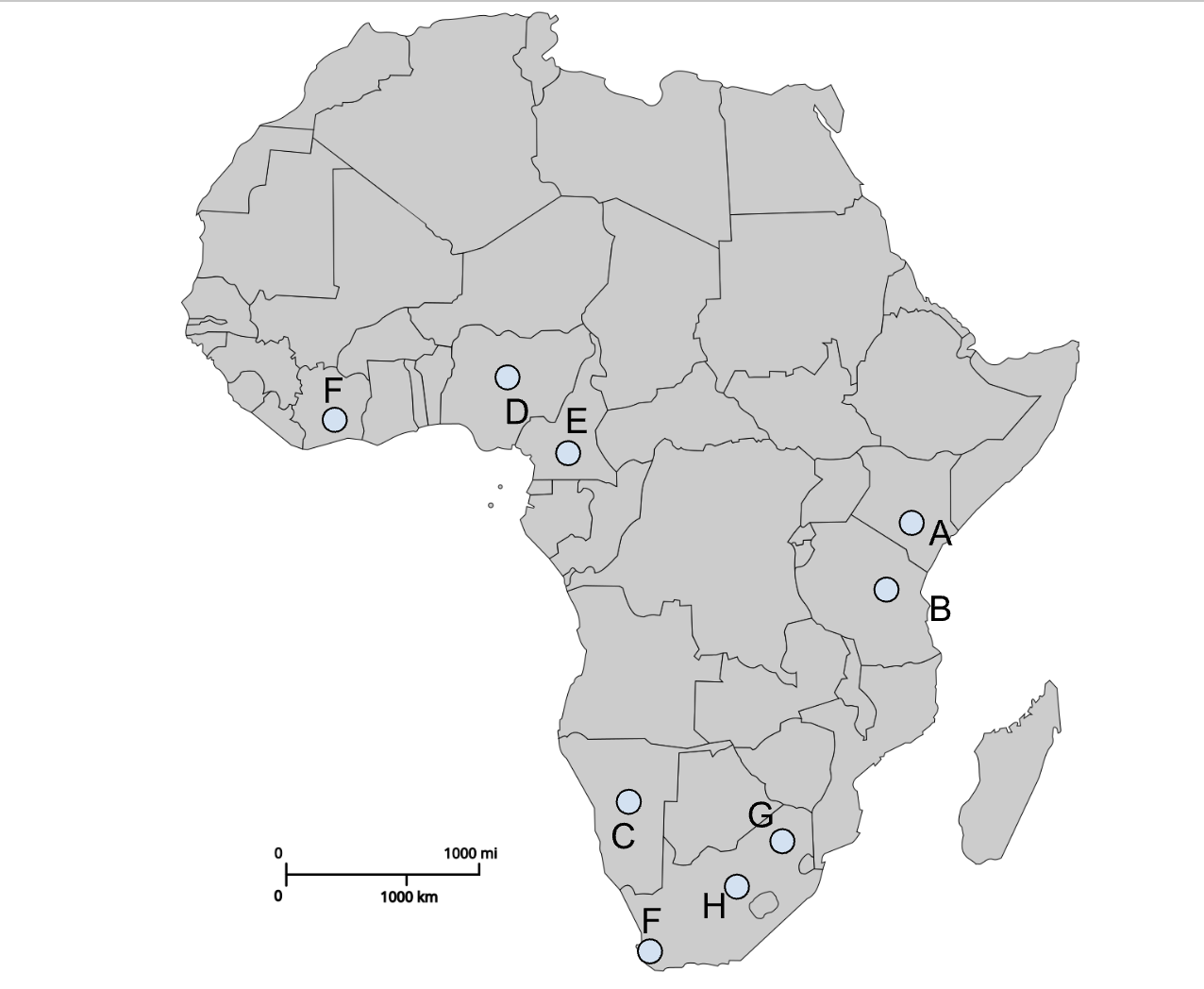
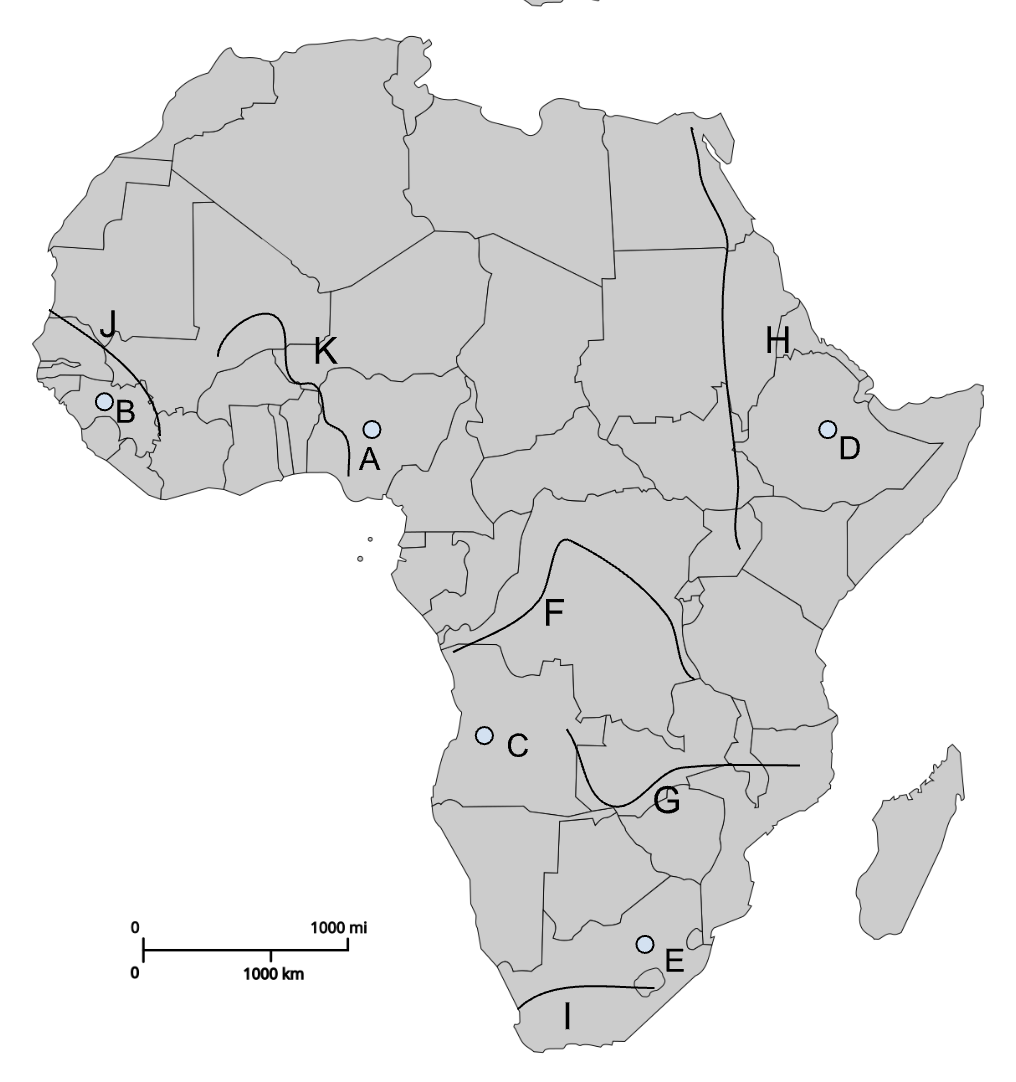
A
Nairobi (Colonial capital)
B
Dodoma (Post-colonial capital)
C
Windhoek (Colonial capital)
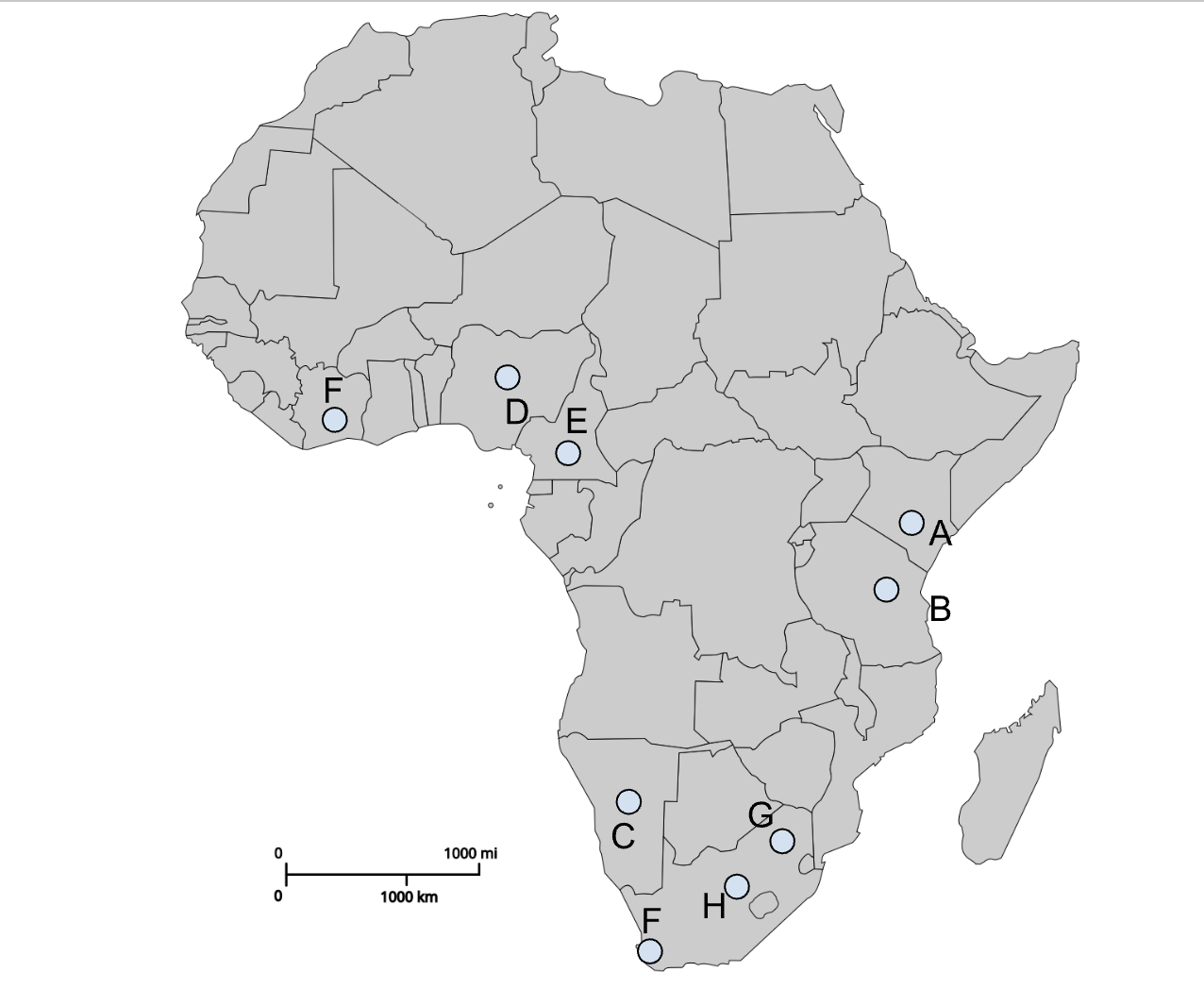
D
Abuja (Post-colonial capital)
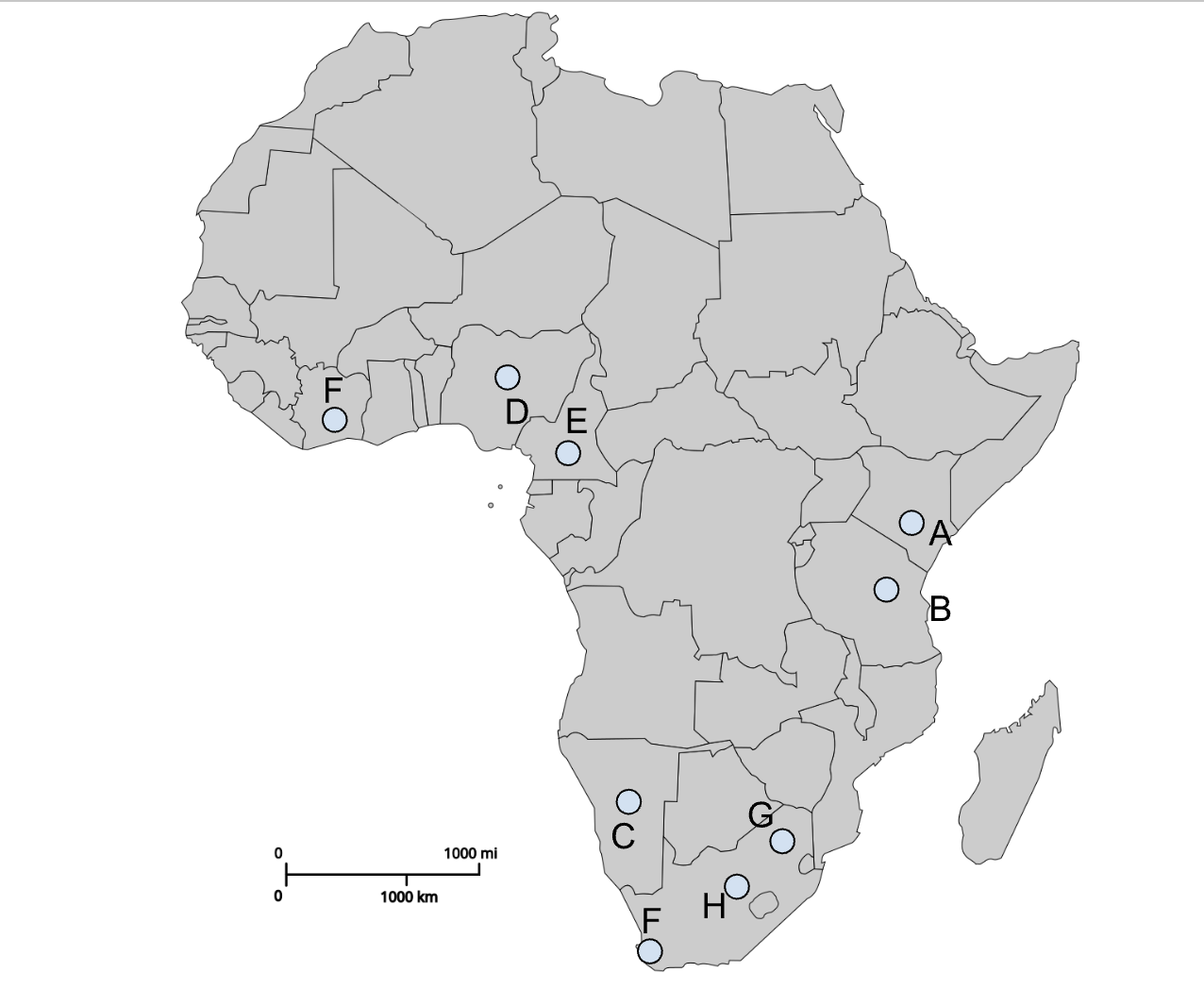
E
Yaoundé (Post-colonial capital)
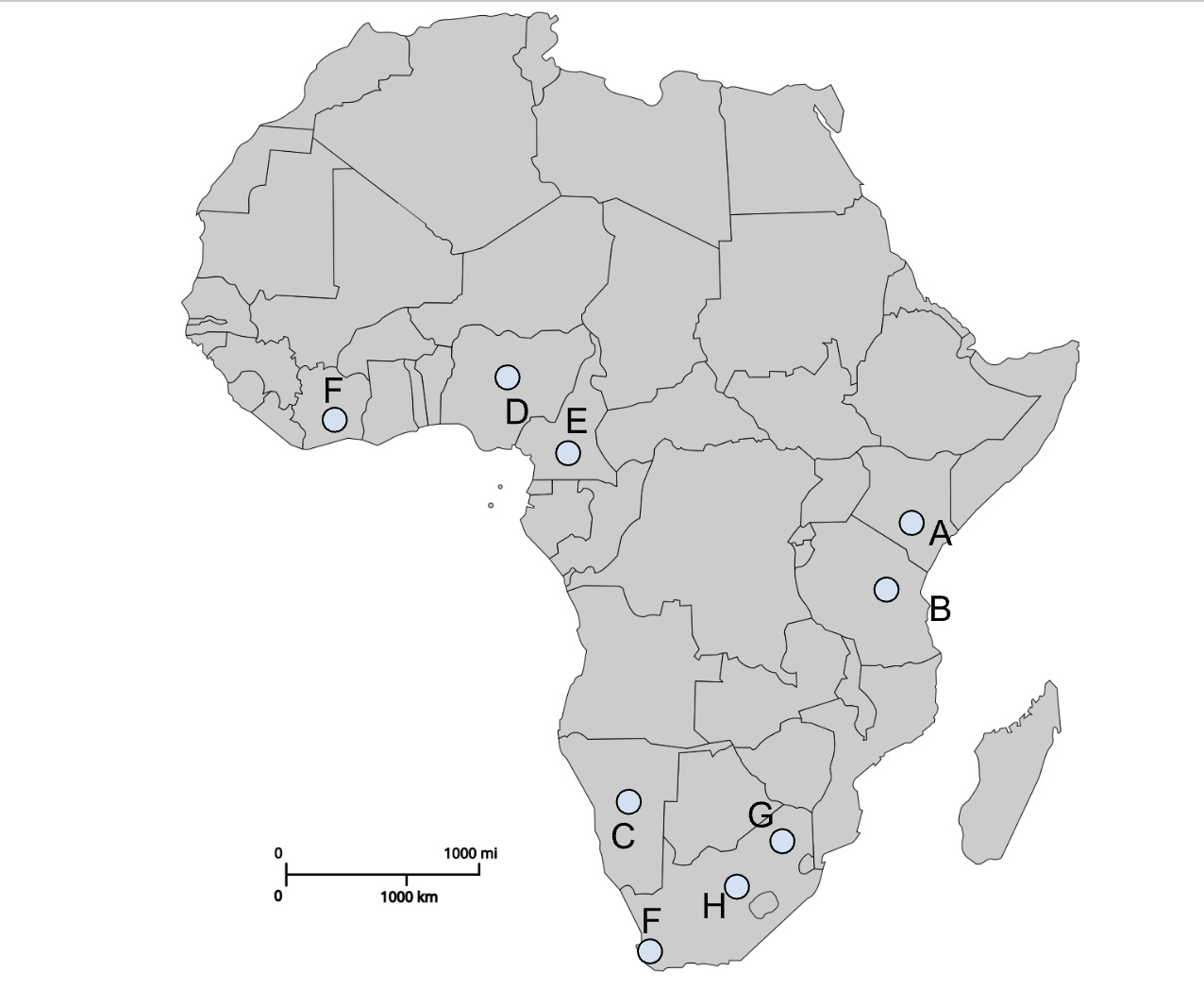
I (southern F)
Cape Town (Colonial capital)
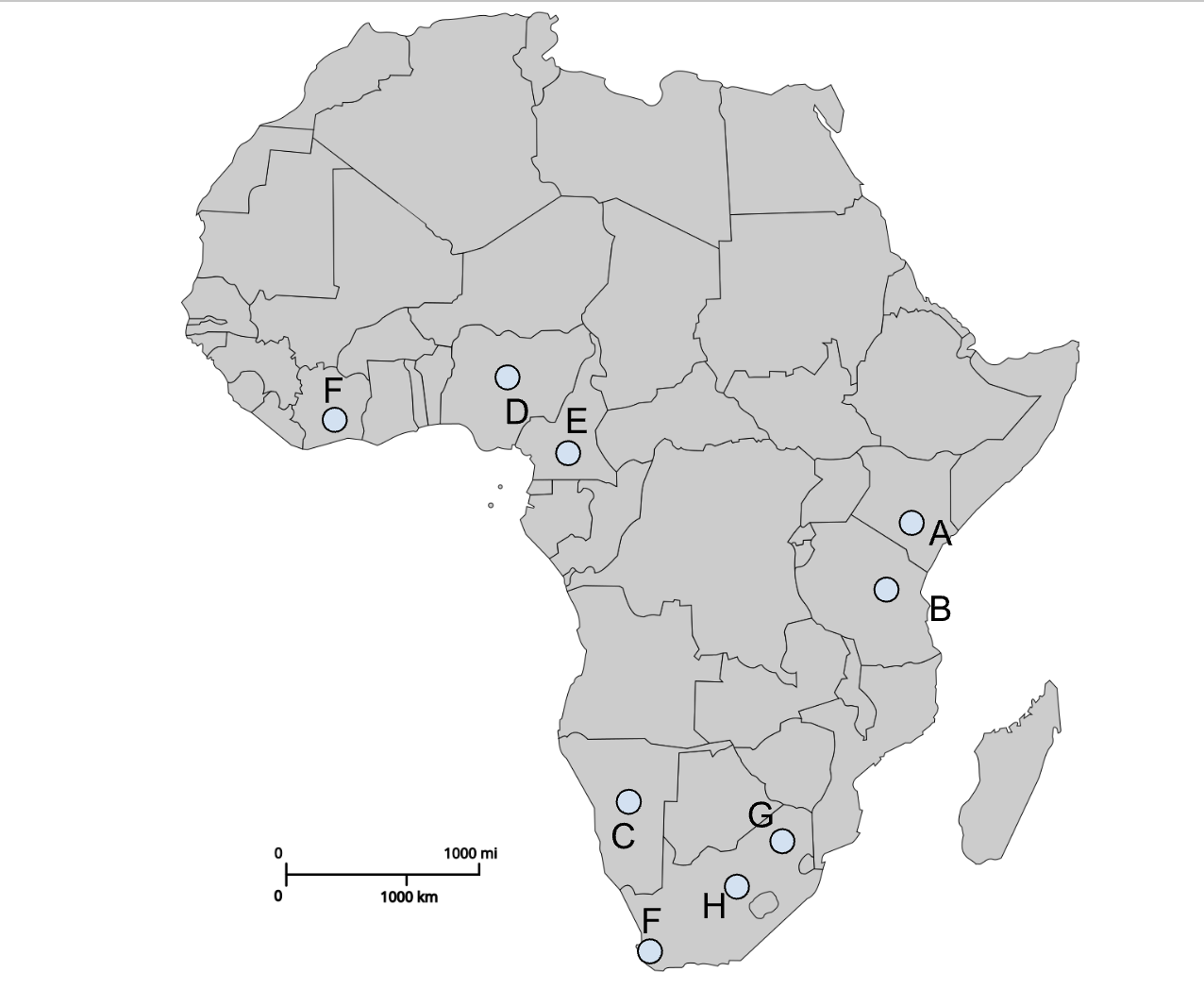
G
Pretoria (Colonial capital)
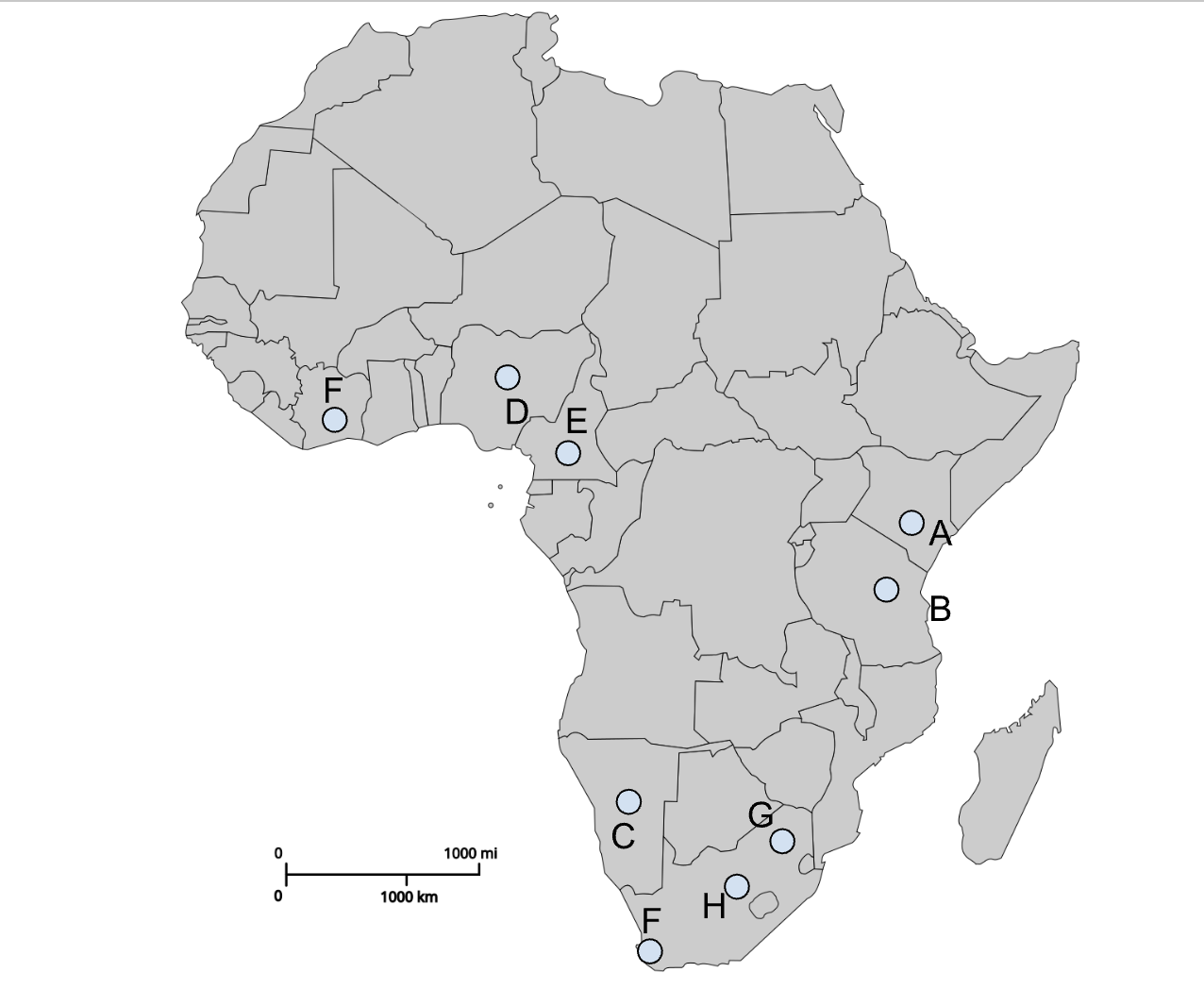
H
Bloemfontein (Colonial capital)
African State/Border Changes
Tanzania — merger of Tanganyika and Zanzibar
Eritrea — split from Ethiopia in 1993 after joining in 1952
South Sudan — split from Sudan in 2011, world’s youngest state
Somaliland — de facto independent from Somalia
Dependency Ratio
Ratio of young and old to those 16-64. Africa has the highest dependency ratio in the world, will have the lowest by 2100. Will have the highest working age population.
SWANA Border Changes
Two Yemens merged in 1990
Western Sahara is de facto part of Morocco, but has world’s longest sand berm.
Palestine/Israel
Orientalism
Defining of other places/peoples from an outside perspective, based on book by Edward Said
Nation
A large population with political aspirations that shares a culture
State
An independent political entity with clear geographic boundaries
Nation-State
A state whose population is made up of a single nation
State-Nation
A state created before those within its borders have developed a shared sense of nationhood
Sykes-Picot
1916 agreement between UK and France to divide the Ottoman Empire into the modern Middle East states
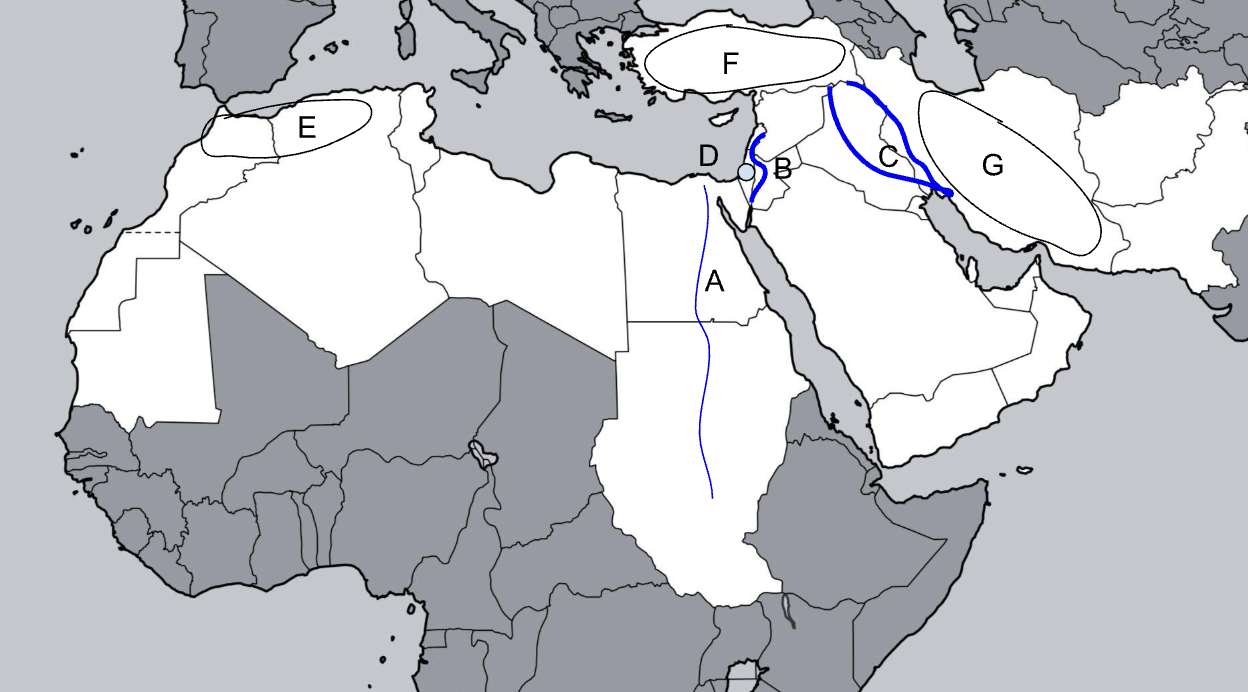
A
Nile River
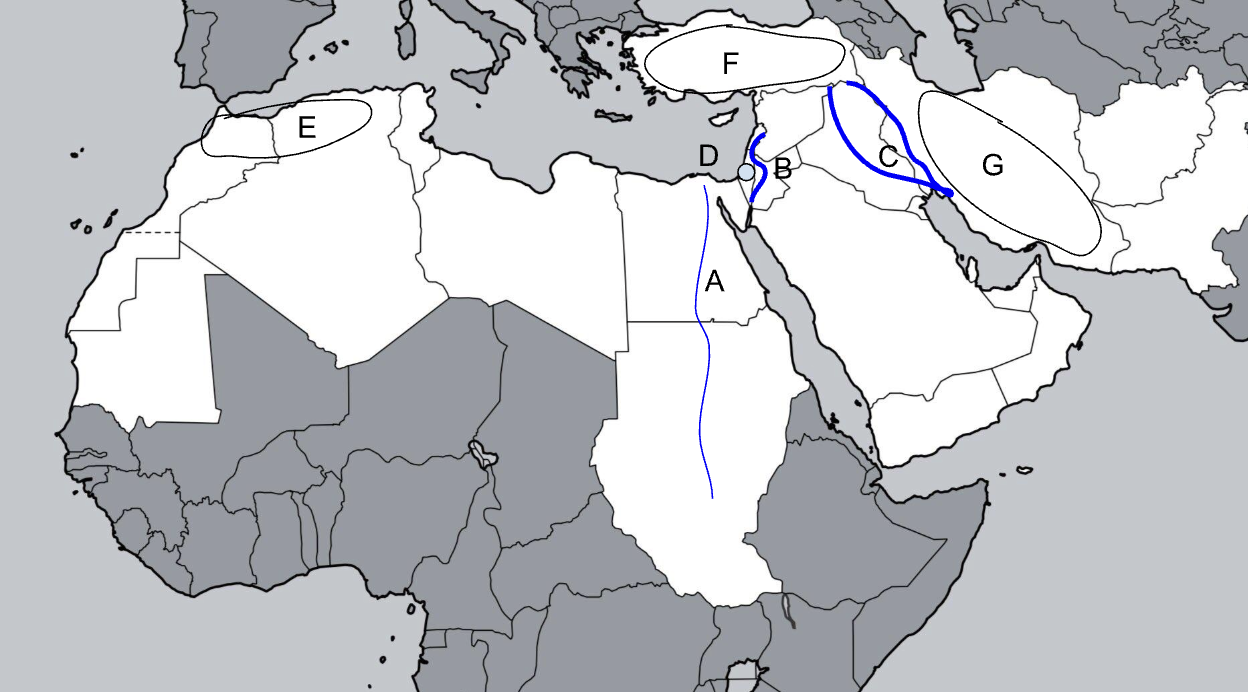
B
Jordan River
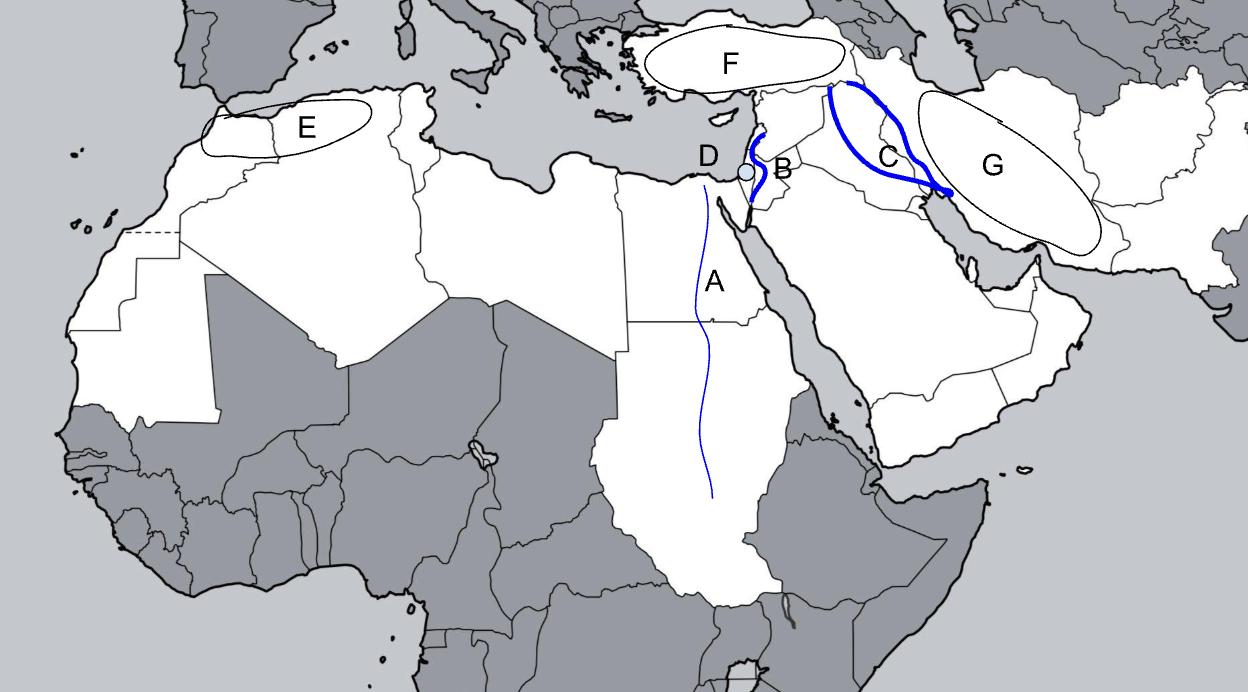
C
Tigris-Euphrates River
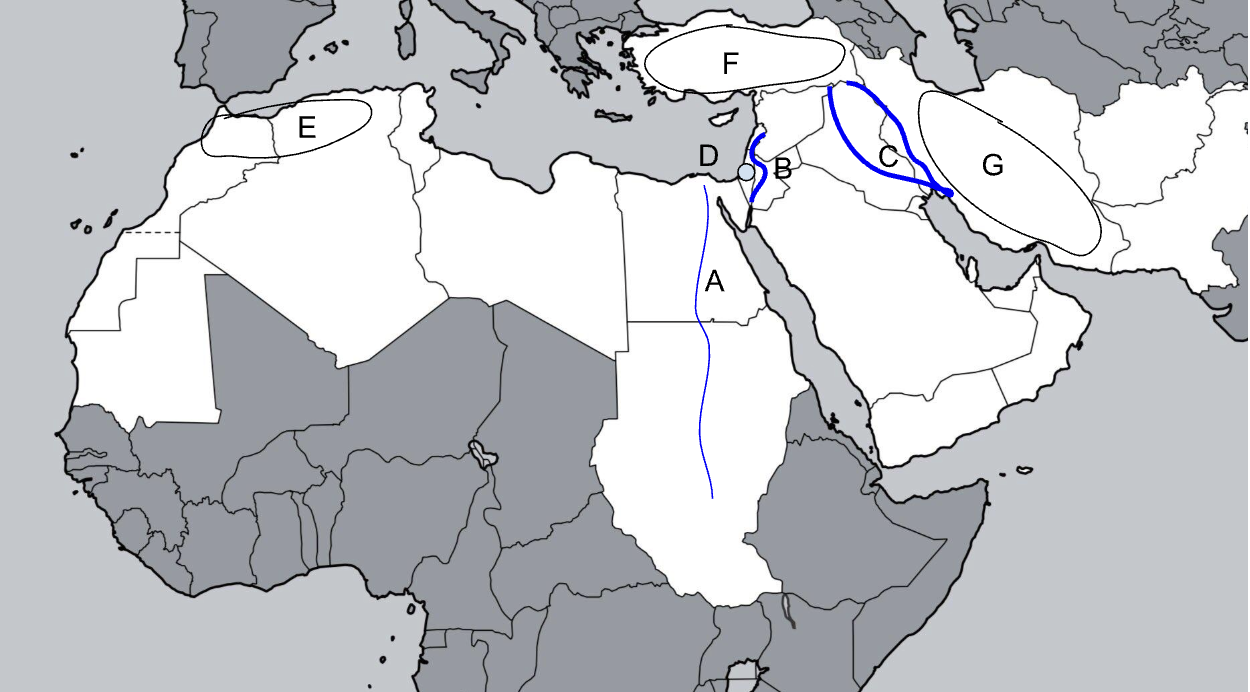
D
Judean Hills
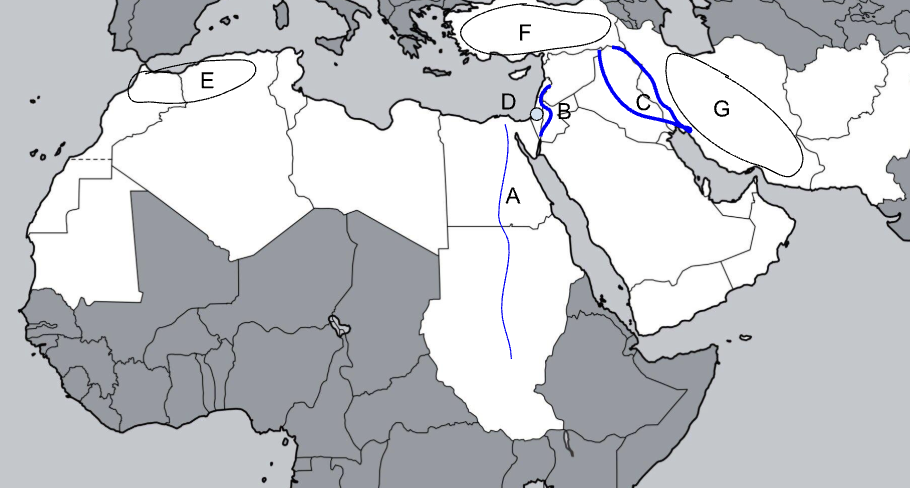
E
Atlas Mountains
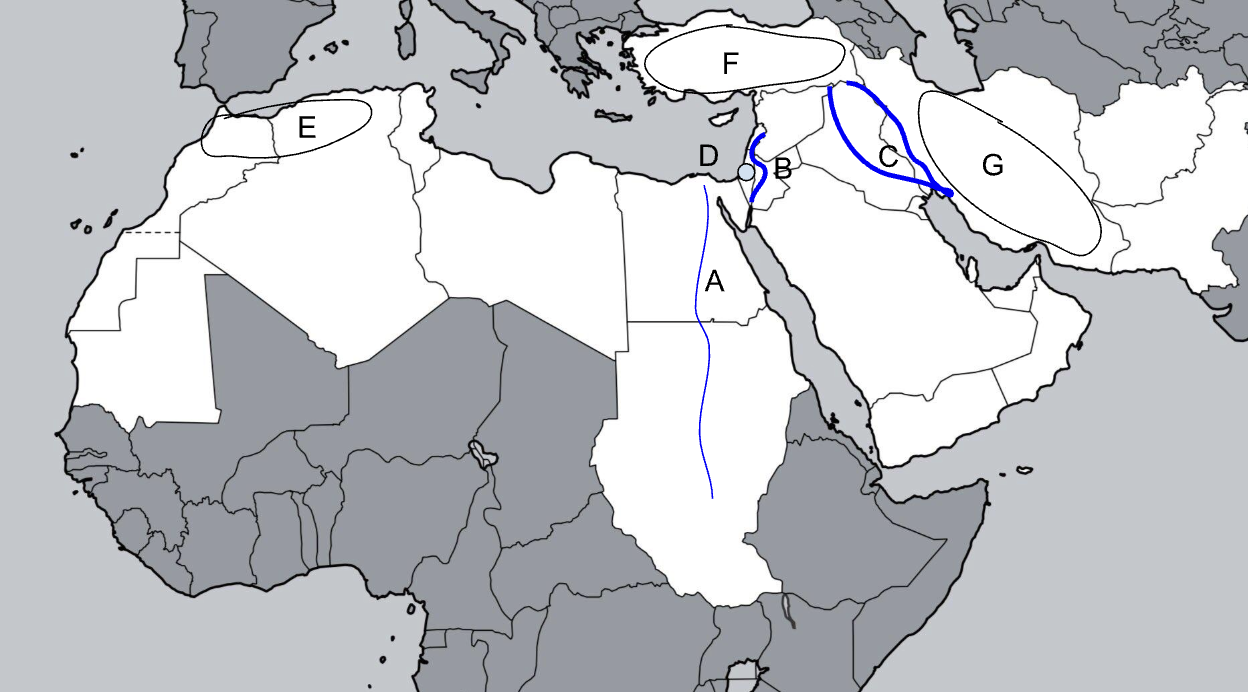
F
Anatolian Plateau
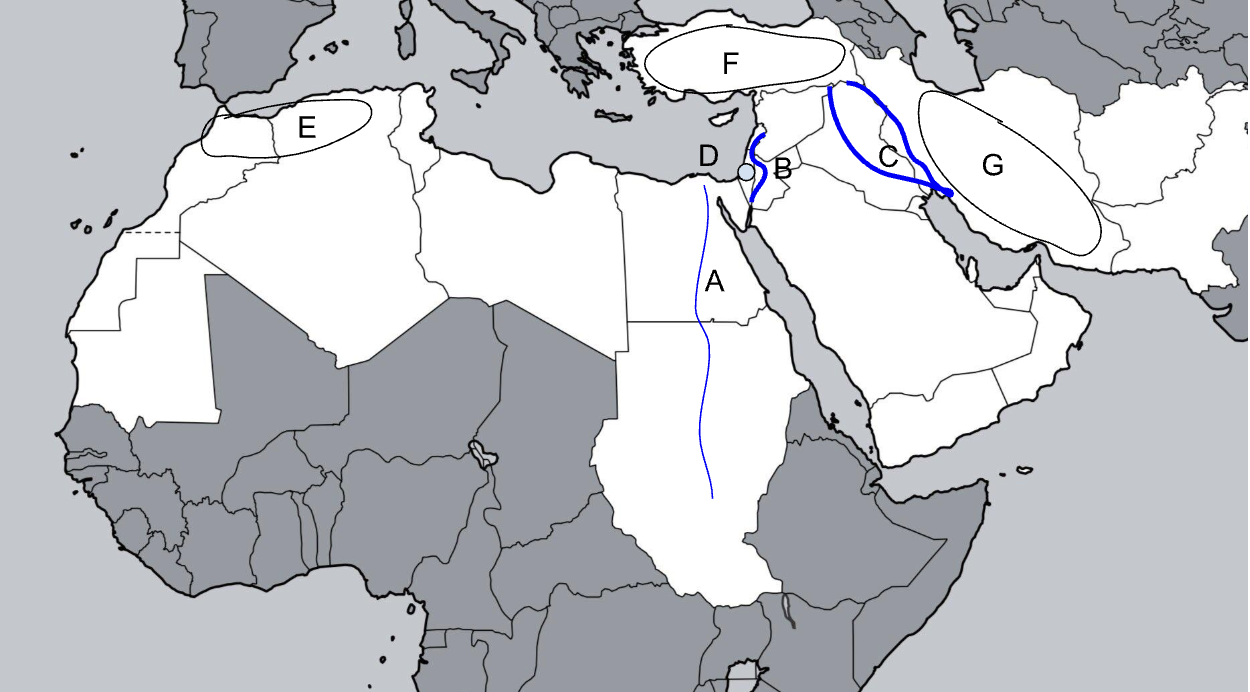
G
Zagros Mountains
Shia Majority
Bahrain, Iran, Iraq
Non-Arab majority
Turkey, Israel, Iran
Yemen and Iraq religious majorities
Yemen has a large Shia minority, Iraq has a large Sunni minority.
Water stress in SWANA
Very dry area, but wealthier countries have significantly less water stress.
Divided Place: Palestine
British Mandate for Palestine established under Sykes-Picot, which was subdivided into Mandate Palestine (current Israel, West Bank, and Gaza), which allowed Jewish settlement, and Transjordan, which did not.
Transjordan becomes independent in 1946.
In 1947, the UN proposed dividing Mandate Palestine into Jewish and Arab states with Jerusalem as an international city.
Arab League rejects this plan, and war breaks out in 1948 when Israel declares independence.
The war resulted in the expansion of Israeli territory beyond the UN plan: creation of Jordanian-controlled West Bank, Egyptian-controlled Gaza, Israeli West Jerusalem and Jordanian East Jerusalem
Israel captured Golan Heights from Syria in 1967
Gaza, the West Bank, and West Jerusalem are nominally under Palestinian Control.
Giordano Line
Drawn from St Petersburg to Sea of Azov. 43 countries on one side, 1 on the other
Strategic Depth
Distance between the front lines or battle sectors and the combatants’ industrial core areas, capital cities, heartlands, and other key population and military centers.
Irredentism
Territorial claim based on a national, ethnic, or historical basis
Yalta
Post-WWII conference that split Europe and created Soviet satellite states.
The Steppe
Extends Slavic Black Soil region eastward through Mongolia.
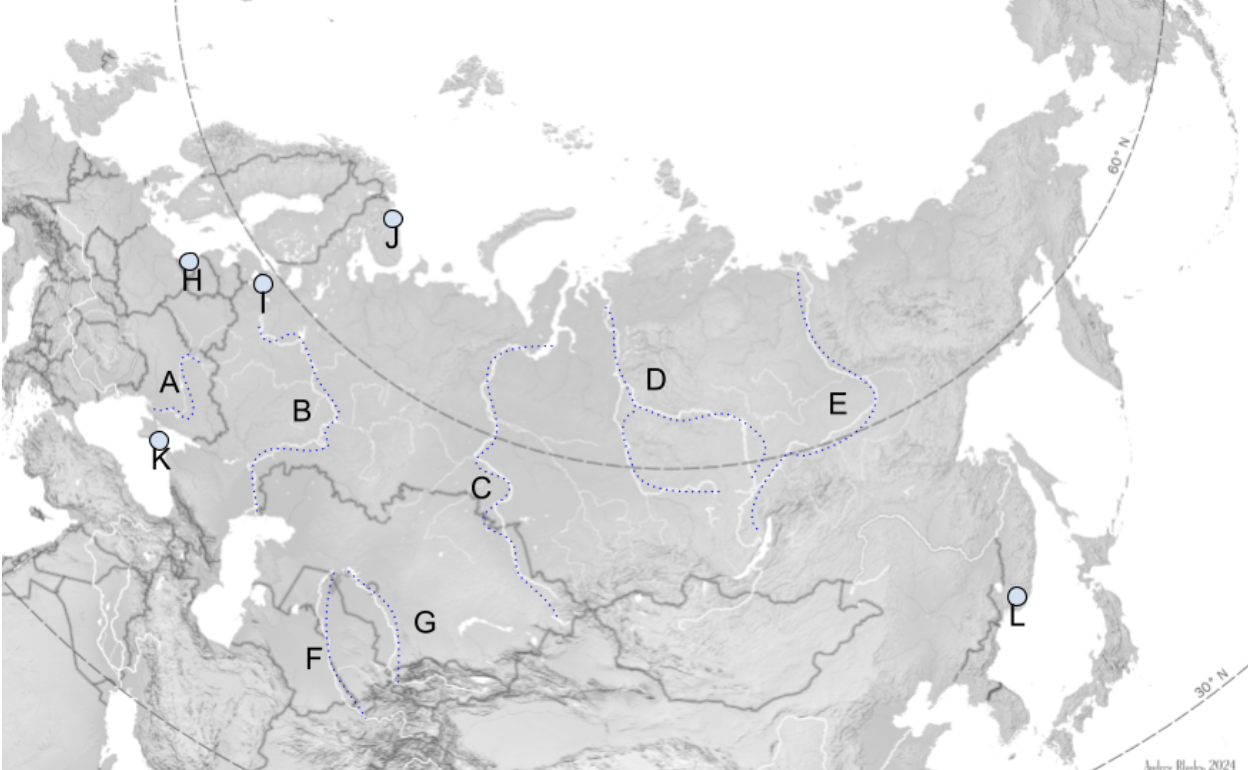
A
Dniepro River
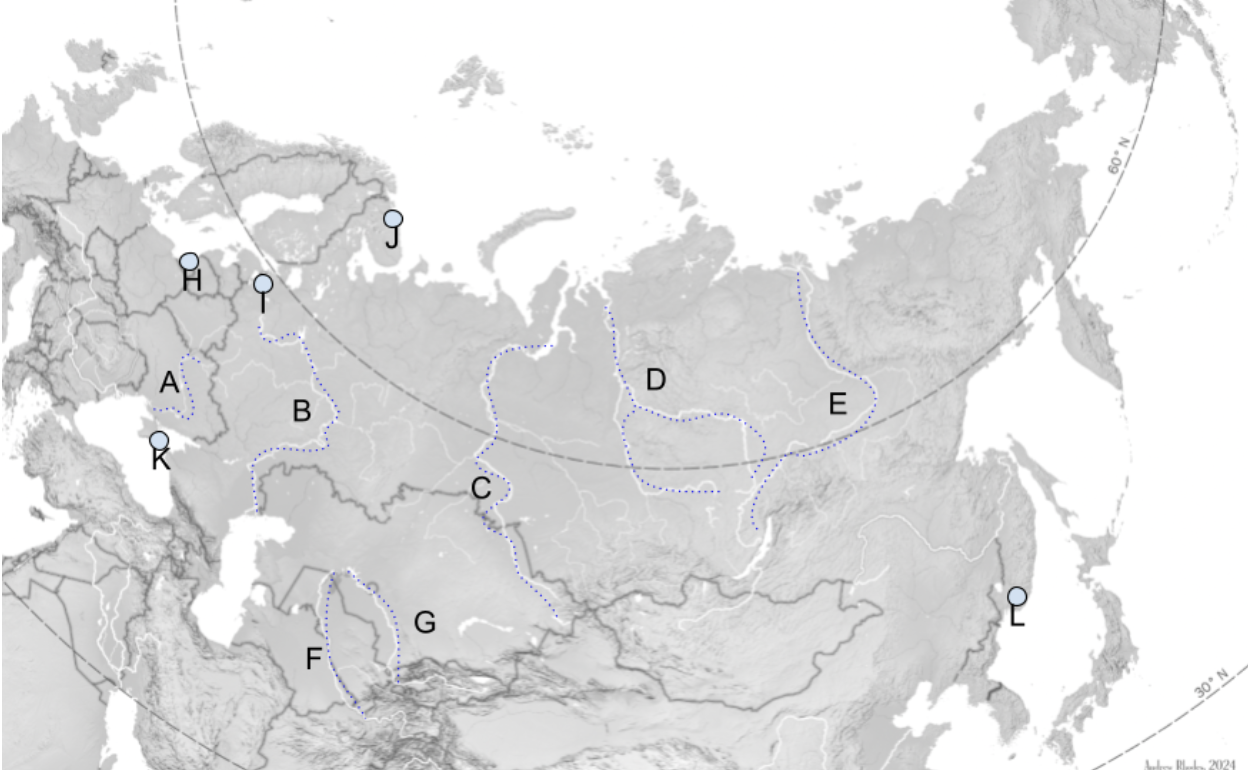
B
Volga River
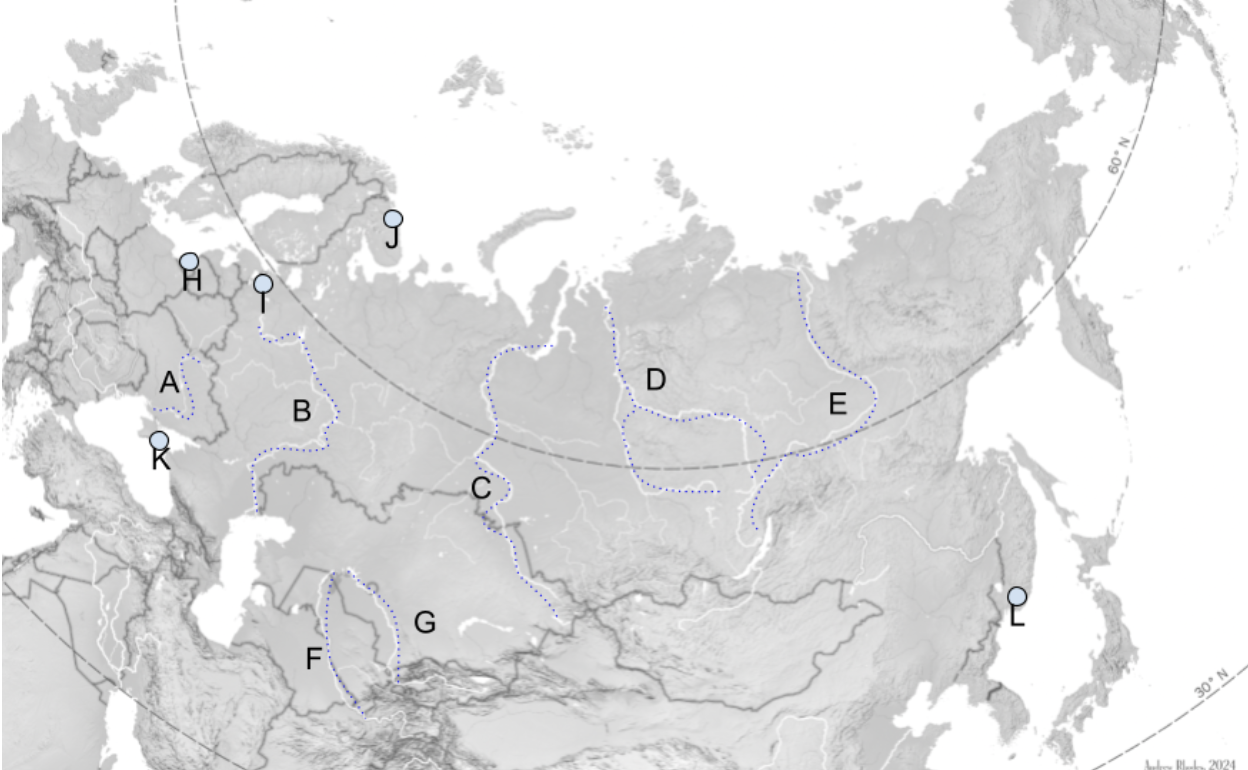
C
Lena River
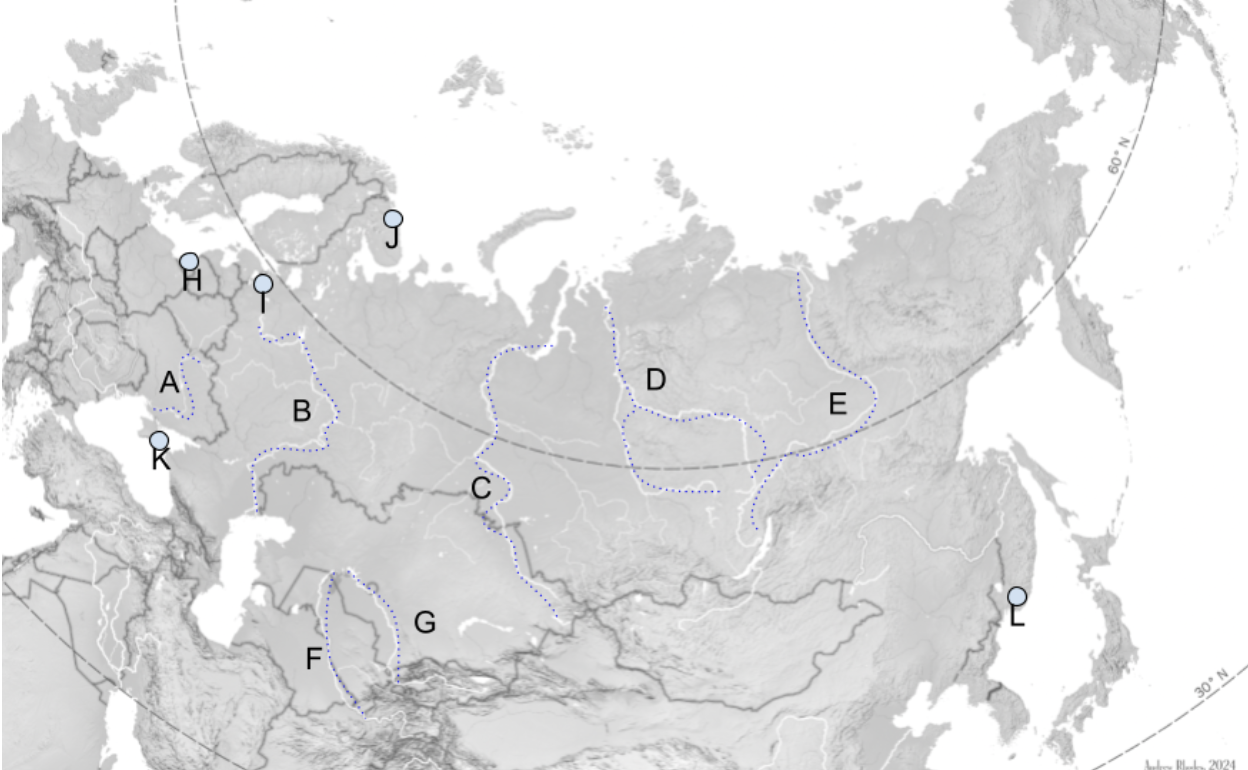
D
Ob River
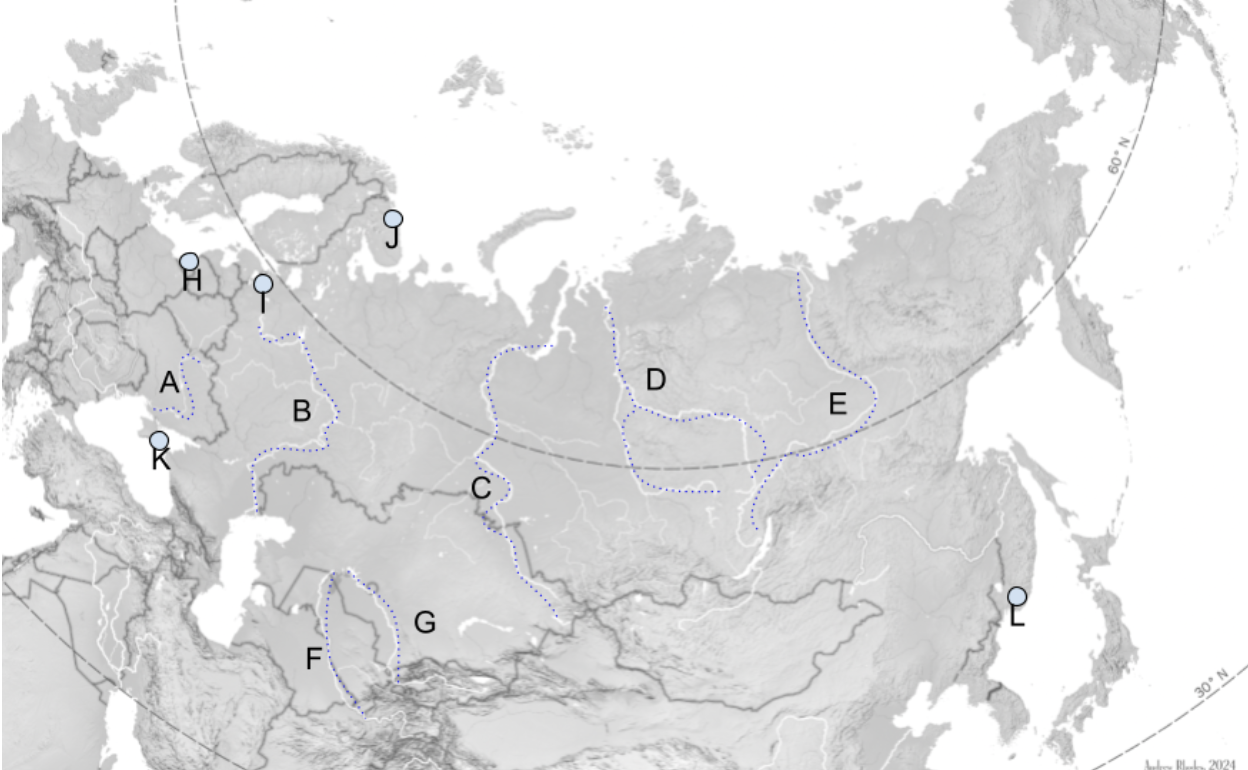
E
Yenisei River
F
Amu Darya
G
Syr Darya
H
Kaliningrad
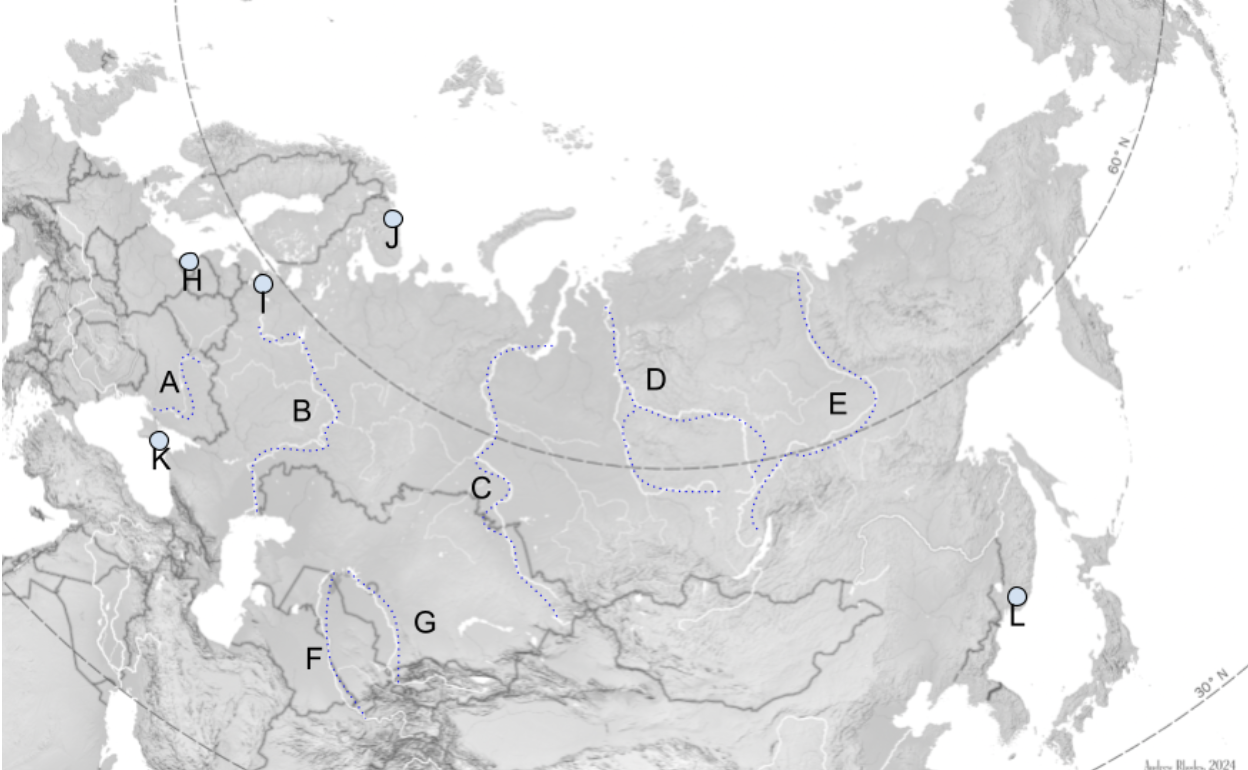
I
St. Petersburg
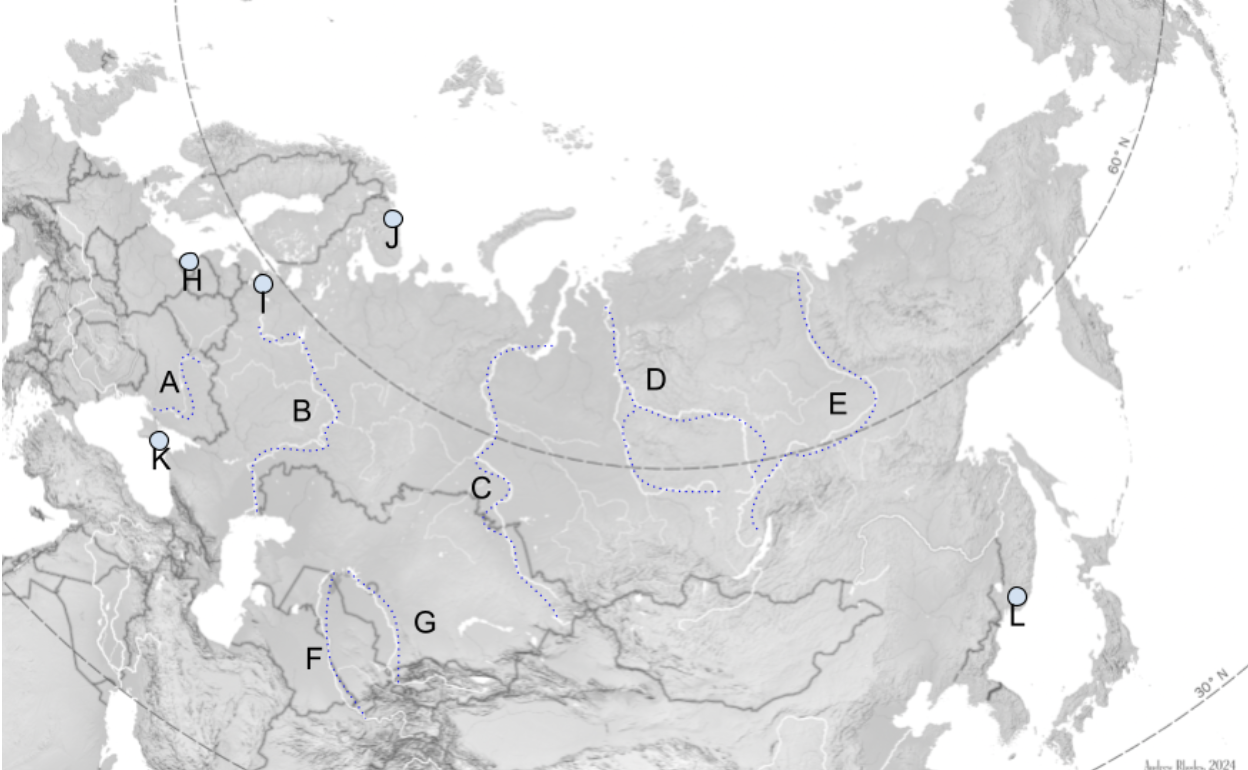
J
Murmansk
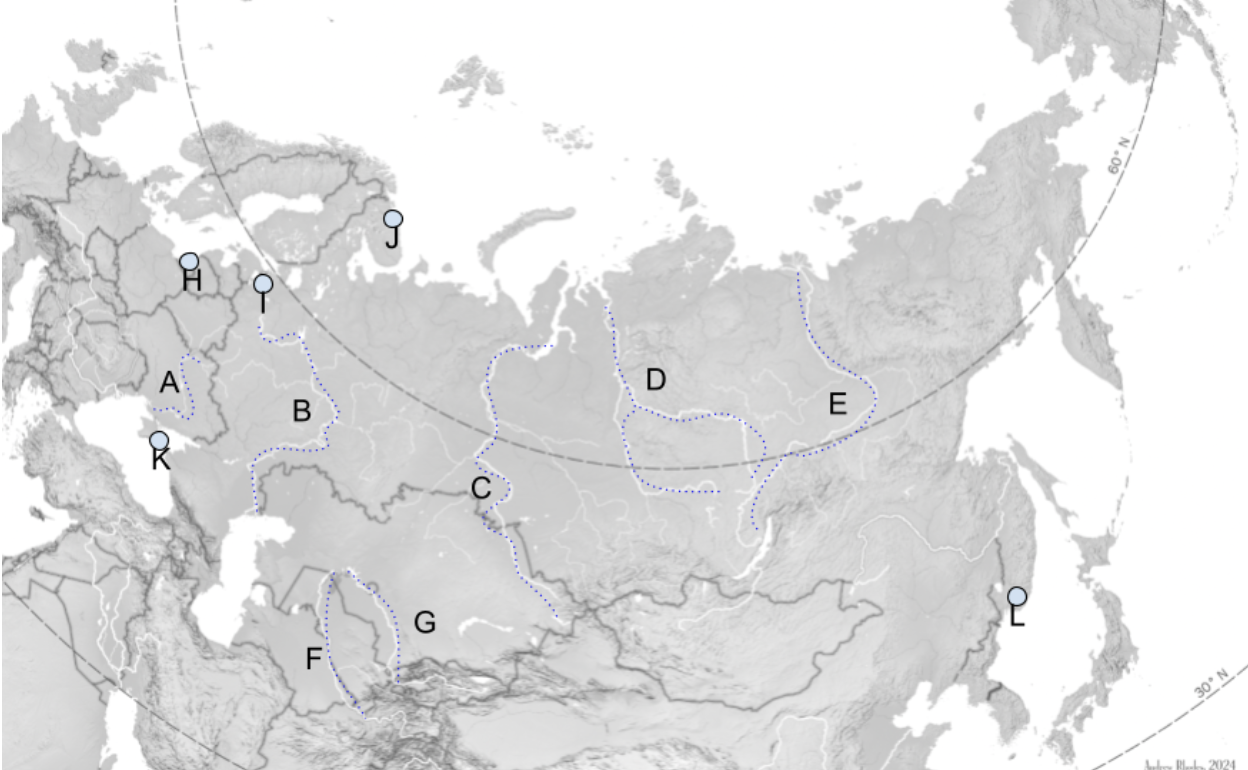
K
Sevastopol
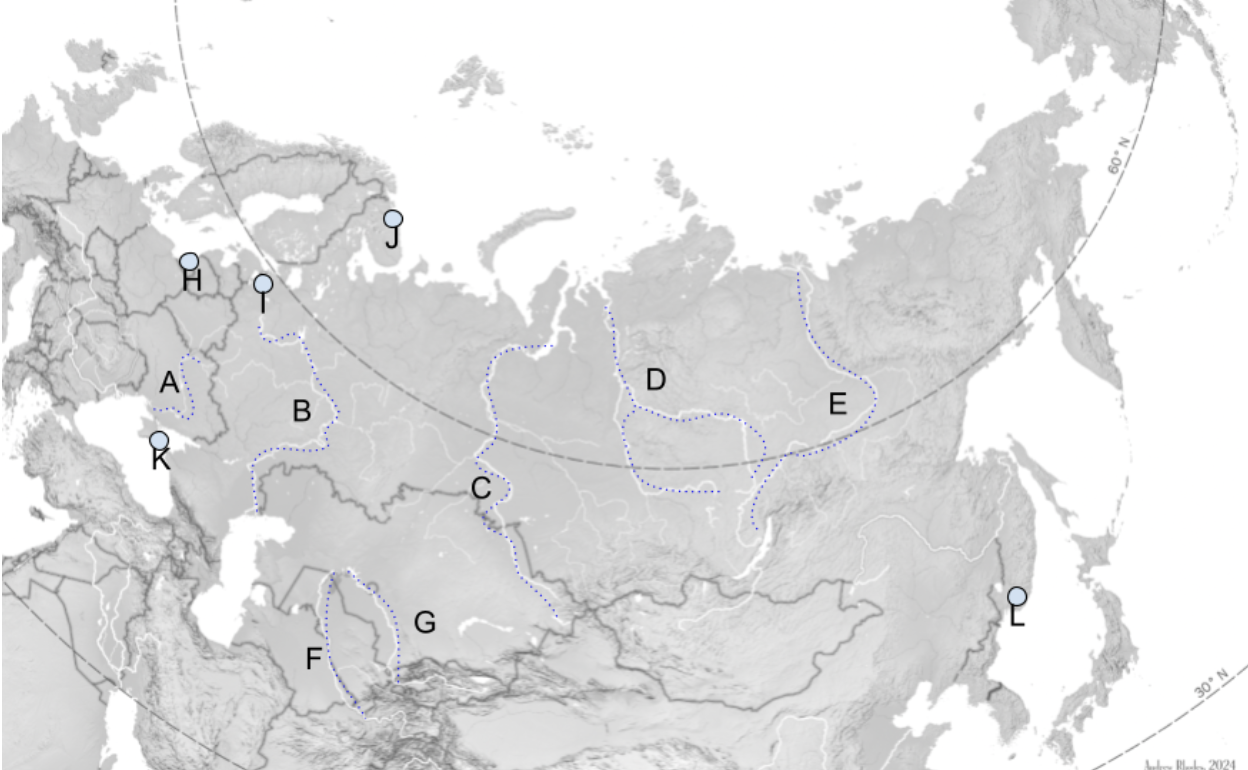
L
Vladivostok
GIUK Gap
Gap between Iceland and the UK that limits the utility of Russian ports, along with other choke points.
Soviet Union States
Armenia, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Estonia, Georgia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Latvia, Lithuania, Moldova, Russia, Ukraine, Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan
Warsaw Pact
Soviet Union, Bulgaria, Czechoslovakia, East Germany, Hungary, Poland, Romania
Ethnically Russian Baltic States
Estonia and Latvia
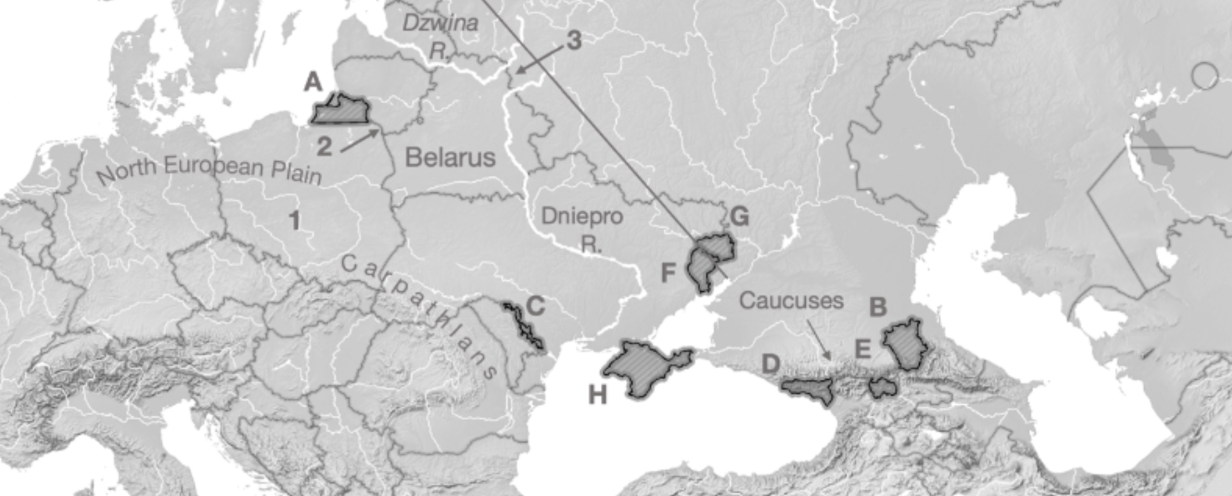
A
Kaliningrad
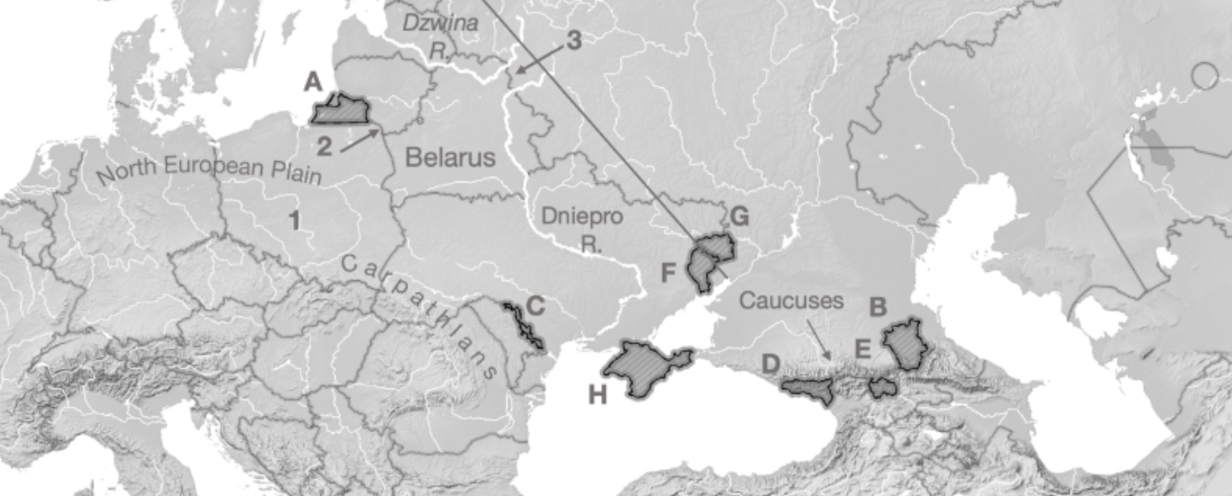
B
Chechnya
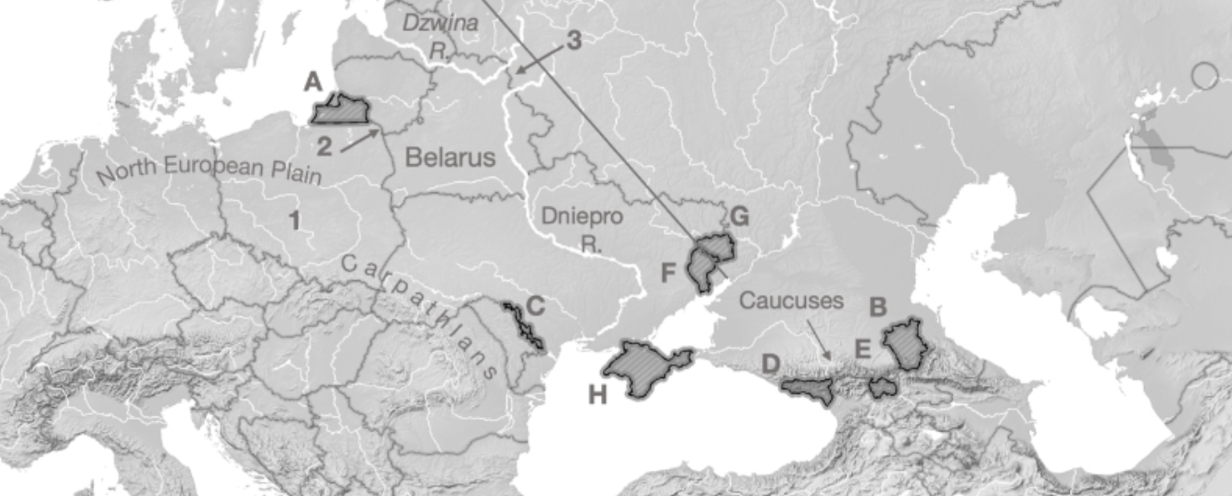
C
Transnistria
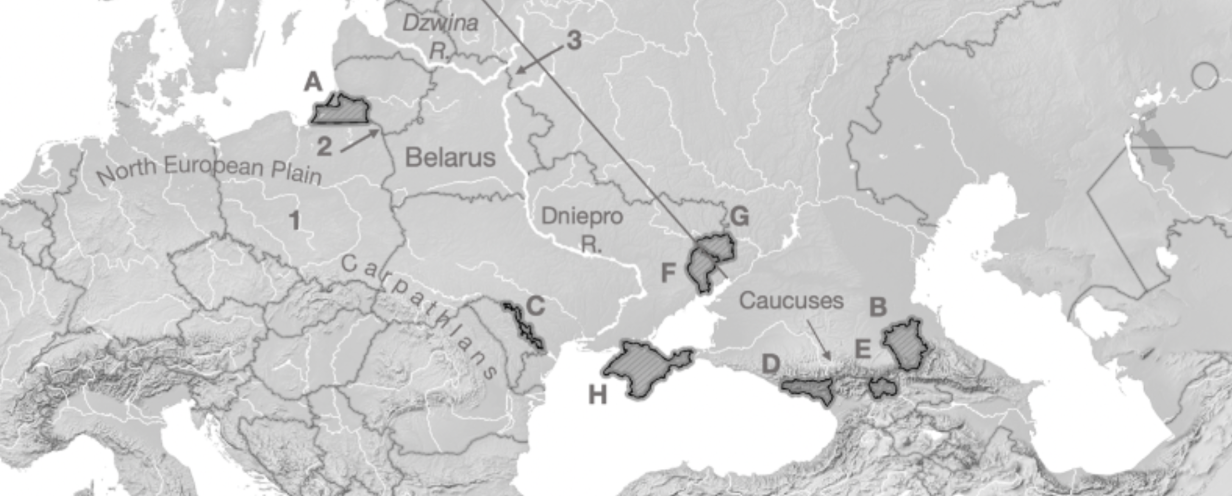
D
Abkhazia
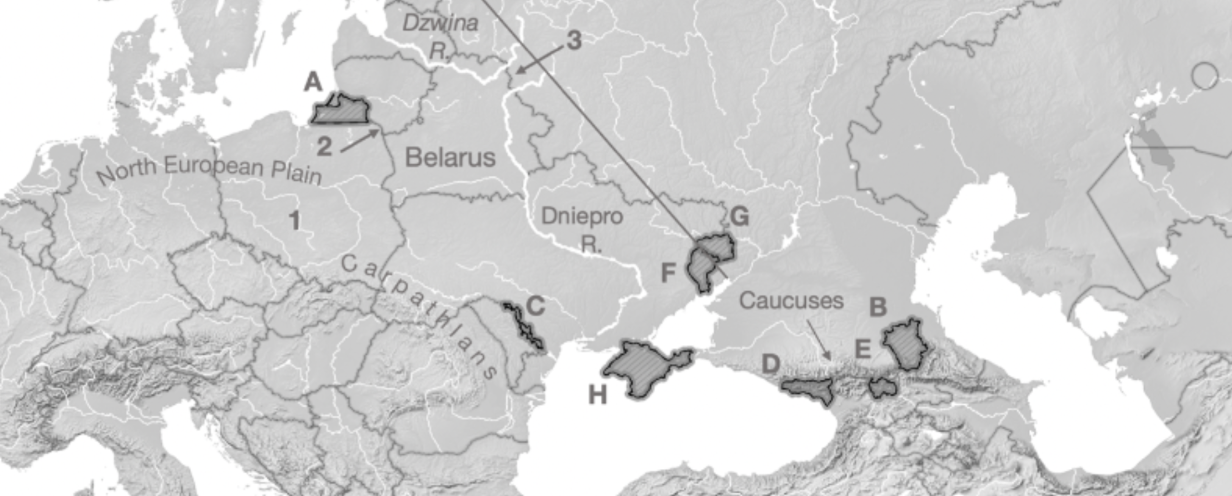
E
South Ossetia
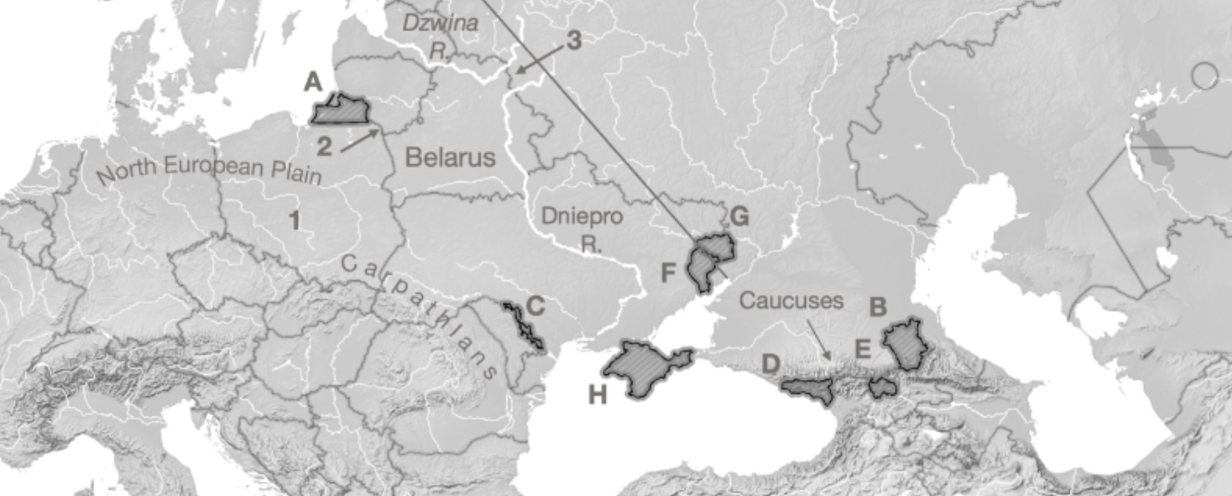
F
Luhansk
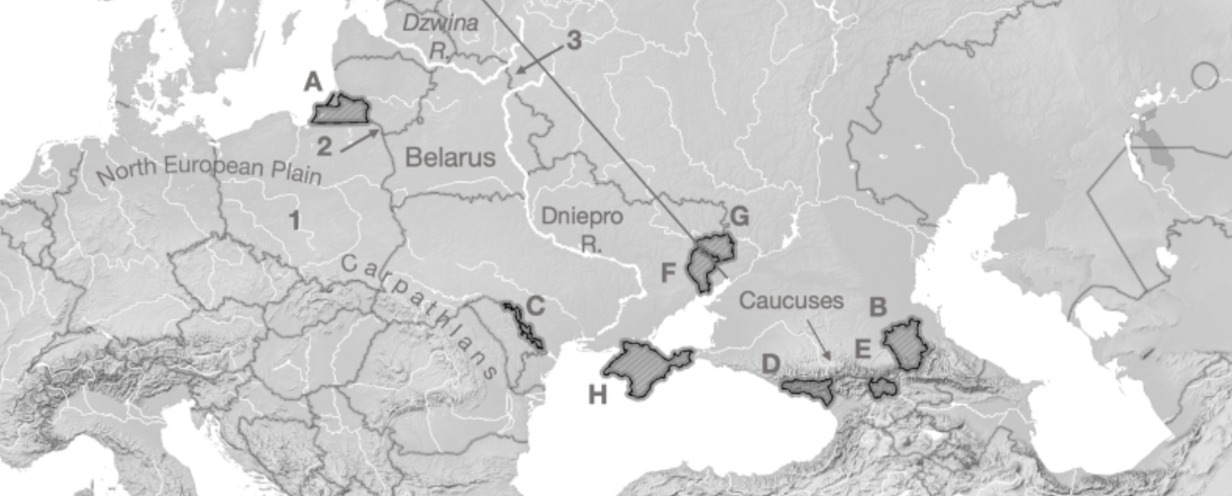
G
Donetsk
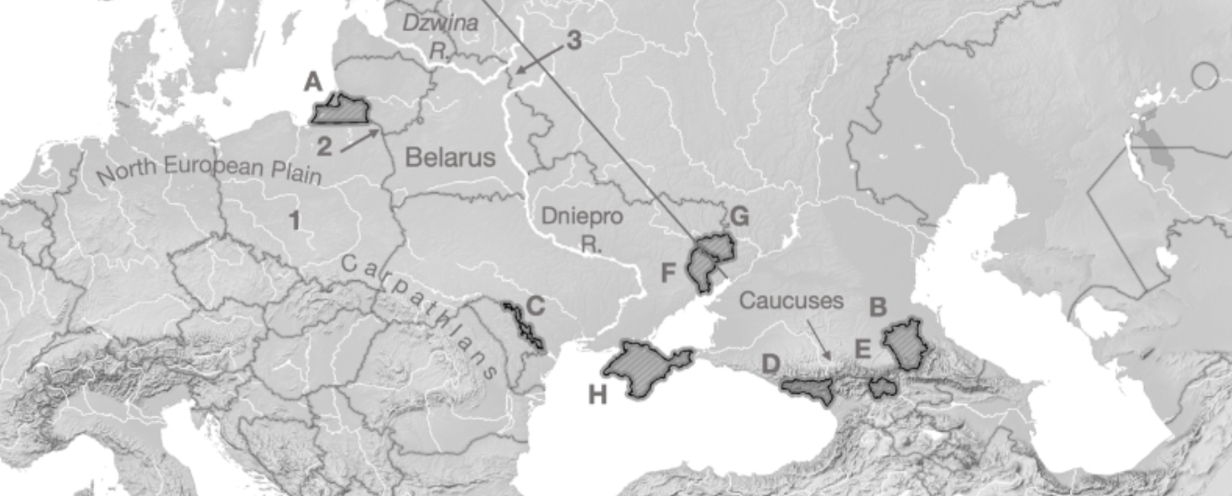
H
Crimea
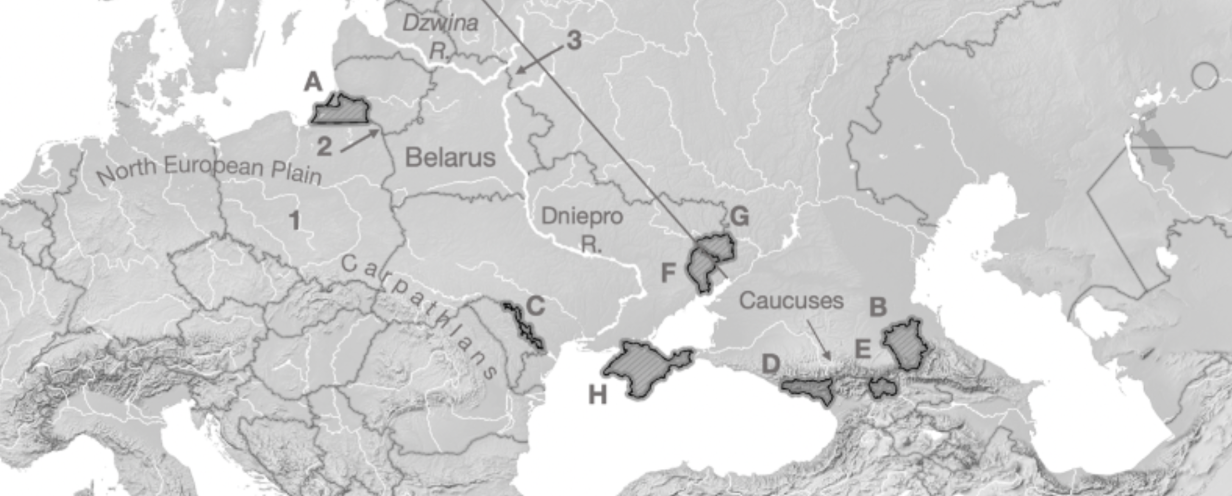
1
Fulda Gap
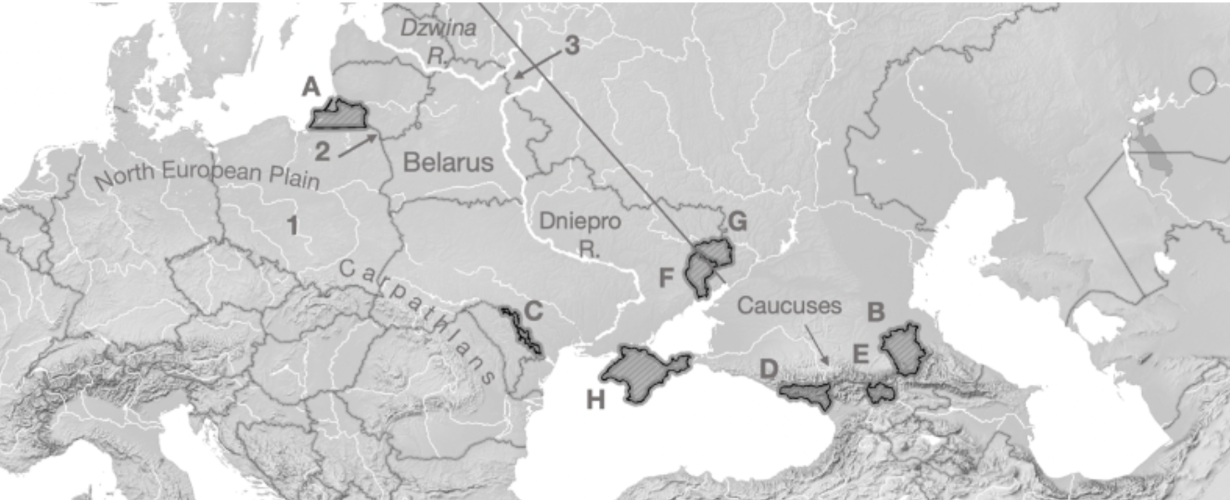
2
Sulwalki Gap
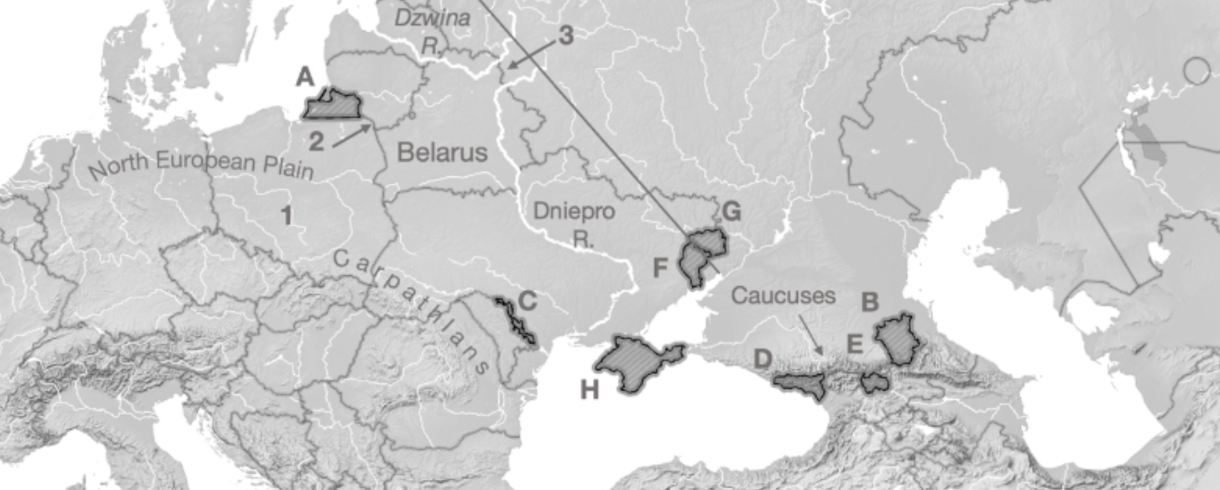
3
Smolensk Gate
Carpathians
Mountain range crossing through Romania, Ukraine, and Poland
Caucuses
Mountain range across Georgia, Azerbaijan, Armenia, and Russia
Centrifugal forces
Forces that pull a state/area apart — geographic features, natural borders, poor governance, poor infrastructure
Centripetal forces
Forces that pull a state/area together — shared culture, religion, “civilization”
EU Countries
Ireland, Portugal, Spain, France, Luxembourg, Belgium, Netherlands, Germany, Denmark, Sweden, Finland, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Czechia, Austria, Italy, Slovenia, Croatia, Hungary, Slovakia, Romania, Bulgaria, Greece, Cyprus, Malta
NATO Countries
EU Countries + Iceland, Norway, UK, Montenegro, Albania, North Macedonia, Turkey, US, Canada - Sweden, Austria, Malta, Cyprus
NATO/EU and Europe Unification
Overcoming centrifugal forces and break cycle of European conflict
Divided Place: Ireland
Protestant England took control of Catholic Ireland in the 16th century
English and Scottish Protestant settlers displaced many Irish, particularly in the North
Conflict led to a 1922 partition into an independent Republic of Ireland and Northern Ireland, which became a part of the UK
Violence within Northern Ireland ended with the 1998 Belfast Agreement, which kept an open border
Brexit restarted the open border question, reinvigorated discussion of Irish unification and talk of Scottish and Welsh secession from the UK