Shormann Algebra 1 and 1/2 Geometry Vocabulary ‧₊ ᵎᵎ 🍒 ⋅ ˚✮
1/105
Earn XP
Description and Tags
The Shormann math for 9th grade set available not only on Quizlet!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
106 Terms
Square Root
if x is greater than 0, than the square root of x is the unique positive real number such that the square root of x squared equals x
Digit
any of the Hindu-Arabic numerals 1 through 9, and 0
Counting (Natural) Numbers
numbers used to count objects (like 1, 2, 3, etc.)
Whole Numbers
counting numbers and the number 0
Integers
whole numbers, and all negative numbers
Real Numbers
any number used to describe a positive or negative number - includes all integers, decimals, and fractions
Imaginary Numbers
the result of taking the square root from a negative number - normally, the square root of -1 is factored out and exchanged for the symbol “i” - i2 = -1
Absolute Value Symbol
two vertical bars enclosing a number, like this: IaI
Algebraic Subtraction
if a and b are real numbers, then a-b = a + (-b), and -b is the opposite of b
Ratio
the size of one thing relative to another
Prime Number
a number that is only divisible by itself and one
Numerator
the top value in a fraction
Denomenator
the bottom value in a fraction
%
symbol for percent, which means “per 100”
Proportional
having a constant ratio
Analogy
resemblance in some particulars between things otherwise unlike; similar
Algebra
a generalization of arithmetic, where letters representing numbers are combined according to the rules of arithmetic, often to solve for an unknown value
Don’t Write the 1
1x = x and x to the power of 1 = x
X to the Power of 0 = 1
anything (except 0) raised to the power of 0 equals 1
X.X.X.X…. = X to the Power of “N”
for example, x.x = x squared, x.x.x = x cubed, etc.
X to the Power of -N = 1/X to the Power of N
anything (except 0) raised to a negative power equals 1 over anything raised to the opposite of that power
Polynomial in One Unknown
one term, or the sum of individual terms of the form ax to the power of n, where a is a real number, x is an unknown quantity, and n is a whole number
Polynomial in More than One Unknown
one term, or the sum of individual terms of the form ax to the power of n y to the power of m z to the power of p where a is a real number, and the rest are unknown quantaties
Axiom
a self-evident statement about something obvious, normally common to all sciences
Postulate
a construction (drawing) of something, normally common to a particular science, that may be obvious — assumed to be true without proof
Point
that which has no part — its location is represented by a dot
Line
a widthless length — its location is represented on paper by using a pencil and a straight edge
Line Segment
a line with a start point and end point
Plane
a flat surface having length and width only
Ray
a line with a starting point but no end point
Angle
two rays in the same plane that share a common starting point and do not overlap
Right Angle
formed when two lines or line segments intersect, forming 4 adjacent angles that are equal and perpendicular to each other
Obtuse Angle
an angle greater than a right angle
Acute Angle
an angle less than a right angle
Parallel
two lines that never intersect
Circle
a plane figure contained by one line called the circumference, such that all the straight line segments falling upon it are equal to each other, and have one point in common, the center
Diameter
any line segment drawn through the center of a circle and terminated in both directions by the circumference
Radius
half the diameter
Polygon
simple, closed, coplanar geometric figures whose sides are straight lines
Equilateral Triangle
all sides are congruent (equal)
Isosceles Triangle
two sides are congruent
Scalene Triangle
no sides are congruent
Right Triangle
one right angle
Obtuse Triangle
one angle greater than a right angle
Acute Triangle
three acute angles
Parallelogram
two pairs of parallel sides
Trapezoid
one pair of parallel sides
Rectangle
a parallelogram with four right angles
Rhombus
an equilateral parallelogram
Square
a rhombus with four right angles
Polyhedron
formed by four or more polygons that intersect only at their edges
Solid
three dimensional figures
Cone
circular base and a lateral surface that comes to a point
Cylinder
two parallel circular bases connected by a lateral surface
Sphere
the set of points a given distance from a given point called the center
Deductive Reasoning
applying rules
Inductive Reasoning
finding rules
Mathematical Proof
a deductive argument where rules and definitions are applied to reach a logical conclusion
Theorem
also called propositions, these are true mathematical statements requiring proof — theorems particular to a certain discipline are sometimes called lemma, such as the lemma found in Newton’s science book, Principia
Side
a segment of a polygon
Vertex
where two sides of a polygon, or two rays of an angle, meet
Convex Polygon
a polygon with no indentations
Concave Polygon
a polygon that has at least one indentation
Hypotenuse
in a right triangle, it is the side opposite the right angle
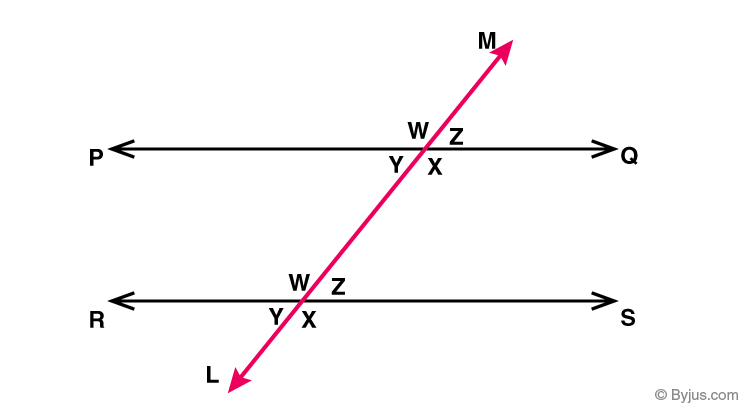
Transversal
a line that intersects two or more parallel lines, and is not perpendicular to those lines
Tesselation
a repeating pattern of shapes that covers a plane with no gaps or overlaps

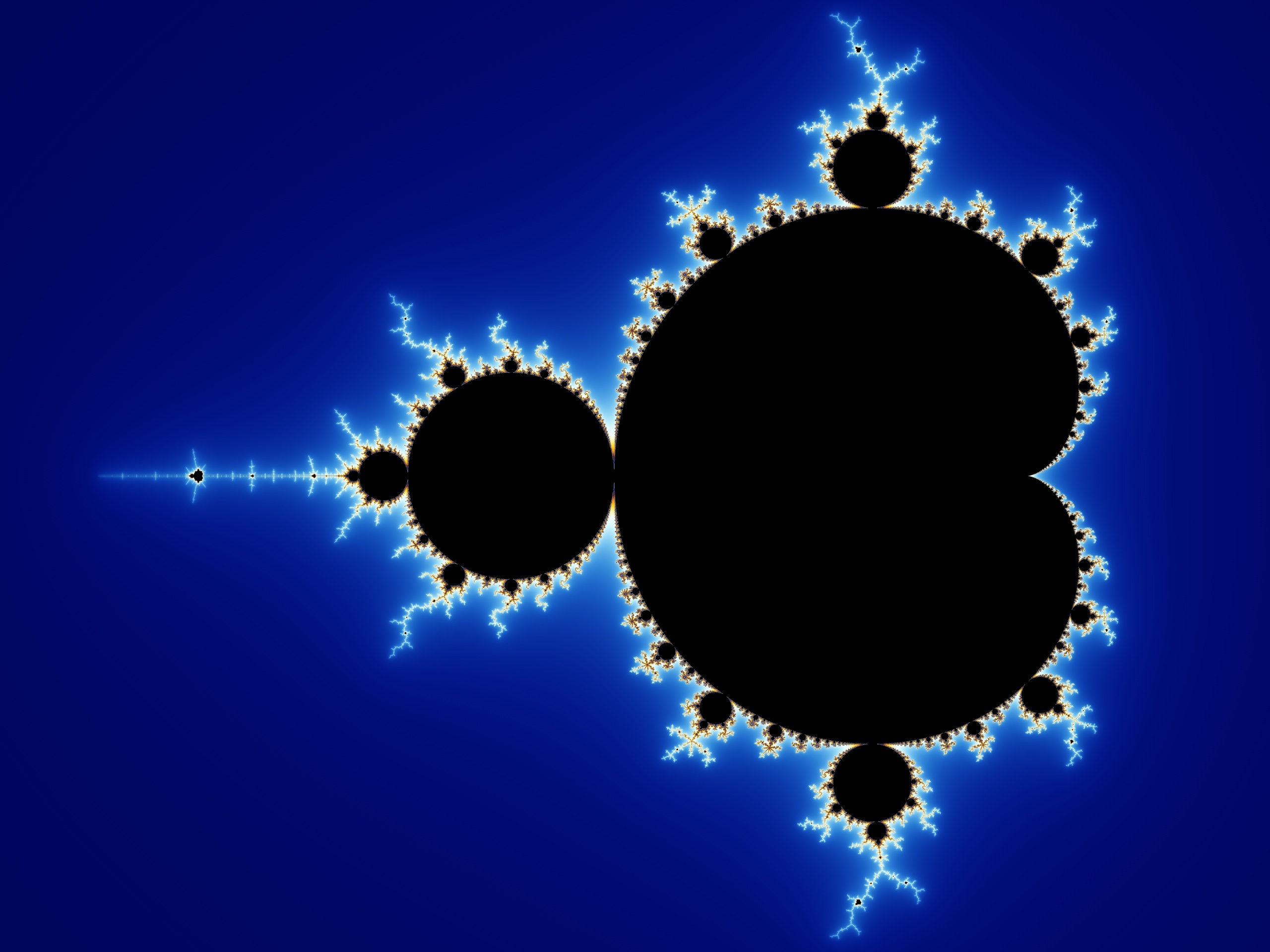
Fractal
an object or quantity that displays self similarity on all scales
Analytical Geometry
where algebra and geometry meet on the coordinate plane
Ordered Pair
a pair of numbers, written in a specific order — on a coordinate plane, an ordered pair is used to identify the location of a point, and has the form (x,y)
Function
a relationship where the output (y) depends on the input (x) — each input, or domain value, maps to one, and the only one value in the output, or range
Relation
like a function, except the input (x), can map to more than one output (y)
Undefined
a function is said to be undefined when a value is not part of its domain
Indeterminate
when both the numerator and denominator equal zero
y = mx + b
the standard form for the equation of a line; where m is the slope and y is the y-intercept
Slope
a ratio expressing the change in the dependent variable (y) with respect to the independent variable (x) — also referred to as “rise over run”
Y-Intercept
the location where a function crosses the y-axis
Cartesian Coordinate System
also called a coordinate plane, it is a plane containing a horizontal “x” axis and a vertical “y” axis — it is used to graph pairs, functions, experimental data, etc.
Data
a collection of facts and information recorded during an experiment, from which conclusions and decisions can be made
Right Solid
any geometric solid whose sides are perpendicular to its base
Calculus
the mathematical study of rates of change
Delta
the symbol used in calculus that means “change in”
Infinitesimal
the idea that a quantity can be close to, but not equal to zero
Limit
the application of infinitesimals to evaluating a function
Tangent Line
a line that touches a function essentially at one point
Derivative
the slope for a line drawn between two points on a function that are an infinitesimally small delta x apart
Integral
the use of infinitesimals to calculate area
Mean
the average of a set of numbers
Median
the middle number in a set of numbers
Mode
the most often occurring number in a set of numbers
Range
the difference between the smallest and largest numbers in a set of numbers
Statistics
mathematics related to the collection, organization, and interpretation of mathematical data
Histogram
a type of bar graph where each set of data is organized into groups, and the frequency of values in each group is graphed
Normal Distribution
also called a bell curve, this is a common pattern obtained from a histogram
Bit
a digit in a binary number system — it can have two values, 1, or 0 — in computer memory, this is a small electrical switch which is either on (value 1) or off (value 0)
Byte
in computer memory, this equals 8 bits
Pixel
abbreviation for “picture element,” the small discrete elements of digital photography and computer/television screens containing color information
Matrix
a two-dimensional array consisting of rows and columns of numbers
Array
like a matrix, but not limited to two dimensions — used in computer data storage
Sequence
numbers ordered in a way that they form a definite pattern