🔌| Chapter 14: Peripheral Nervous System
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
What are the two main divisions of the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)?
Motor (efferent) division and Sensory (afferent) division.
What are the two types of peripheral nerves?
They are classified as cranial or spinal nerves.
What are the three connective tissue coverings of a nerve?
1) Endoneurium - loose connective tissue that encloses axons and their myelin sheaths; 2) Perineurium - coarse connective tissue that bundles fibers into fascicles; 3) Epineurium - tough fibrous sheath around a nerve.
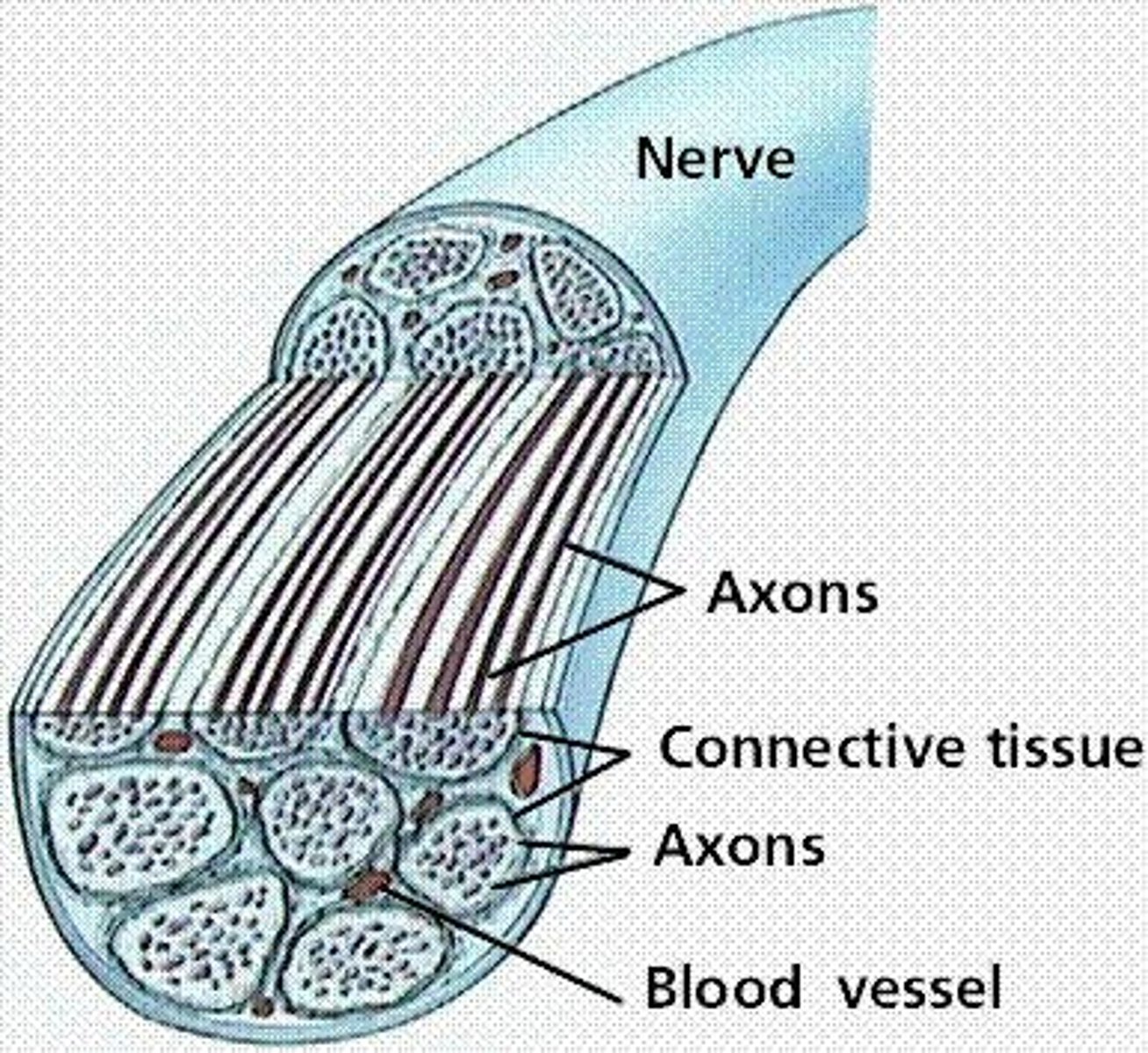
How are nerves classified based on impulse direction?
1) Mixed nerves - both sensory and motor fibers; impulses both to and from CNS; 2) Afferent nerves - impulses only toward CNS; 3) Efferent nerves - impulses only away from CNS.
What do ganglia contain in the PNS?
Neuron cell bodies associated with nerves.
What type of ganglia are associated with afferent nerve fibers?
Sensory ganglia.
What type of ganglia are associated with efferent nerve fibers?
Motor (visceral) ganglia.
What is the regeneration potential of mature neurons in the PNS?
Mature neurons are amitotic, but if the soma of a damaged nerve is intact, the peripheral axon may regenerate.
What occurs during Wallerian degeneration?
Axon fragments spread distally from the injury, and macrophages clean the dead axon while the myelin sheath remains intact.
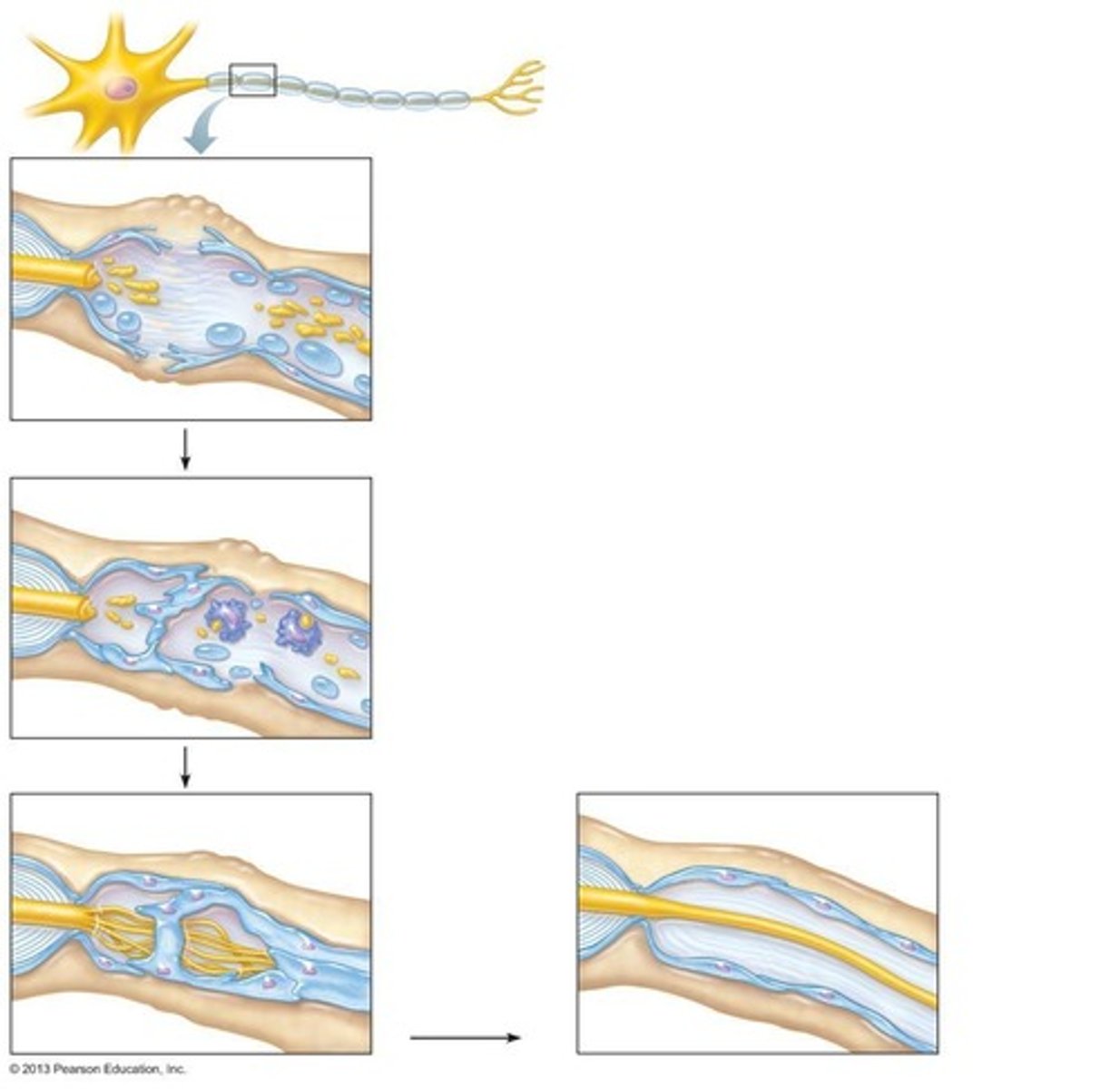
What is the role of Schwann cells in nerve regeneration?
They form a regeneration tube that guides the growth of the axon and help in the formation of a new myelin sheath.
What inhibits regeneration of CNS fibers?
CNS fibers bear growth-inhibiting proteins that prevent regeneration.
What is the treatment approach for promoting CNS nerve regeneration?
Neutralizing growth inhibitors, blocking receptors for inhibitory proteins, and destroying chondroitin sulfate.
How many pairs of cranial nerves are there?
Twelve pairs.
Which cranial nerves attach to the forebrain?
Two cranial nerves attach to the forebrain; the rest are associated with the brain stem.
What is the general classification of most cranial nerves?
Most cranial nerves are mixed nerves; two pairs are purely sensory.
How are cranial nerves numbered?
They are numbered (I through XII) and named from rostral to caudal.
What mnemonic helps remember the cranial nerves?
"On occasion, our trusty truck acts funny—very good vehicle anyhow" and "Oh once one takes the anatomy final, very good vacations are heavenly."
What is the primary function of the Olfactory Nerves (I)?
Purely sensory function related to smell.
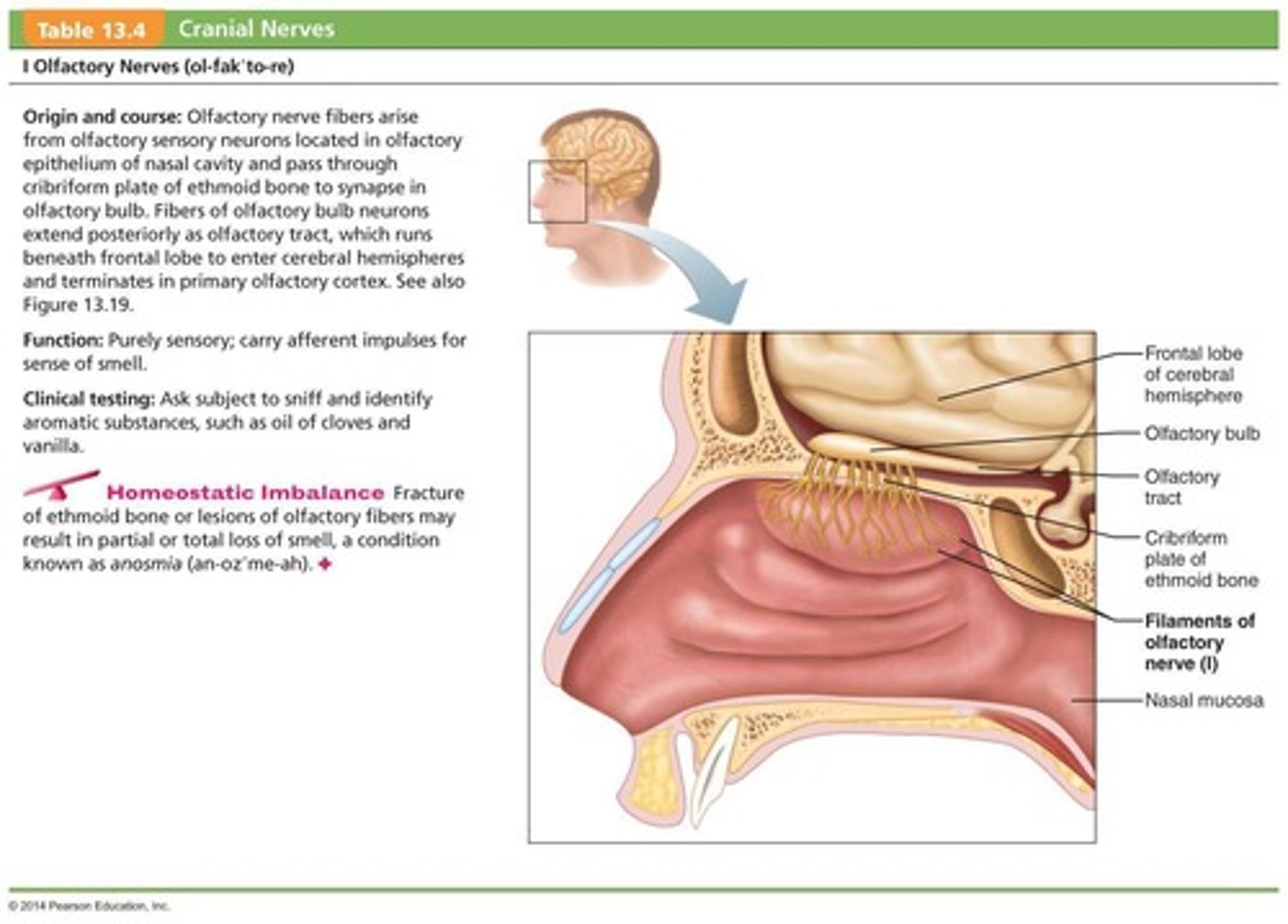
Where do the Olfactory Nerves (I) run from and to?
They run from the nasal mucosa to the olfactory bulbs.
What anatomical structure do the Olfactory Nerves (I) pass through?
They pass through the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone.
What is the primary function of the Optic Nerves (II)?
Purely sensory function related to vision.
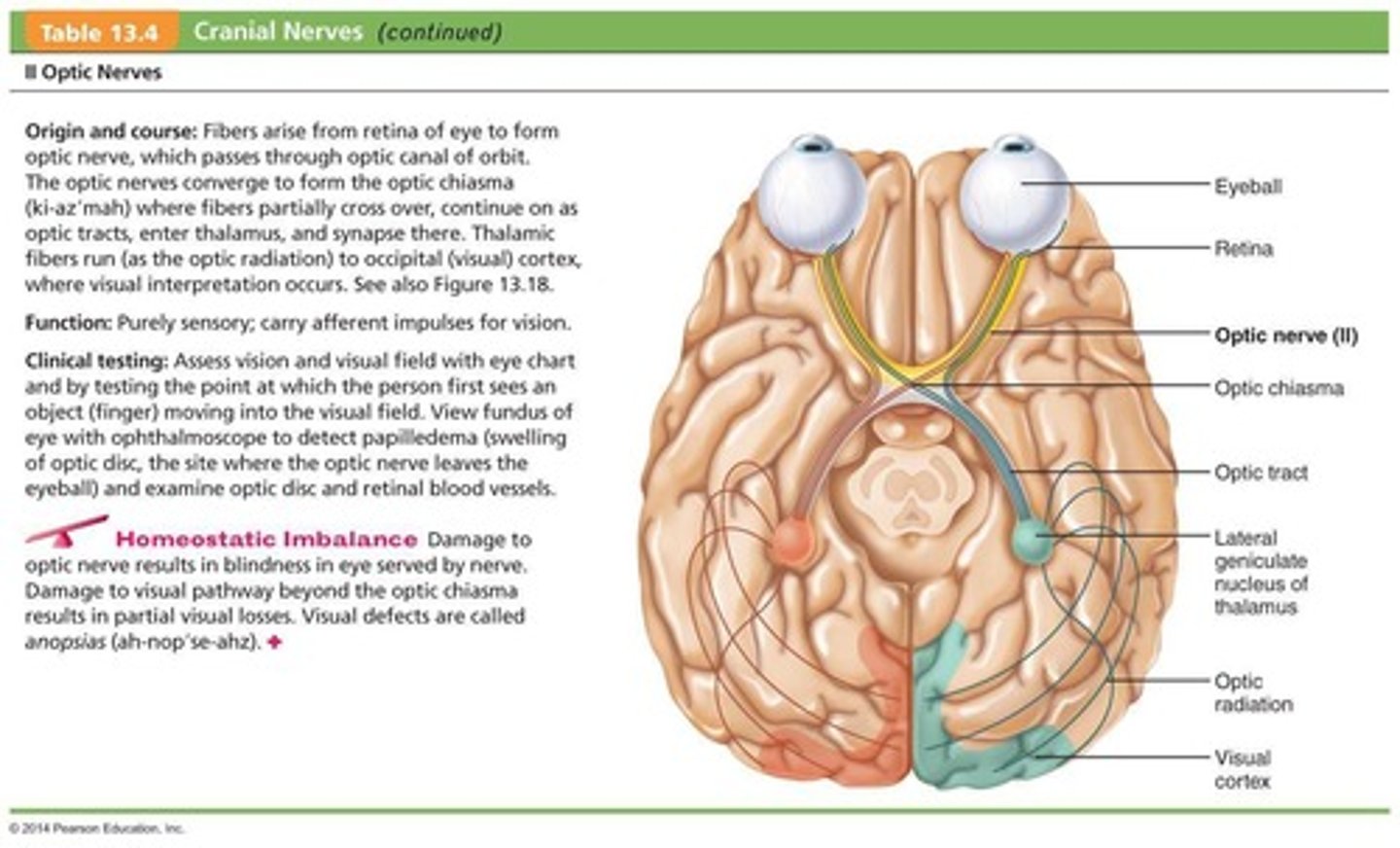
Where do the Optic Nerves (II) arise from?
They arise from the retina and are considered a brain tract.
What is the significance of the Optic Chiasma in the visual pathway?
It is where the optic nerves partially cross over.
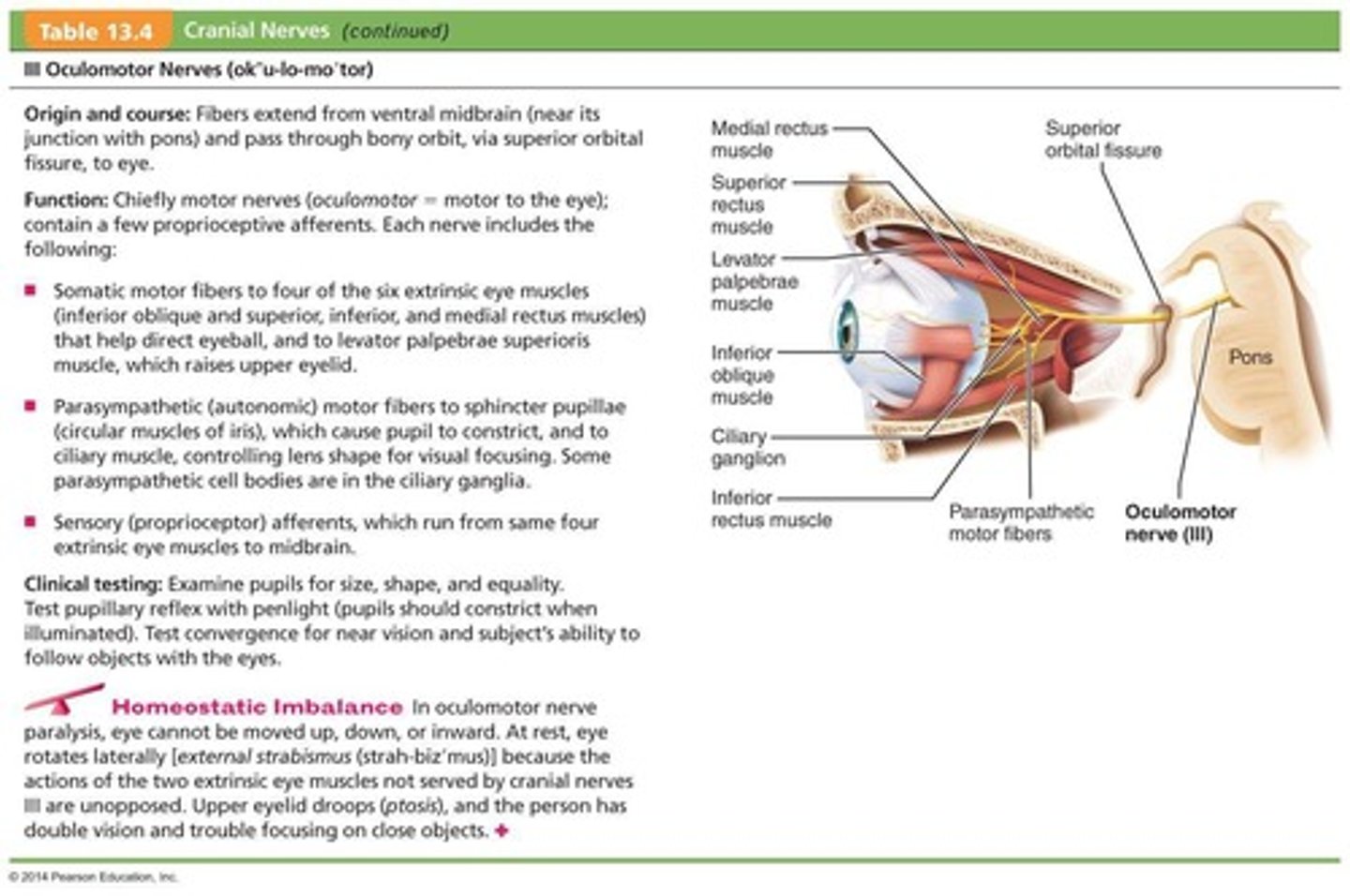
What is the primary function of the Oculomotor Nerves (III)?
They control eye movement, eyelid elevation, and pupil constriction.
What muscles do the Oculomotor Nerves (III) innervate?
They innervate four of the six extrinsic eye muscles.
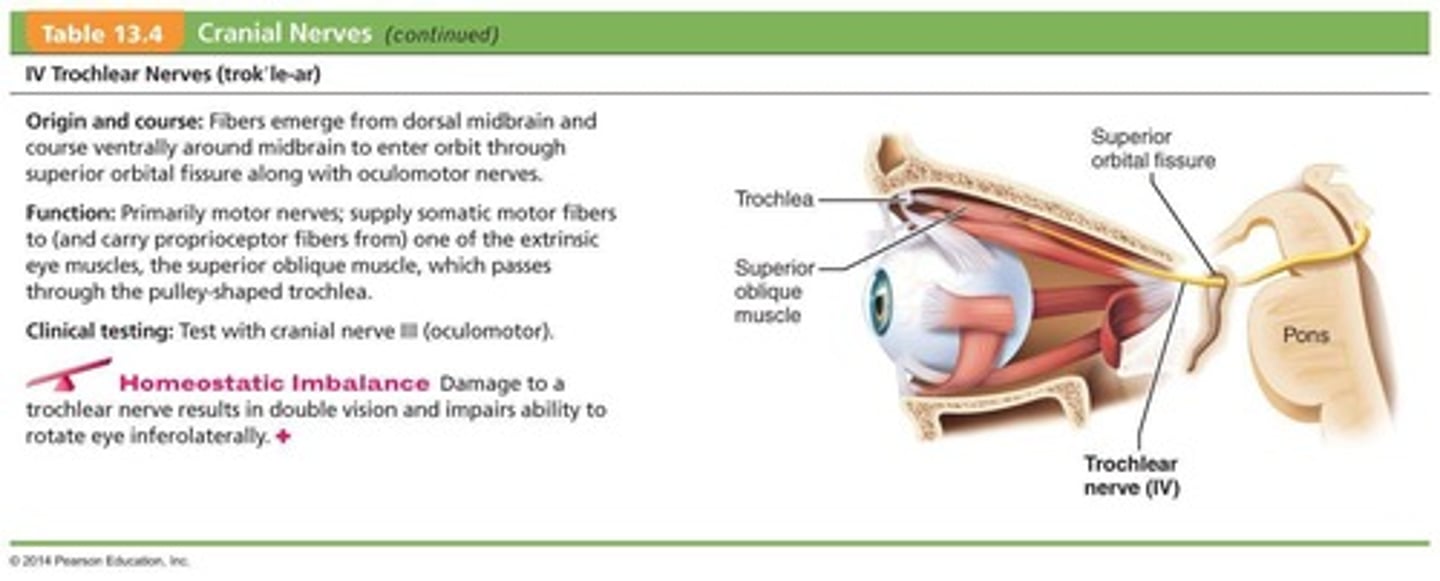
What is the primary function of the Trochlear Nerves (IV)?
Primarily motor function that directs the eyeball.
What muscle is innervated by the Trochlear Nerves (IV)?
The superior oblique muscle.
What is the largest cranial nerve?
The Trigeminal Nerves (V).
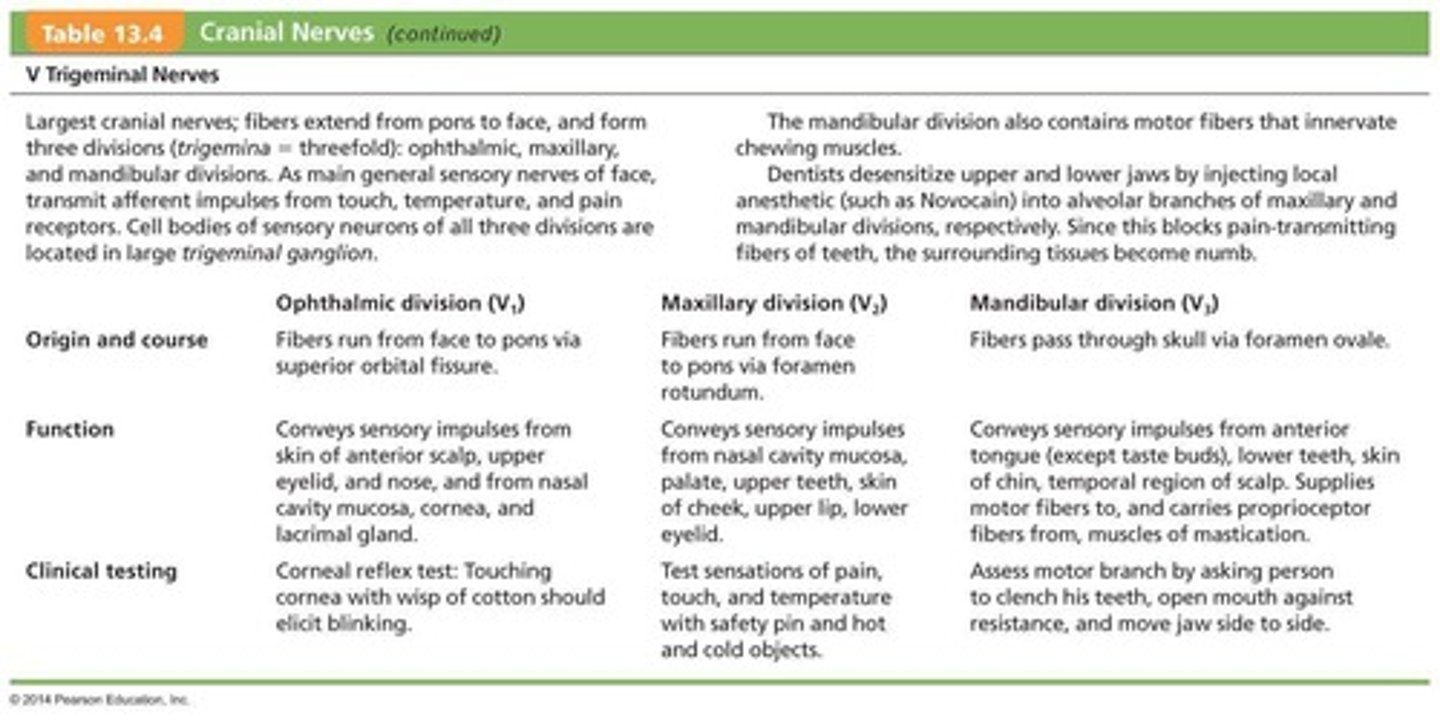
What are the three divisions of the Trigeminal Nerves (V)?
Ophthalmic (V1), Maxillary (V2), and Mandibular (V3).
What type of impulses do the Trigeminal Nerves (V) convey?
Sensory impulses from the face and motor fibers for mastication.
What is the primary function of the Abducens Nerves (VI)?
Primarily a motor nerve that innervates the lateral rectus muscle.
What are the main functions of the Facial Nerves (VII)?
They are chief motor nerves of the face and convey taste impulses from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue.
What functions do the Facial Nerves (VII) include besides motor?
They include parasympathetic functions to lacrimal and salivary glands.
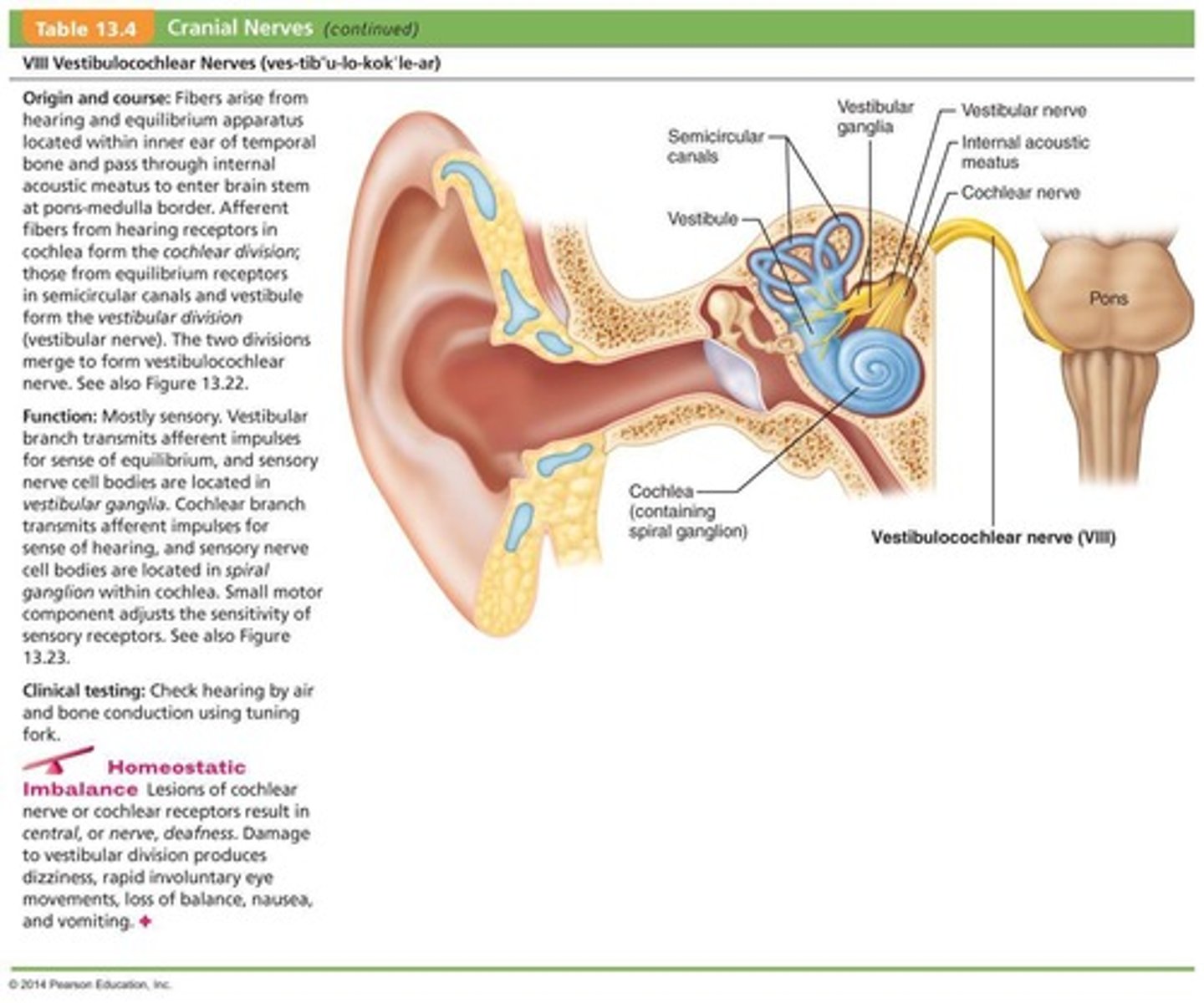
What is the primary function of the Vestibulocochlear Nerves (VIII)?
Sensory function related to hearing and balance.
What is the primary function of the Glossopharyngeal Nerves (IX)?
Mixed function including taste from the posterior one-third of the tongue and sensory from the pharynx.
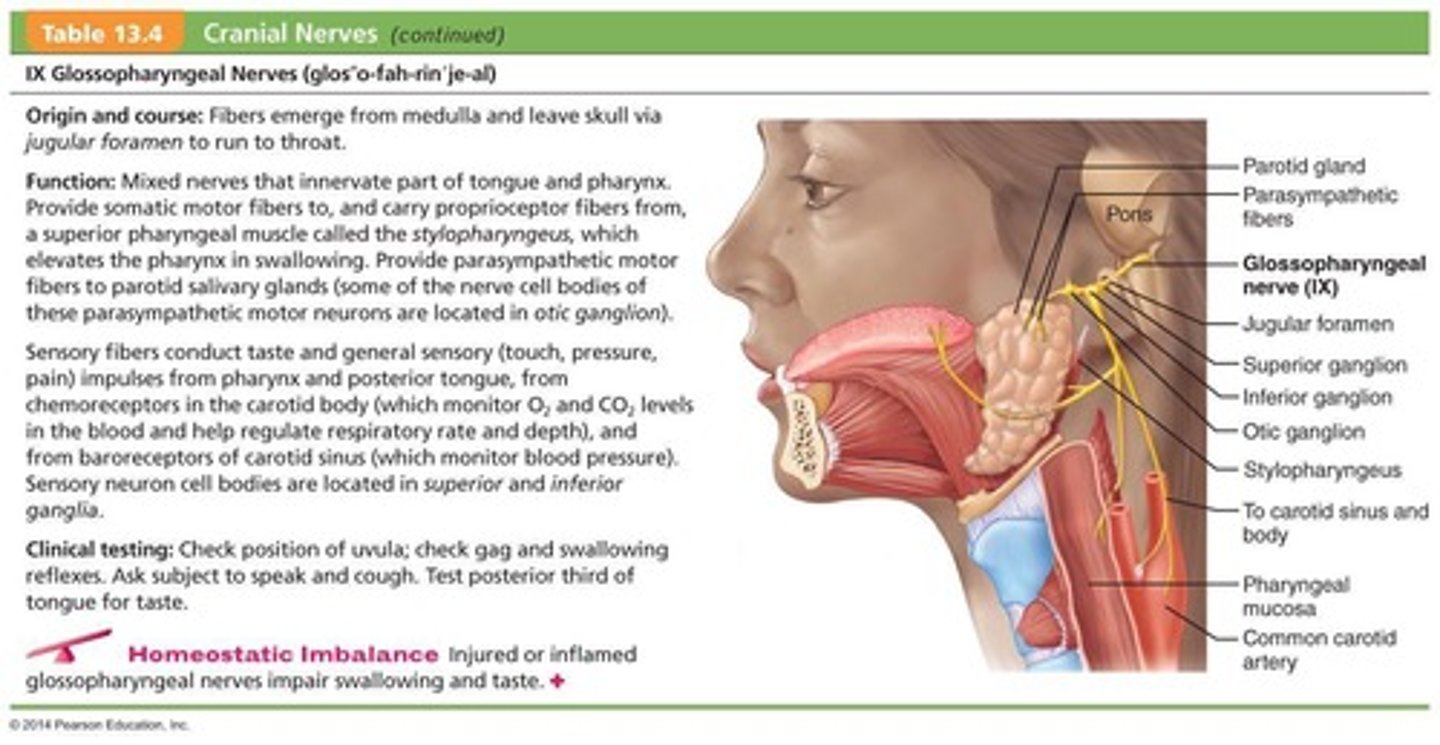
What is the primary function of the Vagus Nerves (X)?
Mixed function including autonomic control of the heart, lungs, and digestive tract.
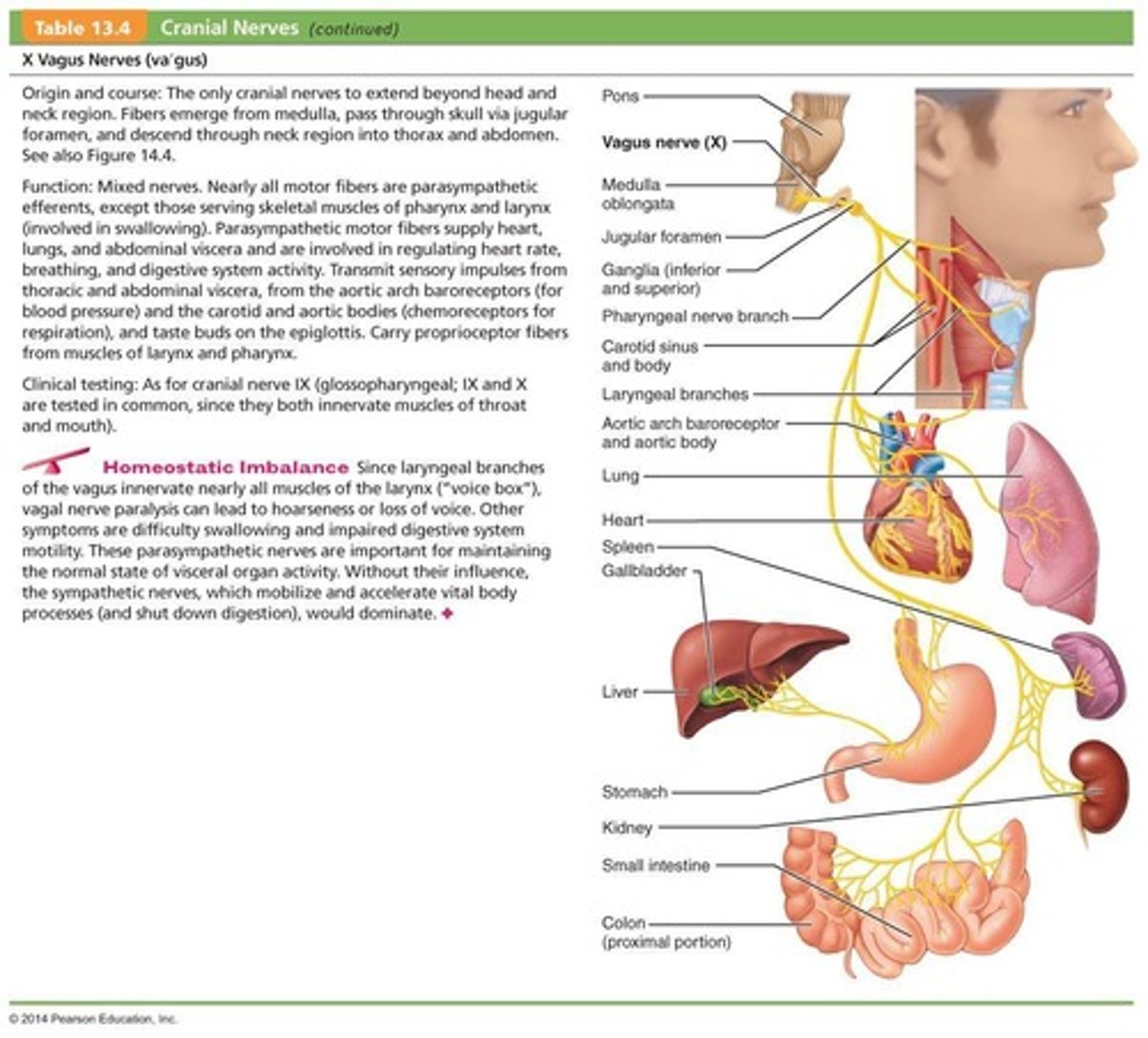
What is the primary function of the Accessory Nerves (XI)?
Primarily motor function to the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles.
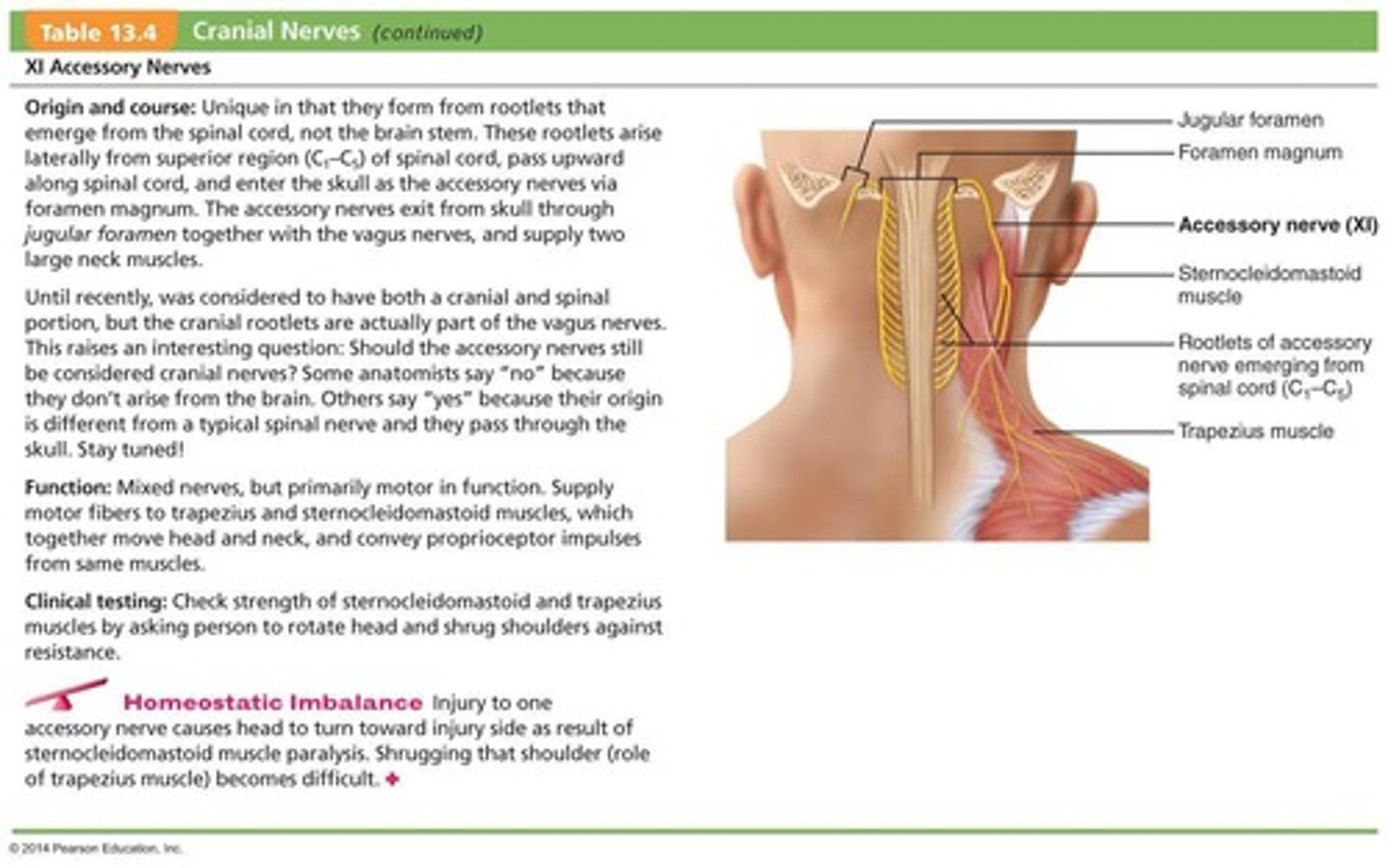
What is the primary function of the Hypoglossal Nerves (XII)?
Primarily motor function for tongue movements.
What does PS stand for in the context of cranial nerves?
PS stands for parasympathetic.
What types of receptors do the afferent fibers of the vestibulocochlear nerves originate from?
Cochlear receptors (hearing) and vestibular receptors (balance).
What is the primary function of the vestibulocochlear nerves?
Mostly sensory function, with a small motor component for adjusting sensitivity of receptors.
What was the former name of the vestibulocochlear nerves?
Auditory nerve.
Where do the glossopharyngeal nerves exit the skull?
Via the jugular foramen.
What are the two main functions of the glossopharyngeal nerves?
Motor functions to innervate part of the throat and pharynx for swallowing, and provide parasympathetic fibers to parotid salivary glands.
What sensory functions do the glossopharyngeal nerves perform?
Conduct taste and general sensory impulses from the pharynx and posterior tongue, and impulses from carotid chemoreceptors and baroreceptors.
What is unique about the vagus nerves compared to other cranial nerves?
They extend beyond the head and neck region.
What type of fibers are primarily found in the vagus nerves?
Most fibers are parasympathetic fibers that help regulate activities of the heart, lungs, and abdominal viscera.
What do the vagus nerves carry impulses from?
Thoracic and abdominal viscera, baroreceptors, chemoreceptors, and taste buds of the posterior tongue and pharynx.
From which spinal cord region are the accessory nerves formed?
Ventral rootlets from the C1-C5 region.
How do accessory nerves exit the skull?
Via the jugular foramina.
What muscles do the accessory nerves innervate?
Sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles.
What is the primary function of the hypoglossal nerves?
Innervate extrinsic and intrinsic muscles of the tongue that contribute to swallowing and speech.
What mnemonic can help remember the primary functions of cranial nerves?
"Some say marry money, but my brother believes (it's) bad business (to) marry money.".
How many pairs of spinal nerves are there?
31 pairs of mixed nerves.
What body parts do spinal nerves supply?
All body parts except the head and part of the neck.
How many cervical spinal nerves are there, and how are they named?
8 pairs of cervical spinal nerves, named for the vertebrae they exit.
What is the difference in exit points for cervical spinal nerves compared to other spinal nerves?
7 cervical vertebrae exist, yet 8 pairs of cervical spinal nerves exit the vertebral canal, with one exiting inferior to C7.
What are the two types of roots that each spinal nerve connects to the spinal cord through?
Ventral roots and dorsal roots.
What do the ventral roots contain?
Efferent (motor) fibers from ventral horn motor neurons that innervate skeletal muscles.
What do the dorsal roots contain?
Afferent (sensory) fibers from sensory neurons in dorsal root ganglia that conduct impulses from peripheral receptors.
How do spinal nerves emerge from the vertebral column?
Via intervertebral foramina.
What are the two types of matter in the spinal cord?
Gray matter and white matter.
What do the dorsal and ventral roots of the spinal nerve arise as?
They arise medially as rootlets.
What is the function of the dorsal ramus of the spinal nerve?
It innervates the back via several branches.
What is the difference between the dorsal ramus and the ventral ramus?
The ventral ramus is larger and forms interlacing nerve networks called plexuses, except for T2-T12 which are intercostal nerves.
What are the major nerve plexuses formed by the ventral rami?
Cervical, brachial, lumbar, and sacral plexuses.
What is the cervical plexus formed by?
The ventral rami of C1-C4.
What does the phrenic nerve innervate?
It is the major motor and sensory nerve of the diaphragm, receiving fibers from C3-C5.
What can irritation of the phrenic nerve cause?
Hiccups.
What is the brachial plexus formed by?
The ventral rami of C5-C8 and T1 (and often C4 and/or T2).
What is the function of the axillary nerve?
It innervates the deltoid, teres minor, and skin and joint capsule of the shoulder.
Which nerve innervates the biceps brachii and brachialis?
The musculocutaneous nerve.
What does the median nerve innervate?
It innervates skin, most flexors, forearm pronators, wrist and finger flexors, and thumb opposition muscles.
What does the ulnar nerve supply?
It supplies the flexor carpi ulnaris, part of the flexor digitorum profundus, most intrinsic hand muscles, and skin of the medial aspect of the hand.
What does the radial nerve innervate?
It innervates essentially all extensor muscles, supinators, and the posterior skin of the limb.
What does the lumbar plexus arise from?
It arises from L1-L4.
What does the femoral nerve innervate?
It innervates the quadriceps and skin of the anterior thigh and medial surface of the leg.
What does the obturator nerve innervate?
It innervates the adductor muscles.
What does the sacral plexus arise from?
It arises from L4-S4.
What is the longest and thickest nerve of the body?
The sciatic nerve.
What muscles does the sciatic nerve innervate?
It innervates the hamstring muscles, adductor magnus, and most muscles in the leg and foot.
What are the two nerves that compose the sciatic nerve?
The tibial nerve and the common fibular nerve.
What areas does the sacral plexus serve?
It serves the buttock, lower limb, pelvic structures, and perineum.
What is the function of the superior gluteal nerve?
It innervates the gluteus medius and minimus muscles.
What is the function of the inferior gluteal nerve?
It innervates the gluteus maximus muscle.
What does the pudendal nerve innervate?
It innervates the perineum and pelvic floor muscles.