Reconstruction
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
finale?
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Horace Greeley
Ran against Grant in the election of 1872
Was nominated for the Democratic party and Liberal Republican party
Grant still won in a landslide
Hiram Revels
First African American to join the senate (Mississippi)
Caused resentment in ex-Confederates
Ulysses S. Grant
Lead general of the Union
Elected president in 1868 republican
He won because blacks in the south were able to vote
He was a bad president because his cabinet manipulated him a lot
William T. Sherman
Sherman’s march to the sea during civil war
Influenced military presence in southern states during reconstruction
Andrew Johnson
Abraham Lincoln’s vice president that became president after Lincoln’s death
Johnson is a democrat at heart
He shares many similarities with poor whites: disliking black people and disliking rich white people
Impeached
Vetoed laws that would benefit black people
Disliked as a president by everyone
Thaddeus Stevens
Speaker of the house during Johnson until 1868
Believed in rights for black people
Rutherford B. Hayes
Ran for president in 1876
Very bad election because there was no majority in the electoral college
Went to the south, but they came to the conclusion that the North elector (Hayes) would win and military reconstruction would end in the south and a railroad in the south
Samuel J. Tilden
Ran against Rutherford B. Hayes in 1876
Returns were contested, Tilden won popular vote but he could not get majority
Resulted in Compromise of 1877
Edwin Stanton
Secretary of War in 1867
Was dismissed by Andrew Johnson after the passing of the Tenure of Office Act
Congressional reconstruction
Republicans controlled congress (radicals vs moderates)
Reconstruction Act of 1867 divided south into 5 military groups
10% rule
radical reconstruction
They did not support Johnson’s ideas
They felt that the South started the conflict and they must be punished
Because they hated Johnson so much, they wanted reconstruction lead by congress and not the president
They passed aid to the Freedmen bureau and passed the Civil rights act of 1866 giving black people citizenship and equal protection under the law
economy of the South
South lost their primary labor force due to emancipation
Landowners forced blacks to sign contracts, effectively making them slaves again
Sharecropping
Panic of 1873
Collapse of southern economy
Cotton ½ value
Widespread bankruptcy
Lost Cause Theory
Dismisses slavery as the primary cause for the civil war saying it was a “lost cause”
Claims the war was about preserving southern culture
Freedmen
Black people that used to be slaves but are not slaves anymore
They were not wanted in the North bc America is racist
The Freedmen's Bureau
Early welfare agency, proving food, shelter and medical aid
For blacks and homeless whites
Built 3000 schools and taught 200000 black people to read
Wade Davis Bill
Unsuccessful attempt to to impose stricter conditions on Southern states for their readmission into the Union
50% of people in seceded states must swear allegiance to the union instead on Lincoln’s 10%
10% plan
States can draw constitution and be reestablished as soon as ten percent of voters took oath
Oath of allegiance to the Union and accepted emancipation of slaves
When Johnson entered office, he added the disfranchisement of former leaders and officeholders of the Confederacy and disfranchisement of Confederates with more than $20K in taxable property
Black Codes
Prohibited blacks from buying land or renting money to buy land
Placed freedmen in semibondage by forcing them to sign contracts as “vagrants” or “apprentices”
Prohibited blacks from testifying against whites in court
Also added a lot of unfair laws for black people that aimed to put black people in jail
Black people in jail could be put to work and not be paid
Attempt to bring back slavery.
End of the 3/5 compromise
Increased southern population
South would get more representation in congress, made Republicans nervous because Democrats could gain more power
14th Amendment
Amendment that granted citizenship to anyone born in America AND that each citizen would enjoy equal protection of the laws
Reconstruction controversies
Amnesty act of 1872, removing last of restriction of ex-Confederates (besides top leaders)
Allowed southern Democrats to vote & retake control of state governments
Overall government corruption and return of spoilsmen
Panic of 1873 collapsing US economy
KKK
Election of 1876 and Compromise of 1877
the KKK
Deeply embittered, some Southern whites resorted to savage measures against “radical” rule
Founded in 1867 by Nathaniel Bedford Forrest
Burned black-owned buildings and murdered freedmen
Resulted in Force Acts of 1870 & 1871
Johnson's impeachment
Passage of Tenure of Office Act
Senate’s “advise and consent” applies not only to nominations, but termination as well
To combat the military reconstruction & command of the army acts, Johnson fires Edwin Stanton, Secretary of War
House responds by drawing up 11 articles and impeaching Johnson for “high crimes and misdemeanors”
Senate falls one vote short of removal
Compromise of 1877
Rutherford B Hayes elected as president, highly disputed
Democrats agreed to this as long as they end federal support for Republicans in the southern states
Ended reconstruction, and African American rights were gradually removed in the south
15th Amendment
No prevention of voting based on race, ethnicity, or previous servitude
Sharecropping
Freedmen would work for white plantation owners in return for a share of the wealth generated by the owner
This turned out to be an evil system as the plantation owner could lie about the money made, underpaying the black workers
The black workers would build debt doing this because the plantation owners would charge them in credit for their housing. This meant that the workers were tied to the owner through an increasing debt and couldn’t leave
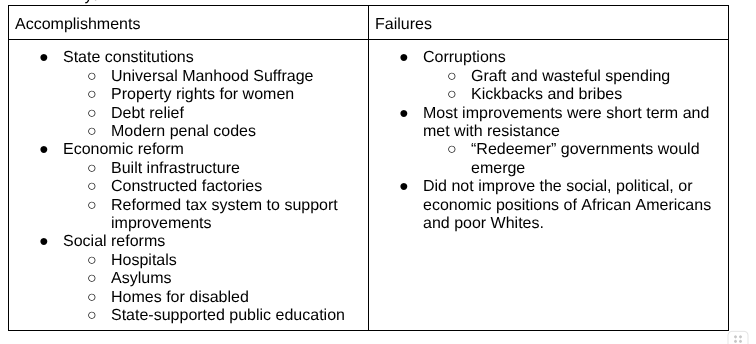
Was reconstruction a success?