QCAA UNIT 4 ECONOMICS
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
Current account
in the balance of payments, records transactions involving the export or import of goods and services
Aggregate demand
total demand for goods and services
Current account deficit (CAD)
when the value of a country's imports of goods and services is greater than its exports
Current account surplus (CAS)
when the value of a country's exports of goods and services is greater than its imports
Aggregate Supply
total value of goods and services produced
What is on the x and y axis for an AD/AS graph?
Price Level + Real Output
3 multiple choice options
In an AS graph, what does an increase in output mean?
more resources used; cost of production increases, price raised to gain profit
In an AD graph, what do changes in price and output do?
make movements along the curve
In an AD graph, what do changes in components of AD do?
shift the curve
What are the 4 phases of the business cycle
expansion, peak, contraction, trough
what is the ideal economic growth rate
3-4%
3 multiple choice options
what is the ideal unemployment rate
4-5%
3 multiple choice options
what is the ideal inflation rate
2-3%
3 multiple choice options
Fiscal policy
the macroeconomic policy used by the government to change spending and taxation to influence the economy
purposes/objectives of fiscal policy
Redistribute income - income tax and transfer payments (equitable)
Resource allocation - redirect resources toward merit goods (roads, hospitals) rather than demerit goods
Reduce fluctuations in the business cycle - if growth is too high or low, gov can alter spending nd taxation
What is the aggregate demand equation
AD = C + I + G + (X-M)
How does gov spending influence AD and which policy
In fiscal policy, an increase in G will increase AD as it is a factor of the equation. A decrease in G will decrease AD.
The budget
a record of all planned spending and revenue for the financial year
Measuring the budget
Headline: revenue -spending
Underlying: revenue - spending (not including the sale of purchasing of government assets). The best indication of short term impacts of fiscal policy (most preferred).
Budget outcomes
Surplus: T>G
Deficit: G>T
Balance: G=T
Budget stances
Expansionary: increase gov spending and reduce taxation to increase budget deficit or decrease budget surplus. simulates eco growth
Contractionary: increase taxation and reduce gov spending to decrease budget deficit or increase budget surplus. dampens economic growth
Neutral: budget outcome is constant. wont impact economic growth
What is the difference between a stance and outcome
Budget outcome is the relative spending and revenue in ONE year
Budget stance is comparing the budget outcomes in TWO different years
On a fiscal policy number line, which way is expansionary and which way is contractionary
<<<
Discretionary fiscal policy
planned spending and revenue measures decided by the government and recorded in the budget
Non-discretionary fiscal policy
changes in spending and revenue that arise due to changes in the business cycle, due to automatic stabilisers.
Automatic stabilisers
Features of fiscal policy that act to offset changes in economic activity
What are types of economic stabilisers
taxation system (dampen excessive growth) and transfer system (boost stagnant growth).
Taxation system
Government revenue
Direct Tax - tax directly applied to income
Indirect tax - tax not directly applied (GST and Sales tax)
Regressive tax - tax applied uniformly regardless of income. it is set at a flat rate.
Progressive tax system - tax based on income level
Tax-free threshold
The amount of income you can earn before you are required to pay tax.
Managing budget surplus + examples
1. Pay off debt - e.g domestic borrowers
2. Deposit with RBA - to earn interest on money
3. Special wealth fund - building Australia fund
Managing budget deficit + examples
1. Borrowing from RBA (monetary financing) - RBA prints money to fund deficit, causes inflation, isn't used
2. Borrowing domestically (debt financing) - gov sells bonds then owes lenders the value of bonds and interest, causing crowding out effect
3. Borrowing overseas - eases pressure on domestic financial markets, eases crowding out effect. threatens external stability.
4) Sell gov assets - fast acquisition of funds but causes a loss of public ownership.
Crowing out effect
Increased government spending decreases private spending. Caused when the RBA borrows domestically
Benefits of fiscal policy
Specific targeting - all states, sectors and industries experience different economic situations, so fiscal policy is specifically targeted to specific areas to have the most beneficial effect. Fiscal policy is a versatile and precise entrustment able to target specific sectors.
Supply-side benefits - policies can have long term benefits for AS. decreased company tax means firms have more money to invest. Represented by a rightwards shift of AS curve
Short run - boost growth
Long run - increase investment in capital
- increase productive capacity
-increase A
Limitations of fiscal policy
Time lags:
-Recognition lag
-Decision-making lag
-Implementation lag - large time lag as the federal budget is formulated once per year
-Impact lag - relatively fast as consumption will show increases fast
Political consideration:
-Within government - implementation needs a majority of votes, many govs have struggled to reach a majority
-Public popularity - often reluctant to introduce long-term policies with negative short-term effects, these lose votes. e.g can increase growth in the long run but people can lose jobs in the short run
Global considerations:
-Gov has to keep within expectations of financial markets and investors
-Integration of the international business cycle - when global growth is low, so is global investment and trade levels
-Incompatible economic objectives - fiscal policy cannot achieve all goals, the gov has to compromise and pick an adequate level of each
CAD and debt
-sustained budget deficit worsens the CAD and foreign debt
Monetary Policy
The management of interest rates by the RBA to influence economic activity.
Every month the RBA (except january) meets to decide to increase or decrease or maintain the cash rate.
What factors does the monetary policy influence
-inflation
-economic growth
-employment
-wages growth
-exchange rate
(weeei)
What happens when interest rates increase
The cash rate is contractionary, dampens eco growth and results in MPS due to less disposable income, decreasing consumption. decreased investment.
What happens when interest rates decrease
The cash rate is expansionary, stimulating eco growth and results in MPC due to more disposable income and more consumption. increased investment
What is expansionary monetary policy
Cutting the cash rate by buying gov bonds and securities which decreases interest rates. stimulates eco growth.
What is contractionary monetary policy
Raising the cash rates by selling gov bonds and securities which increases interest rates, dampening eco growth.
Who utilises the monetary policy?
RBA (Royal Bank of Australia)
Who utilises the fiscal policy?
The Australian Government
RBA objectives
Price stability - keeping inflation at 2-3%
Full employment - avoiding cyclical UE and operating at the NAIRU
Economic welfare - encourage a sustained level of economic welfare at 3-4%
Are monetary and fiscal policy both macroeconomic policies?
YES
Cash rate
the interest rate within the short-term money market
Short term money market
financial institutions hold settlement accounts with the RBA, allowing them to settle debts between each other ( the market for overnight loans between financial institutions).
Policy interest rate corridor
a range of potential rates with a lower and upper bound around the target cash rate. determined by demand and suply.
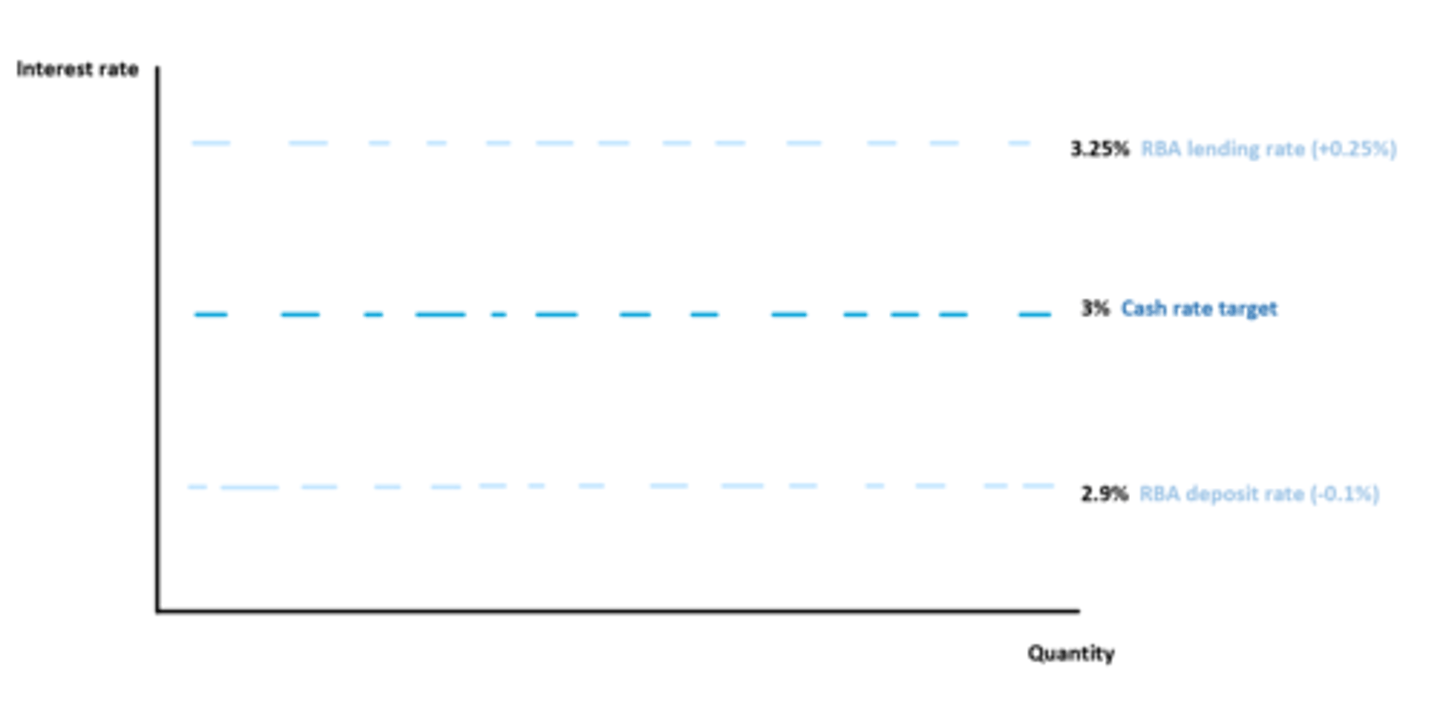
What is the RBA lending rate in the Policy interest rate corridor?
the rate that the RBA will lend funds to banks that need to fund a shortfall in their exchange settlement account balance.
What is the RBA deposit rate in the Policy interest rate corridor?
The rate that the RBA will pay on deposits made by banks with extra funds in their exchange settlement accounts.
Domestic market operations
The RBA buys or sells Commonwealth Government securities to financial institutions (changes the amount of money banks have and their supply of money in the short-term money markets.
Buying - increases money supply, decrease cash rate (expansionary)
Selling - decreases the money supply, increase cash rate (contractionary)
How does the cash rate affect interest rates?
The cash rate informs other interest rates and banks follow the cash rate that the RBA sets.
^ cash rate means banks have to pay more, to maintain profits the interest rates offered to households and firms increase.
The transmission mechanism + channels
How monetary policy impacts the economy
Internal channels
- cash flow
- savings and investment
- asset prices and wealth
External channels
-the exchange rate
Savings and investment channel
The cash rate represents the cost of borrowing

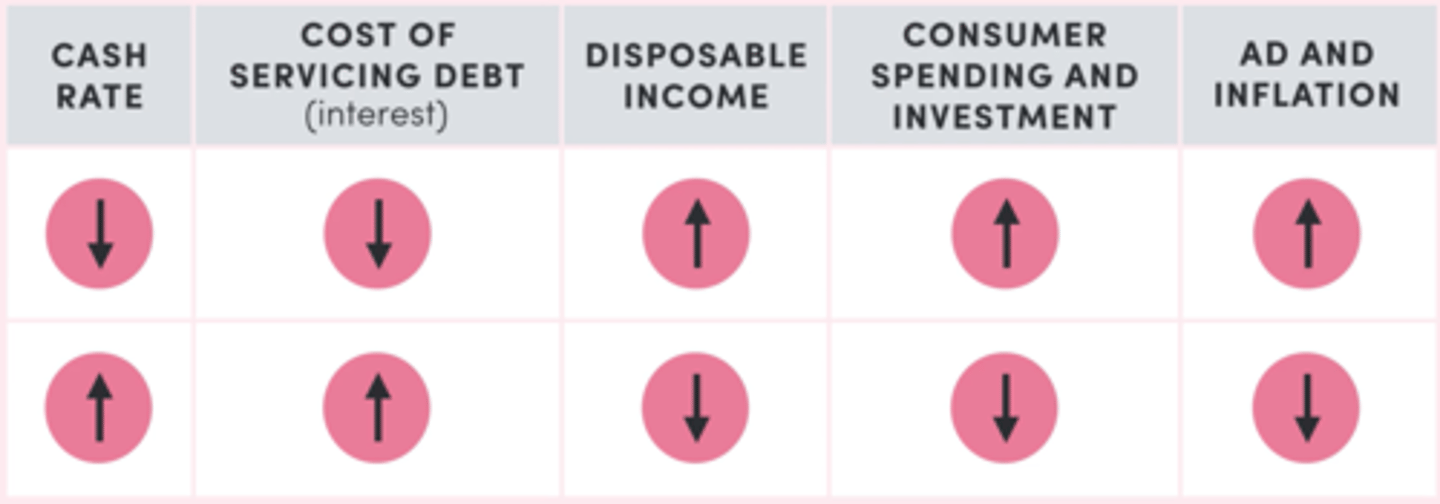
The cash flow channel
Cash rate significantly influences the cash that consumers and firms have available
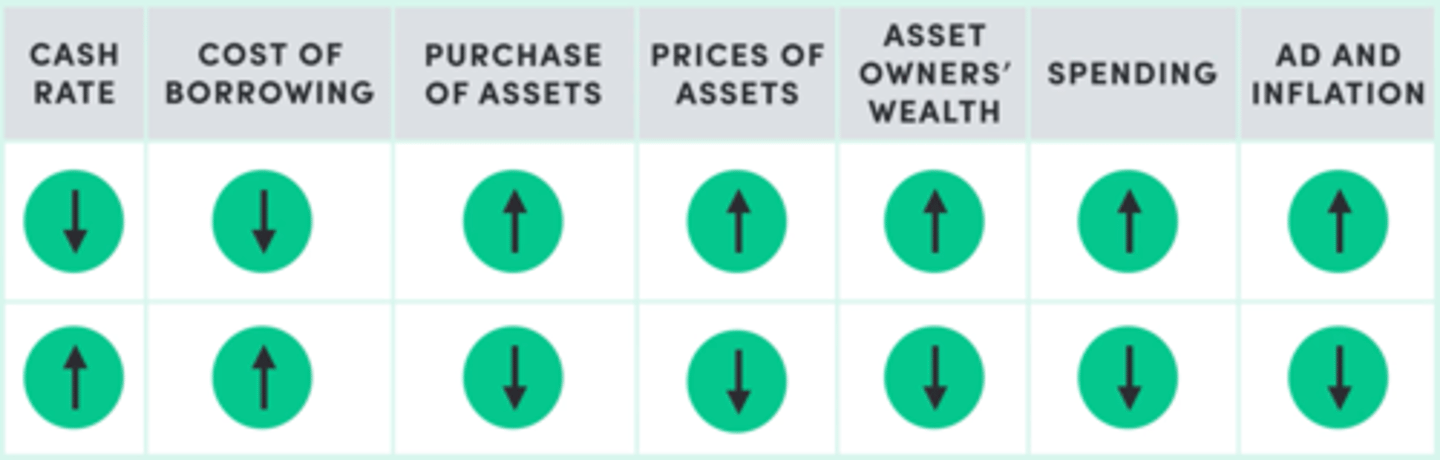
Assets prices and wealth channel
Cash rate impacts the purchasing of assets by influencing the cost of borrowing
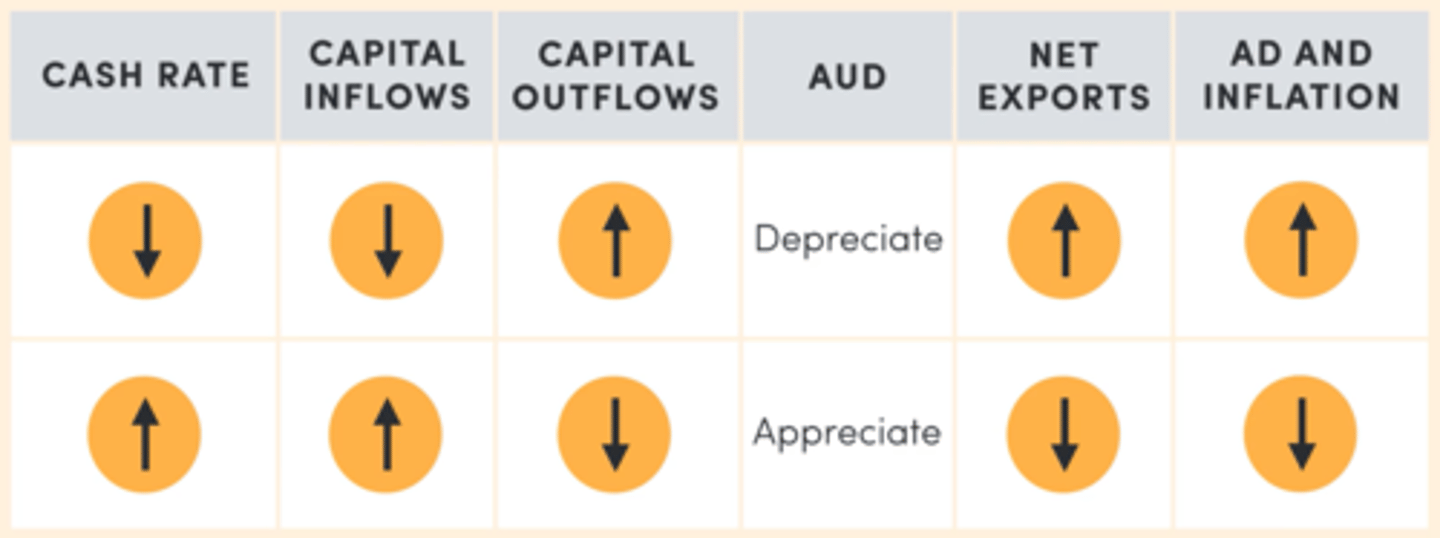
The exchange rate channel
The domestic cash rate affects the exchange rate which influences AD via net exports. Investors invest in countries with high interest rates which offer high return.
Benefits of monetary policy
Short implementation lag (inside lag):
issues in the economy can be addressed fast as the RBA meets every month, can react faster than fiscal policy to e.g low eco growth
Free from political constraints:
considers their objectives and the economy, not what the public thinks.
Limitations of the monetary policy
Blunt instrument:
Changes in the cash rate affect the whole economy, whether or not that policy is appropriate for all sectors. Cannot target issues in specific sectors like fiscal policy.
Long impact lag (outside lag):
- changes to cash rate can take around 18 months to impact the economy due to the time it takes for households and businesses to adjust their sending and saving to a new cash rate.
- RBA must predict economic conditions as the policy may not be appropriate if economic conditions change.
Contradictory fiscal policy stance
can contradict when monetary policy is contractionary while fiscal is expansionary or vice versa. it can limit the effectiveness of monetary policy.
Productivity
How efficiently an economy converts inputs to outputs per unit in time
What are inputs
Factors of production (materials the go into production) - land, labour, enterprise, capital
What are outputs
Final goods and services produced
Measuring productivity
Labour productivity - ratio of output to the input of labour (hours worked).
Multifactor productivity - ratio of output to the inputs or labour and capital( how much technology is used), is a broader measure
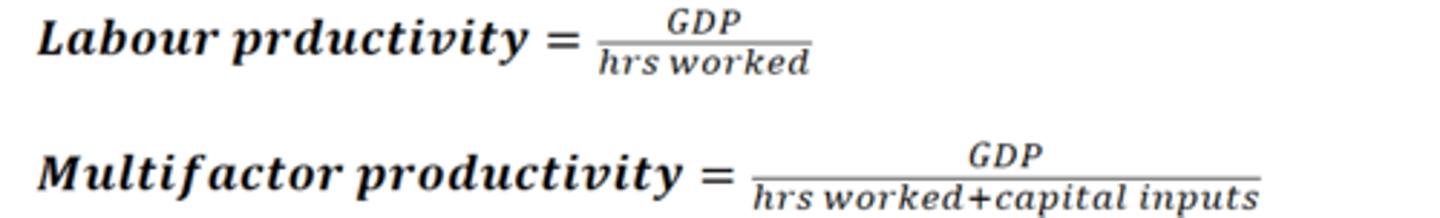
What are the 3 types of efficiency
Technical/productive efficiency
Allocative efficiency
Dynamic efficiency
Technical/Productive efficiency
When firms maximise he output they can make from an input
Firms can improve efficiency by:
Technical innovation - when a firm expands access to a new machinery or equipment
Specialisation - uses inputs in a specific production process over a period of time
This reduces the cost of production, allowing for more outputs with given inputs
Allocative efficiency
how well inputs are used to produce the right combination of outputs based on consumer preferences. e.g a company sells windows and doors, if demand for doors increases, he firm will respond
Dynamic efficiency
how effectively a firm can respond to changing market conditions
e.g new technology (UV resistant glass), the faster the implementation, the more dynamically efficient
Structural change
Shifts in the composition and location of production and employment within an economy.
Results in resources being reallocated from struggling industries to those growing faster. Older industries are replaced with emerging ones
Why does structural change occur
businesses adapt to changes including:
Technological progress:
more efficient technology causes a shift in resources to more productive industries
* technological advancements cause structural change*
Available inputs (factor endowment):
alters the patterns of production that might be possible or most efficient. e.g, a decrease in mining and increase in service (mining is less attractive as a source of GDP, due to shifts in factor endowment
*changes in quality and quantity influence structural change*
Global forces
affects domestic markets, foreign competition and growth are global forces that affect structural change
Consequences of structural change: Structural unemployment
occurs when the skills possessed by workers don't match the skills demanded by employers because inefficient sectors close down, leaving workers unemployed.
Resolution: retrain UE for a different industry - but requires time and money
Consequences of structural change: Significant economic growth
^ efficiency and productivity (therefor ^ AS), boosts eco growth in the long term. if firms become more productive, they can produce more goods at any price point
Consequences of structural change: International competitiveness
as efficiency and productivity ^ improve, firms can lower prices and increase the quality of their goods.
Microeconomic policy
Governments action aimed to improve efficiency and productivity within individual sectors
Industries divided into 2 categories
Product markets - final goods and services are bought and sold ( the interaction between firms and buyers)
Factor markets - factors of production are bought and sold ( e.g the labour market)
Demand-pull inflation
when the total demand for goods and services increases to exceed the supply of goods and services that can be sustainably produced.
What does an outward shift of PPF mean?
increased availability of inputs e.g physical labour or capital or a more efficient way to convert inputs to outputs
What does it mean if there is a point inside the PPF curve?
Can be produced but is productively inefficient
What does it mean if there is a point outside the PPF curve?
Cannot be produced with existing resources
What does an inward shift of PPF mean?
labour force shrinks
or
supply of raw materials is depleted
or
natural disaster occurs decreasing the stock of physical capital
What is the x axis of the PPF
consumer goods
What is the y axis of the PPF
capital goods
What does the PPF show in microeconomics
shows options open to an individual, household or firm
What does the PPF show in macroeconomics
The production possibilities available to a nation or an economy during a given period of time for broad categories of input
What happens at a peak
economy reaches maximum productivity output, high inflation
What is the difference between headline and underlying inflation
Headline - a measure of the total inflation within an economy, including commodities such as food and energy prices (e.g., oil and gas), which tend to be much more volatile and prone to inflationary spikes.
Underlying - excludes factors that have large prices
What does contractionary fiscal policy do to economy
reduces inflationary pressures due to decreased consumption
What monetary policy stance appreciates the AUD
contractionary appreciates aud as cash rate increases so does aud
What monetary policy stance depreciates the AUD
expansionary depreciates the aud as cash rate decreases so does aud
What fiscal policy stance appreciates the AUD
contractionary
What fiscal policy stance depreciates the aud
expansionary
What does expansionary fiscal policy do to economy
can increase inflation due to increased consumption
what happens at a trough
high unemployment