SEHS UNIT 4.2 - Joint and Movement Type
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Movement types
Flexion, Extension, Adduction, Abduction, Rotation, Circumduction, Plantar, Dorsi, Supination, Pronation, Inversion, Eversion, Depression, Elevation
Muscle contractions
Isotonic, isometric, isokinetic
Isotonic muscle contractions
Concentric and eccentric
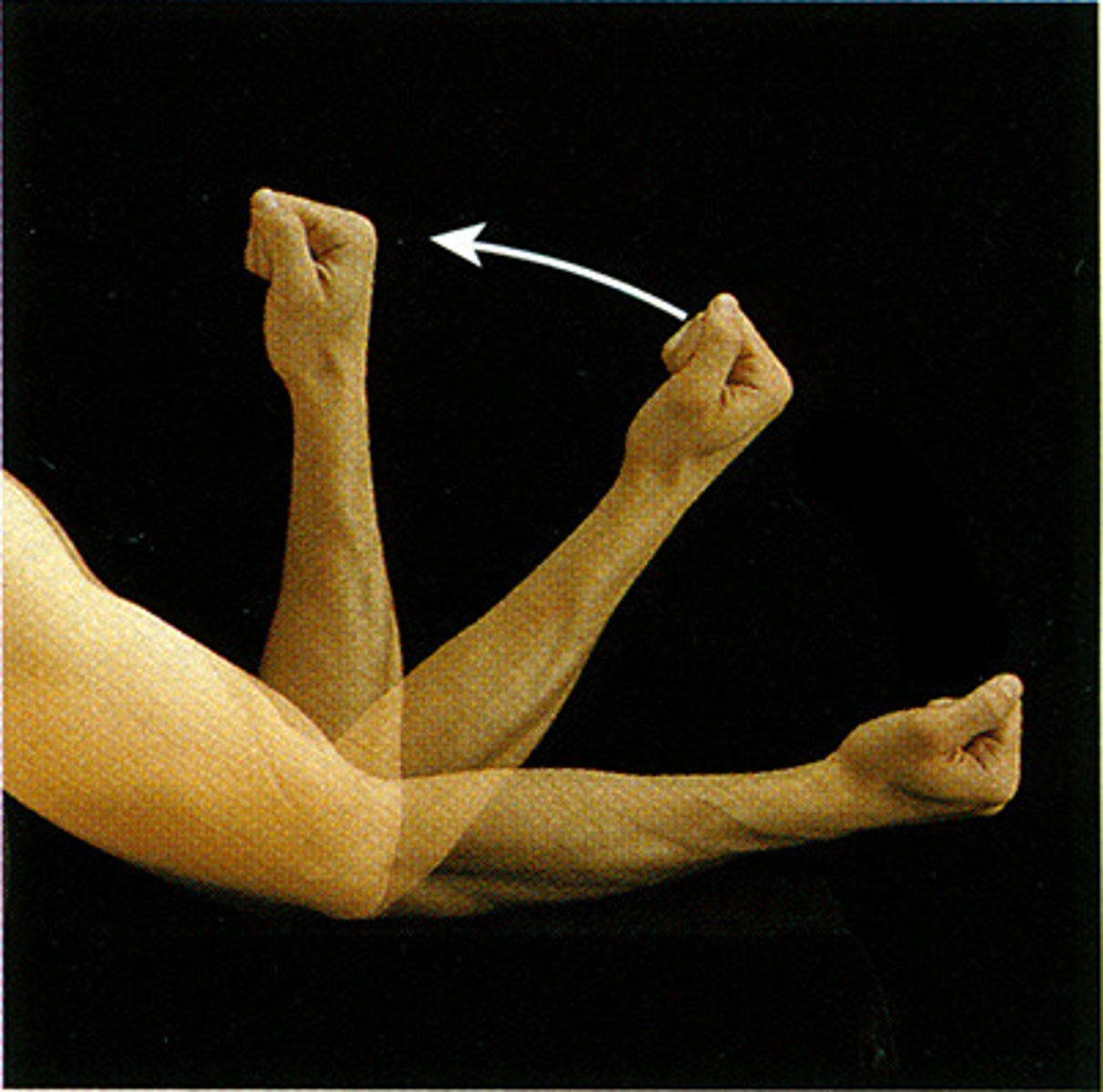
Flexion
Decreases the angle of a joint (bending)
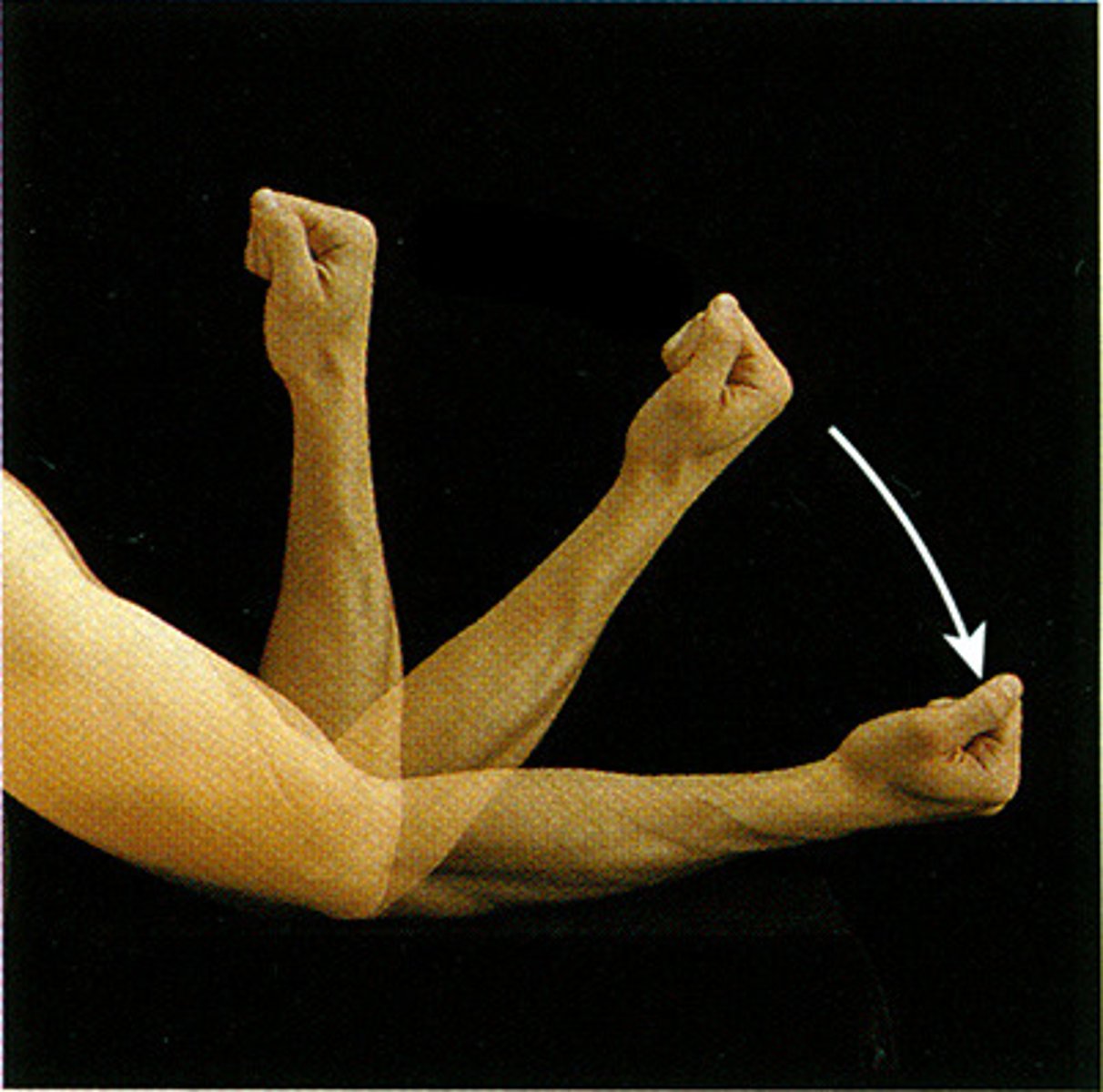
Extension
Increasing the angle of a joint (straightening)
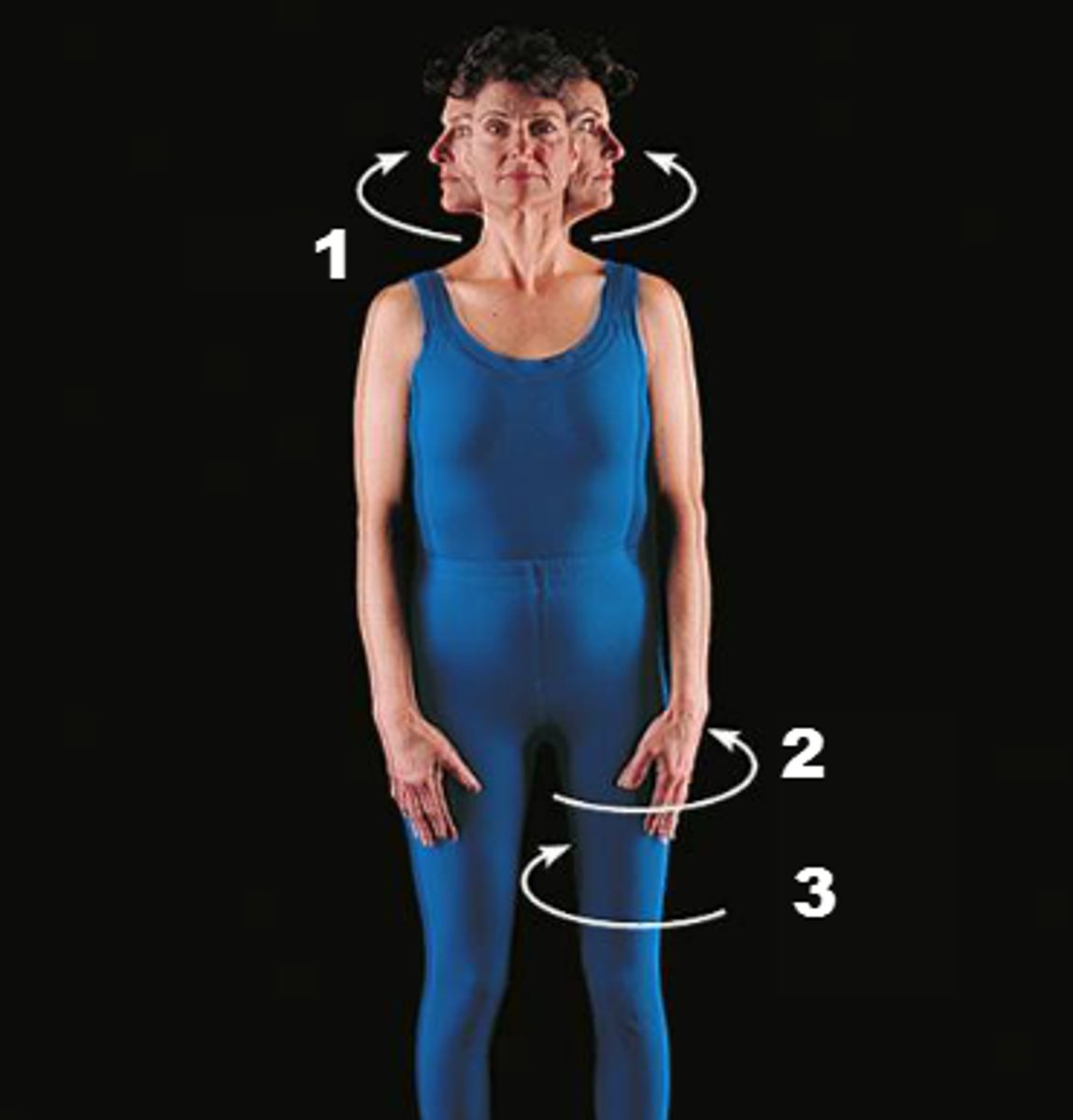
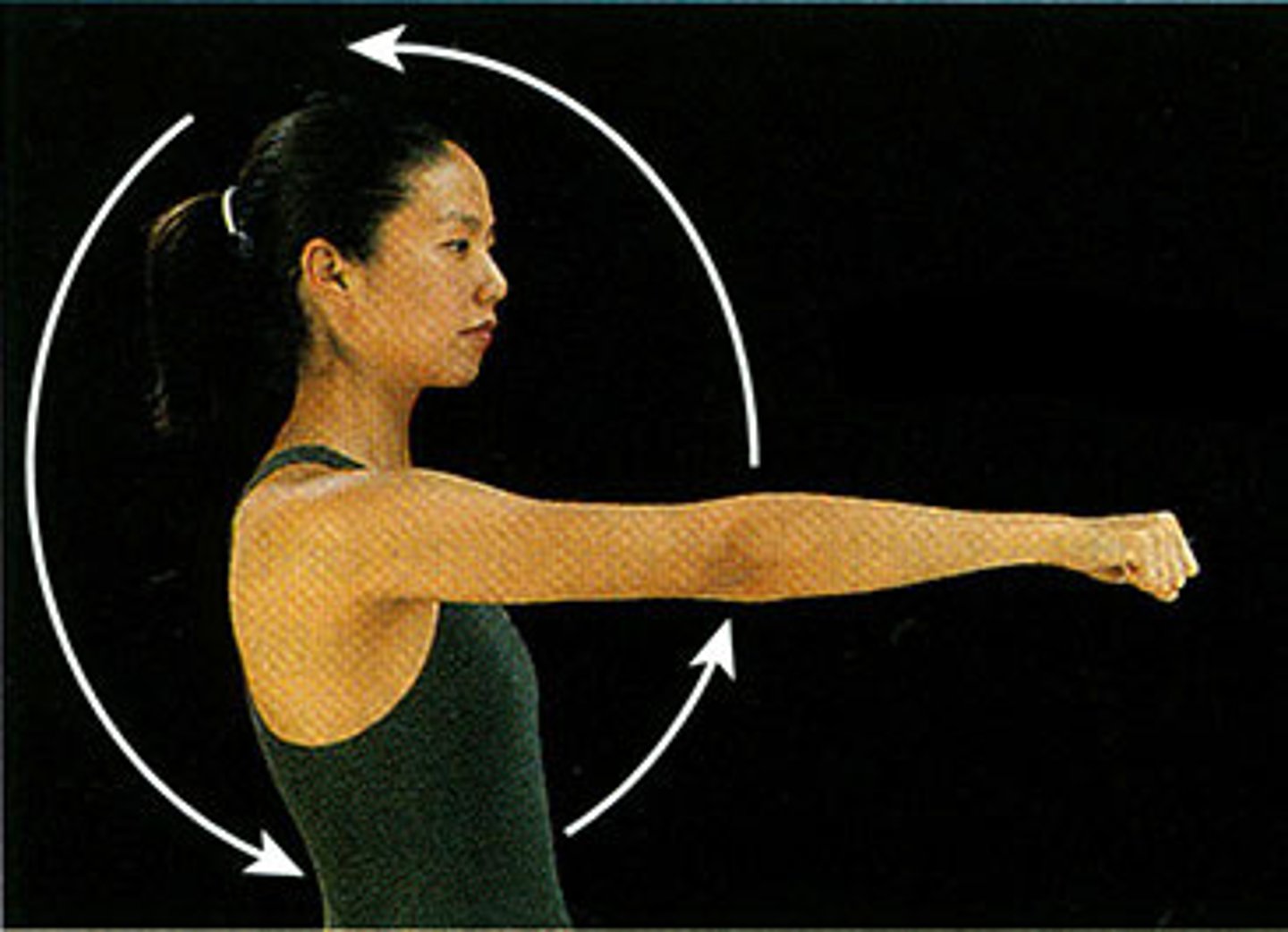
Rotation
Moving a bone around its own axis, with no other movement
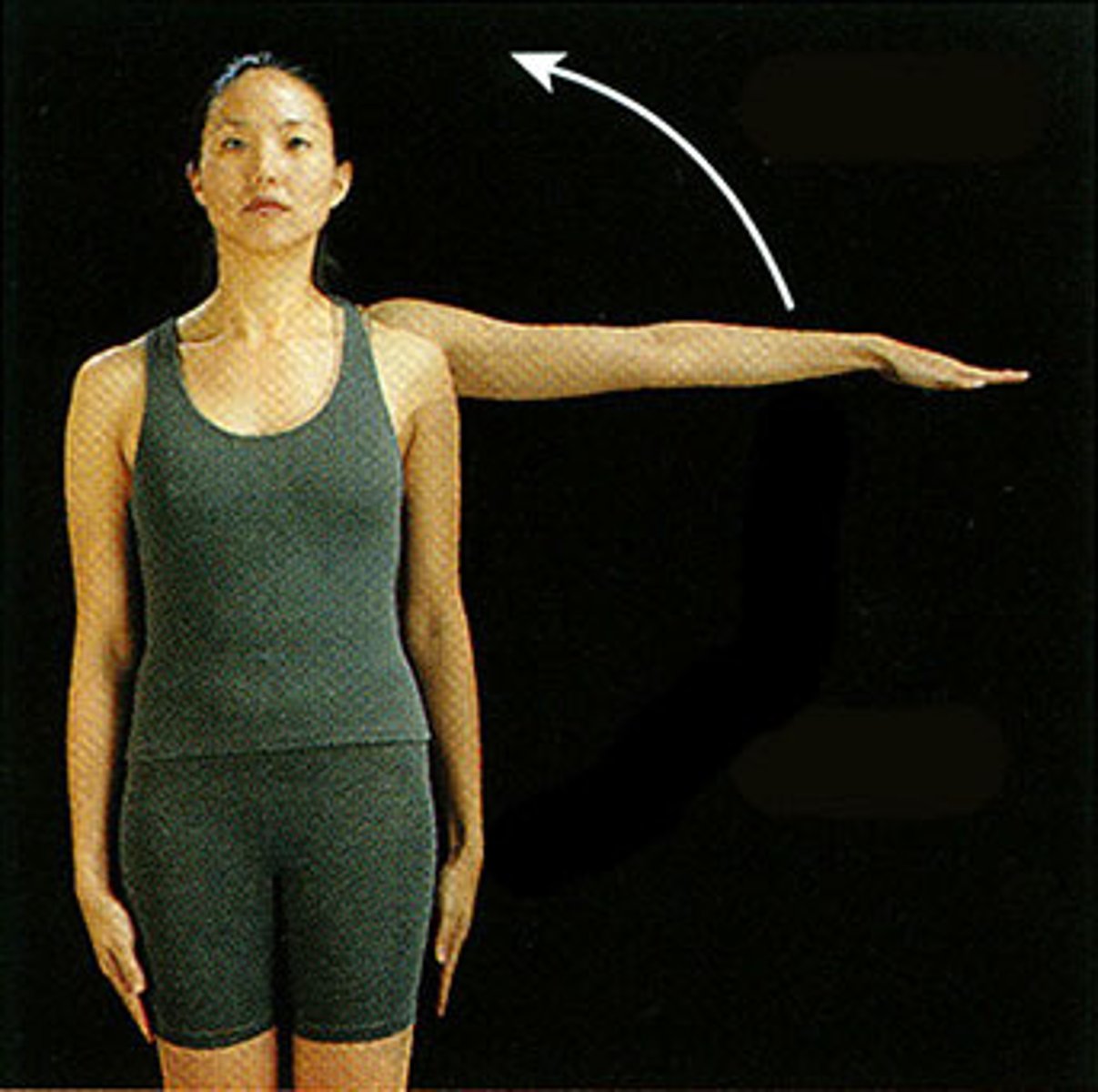
Abduction
Movement away from the midline of the body
Adduction
Movement toward the midline of the body
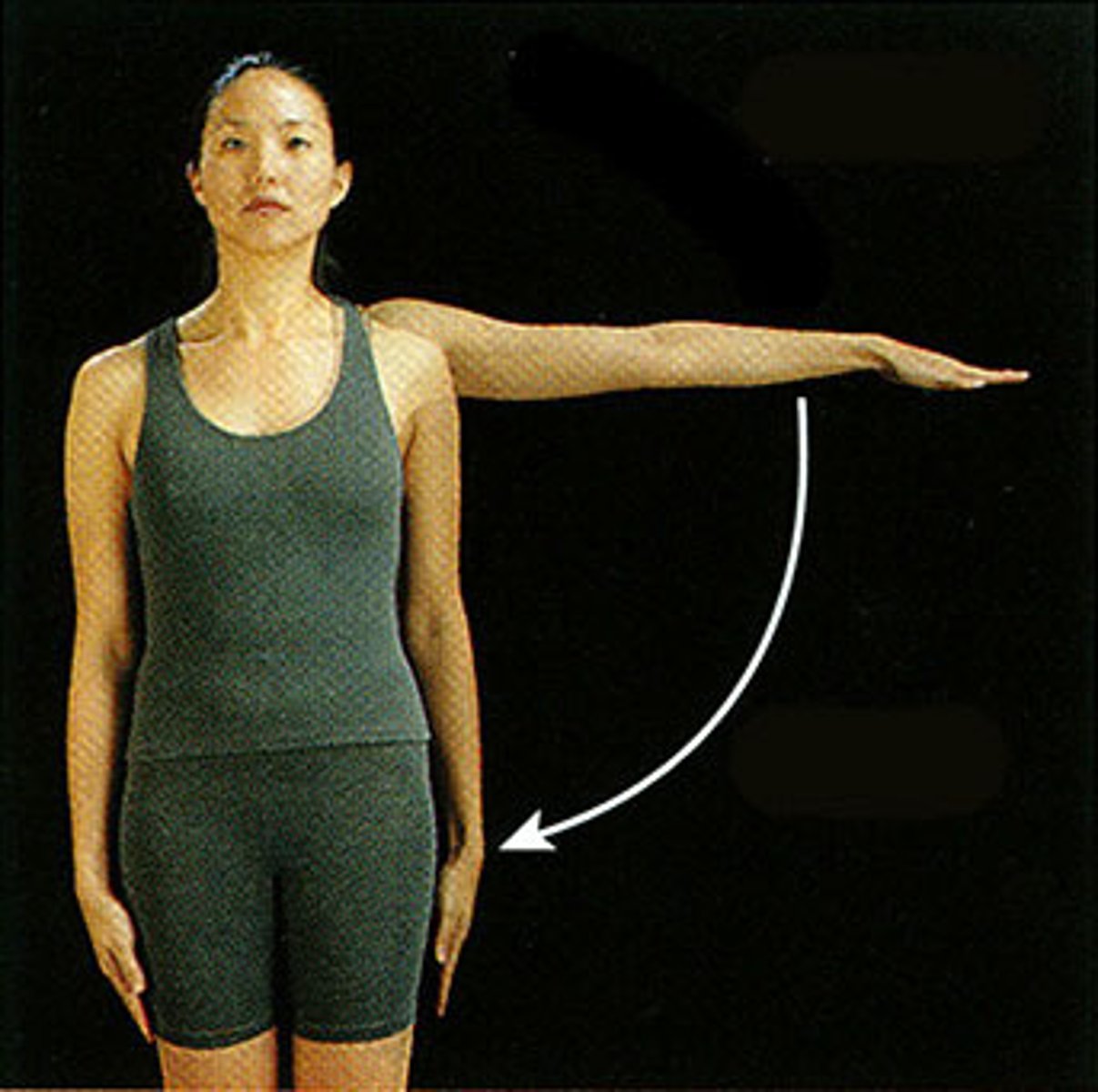

Circumduction
Circular movement of a limb at the far end
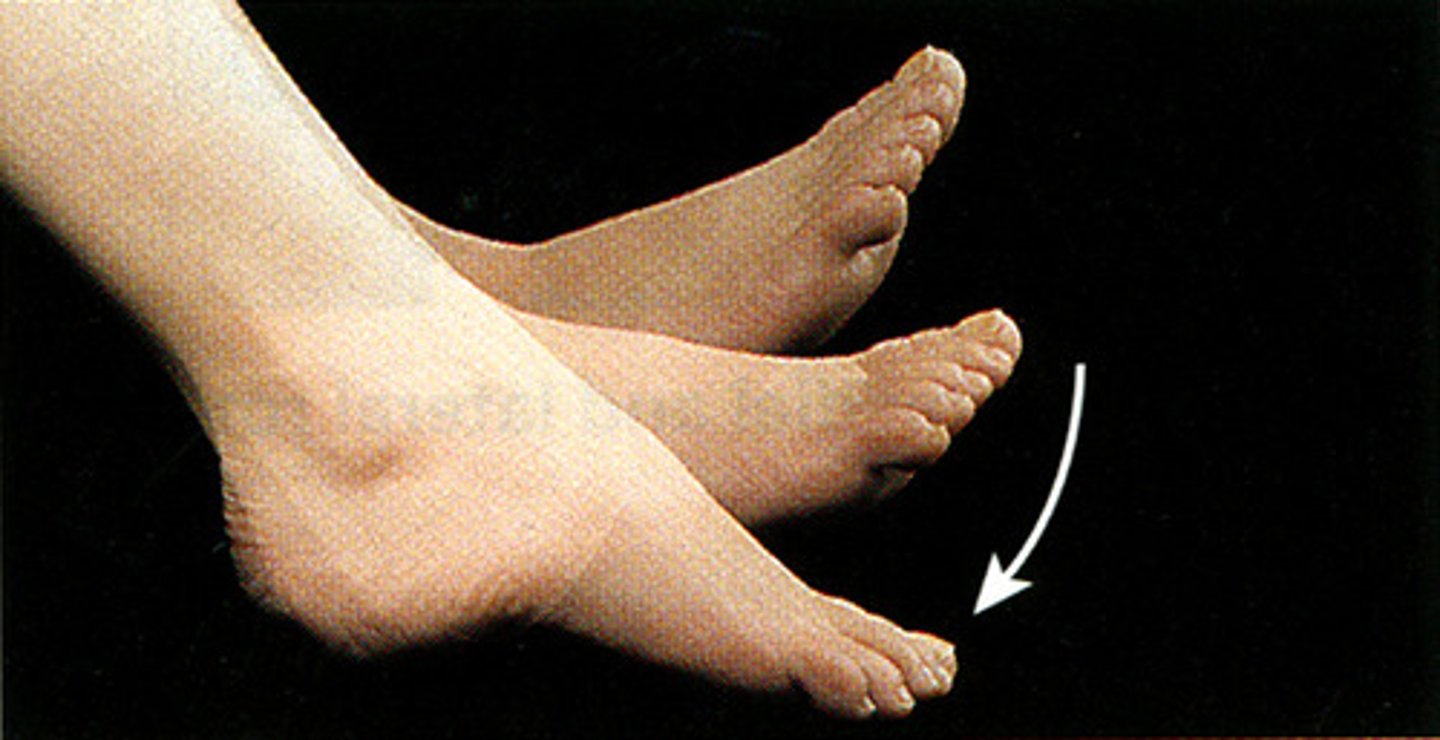
Plantar flexion
Pointing toes down
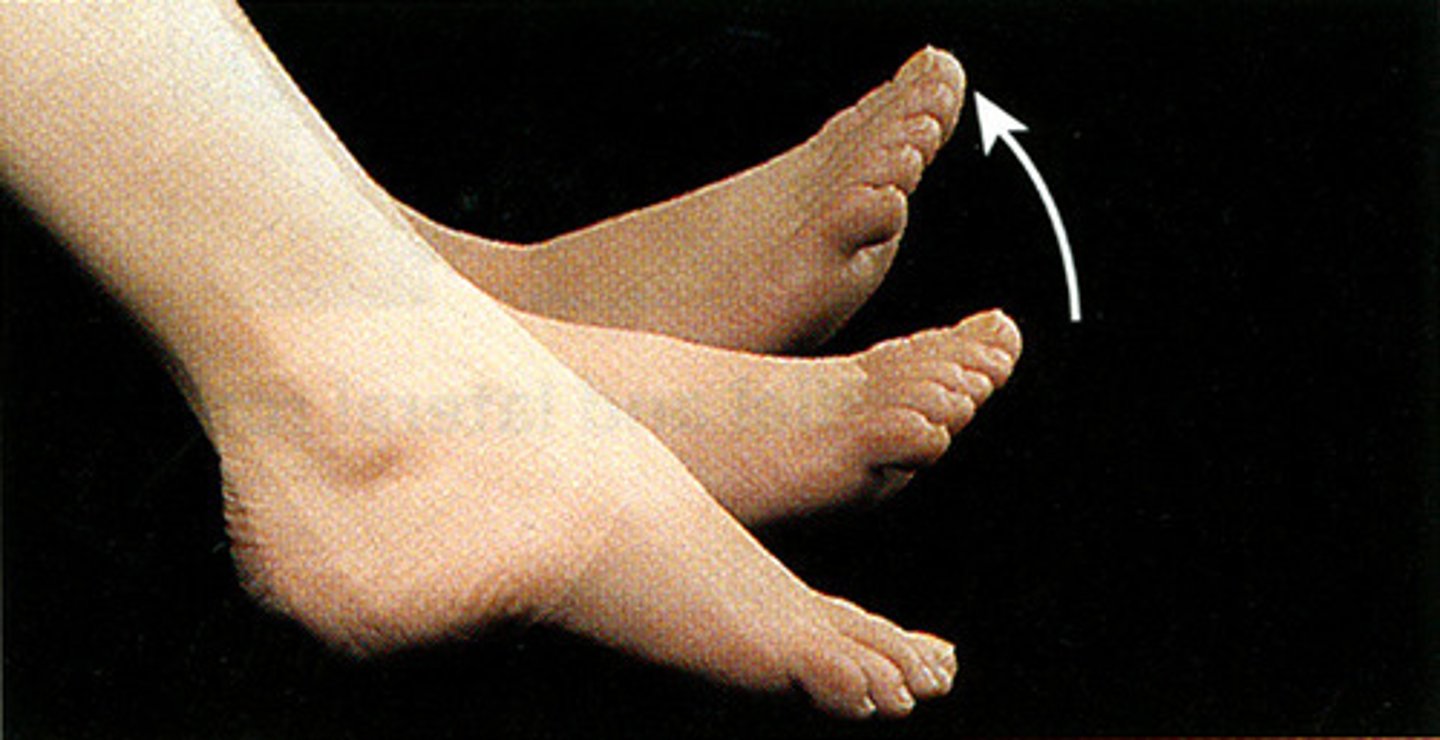
Dorsi flexion
Lifting toes up
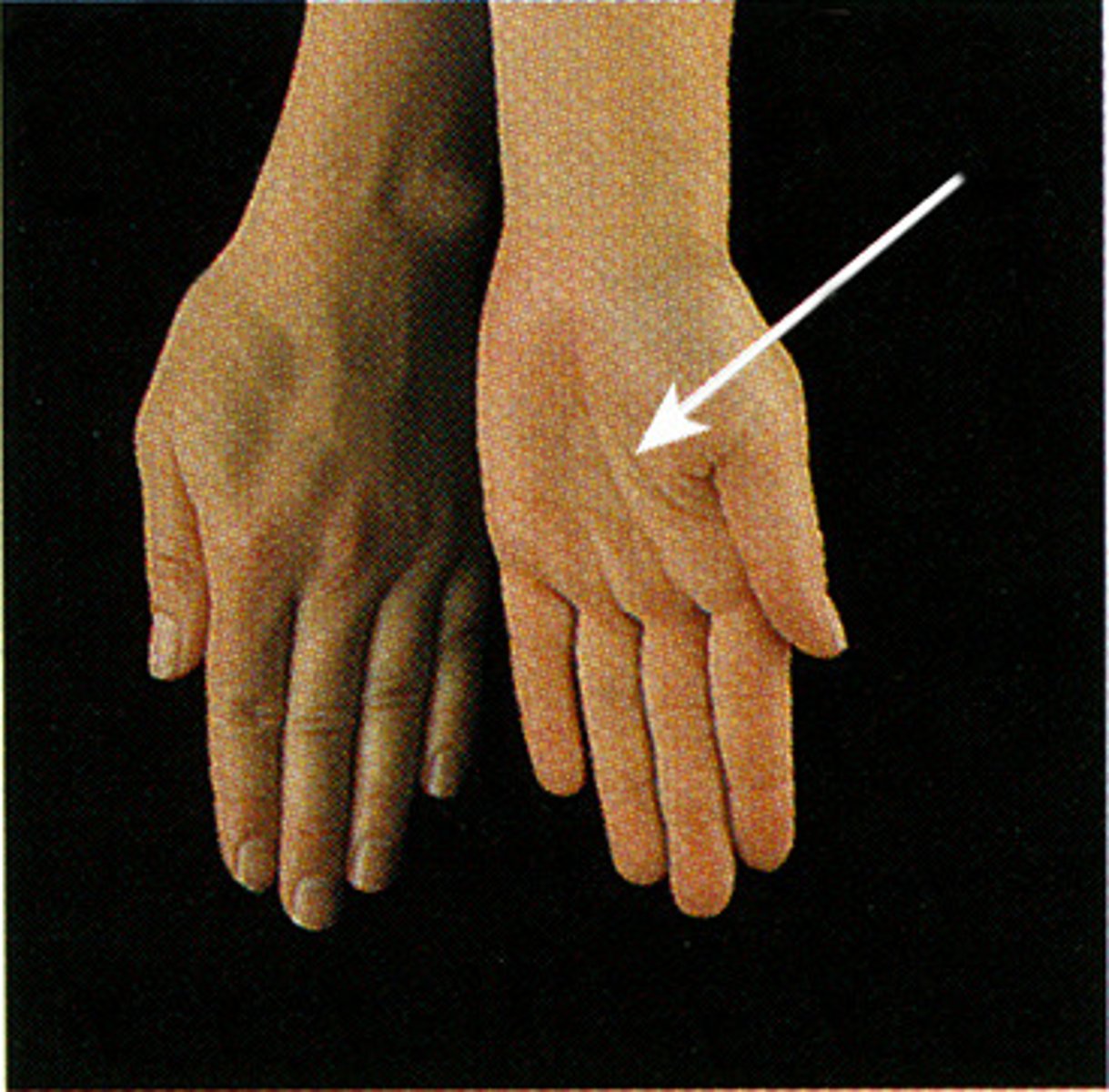
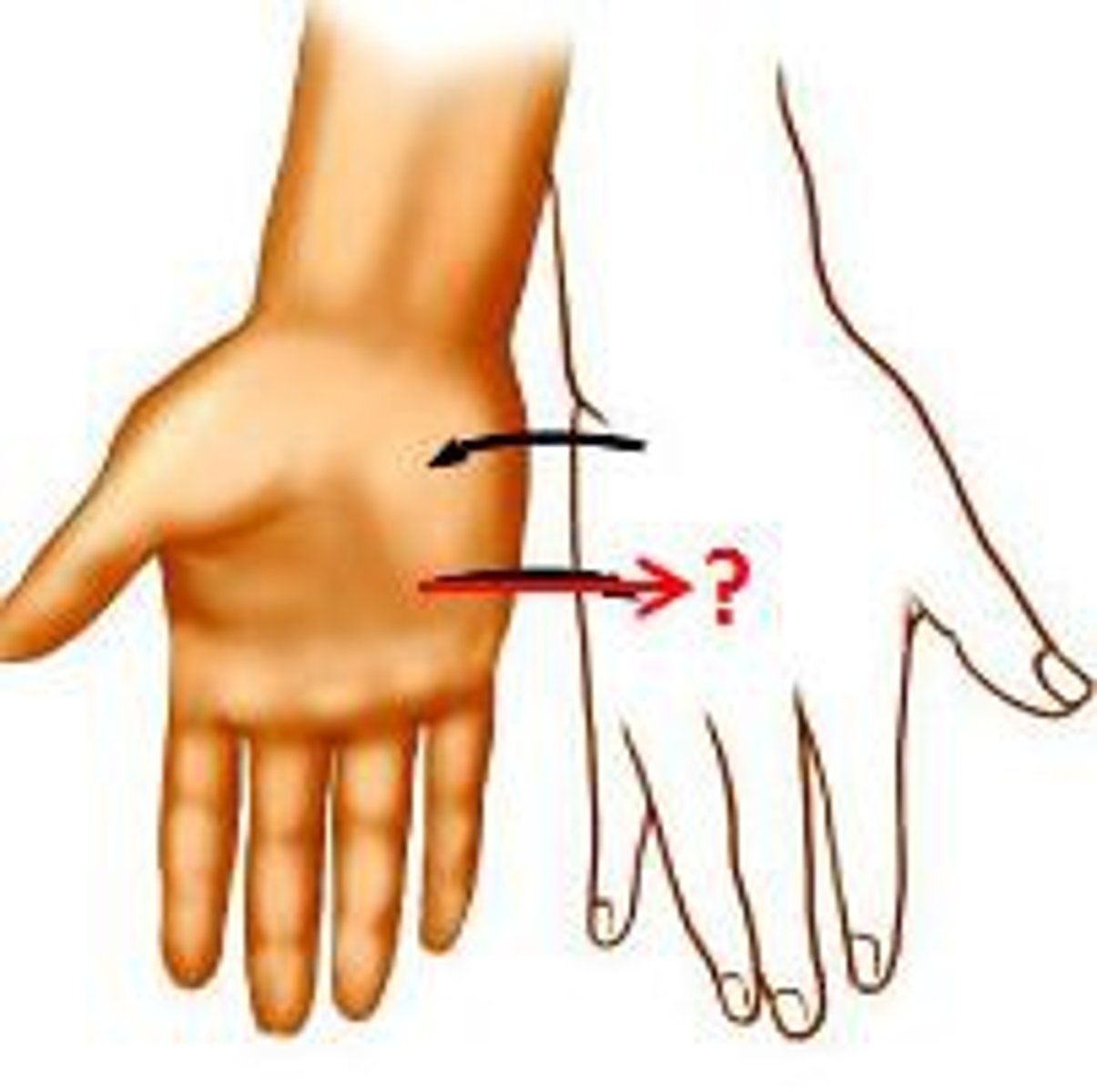
Supination
Turning the palm upward
Pronation
Turning the palm downward
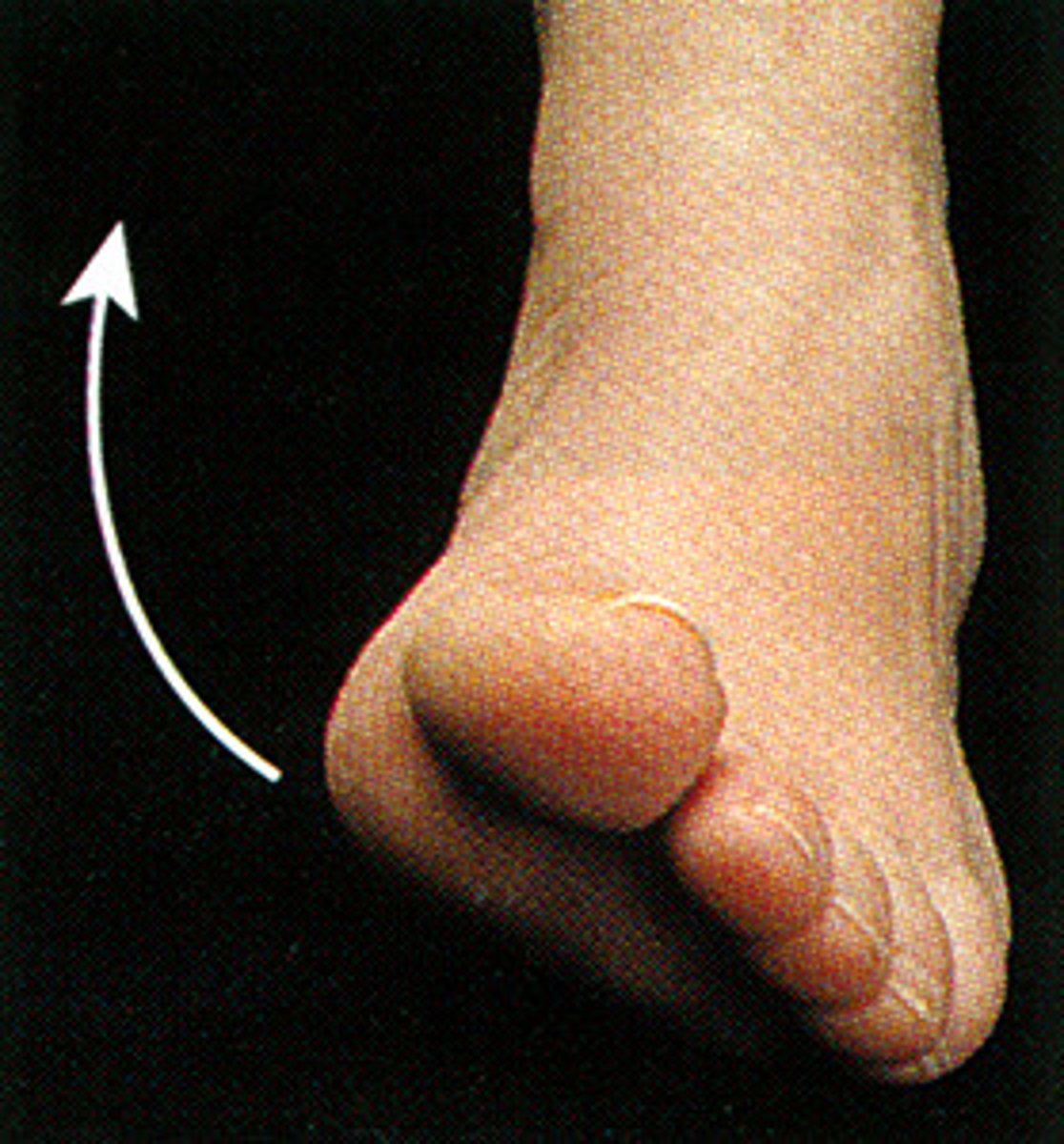
Inversion
Turning the sole of the foot inward
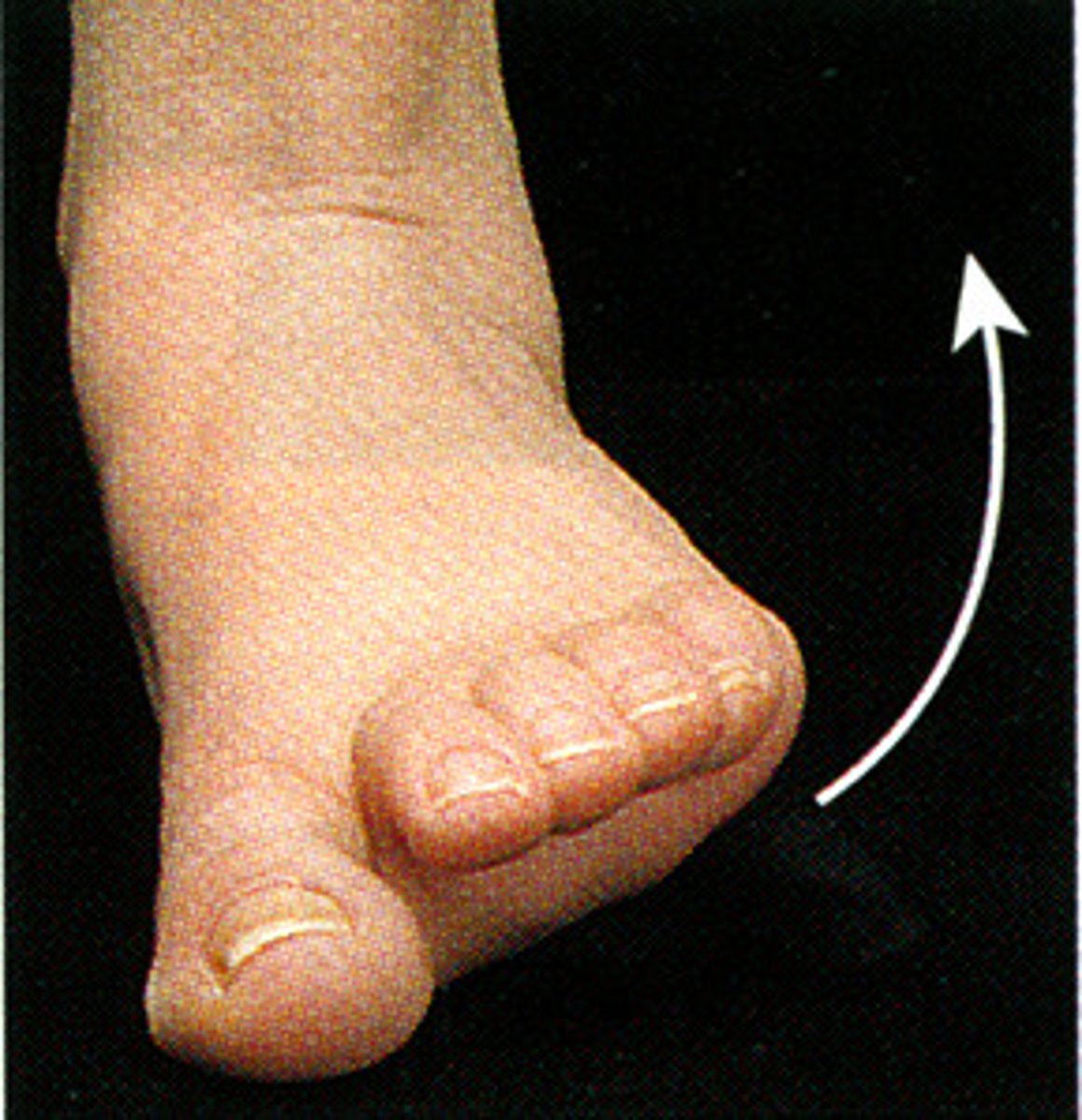
Eversion
Turning the sole of the foot outward
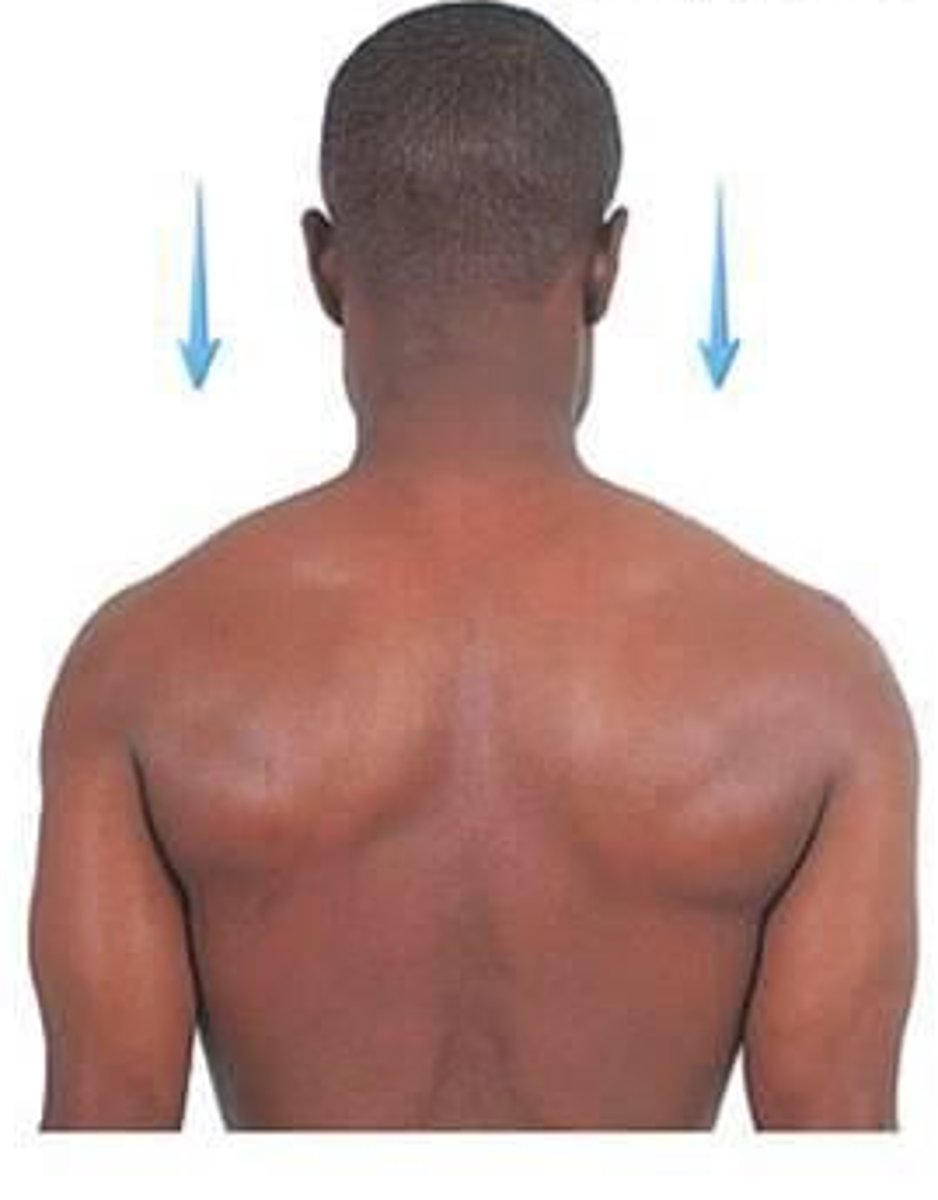
Depression
Lowering a body part
Elevation
Raising a body part
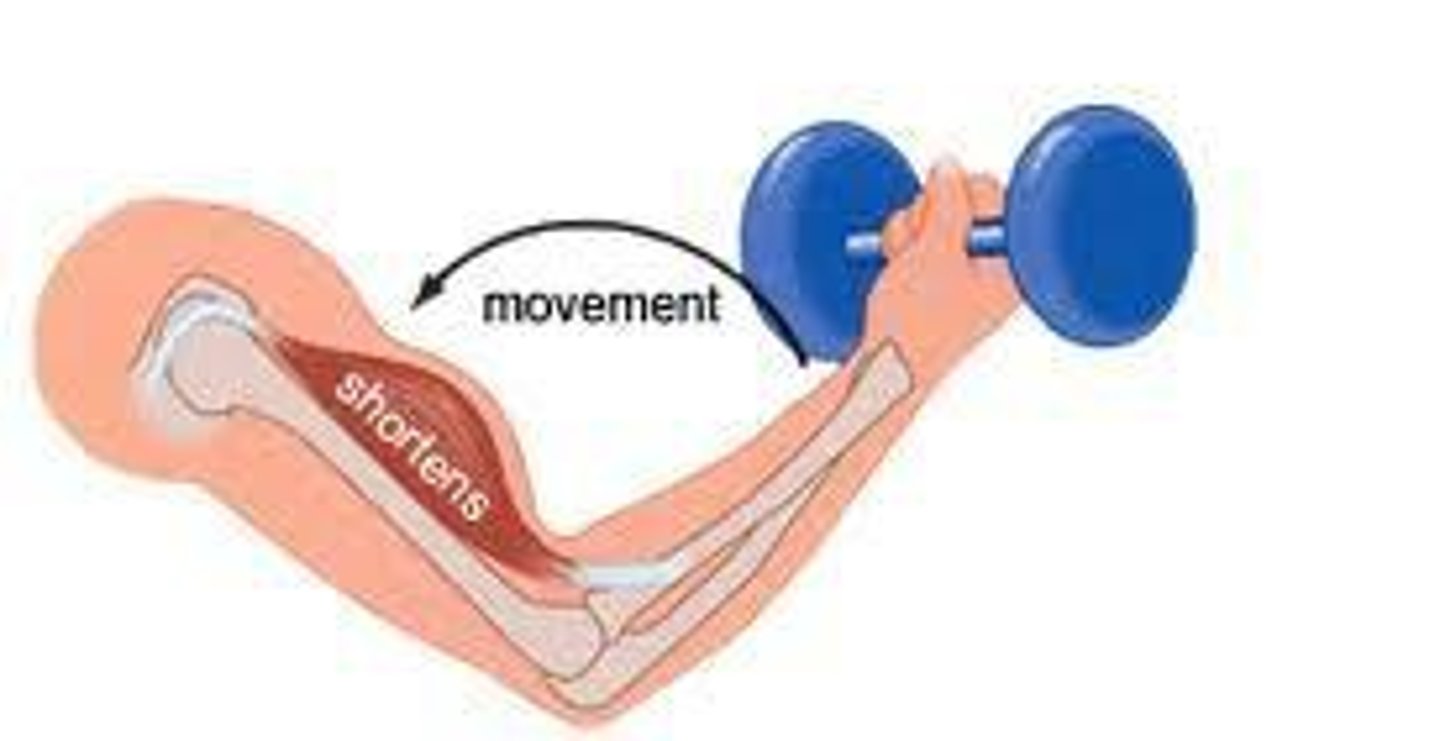
Isotonic contraction
A muscle contraction where the muscle change in length pulling on the bone and producing movements of body parts.
Concentric
Where the muscle shortens as the fibres contract
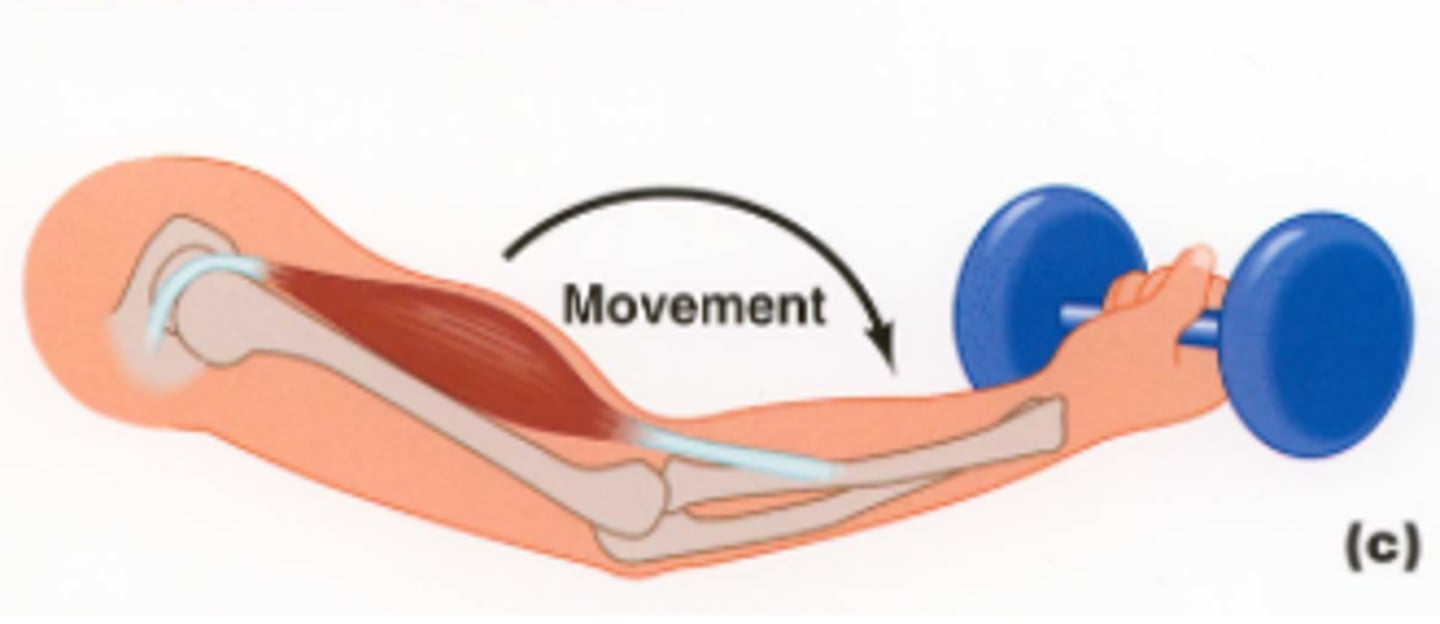
Eccentric
Muscle lengthens under tension
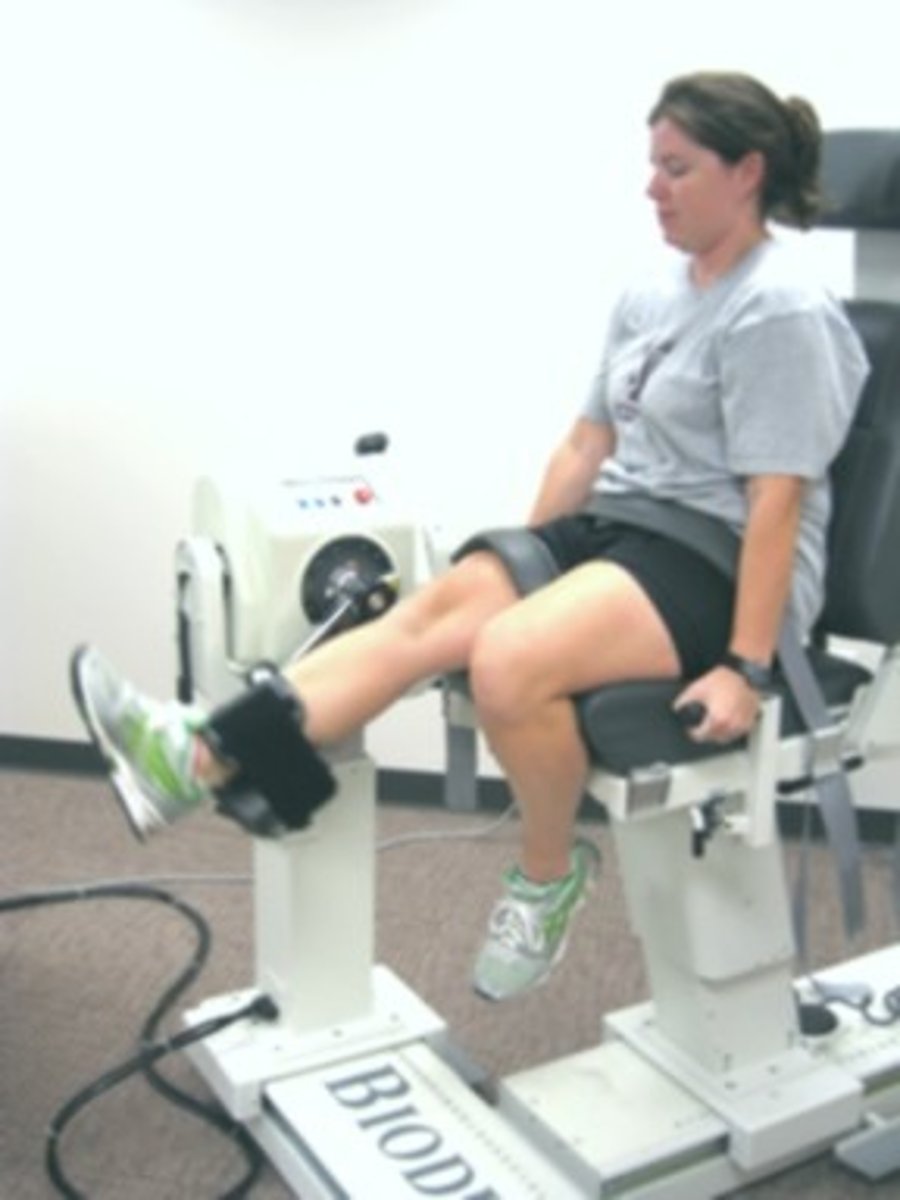
Isometric
When a muscle contracts with no resulting movement

Isokinetic
A muscle contraction with constant speed
Reciprocal inhibition
The simultaneous contraction of one muscle and the relaxation of its antagonist to allow movement to take place.
Agonist
Prime mover - muscle which contracts to cause movement
Antagonist
Relaxes to allow movement. The triceps brachii when you flex your arm.
Why the antagonistic muscle relaxes?
Because the nerve impulse is restricted within the muscle, allowing the opposite muscle to contract.
What is Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness. (DOMS)
Micro tears in muscle fibres causing structural damage and inflammatory reactions in muscles; brought on by overstretching and overtraining the muscles.
Type of muscular contraction which primarily brings about the
onset of DOMS?
Eccentric contraction
How can DOMS be prevented?
Reducing amount of eccentric contractions under load during early stages of training.
Starting at a low intensity and gradually increasing the intensity/weight.
Warming up and cooling down effectively.