Bone and Cartilage (1-3)
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
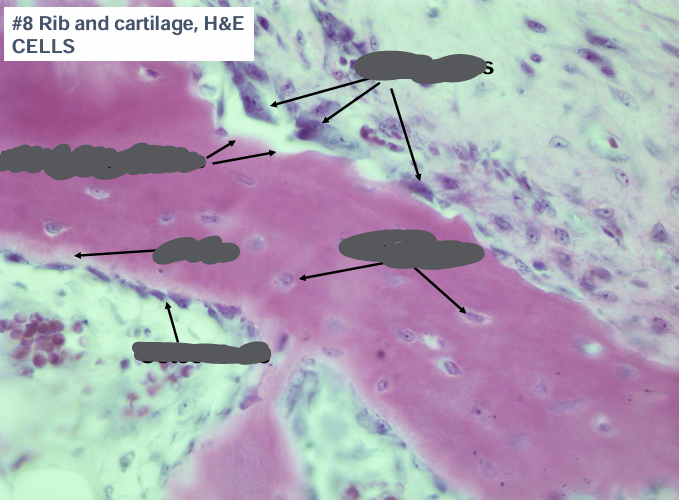
cartilage
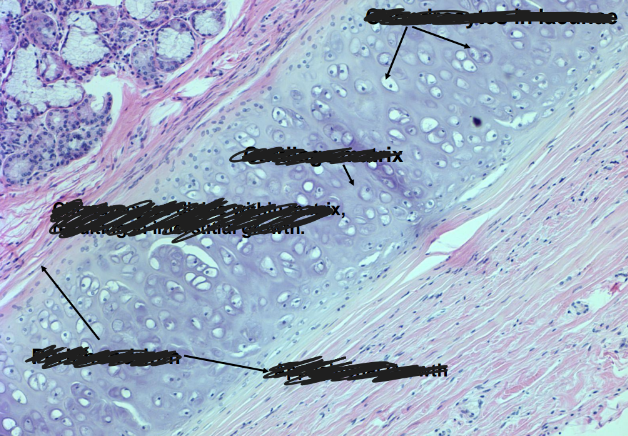
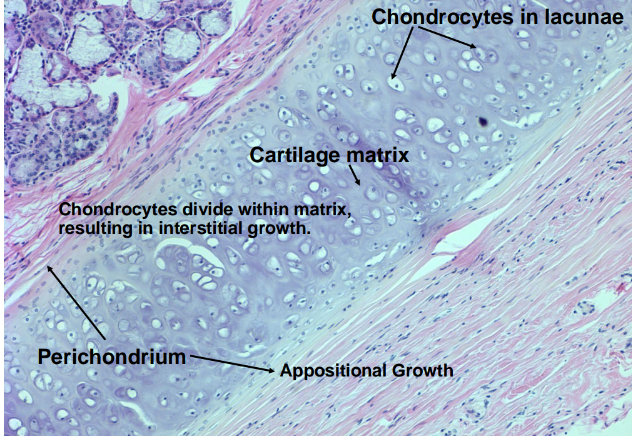
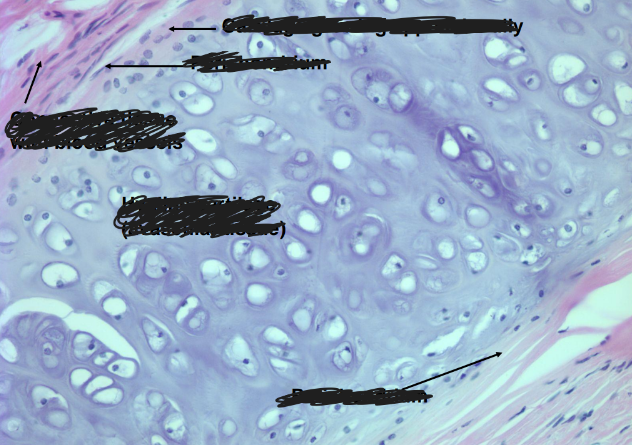
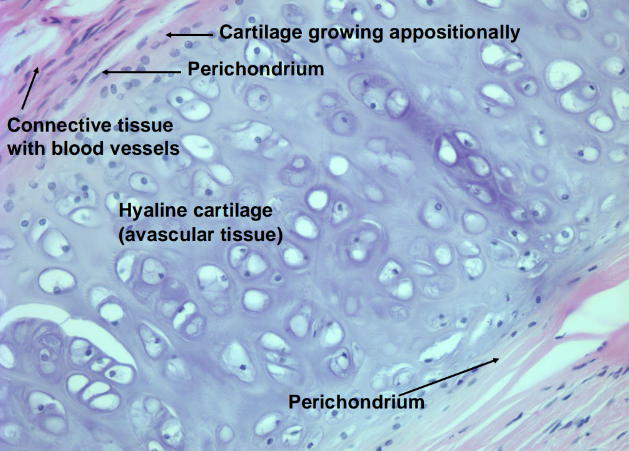
-both appositional growth (from perichondrium) and interstitial growth (from within)
-no vasculature
-compression function
-permeable matrix
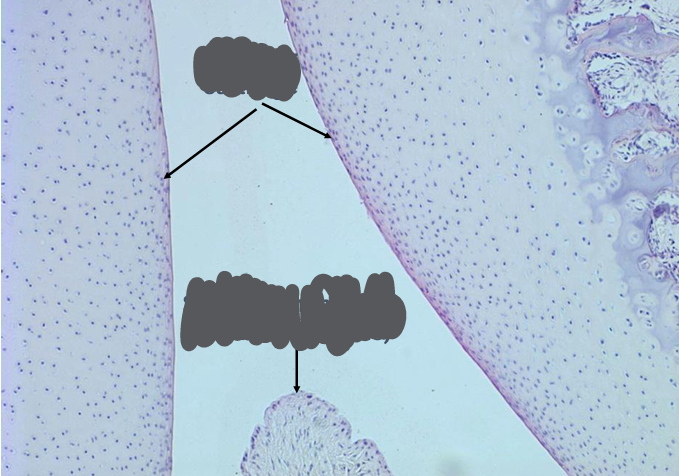
-articular cartilage has no perichondrium
cartilage characteristics
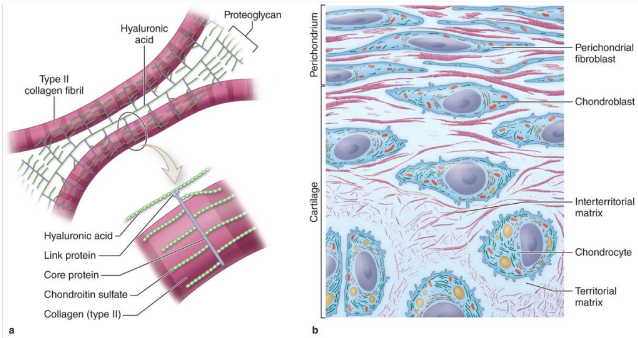
-tough and flexible- GAGs, PGs, collagen, and elastin
-high water content due to sulfates on GAGs of matrix- shock absorber!
-chondrocytes in lacunae (spaces)
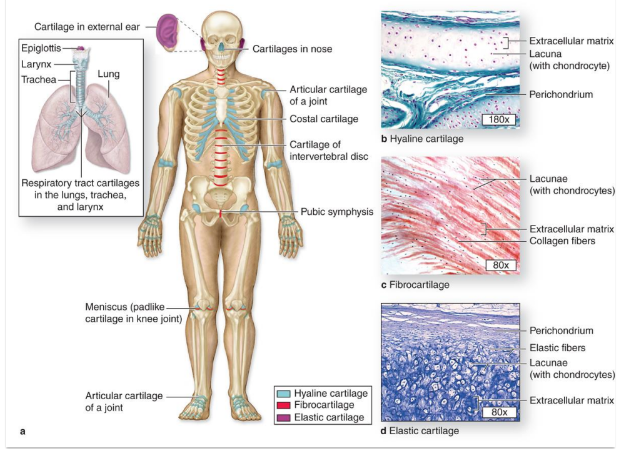
types of cartilage
-hyaline cartilage: articular, rib ends
-fibrocartilage: intervertebral discs
-elastic cartilage: ear, epiglottis
cartilage- cellular level
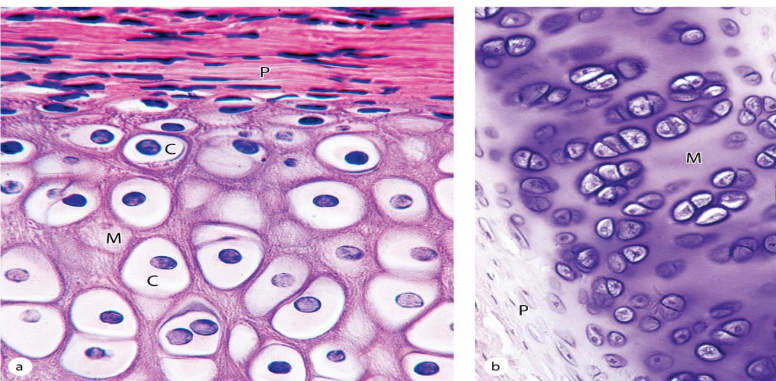
hyaline cartilage
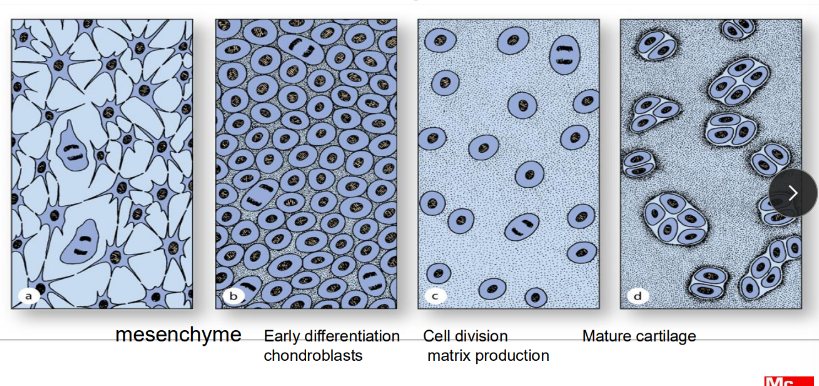
chondrogenesis
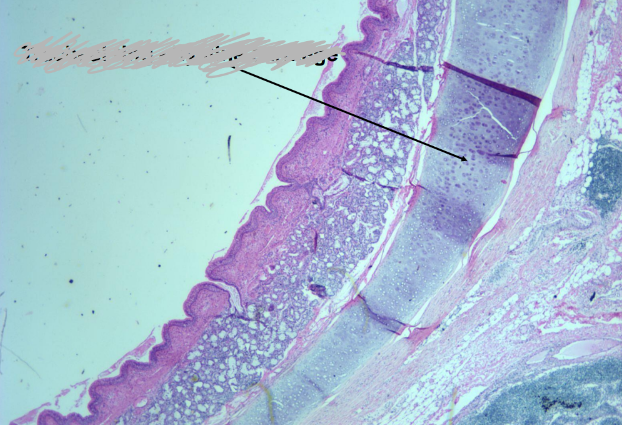
-tracheal ring- hyaline cartilage
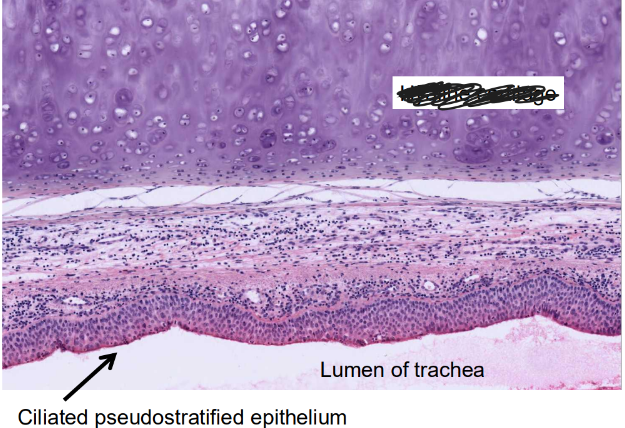
-hyaline cartilage
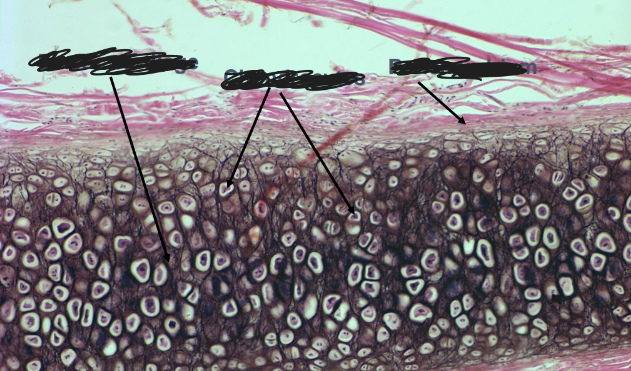
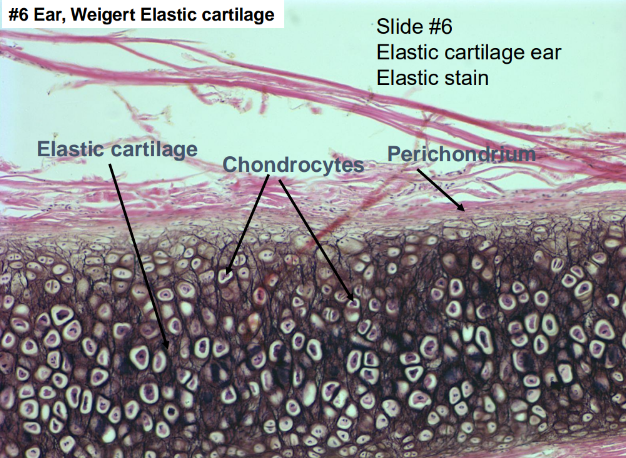
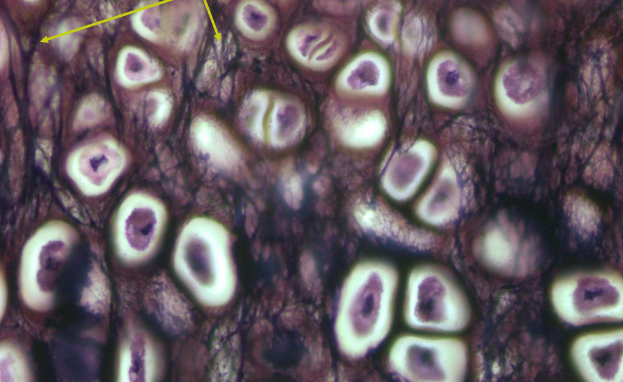
-elastic fibers in cartilage matrix
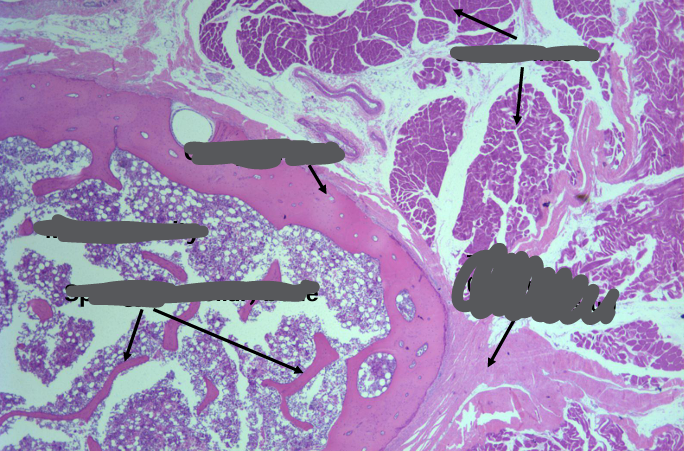
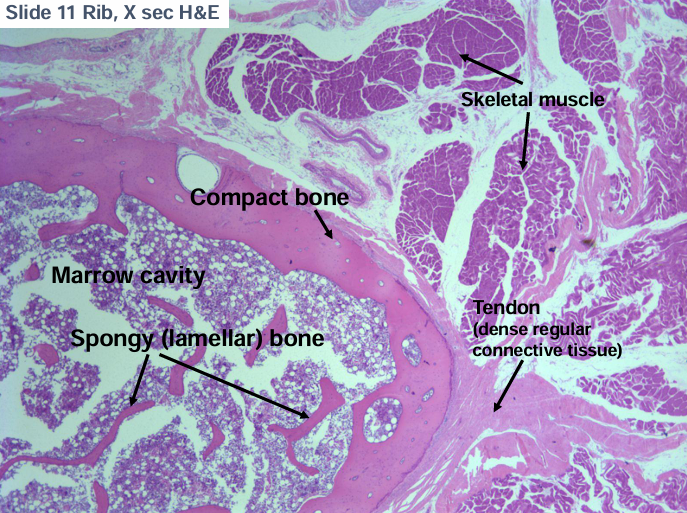
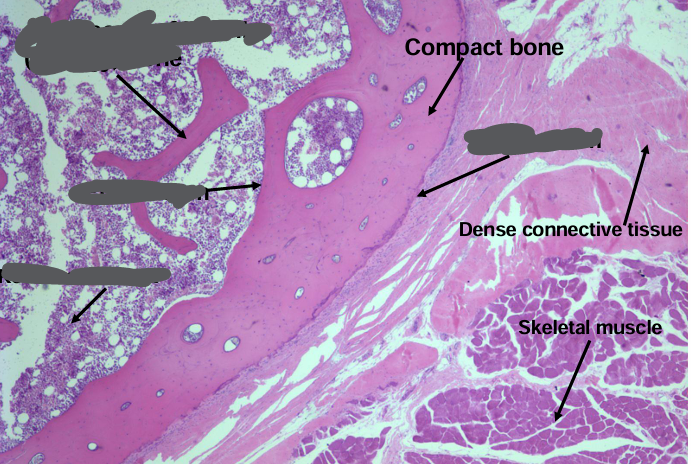
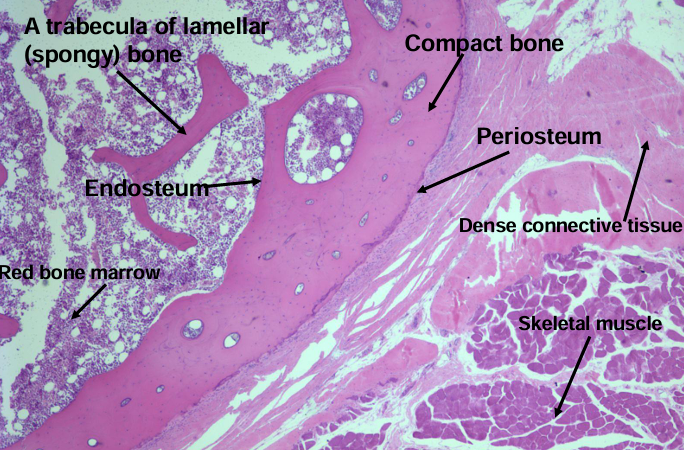
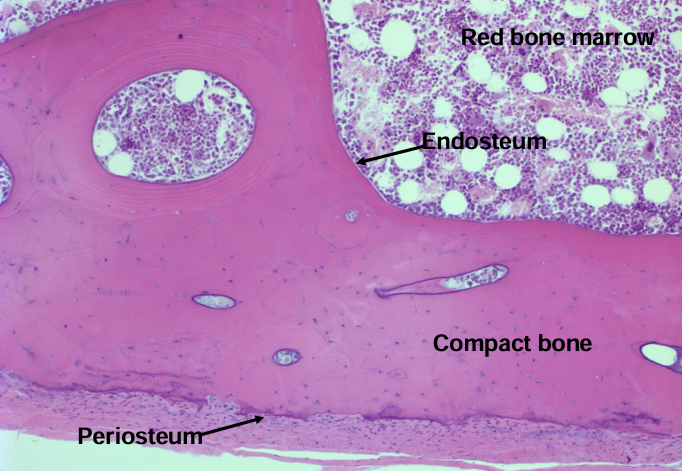
bone
-endochondral: long bones
-intramembranous: parietal bones (skull), clavicle
bone components
-reservoir for calcium, phosphate, and ions
-calcified matrix
-contains vessels and nerves
-Harversian system- structure
-type I collagen, proteoglycans, and glycoproteins
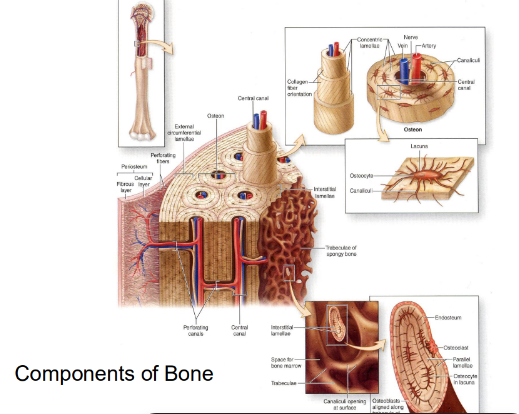
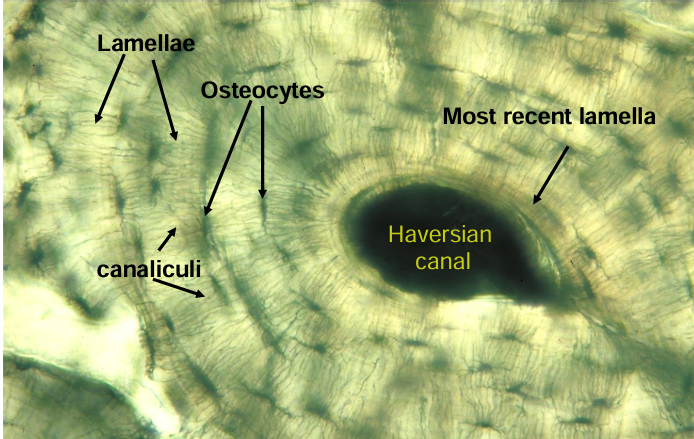
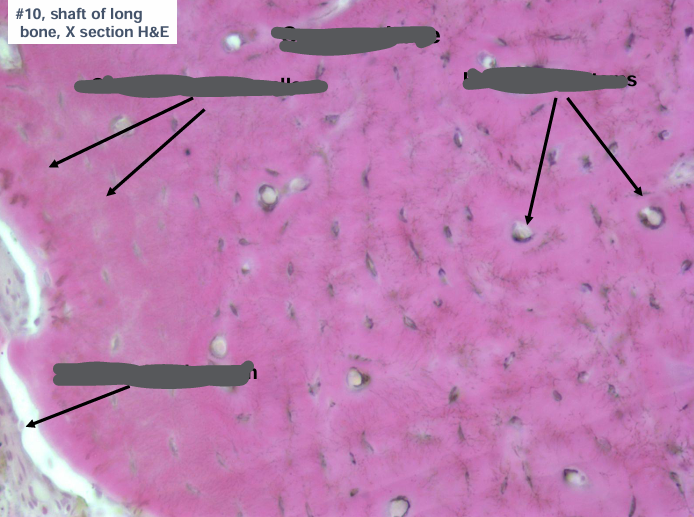
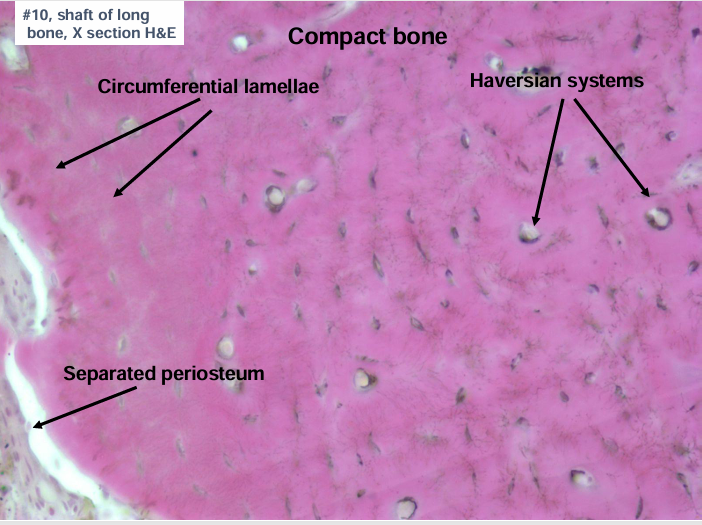
haversian system (osteons)
-haversian canal surrounded by concentric lamellae (layers) of bone
-lacunae lie between lamellae and contain osteocytes
-lacunae are connected by canaliculi
-Volkmann’s canals are perpendicular to Harvesian canals
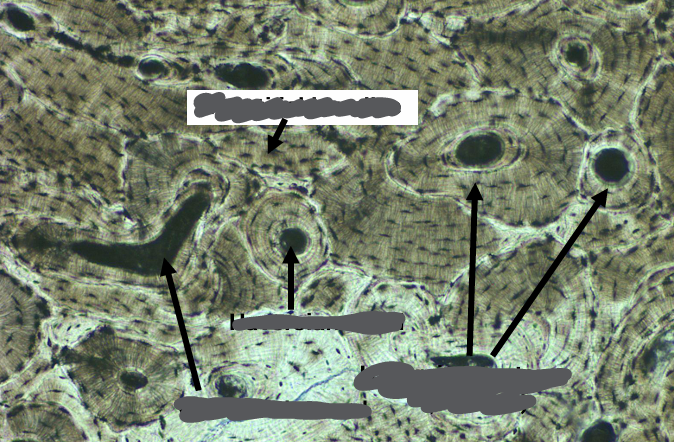
-dried bone
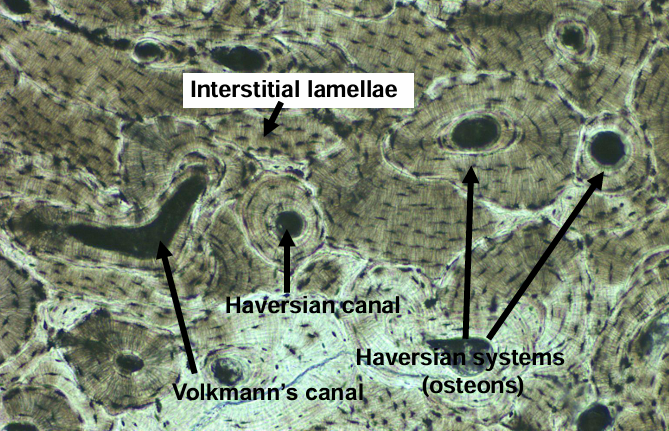
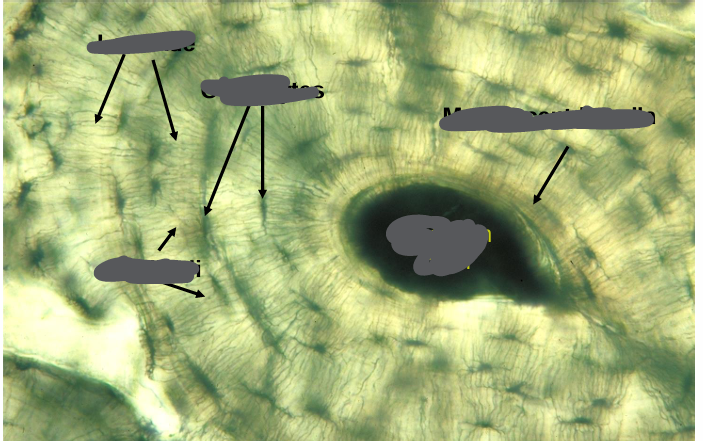
-one haversian system (osteon)
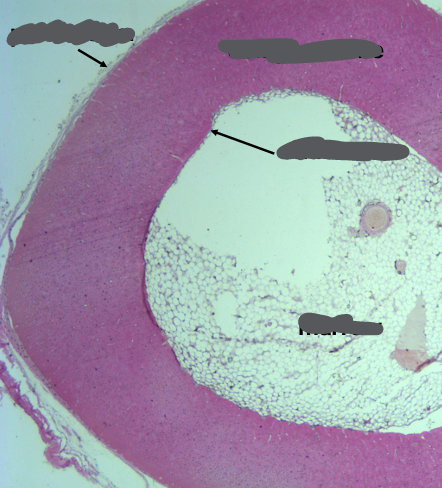
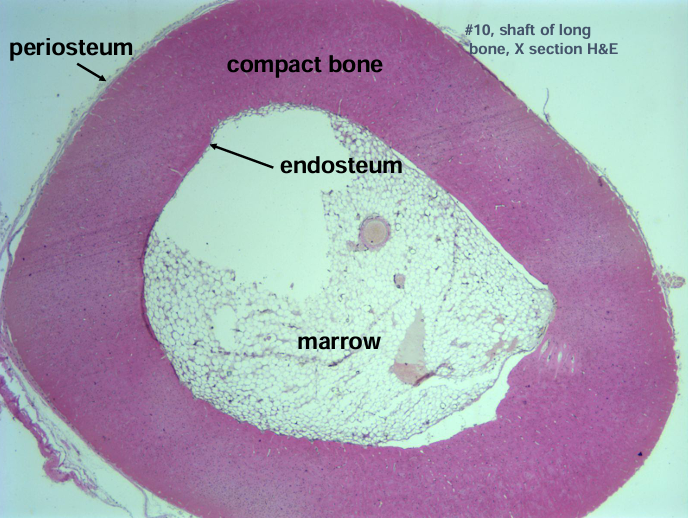
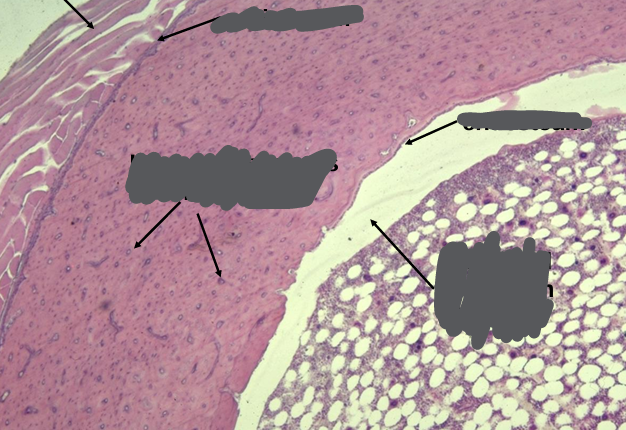
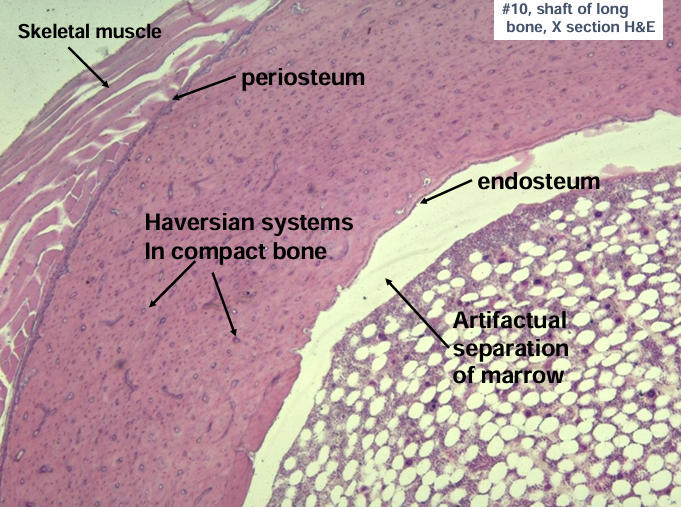
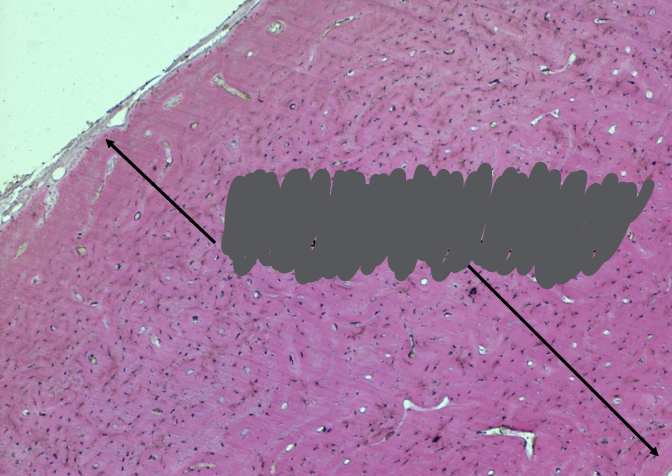
-circumferential lamellae of bone at the periosteal and endosteal surfaces
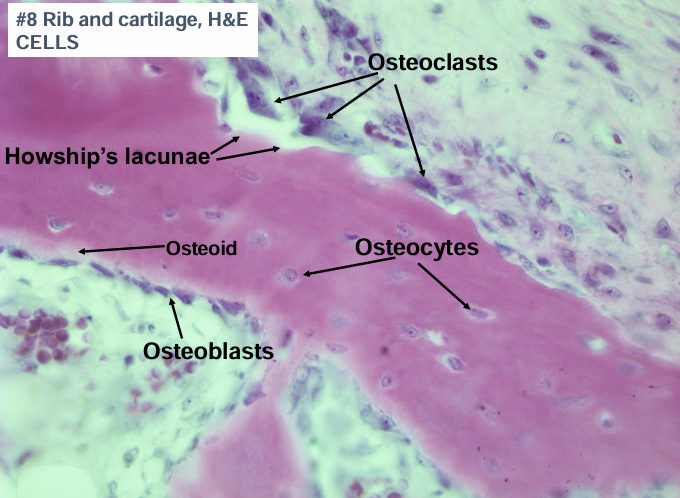
osteoclast
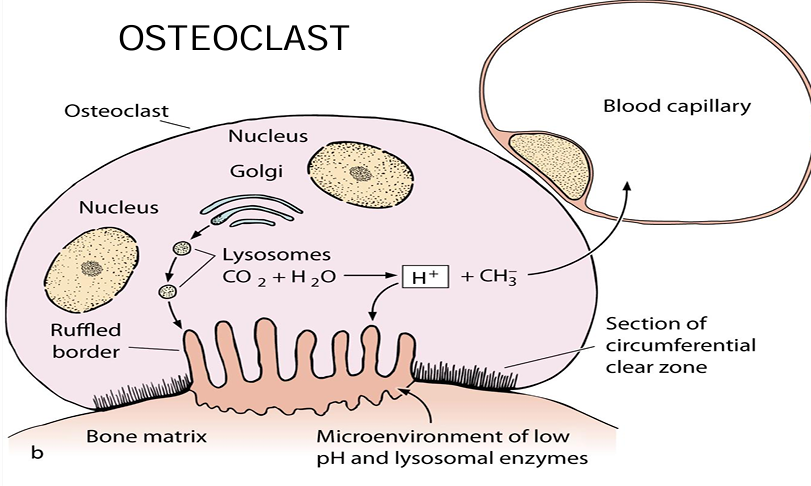
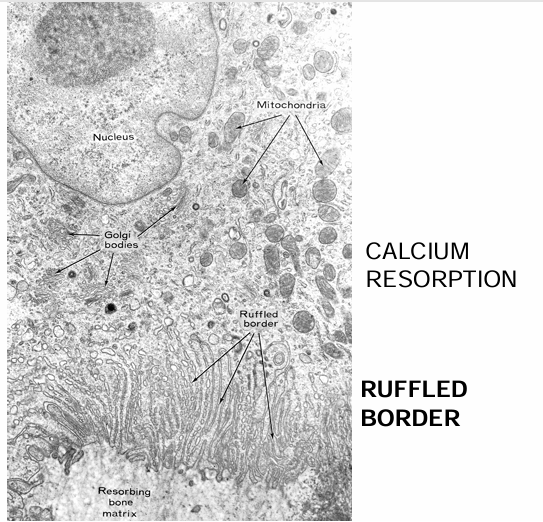
osteoclast electron micrograph
intramembranous bone formation
-most flat bones and mandible and maxilla
-parietal bone skull here
-NO cartilage model as base- condensations (membranes) of embryonic mesenchymal tissue
-direct synthesis of bone matrix
intramembranous bone formation
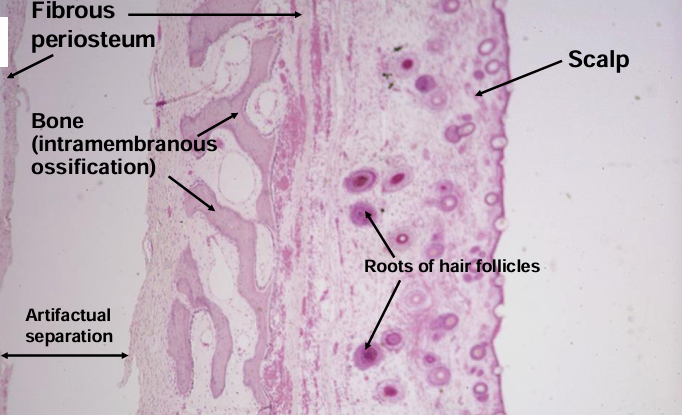
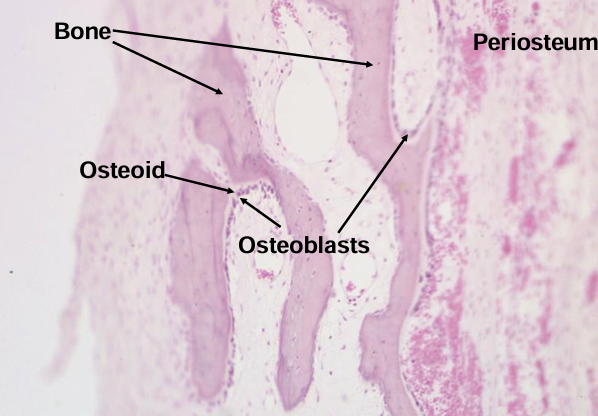
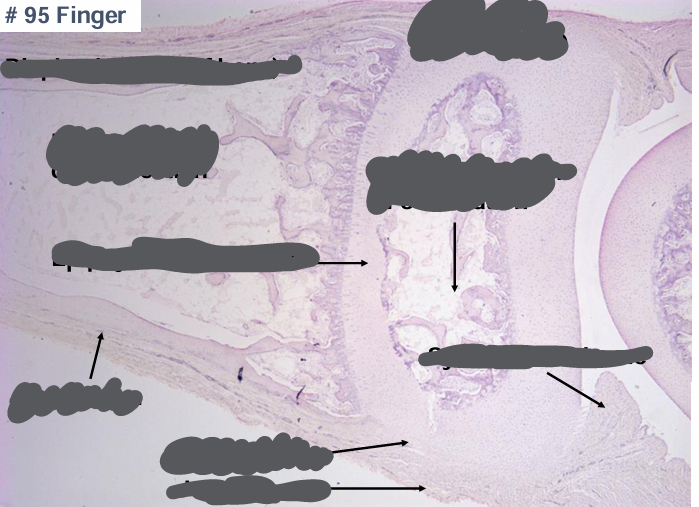
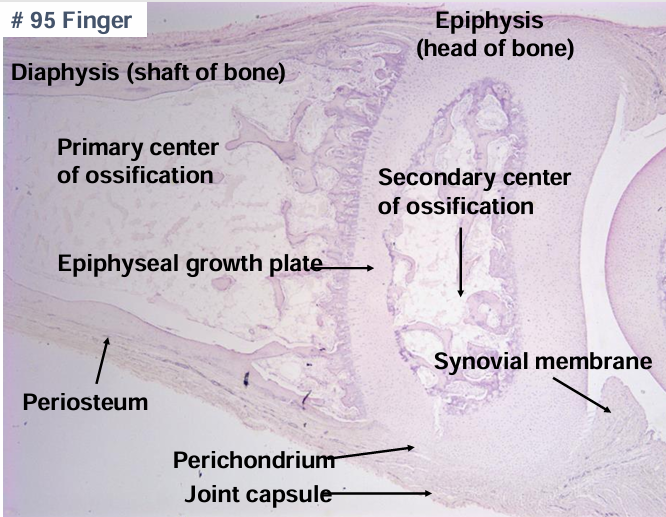
endochondral bone formation
-hyaline cartilage model
-bone collar forms
-vessels enter (VEGF)
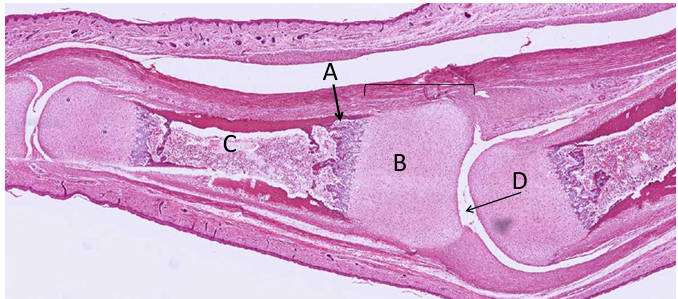
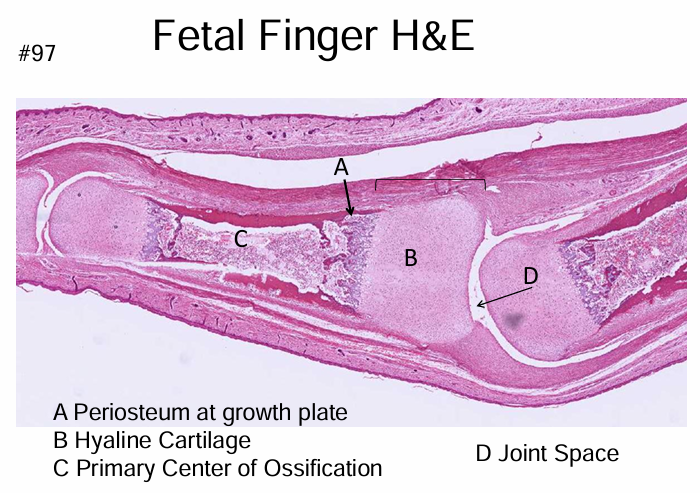
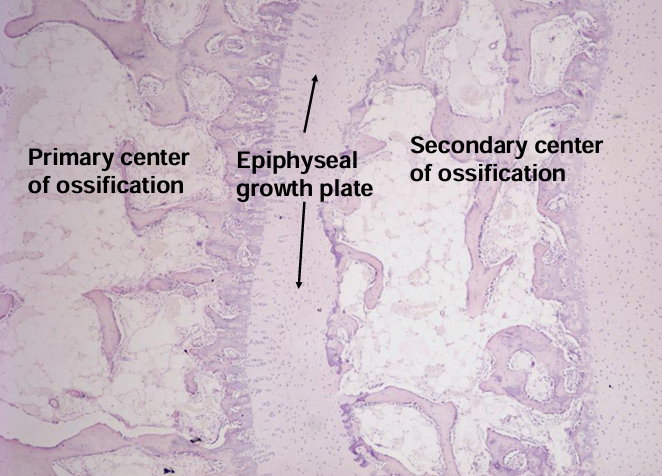
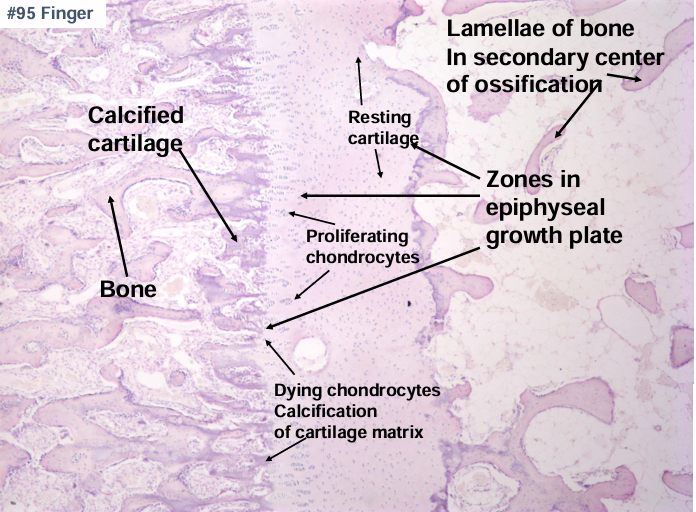
-primary center of ossification
-secondary center of ossification after birth
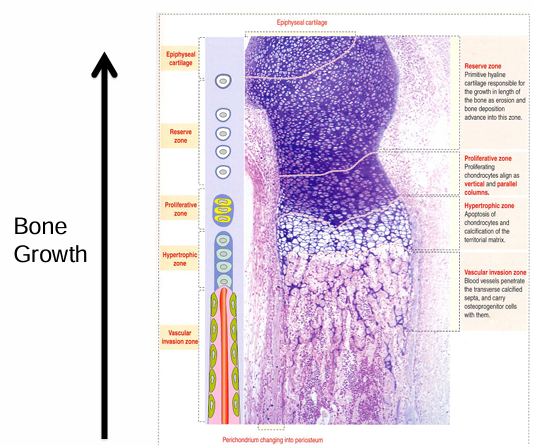
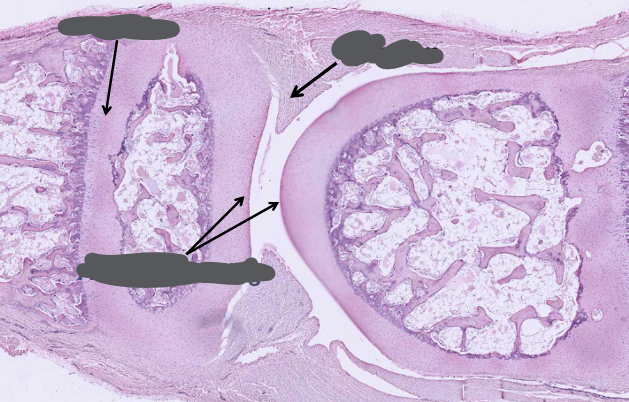
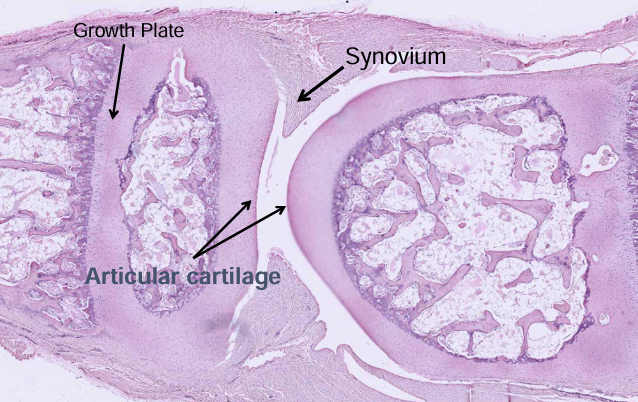
-growth plate grows cartilage toward ends of bone
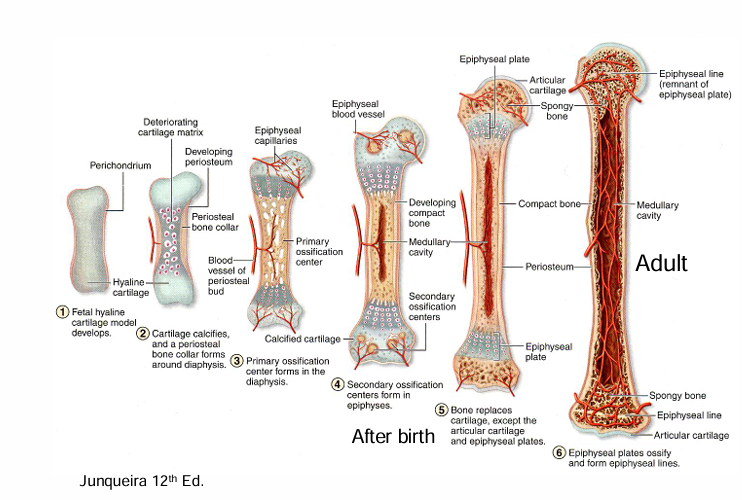
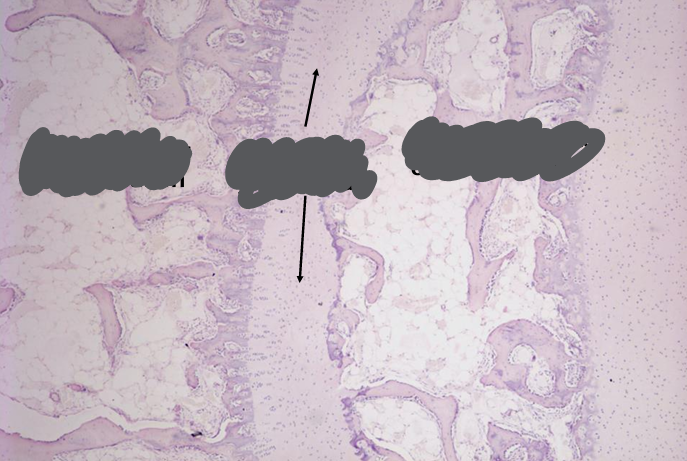
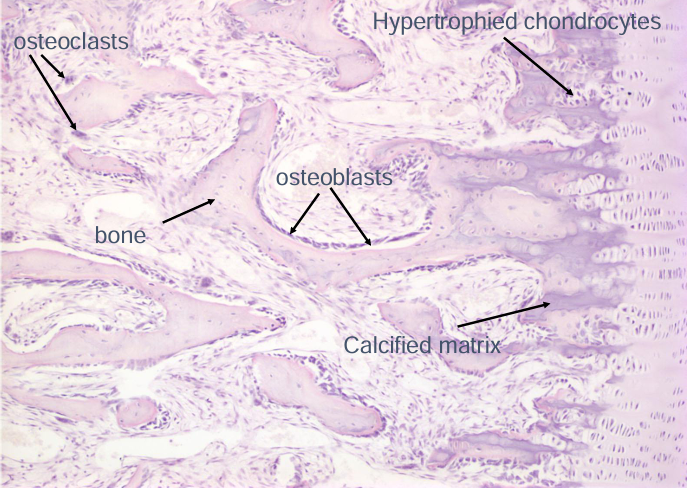
endochondral ossification four major zones
endochondral ossification
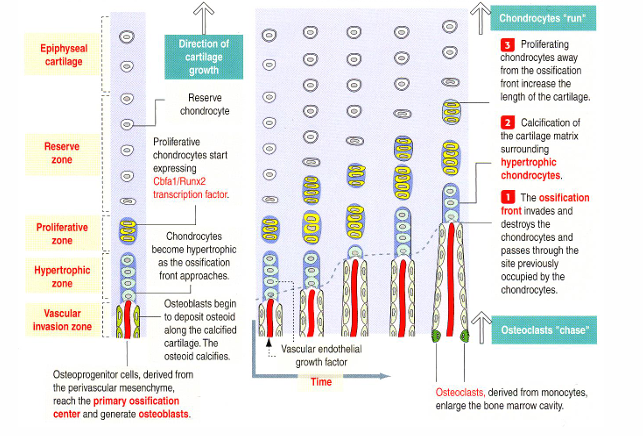
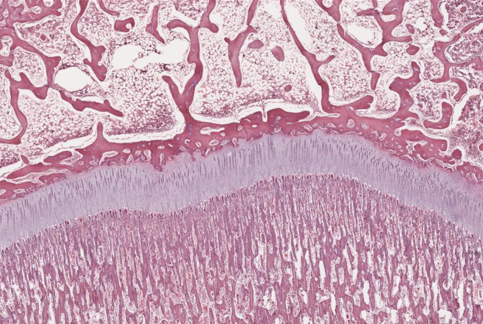
-cartilage growth plate
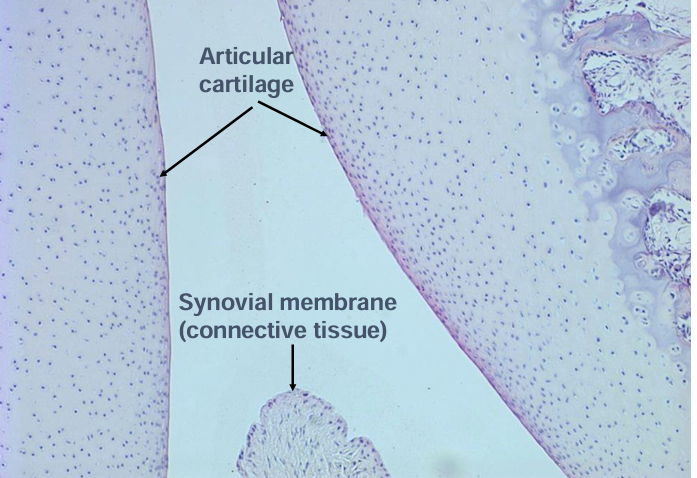
what are the mechanisms of cartilage growth?
-appositional and interstitial growth
what is the distribution of blood vessels in cartilage, and how does this relate to the nutrition of cartilage?
-blood vessels found only in perichondrium
-nutrition by diffusion through ground substance
the cementing lines that delimit the Haversian systems may appear refractile or slightly basophilic- what accounts for this basophilia?
-proteoglycans
what structures are found within Haversian canals?
-capillaries and nerves
is the osseous lamella adjacent to Haversian canal the youngest or the oldest lamella of a particular osteon?
-the youngest
what structure in mature bone is created by the zone of resportion?
-the marrow canal
what are the differences between intramembranous ossification and endochondral ossification?
-intramembranous ossification: does not use a cartilage framework, bone develops directly on or within mesenchyme; bone growth is appositional; found in irregular bones
-endochondral ossification: replaces a preexisting cartilage framework; bone lengthens through interstitial growth and changes diameter through appositional growth; found in long bones