Circulation and Gas Exchange in Humans (Part 1)
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
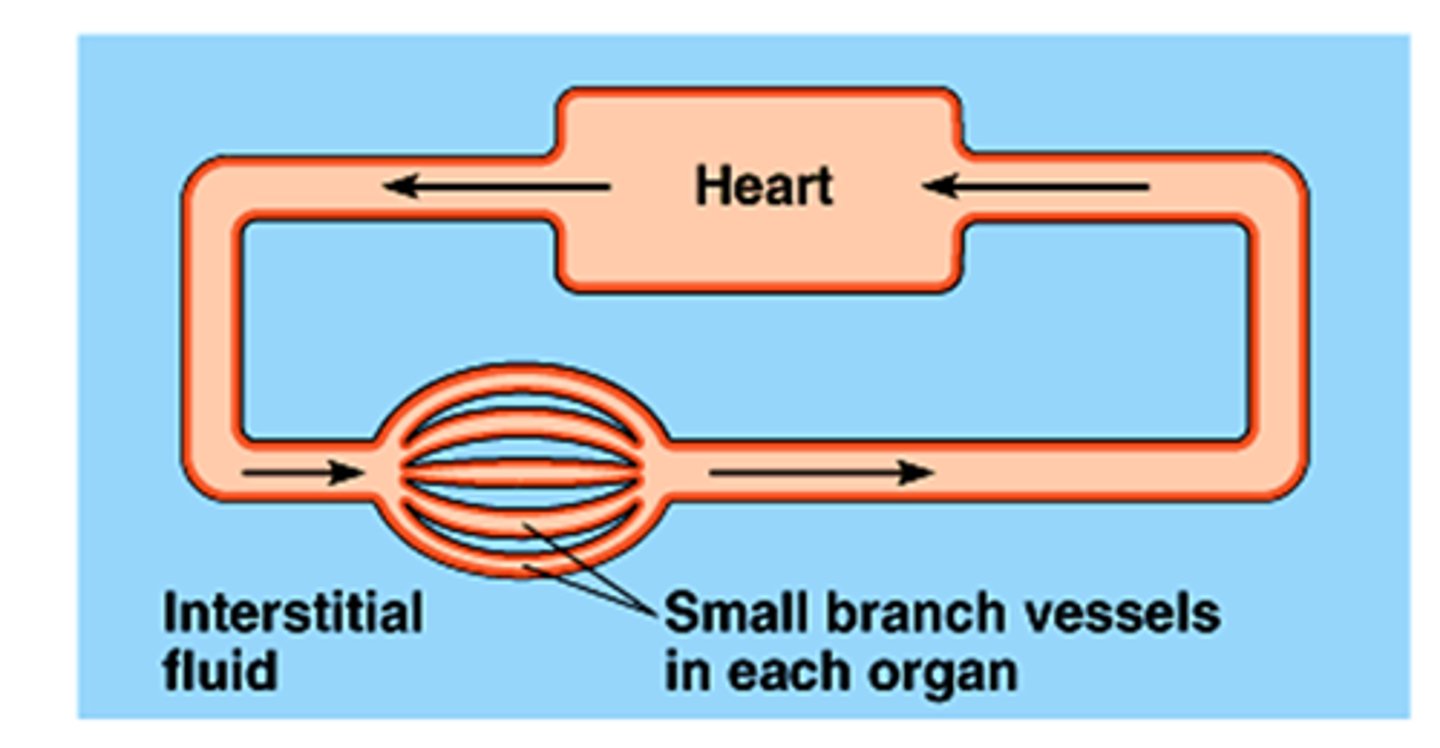
Interstitial fluid (ISF)
The fluid filling the spaces between cells in most animals.
Closed circulatory system
A system where blood is contained within vessels and is pumped by the heart.
Hydrostatic pressure
The pressure exerted by a fluid at equilibrium due to the force of gravity; greater at the arterial end (35 mm Hg) than at the venule end (17 mm Hg).
Blood pressure
- The pressure of circulating blood on the walls of blood vessels.
- the hydrostatic force that blood exerts against vessel walls
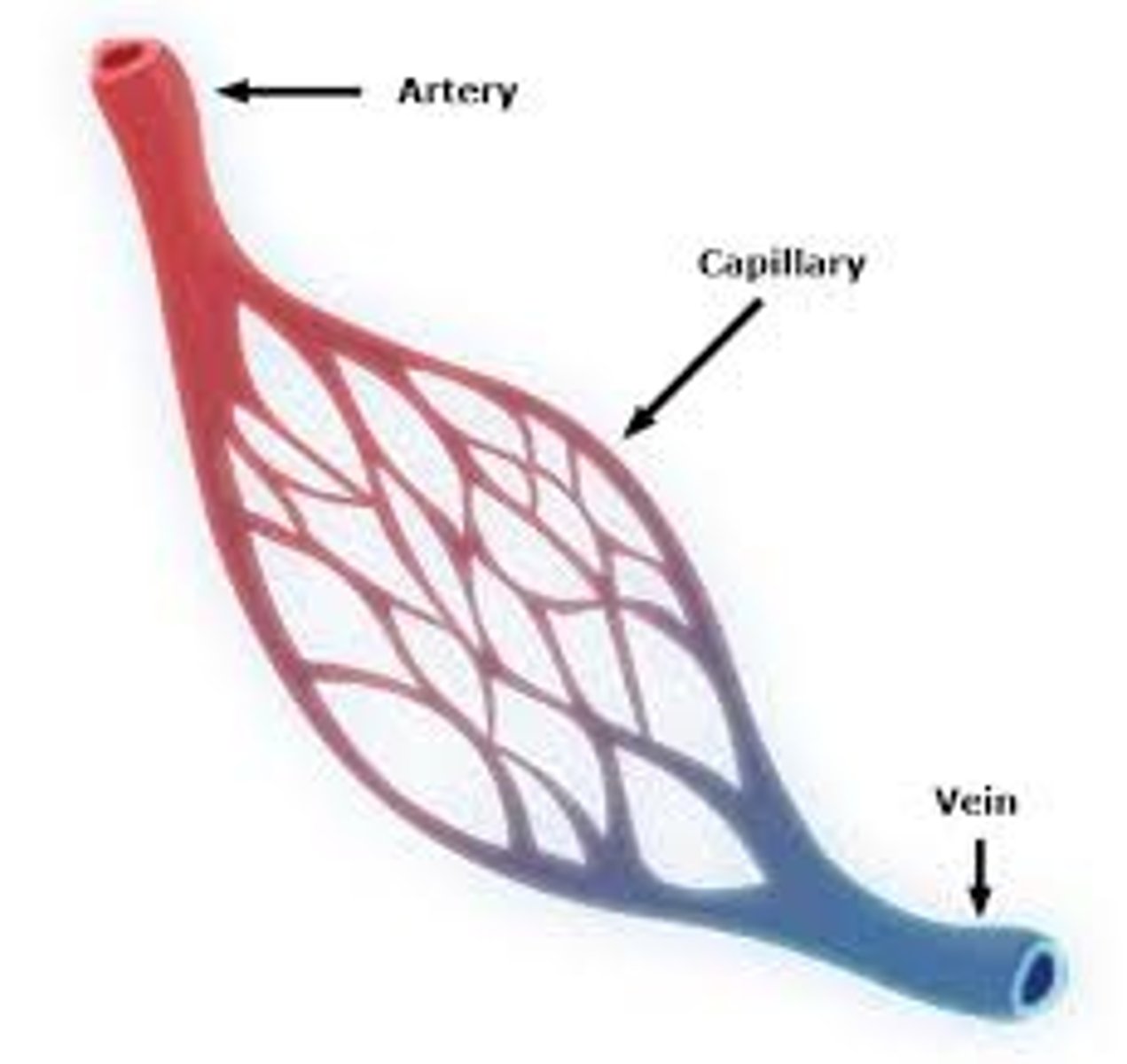
Arteries
- Blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to organs.
- have thicker middle and outer layers to accommodate high pressure
Capillaries
Very thin, porous blood vessels where the exchange of chemicals occurs between blood and interstitial fluid.
Capillary beds
Networks of capillaries that infiltrate each tissue.

Venules
Small blood vessels that converge from capillaries and lead to veins.
Veins
thinner-walled blood vessels that return blood to the heart at low pressure from capillaries.
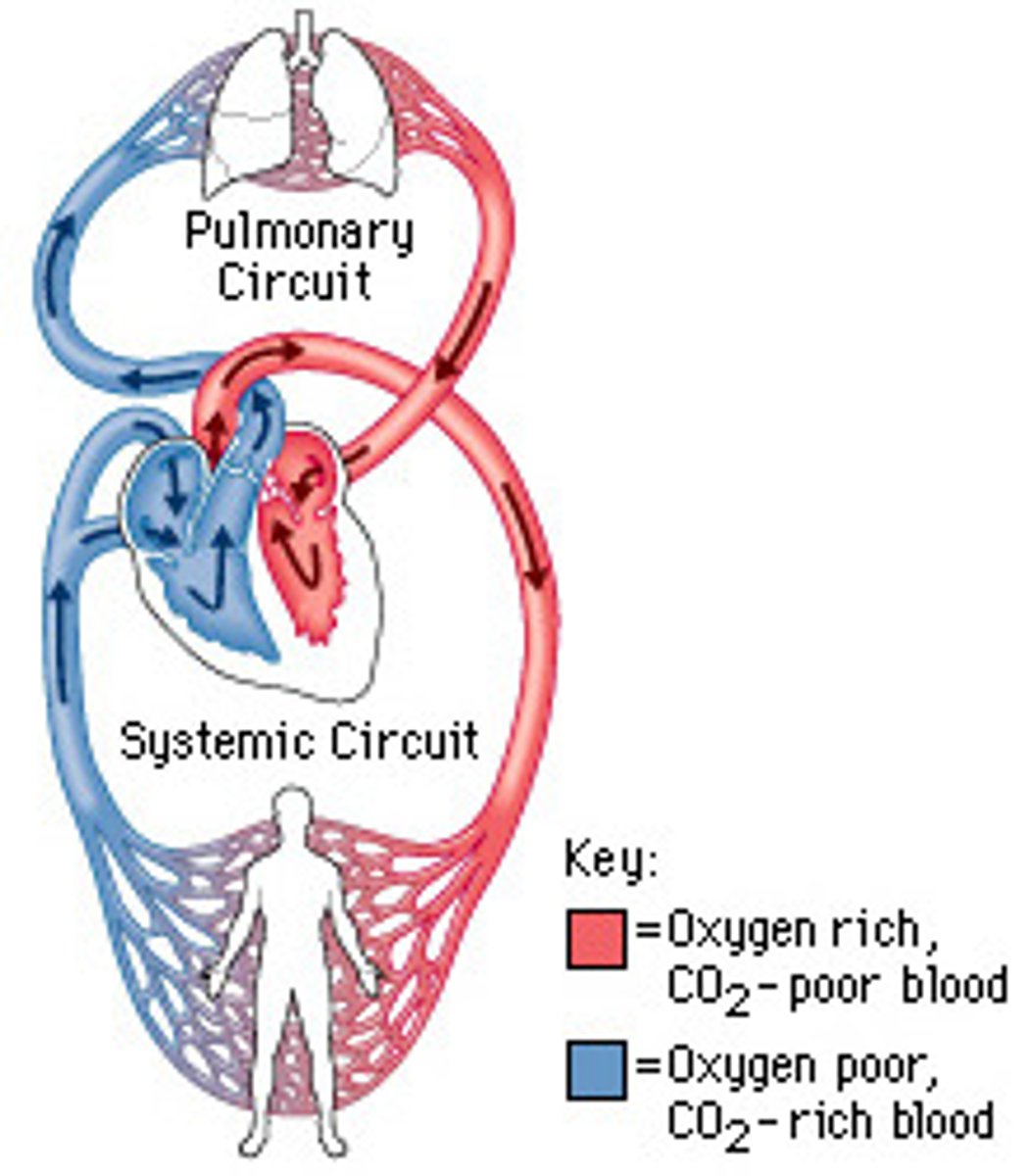
Double circulation
A system where the pulmonary and systemic circuits operate simultaneously, preventing mixing of oxygen-rich and oxygen-poor blood.
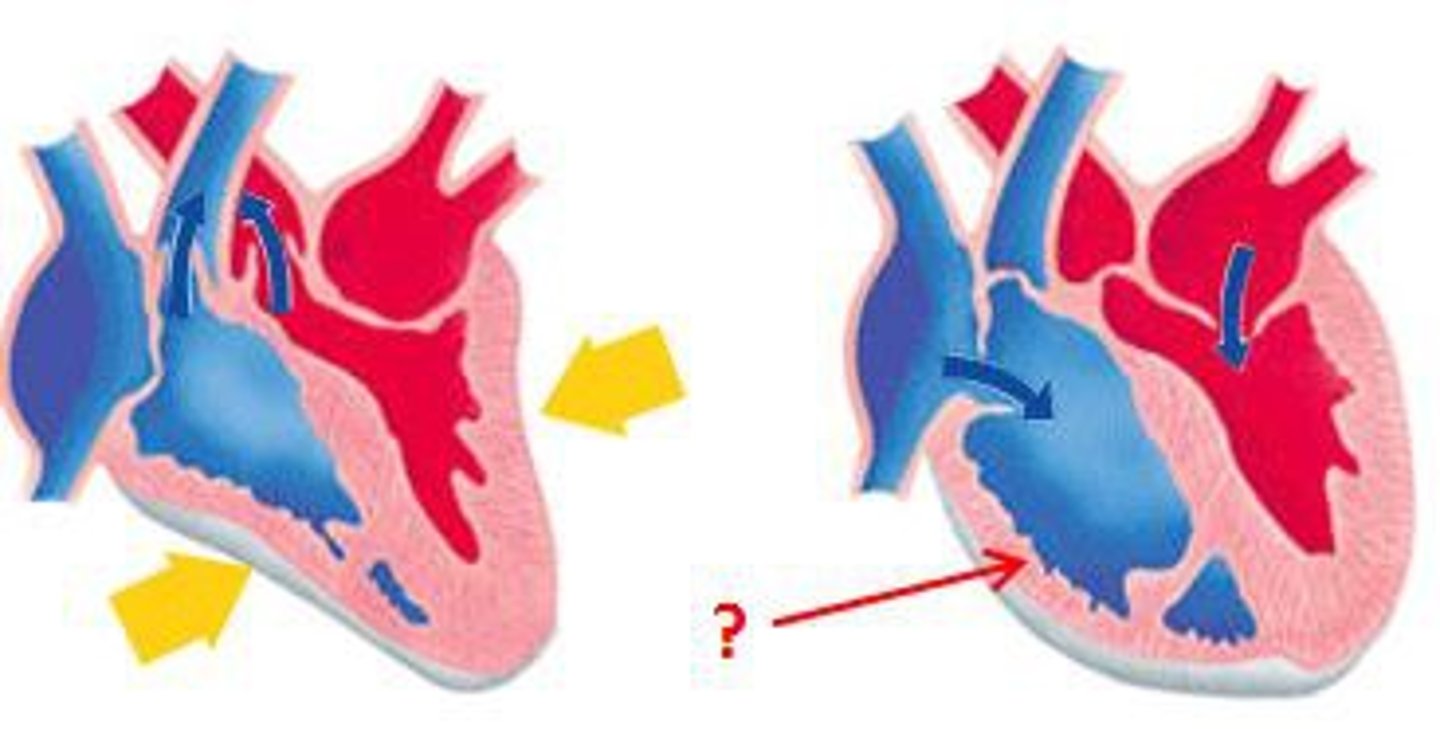
Cardiac cycle
One complete sequence of pumping and filling of the heart.
Regulated by electrical impulses that radiate throughout the heart.
Systole
The phase of the cardiac cycle when the heart contracts.
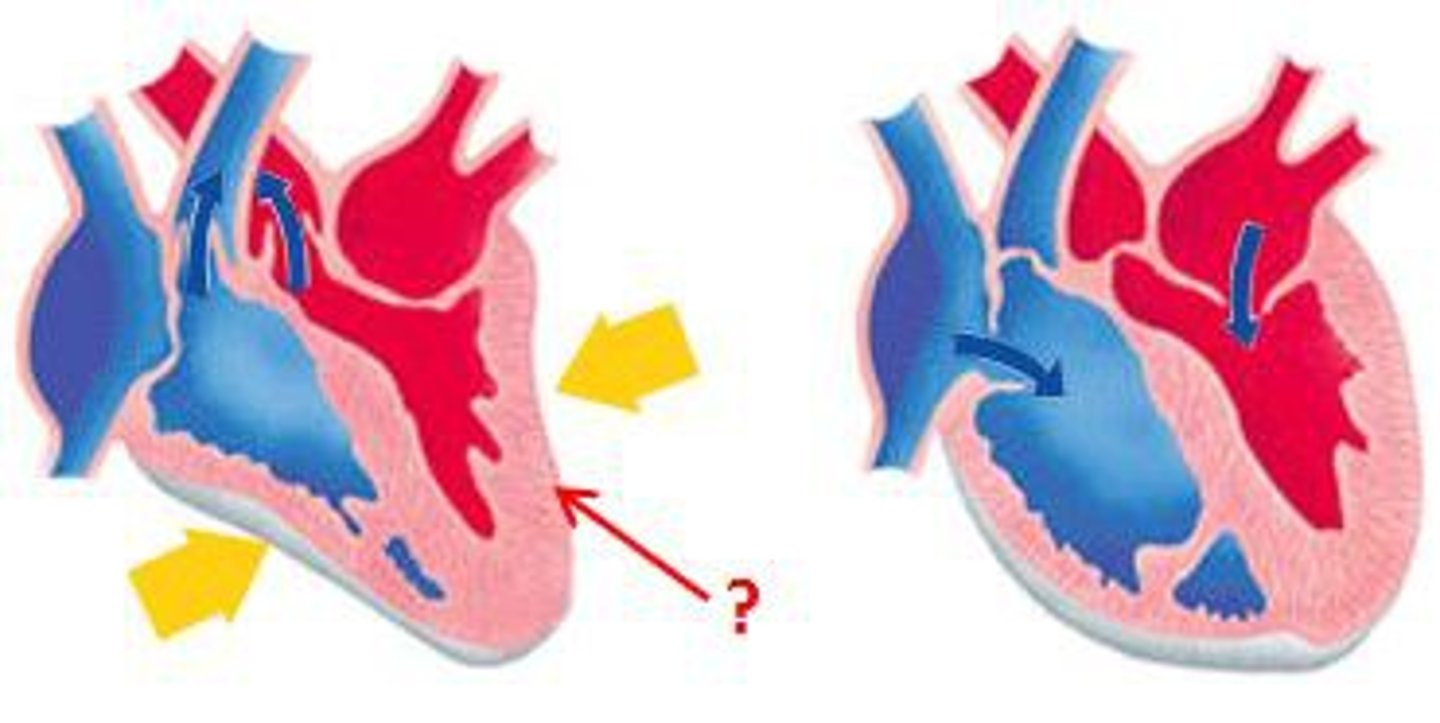
Diastole
The phase of the cardiac cycle when the heart relaxes and fills with blood.
Average pulse rate at rest
About 75 beats per minute.
Duration of complete cardiac cycle
About 0.8 seconds.
Duration of atrial and ventricular diastole
About 0.4 seconds.
Duration of atrial systole
About 0.1 seconds.
Duration of ventricular systole
About 0.3 seconds.
Cardiac output
The amount of blood the heart pumps in a given time, depending on heart rate and stroke volume which increases during exercise to maintain blood pressure.
Stroke volume
The amount of blood pumped by the left ventricle in each contraction, averaging about 75 mL.
Coronary arteries
The first branches from the aorta that supply blood to the heart muscle.
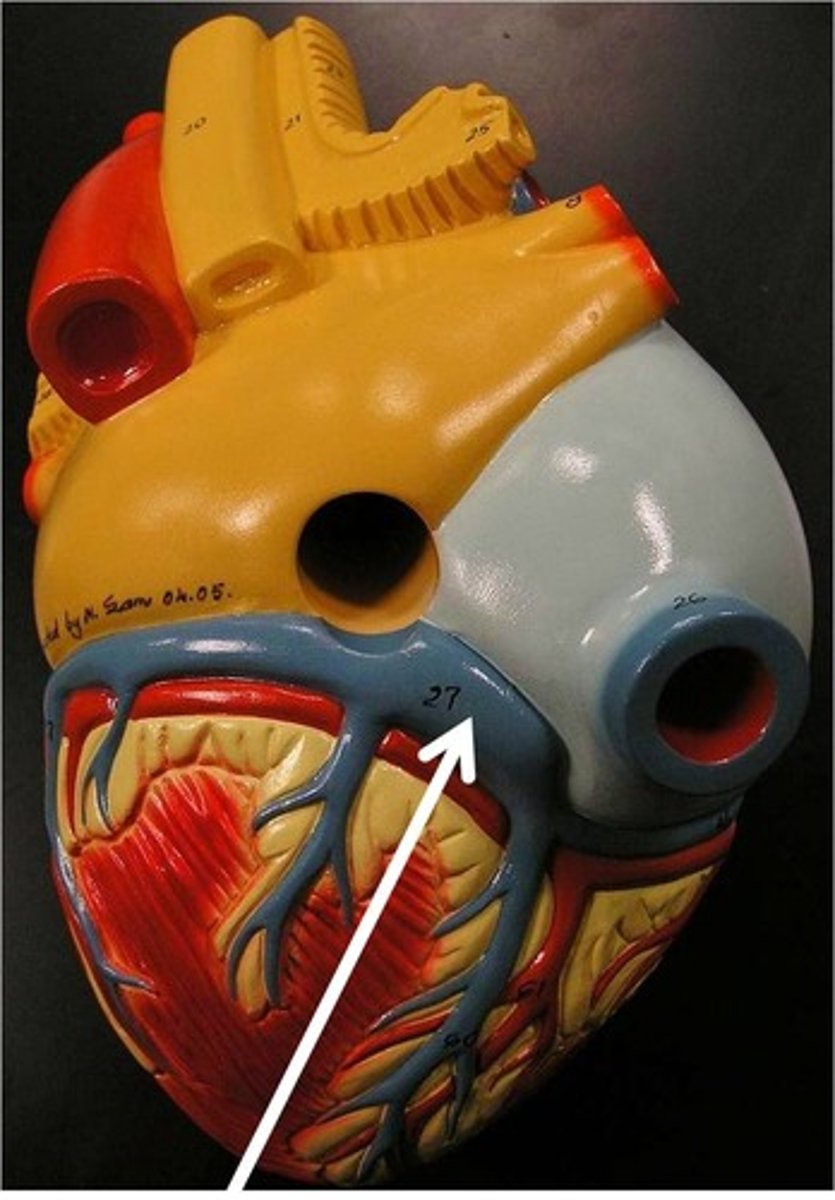
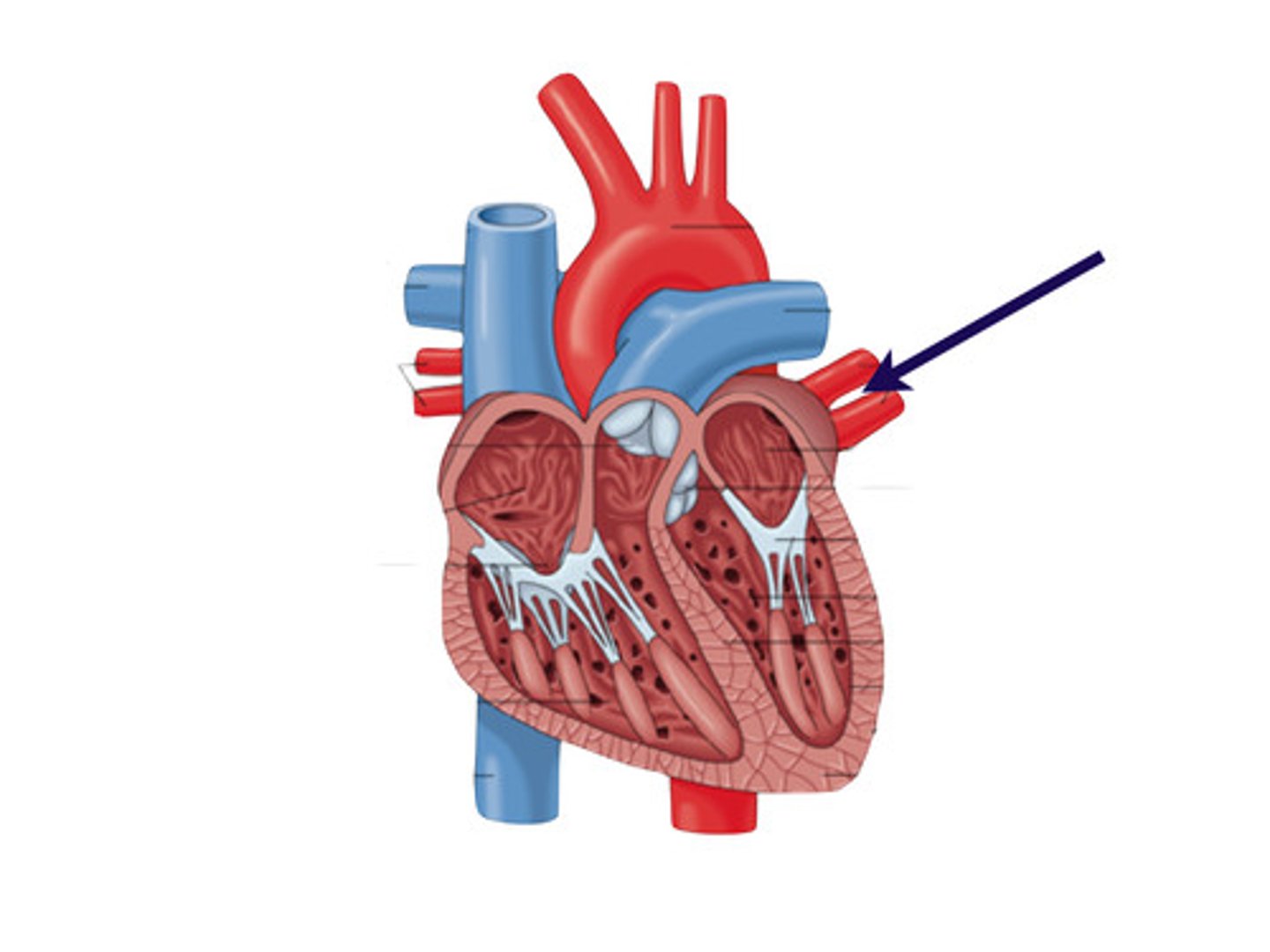
Atria
The two upper chambers of the heart that function as collection chambers for blood returning to the heart.
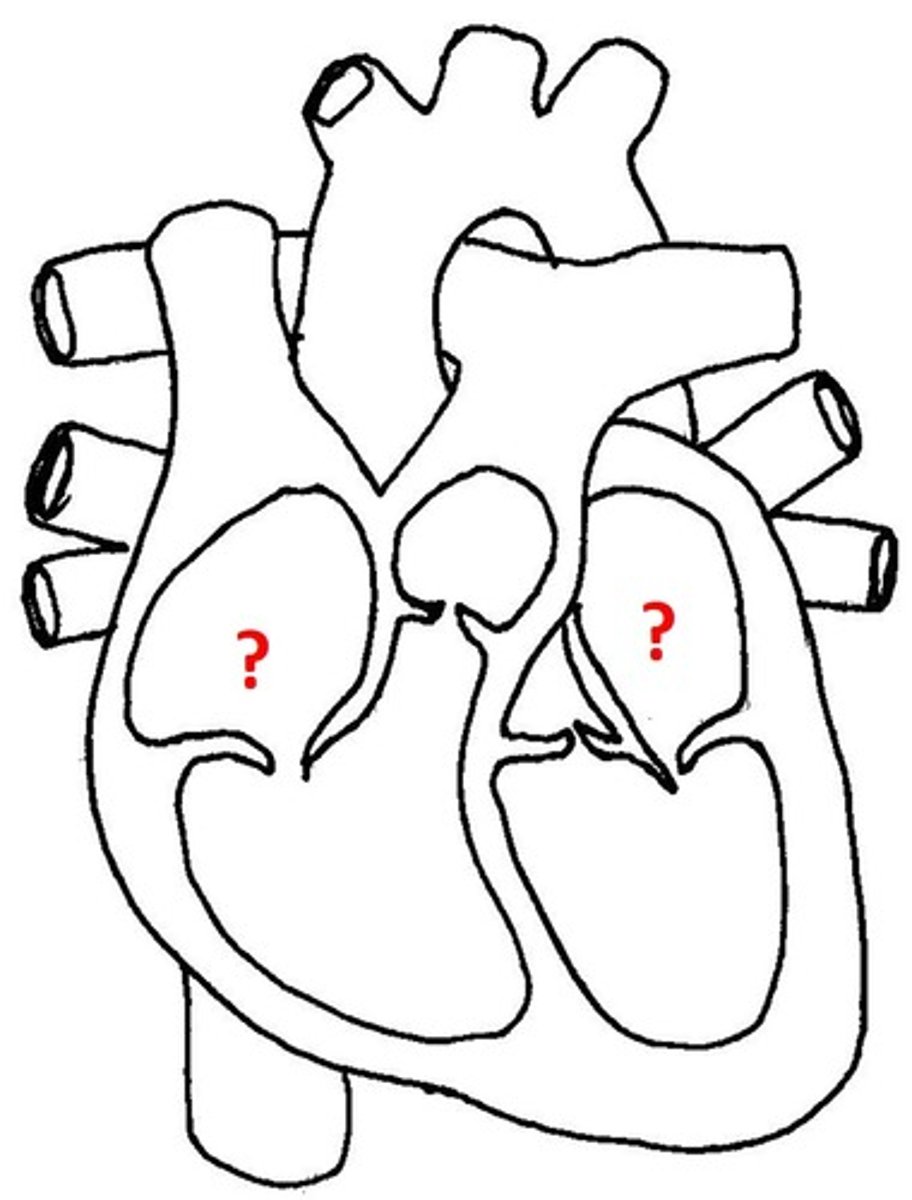
Ventricles
The two lower chambers of the heart with thicker walls that contract strongly to pump blood.
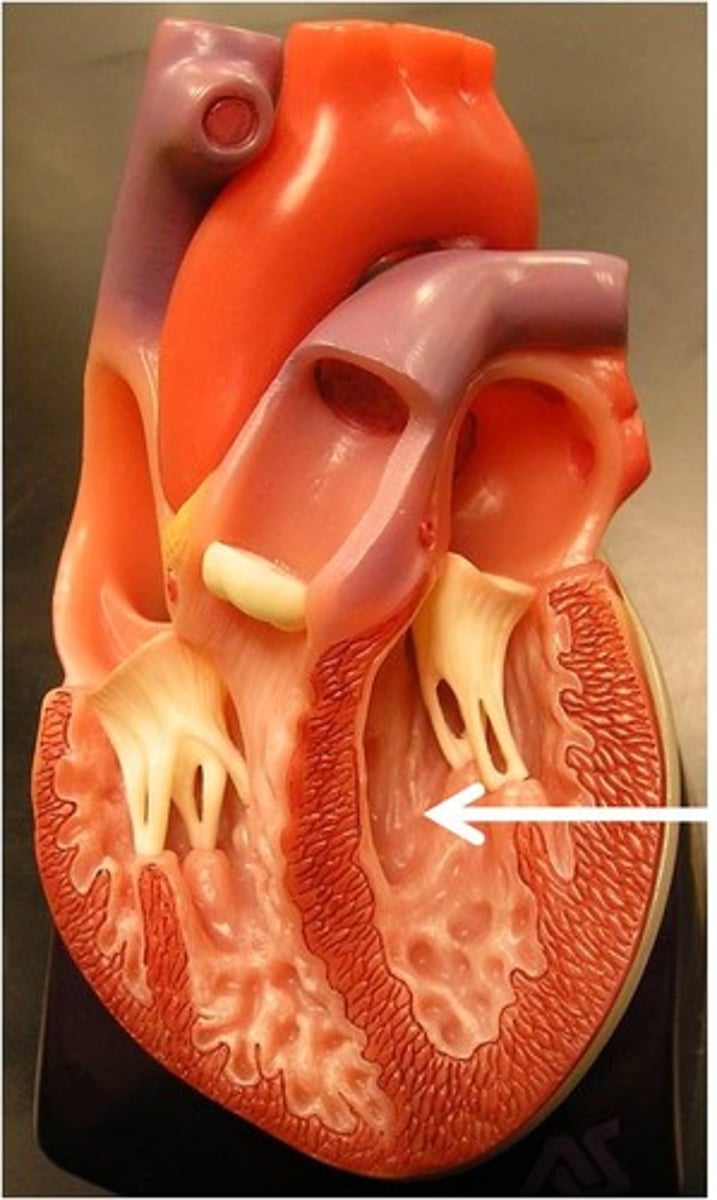
Resting cardiac output
About 5.25 L / min, equivalent to the total volume of blood in the human body.
Heart rate measurement
Can be measured indirectly by measuring pulse, which is the rhythmic stretching of arteries caused by the pressure of blood pumped by the ventricles.
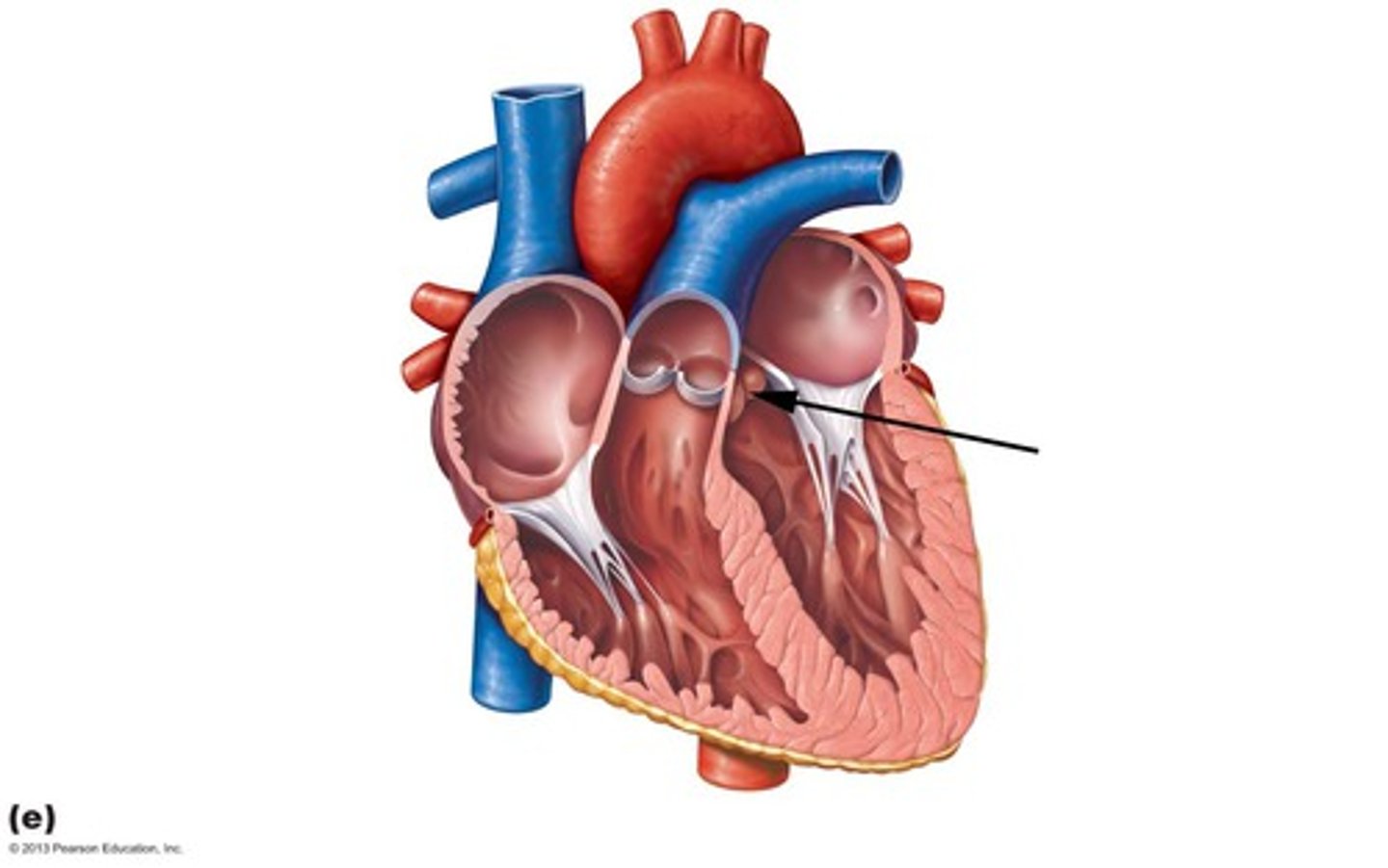
Atrioventricular (AV) valves
Prevent backflow into the atria when the ventricles contract; include the mitral (bicuspid) valve and the tricuspid valve.
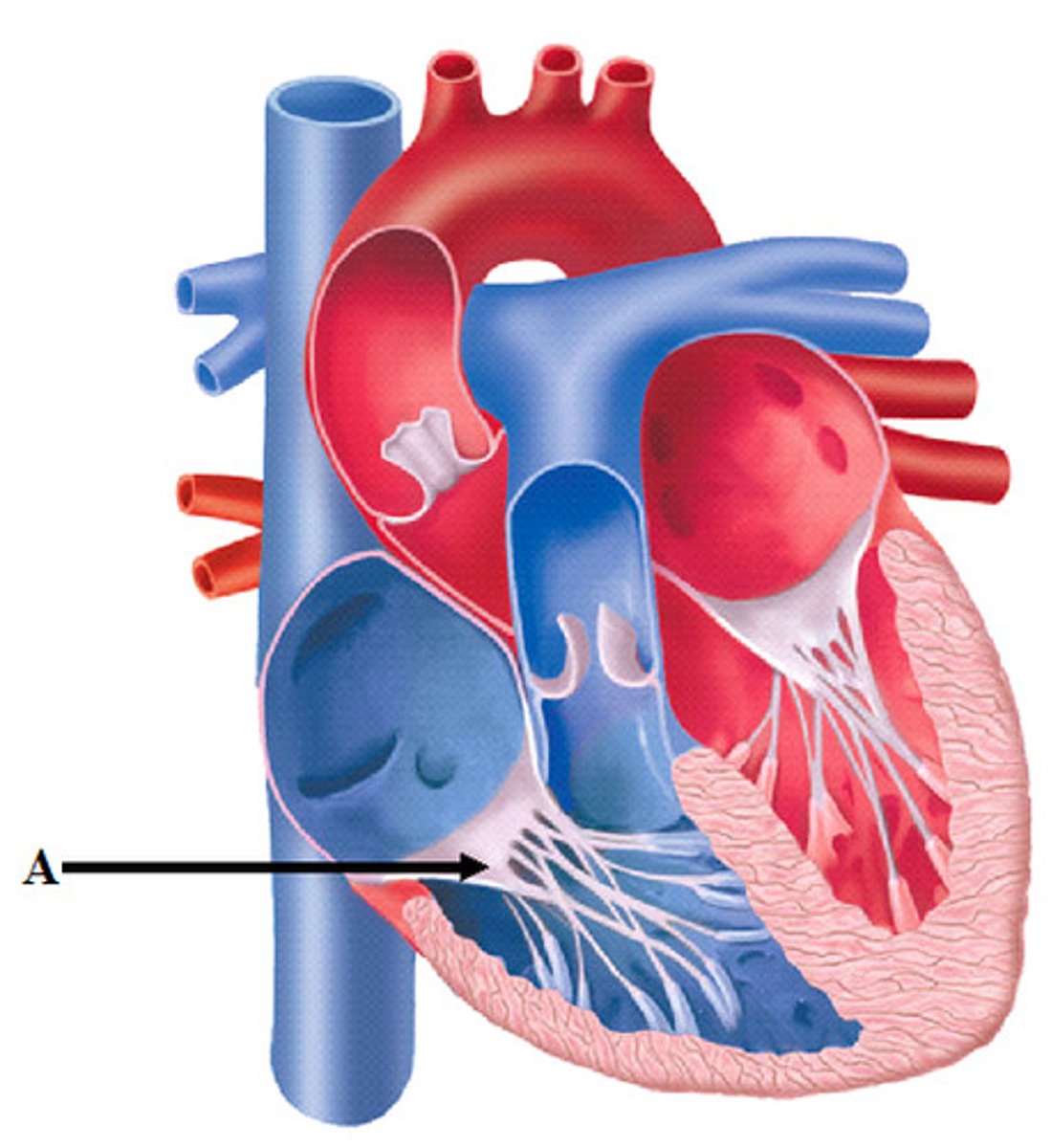
Tricuspid valve
Right AV valve made up of three cusps, located between the right atria and ventricle.
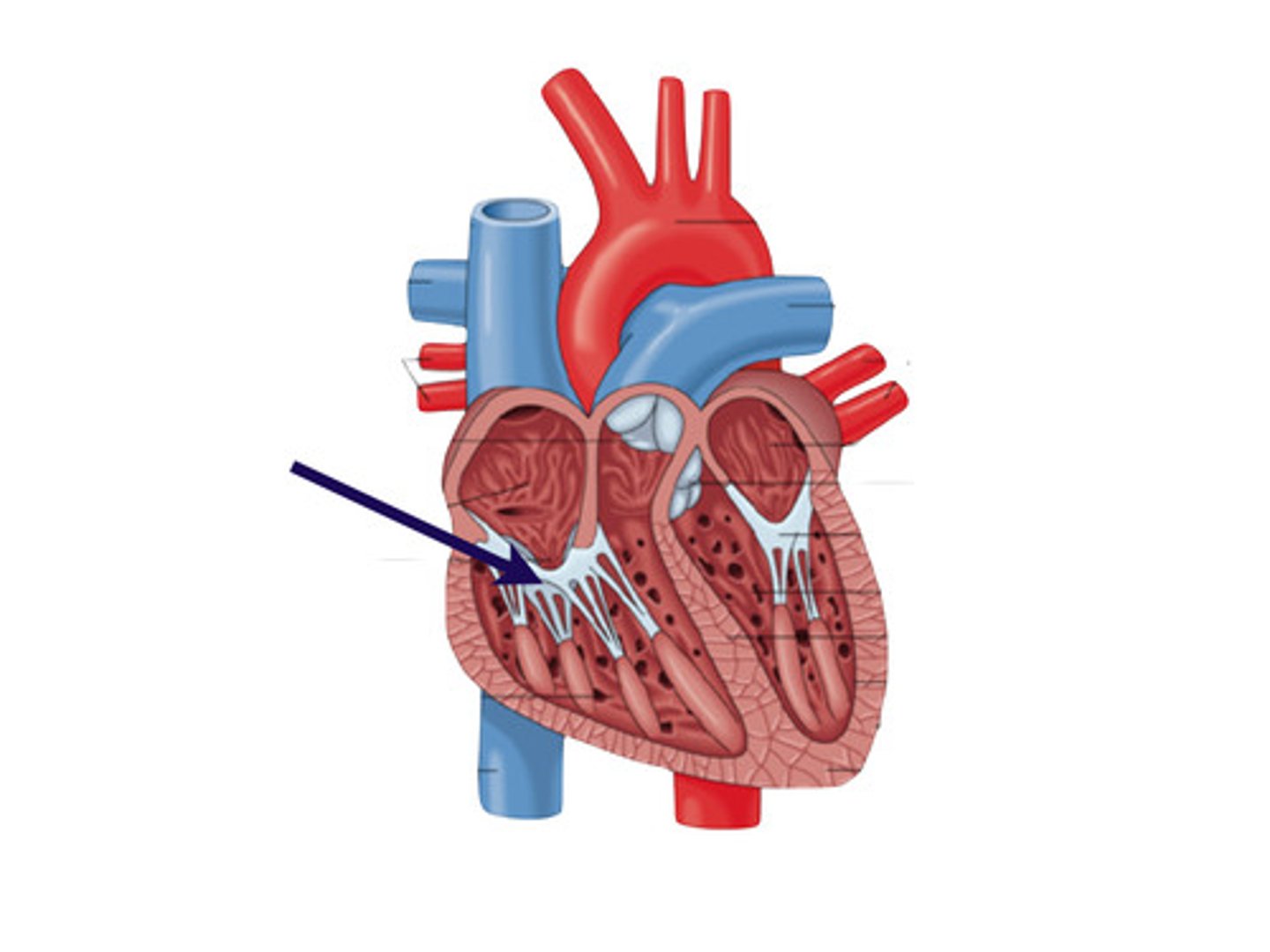
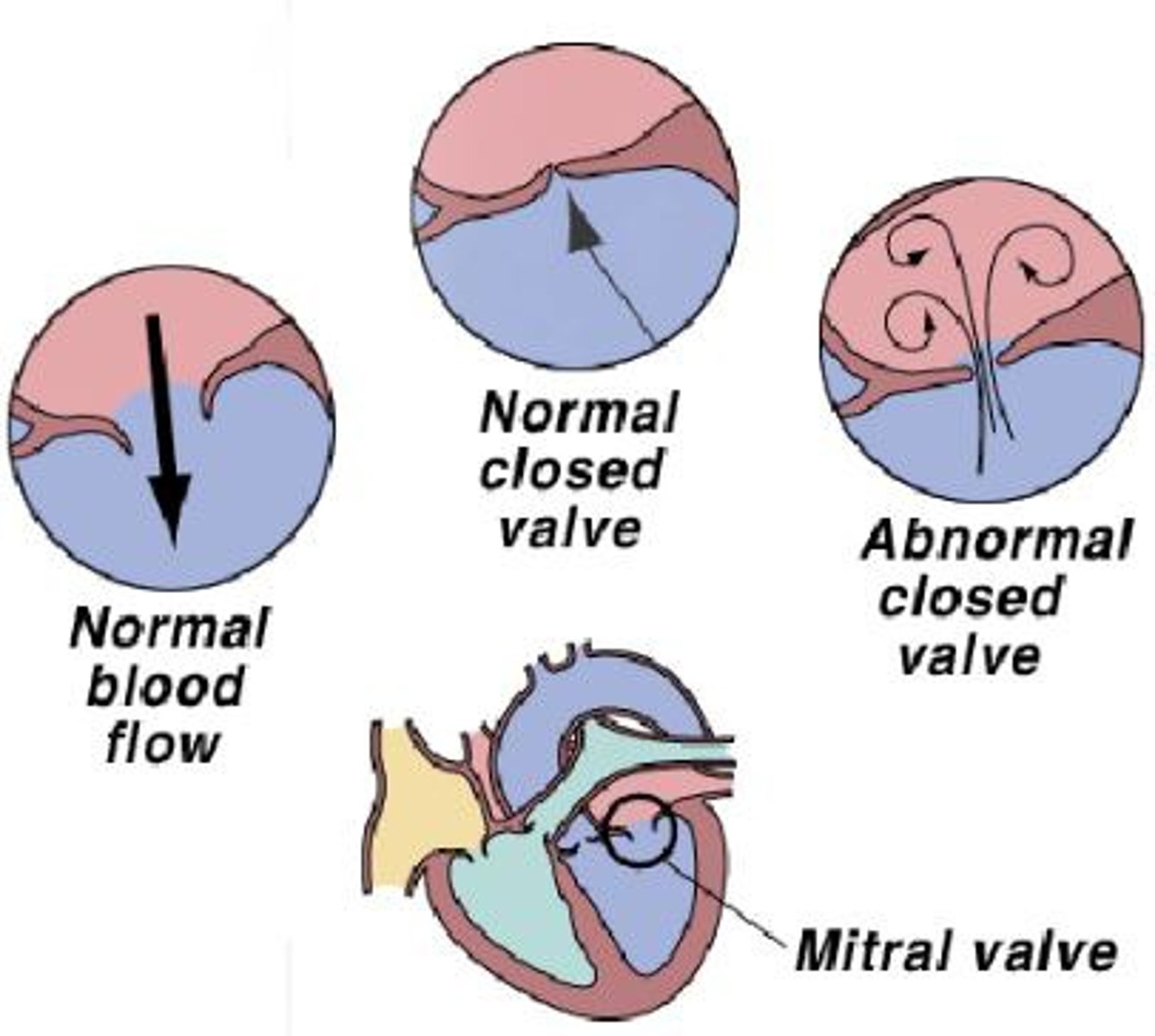
Mitral valve
Left AV valve (bicuspid) made up of two cusps, located between the left atria and ventricle.
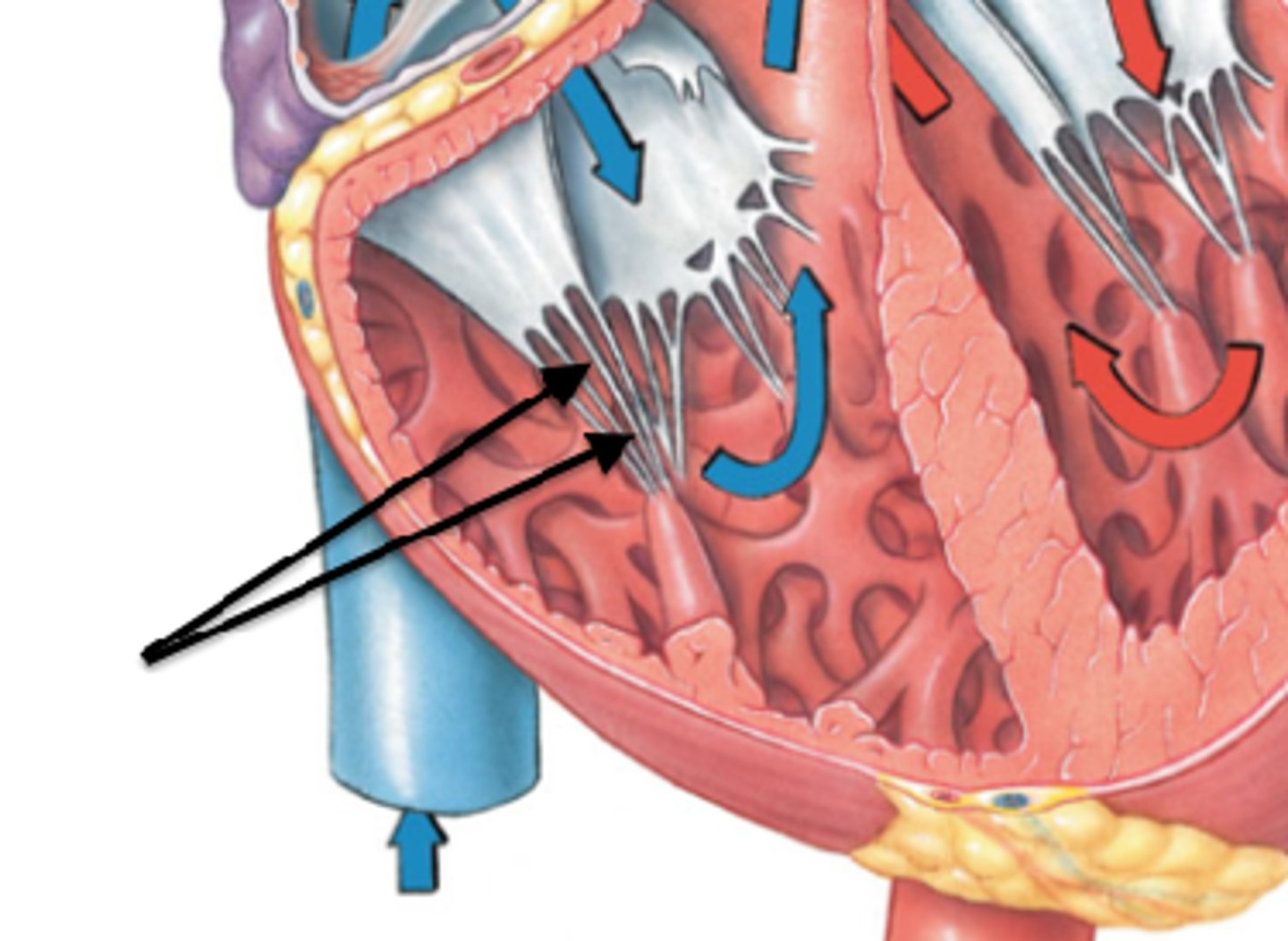
Chordae tendineae
Structures that anchor the cusps of the AV valves.
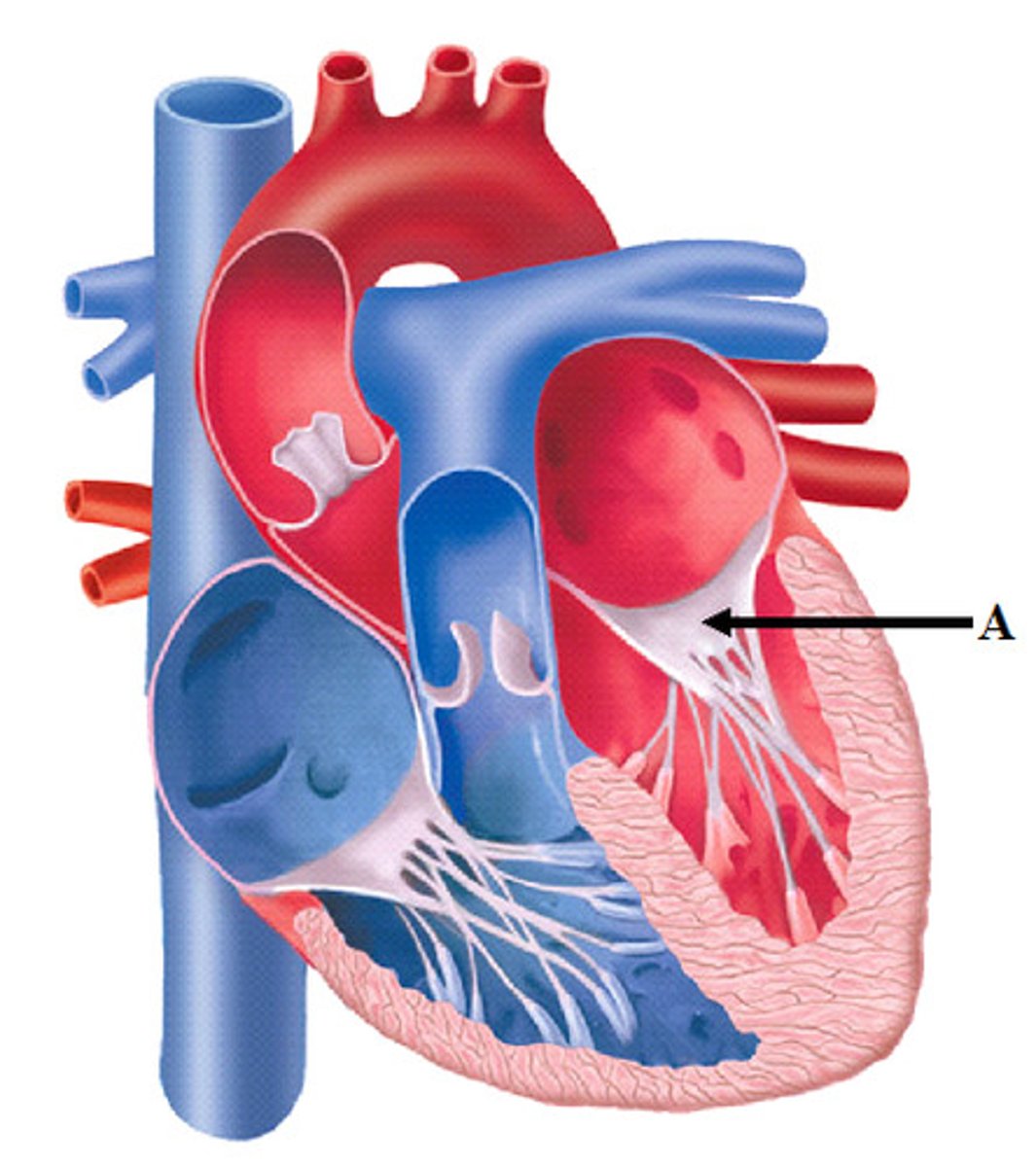
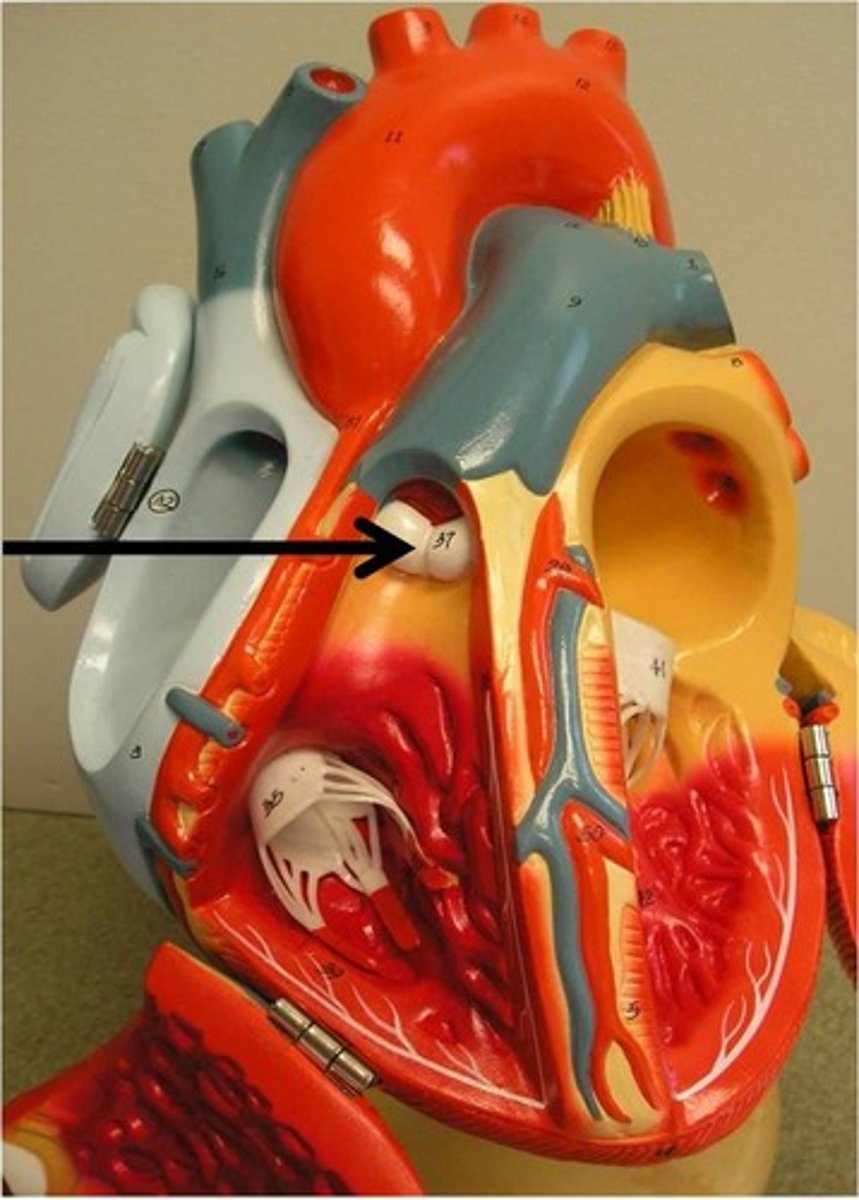
Semilunar valves
Prevent backflow from the aorta and pulmonary artery into the ventricles while they are relaxing; include the aortic valve and the pulmonary valve.
Pulmonary semilunar valve
Located between the right ventricle and the pulmonary trunk.
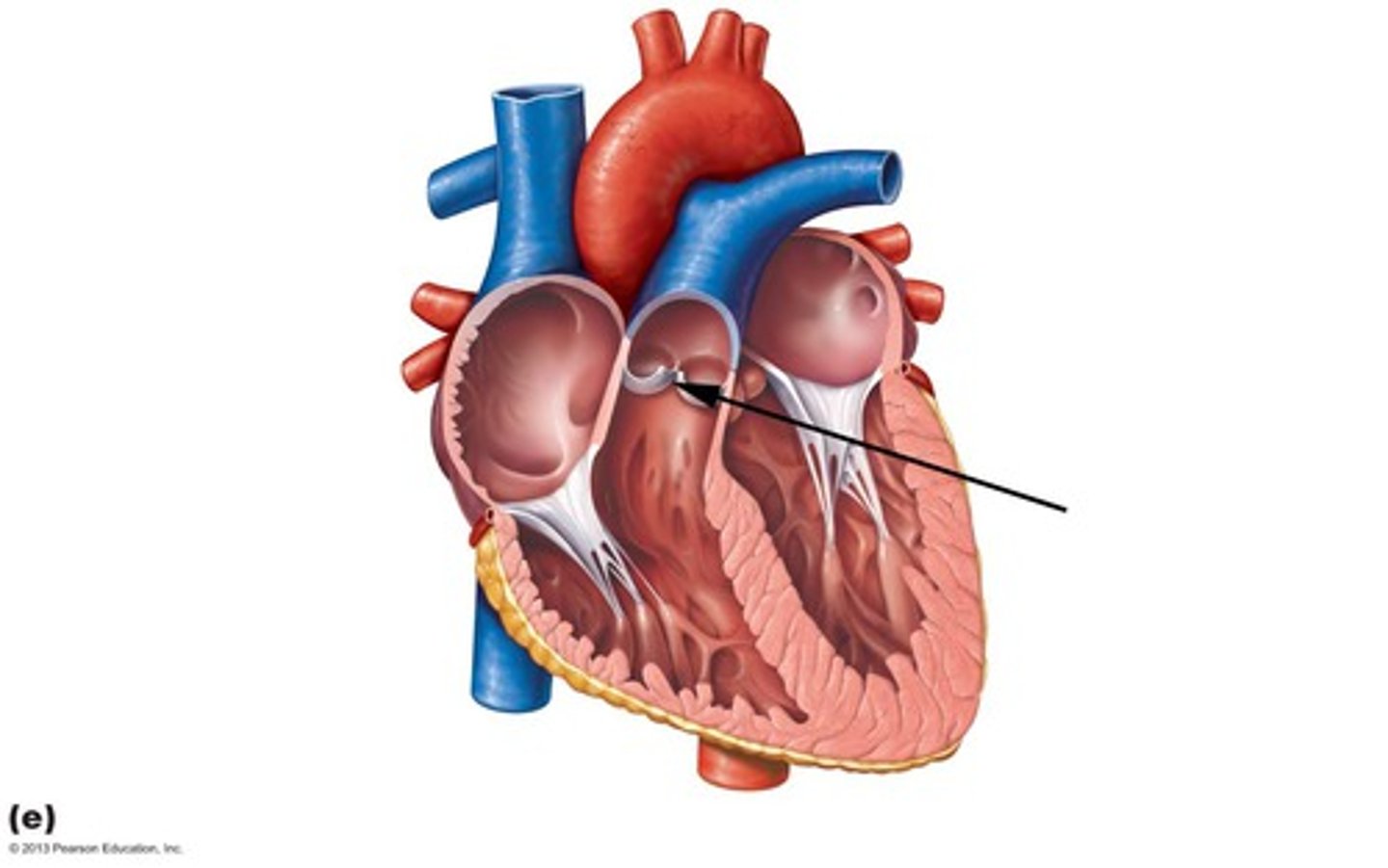
Aortic semilunar valve
Located between the left ventricle and the aorta.
Heart sounds
Caused by the closing of the valves, characterized by the pattern 'lub-dup, lub-dup, lub-dup.'
Lub sound
Created by the sound of blood rushing through the AV valves as they are narrowing and about to close.
Dup sound
Created by the sound of blood rushing through the semilunar valves as they are narrowing and about to close.
Heart murmur
A defect in one or more valves causing a hissing sound when blood squirts backward through a valve.
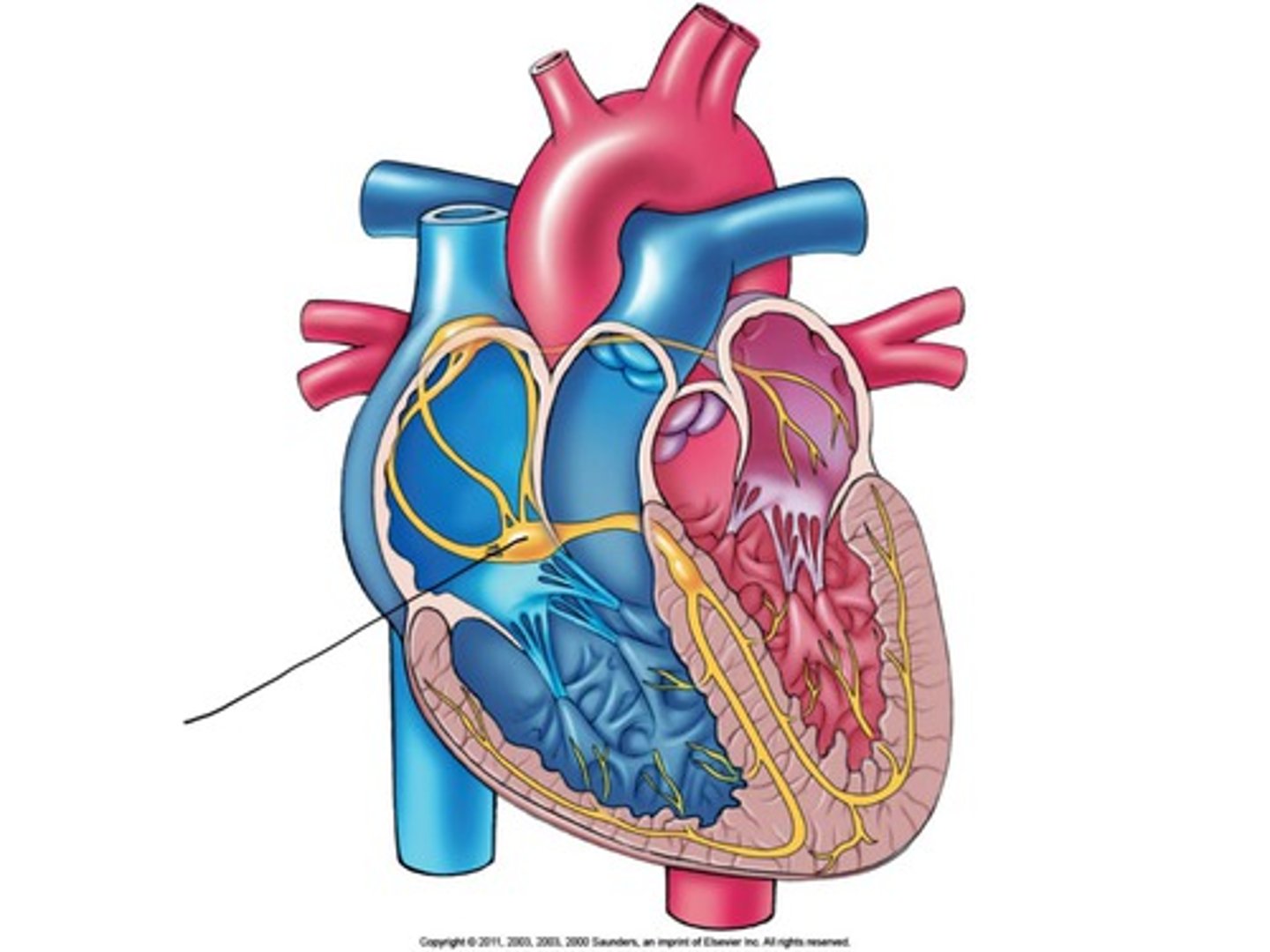
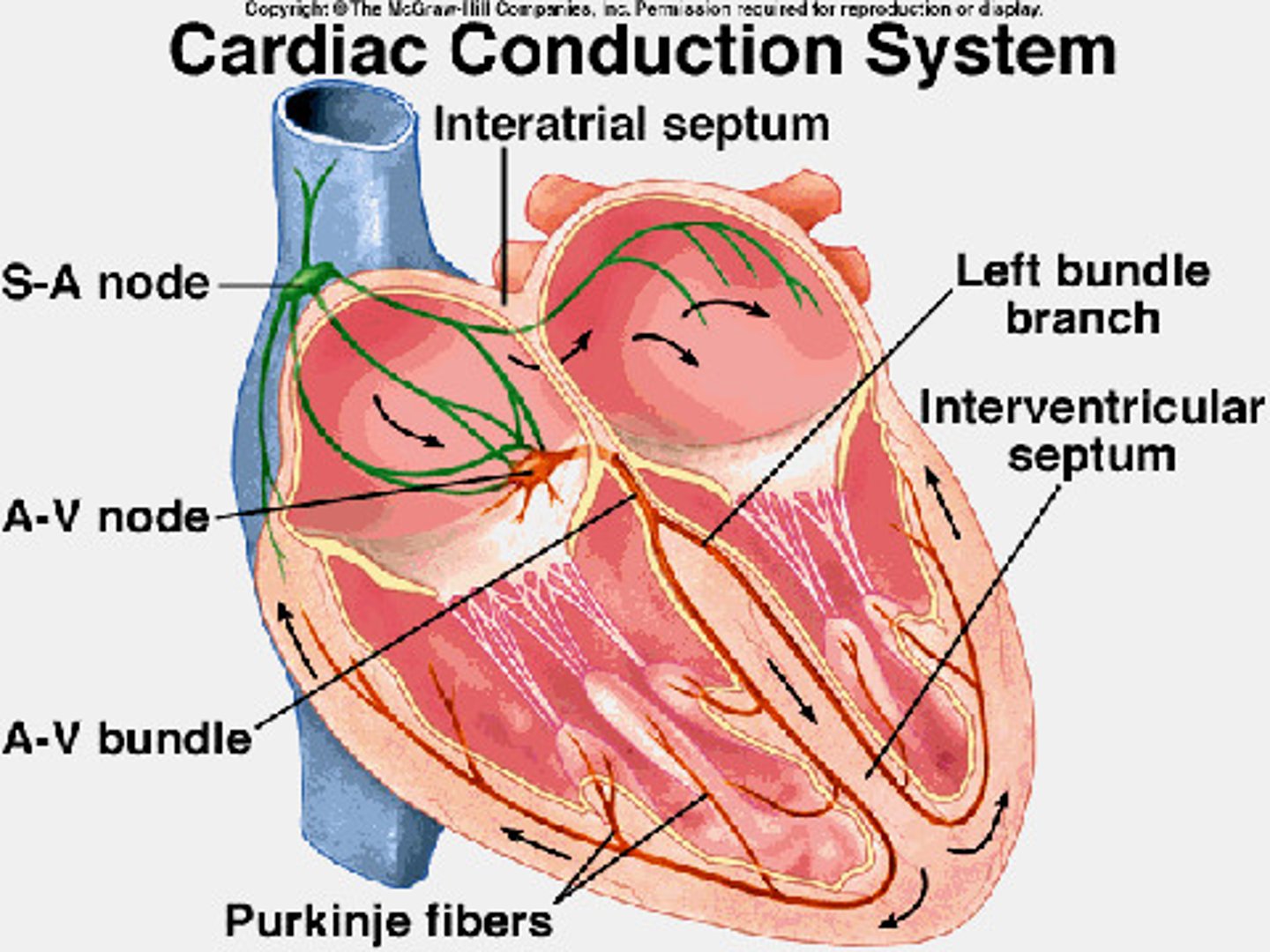
Sinoatrial (SA) node
The pacemaker of the heart, located in the wall of the right atrium, setting the rate and timing of cardiac muscle contractions.
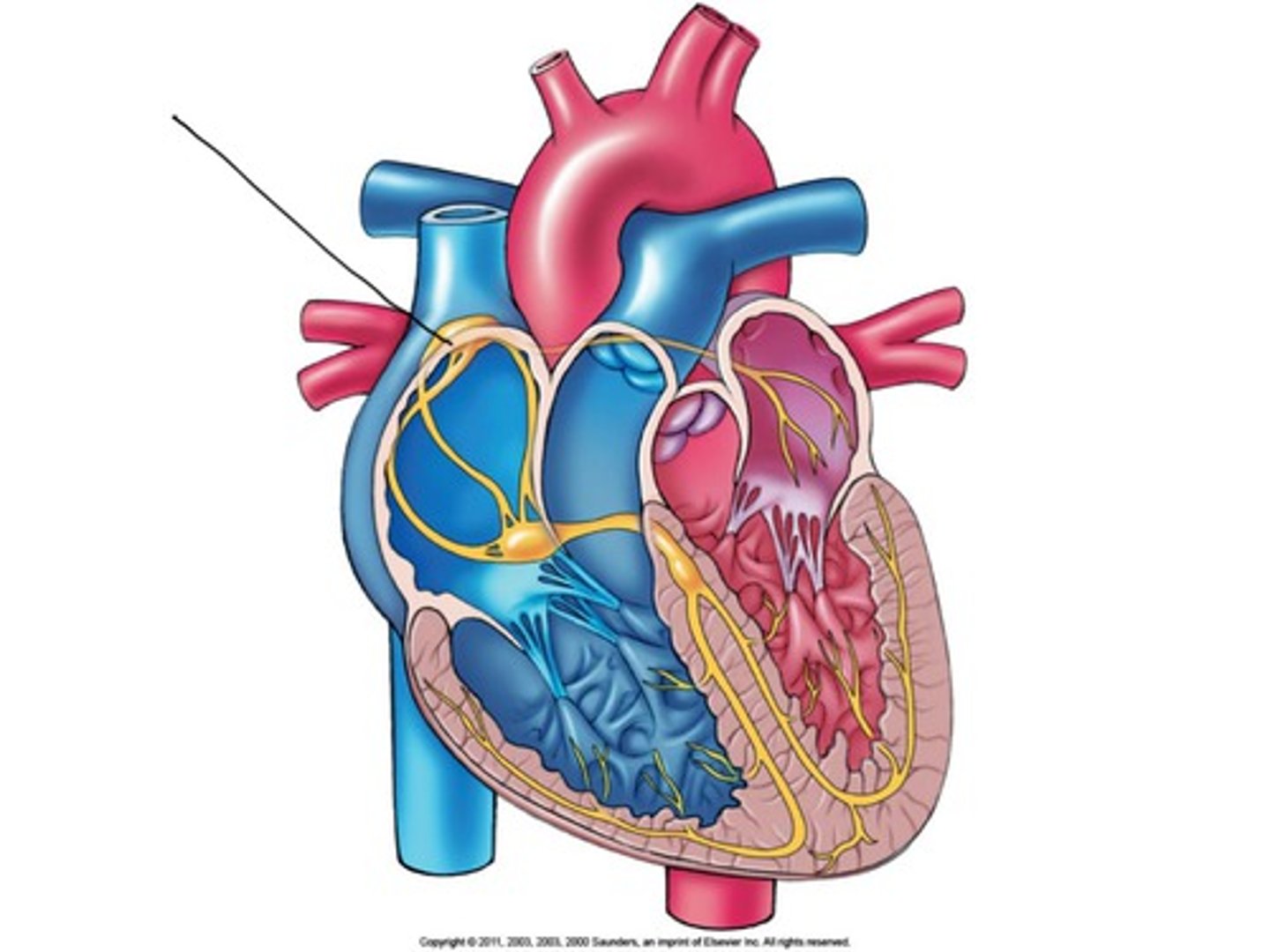
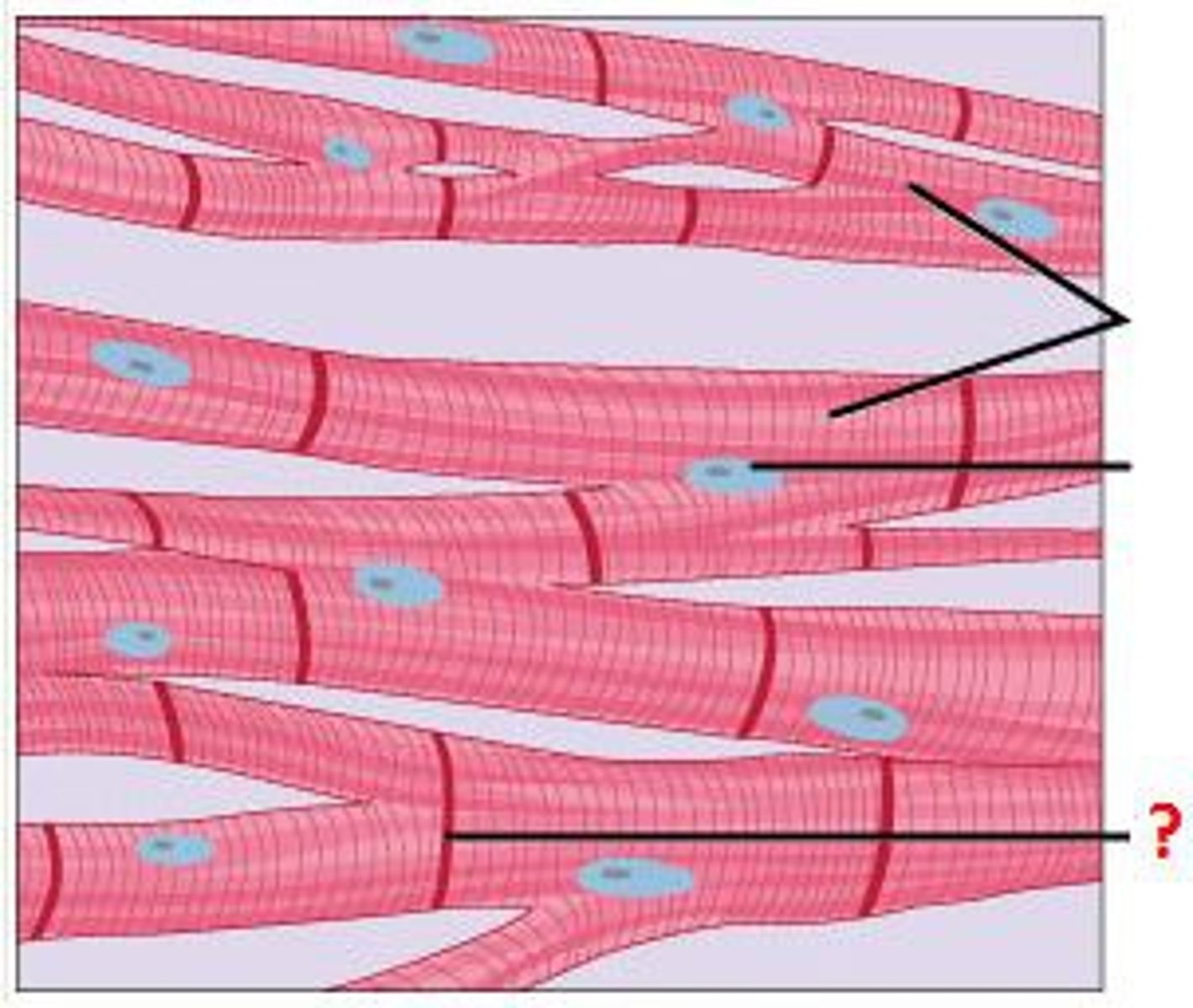
Intercalated disks
Structures that electrically couple cardiac muscle cells, allowing them to contract in unison.
Atrioventricular (AV) node
The relay point for impulses from the SA node to the ventricles, delaying the impulse by about 0.1 sec.
Bundle branches and Purkinje fibers
Specialized muscle fibers that conduct signals to the apex of the heart and throughout the ventricular walls.
Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG)
A recording of electrical currents generated during the heart cycle, detected by electrodes on the skin.
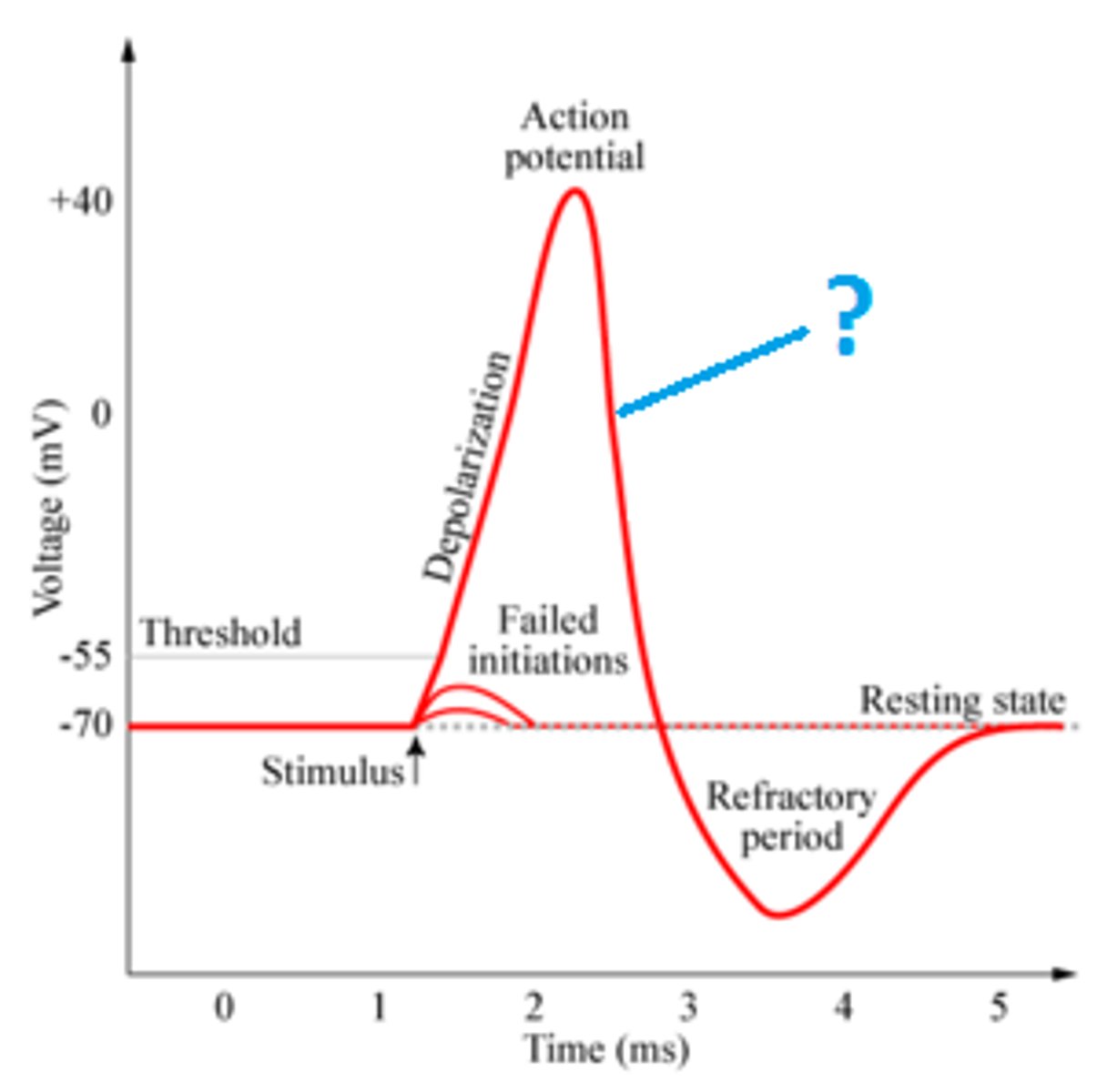
Depolarization
The process that causes the contraction of cardiac chambers.
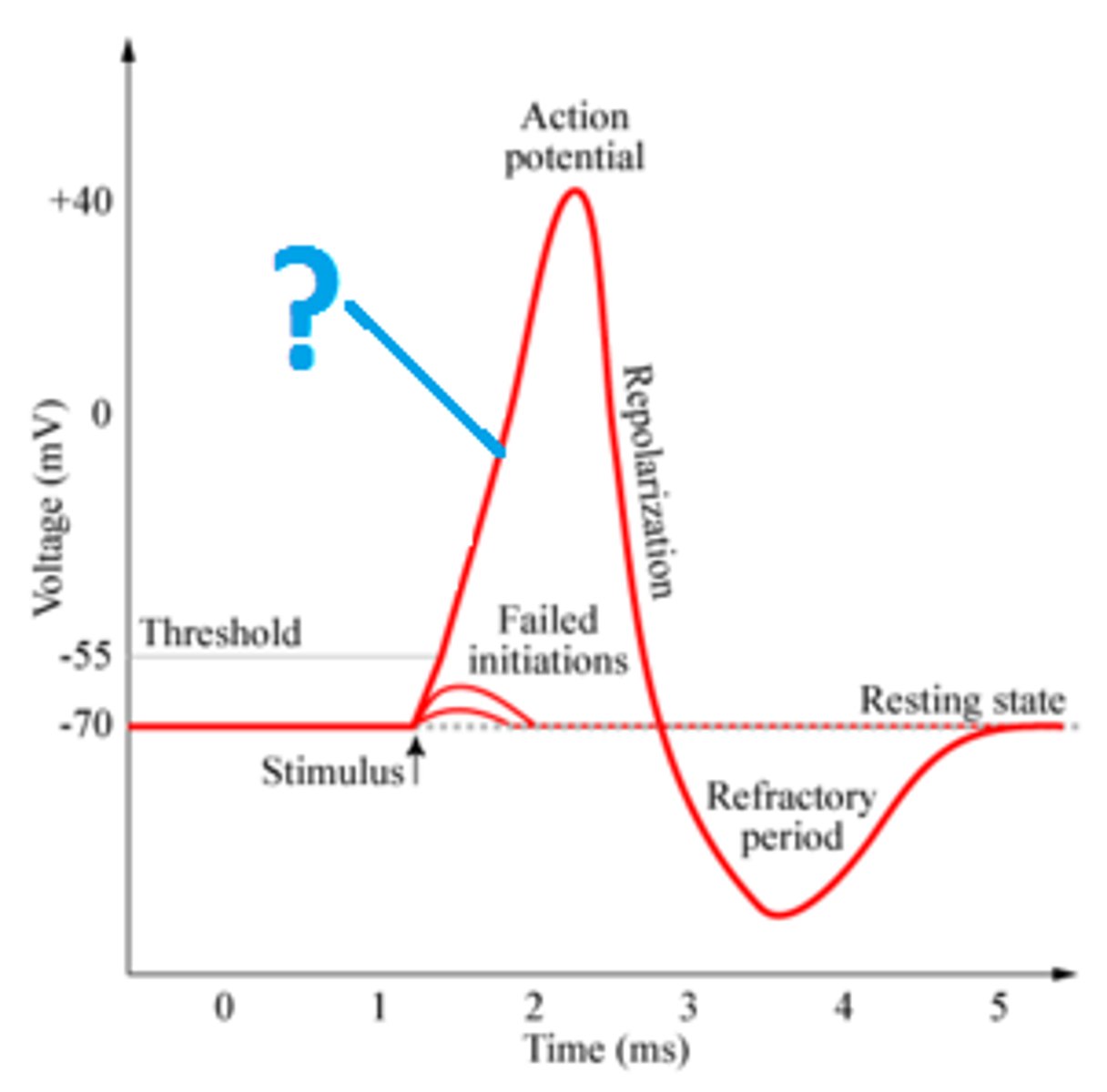
Repolarization
Refers to the relaxation of cardiac chambers.
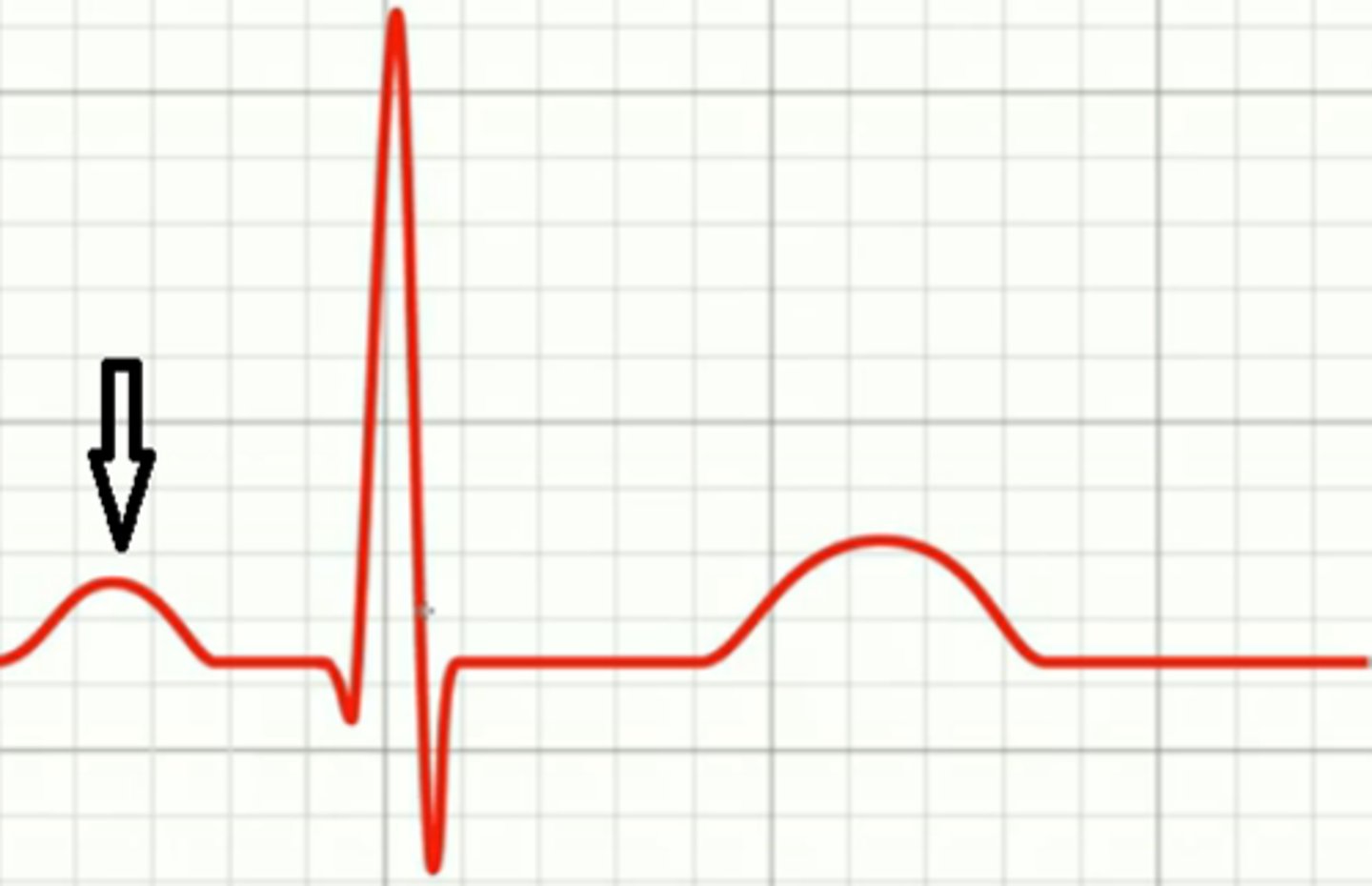
P wave
depolarization of SA node and atria
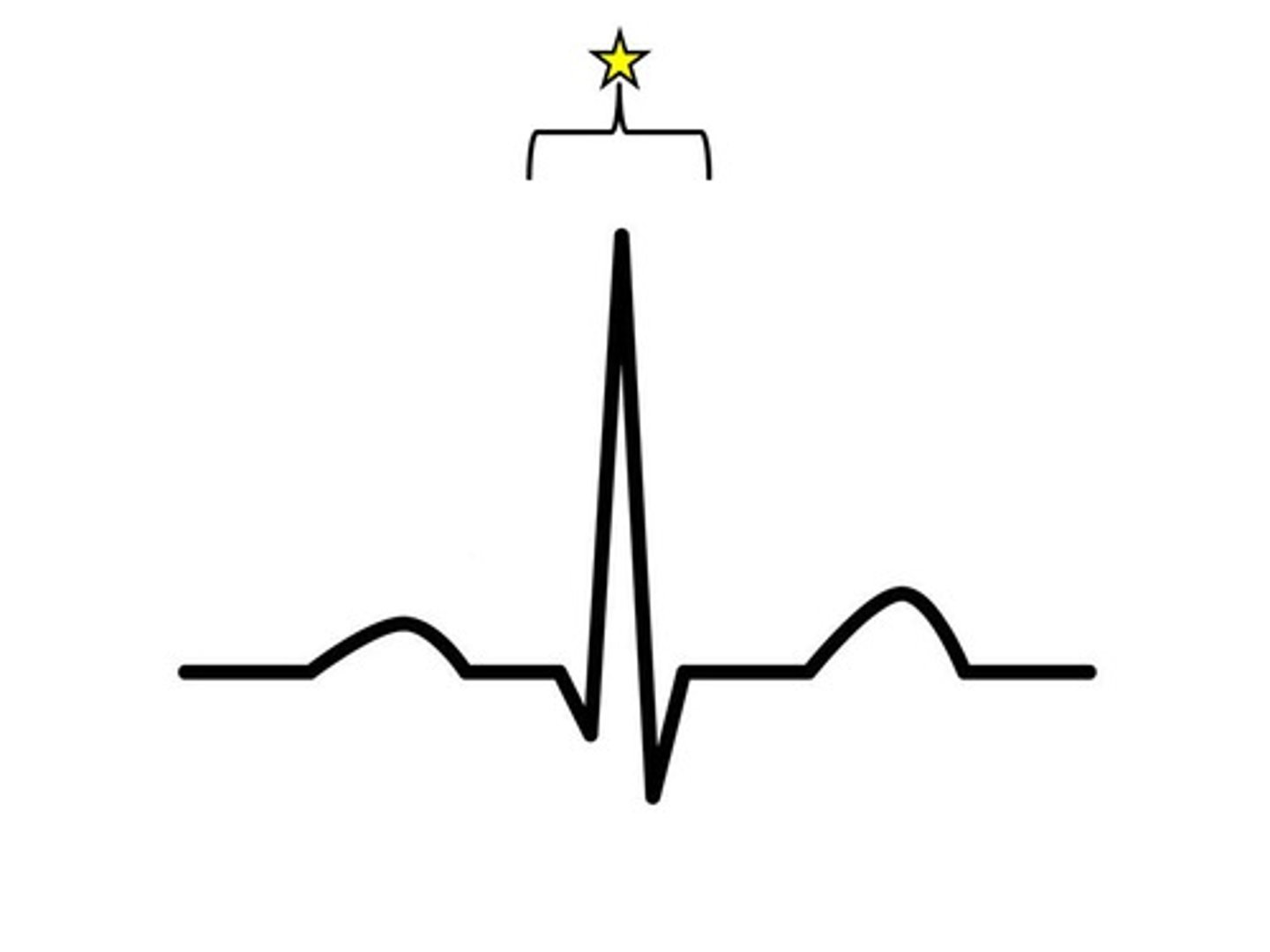
QRS complex
ventricular depolarization and atrial repolarization
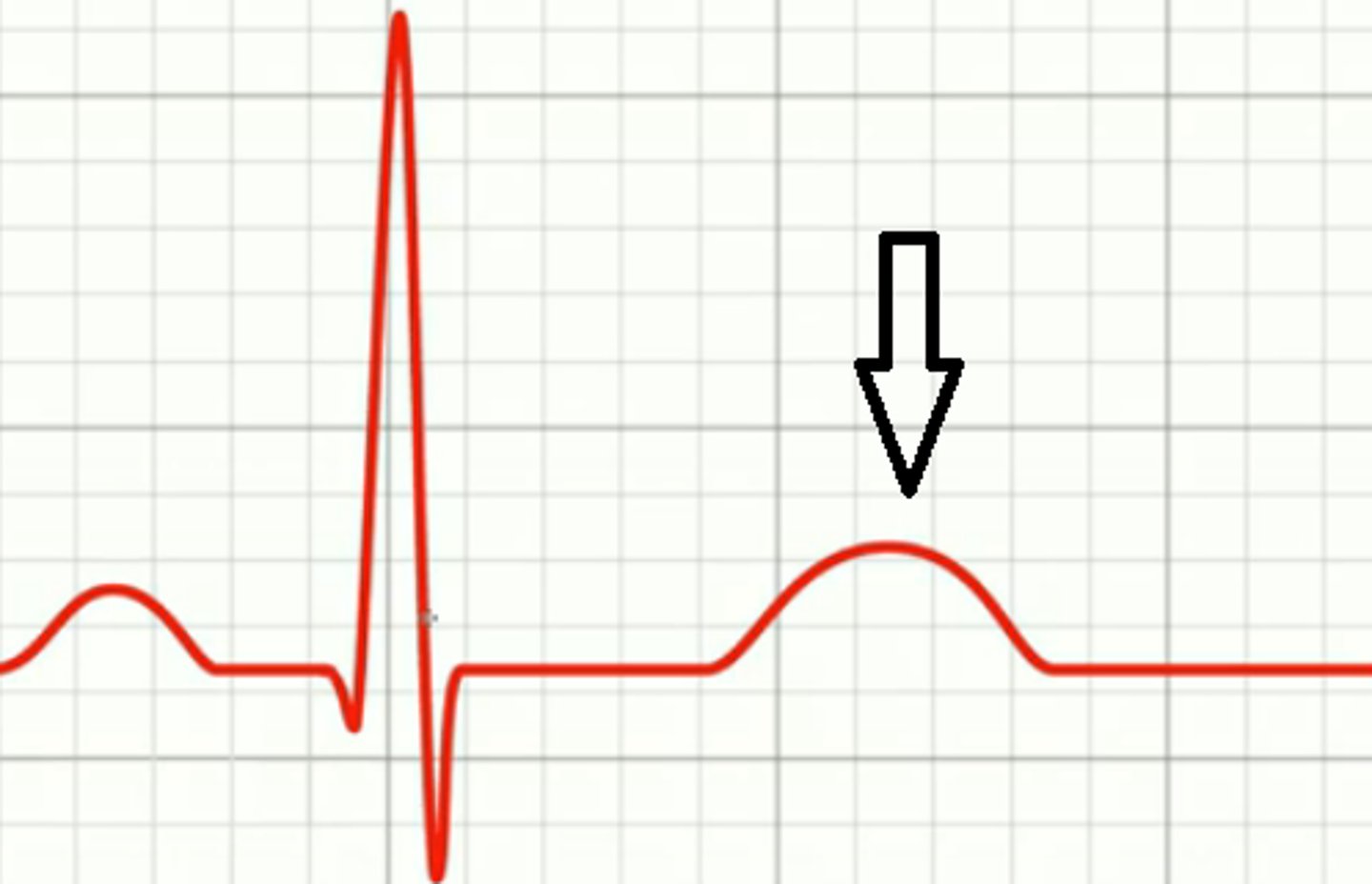
T wave
ventricular repolarization
P-R interval
beginning of atrial excitation to beginning of ventricular excitation
S-T segment
entire ventricular myocardium depolarized
Q-T interval
beginning of ventricular depolarization through ventricular repolarization
SA node
sets the tempo for the entire heart
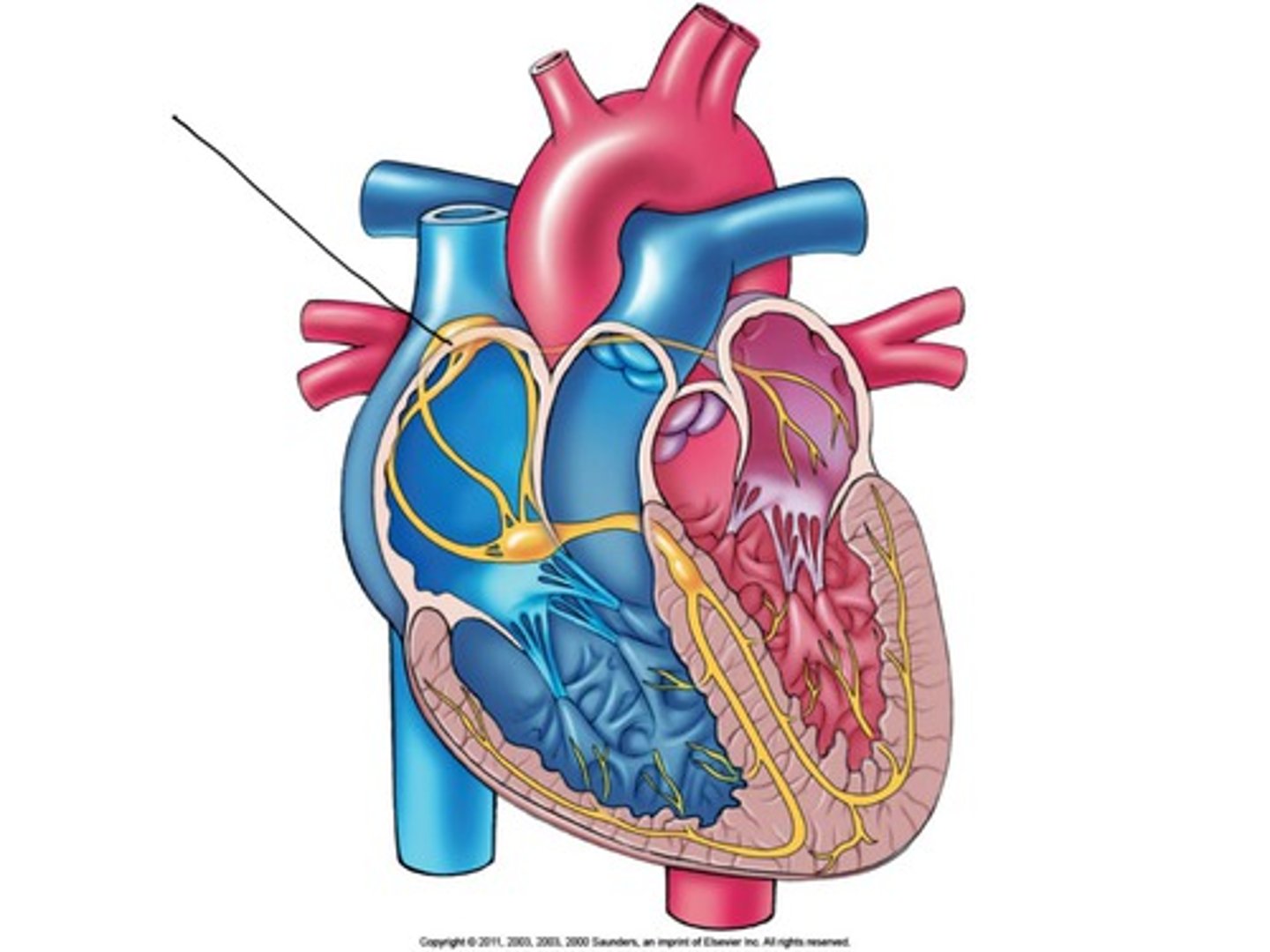
Epinephrine
hormone from adrenal glands that increases heart rate
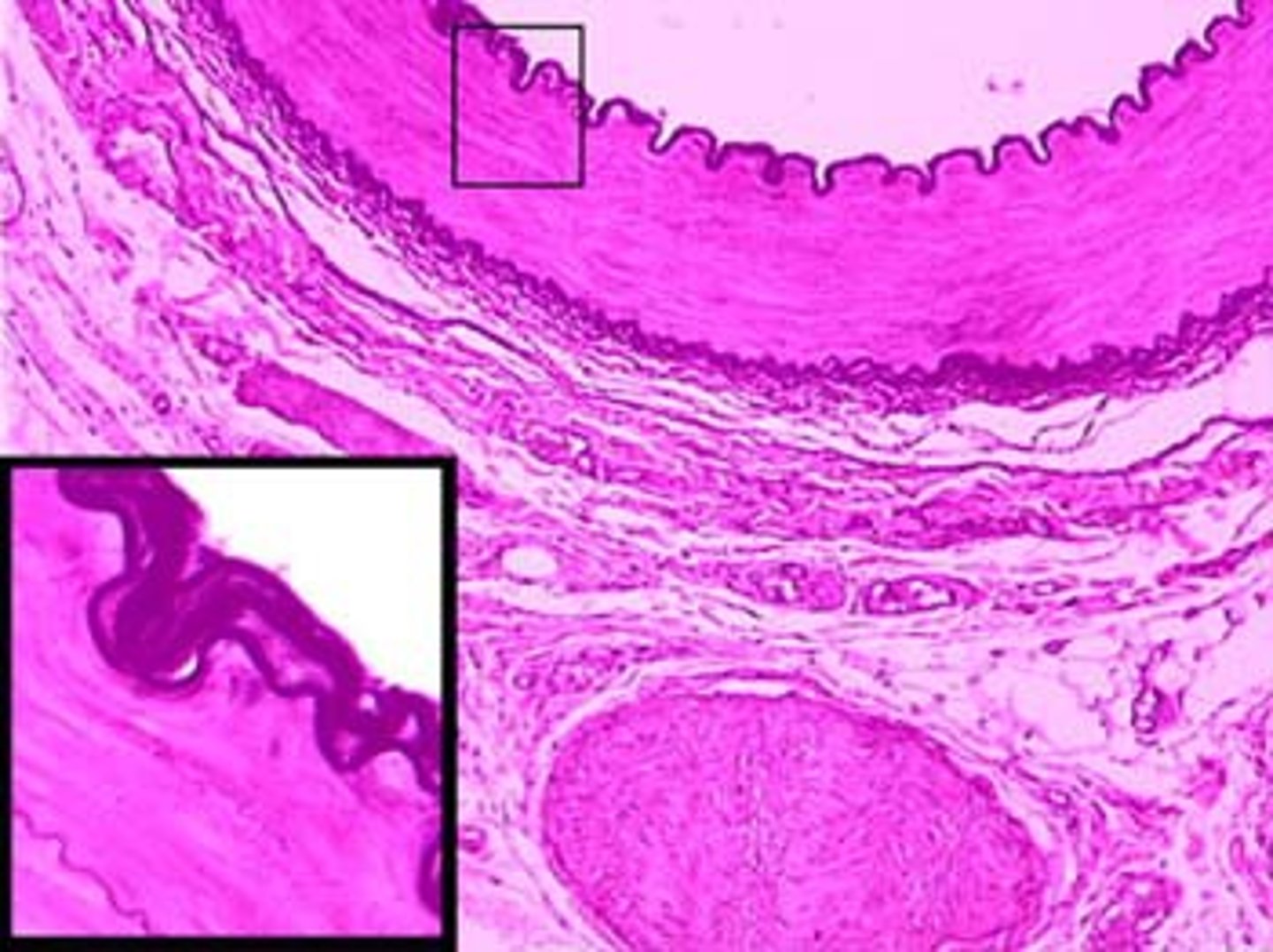
Blood vessel structure
all blood vessels are built of similar tissues with three layers
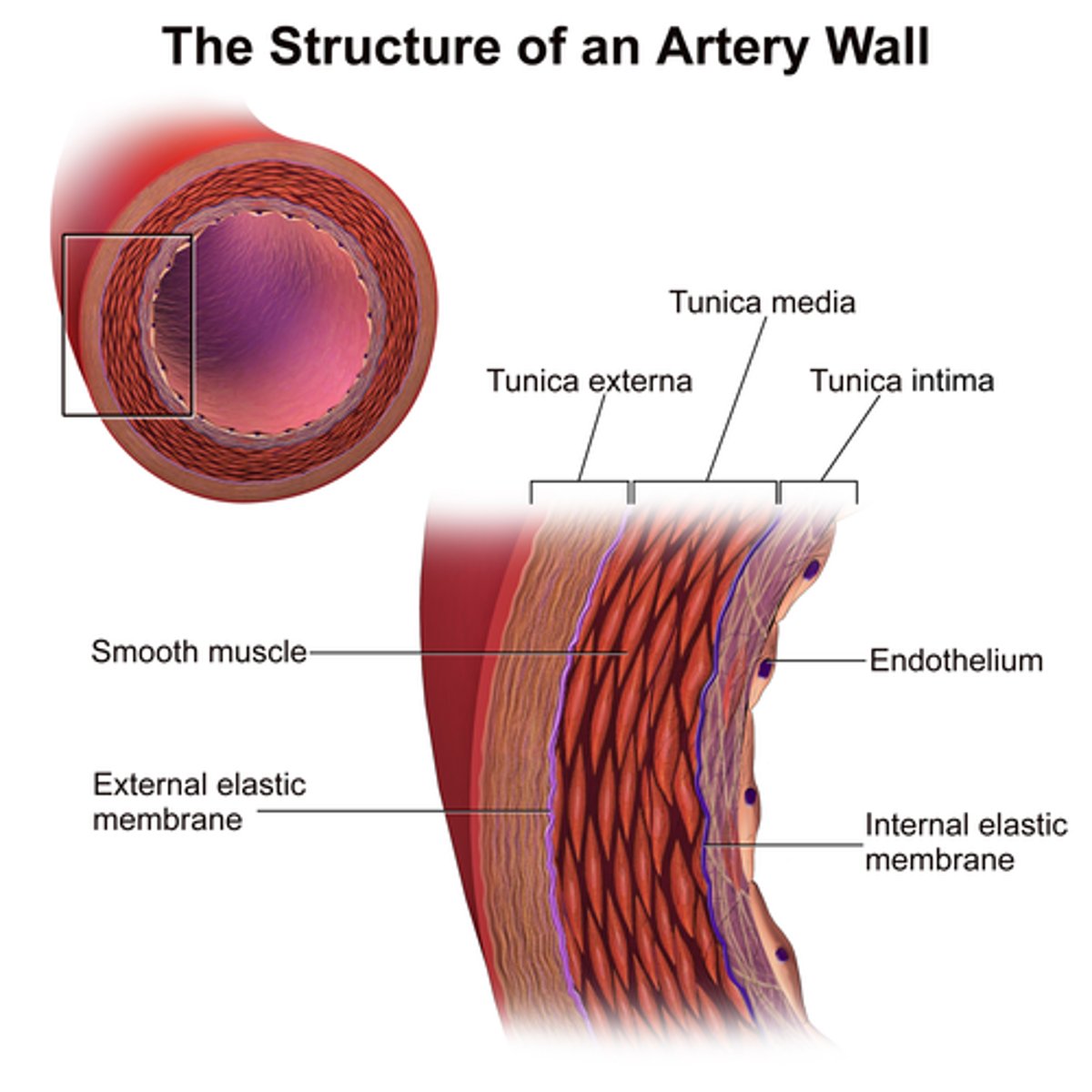
Connective tissue
outer layer of blood vessels that allows stretching and recoiling
Smooth muscle
middle layer of blood vessels that provides elasticity
Endothelium
single layer of flattened cells lining the lumen of blood vessels
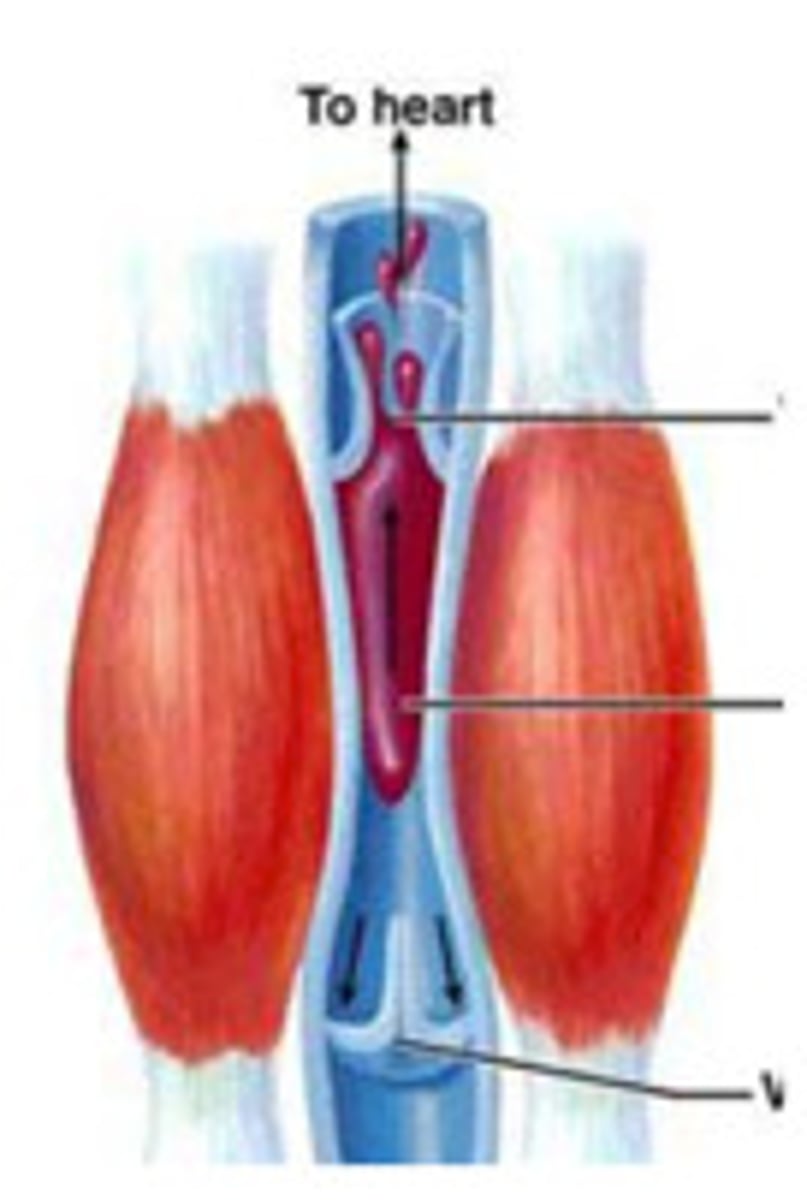
Skeletal muscle contractions
help blood flow in veins by squeezing blood toward the heart
One-way valves
flaps of tissue in larger veins that allow blood to flow only toward the heart
Law of continuity
describes fluid movement through pipes, stating that fluid flows faster through narrower segments
Total cross-sectional area
greater in capillary beds than in any other part of the circulatory system
Systolic pressure
blood pressure is highest in arteries when the heart contracts during ventricular systole averages 120 mm Hg in normal adult.
Pressure gradient
Driving force that keeps blood moving from higher- to lower-pressure areas.
Resistance (peripheral resistance)
Opposition to flow; measurement of the amount of friction blood encounters with vessel walls, generally in peripheral (systemic) circulation.
Three important sources of resistance
Blood viscosity, total blood vessel length, blood vessel diameter.
Systemic pressure
Highest in aorta and declines throughout the pathway; steepest drop occurs in arterioles.
Diastolic pressure
Lowest level of aortic pressure when the heart is at rest.
Factors regulating blood pressure
Cardiac output (CO), peripheral resistance (PR), blood volume, elasticity (compliance or distensibility) of arteries close to heart.
Blood pressure regulation goal
To keep blood pressure high enough to provide adequate tissue perfusion, but not so high that blood vessels are damaged.
Stroke
A medical condition in which poor blood flow to the brain results in cell death; two main types are ischemic and hemorrhagic.
Pulse
Surge of pressure felt by placing fingers on wrist due to the narrow openings of arterioles impeding blood exit from arteries.
Peripheral resistance factors
State of smooth muscles in arteriole walls; physical or emotional stress can trigger contraction, leading to increased blood pressure.
Nitric oxide (NO)
Induces vasodilation.
Endothelin
A peptide that induces vasoconstriction.
Increased blood volume
Can be due to water retention after excessive salt intake, which will increase blood pressure.
Vessel elasticity
Loss of vessel elasticity in arteriosclerosis will increase blood pressure.
Increased cardiac output
Cardiac Output = Heart Rate X Stroke Volume; will also increase blood pressure.
Sphygmomanometer
An inflatable cuff attached to a pressure gauge that measures blood pressure fluctuations in the brachial artery of the arm over the cardiac cycle.
Arterial blood pressure
Oscillates between about 120 mm Hg at systole and 70 mm Hg at diastole in a healthy human.
Nerve impulses and hormones
Control the arteriole wall muscles; stress can raise blood pressure by constricting blood vessels.
Cardiac output adjustment
Adjusted in concert with changes in peripheral resistance to maintain adequate blood flow as demands on the circulatory system change.
Arterioles
Small blood vessels that dilate during heavy exercise to admit a greater flow of oxygen-rich blood to the muscles.
Control flow into capillary beds via vasodilation and vasoconstriction of smooth muscle
Blood pressure and gravity
In large land animals, blood pressure is affected by gravity, requiring additional pressure to push blood above the heart level.
Pressure to the brain
In a standing human, it takes an extra 27 mm of Hg pressure to move blood from the heart to the brain.
Veins and venules
Blood movement through veins is aided by rhythmic contractions of smooth muscles and the activity of skeletal muscles.
Inhalation effect
Inhaling causes a change of pressure in the thoracic cavity, expanding the venae cavae and filling them with blood.
Capillary blood flow
At any given time, only about 5-10% of the body's capillaries have blood flowing through them.
Blood supply variation
Blood supply to various organs varies over time, increasing to the digestive tract after a meal and diverting from it during exercise.
Smooth muscle contraction
Contraction of the smooth muscle layer in the wall of an arteriole constricts the vessel, decreasing blood flow to a capillary bed.
Precapillary sphincters
Rings of smooth muscles that control the flow of blood between arterioles and venules.
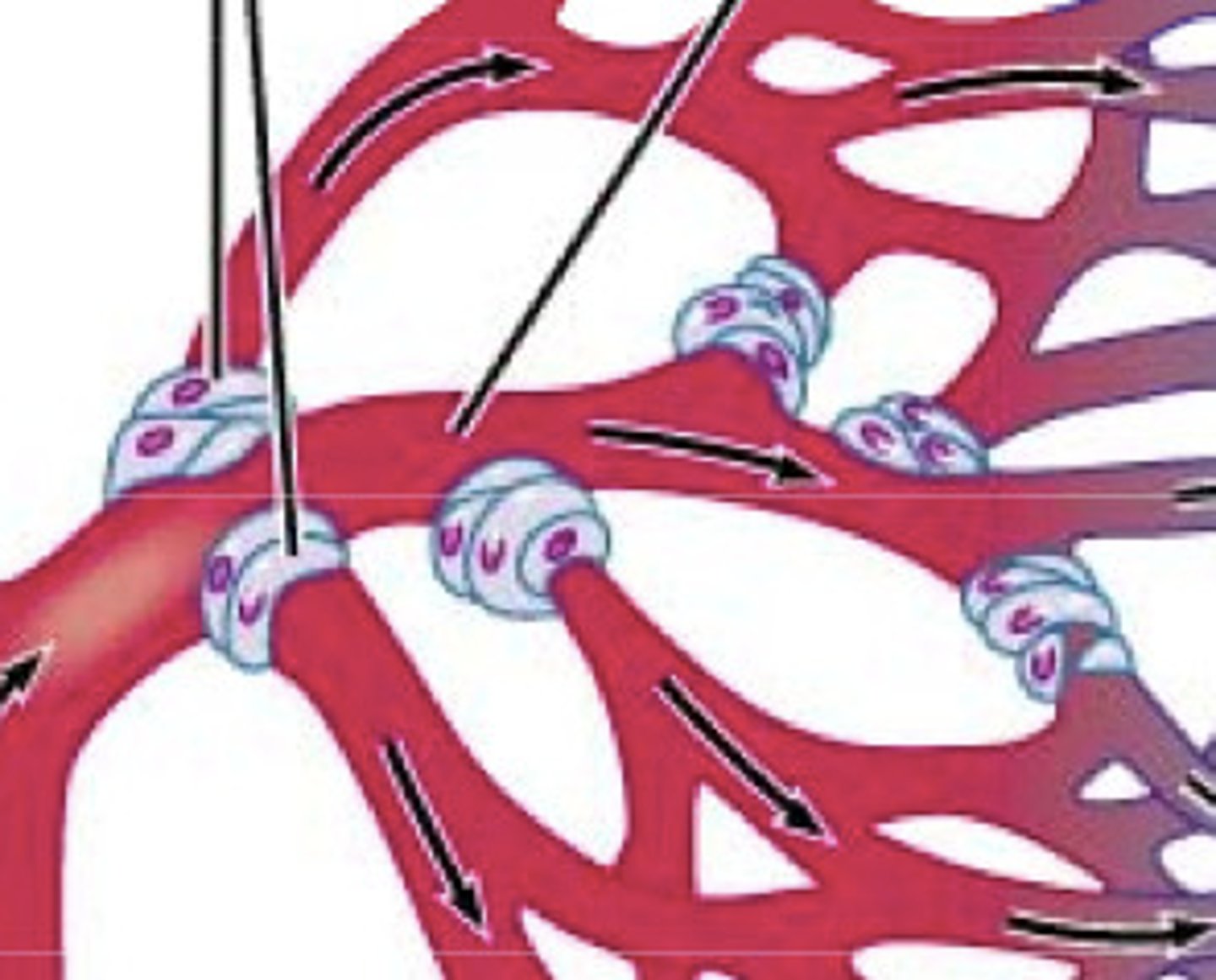
Thoroughfare channels
Channels that allow some blood to flow directly from arterioles to venules and are always open.
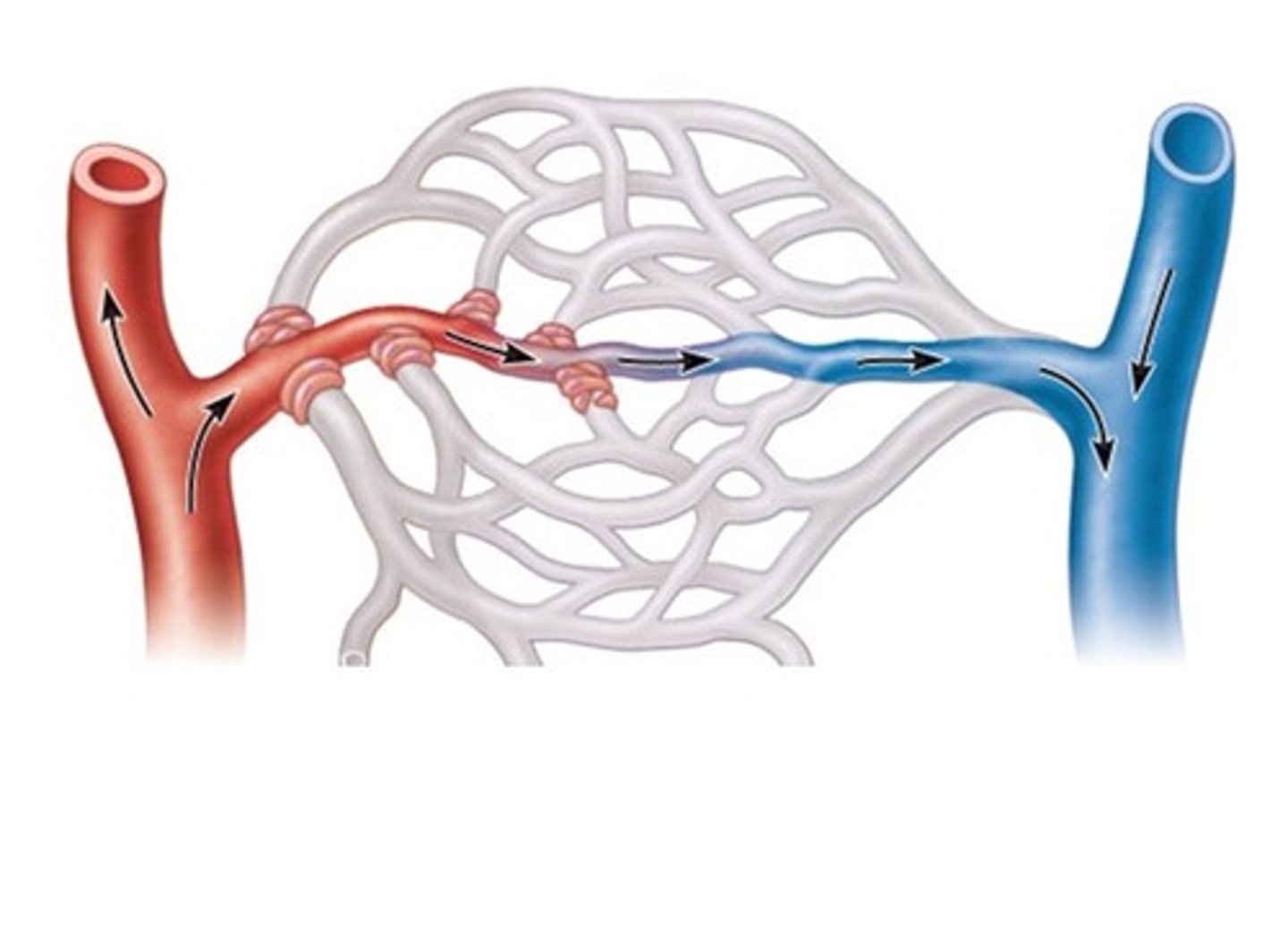
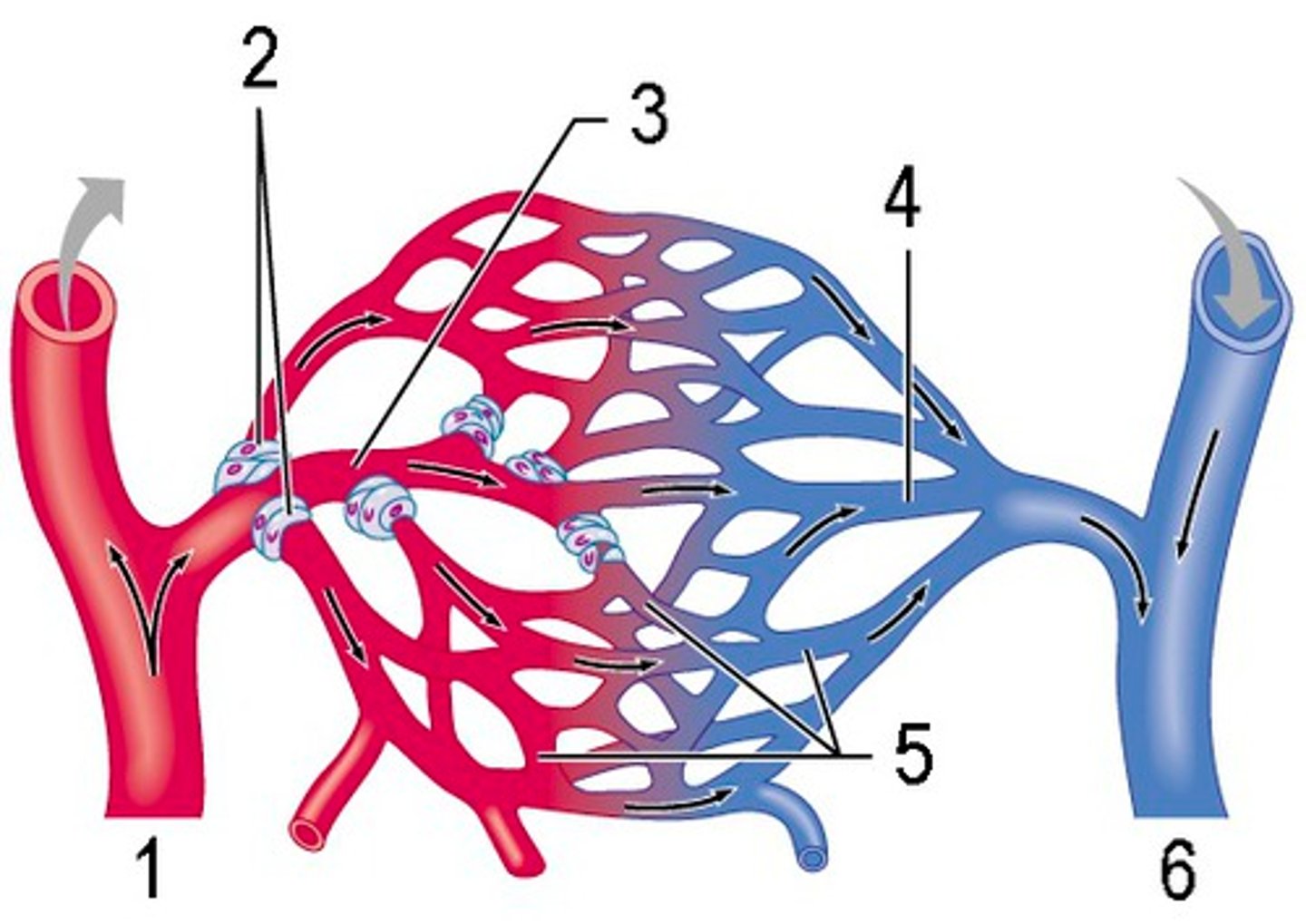
Substance exchange methods
Methods include vesicle transport, diffusion across cells, and transport through clefts between adjoining cells.
Capillary osmotic pressure
The 'sucking' pressure created by nondiffusible plasma proteins pulling water back into the capillary.
Fluid loss at capillary upstream
Blood pressure within the capillary pushes fluid through the clefts, causing a net loss of fluid at the upstream end.
Fluid return at capillary downstream
Near the downstream end, osmotic gradient pulls water into the capillary, with about 85% of fluid re-entering from interstitial fluid.
Edema
Abnormally large fluid volume in the circulatory system or interstitial spaces, caused by decreased capillary osmotic pressure.
Hypoproteinemia
Low levels of plasma proteins caused by malnutrition, liver disease, or glomerulonephritis, leading to edema.
Lymphatic system
Returns fluids and some blood proteins that leak from capillaries into the blood, entering via tiny lacteals.
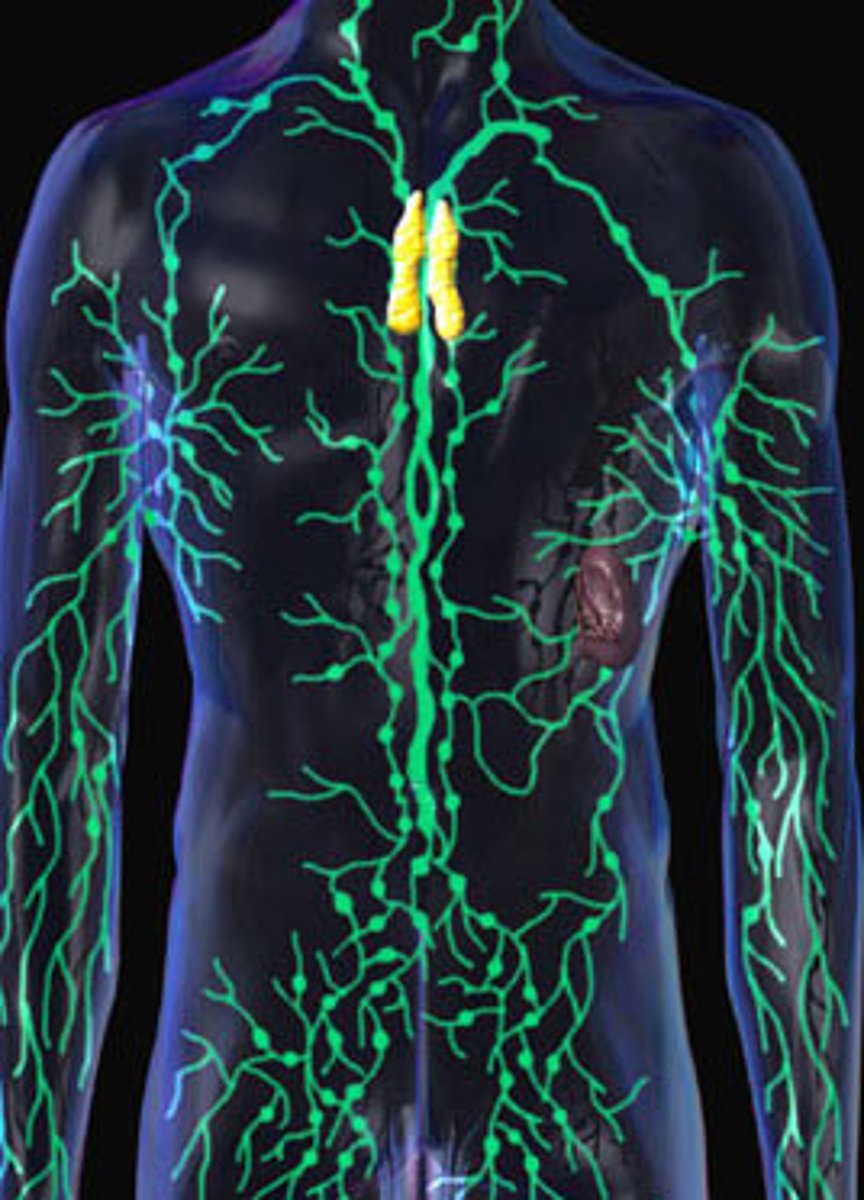
Lymphatic drainage
The lymphatic system drains into the circulatory system near the junction of the venae cavae with the right atrium.
Lymphatic valves
Valves in lymph vessels that prevent backflow of fluid toward the capillaries.
Lymph nodes
Organs along lymph vessels that filter lymph and attack viruses and bacteria, swelling when fighting infection.
Lymphatic function
Helps maintain blood volume and protein concentration and transports fats from the digestive tract to the circulatory system.