Understanding the Immune System in BIOS 101
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
Three lines of defense
The vertebrate body is defended from infection by three lines of defense: skin and mucous membranes, cellular counterattack, and specific immune response.
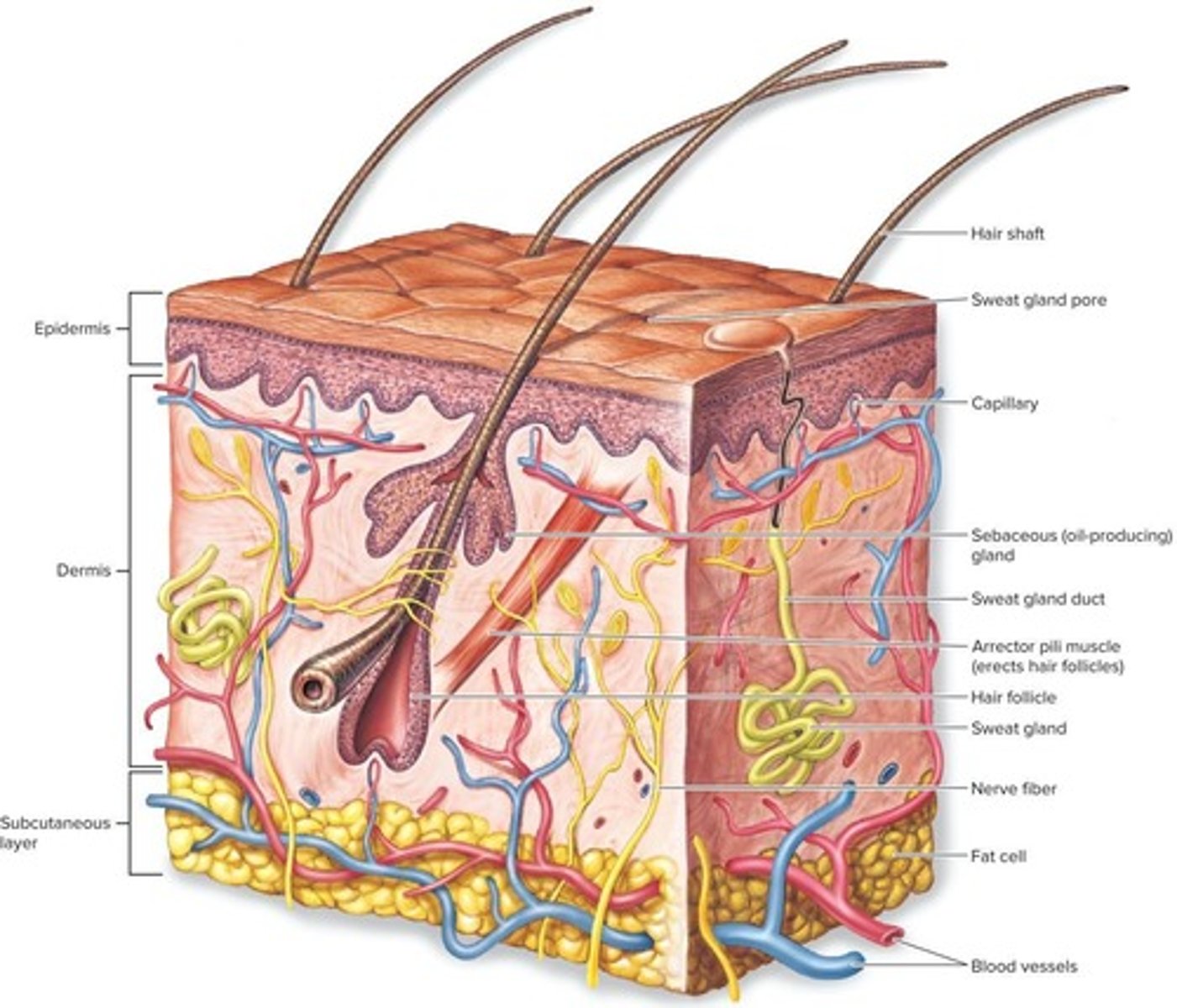
Skin
The first defense against invasion by microbes, consisting of an outer epidermis and a lower dermis.
Epidermis
The outer layer of skin, 10 to 30 cells thick, continuously shed and replaced.
Stratum corneum
The outer layer of the epidermis, where cells are continuously shed.
Basal layer
The layer of the epidermis below the stratum corneum, where cells are actively dividing.
Dermis
15 to 40 times thicker than the epidermis, providing structural support.
Subcutaneous layer
Layer beneath the dermis comprised of fat-rich cells that act as shock absorbers and provide insulation.
Chemical defense of skin
Includes oil glands that make the skin surface very acidic and sweat containing lysozyme, which digests the cell walls of bacteria.
Tears
Contain lysozyme to fight bacterial infections.
Digestive tract protection
Stomach acid and digestive enzymes provide protection, while sticky mucus traps microorganisms.
Cellular counterattack
The second line of defense involving cellular and chemical defenses that include cells and proteins that kill invading microbes.
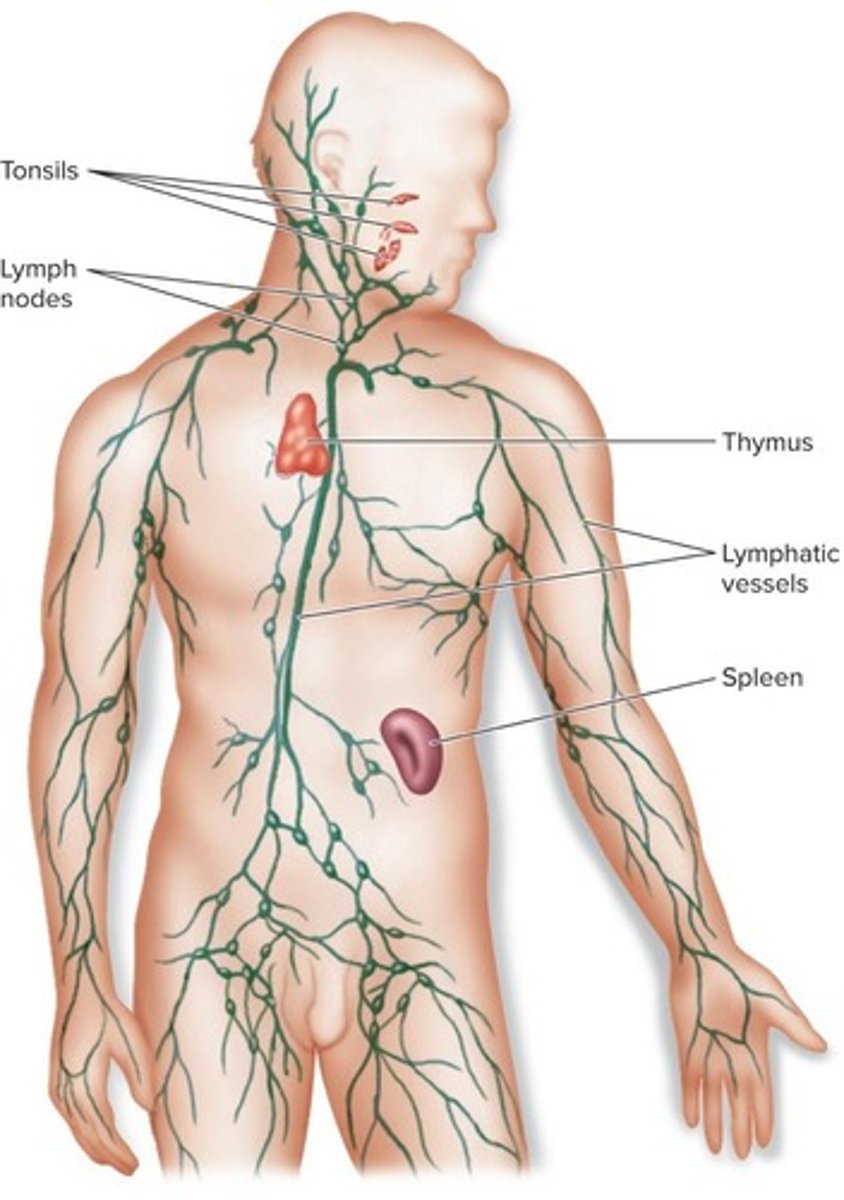
Lymphatic system
The central location for the storage and distribution of substances involved in the second line of defense.
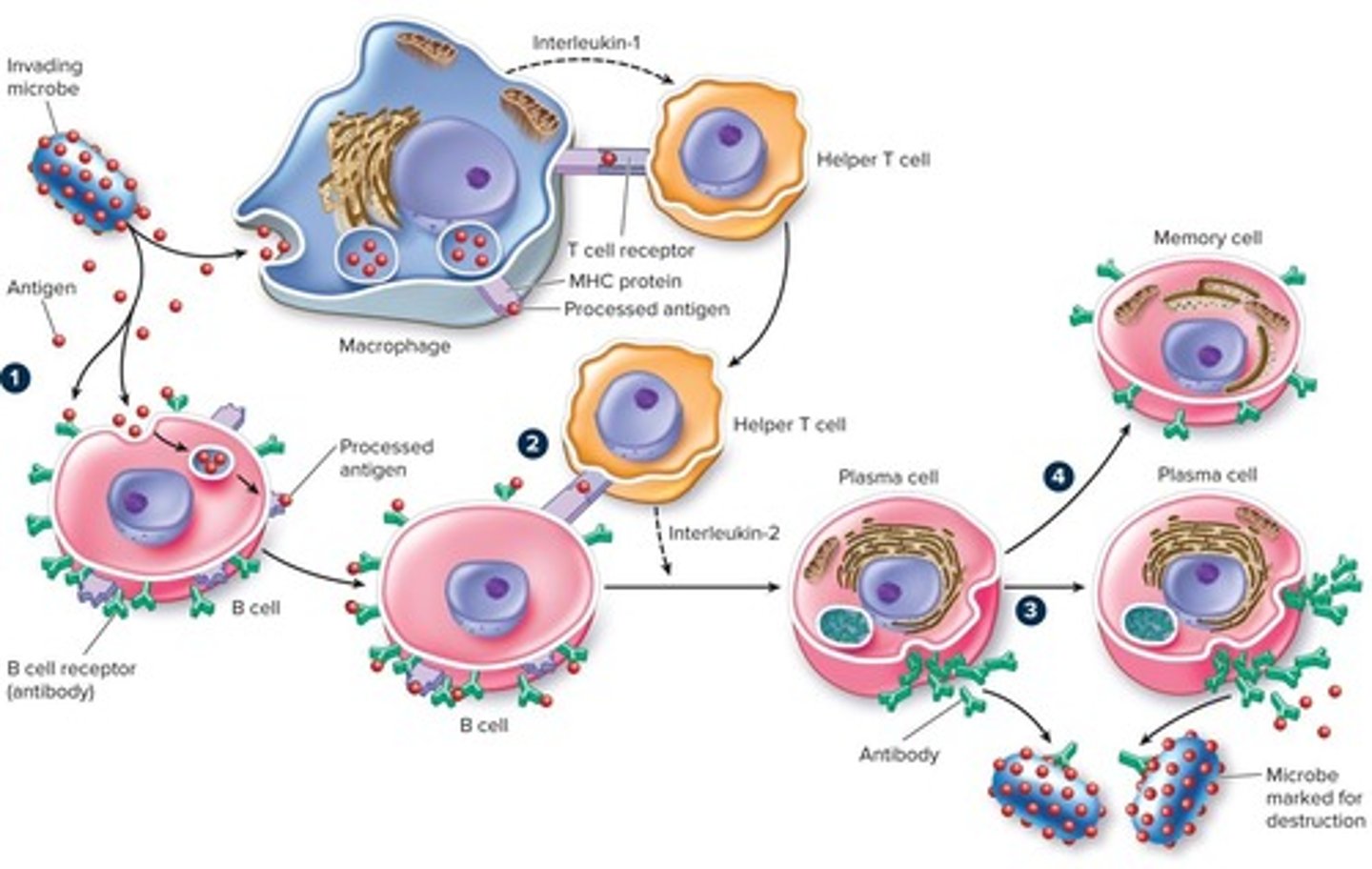
Macrophages
Cells that kill bacteria by ingesting them; a type of white blood cell.
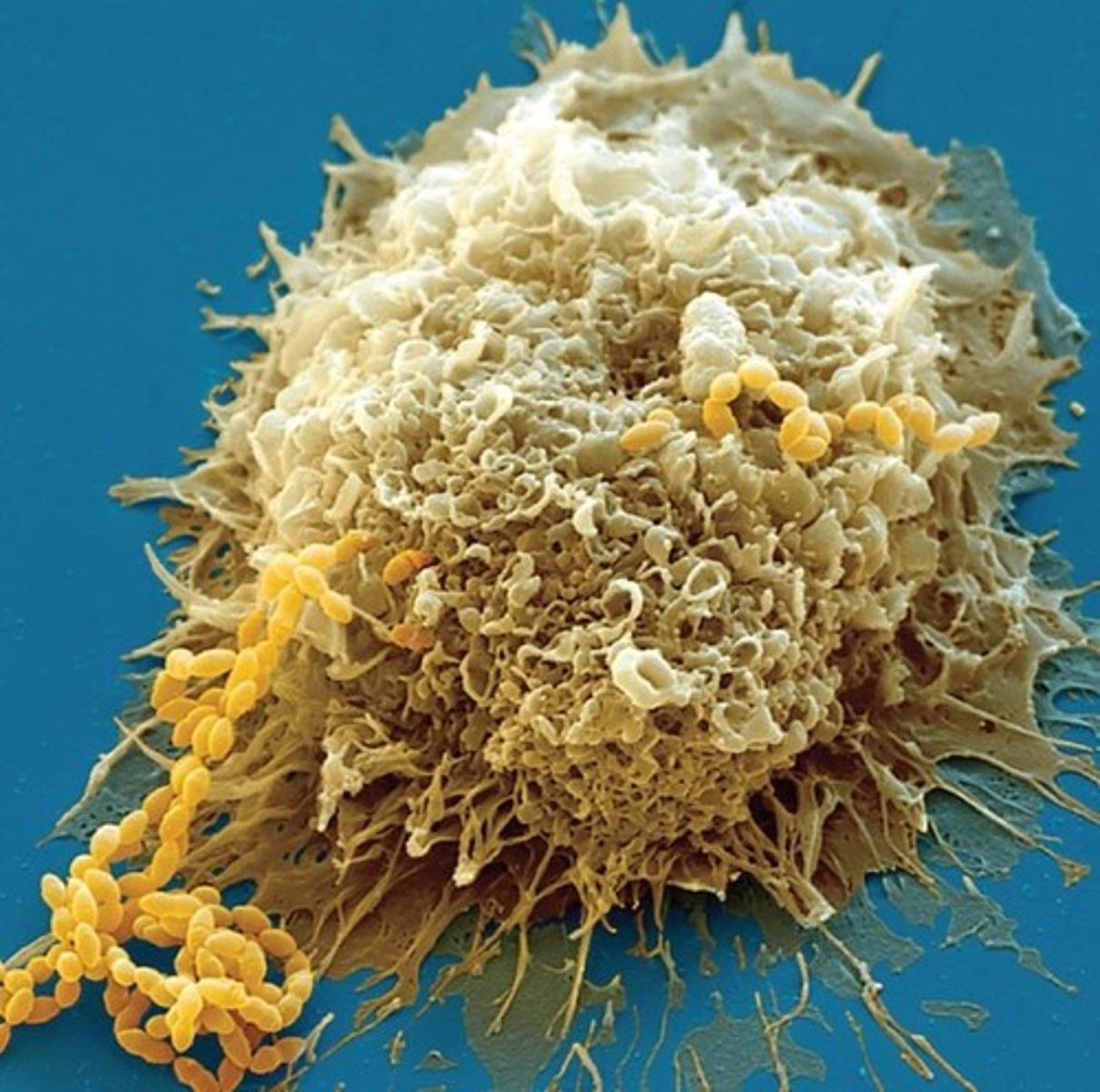
Neutrophils
White blood cells that ingest bacteria and secrete chemicals to neutralize everything living in the infected area.
Natural Killer Cell
A type of white blood cell that attacks infected body cells and punctures their membranes with perforin.
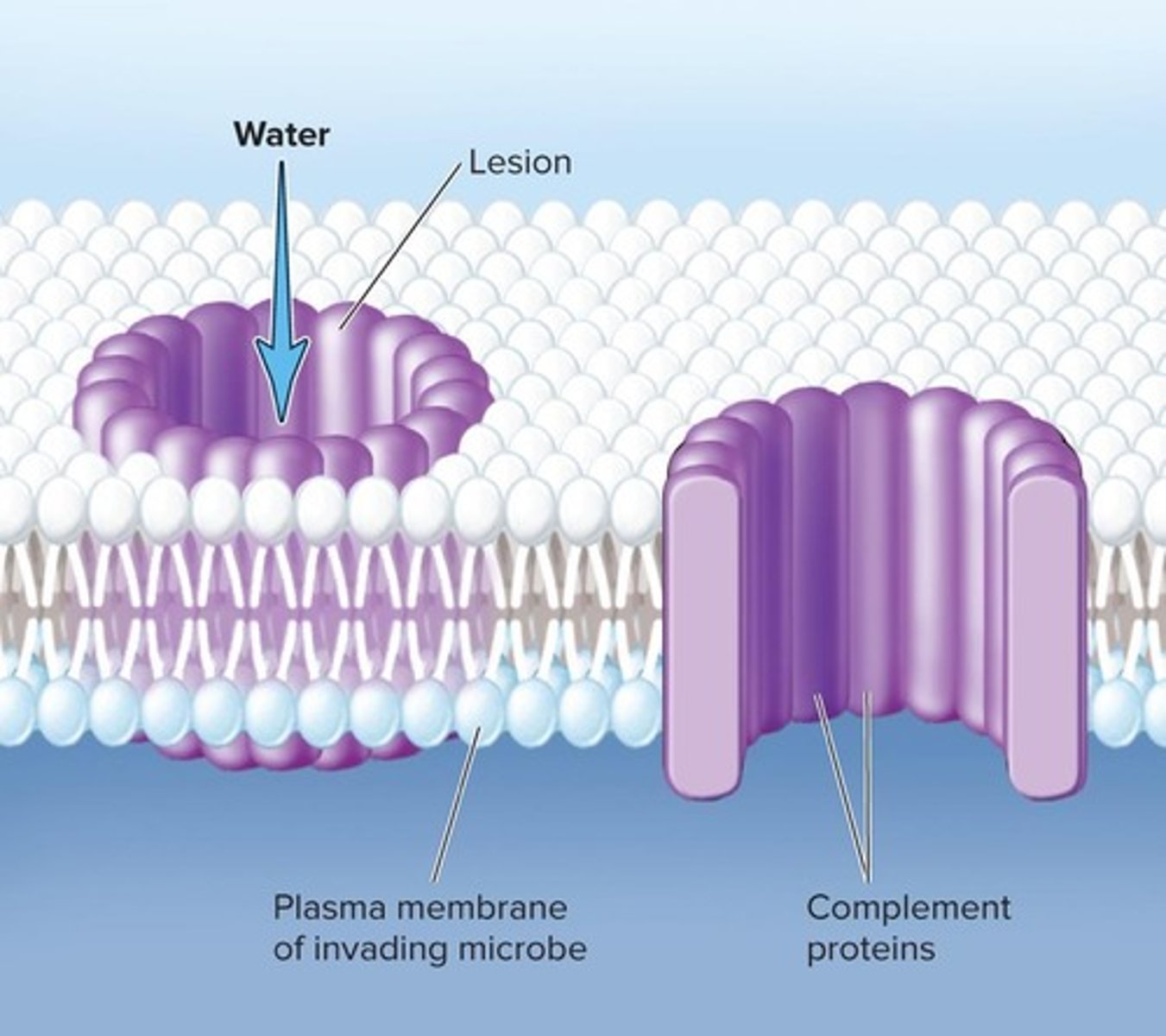
Complement System
A system of ~20 proteins that circulate in the plasma in an inactive state until they encounter a fungal or bacterial cell wall.
Complement proteins
Proteins that aggregate to form a membrane attack complex that creates a pore in the foreign cell's membrane, causing water to burst the cell.
Interferons
Act as messengers to prevent a virus from spreading to new cells; the viruses still infect but cannot make new viruses in the cells that received the interferon message.
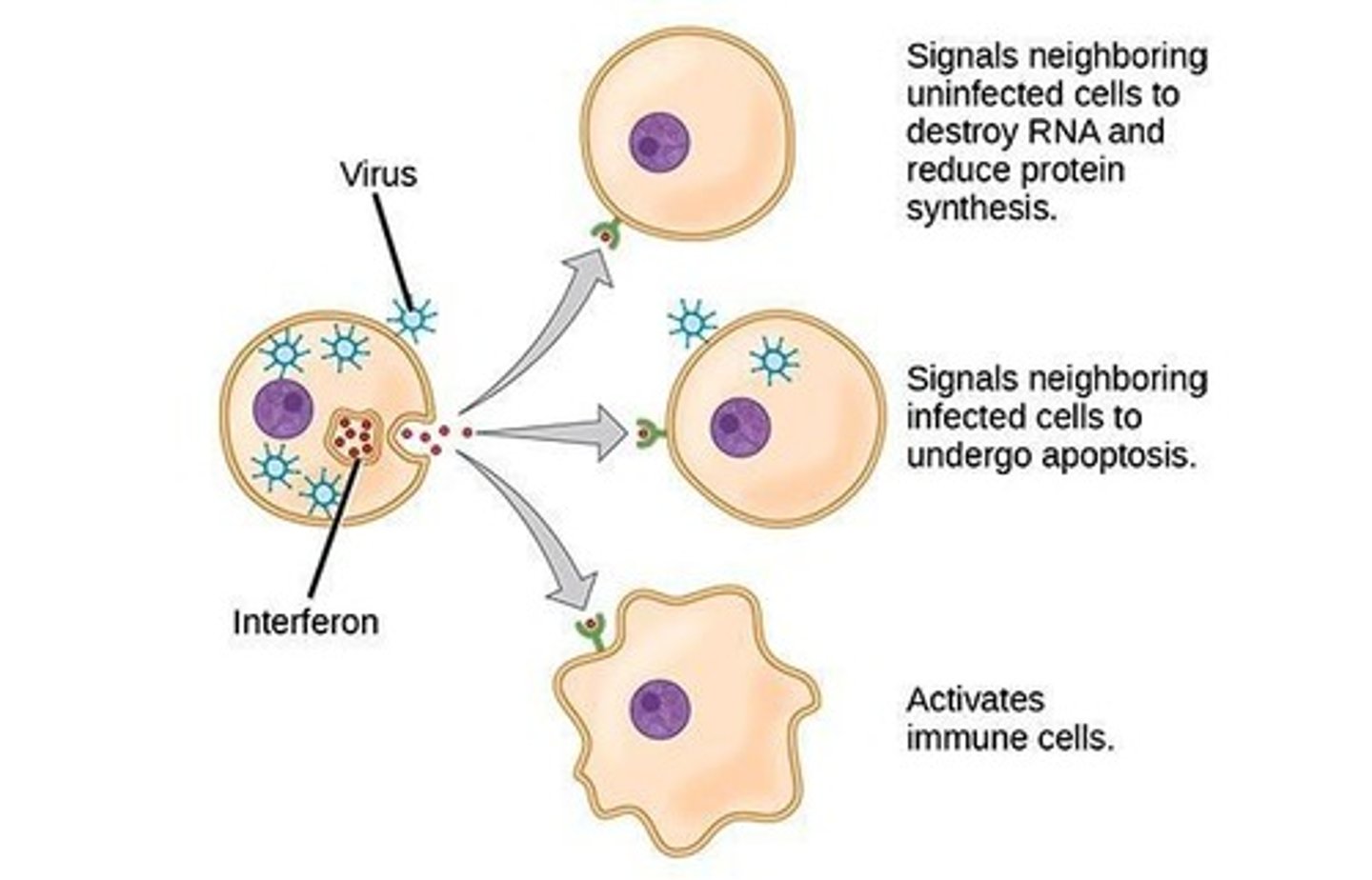
The Inflammatory Response
The infected/injured cell releases chemical alarm signals, such as histamine, increasing blood flow to the area, allowing phagocytes to migrate to the site of infection and attack the invaders.
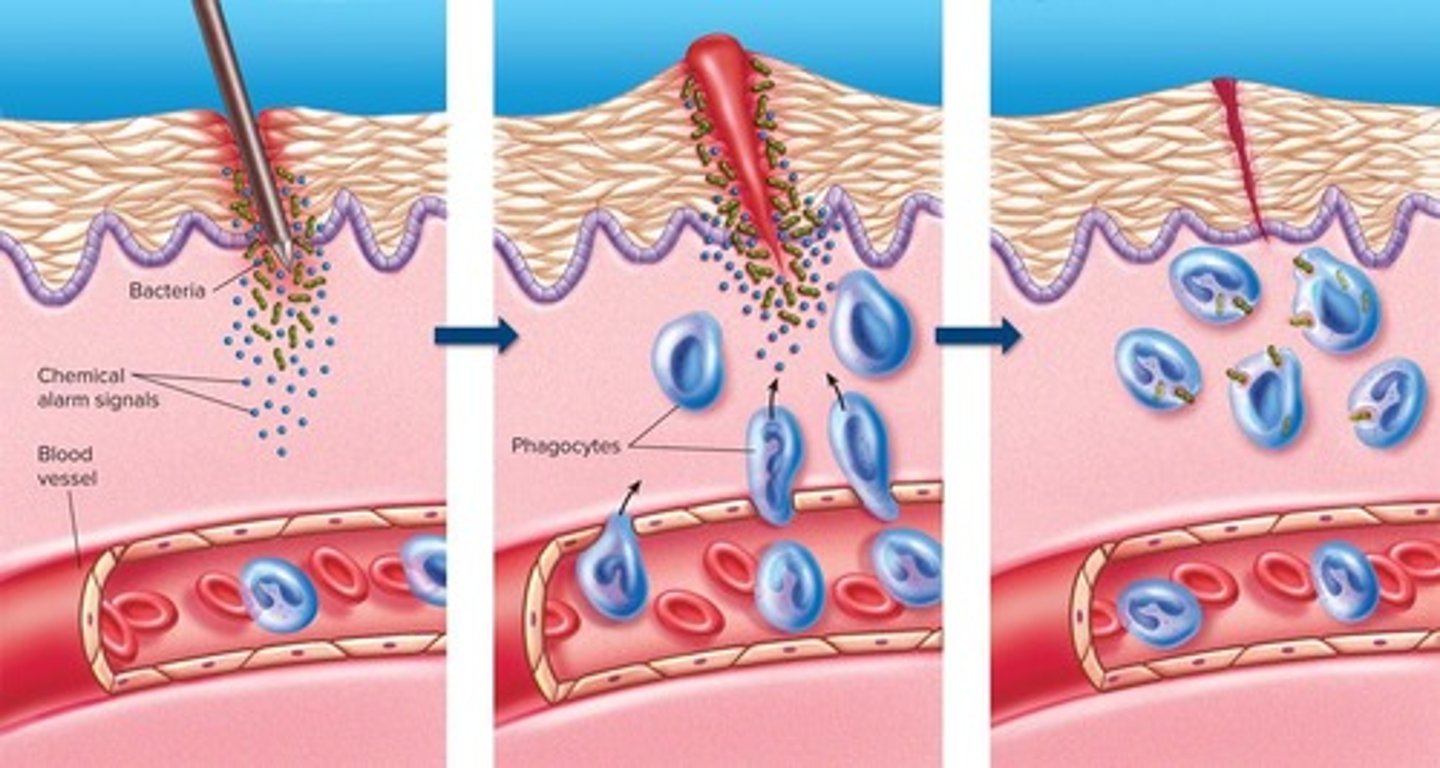
Pus
The accumulation of dead phagocytes that form as a result of the inflammatory response.
The Temperature Response (Fever)
Bacteria that cause disease do not grow well at high temperatures; macrophages send a signal to the brain to raise the body's temperature above normal, producing a fever.
Specific Immunity
The third line of defense involving lymphocytes that are critical to the specific immune response.
Lymphocytes
White blood cells critical to the specific immune response, including T cell and B cell lymphocytes.
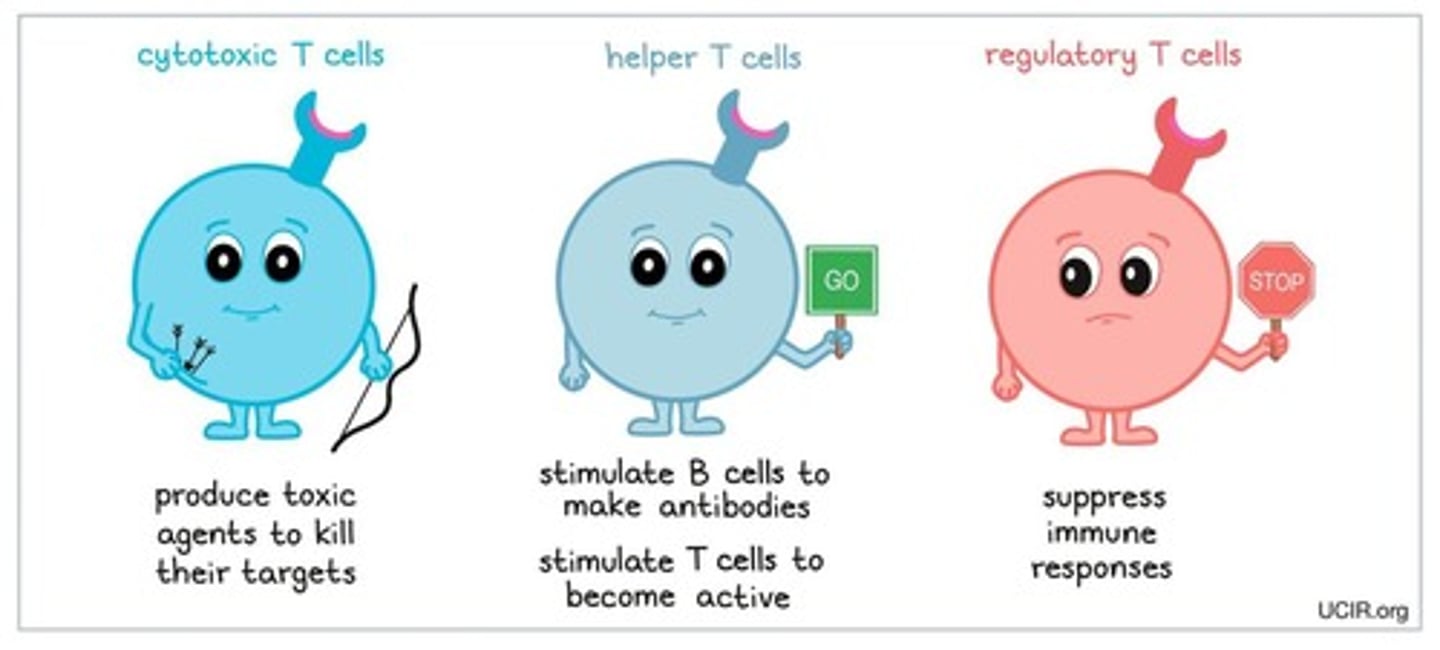
T cell lymphocytes
Lymphocytes that originate in the bone marrow but migrate to the thymus gland for maturation and recognize microorganisms and viruses by the chemical markers, or antigens, on their surfaces.
B cell lymphocytes
Lymphocytes that complete their maturation in the bone marrow and produce antibodies that coat antigens and mark cells for destruction.
Memory Cells
Cells produced by both B and T cells that recall previous exposure to an antigen and mount a quick attack against that antigen.
Macrophages
Cells that initiate the immune response by inspecting the surfaces of all cells they encounter.
Major Histocompatibility Proteins (MHC)
Special marker proteins carried by every cell in the body that attract T cells when complexed with antigens.
Antigens
Small pieces of foreign particles that remain after a foreign particle is taken in by cells and partially digested.
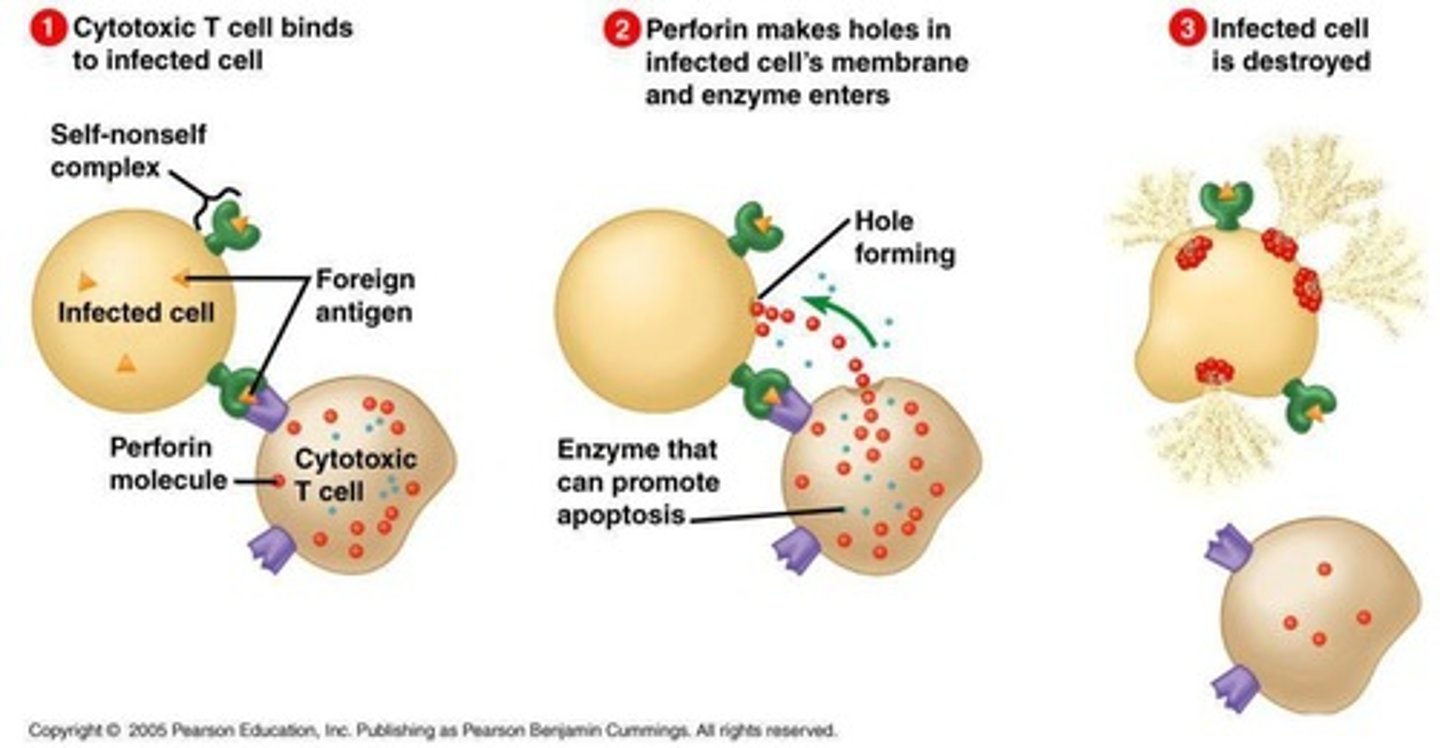
Cytotoxic T Cells
A type of T cell involved in directly killing infected cells.
B Cells: The Humoral Response
B cells respond to helper T cells, marking pathogens for destruction without directly attacking infected cells.
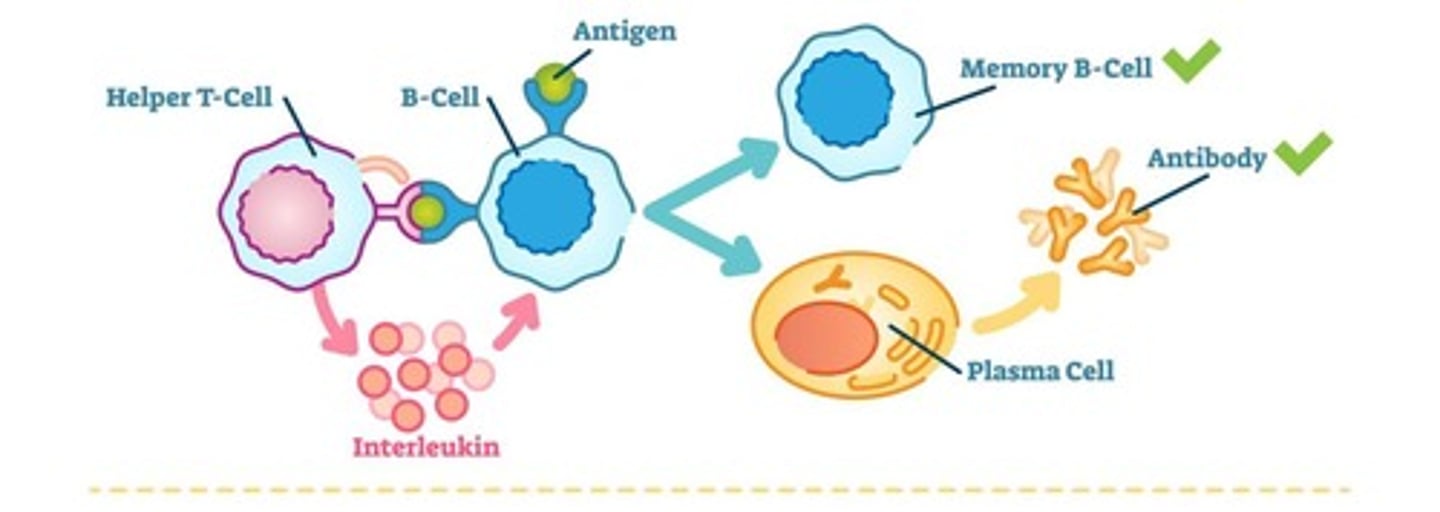
Antibodies
Markers produced by B cells that bind to antigens, allowing antigen particles to enter the B cell and marking cells for destruction.
Secondary Immune Response
A more effective immune response that occurs when a large group of lymphocytes that can recognize a pathogen remains after the first infection.
Helper T Cells
T cells that assist B cells in the immune response.
Phagocytes
Cells that migrate to the site of infection to attack invaders.
Infection by a Foreign Particle
The process where a foreign particle infects the body, is taken in by cells, and its antigens are moved to the cell surface.
Markers placed by B cells
Alert the immune system to kill pathogens.
Initial Immune Response
The delayed response to an antigen encountered for the first time.
T cell immune defense
The defense mechanism involving T cells that specialize in recognizing specific antigens.
Overactive Immune System
Many diseases reflect an overactive immune system.
Autoimmune disease
The body attacks its own tissues.
Examples of Autoimmune diseases
Multiple sclerosis, type 1 diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and Graves' disease.
Allergy
The body mounts a major defense against harmless antigens.
Asthma
A condition where the body reacts to harmless antigens, leading to breathing difficulties.
Vaccination
The introduction of a dead or disabled pathogen into a body.
How Vaccination Works
Vaccination triggers an immune response against the pathogen, without an infection occurring.
First Vaccine
The first vaccine used cowpox to prevent smallpox.
Flu Vaccine Design
The flu changes quickly so new vaccines are always needed.
Antigen Makeup Change
Some viruses change their antigen makeup and prevent detection even after a vaccination.
Flu Viral Genes
Flu viral genes that code for surface proteins mutate quickly.
mRNA Vaccines
A new type of vaccines that use messenger RNA to instruct cells to produce a protein that triggers an immune response.
Primary Response
The initial immune response to an antigen.
Secondary Response
The immune response upon re-exposure to an antigen, which is typically faster and stronger.
SARS Antigen Impact
Prior exposure to the SARS antigen impacts the speed or magnitude of the primary response to the COVID-19 antigen.
Lines of Defense
The body has multiple lines of defense to protect us from pathogens.
Cells of the Immune System
The immune system contains many cells that are able to detect, attack, and generate antibodies to foreign invaders.
Antibodies
Proteins that mark invaders so that the immune system knows they need to attack.
Memory of Invaders
Once you have met an invader, the immune system keeps a record so they can make antibodies more quickly the next time.
Function of Helper T Cell
Commander of the immune response; detects infection and sounds the alarm, initiating both T cell and B cell responses.
Memory T Cell
Provides a quick and effective response to an antigen previously encountered by the body.
Cytotoxic T Cell
Detects and kills infected body cells; recruited by helper T cells.
Suppressor T Cell
Dampens the activity of T and B cells, scaling back the defense after the infection has been checked.
B Cell
Precursor of plasma and memory cells; specialized to recognize specific foreign antigens.
Plasma Cell
Biochemical factory devoted to the production of antibodies directed against specific foreign antigens.
Mast Cell
Initiator of the inflammatory response, which aids the arrival of leukocytes at a site of infection; secretes histamine and is important in allergic responses.
Monocyte
Precursor of macrophage.
Macrophage
The body's first cellular line of defense; also serves as antigen-presenting cell to B and T cells and engulfs antibody-covered cells.
Natural Killer Cell
Recognizes and kills infected body cells; detects and kills cells infected by a broad range of invaders.