Microbiology CH17 Adaptive Immunity pt1
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
adaptive immunity
defenses that target a specific pathogen after exposure
adaptive immunity characteristics (3)
- distinguish self from nonself
- active when innate defenses fail to stop microbe
- acquired through infection or vaccination
primary response
first time the immune system combats a particular foreign substance
secondary response
later interactions with the same foreign substance; faster & more effective due to "memory"
2 natures of adaptive immune system
- humoral immunity
- cellular immunity
humoral immunity
prod. antibodies that combat foreign molecules
humoral immunity antibodies
B cells
humoral immunity B cells charcateristics (3)
- lymphocytes
- created & mature in Bone marrow
- recognize antigens & make antibodies
cellular immunity (cell-mediated immunity)
prod. t lymphocytes which recognize antigenic peptides processed by phagocytic cells
cellular immunity t lymphocytes characteristics
- mature in Thymus
- have t cell receptors (TCRs) on t cell surface
TCRs (t cell receptors) function
contact antigens, causing t cells to screte cytokines instead of antibodies
cellular immunity vs humoral immunity
- cellular immunity attacks antigens that have ALREADY entered cells
- humoral immunity fights invaders & threats OUTSIDE cells
Cytokines
chemical messengers prod. in response to a stimulus
Types of cytokines (5)
- interleukins
- chemokines
- interferons
- tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-a)
- hematopoietic cytokines
interleukins
cytokines between leukocytes
chemokines
induce migration of leukocytes
interferons
interfere with the viral infections of host cells
tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-a)
involved in the inflammation of autoimmune diseases
hematopoietic cytokines
control stem cells that develop into red & white blood cells
Cytokine storm
overproduction of cytokines
antigens
substances that cause the prod. of antibodies
epitopes/antigenic determinant
specific regions on the antigen where antibodies interact with
antigen characteristics (7)
- components of invading microbes
- capsules
- cell walls
- flagella
- fimbriae
- toxins
- viral capsids
- viral spikes
nonmicrobial antigens (3)
- egg white
- pollen
- cell surface molecules
Haptens
molecules too small to be antigenic; attach to carrier molecules & provoke an immune response
Humoral immunity antibodies
immunoglobulins (compact soluble proteins)
humoral immunity immunoglobulin
recognize & bind to specific antigens, targeting them for destruction
valence
# of antigen-binding sites on an antibody (bivalent antibody = 2 binding sites)
humoral immunity antibody structure
- 4 protein chains in a Y shape (2 identical light chains & 2 identical heavy chains joined by disulfide links)
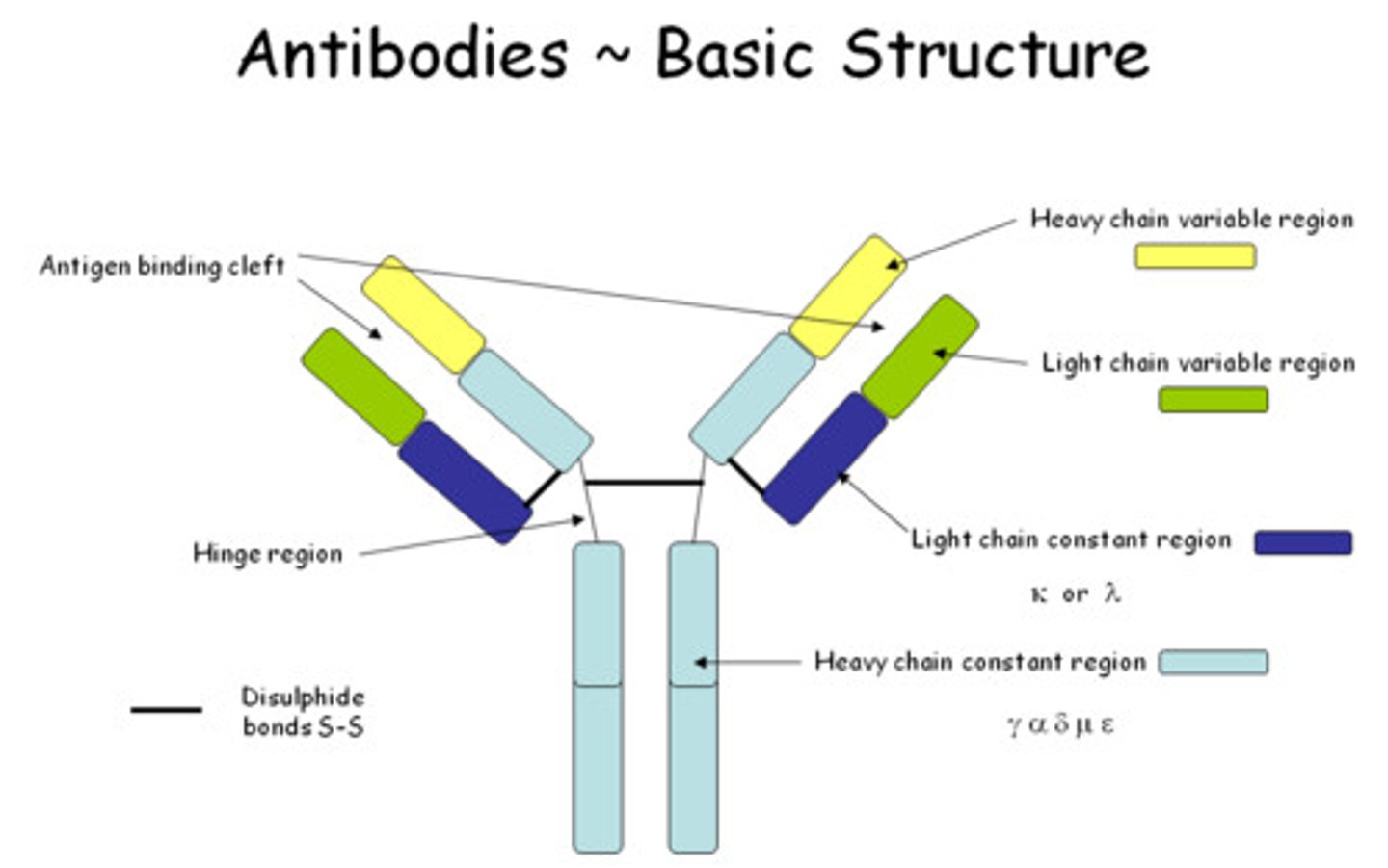
humoral immunity antibody structure regions
- variable (v) regions at the ends of the arms (bind epitopes)
- constant (Fc) region is the stem (identical for a particular Ig class)
types of humoral immunity antibodies (5)
- IgG
- IgM
- IgA
- IgD
- IgE
IgG (3)
- monomer
- in blood, lymph, intestine
- 80% of serum antibodies
IgG actions (4)
- cross placenta & protect fetus
- trigger complement activation
- enhance phagocytosis
- neutralize toxins & viruses
IgM (4)
- pentamer (5 monomers held with a J chain)
- valence of 10 (pentamer valence=10)
- 6% of serum antibodies
- remains in blood vessels
IgM actions (3)
- causes agglutination (clumping) of cells & viruses
- activates complement
- released as first response to an infection (short lived)
IgA (3)
- monomer in serum; dimer in secretions
- 13% of serum antibodies
- in mucous membranes, saliva, tears, breast milk
IgA action
prevent microbial attachment to mucous membranes
IgD (4)
- monomer
- .02% of serum antibodies
- similar structure to IgG
- in blood, lymph, on B cells
IgD action (2)
- no well-defined action
- may play a role as membrane immunoglobin on B cells
IgE (3)
- monomer
- .002% of serum antibodies
- on mast cells, basophils, in blood
IgE actions (2)
- release histamine when bound to antigen; lysis of parasitic worms
- important role in Type I hypersensitivity reactions (allergies)
activation of antibody producing cells
antigen-presenting cells must display antigen on their surface in association with major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II protein
MHC (major histocompatibility complex)
genes encode molecules on the cell surface
types of MHC (2)
- Class I
- Class II
Class I MHC (2)
- on membrane of nucleated cells
- identifies a cell as "self"
Class II MHC
- on the surface of antigen-presenting cells (APCs) (b cells, macrophages, dendritic cells)
inactive B cells process with antigens (3)
- contain surface Ig that bind to antigen
- internalizes & processes antigen
- antigen fragments displayed on MHC class II molecules
T helper cells
contacts the displayed antigen fragment & releases cytokines that activate B cells (activating clonal expression (proliferation of B cell))
clonal expansion and differentiation
differentiate activated B cells into:
- antibody-producing plasmacytes
- memory cells
clonal deletion
elims. harmful B cells
t-dependent antigen
antigen that requires a t helper cell to prod. antibodies
t-independent antigens (3)
- stim. the b cell w/o help of t cells
- provoke a weak immune response (usually prod. IgM)
- NO MEMORY cells generated
diversity of antibodies (2)
- 100 billion dif. antibodies can be made by one indivudal
- immuunoglobulin genes have segmenta that rearrange to prod. diversity in the antigen-binding section of antibody molecule
antigen-antibody complex (function & location) (2)
- forms when antibodies bind to antigens
- prot. the host by tagging foreign molecules or cells for destruction
affinity
strength of the antigen-antibody complex bond
methods of protection via antigen-antibody complex (5)
- agglutination
- opsonization
- antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity
- neutralization
- activation of the complement system
t cells function
combat intracellular pathogens & abnormal host cells (cancer)
t cells characteristics (4)
- mature in thymus
- thymic selection: elim. immature & self-reactive t cells
- migrate from thymus to lymphoid tissues
- attach to antigens via t-cell receptors (TCRs)
pathogens entering gastrointestinal tract... (route)
pass through microfold (M cells) located over Peyer's patches (aggregated lymphoid nodules)
pathogens entering gastrointestinal tract (purpose)
transfer antigens to lymphocytes & antigen-presenting cells (APCs)
types of APCs (2)
- dendritic cells (DCs)
- macrophages
dendritic cells (2)
- engulf and degrade microbes & display them to T cells
- found in the skin, genital tract, lymph nodes, spleen, thymus, & blood
macrophages (2)
- activated by cytokines or the ingestion of antigenic material
- migrate to the lymph tissue, presenting antigen to T cells