Secretion and Reabsorption
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
how much filtrate> how much urine?
180 L, 1-2 liters of urine, most filtrate is reabsorbed by kidney tubule
what types of substances are reabsorbed?
water
good solutes (ions Na+, k+, Cl-, Ca++)
nutrients
waste produces (creatine or urea)
physiological control:
water: yes up to 99%
good solutes: yes up to 99% Na
not under control
nutrients: 100%
waste: no creatine, half urea
diffusion is ___ while mediated transport is __
passive, active
paracellular goes thru?
transcellular goes thru?
para: tight junction
trans: thru cell:
luminal membrane, basolateral membrane
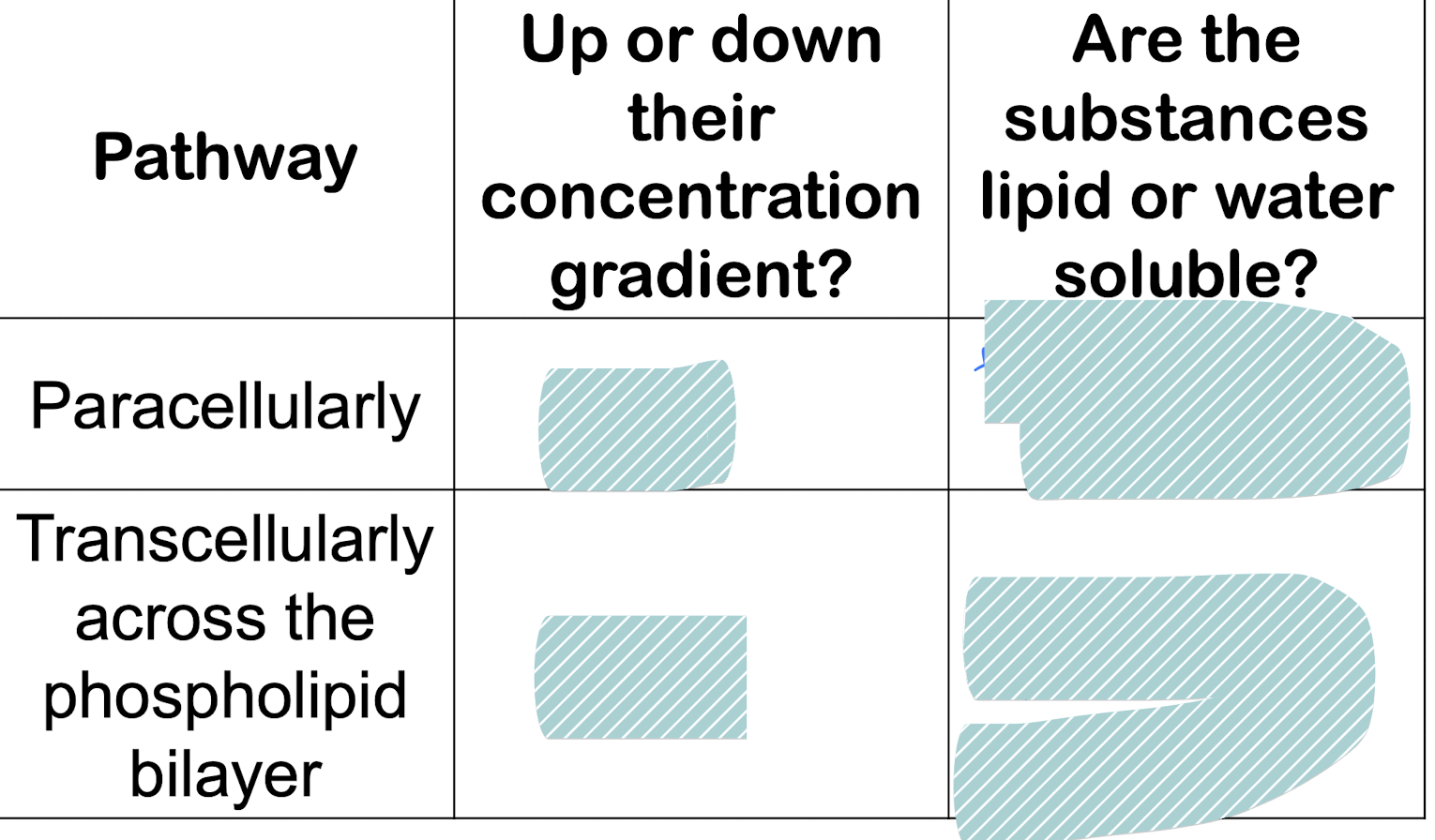
diffusion:
down, water soluble
down: lipid soluble, urea
if the solute conc is the same between filtrate and interstitial fluid, how can there be transepithelial movement of substances by diffusion
conc gradient has to be established
concentration gradient is established by the readorption of water
aquaporin
makes cell highly permeable to water
where does reabsorption of glucose via cotransport with Na occur?
proximal tubule
steps in the mediated transport
1. maintain Na+ concentration gradient (intracellular conc. of na in tubular cells is low compared to fluid)
ATPase, using K+,produces continous conc. gradient of Na+ on basolateral side
2. reabsorption of Na+ and another molecule (glucose)
Na-glucose cotransporter
secondary active transport
3/4: reabsorption of water and movement of solutes and water into capillary
aquaporin channels on both luminal and basolateral side
water moves by osmosis either thru the channels or leaky tight junction
why is there net movement of water and solute from interstitial space to peritubular capillary via bulk flow?
Startling forces favor absorption
what does reabsorption of Na accomplish (4)
reabsorption of other solutes by facilitated transport (transcellular)
glucose + amino: all that is filtered
phosphate + cl-: some that is filtered
Reabsorption of water
reabsorption of urea (bec of water)
Reabsorption of K+, Ca++, Cl-
because of paracellular movement of water - solvent drag
reabsorption of glucose and amino acid is carrier mediated… so?
limit of the rate → how people w diabetes have glucose in urine
What is the osmolairty of filtrate that enters prox tubule? that exits?
iso, iso
take home message for reabsorption in PCT: (5)
2/3 of Na+/K+/H20
all of glucose, amino acids
most bicarbonate
start to concentrate wastes
isomotic amount of water
beg and end osmolarity is 300
what happens in the loop of henle?
reabsorb electrolytes and water (na+, Cl, K, Ca, Mg)
thin descending limb:
thin/thick ascending limb:
thin descending: aquaporins: permeable to water
reabsorbs water
ascending: impermeable to water transport NaCl
thin diffusion (na+ channels)
thick ascending: active (reabsorbs Na+ and other ions)
reabsorption in the thick ascending loop
Na+, K+, Cl- enter cell via Na-K-2Cl cotransporter on luminal membrane using energy of Na+ electrochemical gradient
Na+ exits the cell via, ATPase, keeping intracellular conc of Na low
Cl- exits via Cl- on basolateral membrane, K+ is receycle back into lumen via K+ channel on luminal membrane
paracellular reabsoprtion of Na+ and other + ions in loop of henle
lose + and 2- from henle → +6 mV charge
na, mg, k, ca paraceullar reabsorb to cancel charge
take home message for reabsorption of loop of henle
20% NaCl is reabsorbed
more solute than water is reabsorbed
Beg of loop: 300 osmo
End: 100 osmo
Reabsorption in early distal convoluted tubule
Na-Cl cotransporter: cl enters the cell then leaves the cell on basolateral side
Ca+ enters cell regulated by parathyroid hormone
impermeable to water
what happens to filtrate as it moves down distal convuluated tubule
becomes more dilute
take home message for reabsorption in distal convoluted tubule
10% of NaCl is reabsorbed
No more water is reabsorbed
Osmolarity:
beg: 100 osmolarity
end: 80: osmolarity
what happens in the collecting duct
Na+ enters the cell via Na+ channel on luminal membrane moving down its electrochemical gradient
Na+ exits the cell via Na-K ATPase on basolateral side, keeping intracellular conc of Na low
Loss of Na+ from tubular fluid produces lumen negative electrochemical which drives K+
(basically:Na+ is reabsorbed for exchange in secretion of K+): controlled by aldosterone
Aquarporin 2 on luminal side, 3,4 on basolateral side: variable permeability to water: controlled by ADH
Take home message for reabsorption in collecting duct
2-5% of Na+ is reasborbed, K+ is secreted
variable based on aldosterone
helps regulate total body Na+ and K+
Water is reabsorbed
variable on ADH
Osmo
beg: 80
end: variable
helps regulate total body water