Morphology and Maturation of human blood cells: Hematopoiesis
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Hematopoiesis
The dynamic processes of production and development of various blood and marrow cells.
Development starts in bone marrow, hematopoietic stem cell reside in bone marrow (can become any cell)
Responsible for maturation and division of HSC’s into stages that transport oxygen and excrete carbon dioxide(erythrocytes), fight infection (granulocytes), support humoral immunity (lymphocytes) and maintain homeostasis, blood clots and bleeding is halted (platelets)
HSC’s: self-replicating cells
If you need more oxygen caring capacity due to loss of blood: increase erythrocytes
If your fighting infection: increase in granulocytes/ lymphocytes
Huge wound: release platelets
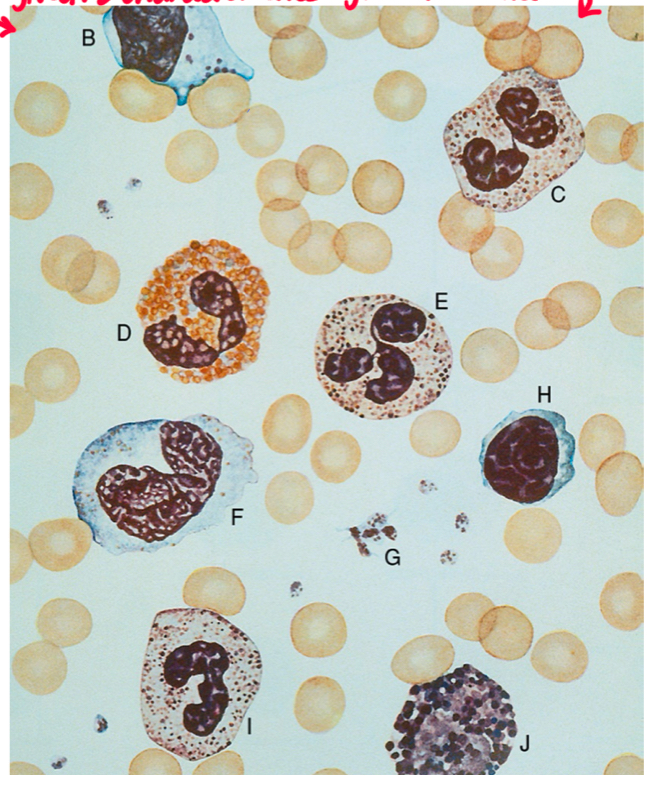
Identify the blood cells found on a normal peripheral smear.
A) RBC
B) Lymphocyte
C) segmented neutrophil
D) Eosinophil
E) segmented neutrophil
F) monocyte
G) Platelets
H) lymphocyte
I) Band neutrophil
J) Basophil
The hematopoietic system consists of:
bone marrow
Liver
spleen
lymph nodes
Thymus
These tissues and organs are involved in the:
Production
Maturation
Destruction of blood cells
More than 500 billion blood cells are produced everyday by _____ (blood cells production and maturation)
Hematopoiesis
Blood is composed of __ %, and __% cells, formed elements (red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets)
55%
45%
Average blood volume in an adult is 4 to 6 L.
Male: __ L
Female: __ L
5-6 L
4-5 L
1% of the tube contains platelets and white blood cells which include:
Lymphocytes
Granulocytes
Monocytes
Characteristics of platelets:
form in cytoplasm; before entering peripheral blood they are released from cytoplasm of megakaryocyte.
1-4 micrometers in diameter
Also known as thrombocytes with no nucleus and comes from a megakaryocyte that develops with in bone marrow
Describe two main differences between neutrophilic band and neutrophilic segmented cells.
segmented neutrophil: 3-6 lobes, segmented nucleus in mature form
Band neutrophil: eventually mature into segmented neutrophil but not fully mature
Segmented neutrophil characteristics:
leukocyte (white blood cell)
Normal peripheral blood of older children and adults (50-70%) of mature granulocytes
Most common type of WBC
1st line of defense
3-6 lobes
Segmented nucleus is mature
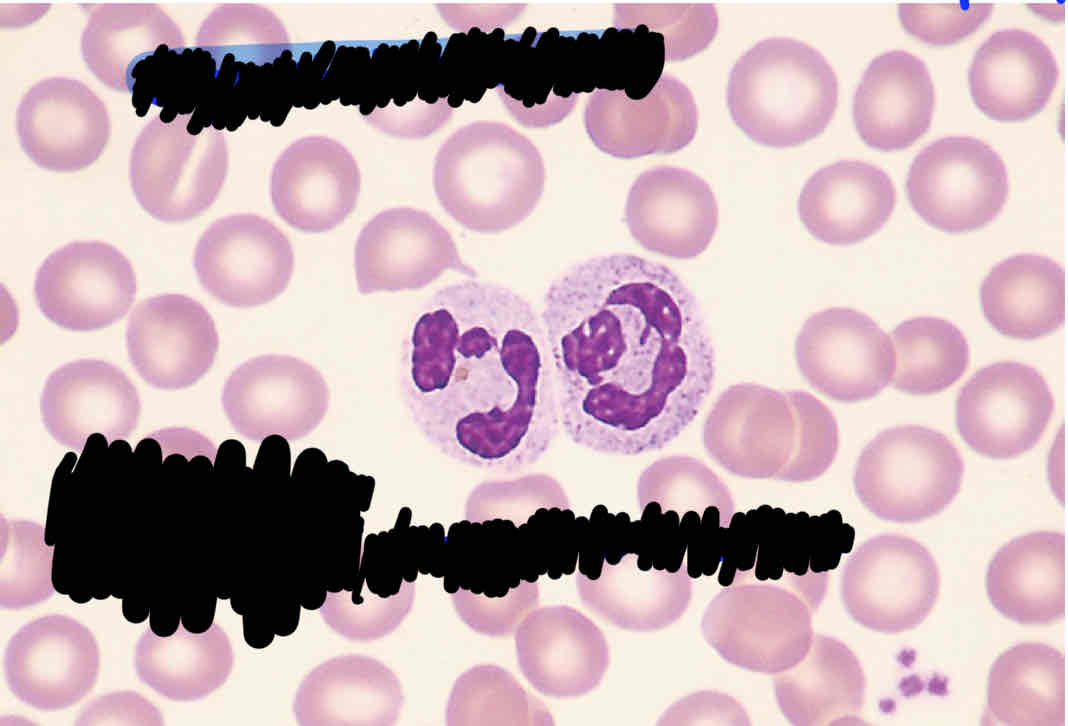
Neutrophil Band characteristics:
leukocyte (WBC)
Eventually mature into a segmented neutrophil
Not fully mature
In peripheral blood
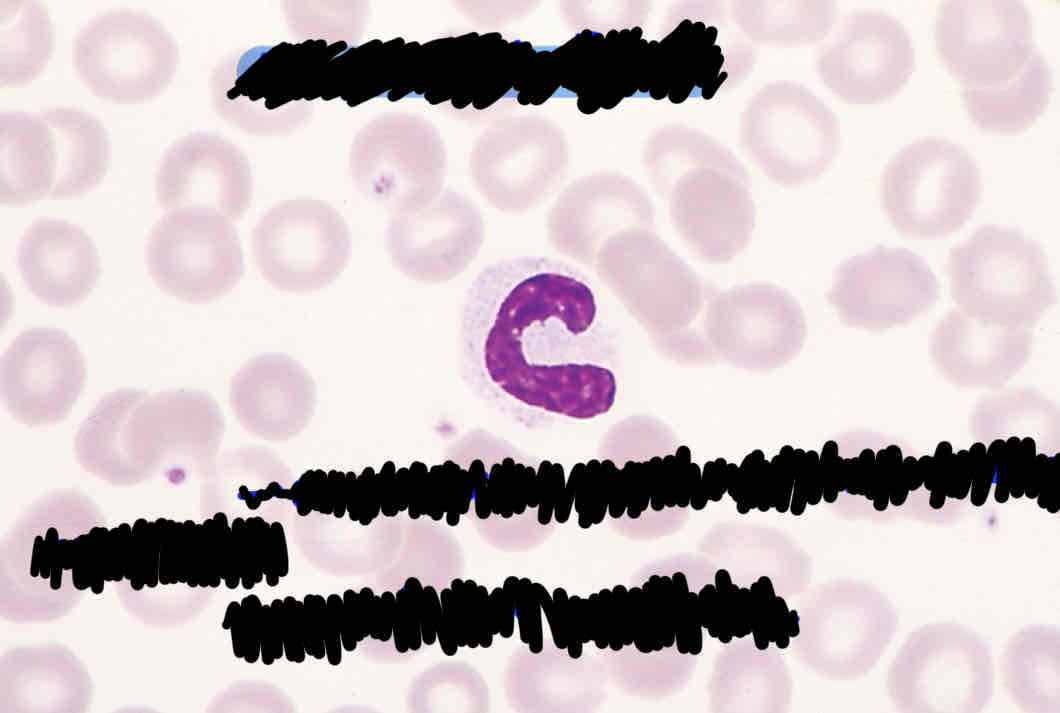
Granulocytes:
neutrophils
Basophils
Eosinophils
(White blood cells) All have a segmented nucleus in mature form they have granules in their cytoplasm
Characteristics of Eosinophils:
increase in response to parasitic infections (worms)
Granules inside of their cytoplasm releasing histamines. Medication anti-histamine for allergies.
Has segmented nucleus
14-16 micrometers in diameter
0-4% of peripheral blood cells in adults
Large, round, and stain orange to reddish-orange
Characteristics of Basophils:
genetic/ hypersensitivity
Dangerous histamine in cytoplasm when released causes anaphalaxyes (allergic to peanuts)
0-2% of peripheral blood cells
Large, violet-blue (purple black) granules aid in recognition of cell
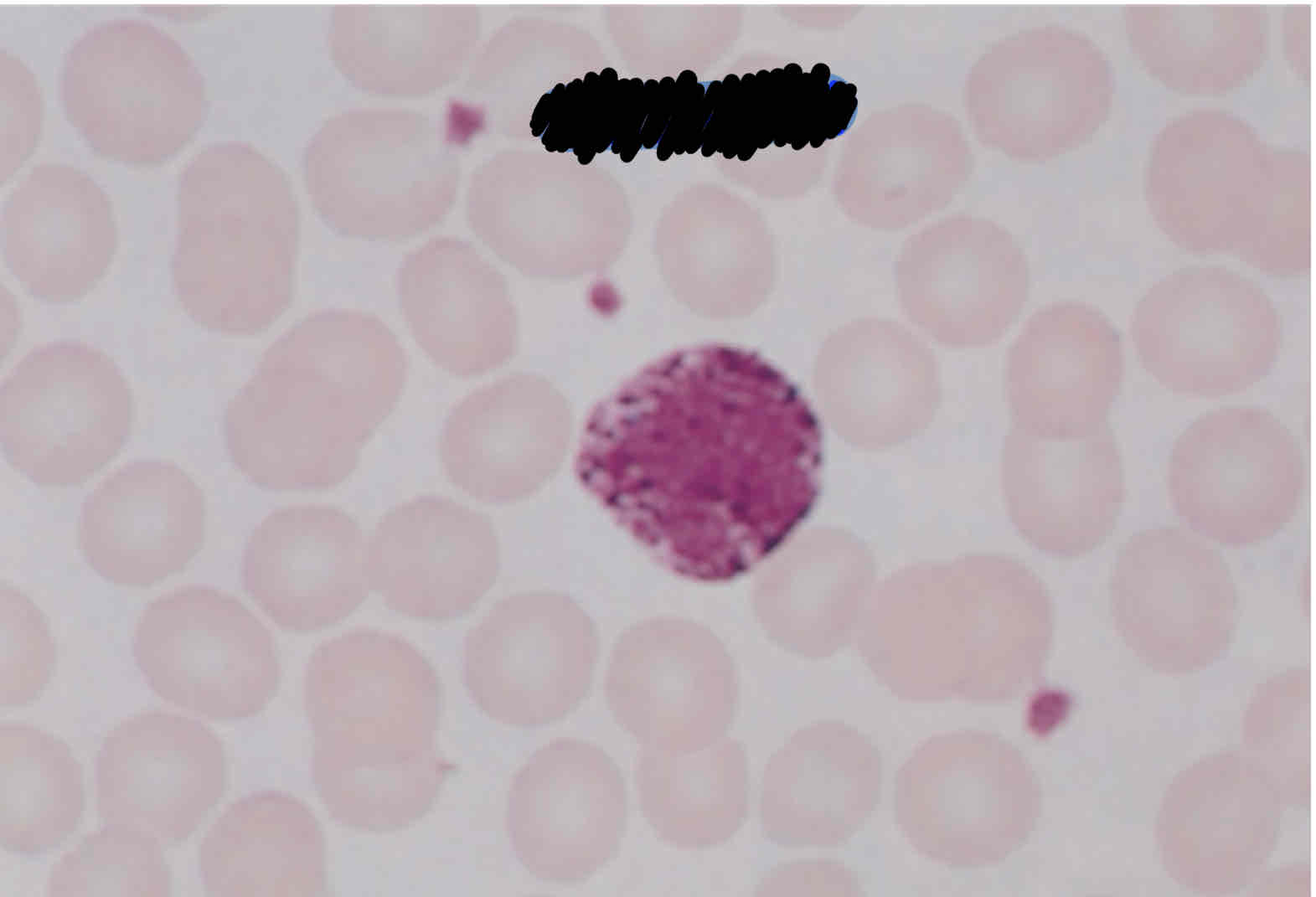
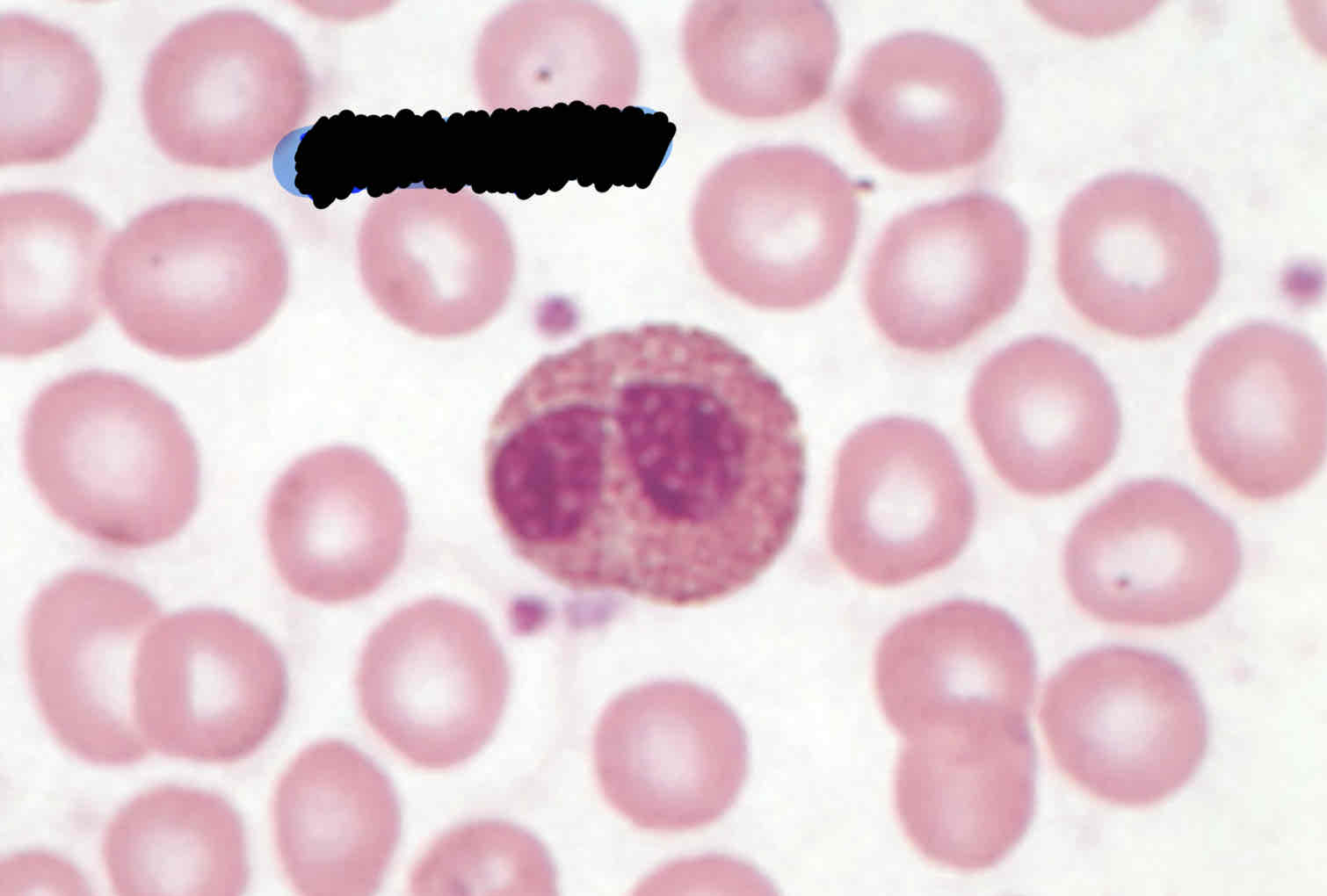
Describe four morphological features that are helpful in identifying monocytes.
Not round shaped but kidney/ band shape
Dark-blue greyish cytoplasm
Has a convoluted nucleus (brainlike)
Reddish/ purplish evenly distributed granules
Lacy delicate chromatin
Characteristics of Monocytes:
known as scavengers
Tissue macrophages help recycle RBC
Engulfs microbes and plays role of neutrophil in environment that they need to
Larger than mature neutrophil, gray-blue cytoplasm, reddish or purplish even granules, darker cytoplasm
Has convoluted nucleus, not round shape but kidney/band shape
Not going from resting to reactive state
Double size of RBC 14-16 micrometers
comprise 2-9% of blood cells in adults
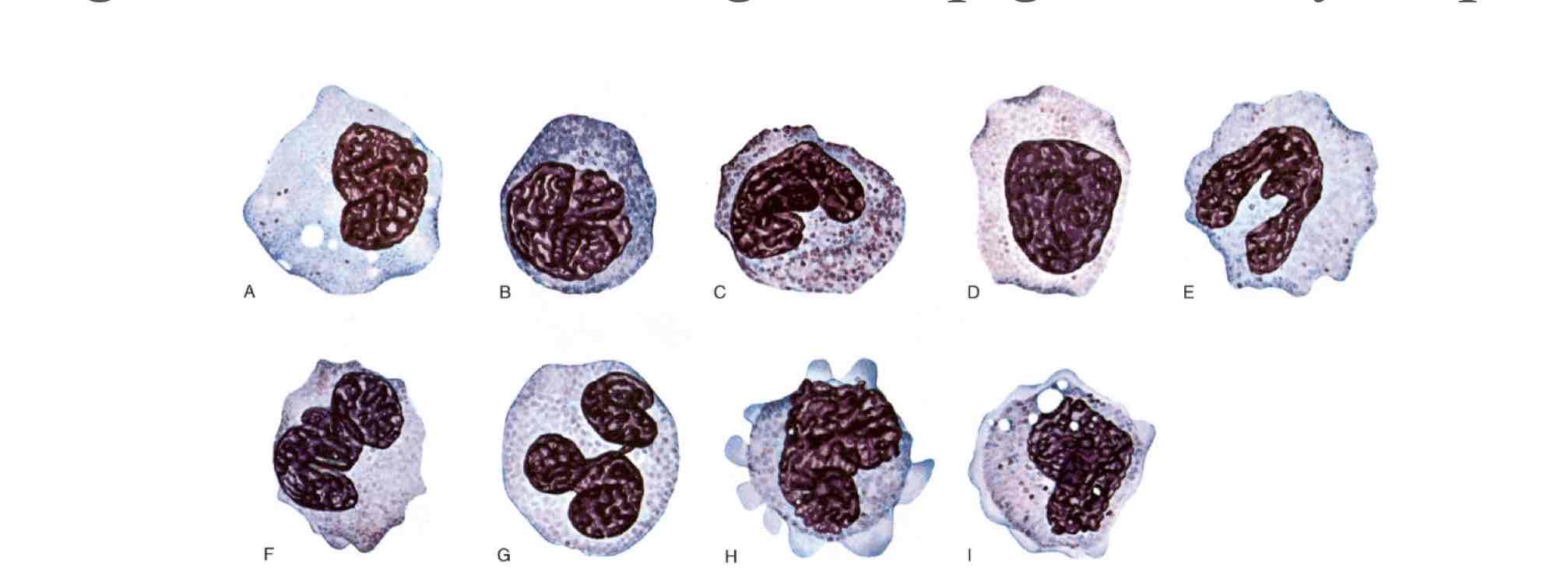
Peripheral blood granulocytes can be divided into:
circulatory pool: granulocytes circulate through blood; RBC circulate for 120 days, neutrophils adhere to vessel endothelium and circulate for 7hrs.
Marginating pool: those granulocytes that line the blood vessel walls and move within blood.
Characteristics of Lymphocytes:
Have round nucleus with clumped and small amount of pale blue cytoplasm
white blood cell involved in the immune response, comprising 20–44% of blood cells in adults
Lymphocytes goes from rested to reactive stage
More cytoplasm in reactive form. (Bright blue cytoplasm and round nucleus)
Resting state size: close to RBC
Reactive state size: double
8-16 micrometers In diameter
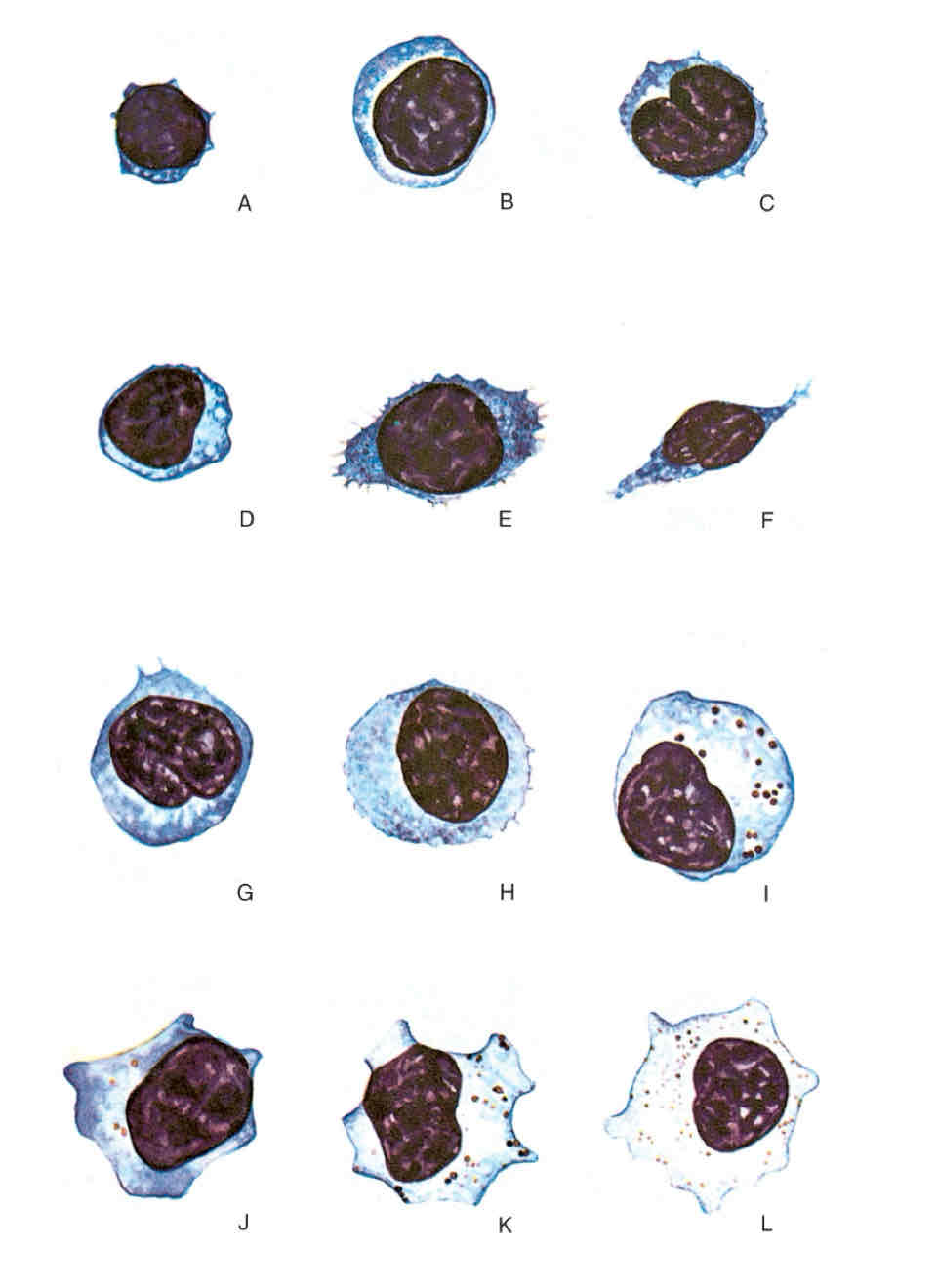
Pluripotent HSC goes into the Progenitor HSC as:
as a lymphoid and becomes a lymphocyte and nothing else
Or as a myeloid can become a granulocyte, monocyte, erythrocyte and develop into megakaryocyte
Bone marrow hematopoietic activity can be divided into:
Stem cell pool: unidentifiable multipotent stem cells and progenitor stem cells reside
Bone marrow pool: cells are in mature state, contain all blood cells in various stages of maturation/development with release of mature cells into peripheral blood. Hematopoietic stem cell receives signal (erythropoeisis) cell goes into development for erythrocyte
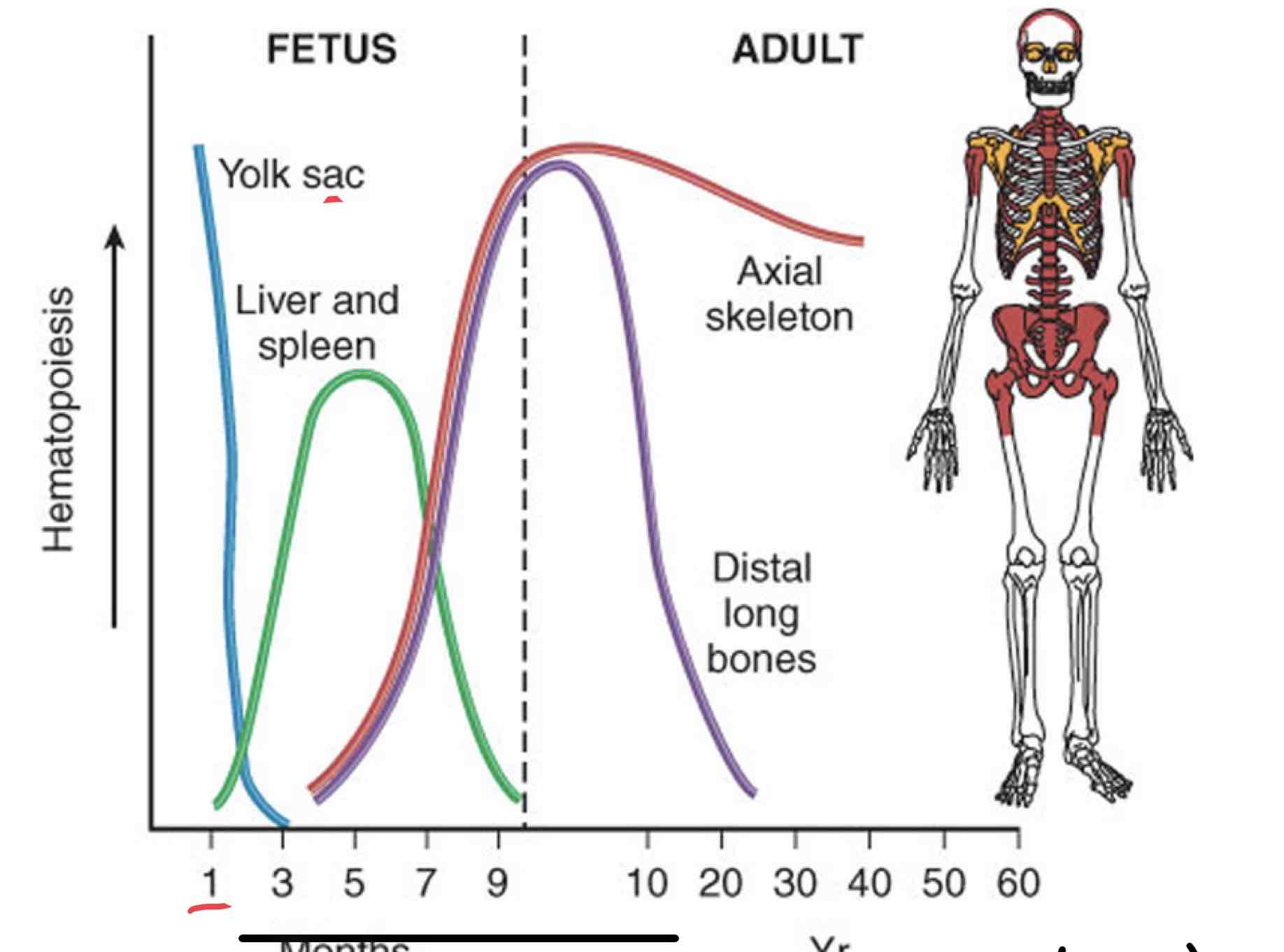
Discuss hematopoiesis in a fetus, child and adult using the following terms: Hematopoiesis, Medullary hematopoiesis, Extramedullary Hematopoiesis
Months after fertilization, Hematopoiesis occurs with in the yolk sac then on month 3 of gestation the liver and spleen start to develop and Extramedullary Hematopoiesis takes over outside of the bone marrow since the bone marrow can’t supply the demand of the body. There will be no Hematopoiesis in the yolk sac at this point.
Month 4 bones start to develop; almost all medullary Hematopoiesis occurring within bone marrow. In adults, medullary hematopoiesis takes over in axial skeleton and distal long bones. As a fully mature adult the axial skeleton becomes the primary site of medullary hematopoiesis and no longer in the distal bones since it has a decrease in medullary Hematopoiesis and can’t aid in the production of hematopoietic stem cells.
Any healthy child/adult should only have medullary Hematopoiesis within bone marrow.
List the proper cell maturation sequence of the erythroid series.
Rubriblast
Prorubricyte
Rubricyte
Metarubricyte
Reticulocyte
Mature erythrocytes
List proper cell maturation sequence for myelopoiesis (granulocytopoiesis).
Myeloblast
Promyelocyte
Neutrophilic myelocyte
Neutrophilic metamyelocyte
Band neutrophil
Mature granulocyte (segmented neutrophil)
Morphological features or a promyelocyte.
Prominent primary granules (dark blue) throughout cytoplasm
Morphological features of a neutrophilic myelocyte.
Round/ oval nucleus
Condensed and uneven stained chromatins strands
Secondary pinkish-staining (neutrophilic) granules
Morphological features of a neutrophilic metamyelocyte.
Bean shaped nucleus
Indentation with less than half the width of arbitrary round nucleus
Morphological features of a band neutrophil.
Mature segmented nucleus
nuclear indentation in early granulocyte greater than half the width of nucleus
What is erythropoiesis?
Production and development of erythrocytes
includes erythropoietin which sends a signal to the bone marrow for production of RBC
RBC comes from HSC takes 7-8 days from stimulus (hypoxia) to mature erythrocyte
1 lineage committed to progenitor cell (pronormoblast) will produce 14-16 RBC
Starts with the stimulus: hypoxia due to decreased levels of RBC, hemoglobin, or oxygen.
Kidney recognizes low levels oxygen carrying capacity and sends erythropoietin to stimulate the bone marrow
Erythropoiesis increases RBC count and then increases oxygen carrying capacity of blood
Ex: menstruation
Characteristics of a Rubriblast:
Most immature cell in the erythropoietic system (white specs)
Has a round nucleus with visible chromatin strands that are dispersed.
Cytoplasm
Nuclear-to-cytoplasmic (N:C) ratio is 8:1 to 6:1
usually divide within 12 hours to make daughter cells (prorubricytes)
Dark bluish-purple cell
Characteristics of a prorubricyte:
daughter cells of rubriblasts
cells require 20 hours to develop
see coarsening of chromatin, smaller than rubriblast by 2 – 10 m
N:C is 6:1 to 4:1
divide to make daughter cells
Pinkish tone comes from producing hemoglobin which binds to the oxygen, there has to be normal hemoglobin production for RBC to transport oxygen
Immature cell
Characteristics of Rubricytes:
smaller than prorubricytes
N:C ratio is 4:1 to 2:1
take around 30 hours to mature in the marrow before dividing
Visible pinkish tone due to production of hemoglobin
Immature cell
Characteristics of a Metarubricyte:
nucleus is pyknotic
N:C ration is 1:1 to 1:2
Maturation time is 48 hours
Does not divide; division stops
Last cell with visible nucleus since nucleus is no longer functional
Ribosomes make protein to produce hemoglobin
Cell extrudes nucleus and macrophages eat the nucleus after being extruded
Develops in bone marrow then extrudes nucleus inside the bone marrow, then becomes reticulocyte, soon leaves the bone marrow to finish maturation in the peripheral blood
Characteristics of a Reticulocyte:
Not fully mature
Contains 2/3 of hemoglobin
released in bone marrow 1-2 days
Finishes maturation in peripheral blood
No ribosomes = can’t produce hemoglobin
Full biconcave shape
Still has ribosomes to produce proteins
When stained with methylene blue, they reveal ribosomes that continuously produce hemoglobin and once produced will loose those ribosomes
Membrane filled with hemoglobin = mature erythrocyte no more hemoglobin produced
A cell that circulates within the peripheral blood and can still produce hemoglobin is considered which cell of the erythrocytic system?
Rubricyte
A cell that resides in the bone marrow with a pyknotic nucleus is considered which cell of the erythrocytic system?
Metarubricyte
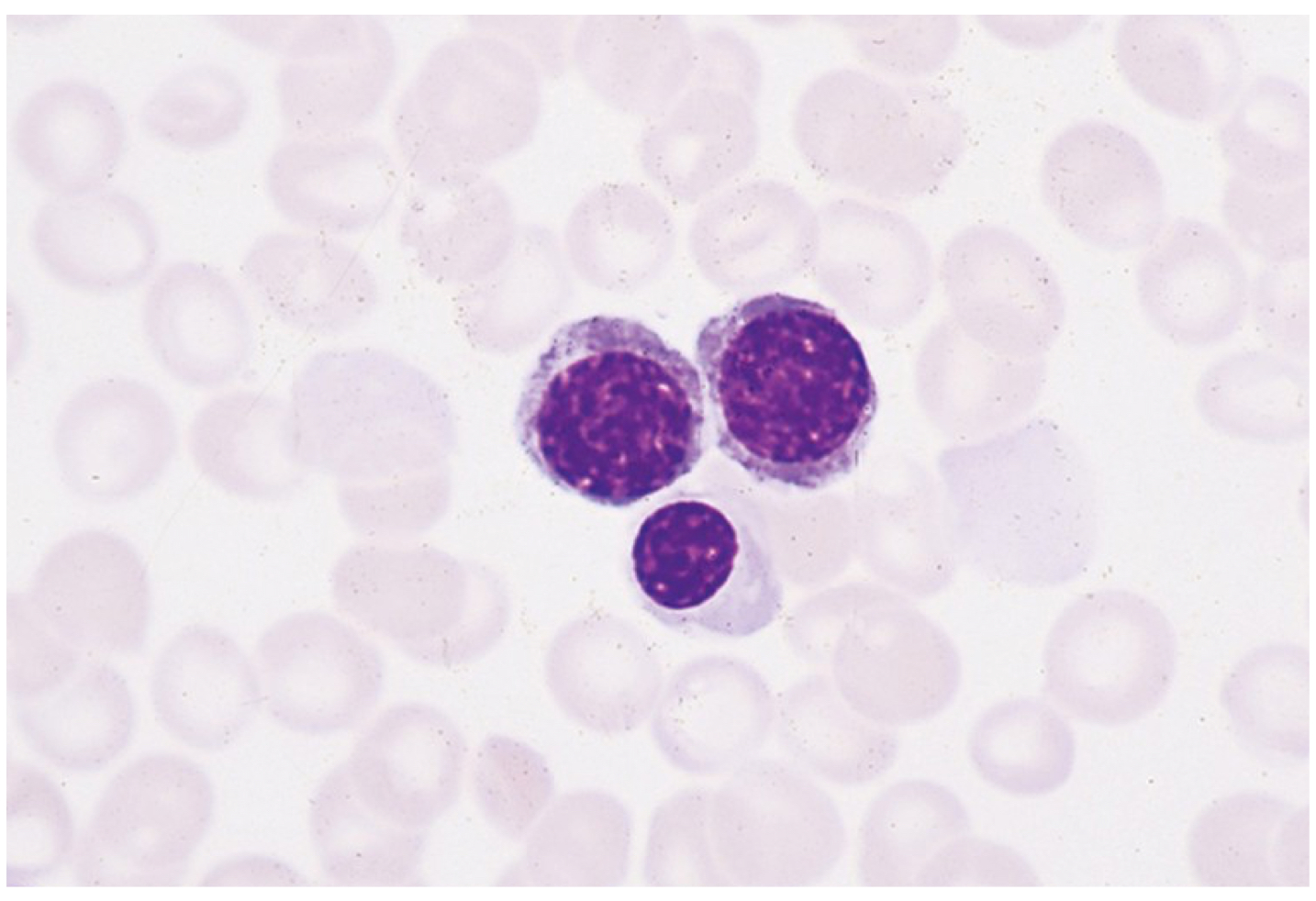
Polychromatophilic normoblast
Rubricyte
Early and later stages
Abnormal
Peripheral blood smear
Decrease in (N:C)
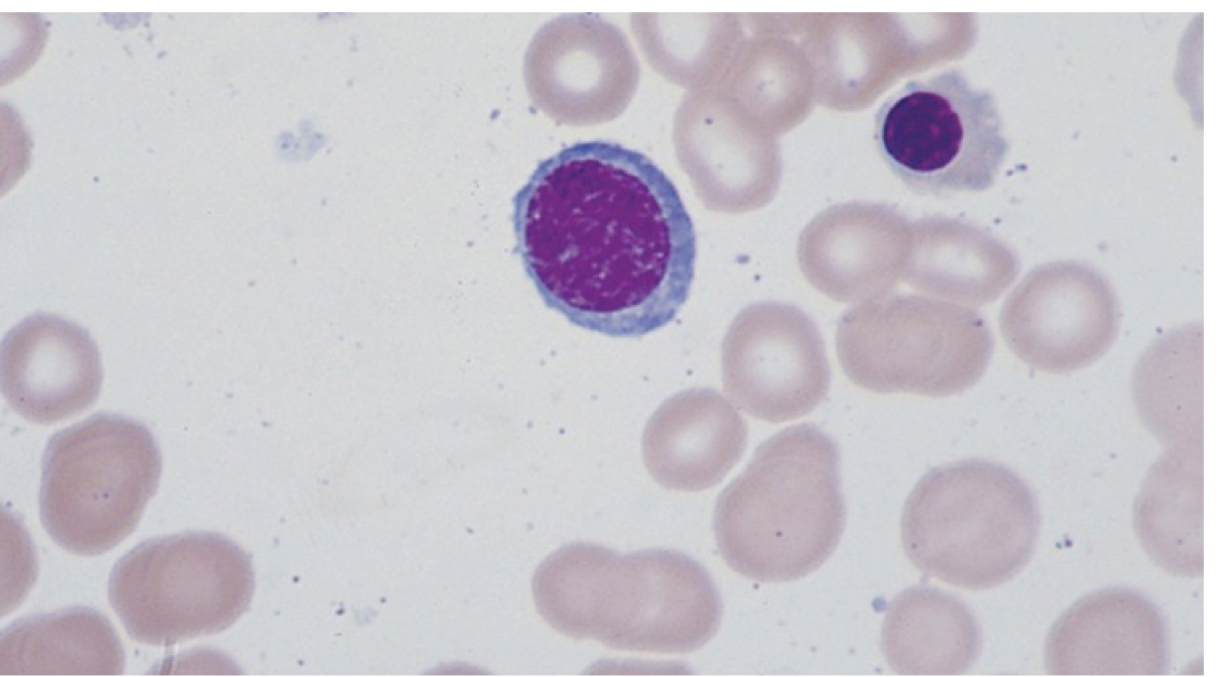
Basophilic normoblast
Prorubricyte
Orthochromatic normoblast Metarubricyte
Myeloma/ anemic
Why is a mature erythrocyte not able to synthesize hemoglobin?
it has no nucleus or ribosomes/ mitochondria
RBC (7-8 micrometers) squeeze through the cynocoid cavity (2-4 micrometers)
What does myelopoiesis (granulocytopoiesis) refer to?
refers to the production, proliferation, differentiation, division, storage, and delivery to the blood of granulocytes (neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils).
Granulocyte production proceeds after cell lineage commitment has determined identity of maturing cell as a member of the myelocytic series.
Development and production of granulocytes