Protists
1/7
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
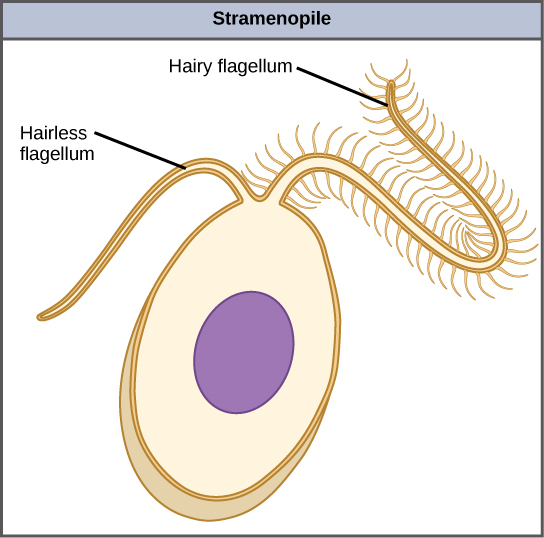
Stramenopiles
Two unequal flagella at some point in their life cycle, the important ones are phototrophs. Ex: Diatoms, brown algae, oomycetes
Haptophytes
gained photosynthesis when a host engulfed a red algae and retained its chloroplast. Ex: coccolithophores and their calcium carbonate plates

Alveolates
Have hollow sacs (alveoli) on their peripheral membrane. Ex: Dinoflagellates and Apicomplexans
Dinoflagellates
Alveolates, mostly photosynthetic (tertiary endosymbiosis), cause red tides, have the harpoon organelle called a nematocyst, consume up to 60% of primary producers in aquatic environments

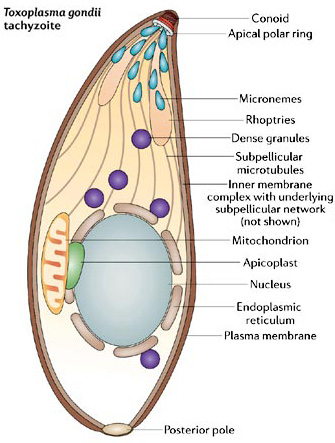
Apicomplexans (parasites)
Alveolates, causes malaria, contain an apicoplast that contains DNA required to invade new host cells, derived from the chloroplast
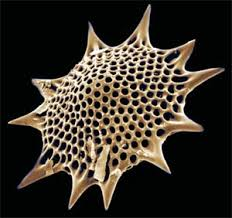
Rhizaria
Thin pseudopods supported by microtubules, mainly amoeboid
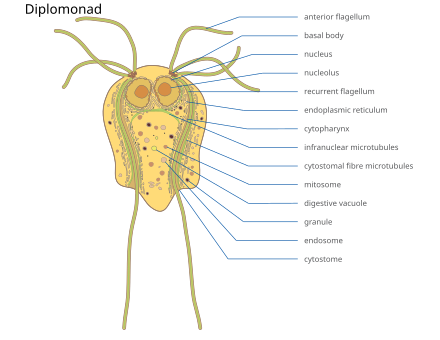
Excavates
Contain reduced mitochondria, Diplomonads cause giardia, Euglenids are photosynthetic
Amoeboza
Thick, lobe shaped pseudopods used for feeding at some point in their life stage. Ex: slime molds
