1.5 Structure of RNA and DNA
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/10
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
1
New cards
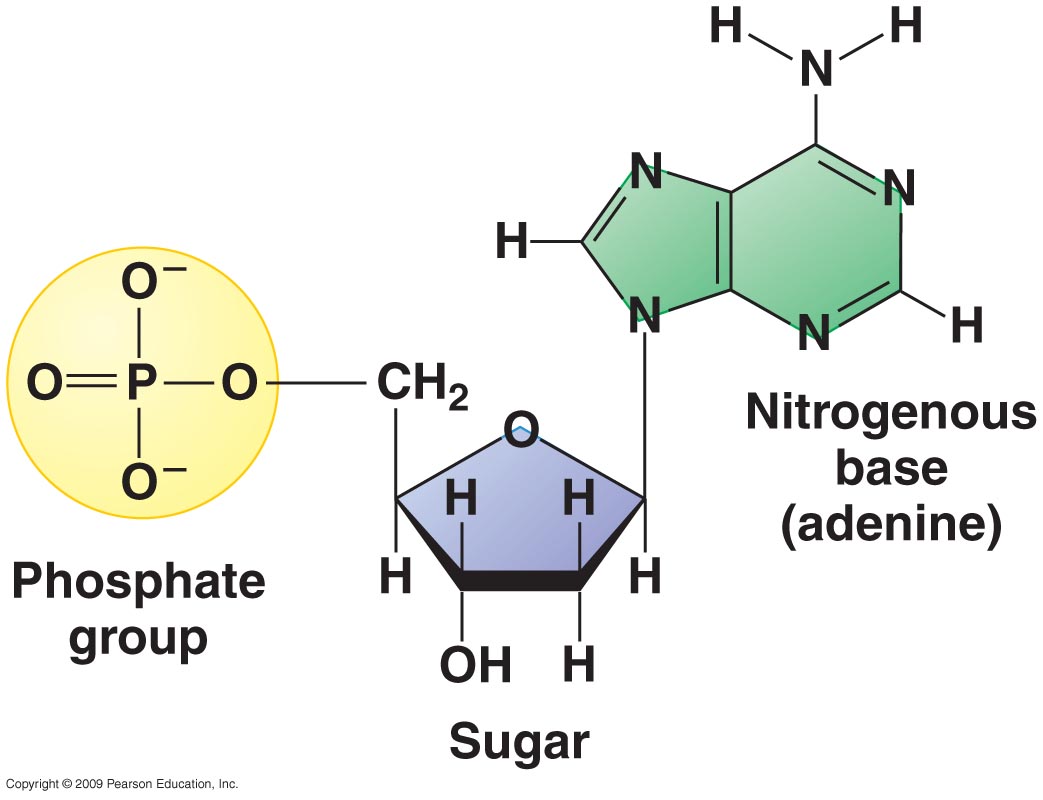
describe the structure of a nucleotide
phosphate joined to a pentose sugar which is joined to a organic, nitrogen-containing base
2
New cards
what is the pentose sugar in DNA and RNA
* in DNA: deoxyribose
* in RNA: ribose
* in RNA: ribose
3
New cards
how do polynucleotides form
through the condensation of many mononucleotides to form a phosphodiester bonds
4
New cards
what is the role of DNA in living cells
base sequence of genes code for functional RNA and the amino acid sequence of polypeptide. DNA forms genes which determines inherited characteristics that influences structure and function of organisms.
5
New cards
what is the role of various types of functional RNA in living cells
mRNA: complementary sequence to one gene from DNA with introns splices out. codons are translated into polypeptides by ribosomes.
rRNA: component of ribosomes
tRNA: supplies complementary amino acid to mRNA codons during translation
rRNA: component of ribosomes
tRNA: supplies complementary amino acid to mRNA codons during translation
6
New cards
describe the structure of DNA
* double helix made of 2 polynucleotide strands
* base pairing: adenine to thymine by 2 H-bonds and guanine to cytosine joined by 3 H-bonds
* purine bonds to pyrimidine to keep the 2 strands the same distance apart
* base pairing: adenine to thymine by 2 H-bonds and guanine to cytosine joined by 3 H-bonds
* purine bonds to pyrimidine to keep the 2 strands the same distance apart
7
New cards
which bases are purine and which are pyrimidine
* A and G are purine (2-ring)
* C, T and U are pyrimidine (1-ring)
* C, T and U are pyrimidine (1-ring)
8
New cards
how is the structure of DNA related to its function
* sugar-phosphate back bone protect the bases, and numerous H-bonds provide stability
* helix is compact for storage in nucleus
* double strand allows it to unzip for semi-conservative replication
* long molecule stores lots of information
* helix is compact for storage in nucleus
* double strand allows it to unzip for semi-conservative replication
* long molecule stores lots of information
9
New cards
describe structure of mRNA
long ribose polynucleotide with uracil instead of thymine. single stranded and contains a codon sequence that’s complementary to the exons of a gene from a DNA strand.
10
New cards
how is the structure of mRNA adapted to its function
* breaks down quickly so there’s no excess polypeptides.
* can be translated into a specific polypeptide by ribosomes
* can be translated into a specific polypeptide by ribosomes
11
New cards
\