DT 4.1 Properties of Materials, Study notes
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
Properties and characteristics of material
- Physical properties
- Mechanical properties
- Aesthetic characteristics
- Properties of smart materials
Physical properties
- Density
- Electrical resistivity
- Thermal conductivity
- Thermal expansion
- Hardness
Density
Mass per unit volume
Important when the weight of a product is a major constraint
E.g. portable, packaging, aircraft, racing cars
Electrical resistance
a measure of a material's ability to conduct electricity
(a material with low resistance will conduct well)
Thermal conductivity
a measure of how fast heat is conducted through a slab of material with a given temperature difference across the slab
Thermal expansion
a measure of the degree of increase in dimensions when an object is heated
Hardness
the resistance a material offers to penetration or scratching
E.g. ceramic floor tiles are extremely hard and resistant to scratching // bearings must be hard to avoid excessive wear
Hardness testing
The Brinell hardness test involves a tungsten carbide sphere indenter being forced into the test surface for 15 seconds; the average diameter of the indentation is then measured
The Vickers and Knopp hardness test uses a square-based diamond pyramid as an indenter, the diagonal length of the indentation being measured
The Rockwell hardness test gives a reading, via a dial, while the specimen is still under load
Mechanical properties
- Tensile and compressive strength
- Stiffness
- Toughness
- Ductility
- Elasticity/plasticity
Tensile strength
The ability of a material to withstand pulling forces
Important in selecting materials for ropes and cables e.g. an elevator
Tensile testing
materials are tested to determine suitability under tensile
E.g. machine pulls the object and elongated length is measured
Stiffness
The ability of a material to resist deflection or bending.
Important when maintaining shape is crucial to performance, e.g. aircraft wings
Toughness testing ??
Usually an impact test where a standard notched bar is fractured by a shock load
The Izod test uses a circular cantilever specimen with a V-notch
The Charpy test uses a simply supported rectangular beam with a similar shaped notch
Ductility
The ability of a material to be drawn or extruded into a wire or other extended shape
Important when metals are extruded (not to be confused with malleability)
Malleability
The ability of a material to be cold worked (i.e. hammered, pressed, folded)
The ability to be shaped plastically
E.g. copper bowl - hammering a disc of sheet copper (raising)
Mild steel is relatively malleable, e.g. car body shells (collection of cold 18 gauge sheet pressings welded together creating a rigid monocoque structure)
Aesthetic characteristics
Beauty or the appreciation of beauty
Characteristics of taste, smell, appearance, texture, and colour
Hedonic properties
Hedonism - the belief that pleasure is the highest good of life.
Taste, smell appearance, texture, feel and colour are hedonic properties humans use to decide of a product, object or place are pleasing to use.
These properties activate people's senses, responses to them vary from one individual to another and are difficult to quantify scientifically.
Hearing
Rely on sound to back up other information.
Feedback is an important part of products and systems
Sight
Reading, working, watching films and television, playing games and countless other activities.
Colour
Can influence mood or feelings
Designers deliberately use colour to make a product easier or safer to use
Switches, controls and handles can be made more obvious if they contrast
Touch
The sense that gives us notice of contact with an object
(aka tactile sense)
We learn the shape, texture and hardness of objects through this sense.
Touching gives rise to feelings of warmth, cold, pain and pressure
Smart materials
Have one or more properties that can be dramatically altered, e.g. viscosity (stickiness), volume, conductivity.
The property that can be altered influences the application of the smart material.
Range of smart materials
One of their properties can be changed by an external condition (e.g. temperature, light, pressure or electricity). This change is reversible and can be repeated many times.
Examples of smart materials
Science and technology develop standard materials (e.g. steel, aluminium, gold)
Some smart materials have the ability to change shape or size by adding a little bit of heat, or to change from liquid to solid almost instantly when near a magnet
Shape-memory alloys (SMA)
Objects that are bent can return to its original shape when heated above a certain temperature (e.g. dipped in hot water)
E.g. spectacle frames, triggers to start the sprinklers in fire alarm systems, controllers for hot water valves in showers or coffee machines
Piezoelectric materials
When squeezed rapidly, it produces a small electrical voltage for a moment. If a voltage is put across the material it makes a tiny change in shape.
E.g. contact sensors for alarm systems, microphones and headphones
Quantum-tunnelling composite (QTC)
A flexible polymer which contains tiny metal particles. It is normally an insulator but if it is squeezed it becomes a conductor
E.g. membrane switches on mobile phones, pressure sensors and speed controllers
Electroluminescent materials
Give out light when an electric current is applied to them
E.g. safety signs, clothing for use at night
Thermochromic materials (colour-change material)
Changes colour as the temperature changes. Used on contact thermometers made from plastic strips and test strips on the side of batteries (where the heat comes from a resistor under a thermochromic film)
E.g. food packaging materials (shows when the product is cooked to the right temperature)
Photochromic materials (colour-change material)
Change colour according to different lighting conditions.
E.g. security markers that can only be seen in UV light
Magnetorheological fluid (MR fluid)
Usually a type of oil
When subjected to a magnetic field, the fluid greatly increases its apparent viscosity.
Yield stress can be controlled very accurately by varying the magnetic field intensity
The fuild's ability to transmit force can be controlled with an electromagnet (gives rise to many possible control-based applications)
Young's modulus
Measure of the stiffness of an elastic material
Can be experimentally determined from the slope of a stress-strain curve created during tensile tests.
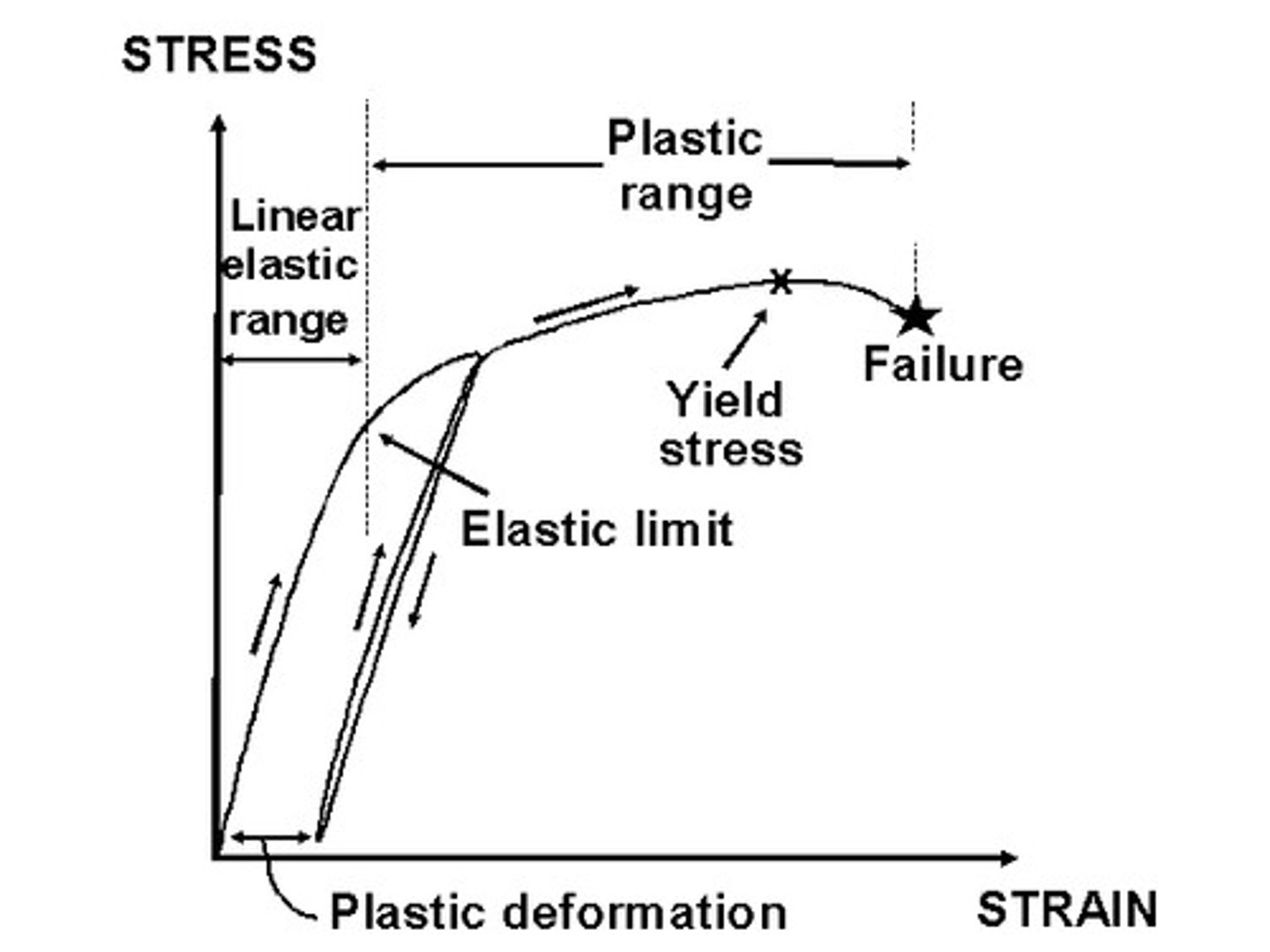
Stress-strain curve
Unique for each material, found by recording the amount of deformation (strain) at distinct intervals of tensile or compressive loading.
Stress-strain curve
(image)
Stress-strain curve typical of...
- ultimate strength
- yield strength
- rupture
- strain hardening region
- necking region
A: apparent stress
B: actual stress
Yield stress
The stress at the yield point on the stress/strain graph
Beyond the yield point, the material undergoes plastic deformation.
Mass (pp)
the amount of matter in an object
Weight (pp)
the force of gravity on an object
weight = mass x acc. of gravity
Volume (pp)
the amount of dimensional space an object occupies
Density (pp)
the mass per unit volume of a material
density = mass x volume
--> important in relation to product weight and size eg. food packaging
Electrical Resistivity (pp)
a measure of a materials ability to conduct electricity
--> low resistivity will conduct electricity well
--> conductors or insulators eg. copper
Thermal Conductivity (pp)
a measure of how fast heat is conducted through a slab of material with a given temperature difference across the slab
eg. cooking utensils
Thermal Expansion (pp)
a measure of the fractional increase in dimensions when an object is heated
eg. oven doors
Hardness (pp)
the resistance a material offers to scratching, cutting, denting or penetration
Strength (mp)
ability of a material to resist an applied force and it is identified as either tensile or compressive strength
Tensile Strength (mp)
the ability of a material to withstand pulling forces
Compressive Strength (mp)
the ability of a material to withstand pushing forces
Stiffness (mp)
the ability of a material to resist a bending deformation
Toughness (mp)
the ability of a material to resist a propagation of cracks
Ductility (mp)
the ability of a material to be drawn or extruded into a wire or other extended shape
Elasticity (mp)
the ability of a material to be deformed and return to its original size and shape
Plasticity (mp)
the ability of a material to undergo permanent deformation
Young's Modulus (mp)
youngs modulus = stress/strain
Aesthetic Characteristics
smell, appearance, taste, texture
Smart Materials
have properties that react and respond to changes in their environment, meaning that one of their properties can be changed by an external condition eg. temp or light, the change is reversible.
1. Piezoelectricity
2. Shape Memory Alloys
3. Magneto-Rheostatic & Electro-Rheostatic
4. Photochromicity
5. Thermoelectricity
Piezoelectricity
when a piezoelectric material is deformed, it gives a small but measurable electrical discharge, contrastingly, when an electrical current is passed through a piezoelectric material it experiences a significant increase in size
eg. sensors/airbags
Shape Memory Alloys
alloys that return to their programmed shape, they exhibit pseudoelasticity and shape memory effect due to the rearrangement of molecules in the material
pseudoelastic springs back to its original shape, eg. eye glass frames
shape memory effect needs a change in temperature eg. robotic limbs
Magneto-Rheostatic & Electro-Rheostatic
MR and ER materials are fluids that , undergo a dramatic change in viscosity
they can change from a fluid to a solid in seconds depending on the magnetic or electric field, and the effect is reversed when the field is removed
mr - car shock absorbers, prosthetic limbs
er - clutches and valves
Photochromicity
react reversibly to light by changing their color eg. color changing lenses
Thermoelectricity
electricity produced directly from heat
Density
Object's mass per unit volume as a property
Electrical Resistivity
How strongly a material reduces the flow of an electrical current. Low resistivity indicates a material easily allows the movement of an electric charge
Thermal Conductivity
K, the property of a material that indicates its ability to conduct heat
Thermal Expansion
Tendency of matter to change in volume in response to a temperature change. Constituent particles move around once heated and the more the motion, the more it maintains greater average separation
Hardness
Resistance of metal to plastic deformation, usually by indentation. Also refers to stiffness or temper, or to resistance to scratching, abrasion, or cutting
Tensile Strength
Resistance of a material to a force without tearing
Stiffness
Resistance of an elastic body to deformation by an applied force
Toughness
Resistance to fracture of a material when stressed
Ductility
The extent to which materials can be deformed plastically without fracture
Taste
Ability to detect the flavor of substances
Smell
Ability to perceive odours
Appearance
Visual appearance of objects by the way in which they reflect and transmit light
Texture
Properties held and sensations caused by external surface of objects registered by sense of touch
Colour
Visual perceptual property determined by the parts of the spectrum of light reflected or transmitted without being absorbed