AP Bio 1st Sem Review (Unit 1-5)
1/143
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
144 Terms
Experimental design
Controlled experiment that tests a hypothesis via using an independent variable, dependent variables, controlled variables, and a control group
Control variables
factor in an experiment that is kept constant to ensure that any changes in the dependent variable can be attributed to the manipulation of the independent variable
Control group
In a controlled experiment, a set of subjects that lacks the specific factor being tested
dependent variable
A variable whose value is measured during an experiment to see whether it is influenced by another variable
independent variable
A variable whose value is manipulated during an experiment to reveal possible effects on another variable
Comparing averages using SEM for Statistical significance
Errors bars = +/- 2 SEM from average > If overlap then no statistical difference/ if no overlap then statistical difference
Carbon bonding characteristics
Form 4 covalent bonds, creates molecule structure (long chains, multiple bonds, and ring structures), and biomolecules made from C-structures
Structures of carbon-based molecules
long chains, multiple bonds, and ring structures
SPONCH Molecules
Sulfur, phosphorous, oxygen, nitrogen, carbon,and hydrogen
Protein
CHONS
Lipids & Carbohydrates
CHO
Nucleic acids
CHONP
Electronegativity
The attraction of a given atom for the electrons of a covalent bond.
Hydrogen bonding
Dotted line where polar molecules are attracted to each other, forming these bonds between molecules (easily broken)
Polar Molecules & Why water is polar
This bond is between atoms that differ in electronegativity. The shared electrons are pulled closer to the more electronegative atom, making it slightly negative and the other atom slightly positive. Water is polar because of O’s electronegativity being partially negative, pulling e- from H+
Properties of water
Forms H-bonds, polar, cohesion (like molecules), adhesion (other molecules), solvent, and high specific heat & vaporizatio
Hydrogen bonding beteen water molecules
Polar molecules attracting to each other because of O’s electronegativity on H+, forming this bond as a dotted line
Dehydration synthesis
A chemical reaction in which two molecules covalently bond to each other with the removal of a water molecule.
Hydrolysis
A chemical process that lyses, or splits, molecules by the addition of water; an essential process in digestion.
Carbohydrates
Biological roles include energy storage and providing structure, ending with -ose. Monomers = monosacchardies (CH2O - 1:2:1)
Structure of polysaccharides
A polymer of many monosaccharides in a chain, formed by dehydration reactions.
Energy Polysaccharides animals vs plants
plants = starch (more separate), animals = glycogen (more branching for quick E release)
Structural Polysaccharides animals vs plants
plants = cellulose (plant cell walls), animals = chitin (arthropod exoskeleton & fungi cell walls)
Lipids
Biological role is to store energy, membrane structure, and hormones
Energy storage lipids
triglycerides (3 fatty acids of long hydrocarbon chains with carboxyl group connected to glycerol)
Membrane lipids
Phospholipids (glycerol, 2 fatty acids, and phosphate group) and cholesterol (steroid forming animal cell membrane components and synthesizes steroids - keeps membrane fluid)
Lipid structure vs carbohydrates
Not polymers, made of C, H, O (glycerol & long hydrocarbon fatty acids), and cone shaped vs monosaccharide polymers, made of C, H, and O (1:2:1), hydrophilic, and ring shaped
Lipid Properties
nonpolar & hydrophobic (minimal oxygen) - Except for phospholipids (amphipathic) 2 fatty acids & phosphate group
Protein
functional biological molecule consisting of one or more polypeptides folded into a specific three-dimensional structure.
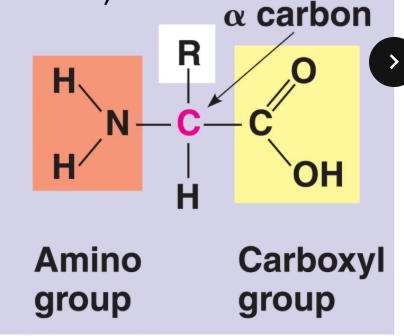
Amino acid structure (central C, amino group, hydrogen, carboxyl, and r group)
R group
part of amino acids that is unique to each specific amino acid
Polar R group
having an O, N, or S at end of R-Group or any type of electronegative atom
Nonpolar R group
Only C and H or having N/S in the middle of the chain despite being electronegative for R groups
Basic R group
Amino group & having a + charge
Acidic R group
Having carboxyl or negative charge
Primary Structural level
AAs of polypeptide in word form that determine 3D shape, with #1 AA being amino end (H3N+), and last AA being Carboxyl end
Secondary Structure
Coiled/folded sections of polypeptide due to H-bonding (H-O) between amino and carboxyl groups (R-Group excluded). Alpha Helix = 1 structure, Beta pleated = 2 structure H - bonded
Tertiary Structure
Folding that results from interactions between R-Groups (ionic via acidic and basic, hydrophobic associating and avoiding water, disulfide bridges with covalent bonds between S atoms of Cysteines, and polar groups of H-bonds with each other (acidic, basic, H2O, and polar)
Quaternary Structure
2+ Polypeptides (2+ tertiary structures) attached to each other that are formed by R-group interactions in tertiary (not all proteins have this structure)
Backbone of Polypeptide
Carboxyl, central carbon, and amino/nitrogen (C-C-N) (Exclude R Group) - repeated coiling/folding of polypeptide backbone due to H-bonds at that location
R-group interactions stabilizing tertiary structure and quaternary structure.
tertiary - H-bonds, ionic bonds, hydrophobic interactions, and disulfide bridges, quaternary - same R group interactions from tertiary but now between 2 polypeptide (tertiary) structures
Denaturation
Disruption of protein shape and function due to environmental conditions (high salt, pH level difference, and high temp), affecting only 2-4 levels (weak bonds) but not 1, due to covalent peptide bonds
Nucleic acid
A polymer (polynucleotide) consisting of many nucleotide monomers; serves as a blueprint for proteins and, through the actions of proteins, for all cellular activities. The two types are DNA and RNA.
Nucleic acid monomer structure
Nucleotides - sugar (deoxyribose - 2 OH/ribose - 3 OH) made from phosphate & nitrogenous base alternating phosphate and sugar

DNA and RNA differences
DNA has 2 OH w/ double helix & T, A, C, G and RNA has 3 OH w/ single helix & U, A, C, G
OH
hydroxyl
DNA bases
adenin, thymine, cytosine, and guanine (TACG)
RNA bases
Uracil, adenin, cytosine, and guanine (UACG)
Endergonic vs exergonic reactions
Absorb free energy, change in free energy (G) > 0, needed for building larg molecules vs Release energy, change in free energy (G) < 0, breaking down large molecules
Enzyme Catalytic Cycle
Enzymes not consumed in reaction, just catalyzes reaction repeatedly (enzyme + substrate > enzyme-substrate complex, enzyme + product)
How enzymes speed up reactions
Lowers activation energy barrier
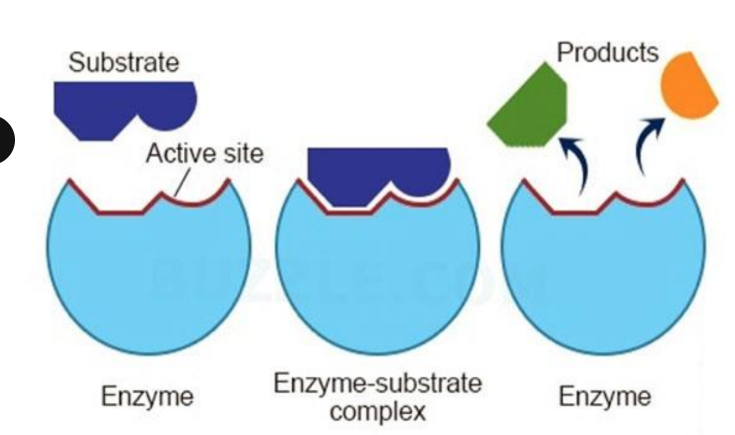
Enzyme structure
Enzyme structure
Active site where substrate/reactant binds to in key in lock > products are output
Enzyme reaction Rate
(Change in substrate or change in products)/t = mmol/sec
Enzyme reaction saturation
Substrate concentration at which all enzymes have substrate molecules in their active site, in which increasing concentration above maximum reaction rate does not affect reaction rate
Enzyme inhibitors
bind to enzymes and decrease enzyme activity
Competitive inhibitors
bind to enzyme’s active site and prevents substrate binding but can be overcome with more substrate concentration
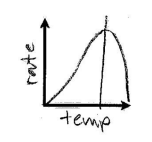
Temperature affecting Rxn Rate
Temperature increasing to optimal temperature results in increased motion and greater reaction rate but above optimal leads to reduction in reaction rate due to denaturing
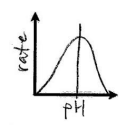
pH affecting reaction rate
Enzyme’s optimal pH matching environment of enzyme’s pH lead sto higher reaction rate but above or below optimal pH leads to denaturing and decreased reaction rate

a. without inhibitor
b. with competitive inhibitor
c. with noncompetitive inhibitor
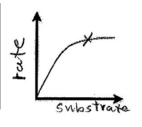
As substrate concentration increases rate increases (increases the frequency to enzyme and substrate colliding). X marks enzyme saturation. Increased substrate concentration above saturation does not increase the rate
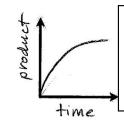
Curve levels off over time as all substrate has been converted to products. Rate of reaction is = to the slope of the line
Plant cell features
Cellulose based cell walls (700x thicker than plasma membrane) & large central vacuole (retains water for turgor pressure, reproduction, growth, and development), and chloroplast
Ribosomes
Synthesizes protein from large and small subunit made from protein and ribosomal RNA
Nucleus
Double bilayer membrane/nuclear envelope with pores to store genetic material with nucleolus (rRNA synthesis & ribosomal subunits), in which proteins & RNA enter/exit via pores
Chloroplast
inner and outer membrane surrounding membrane bound thylakoids that do photosynthesis (absosrb light and synthesize sugar) from CO2 and H2O
Mitochondria
Double bilayer, inner folded for more surface area, for ATP synthesis (has circular DNA)
Endoplasmic reticulum
(builder) membranous network immediately surrounding nucleus (rough - makes membrane proteins and secretes proteins, smooth - makes lipids and detoxifies toxins)
Golgi Appratus
(modifier) series of flattened membrane bound sacs/cisternae to fold and chemically modify proteins then sorting proteins to cellular location
lysosomes
membrane bound organelle with hydroyltic enzymes to break down old/broken organelles and molecules
Animal cell features
no cell wall and has lysosomes (membrane bound organelle with hydroyltic enzymes to break down old/broken organelles and molecules)
Central vs Contractile Vacuole
Plants’ reproduction, turgor pressure, growth, and development vs ATP-based moving water from protists

Fluid mosaic model of membrane structure and behavior
Refers to membrane structure having various liquids in the form of unsaturated fatty acid tails/double bonded kinks & cholesterol preventing tight packing/making it fluid, and patterned/mosaic due to different molecules found in membrane (proteins & cholesterol)
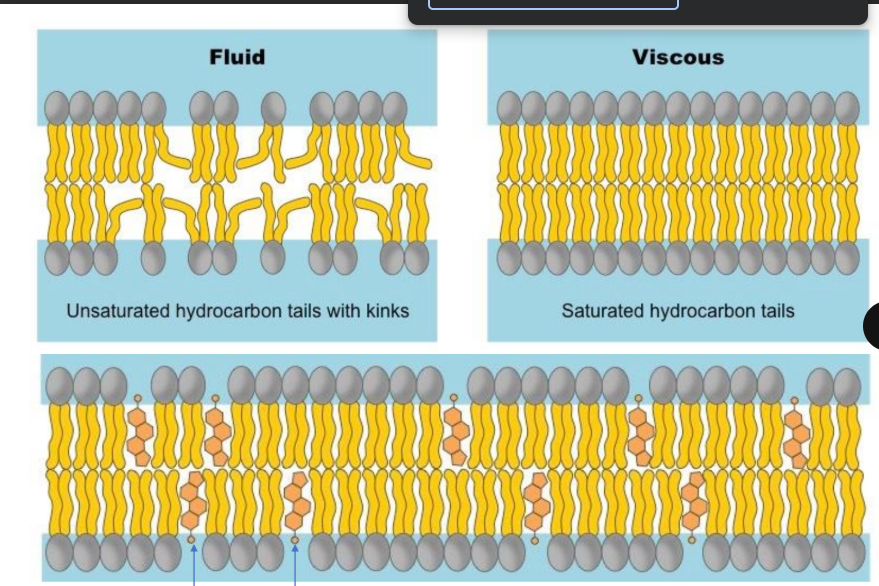
role of cholesteriol = more fluid while fatty acid tail saturation = less fluidity
molecules associated with membrane (protein and carbohydrates)
Glycoprotein, peripheral protein, transmembrane/integral membrain proteins, and glycolipids
glycolipids
lipids with sugar attached
glycoproteins
proteins with sugar attached
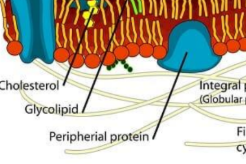
Peripheral protein
A protein loosely bound to the surface of a membrane or to part of an integral protein and not embedded in the lipid bilayer.
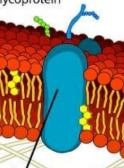
Integral protein
Typically a transmembrane protein with hydrophobic regions that extend into and often completely span the hydrophobic interior of the membrane and with hydrophilic regions in contact with the aqueous solution on either side of the membrane (or lining the channel in the case of a channel protein)
Active vs passive transport
Solute transported against concentration gradient (low to high) in which ATP is used & pumps is the opposite of diffusion vs Follows concentration gradient of high to low & using no energy/ATP
Simple diffusion vs facilitated diffusion
Simple (no proteins) & facilitated diffusion (membrane protein used to diffuse solute across membrane) but still following concentration gradient
solute pumping concentration gradient as energy source/stored energy and role in cellular processes (cellular respiration etc..)
Movement of molecules is from high concentration to low concentration, pumping means to move from low to high which requires energy. In cellular processes, concentration gradient is potential energy, when particles mvoe down gradient (high to low), cells access stored potential energy
Endocytosis
Cellular uptake of biological molecules and particulate matter via formation of new vesicles from the plasma membrane
Exocytosis
The cellular secretion of biological molecules by the fusion of vesicles containing them with the plasma membrane.
Phagocytosis
endocytosis of large particles (bacterium)
Pinocytosis
endocytosis of small solutes near vesicle formation, triggered by ligand/molecule binding to a receptor
Bulk Transport
Transporting large solute/large quantity of small solutes via vesicles/phospholipid bilayer membrane in a sphere
Osmosis
Means that water diffuses across membrane by (from low solute to high solute)
Aquaporin
A channel protein in the plasma membrane of a plant, animal, or microorganism cell that specifically facilitates osmosis, the diffusion of free water across the membrane and down a concentration gradient (high to low water conc or low to high solute conc)
Water potential calculation
(ψ) = solute potential + pressure potential (in bars)
(ψ) Solute potential
0 = pure water, (ψ) decreases as solute concentration increases, positive not possible
(ψ) Pressure potential
pressure push water > pressure +, pressure pull water > pressure -, open container = 0
Net movement of water for water potential
area of higher ψ to lower due to water potential gradient moving from low solute concentration to high solute concentration (& flows to low water potential value)
NaCL - water potential
dissociates into 2 ions (Na and Cl) for water potnetial while sucrose = 1
Cell Surface Area/Plasma Membrane Area
membrane transport capability of cell due to metabolic needs (glucose)/waste (CO2) and efficiency > Bigger cell = more metabolic demands but bigger surface area = efficient transport
Endosymbiosis
Theory that mitochondria and chloroplasts were once prokaryotes that began living inside large prokaryotic cells
Evidence of endosymbiosis for mitochondria and chloroplasts
Multiple membranes (inner is from prokaryotic, outer is from host), DNA (circular chromosomes in both like prokaryotes), ribosomes (similar to prokaryotes, and divides like prokaryotes
Aerobic vs anaerobic respiration
A catabolic pathway that consumes oxygen (O2) and organic molecules, producing ATP. (effcieint catabolic pathway & pro/eukaryotic) vs o2 being low or nonexistent, producing ~2 ATP per glucose molecule (alcoholic fermentation for yeast/plants and lactic acid for animals)
Fermentation vs respiration
catabolic process that makes a limited amount of ATP from glucose without an electron transport chain and that produces a characteristic end product, such as ethyl alcohol or lactic acid. vs catabolic pathways of aerobic and anaerobic respiration, which break down organic molecules and use an electron transport chain for the production of ATP.
Stages & location n Cellular respiration - eukaryotic cell
1. Glycolysis (cytosol)
2. Intermediate step (mitochondrial matrix)
3. Krebs cycle (matrix)
4. Electron transport chain (ETC)/oxidative phosphorylation (inner mitochondrial membrane)