Diabetes - Pharmacology
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
112 Terms
Which organ does glucagon primarily work on?
The liver
What stimulates insulin release in the fed state?
increasing blood sugar
presence of food in intestines
other nutrients
Function of epinephrine in glucose homeostasis
promotes glycogenolysis
promotes gluconeogenesis
inhibits glucose utilization
promotes lipolysis
Function of cortisol in glucose homeostasis
Promotes gluconeogenesis
Function of growth hormone in glucose homeostasis
Decreases peripheral glucose utilization
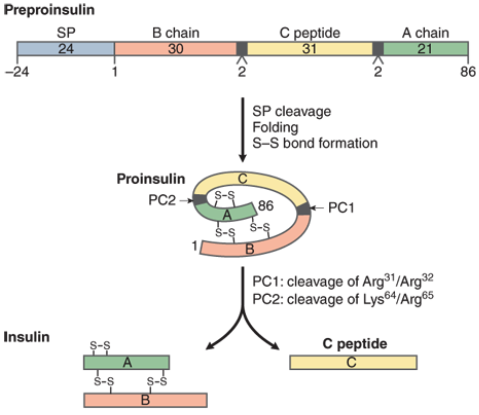
Explain the synthesis of endogenous insulin
pancreatic B-cells synthesize pre-pro-insulin
removal of SP domain = pro-insulin
3 disulfide bridges form and c-peptide is removed
result is insulin (51 amino acids and A & B chains linked by disulfide bonds)
What is the primary regulator of insulin secretion?
Glucose
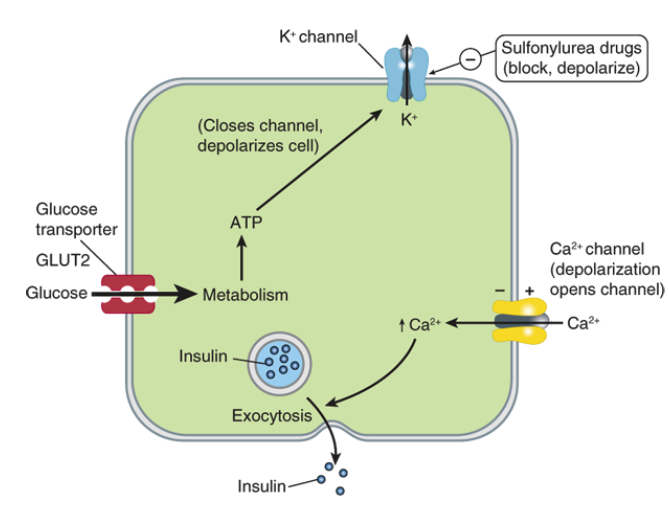
Explain how insulin is secreted from a beta cell
beta-cell is hyperpolarized in resting state with insulin in vesicles
glucose enters cell through glucose transporters
glucose is metabolized in the cell, which increases ATP production
more ATP leads to closing of ATP-sensitive K+ channel
less K+ leaves the cell, so membrane becomes depolarized
depolarization opens voltage-gated Ca2+ channels
Ca2+ enters cell, leads to exocytosis of insulin-filled vesicles
What is the primary effect of insulin at target tissues?
Stimulates uptake of glucose in these tissues
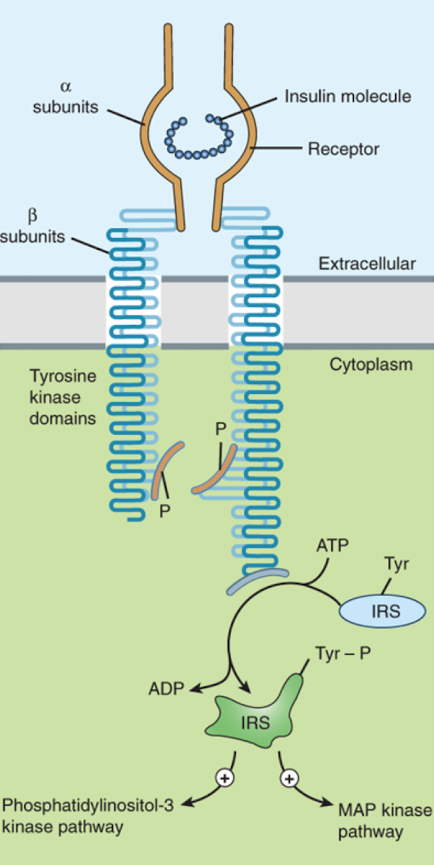
What are the cellular effects caused by insulin when it binds an insulin receptor?
changes in substrate and ion transport
regulation of protein and enzyme activity
translocation of proteins
changes in gene transcription
activation of growth and differentiation-promoting pathways
What type of receptor is the insulin receptor?
Similar to tyrosine-kinase receptor, but receptor is composed of two subunits (alpha and beta)
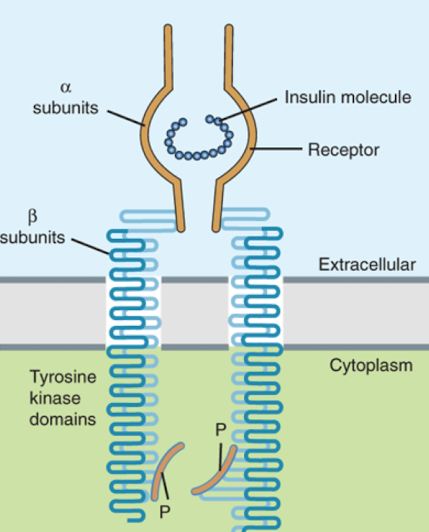
How does the insulin receptor change upon binding insulin?
Binding of insulin to alpha subunit brings the beta subunits together (they dimerize)
Which part of the insulin receptor has tyrosine kinase activity?
The beta subunits (they phosphorylate each other, resulting in activation of several other proteins)
What is the half-life of endogenous insulin?
5-9 minutes
What is the key metabolic step in insulin breakdown?
Breakage of disulfide bonds by insulinase (glutathione insulin transhydrogenase)
Where can insulin be metabolized?
liver
kidneys
muscle
How much insulin metabolism occurs in the kidneys?
Only ~20%, so don’t need to renally adjust!
How does SC injection of insulin differ from pancreatic release?
In SC:
rise and fall of insulin is slower (takes time for absorption)
additional sources of variability (injection site, type of insulin)
How long before a meal does someone need to inject insulin if they are using regular insulin?
~30 minutes before meal (takes 30-45 min for onset)
Why is insulin absorption slow when injected SC?
In solution, insulin forms a hexamer which must dissociate before the monomers can be absorbed into systemic circulation
How is the rate of hexamer dissociation changed?
By modifying the amino acid sequence of regular insulin
True or false. Regular insulin has the same AA sequence as endogenous insulin.
True
Can regular insulin be administered via IV?
Yes
What changes to AA are made in insulin lispro?
Lysine at position 29 is swapper with proline at position 28
What changes to AA are made in insulin aspart?
Proline at position 28 is replaced by an aspartate
What is the structural difference between rapid-acting insulin aspart and Fiasp?
Fiasp has nicotinamide
What changes to AA are made in insulin glulisine?
Lysine at position 29 is replaced by a glutamate and the asparagine at position 3 is replaced by lysine
Why is insulin NPH cloudy?
Regular insulin complexes with NPH and zinc
Why is the absorption of NPH slower than regular insulin?
Proteases are needed to degrade the protamine before absorption, so peak is delayed and the duration is prolonged
What changes to AA are made in insulin detemir?
Threonine at position 30 is deleted and lysine at position 29 is myristoylated to increase aggregation and albumin binding
(myristoylated = addition of larger fatty molecule)
How is insulin detemir released slowly over time?
Albumin-bound insulin forms a depot that is slowly released and able to distribute to target tissues
What changes to AA are made in insulin glargine?
Two arginine residues are added to the B chain and asparagine at position 21 on the A chain is replaced by glycine
What do the AA changes for insulin glargine lead to?
Result in an increased solubility at acidic pH
(soluble in solution (acidic) but precipitates in body to form a depot that is slowly re-solubilized and absorbed)
Which insulin cannot be mixed with other types?
Insulin glargine (will precipitate at normal solution pH)
What changes to AA are made in insulin degludec?
Threonine at B30 is deleted and hexadecanedioic is added to the lysine at B29 via y-L-glutamyl spacer
Why does insulin degludec have such a prolonged effect?
Forms a multihexameric complex that dissociates slower than regular insulin and also binds to albumin
(different from glargine and detemir)
Why is insulin icodec able to be dosed once weekly?
Has strong, reversible binding to albumin which delays SC absorption
Has additional AA substitutions that increase resistance to degradation
What is the biosimilar of Lantus?
Basaglar
What is the biosimilar of Humalog?
Admelog
Why is insulin NPH used less often now?
Had a higher incidence of allergic reactions
Signs and sx of nocturnal hypoglycemia
nightmares
restless sleep
profuse sweating
morning headache
morning “hangover”
could also be asymptomatic
What is a risk of glucagon tx?
Overshooting and causing a spike in glucose
What causes the allergic reactions that are seen with insulin?
The antigens are protein contaminants, not the insulin itself
Do auto-insulin antibodies that are developed cause issues with insulin treatment?
They are not associated with therapeutic resistance
What is glucagon derived from?
Proglucagon (precursor protein)
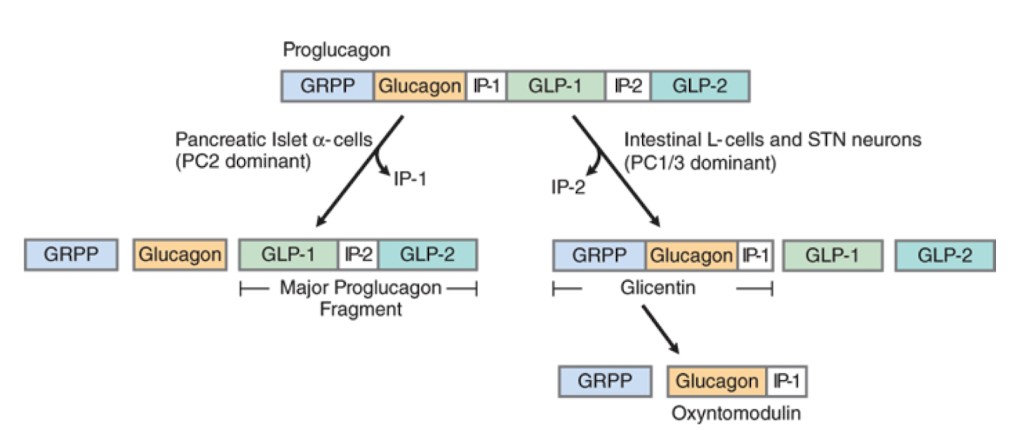
What kind of receptor is the glucagon receptor?
GPCR (coupled G alphas)
What does glucagon promote?
glycogenolysis
gluconeogenesis
ketogenesis
What is glucagon used for clinically?
hypoglycemia tx
reversal of beta blocker overdose
bowel radiology
How many distinct classes of drugs are there for type 2 DM?
9
What is the primary mechanism of sulfonylureas?
Stimulate the release of insulin from beta cells
What are the secondary mechanisms of sulfonylureas?
reduce hepatic insulin clearance
stimulation of somatostatin release (prevents growth hormone, catecholamines)
reduced serum glucagon
Where in the beta cells do sulfonylureas target?
The SUR1 subunit of the ATP-sensitive potassium channel
(blocks and depolarizes cell - leads to insulin release)
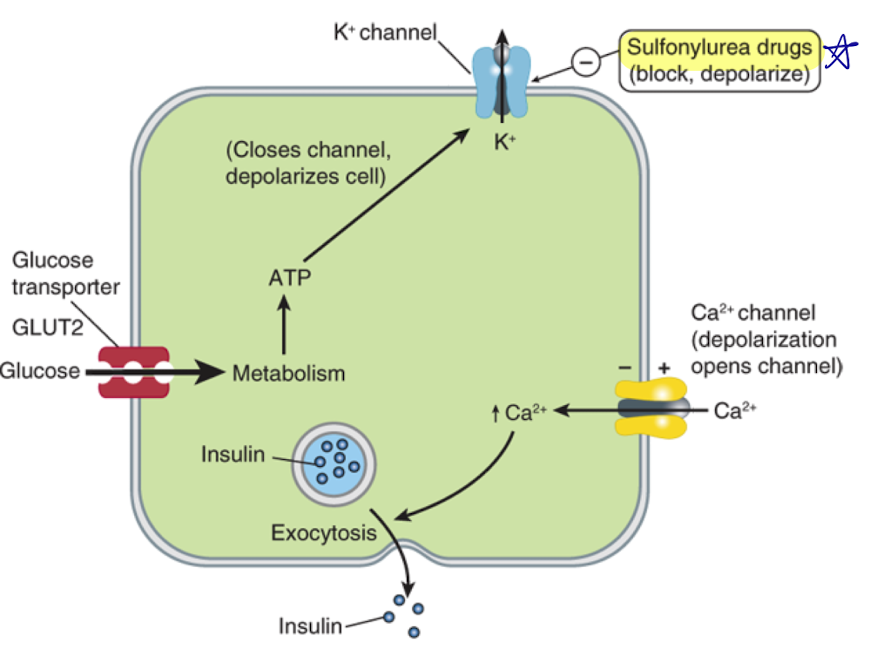
Are certain sulfonylureas more effective than others?
All equally efficacious at equipotent doses
Which generation of sulfonylureas is more potent?
2nd gen are more potent than first gen
1st gen sulfonylureas
chlorpropamide
tolbutamide
2nd gen sulfonylureas
glyburide
gliclazide
glimepiride
Are sulfonylureas used in renal impairment?
Yes
How are sulfonylureas metabolized?
In liver
ADRs of sulfonylureas
mainly hypoglycemia
weight gain
N/V
hypersensitivity
Example of a meglitinide
Repaglinide
Mechanism of action of meglitinides
Binding to ATP-sensitive potassium channels on beta cells
(bind different site than sulfonylureas - but overall same effect)
Do sulfonylureas or meglitinides have higher risk of hypoglycemia?
Sulfonylureas have higher risk
(meglitinides have faster onset and shorter duration of action)
How are meglitinides metabolized?
Primarily in liver
Primary ADR of meglitinides
Hypoglycemia
What is the effect of biguanides?
Increased insulin sensitivity in target tissues
Does metformin have hypoglycemic or antihyperglycemic activity?
Antihyperglycemic
What are the proposed mechanisms of action of metformin?
reduced hepatic gluconeogenesis (via activation of AMPK)
stimulation of glycolysis at target tissue (increase uptake)
decreased GI glucose absorption
reduced plasma glucagon levels
How is metformin excreted?
Excreted unchanged entirely by kidneys
Does metformin need to be renally dosed?
Yes - excretion is dependent on renal function
How is metformin transported into target tissues?
By the organic cation transporter (OCT 1)
(genetic variation in transporter can cause differences in response)
True or false. Metformin carries a risk of hypoglycemia.
False
Primary ADRs for metformin
GI (anorexia, N/V/D
long-term use - vitamin B12 deficiency
What effect does metformin have on weight?
Weight-neutral
Examples of thiazolidinediones
rosiglitazone
pioglitazone
Where do thiazolidinediones bind?
Bind and activate peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARy)
Mechanism of action of thiazolidinediones
Change transcription genes that regulate metabolism and indirectly increases insulin sensitivity
What are the primary targets of thiazolidinediones
Muscle and adipose tissue
(Note: works on other tissues as well like heart, kidneys, bones, etc., so has wide SE profile)
What is required for thiazolidinediones to work?
Sufficient insulin
What type of receptor is PPARy?
A nuclear receptor
Why are thiazolidinediones contraindicated in HF?
They act on the kidneys to increase sodium and fluid retention
Example of alpha-glucosidase inhibitor
Acarbose
Mechanism of action of acarbose
binds to alpha-glucosidase with higher affinity than dietary disaccharides
impairs breakdown of sugars so absorption of carbs is delayed
this means post-prandial BGs are reduced
What is the mechanism of acarbose dependent upon?
The presence of dietary sugars (so must be dosed before meals)
ADRs of alpha-glucosidase inhibitors
Limited to GI tract (flatulence, bloating, abdominal discomfort, diarrhea)
If someone on acarbose has a hypo episode, what cannot be used to treat them?
Sucrose (will have slow breakdown)
Can use glucose, milk (lactose), or honey (fructose and glucose)
When are incretins released?
After meals
Function of incretins
Promotes/compliments glucose-induced insulin secretion
(can promote insulin secretion before glucose levels begin to rise)
How quickly is normal GLP-1 broken down?
Within 1-2 minutes by DPP-IV
Where do GLP1ras bind?
Gas-coupled GLP-1 receptor on beta cells (promotes insulin secretion)
Secondary effects of GLP1ras
reduced glucagon secretion
slowing gastric emptying
weight loss
Examples of GLP-1ras
exenatide
lixisenatide
liraglutide (Victoza)
dulaglutide (Trulicity)
semaglutide
tirzepatide (Mounjaro)
Which is the only oral GLP-1ra?
Semaglutide (Rybelsus)
Which GLP-1ras are mostly cleared by the kidney?
Exenatide and lixisenatide
Which GLP-1ras are metabolized via protein metabolic pathways?
Liraglutide and dulaglutide
What are the most common ADRs of GLP-1ras?
N/V (due to delayed gastric emptying)
How does tirzepatide differ from other GLP-1ras?
Tirzepatide is a dual GIP and GLP-1ra
Do DPP-IV inhibitors cause reduced gastric emptying?
No (differs from GLP-1ras)
How are DPP-IV inhibitors typically dosed?
Once daily
___% inhibition of DPP-IV correlated to a doubling of endogenous GLP-1
80-95%
What kinds of inhibitors are most DPP-IV inhibitors?
Most are competitive inhibors
(saxagliptan covalently binds and inhibits)