A&P Practical: Key Terms & Definitions for Biology
1/173
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
174 Terms
dorsal
toward the back
ventral
toward the belly
cranial
toward the head
caudal
toward the tail
rostral
toward the nose
palmar
bottom surface of forelimb digits
plantar
bottom surface of hindlimb digits
medial
towards median plane
lateral
away from median plane
proximal
Closer to the point of attachment
distal
away from the point of attachment
deep
Away from the body surface; more internal
superficial
near the surface
occipital bone
single bone that forms the "base" of the skull. houses foramen magnum and condyles

occipital condyle
forms a joint with the atlas
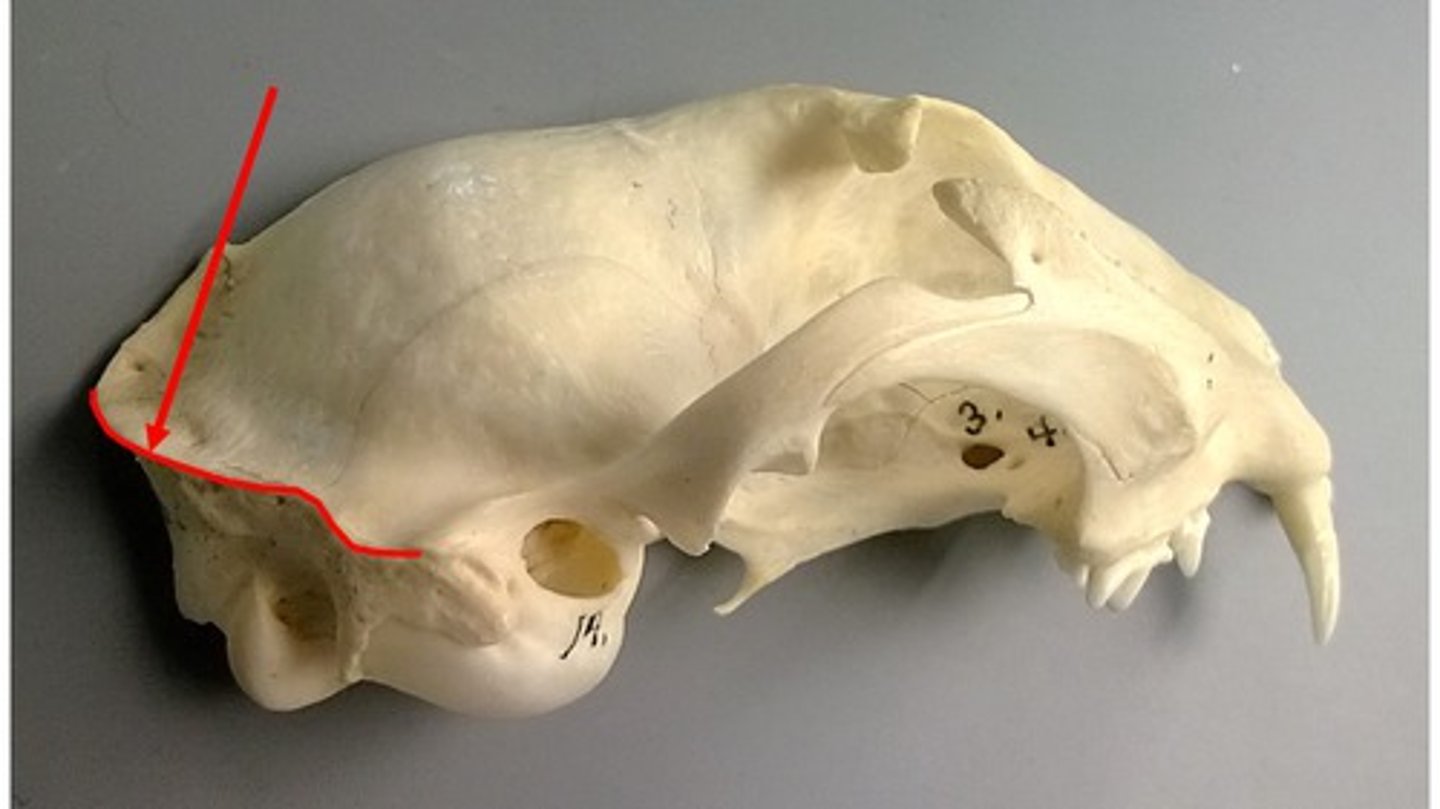
nuchal crest
Part of the skull where the neck muscles attach
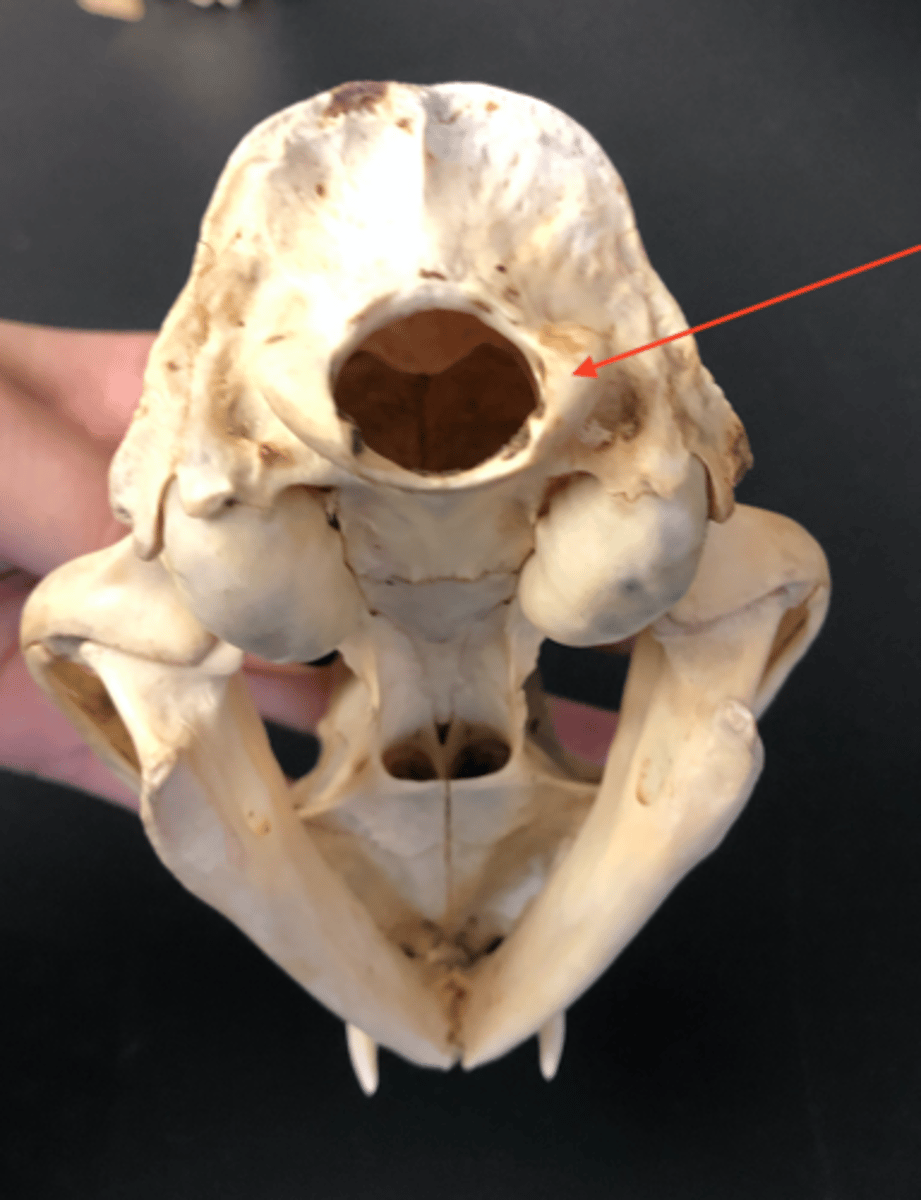
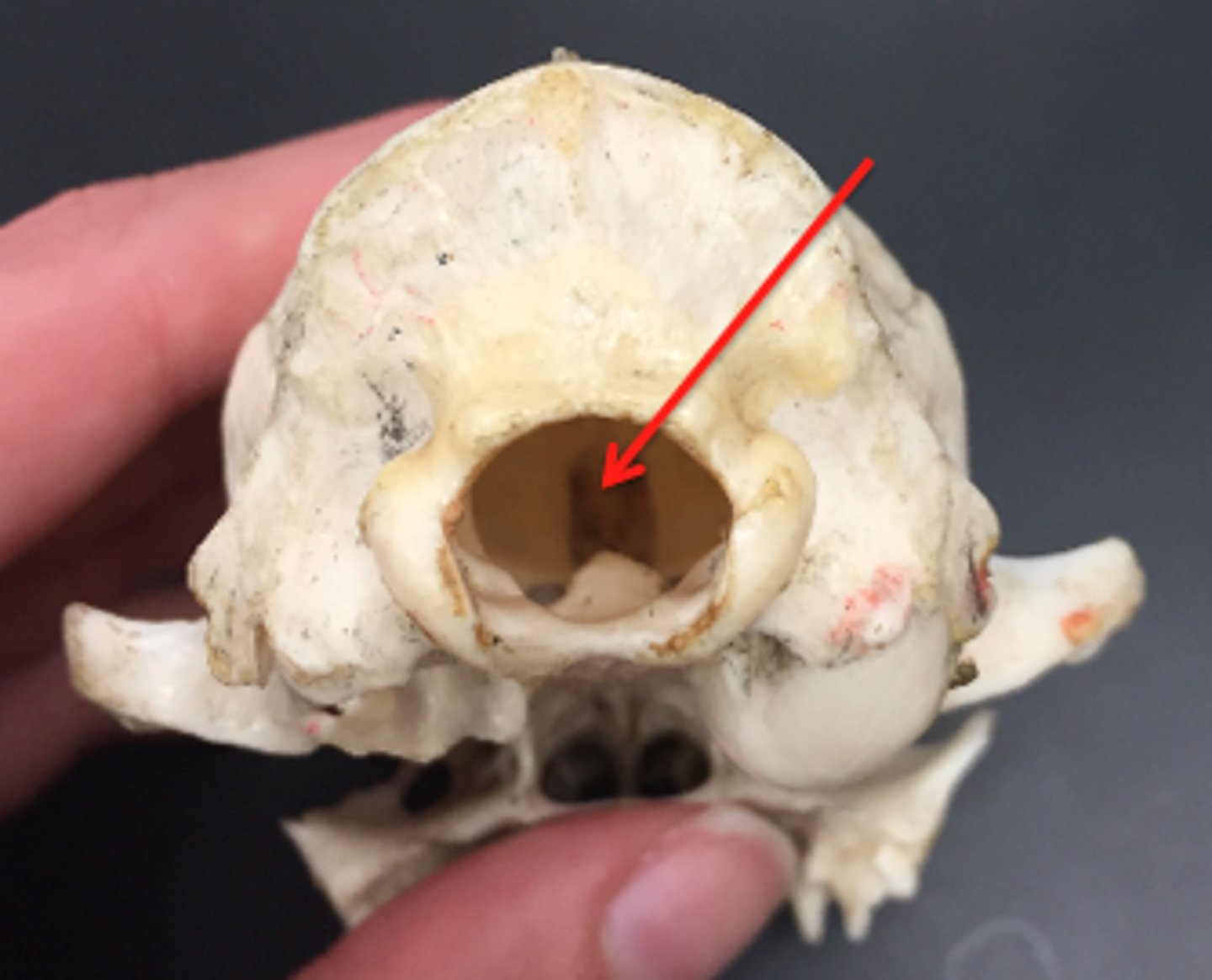
foramen magnum
large opening where the spinal cord exits the skull
temporal bone
paired bones that form the sides of the head in the ear region, forms portion of zygomatic arch. below parietal bone. forms TMJ
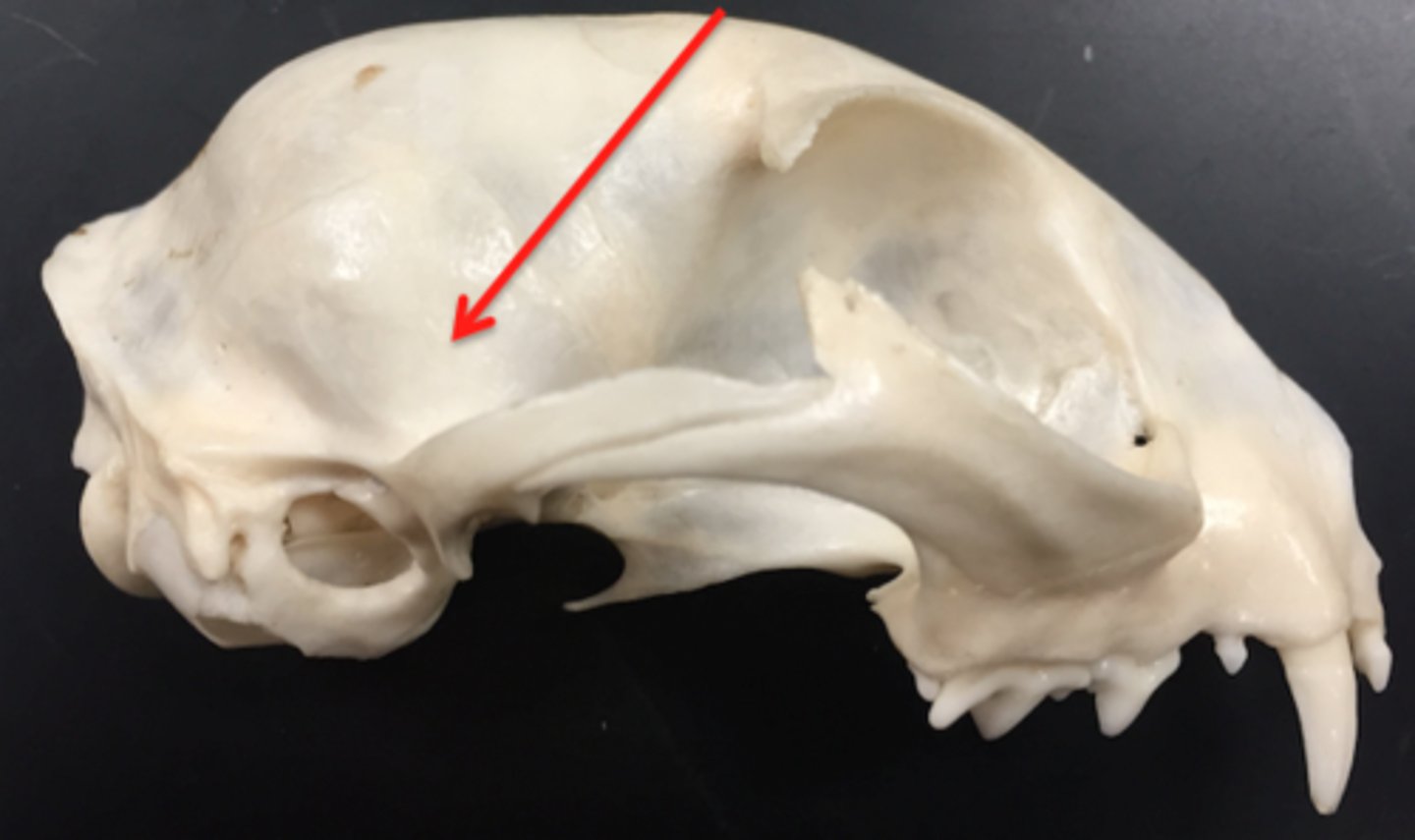
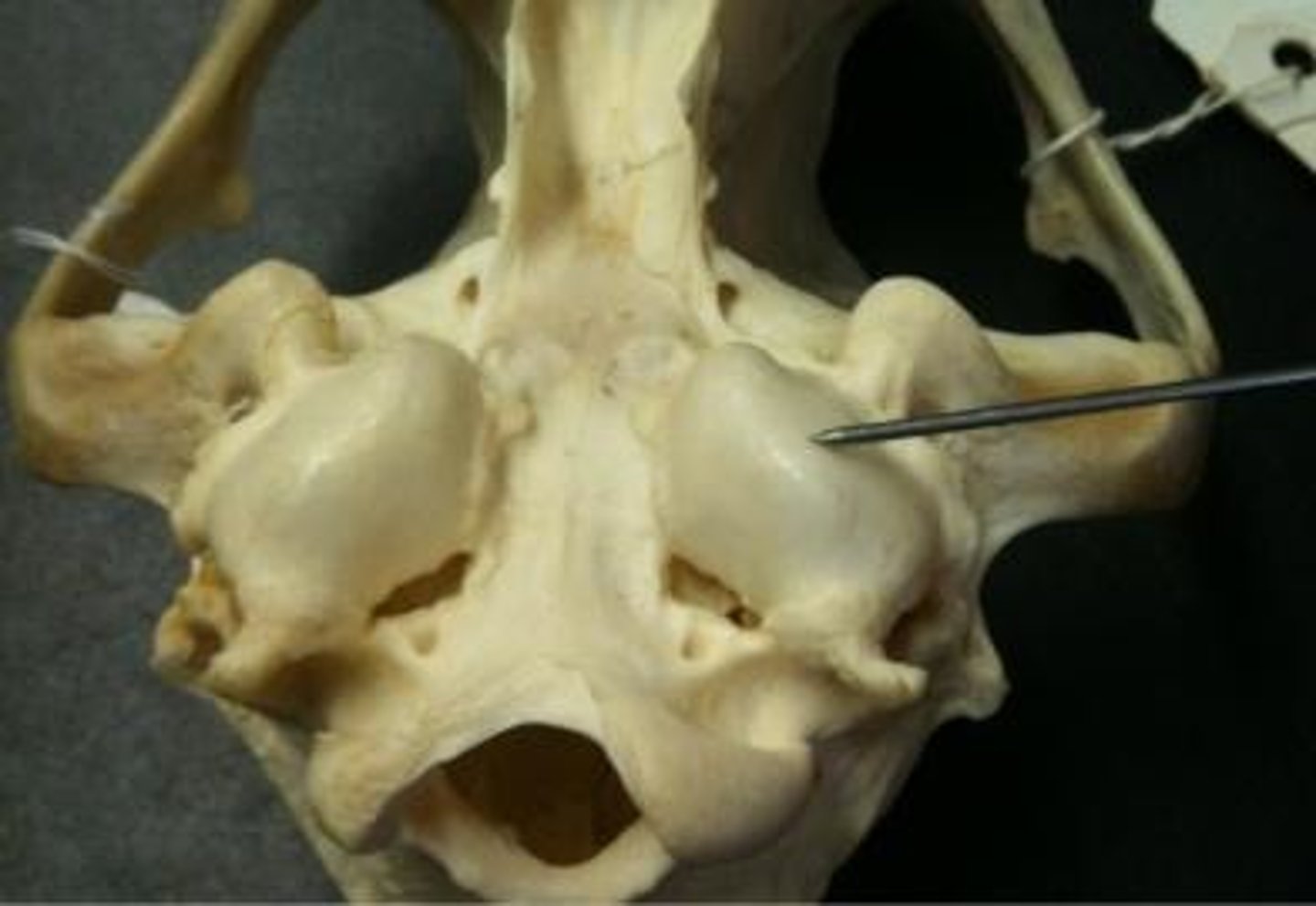
tympanic bullae
egg shaped swelling on the ventral surface, contains middle ear structures
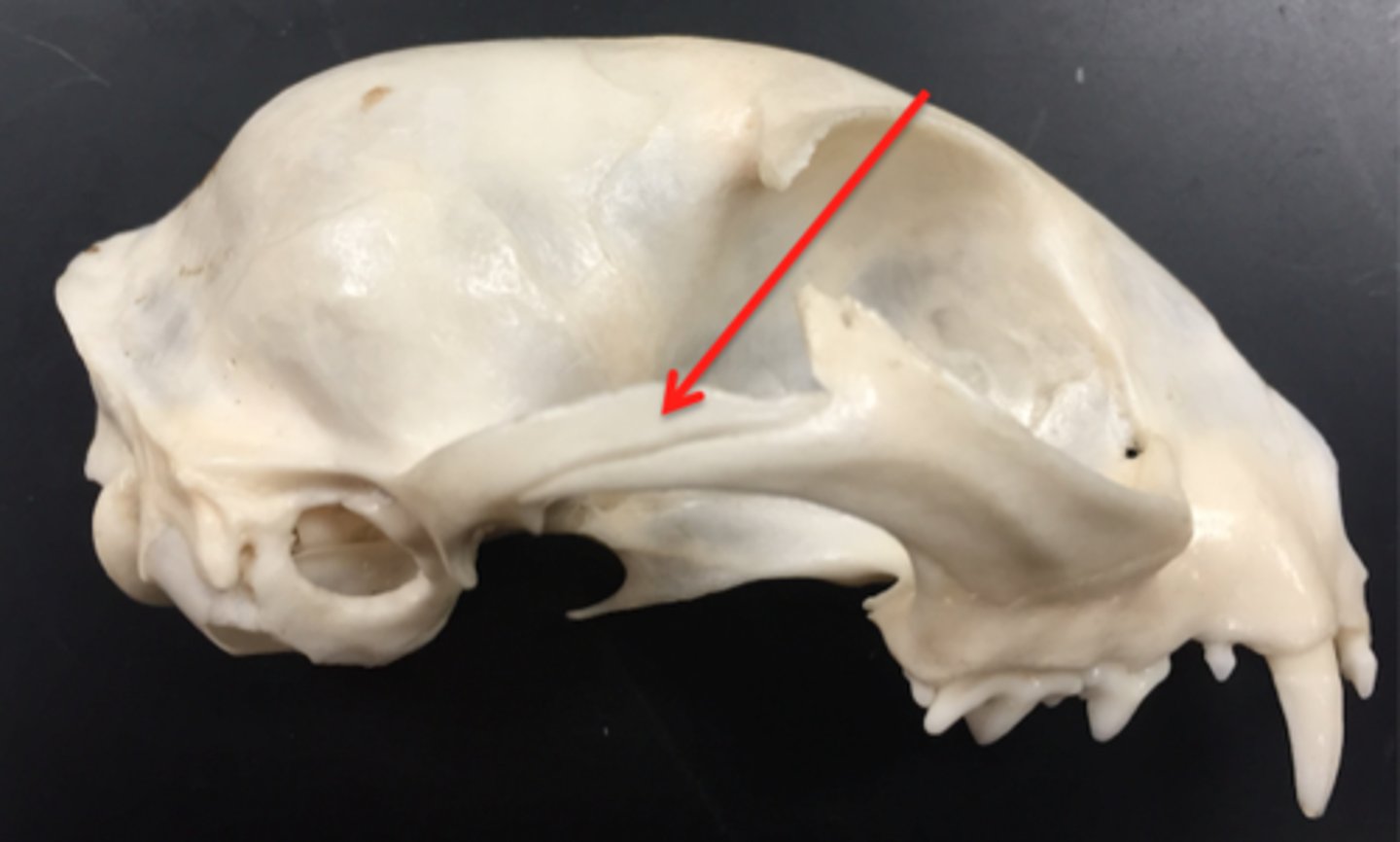
zygomatic process (temporal)
a projection of the temporal bone that forms part of the zygoma
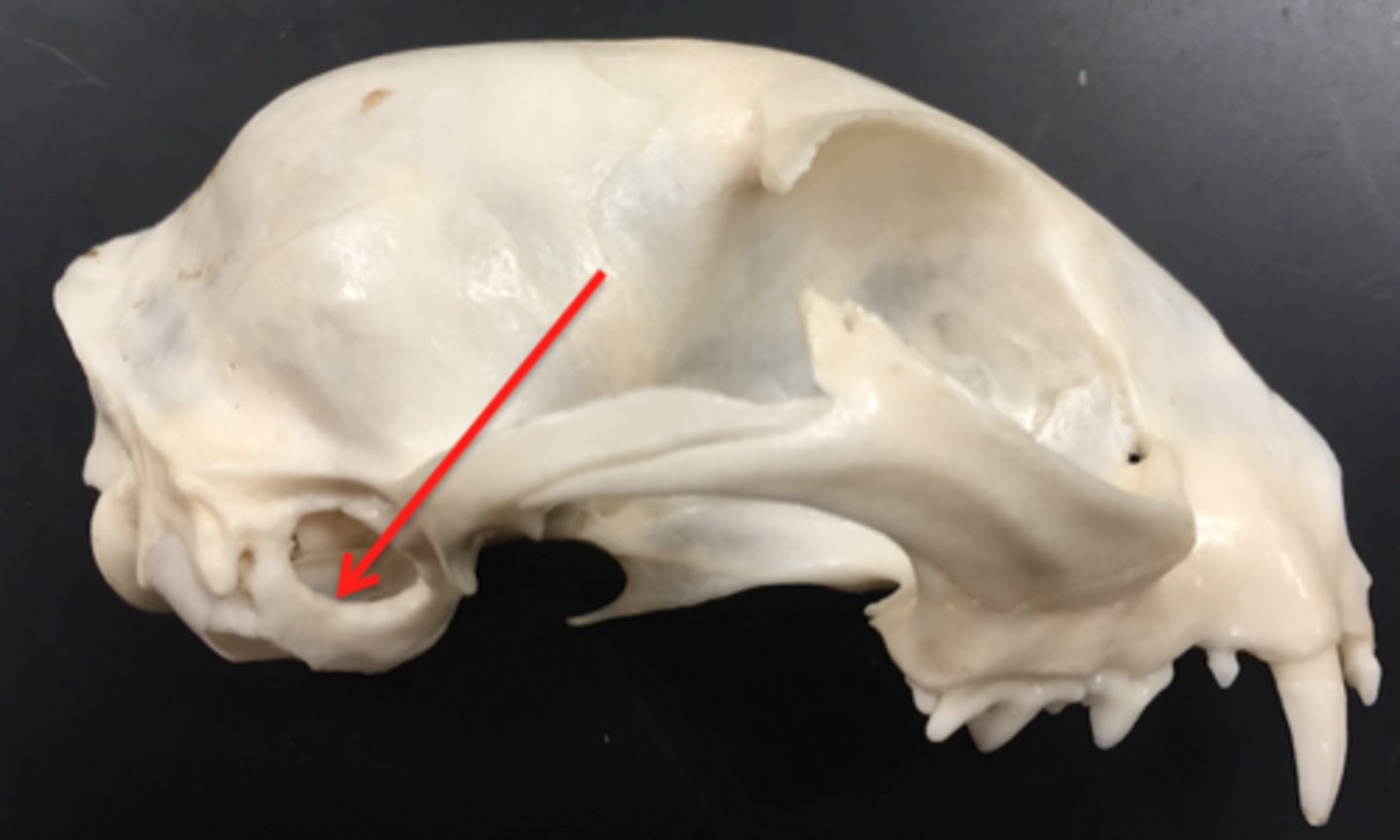
external auditory meatus
opening that leads to the middle and inner ear cavities
zygomatic bone
cheekbones, paired, forms portion of eye orbit and portion of zygomatic arch
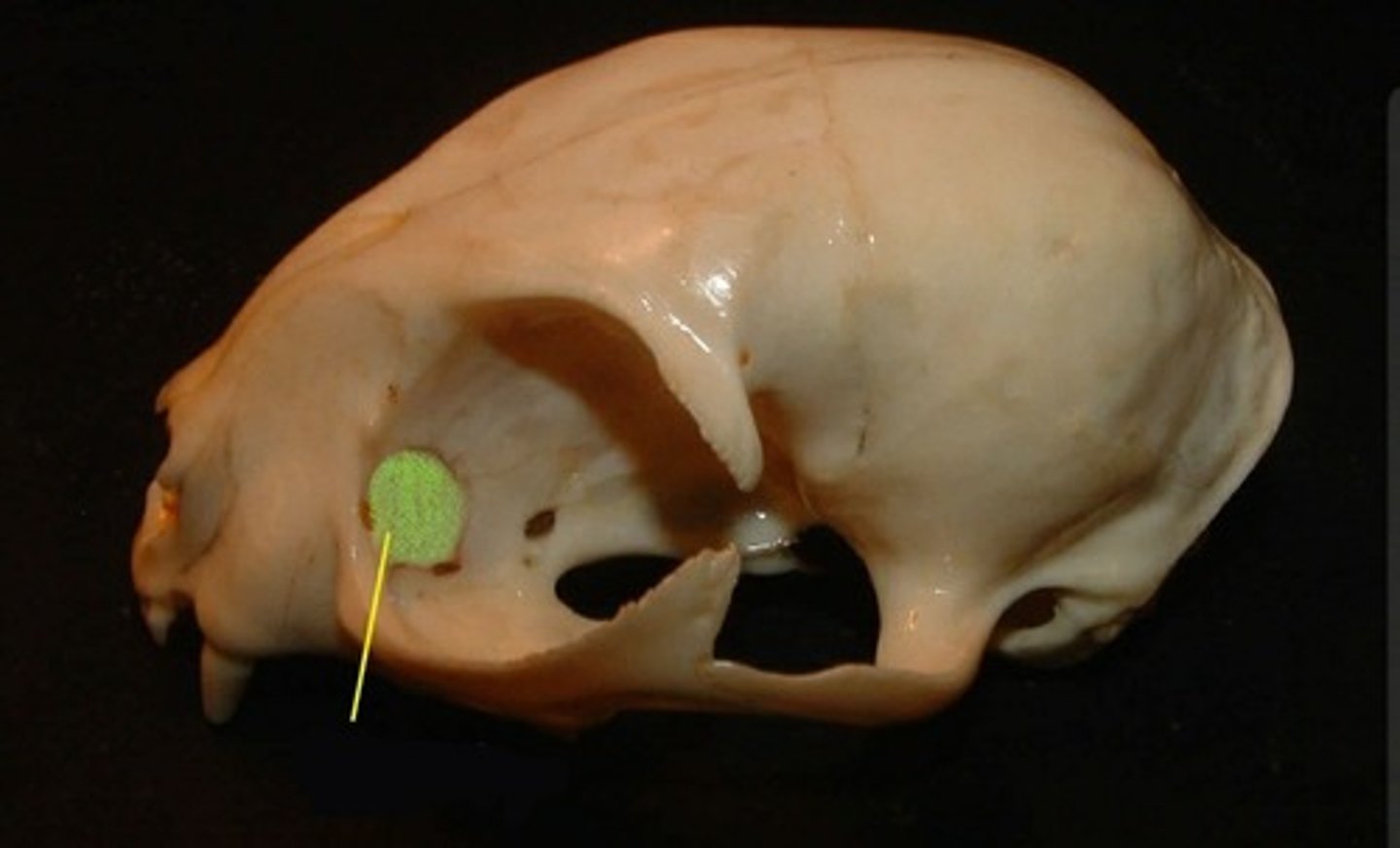
lacrimal bone
small fragile bone making up part of the front inner walls of each eye socket and providing room for the passage of the lacrimal ducts
nasolacrimal canal
allows passage of lacrimal duct
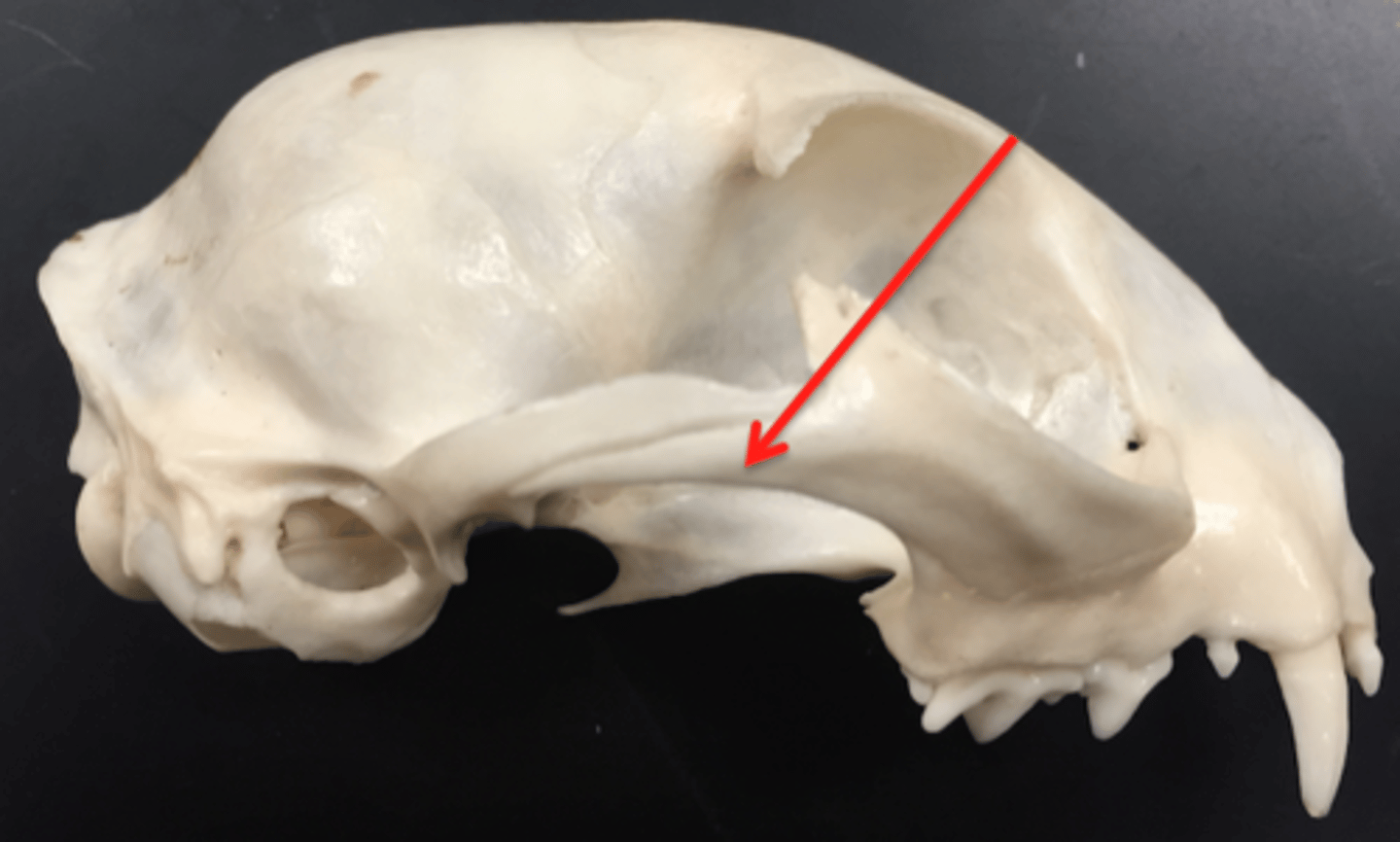
parietal bone
either of two skull bones between the frontal and occipital bones and forming the top and sides of the cranium
sagittal crest
A ridge of bone that runs down the middle of the cranium like a short Mohawk. This serves as the attachment for the large temporal muscles, indicating strong chewing.

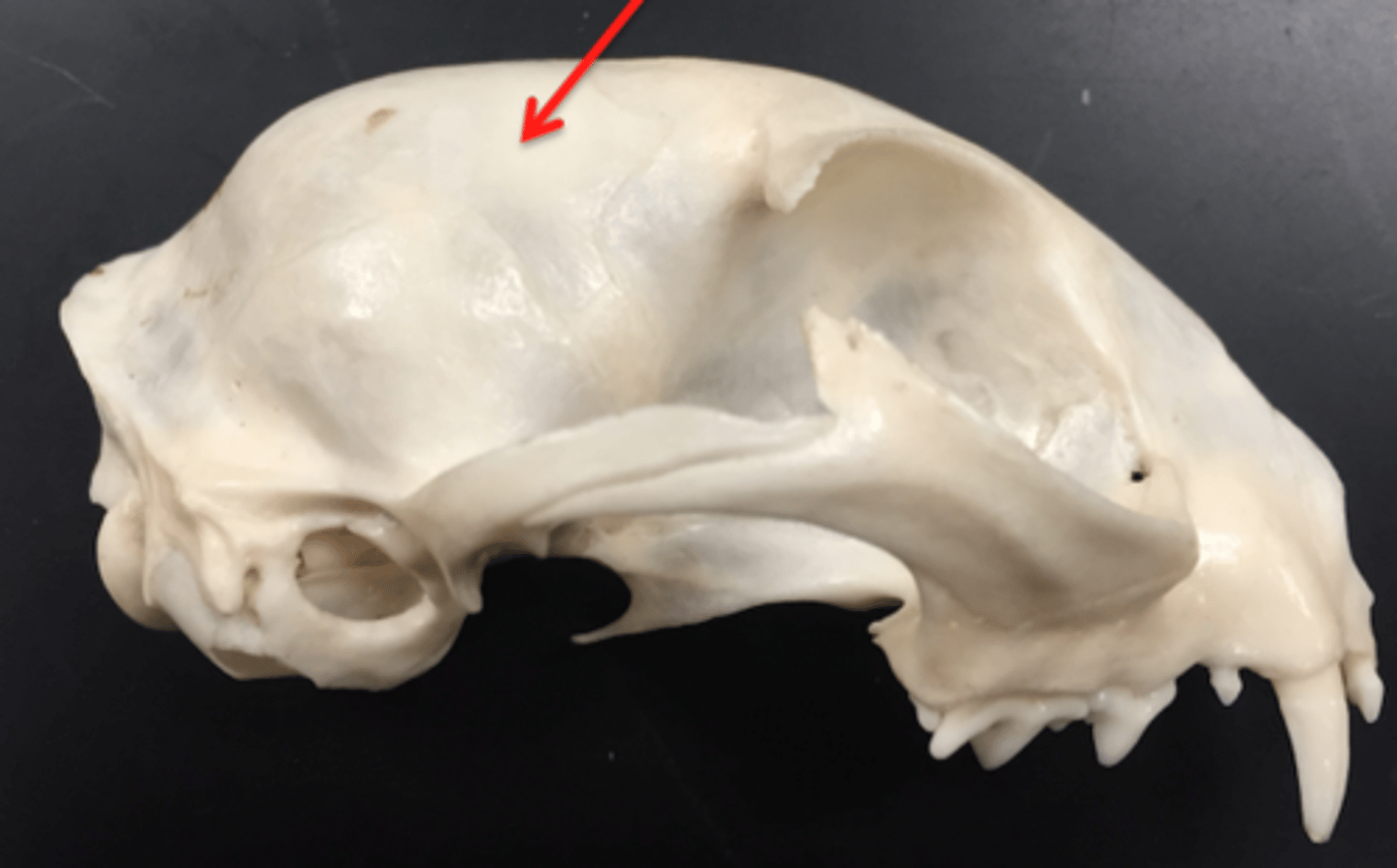
frontal bone
paired, forms forehead part of skull, contains large frontal sinuses. rostral to temporal
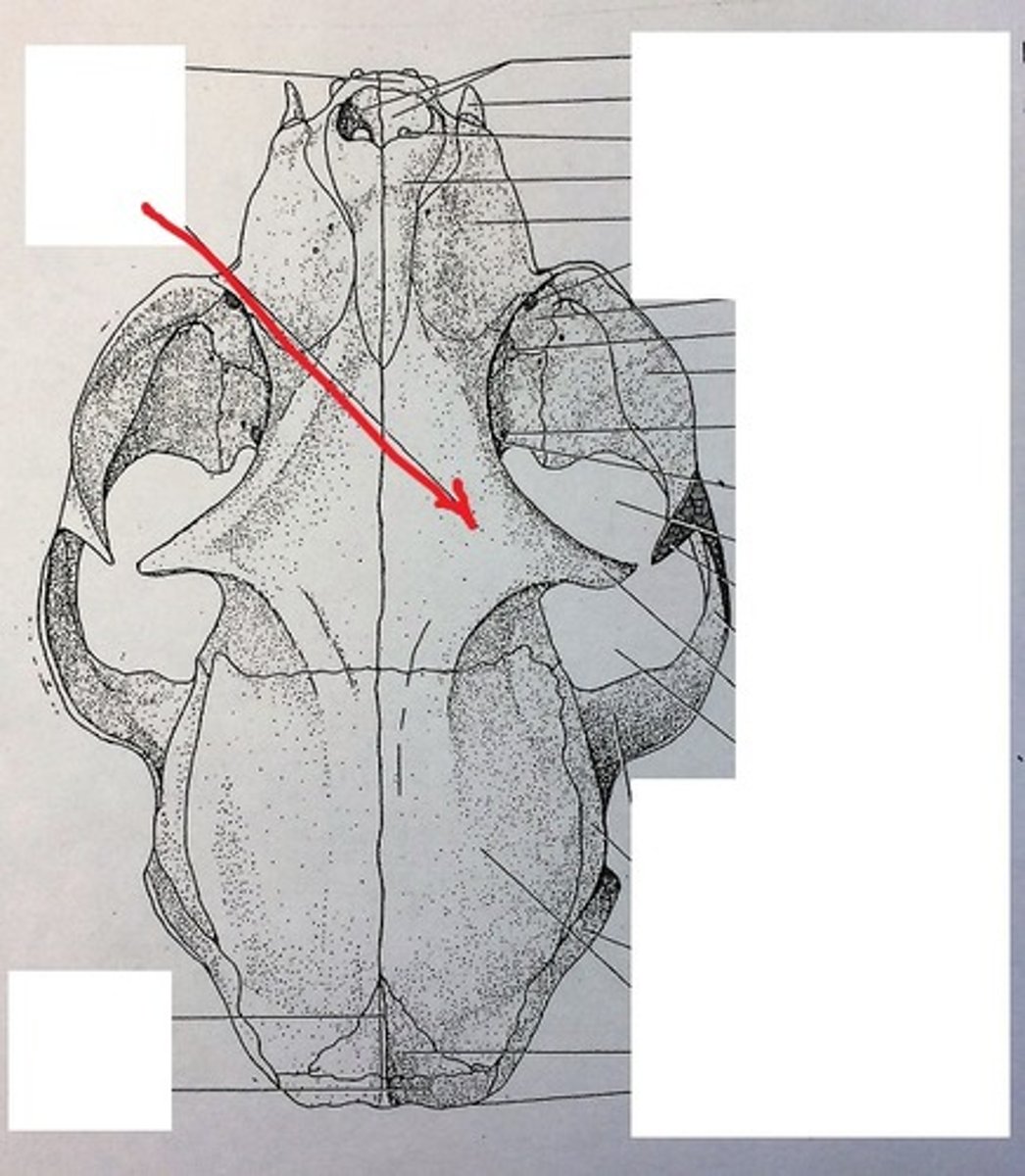
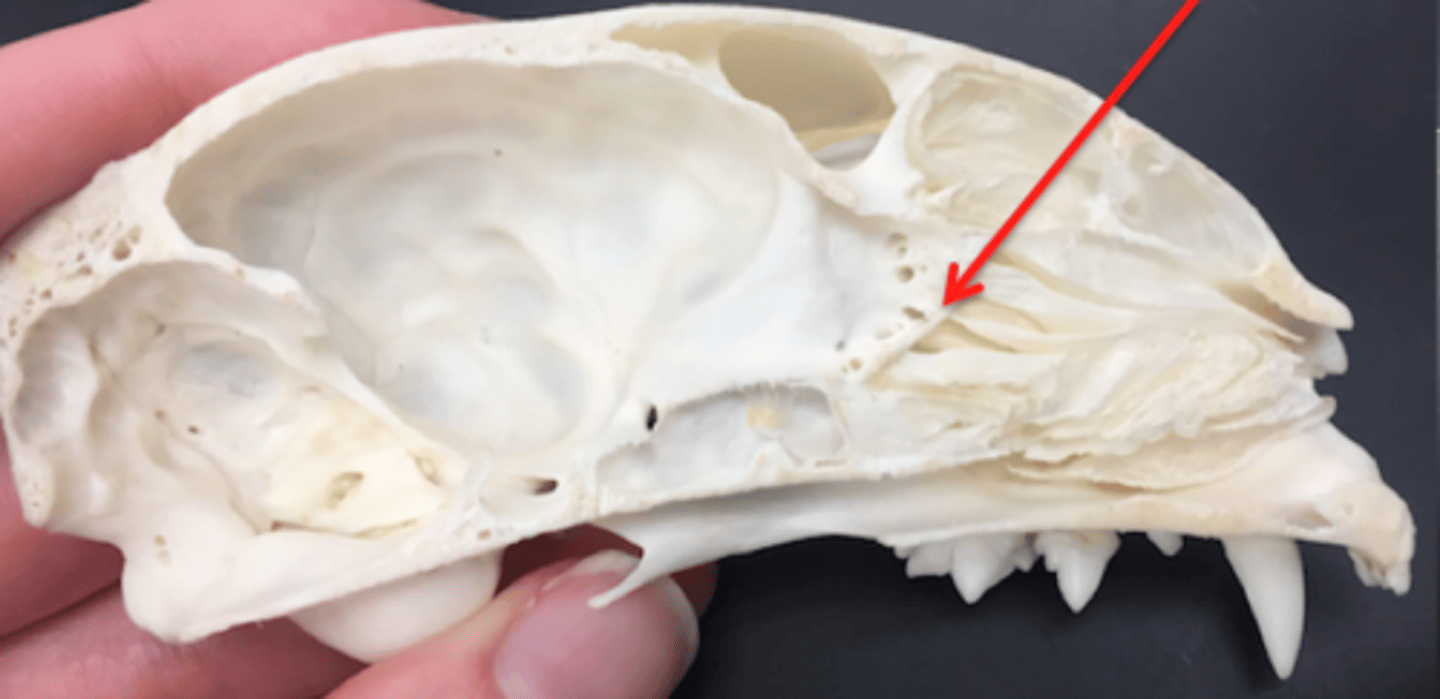
ethmoid bone
forms part of the posterior portion of the nose, the orbit, and the floor of the cranium
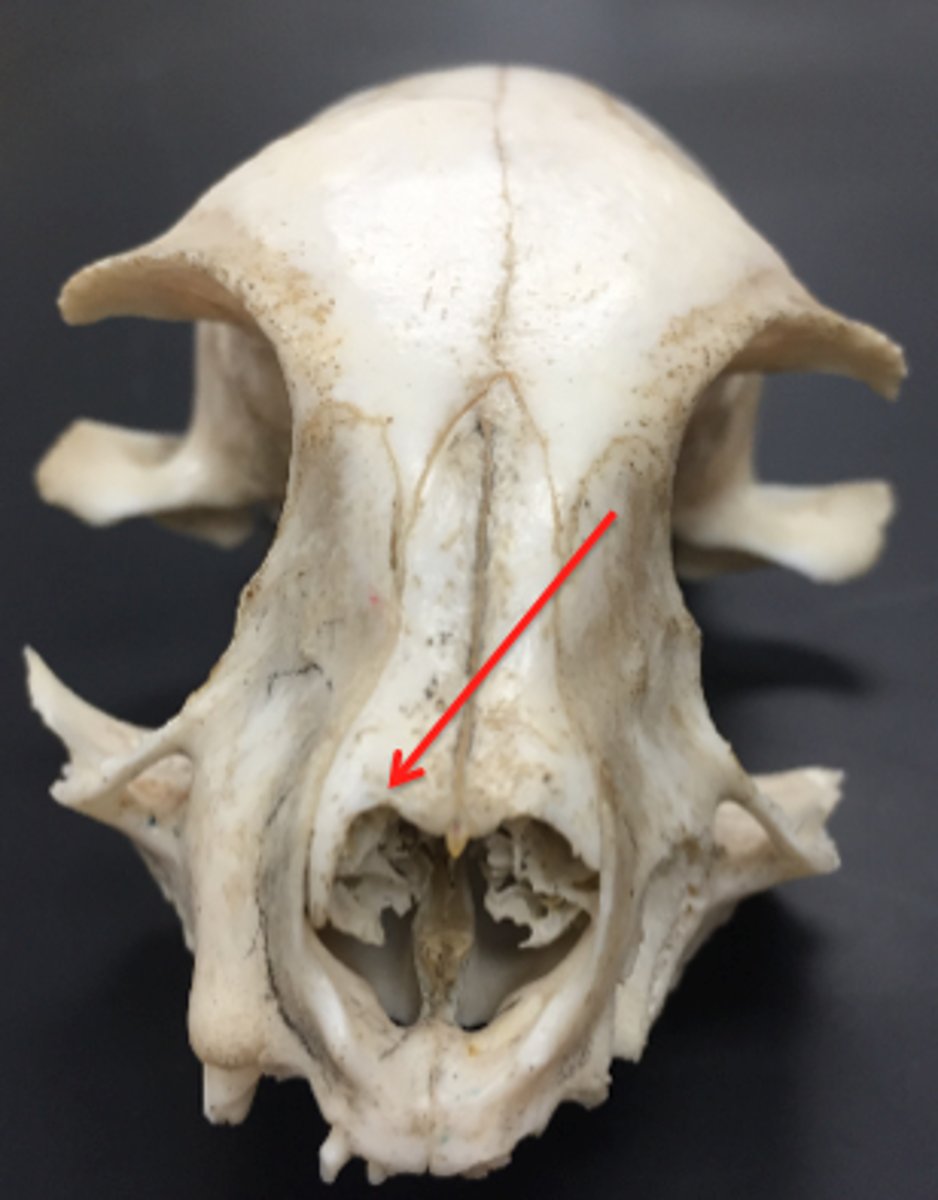
nasal bone
paired, forms the bridge of nose, dorsal part of nasal cavity
maxillary bone
paired, make up most of upper jaw, house upper canine, upper premolar, and molar teeth. forms portion of hard palate
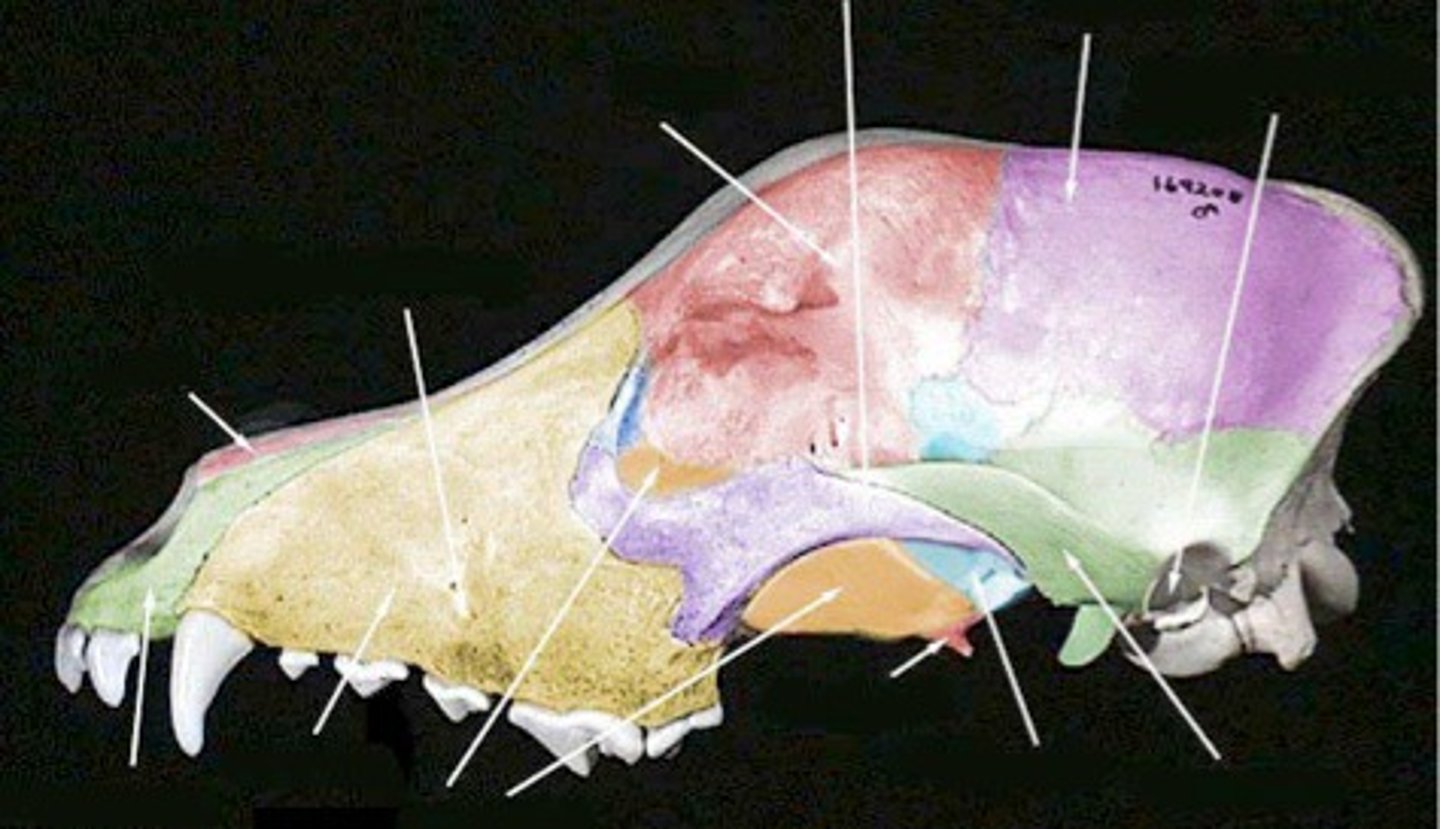
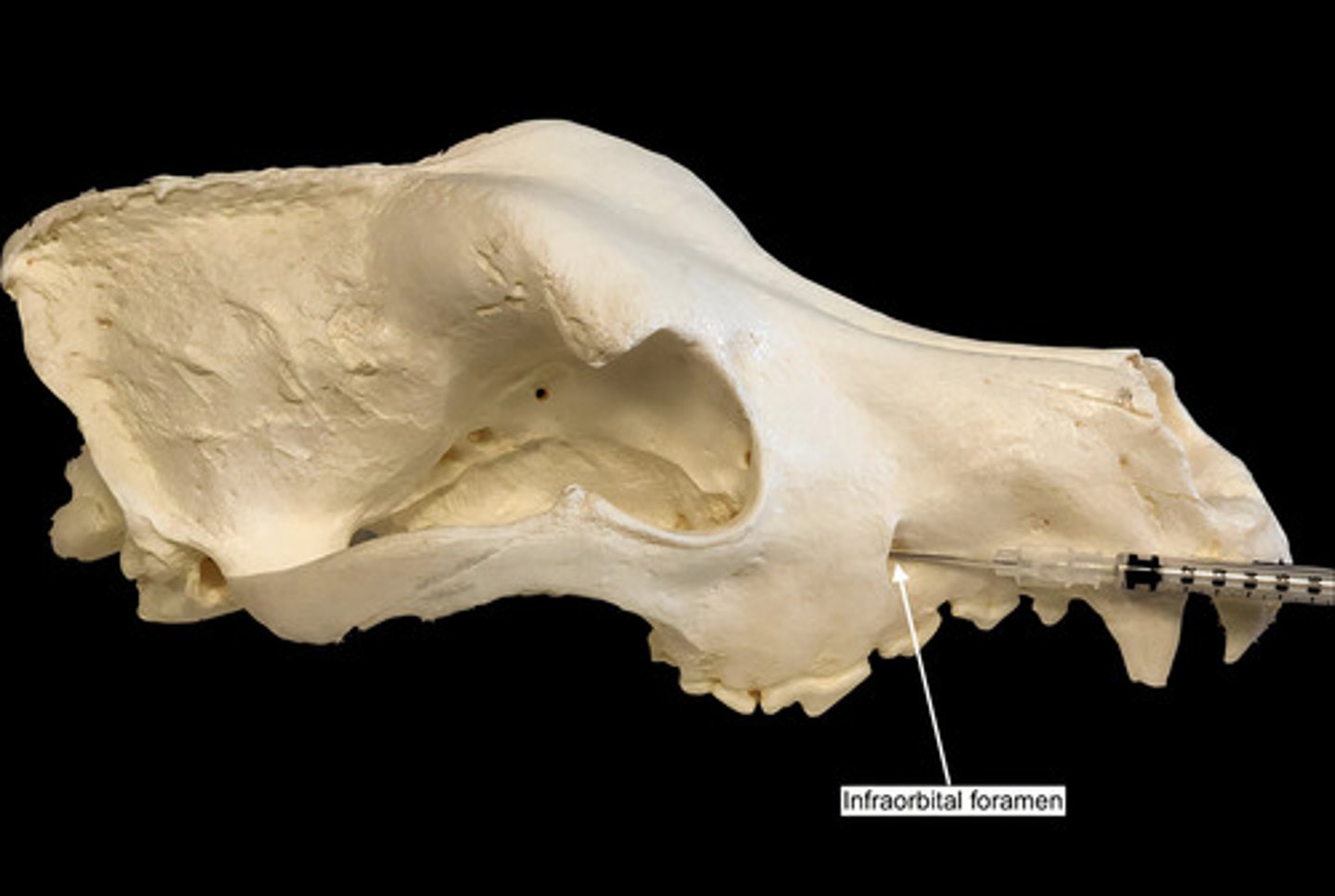
infraorbital foramen
opening under the orbit carrying the infraorbital nerves and blood vessels the the nasal region
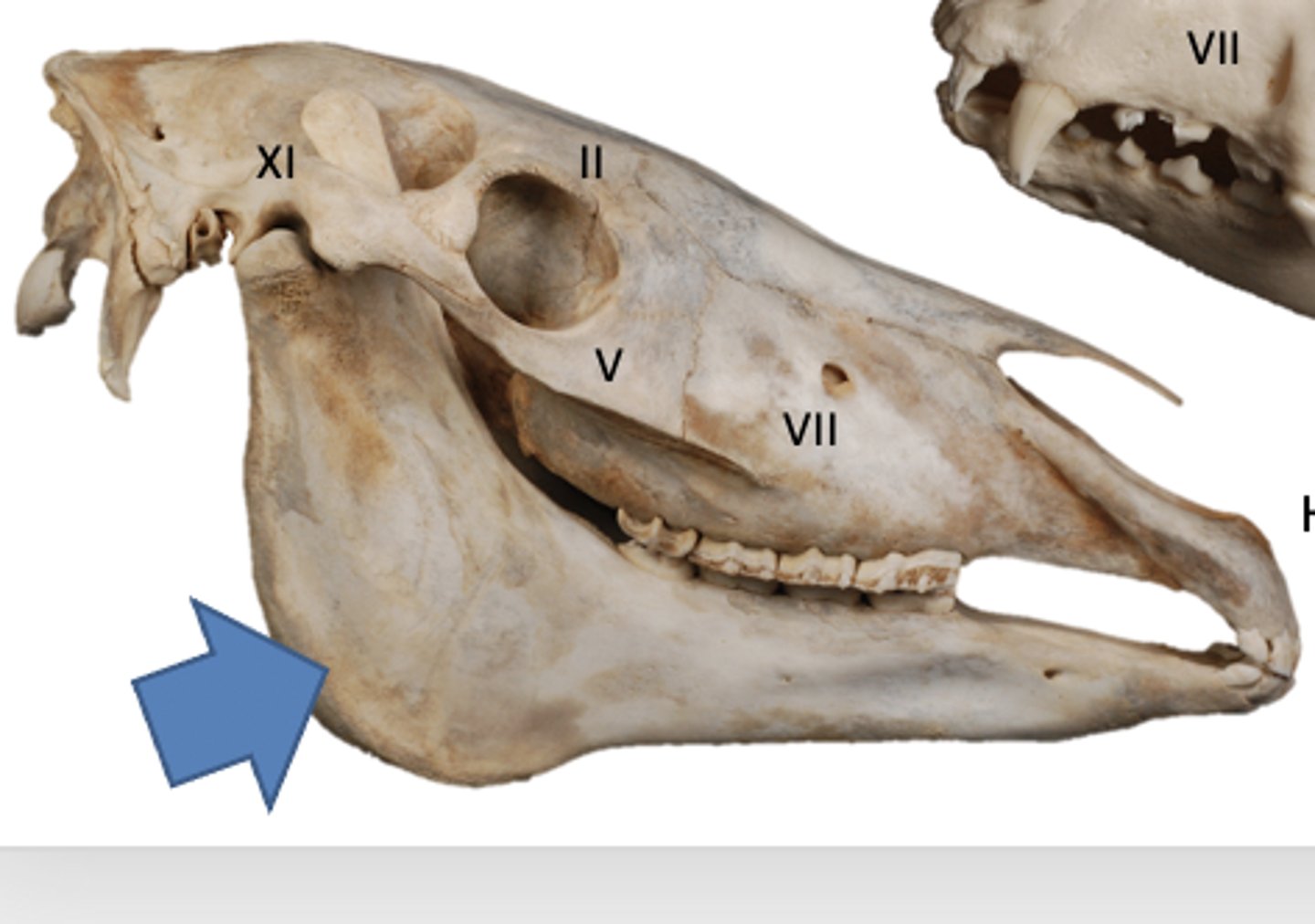
palatine bone
paired, caudal edge of hard palate, very small

mandible bone
lower jaw, paired, united by symphysis in dogs, cats, cattle. solid bone in adult horses and swine
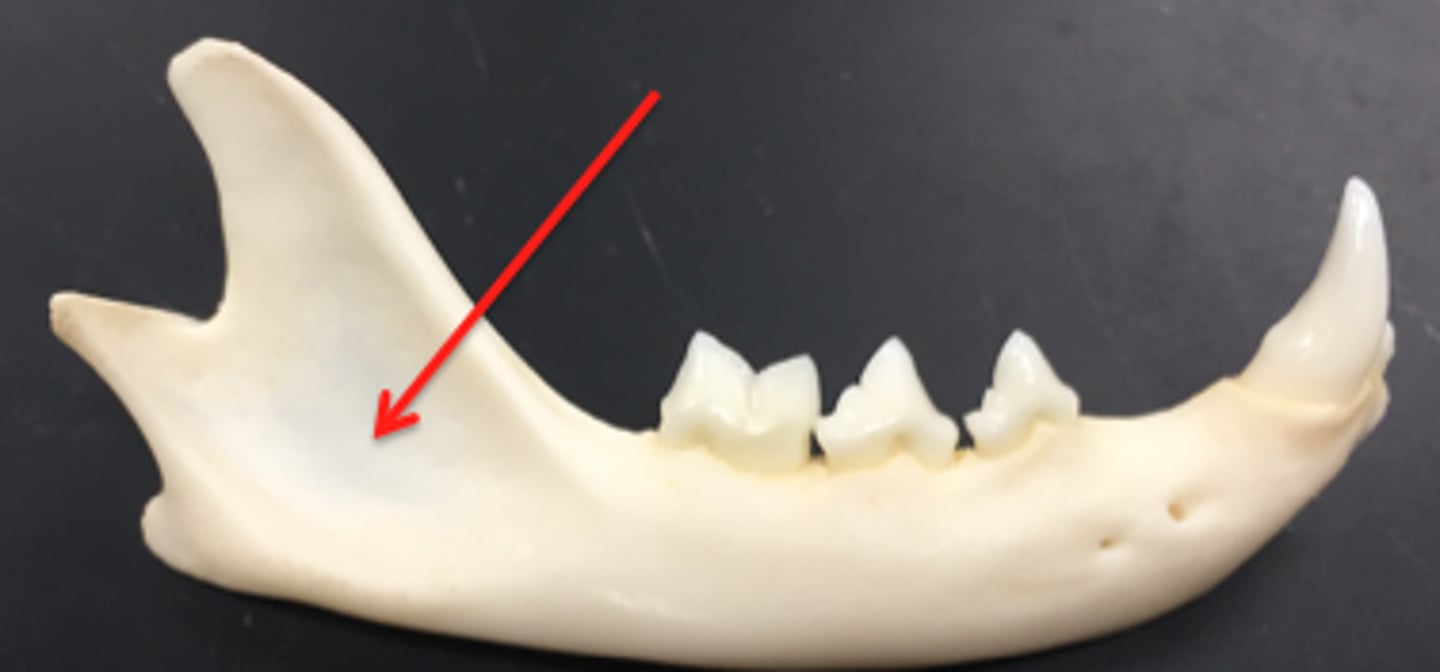
ramus
vertical part at caudal end of mandible that forms the tmj with the temporal bone. jaw muscles attach here
mandibular synthesis
joins both sides of mandible bone
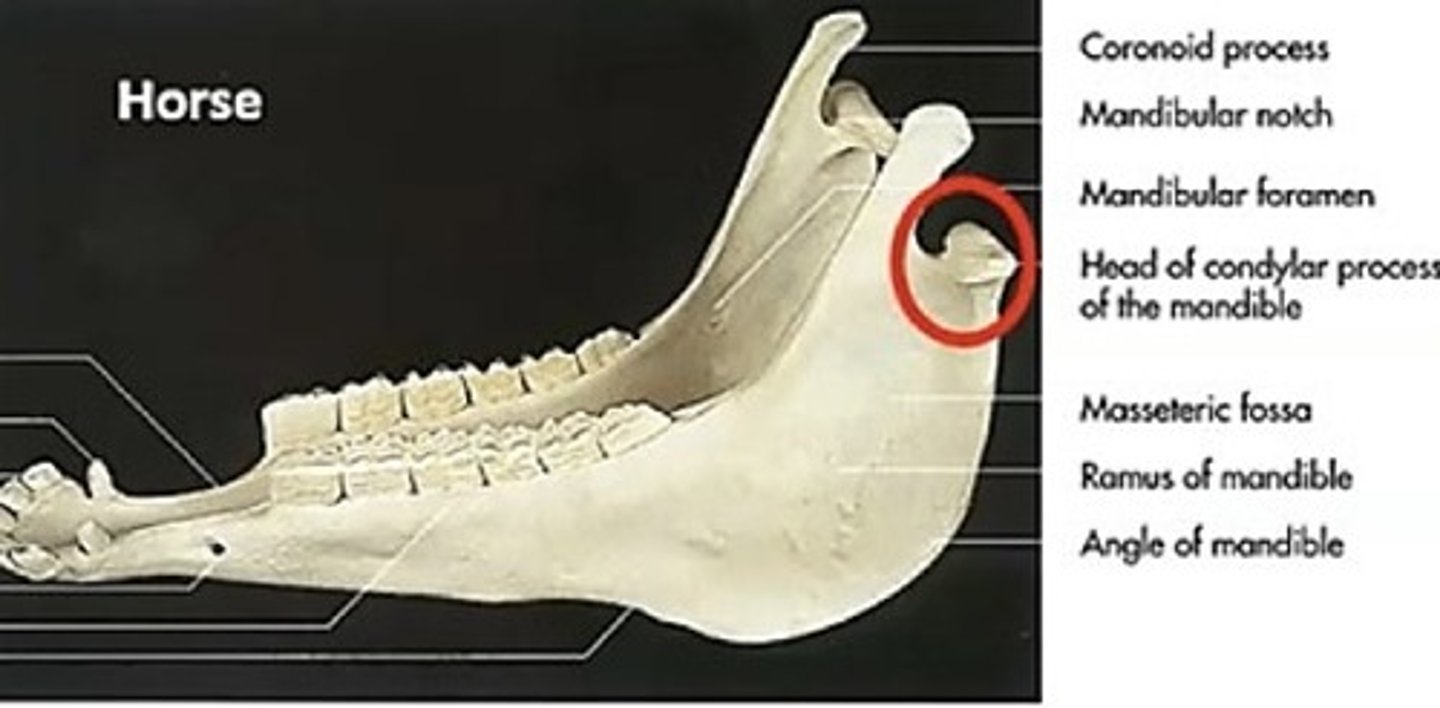
condylar process
the condyle of the ramus of the mandible that articulates with the skull
coronoid process mandible
insertion of temporalis
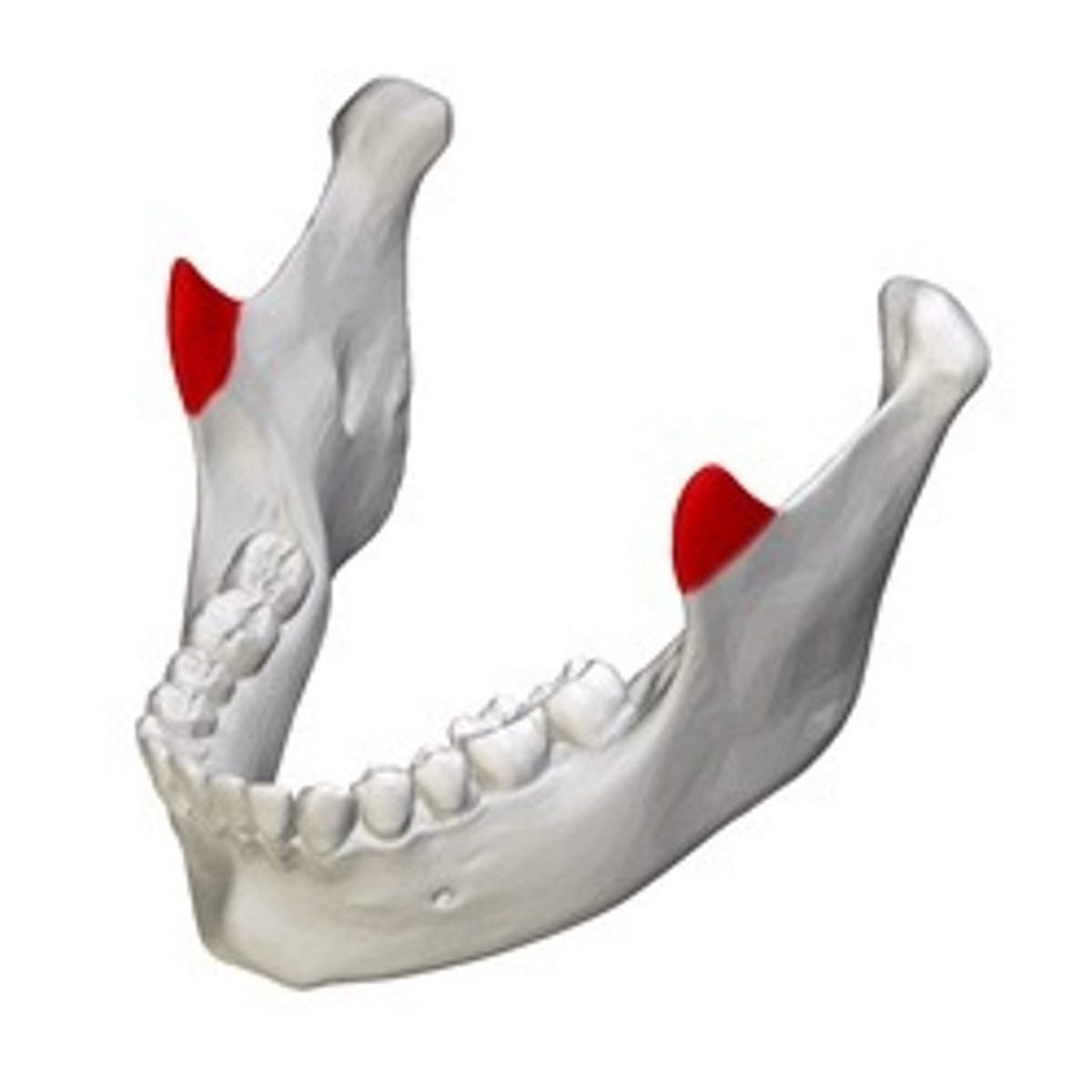
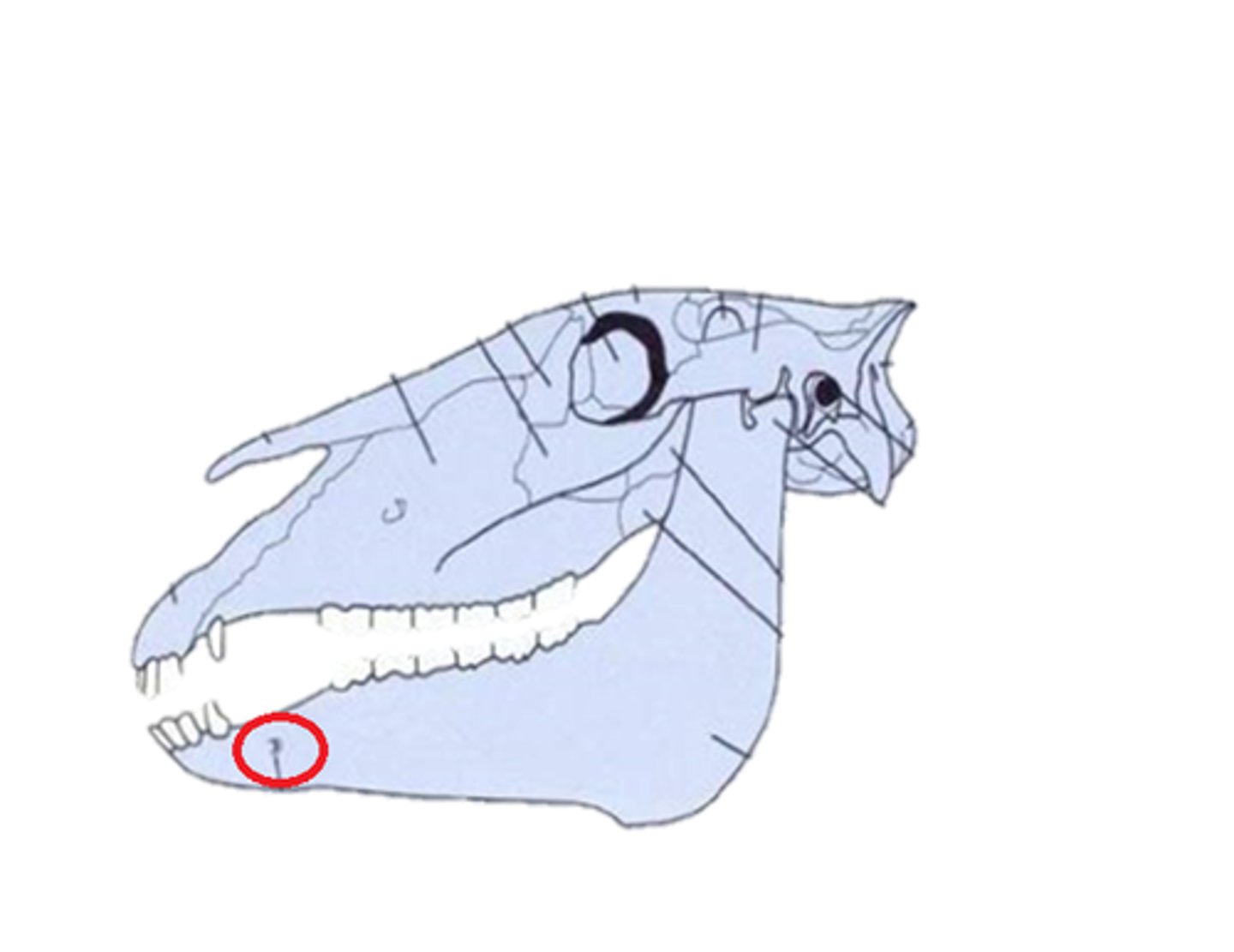
mental foramen
mandible hole
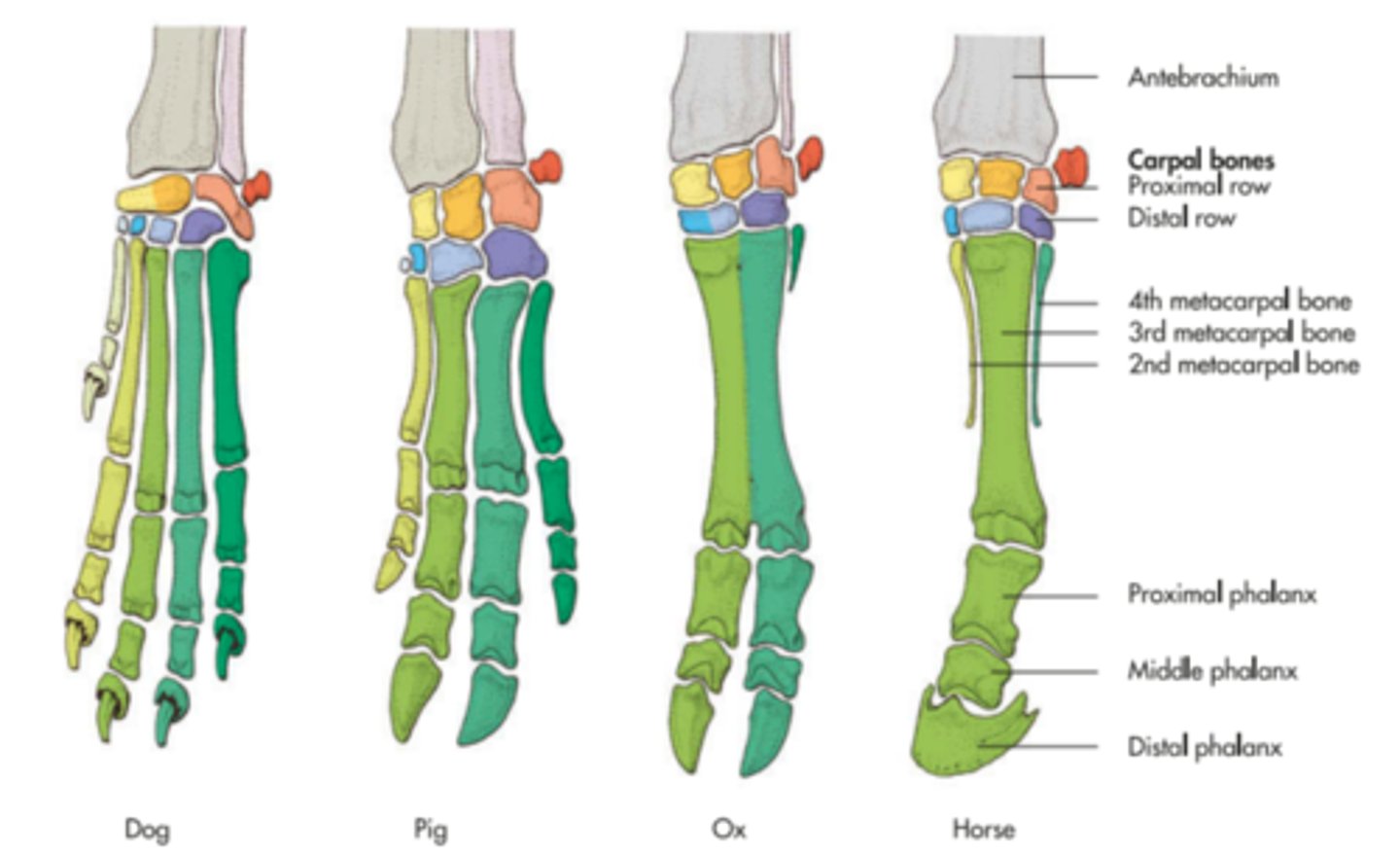
phalanges
digits, numbered 1-5 medial to lateral. proximal, middle, and distal sections
proximal phalanx
P1, long pastern
middle phalanx
P2, short pastern
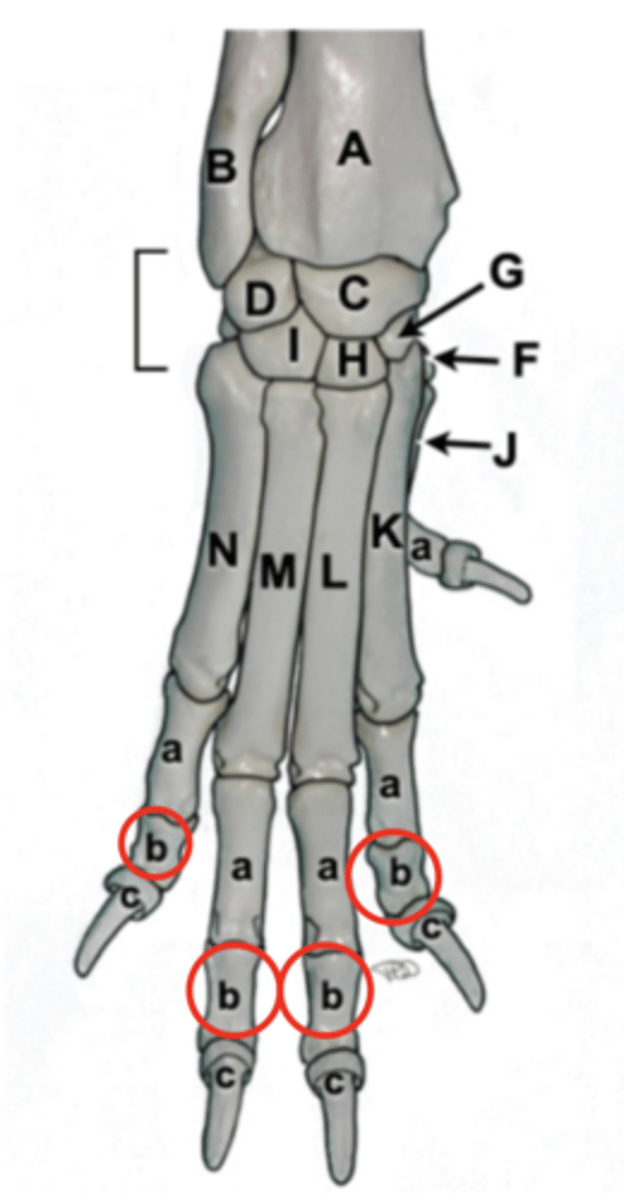
distal phalanx
P3, coffin bone
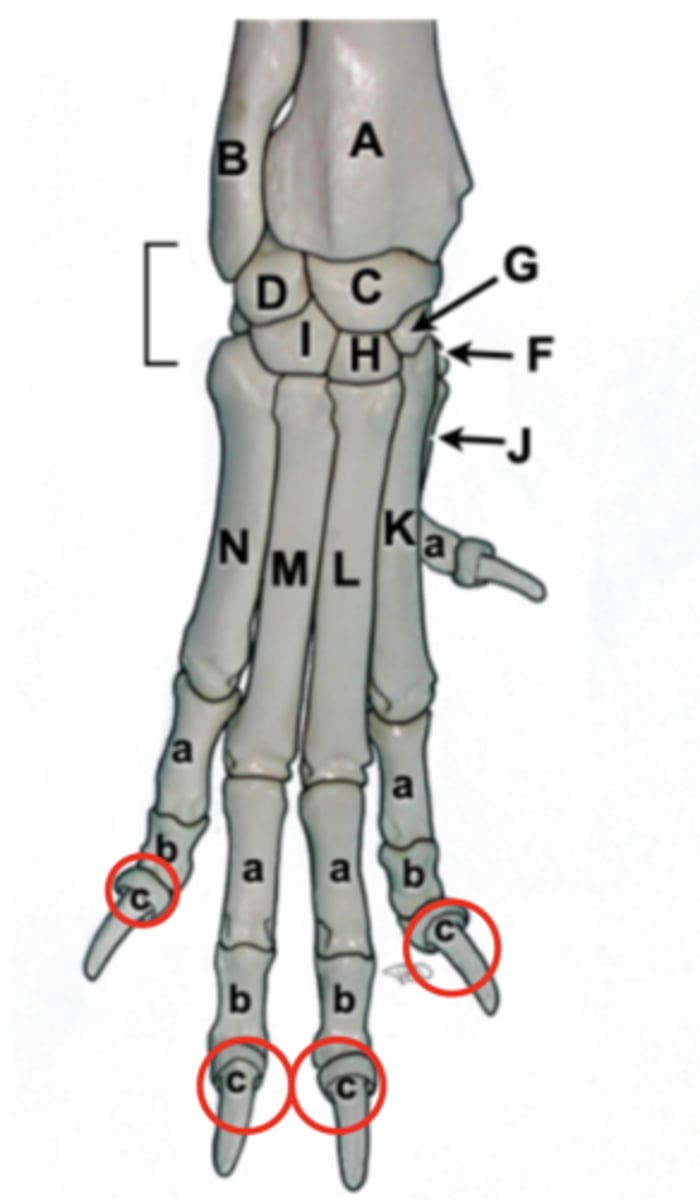
ruminant phalanges
3 and 4 support weight, 2 and 5 are dewclaws

horse phalanges
Horses have one digit on each limb composed of three phalanges and three sesamoid bones

clavicle
collar bone, exclusive to cats. embedded in muscle

scapula
shoulder blade. has spine, glenoid cavity, neck
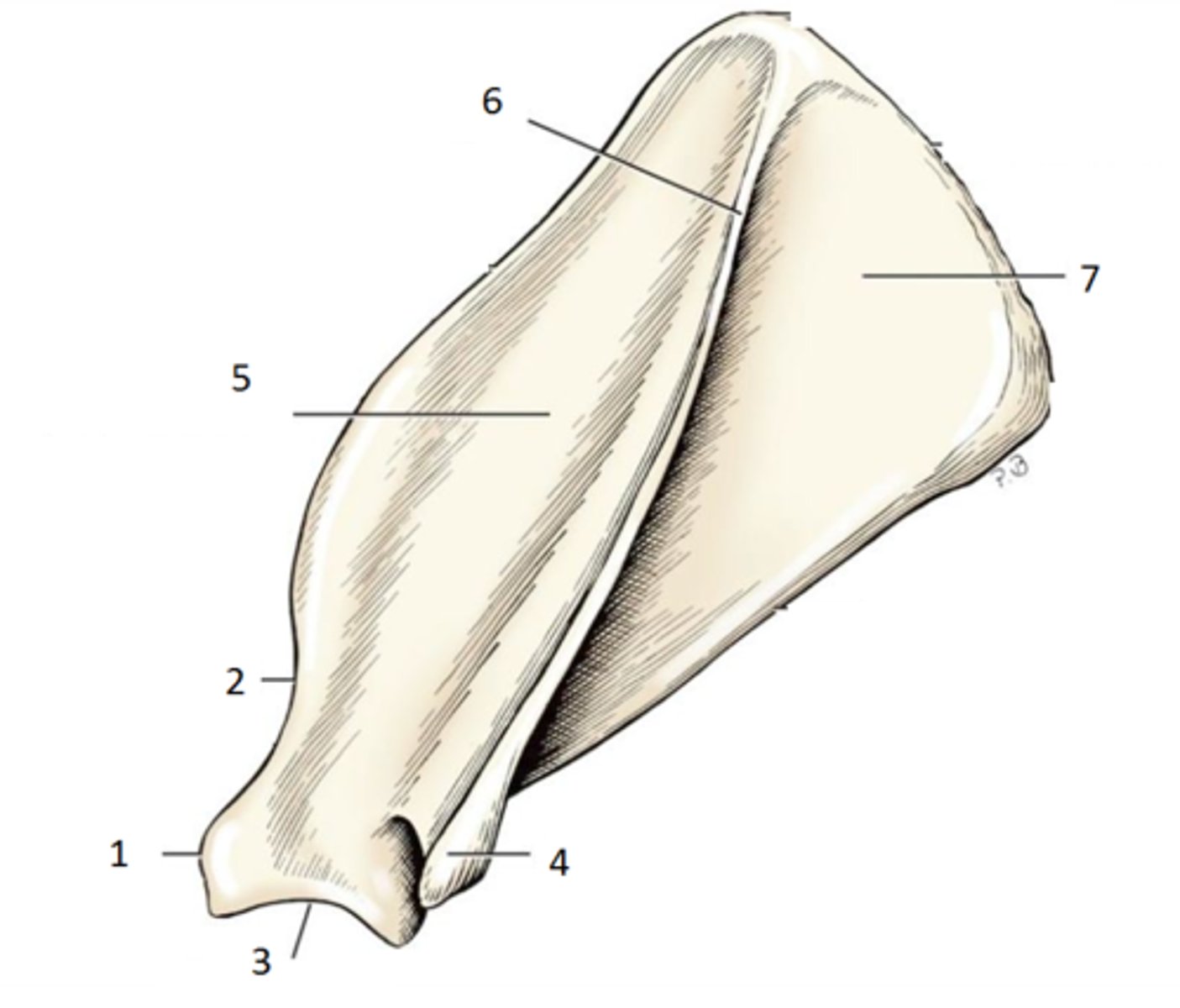
spine
ridge that projects laterally. shoulder muscles attach here
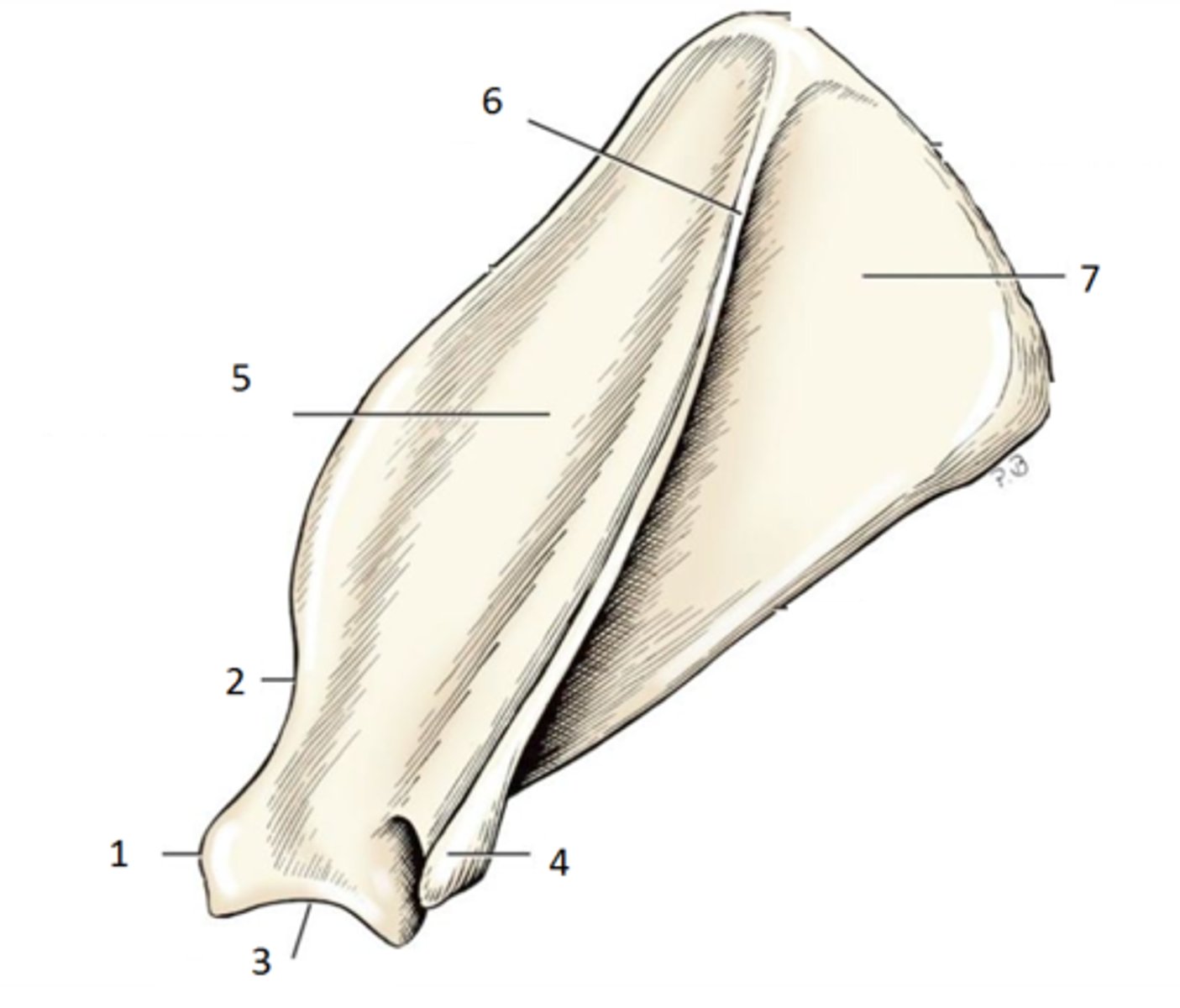
acromion
extension of the scapula, which forms the high point of the shoulder, absent in horses
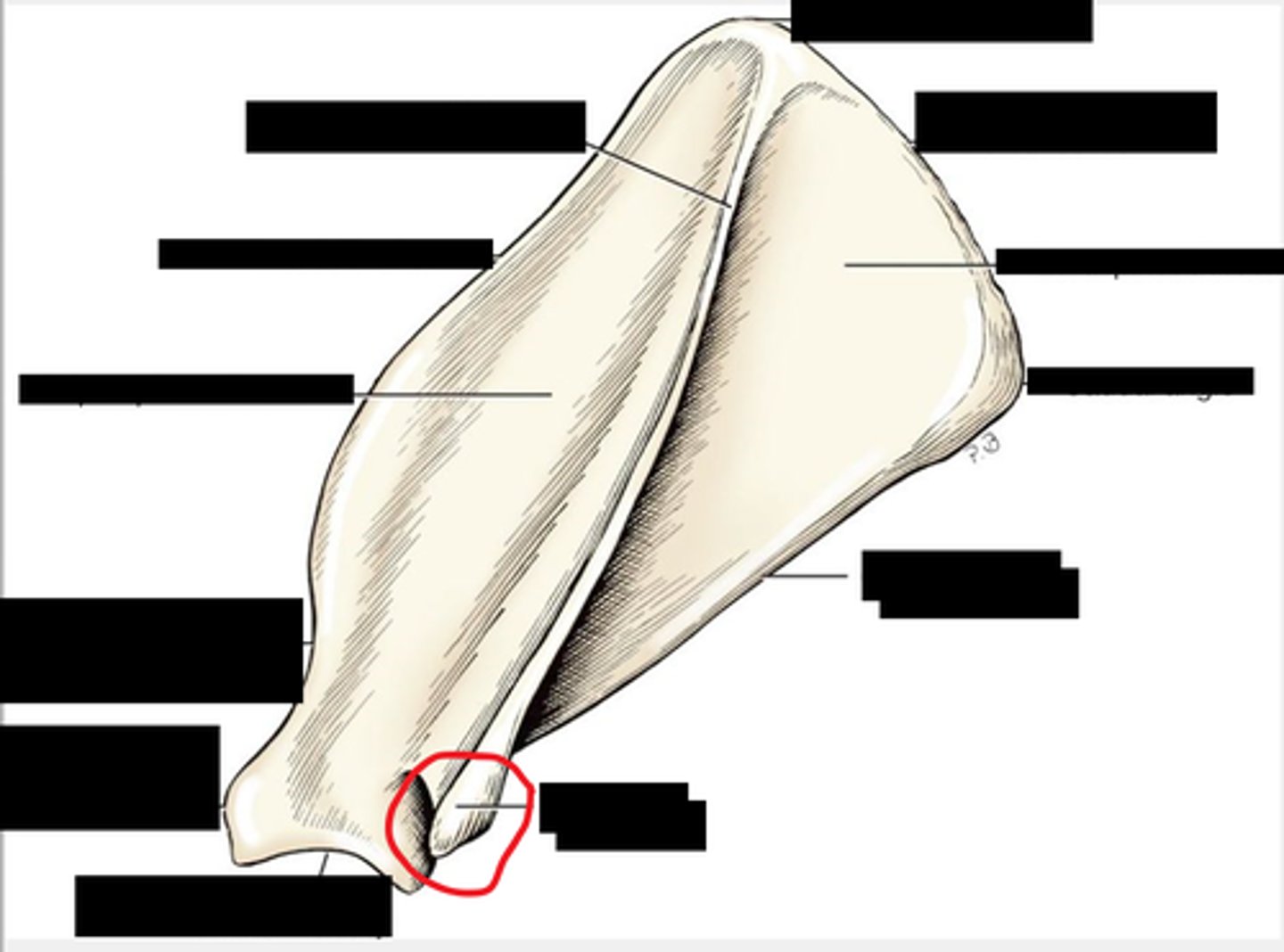

glenoid fossa
scapula cavity where humerus fits, socket part of ball and socket
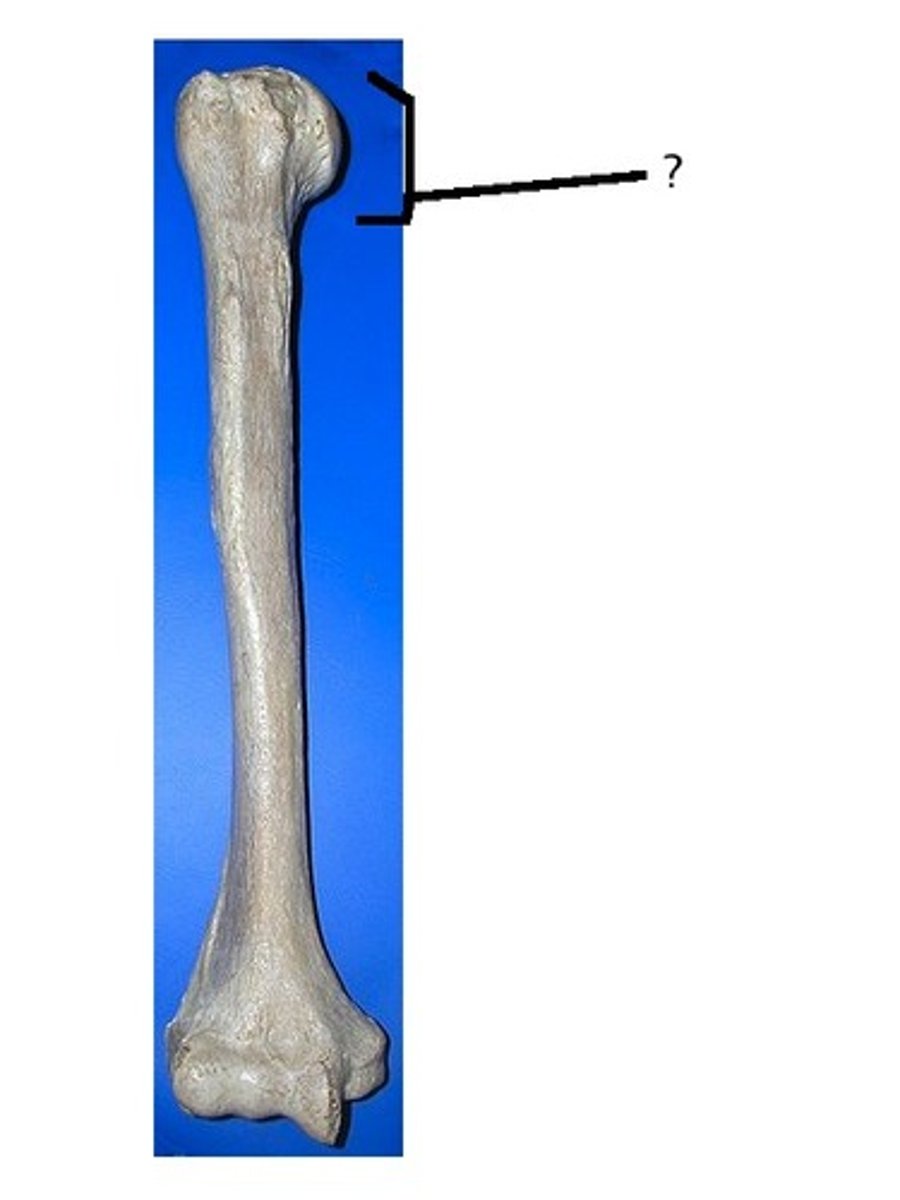
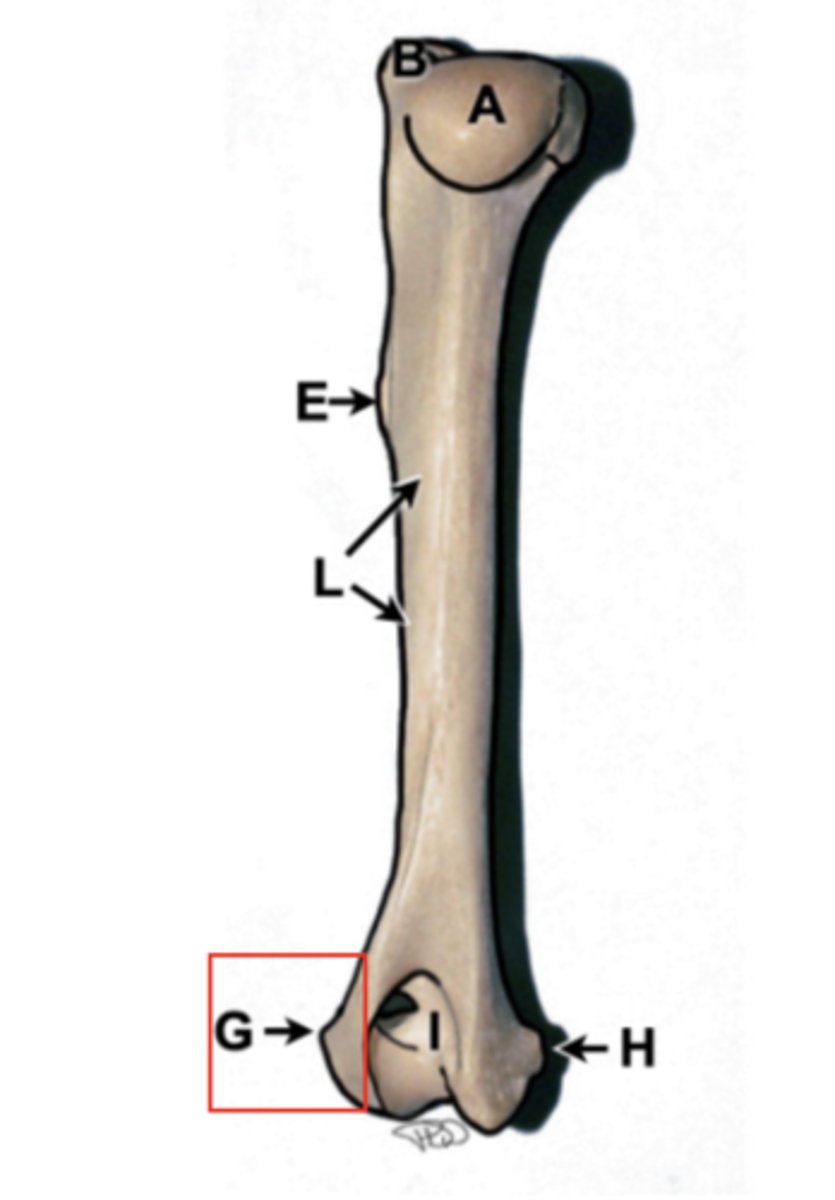
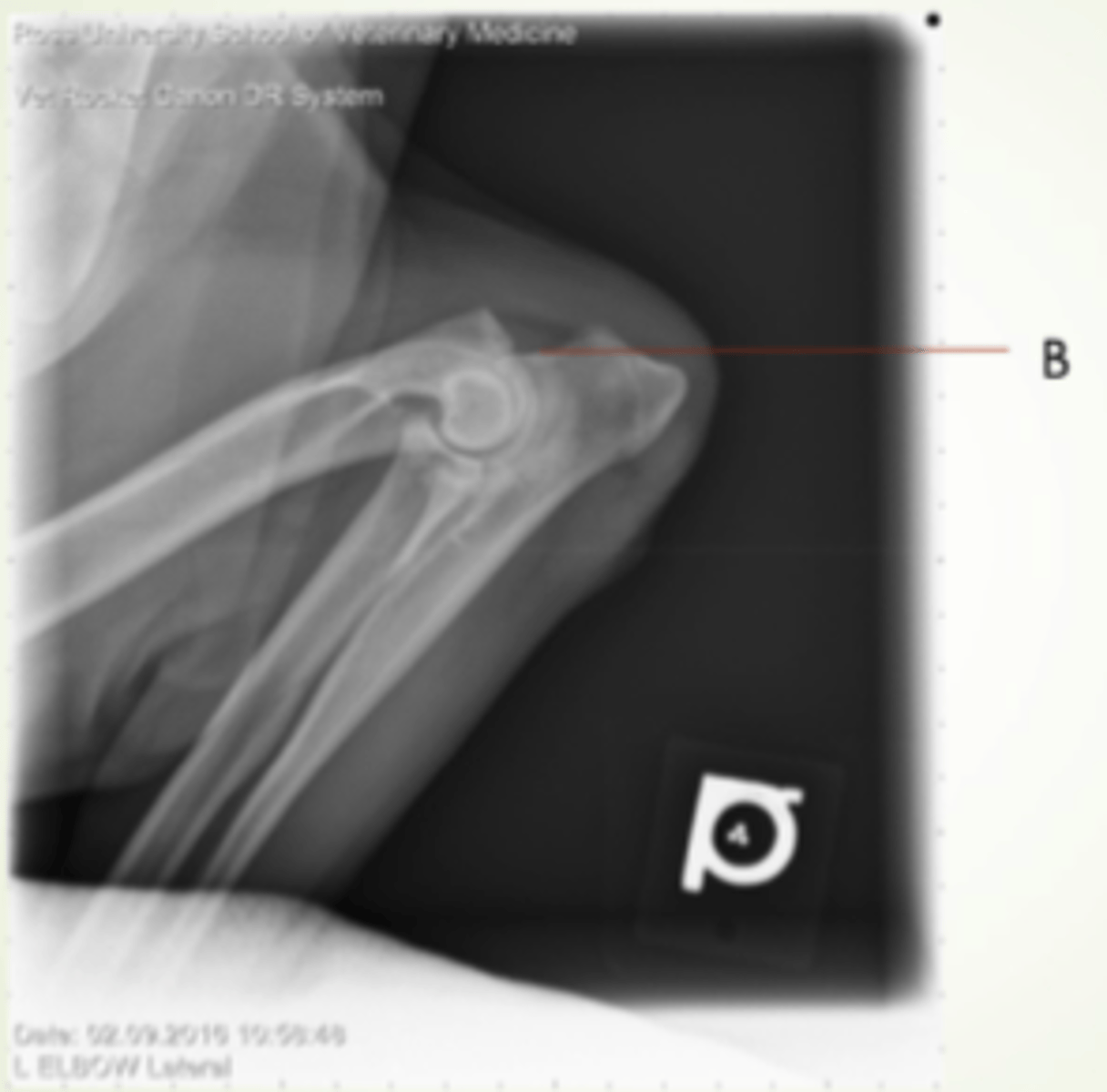
humerus
upper arm bone, has head, greater tubercle, condyles (trochlea and capitulum), epicondyles, and olecranon fossa
humerus head
rounded section of the humerus that articulates with the glenoid cavity of the scapula
greater tubercle
tuberosity, top of humerus, site of many muscle attachments, point of shoulder
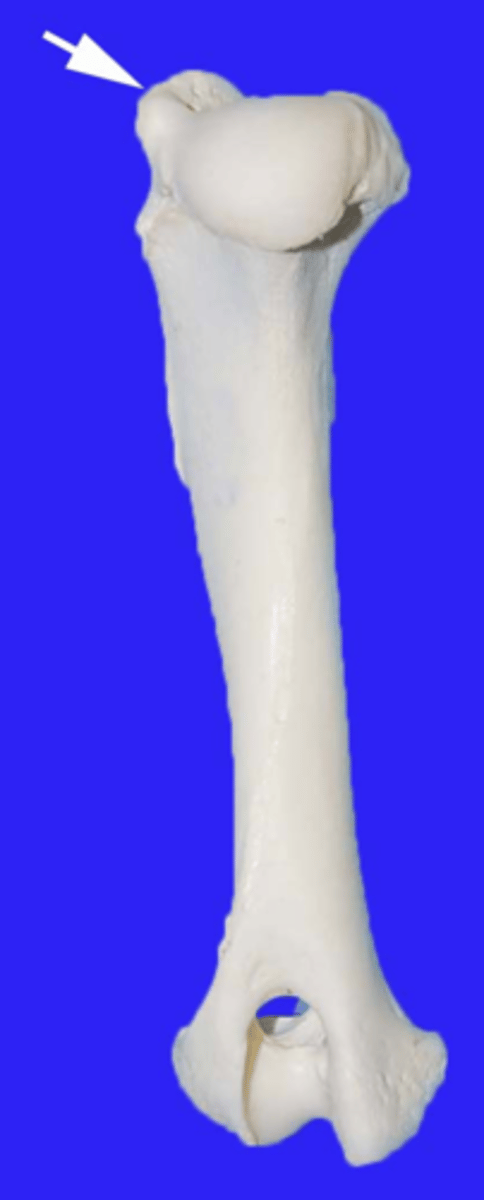

deltoid tuberosity
The ridge on the anterior surface of the humerus that allows for attachment of the deltoid muscle. lateral aspect

lateral epicondyle
humerus
medial epicondyle
humerus

olecranon fossa
Indentation above the condyles of the humerus, depression of distal humerus, receives olecranon on extension
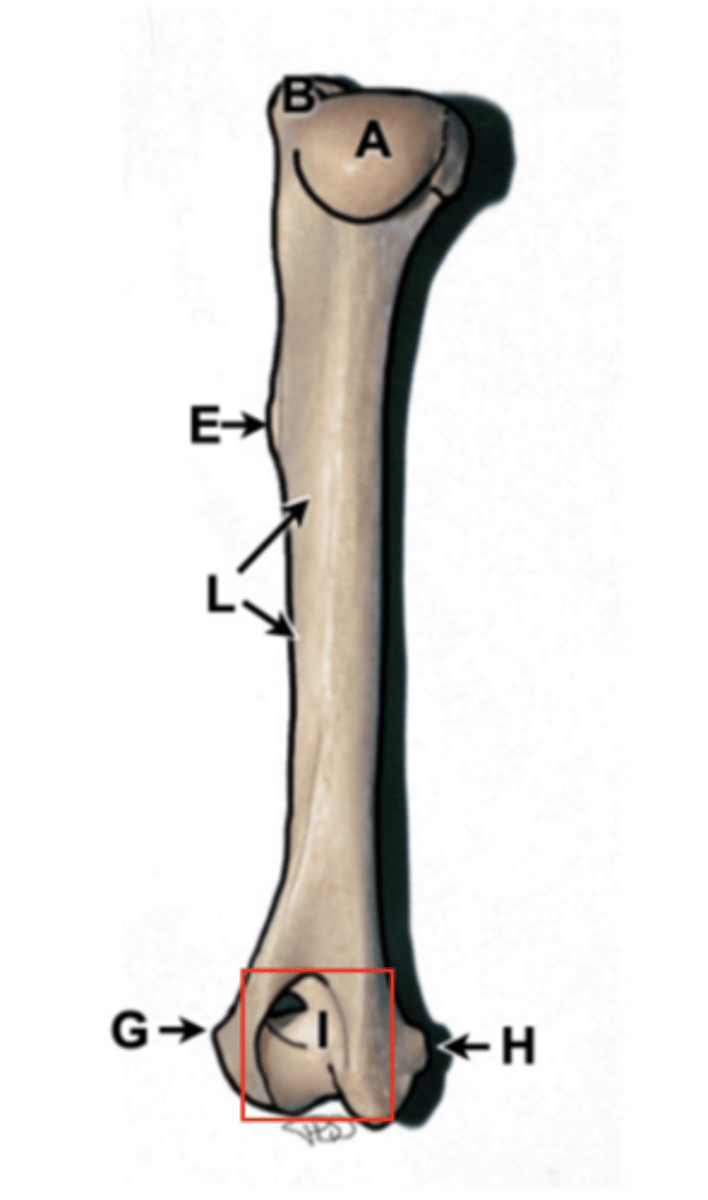
supracondylar foramen
hole on medial surface of humerus in cats
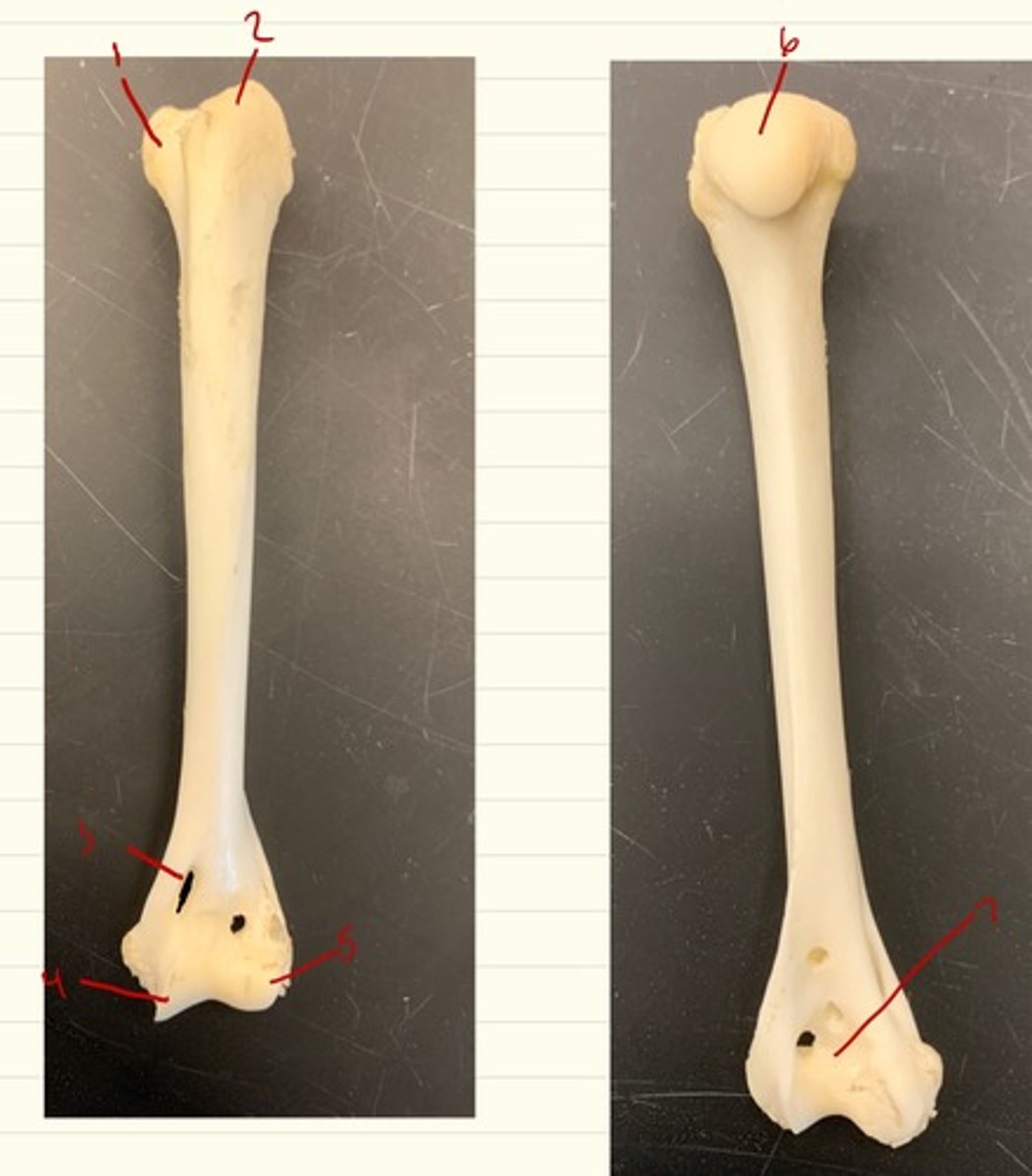
radius
main weight bearing bone of forearm, starts laterally and courses medially. has head and styloid process
radius head
proximal aspect with concave articular surface that articulates with the humerus
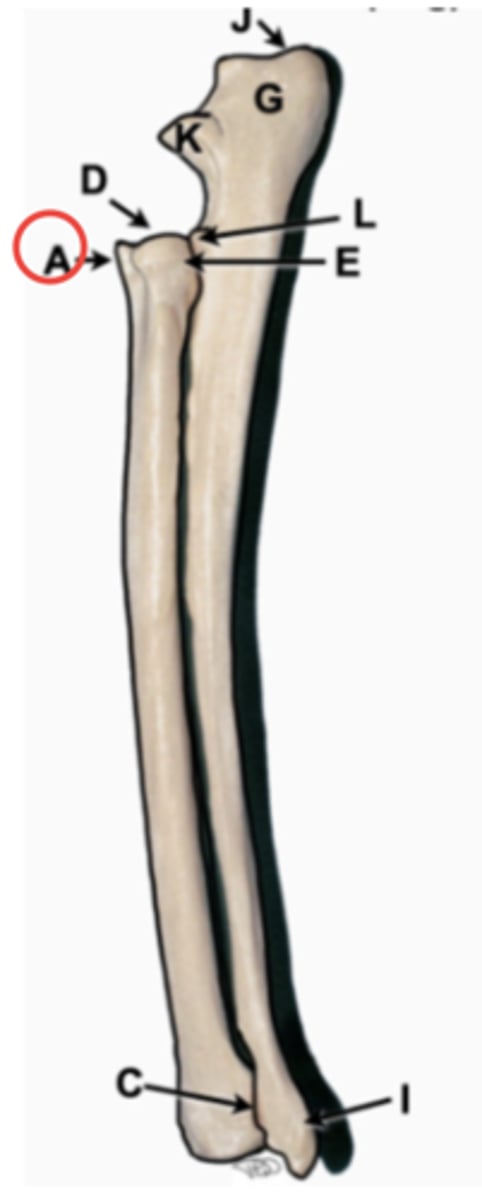
styloid process
distal aspect on radius that articulates with radial carpal bone
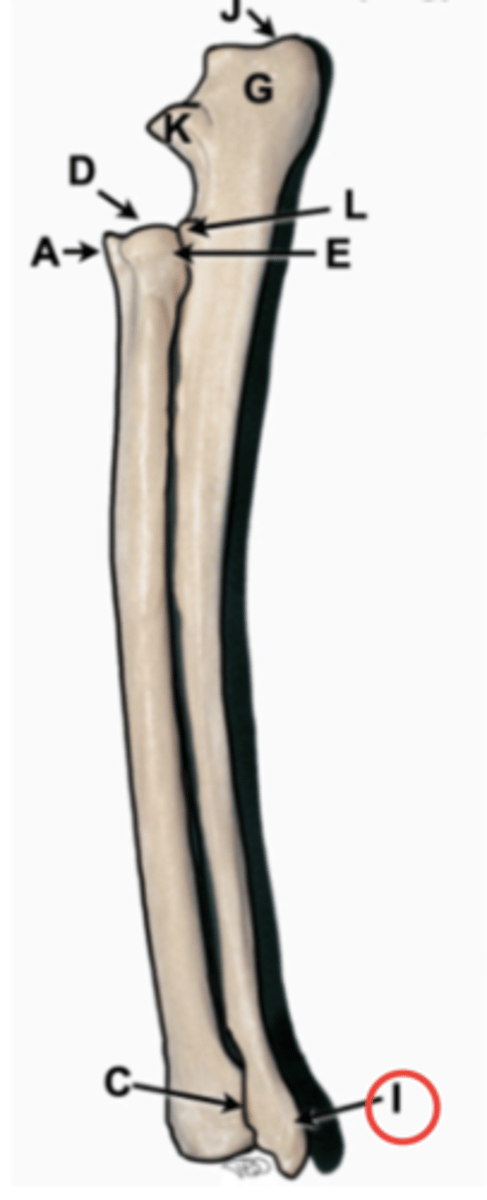
ulna
long thin bone of forearm, starts medially and courses laterally. has olecranon fossa, trochlear notch, anconial process, coronoid process, radial notch, styloid process

olecranon
proximal aspect of ulna, point of elbow
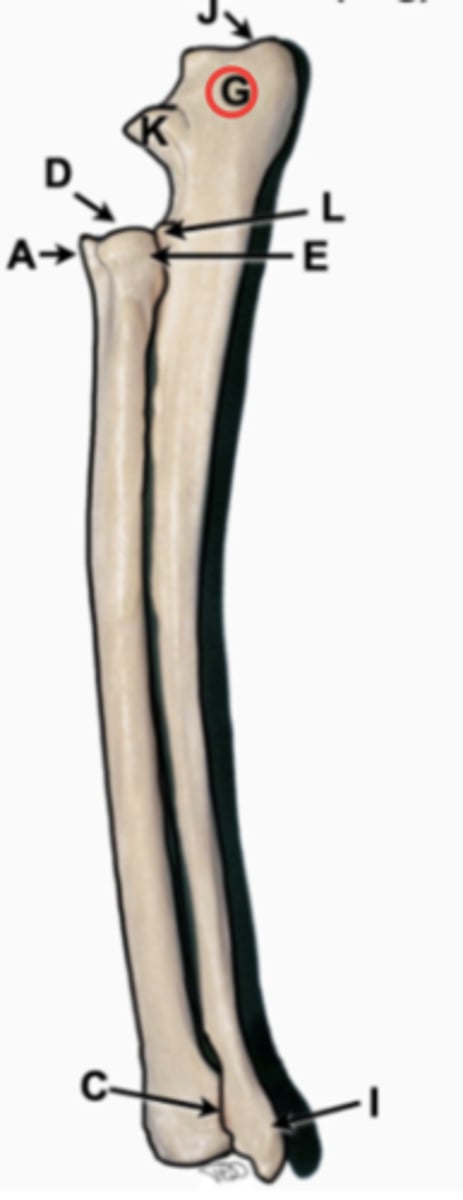
anconceal process
beak shaped at proximal end of trochlear notch, resides into olecranon fossa
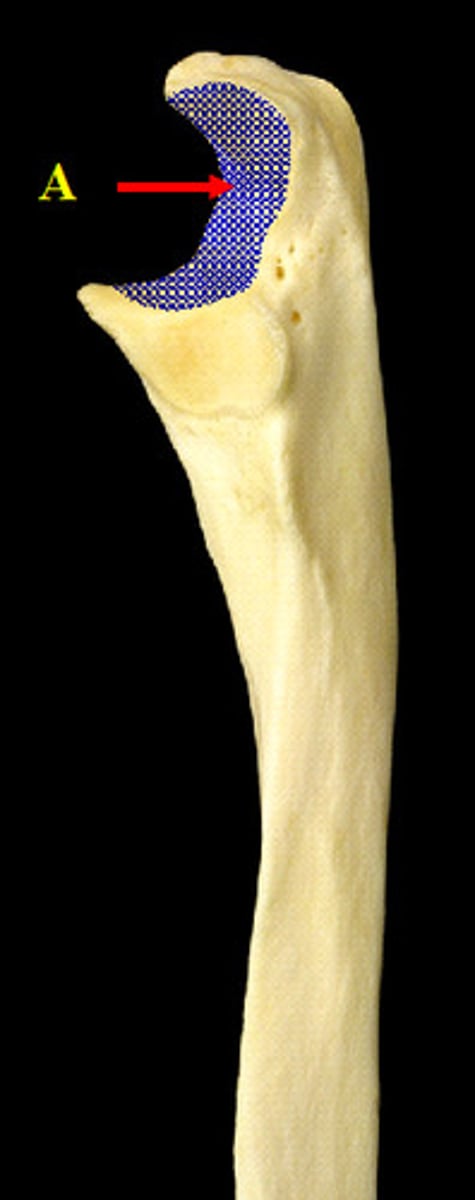
trochlear notch
semilunar notch, wraps around trochlea of humeral condyle and makes joint tight and secure
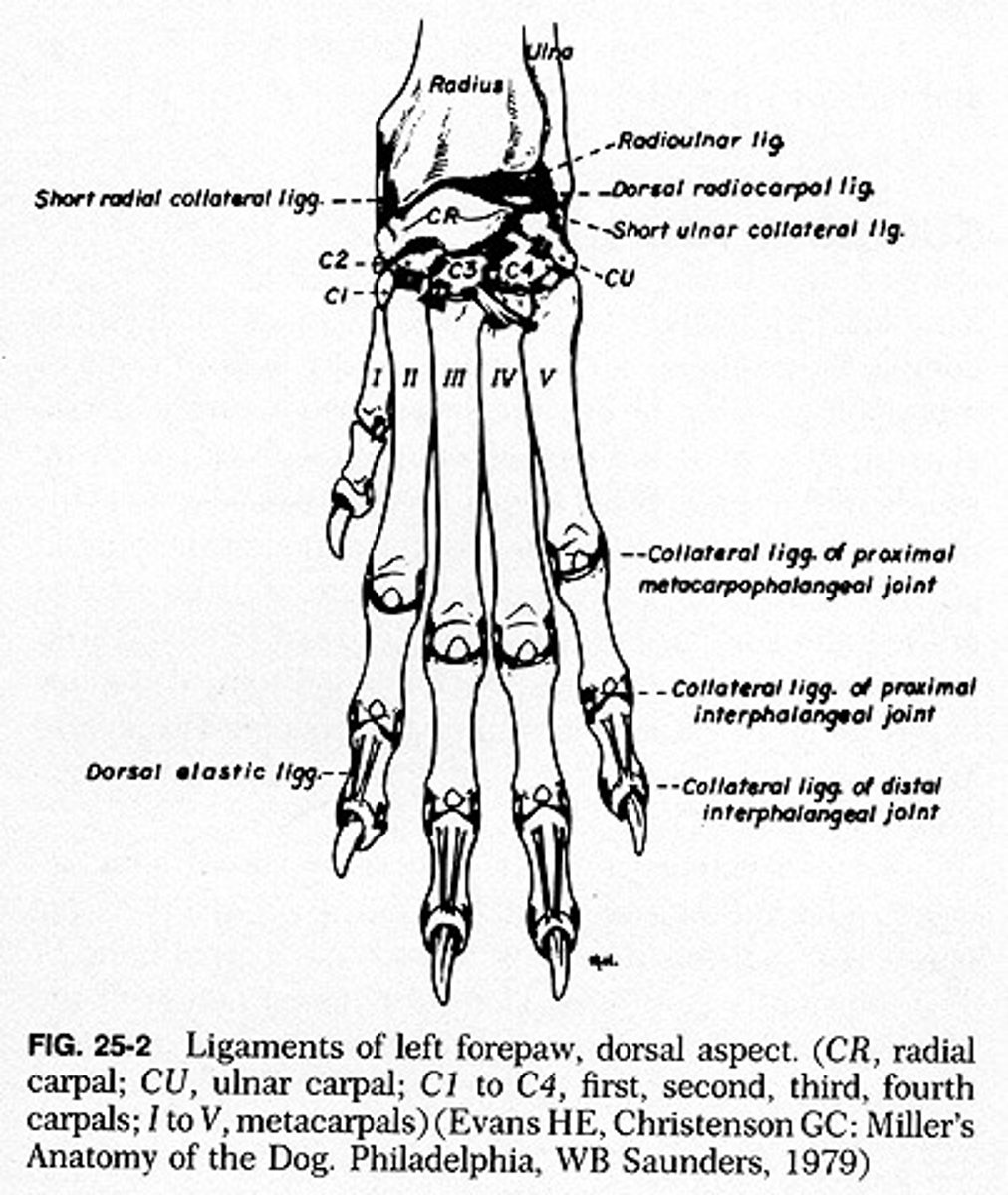
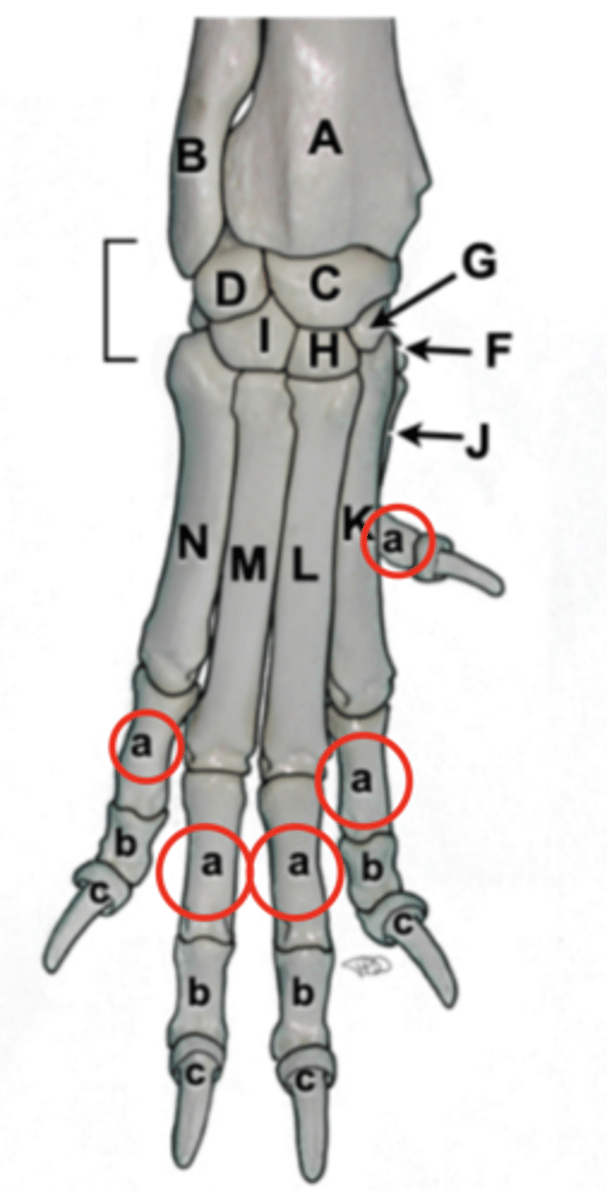
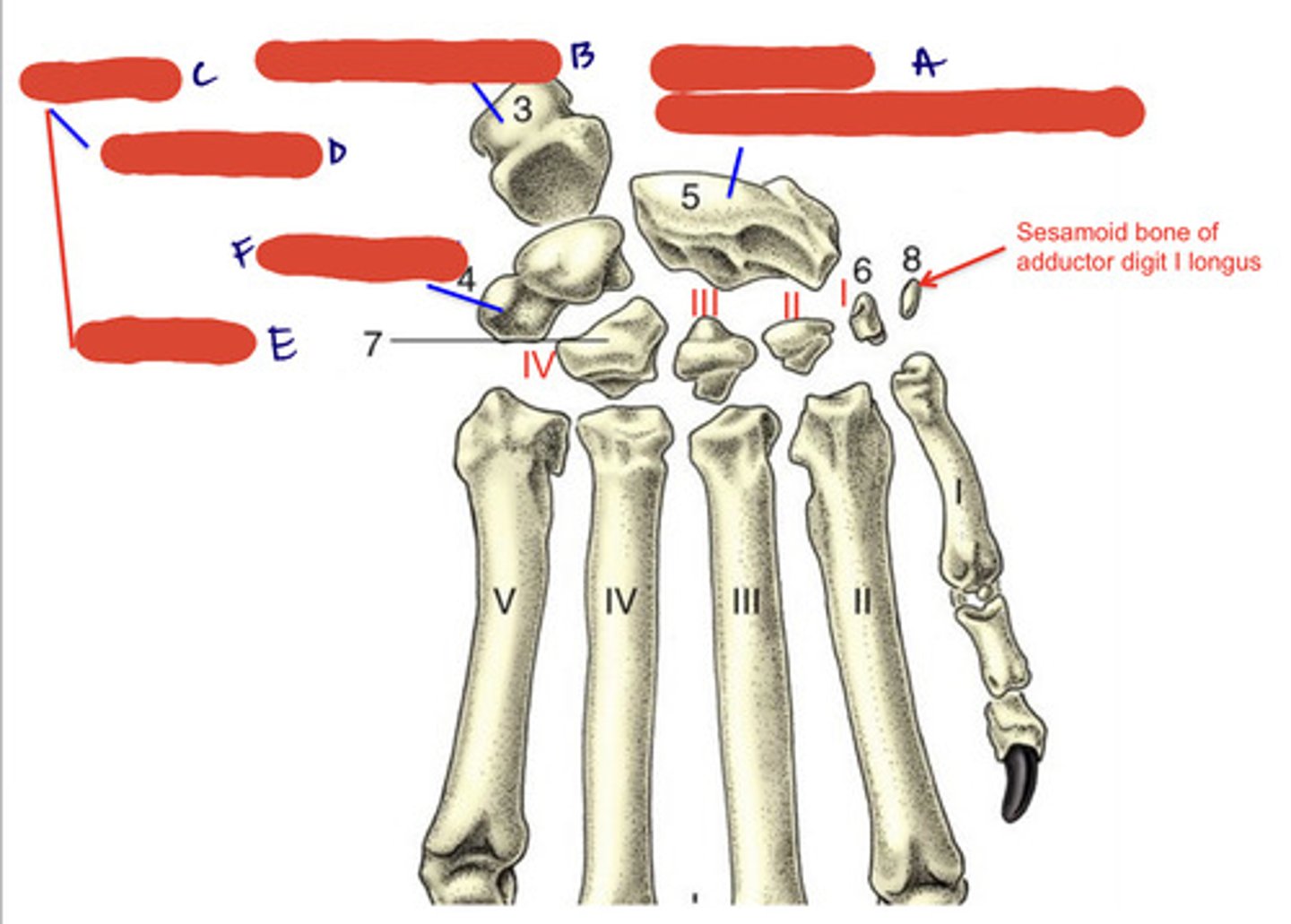
carpus
wrist, consists of two parallel rows of short bones

radial carpal bone
largest, most medial, articulate with radius
ulnar carpal bone
located laterally, articulates with ulna
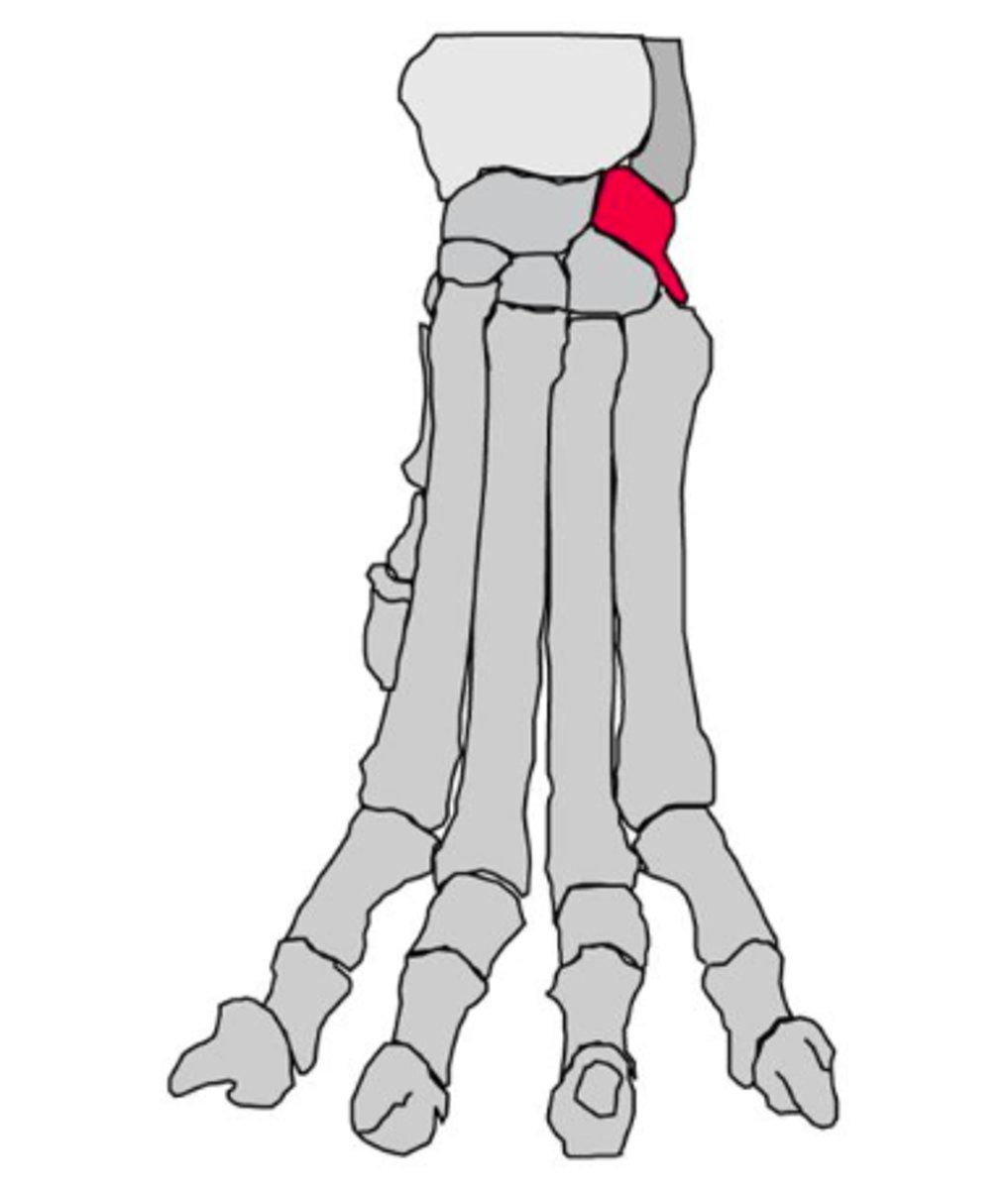
accessory carpal bone
on palmar aspect of carpus, articulates with ulnar carpal bone, only carpal bone with direct muscle attachements

carpal row
1-4 medial to lateral
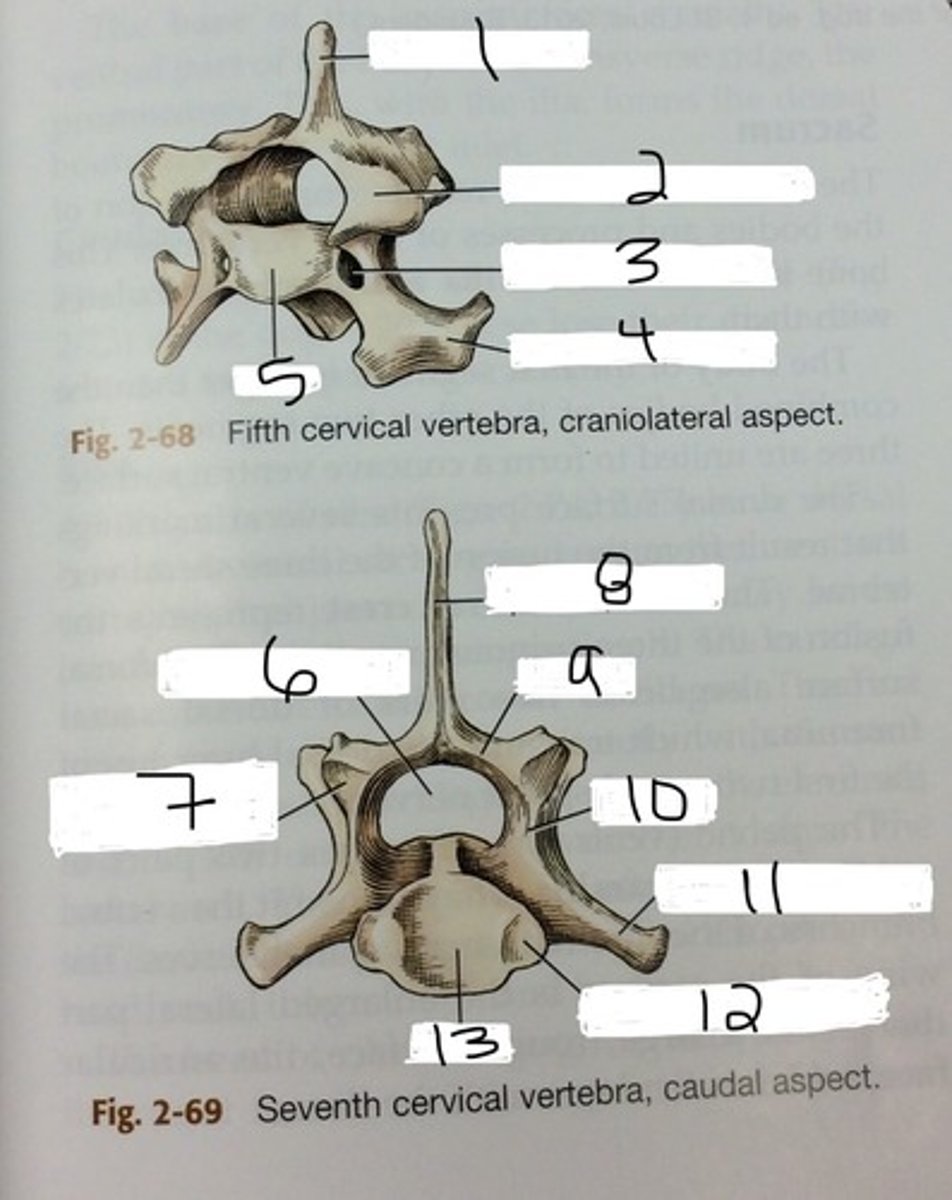
cervical vertebrae
7
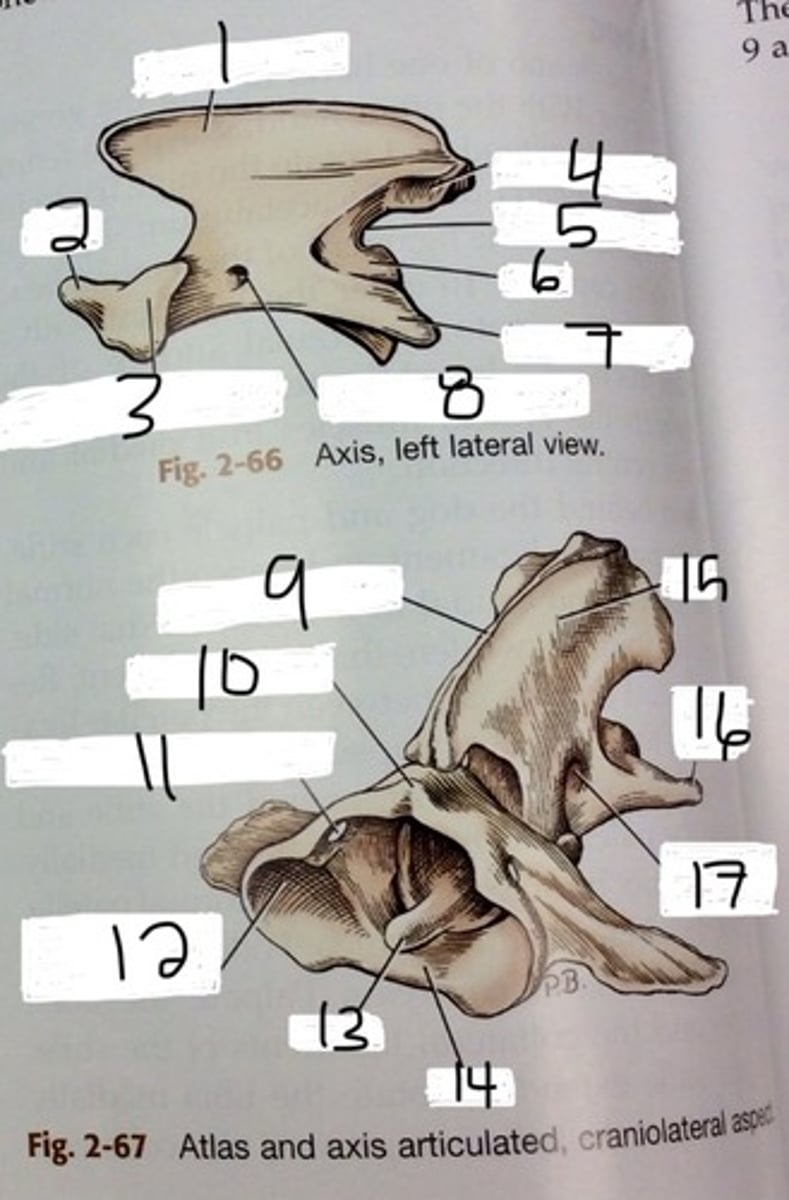
atlas
C1 . no ventral body but consists of a bony ring that the spinal chord passes through, two large transverse process wings. articulates with occipital condyles

axis
C2 large thick spinous process that overlaps. thick bladelike spinous process that overlaps. has peg like dens on its cranial end that tuck into C1
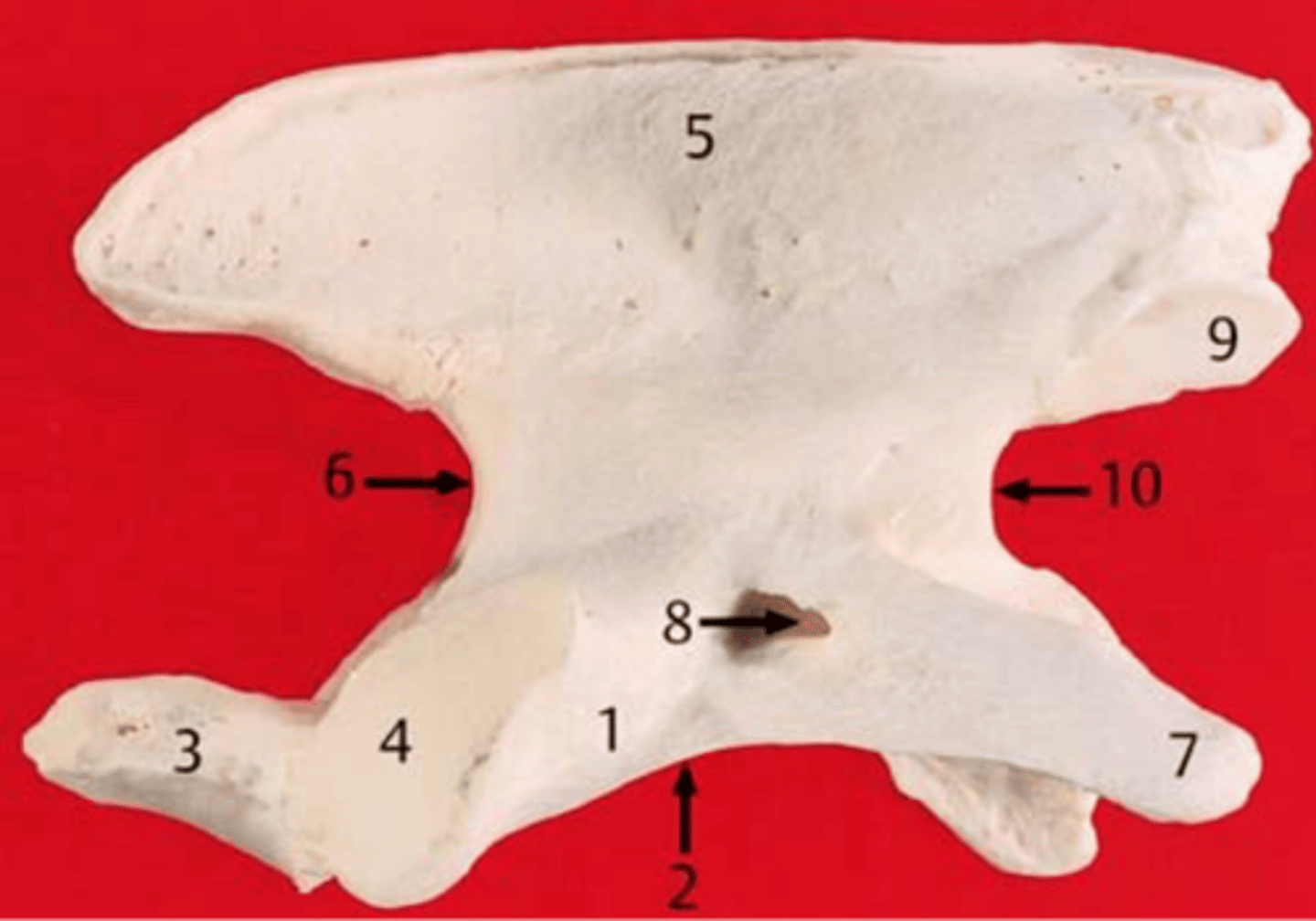
dens
on axis, tuck into C1
thoracic vertebrae
13
spinous process
projects dorsally, allows for flexion of trunk
lumbar vertebrae
7

transverse process
projects laterally. landmark for paravertebral blocks in cattle

sacral vertebrae
3 fused
sacrum
three vertebrae fused together that get smaller as move caudally, forms joint with ilium
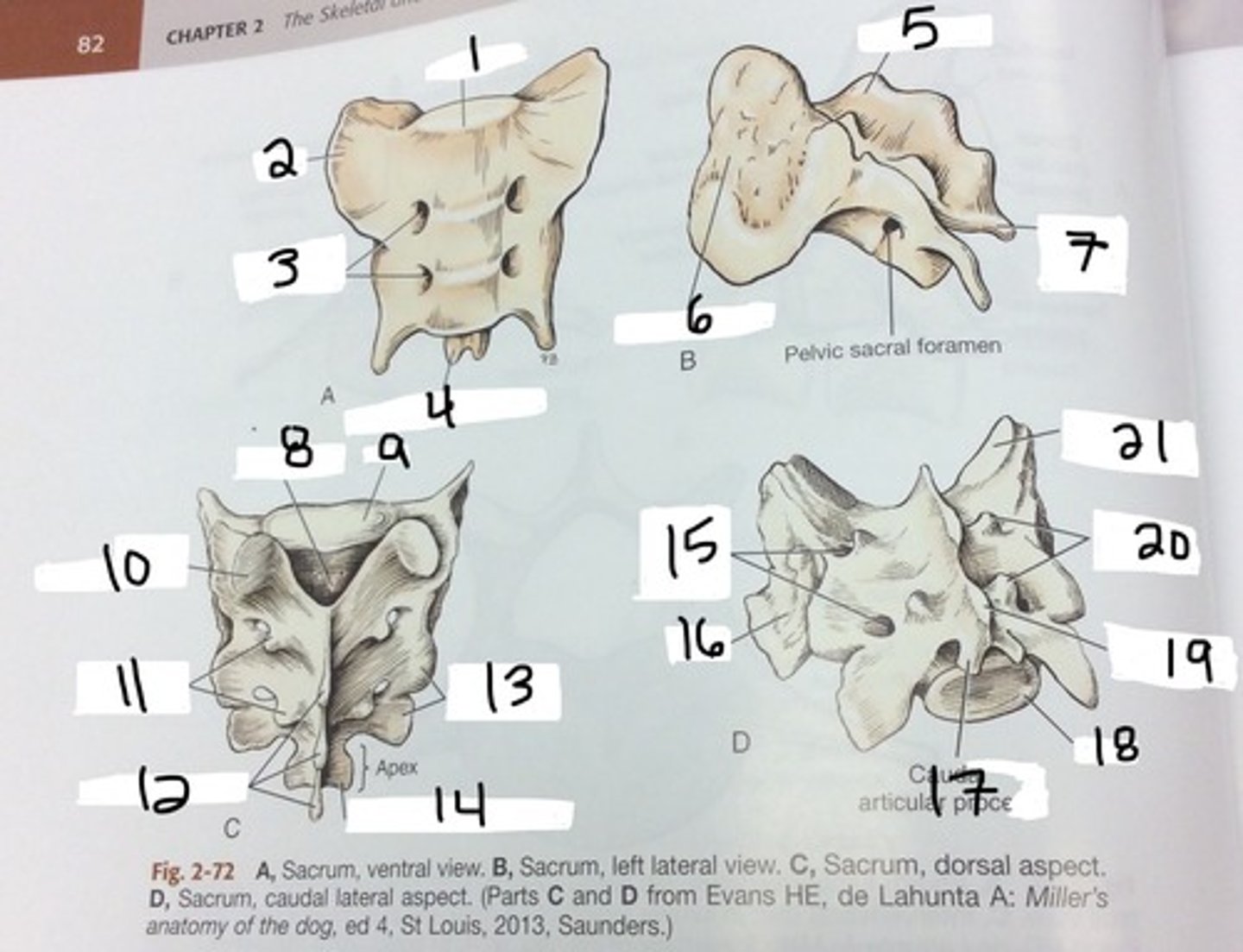
dorsal sacral foramina
foramina found on the posterior side of the sacrum, lateral to the midline
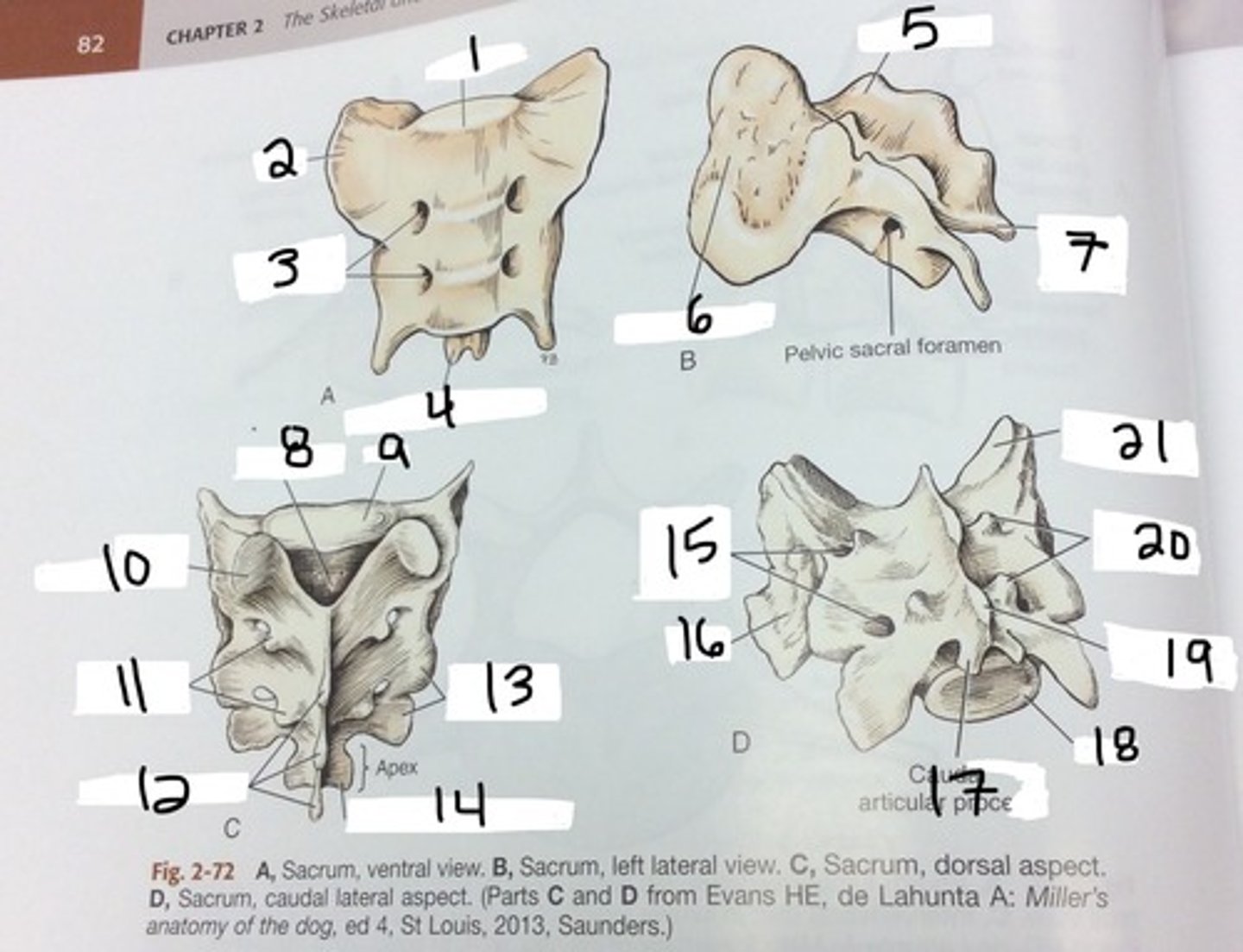
ventral sacral foramina
Foramina found on the anterior side of the sacrum, lateral to the midine
coccygeal vertebrae
20-25
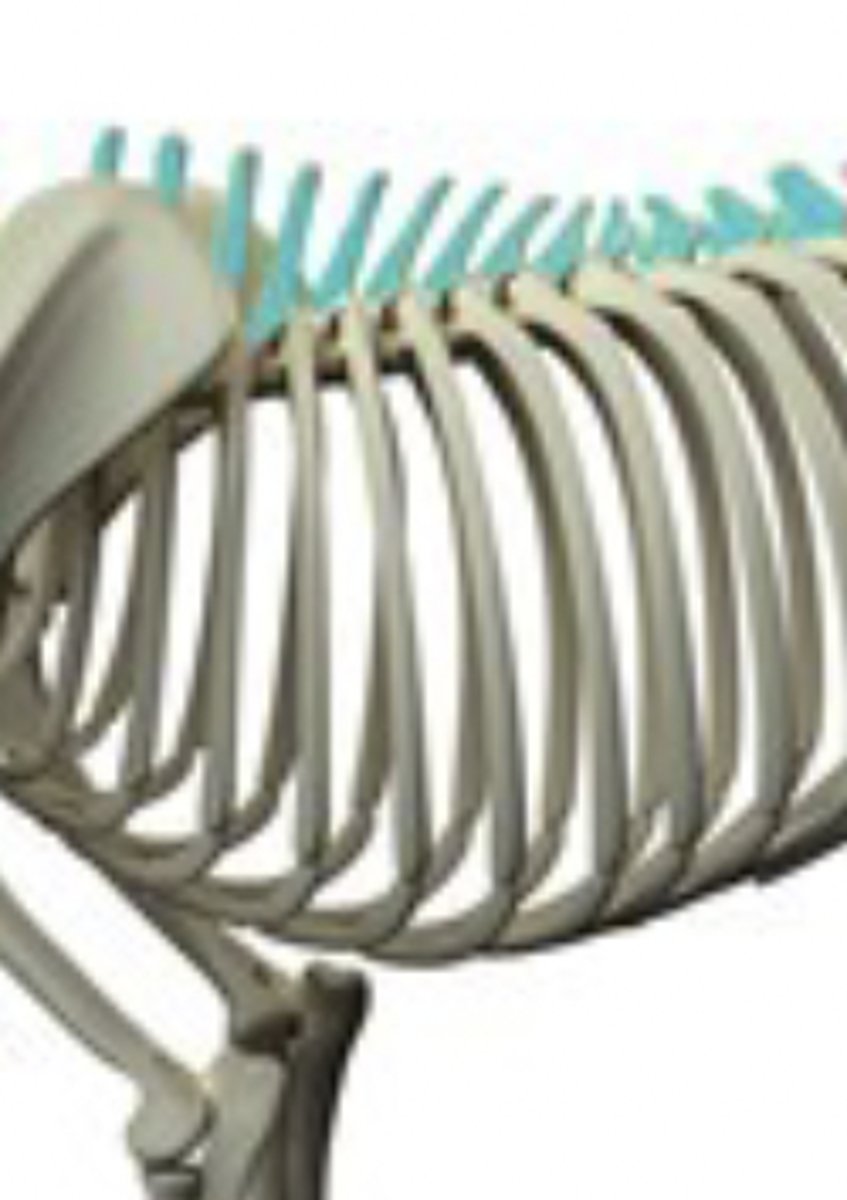
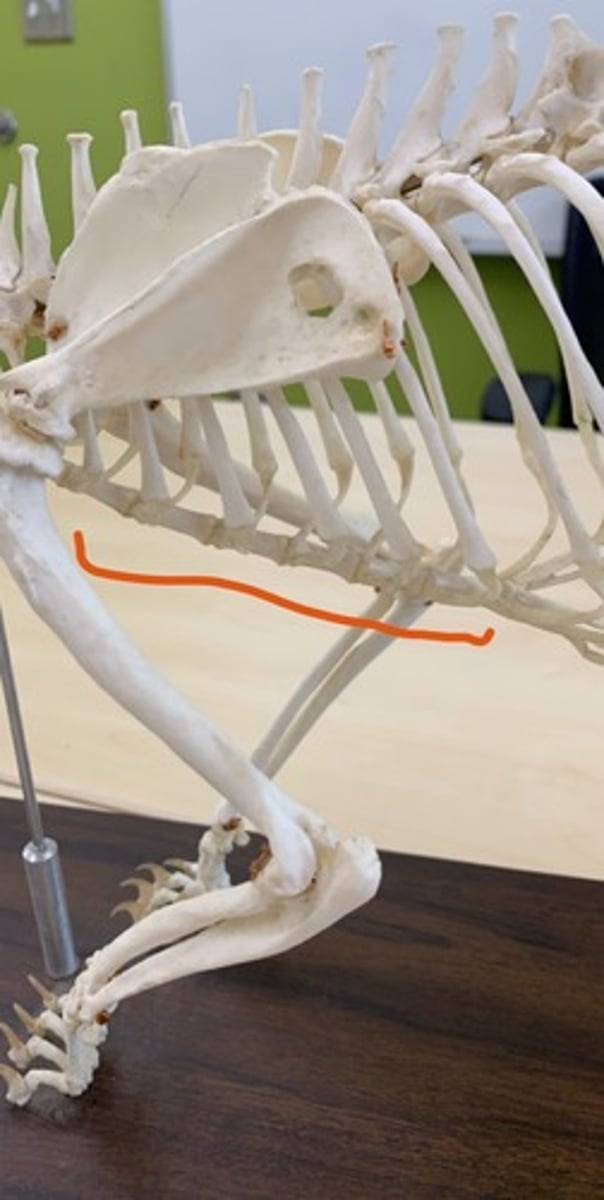
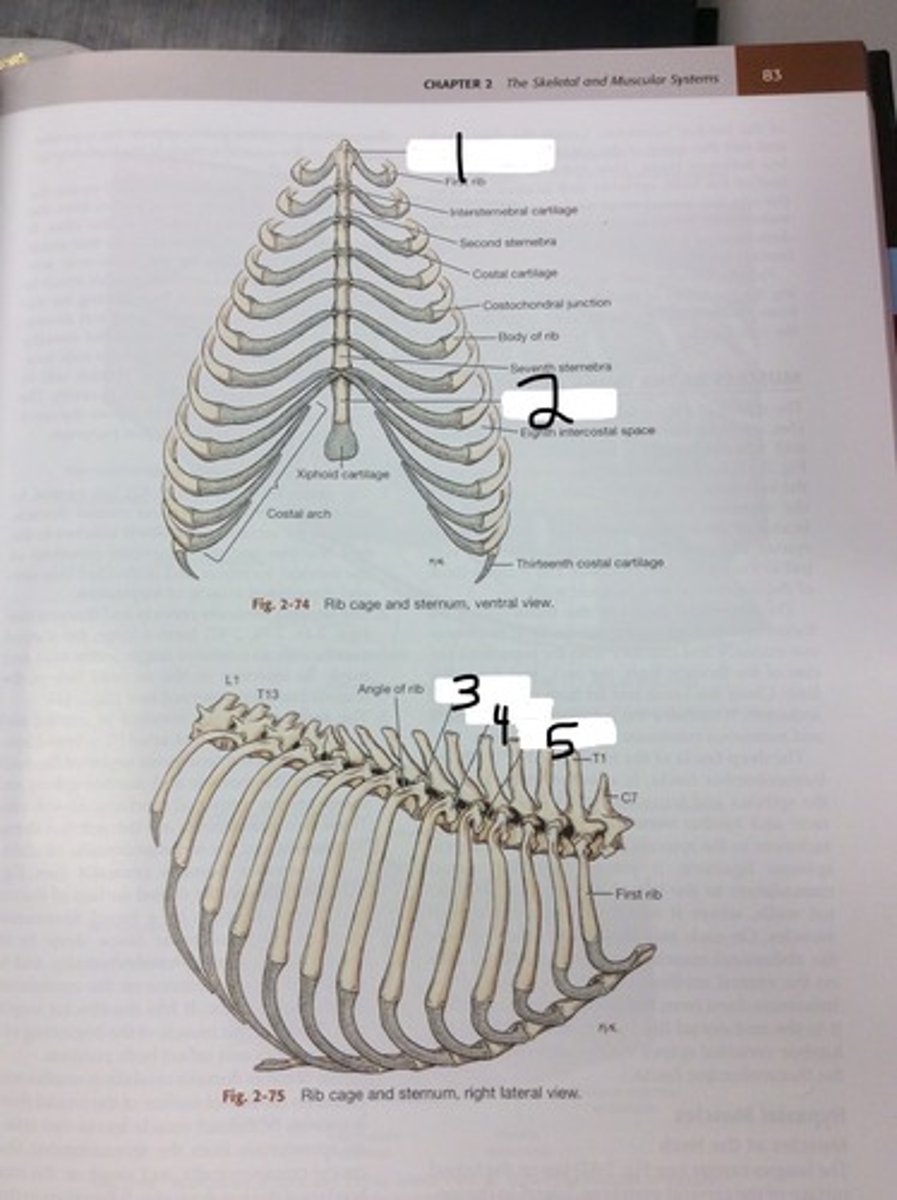
true ribs
firs nine pair of ribs, attach individually to sternum

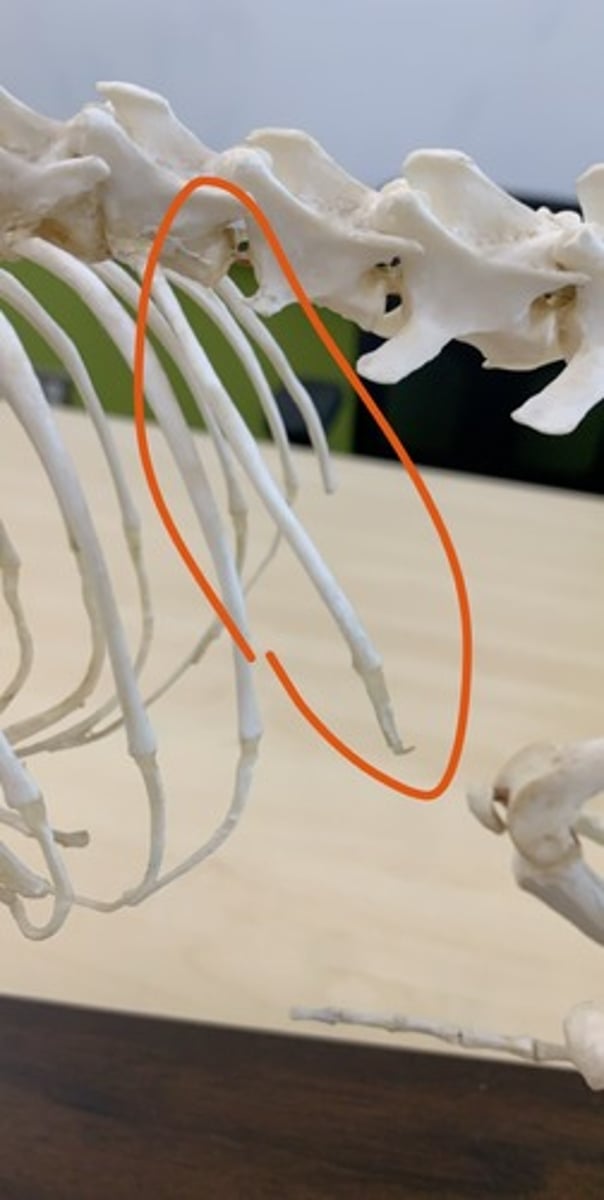
false ribs
next three pairs, attach to sternum via costal cartilage
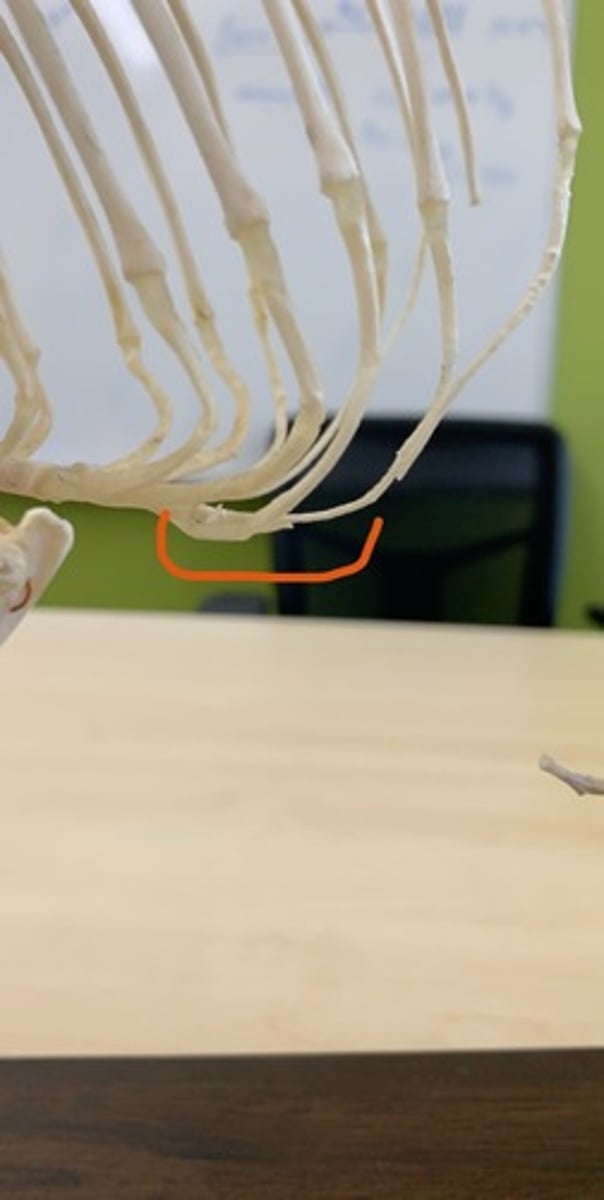

floating ribs
final pair, no attachment to sternum

costal cartilage
the cartilages that connect the sternum and the ends of the ribs

costal arch
curved structure formed by the costal cartilages of the false ribs
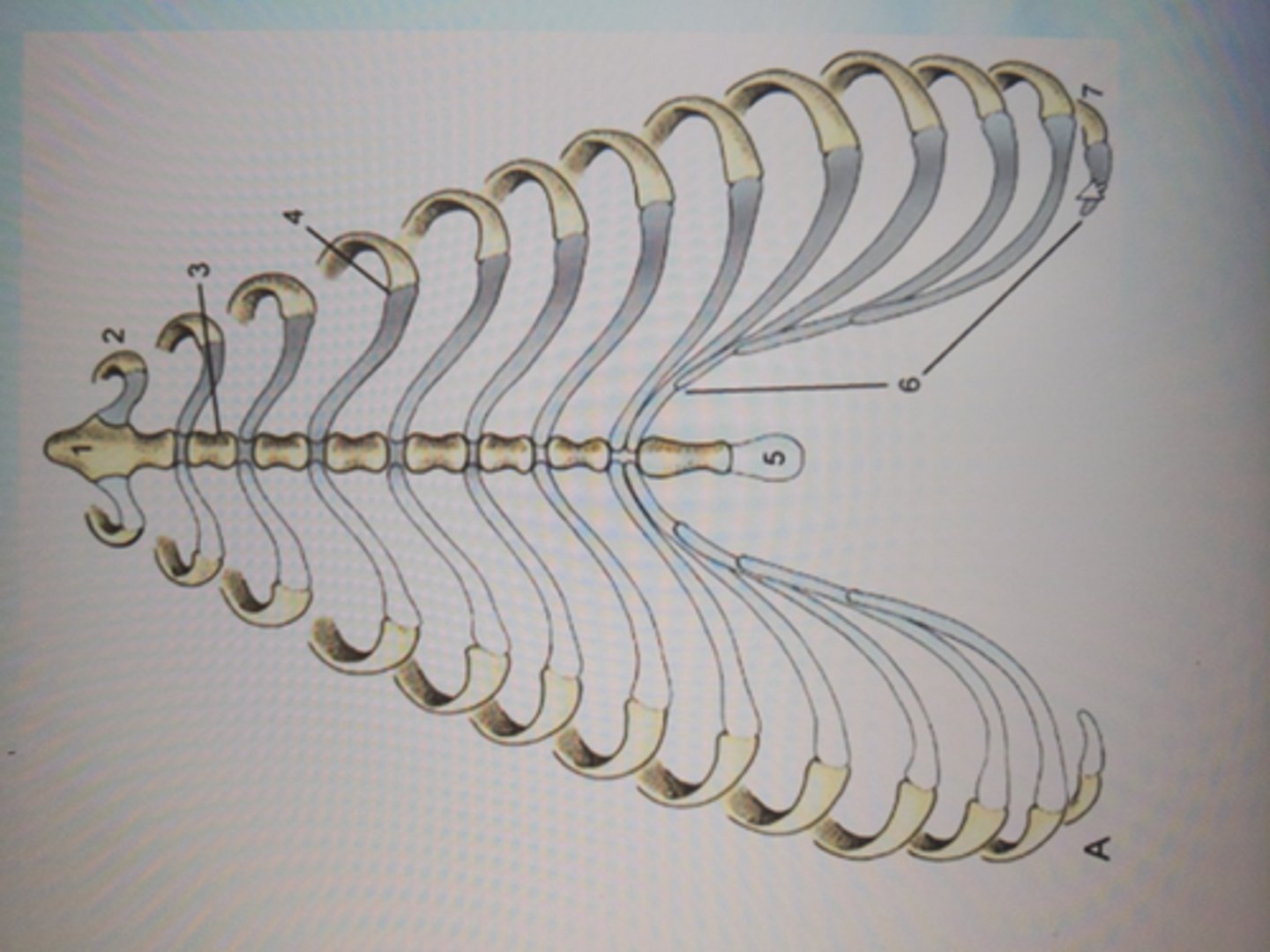
sternum
breastbone made up of sternebrae, lies along ventral middle
manubrium
first sternebrae, cranial part

xiphoid process
last sternebrae, cartilage extends off caudal end, palpable
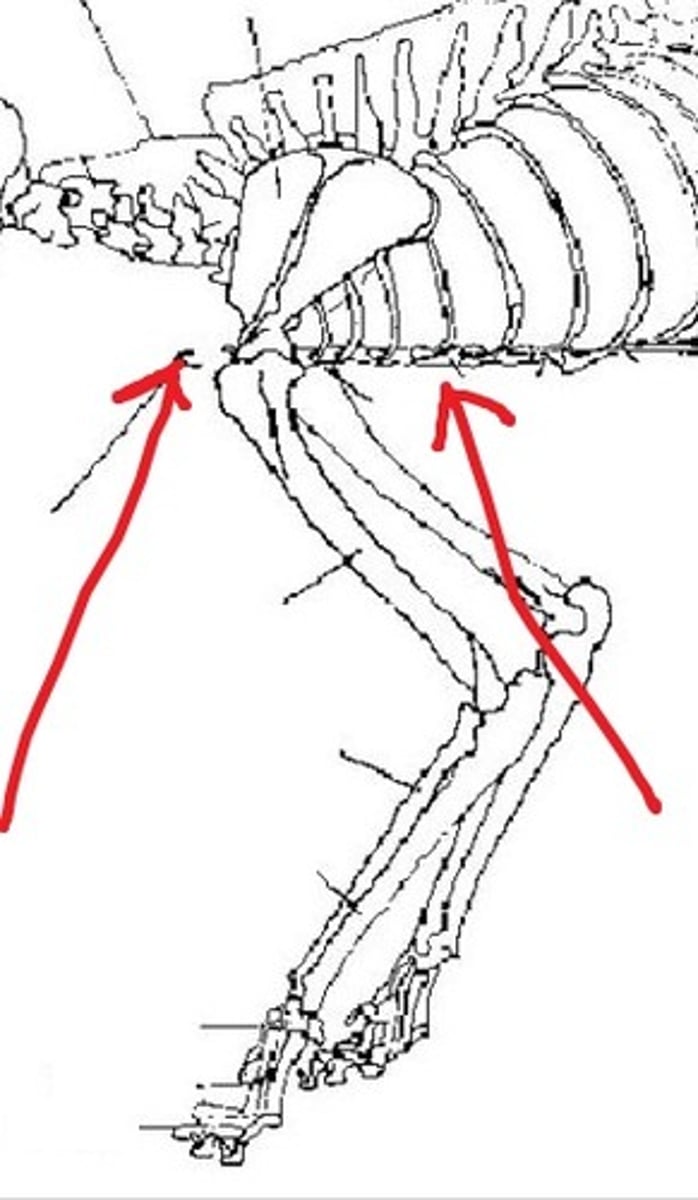
thoracic inlet
Cranial entrance into the chest cavity

thoracic outlet
Exit of the chest
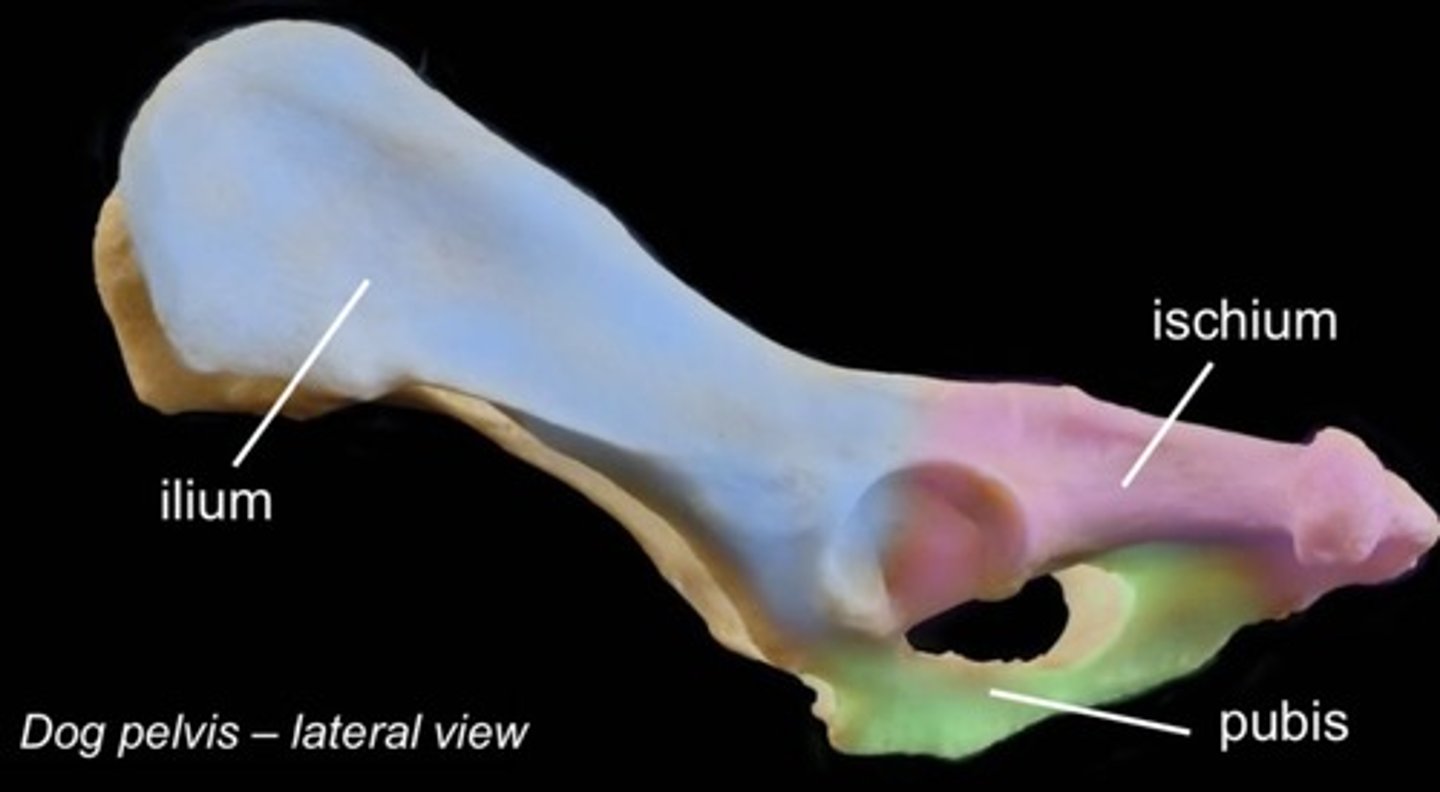
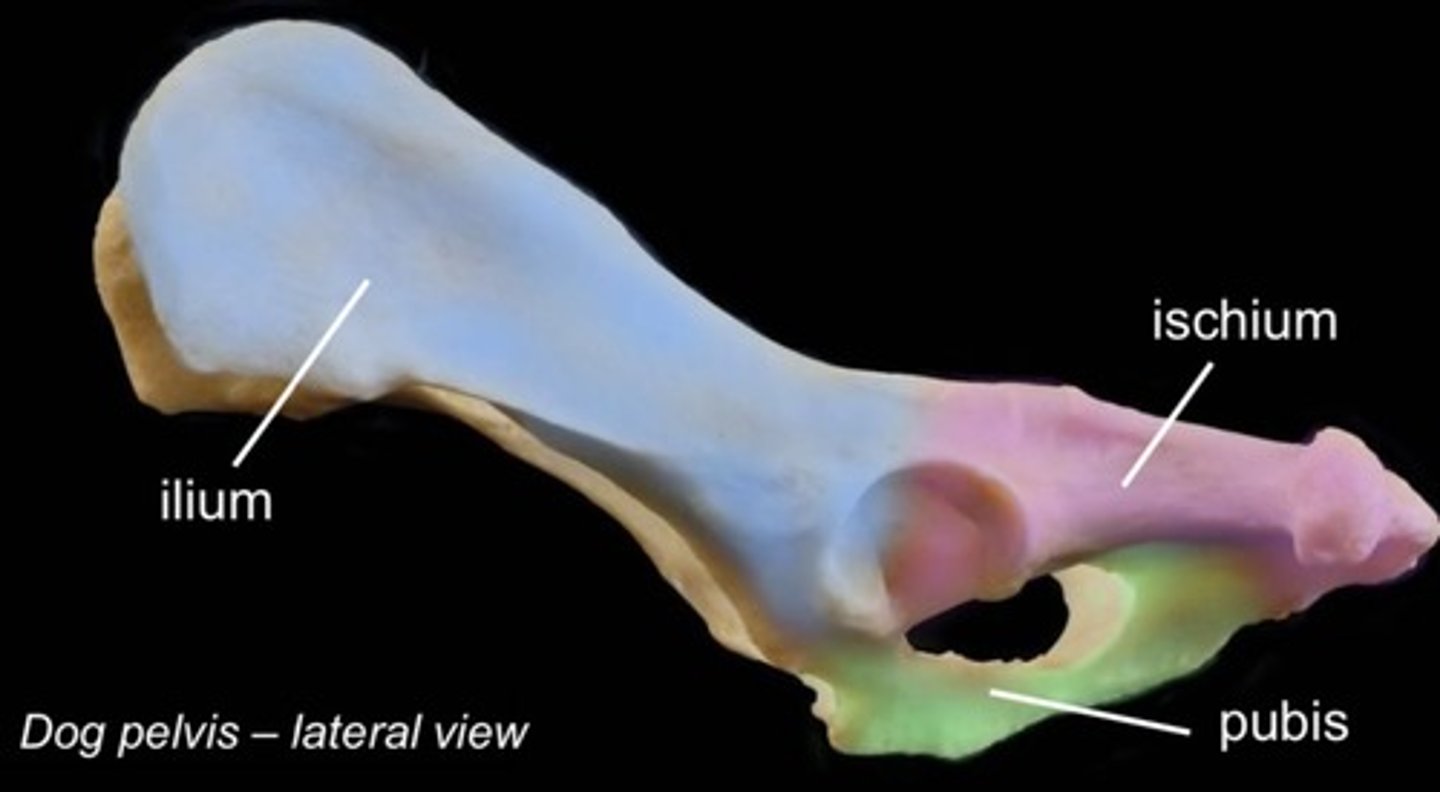
ilium
most cranial bone, wing shaped lateral surface, palpable. medial articulates with sacrum. cranial margin of acetabulum
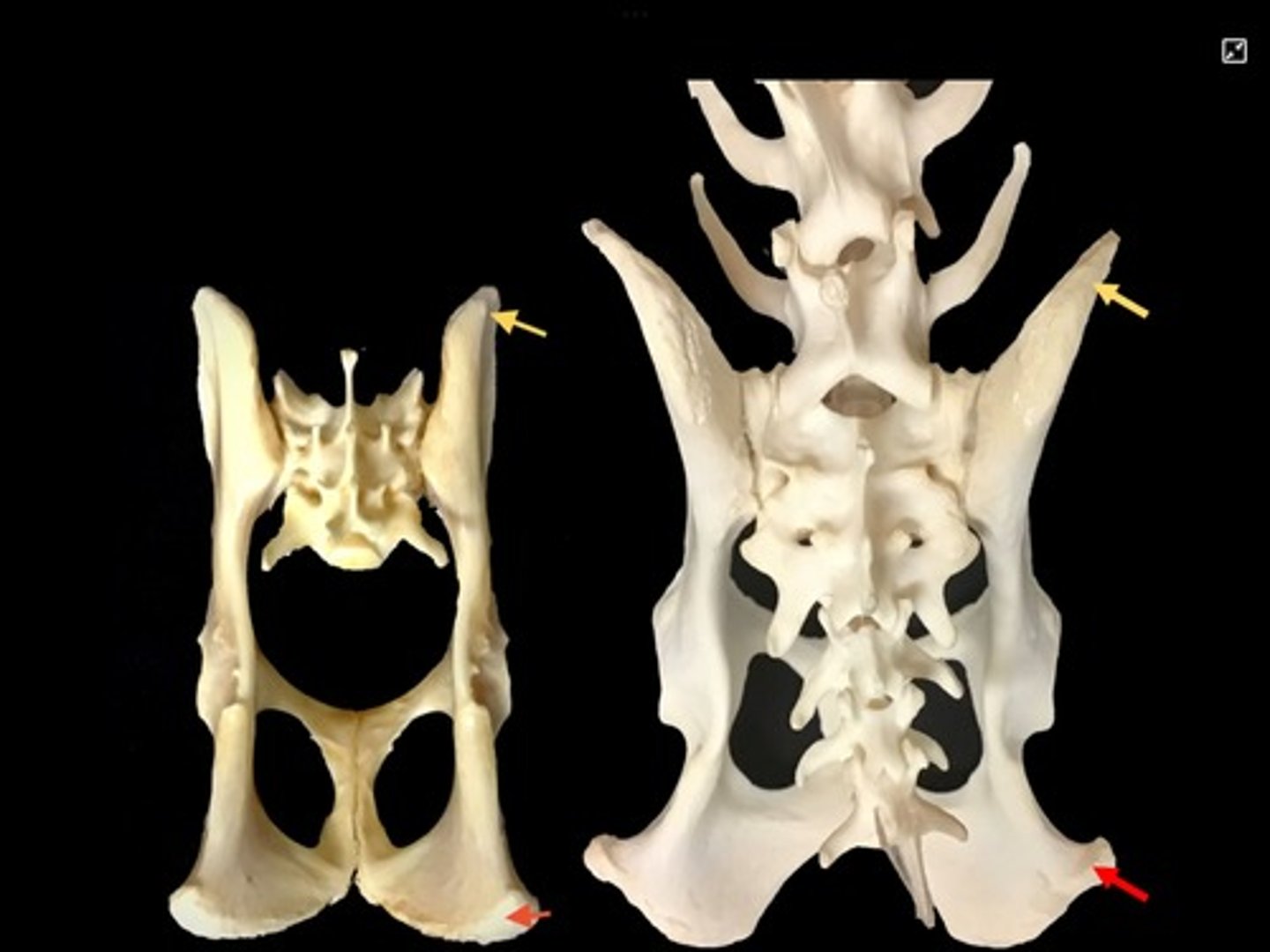
tuber coxae
point of hip, wing of ilium
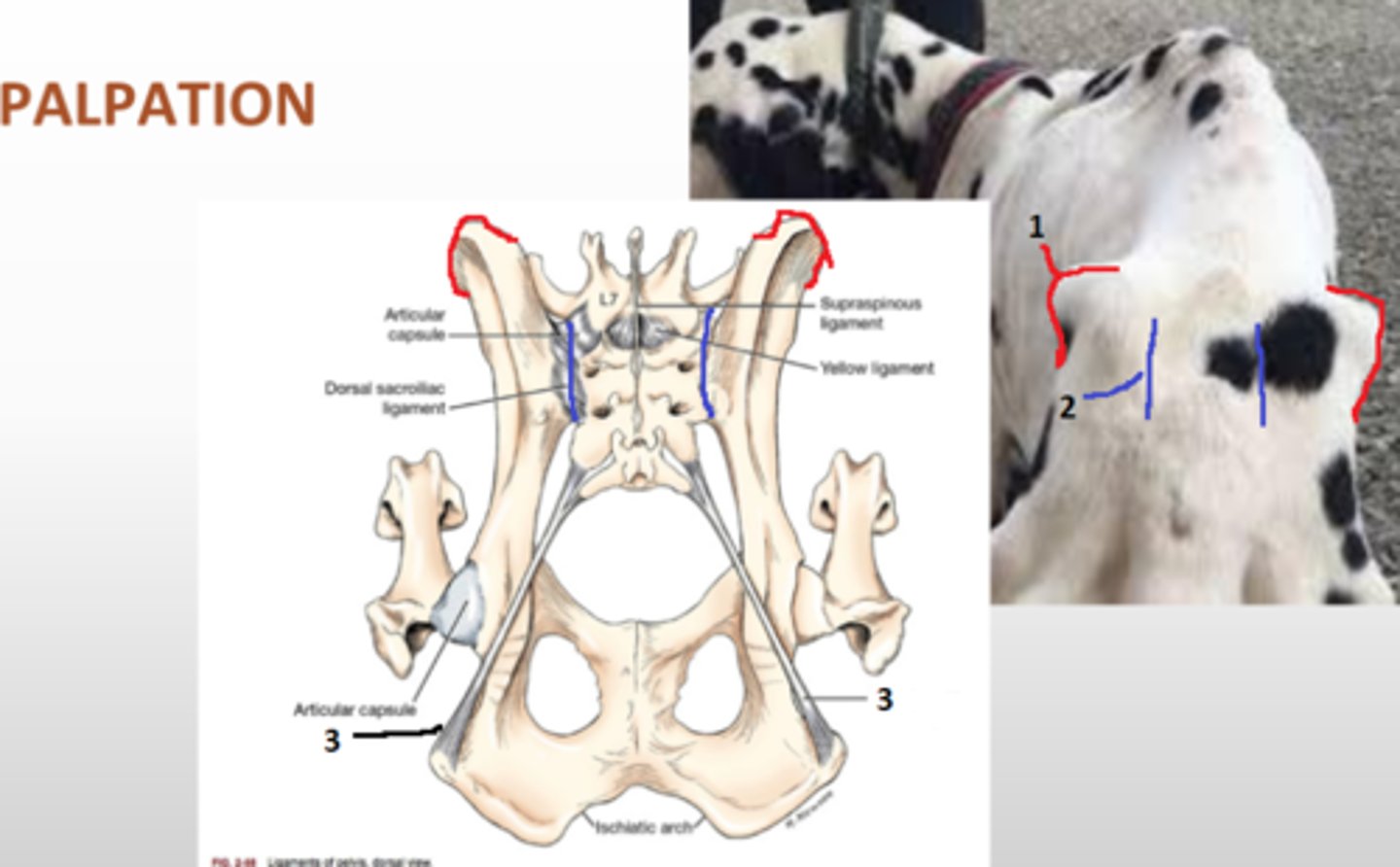
acetabulum
hip joint, site of attachment of the femoral head

ischium
most caudal bone, caudal to obturator foramen, caudal aspect of acetabulum
ischiatic tuberosity
thick caudal protuberance on ischium
pelvic symphysis
two hales of pelvis are joined ventrally by a cartilaginous joint, formed by ischium and pubis bones

obturator foramen
two large holes on either side of the pelvic symphysis that help reduce the weight of the pelvis bones
femur
thigh bone, heaviest in body. has head, greater trochanter, condyles, epicondyles, trochlea