biological psychology
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
three main physical sections of brain
hindbrain, midbrain, forebrain
hindbrain location
base of brain, back of skull
hindbrain function
controls activities we have no conscious control over, breathing, reflex actions, coordinating voluntary muscle movements
hindbrain structures
cerebellum, medulla
cerebellum
info from sensory systems & spinal cord, alcohol consumption, motor learning involving practice, posture, balance, fine muscle movements
medulla
vital functions: breathing, heart rate, digestion, swallowing
damage to medulla
life support machines to regulate breathing and heart function
too severe damage to medulla
brain dead
midbrain location
top of hindbrain under cerebral hemispheres
midbrain function
all senses except smell, brain's sensory switchboard
midbrain structures
reticular formation
reticular formation
network of nerves abt finger thickness, brain's arousal system: suppresses consciousness during sleep, main function: screen incoming info (need/not)
reticular formation damage
lead to coma
forebrain
largest and most developed part of brain
forebrain functions
how we think, feel, behave
forebrain structures
cerebral cortex, thalamus, hypothalamus
thalamus
oval shape in both hemispheres, filers info from all senses except nose, important in regulating level of arousal
thalamus damage
reduces sense of touch, visual/hearing impairment, lethargy or even coma
hypothalamus
below thalamus, regulates hormone release (sex drive, body temp, biological clock, thirst and hunger needs)
cerebral cortex
outer layer on top of cerebrum
cerebrum
largest area of brain, divides brain into two hemispheres
cerebrum location
above and front of cerebellum, most of the forebrain, consists of cerebral cortex,and neural tissues
corpus callosum function
thick band of fibers that attaches the two hemispheres, lets messages be sent from one to the other
contralateral control
left hemisphere=right side of body, right hemisphere: left side of body
left hemisphere
language based tasks, analytical thinking, sequential process, logical reasoning
right hemisphere
visual-spatial tasks, arts appreciation, expression of emotion, face recognition
4 lobes
frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital
location of lobes
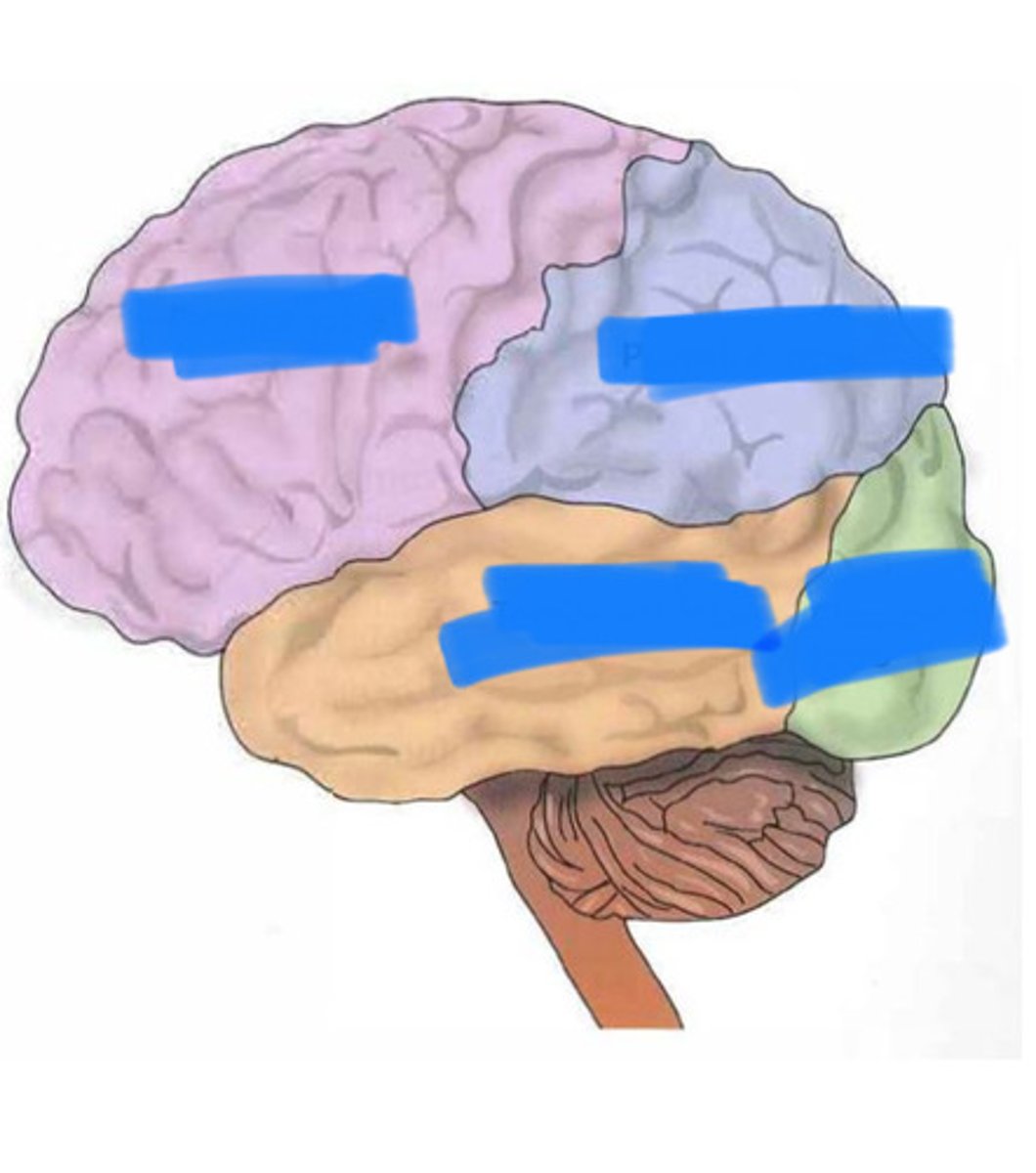
frontal lobe function
thinking, decision making, feeling, behavior, behavioral response, coordinating role as it is final place for sensory info, coordinates functions of other lobes
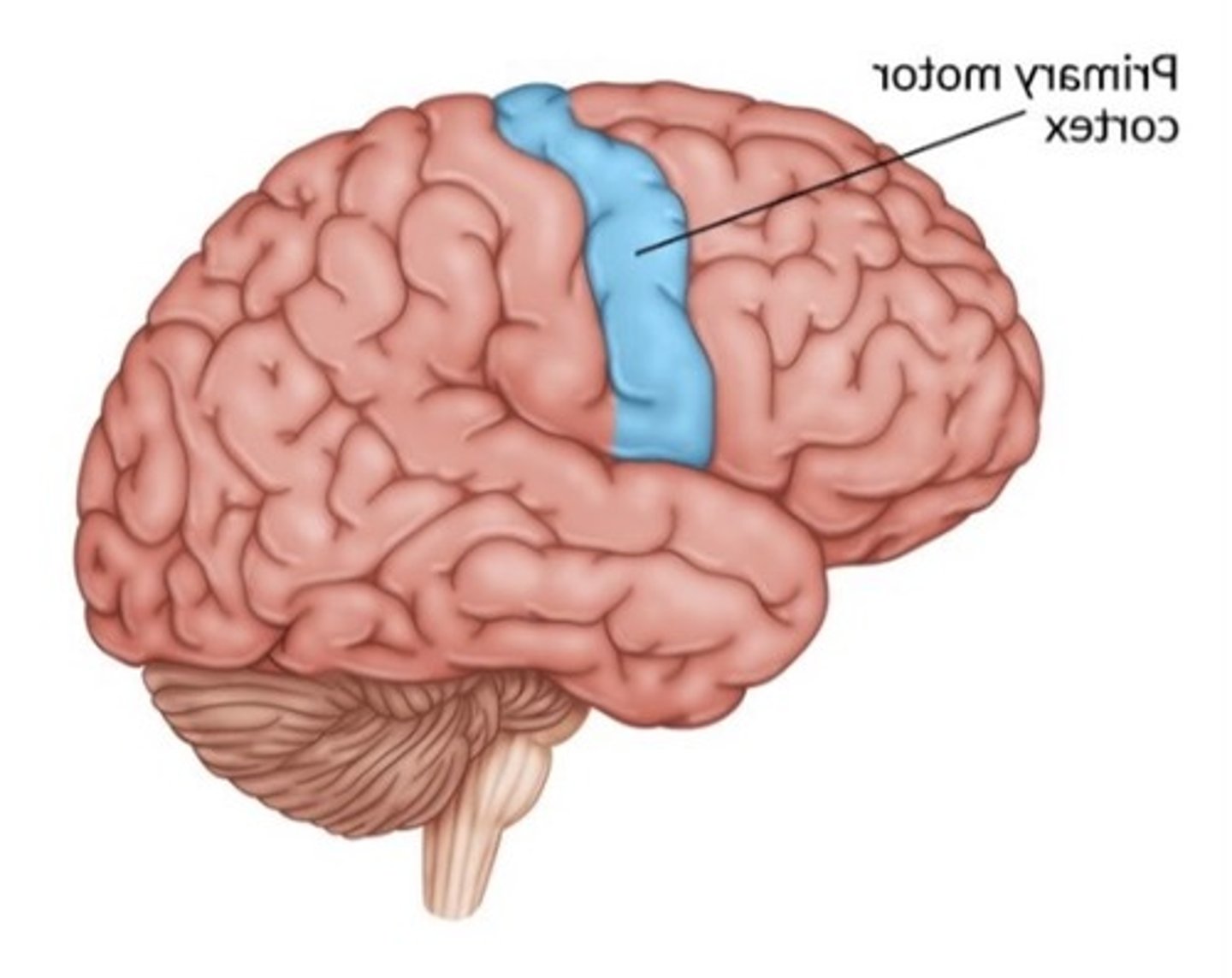
primary motor cortex function
strip of neural tissue controlling voluntary body movements through control of skeletal muscles (contralateral control for muscles on side of body)
Broca's area
production of speech, usually only left frontal lobe
frontal lobe structures
primary motor cortex, Broca's area, prefrontal cortex (cover)
how do we know broca's area controls speech
two patients who lost speech had damage in broca's area
prefrontal cortex location
covers the front part of the frontal lobe
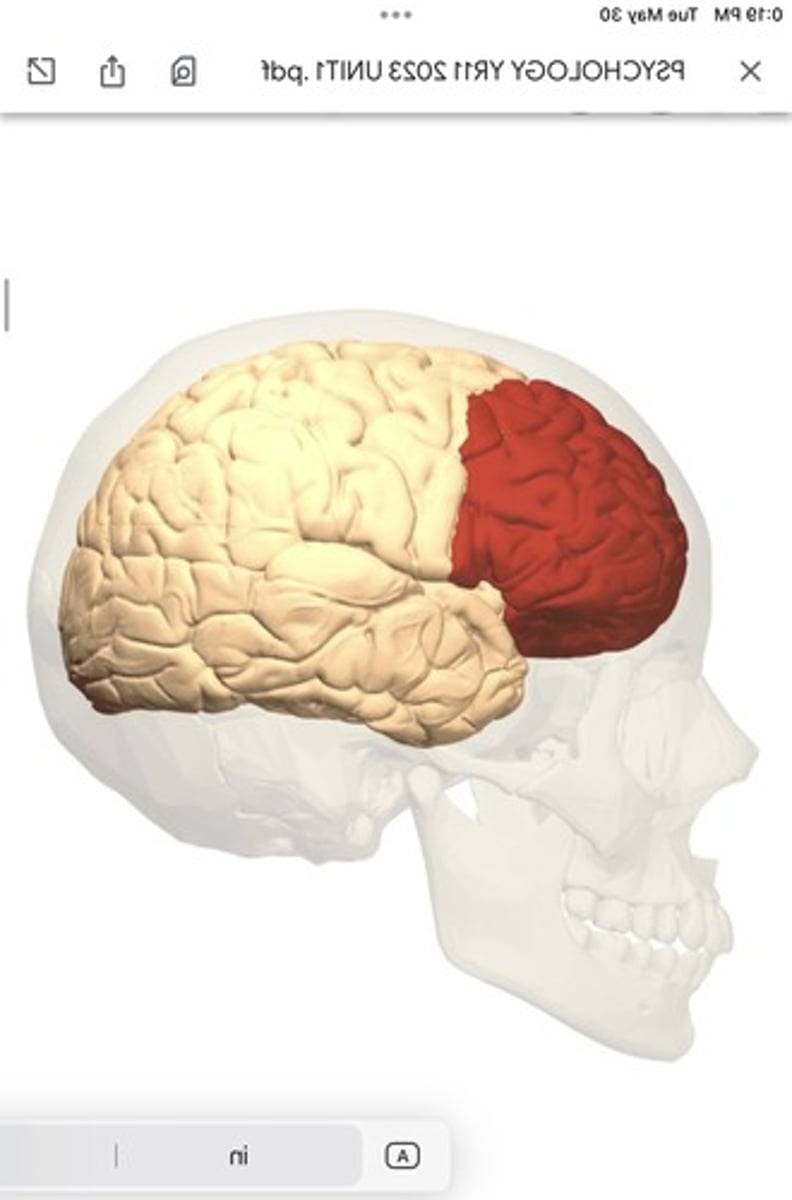
prefrontal cortex function
executive function: planning complex cognitive behavior, personality expression, decision making, and moderating social behavior
executive function abilities
determine good/bad, work toward defined goal, prediction of outcomes, social "control"
parietal lobe function
bodily sensations (mainly touch), spatial awareness, speech
parietal lobe structures
primary somatosensory cortex
primary somatosensory cortex
processes somatic sensations (touch, pain, position of body in space)
when receptors detect sensations, the info is sent to thalamus, then psc
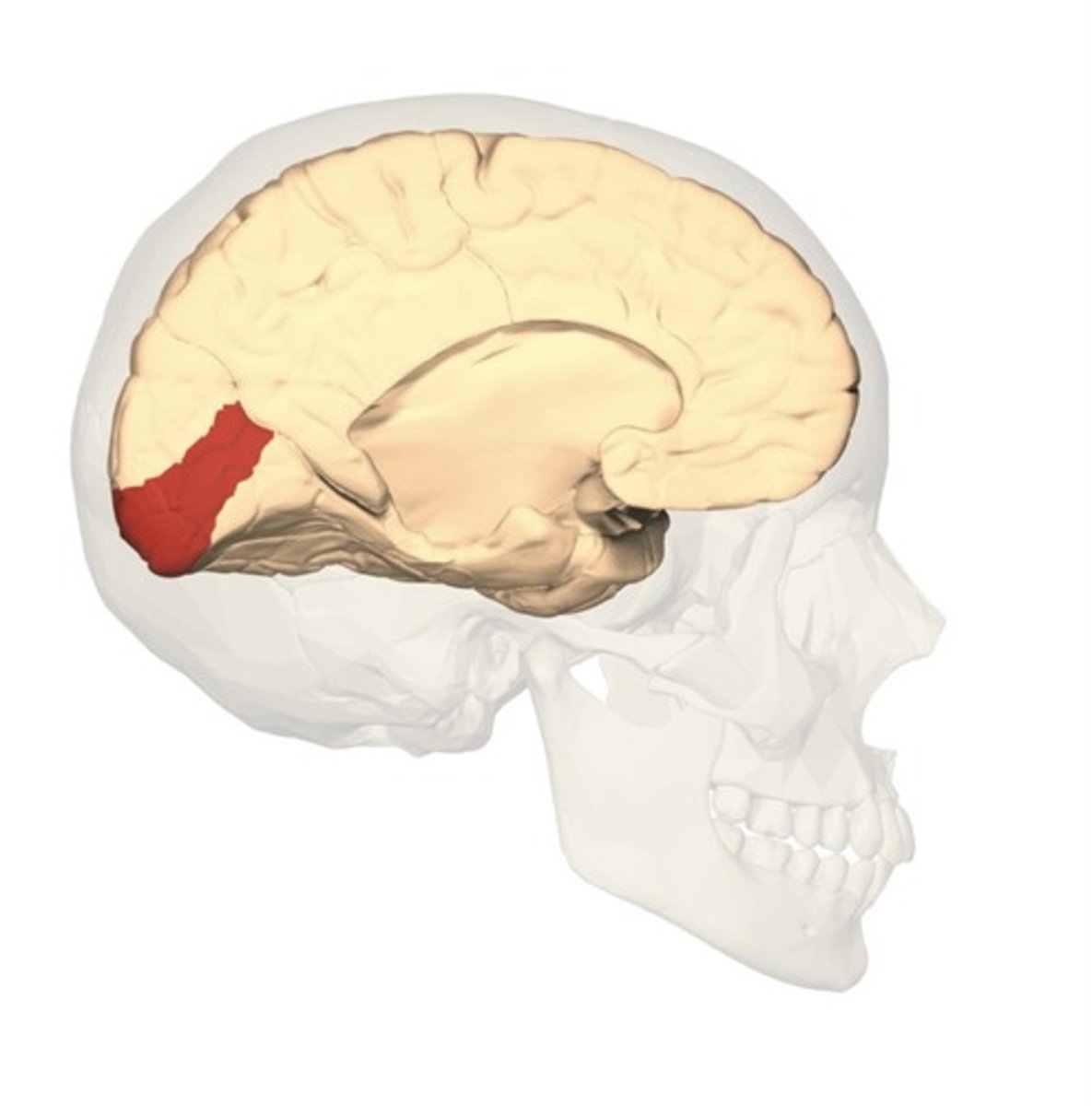
occipital lobe function
visual function of eyes
occipital lobe structures
primary visual cortex
temporal lobe function
hearing, language ad speech production, memory
receives and interprets info from ears
primary visual cortex function
essential to conscious processing of visual stimuli
visual info comes from lateral geniculate nucleus thalamus to primary visual cortex
temporal lobe structures
limbic system, amygdala, hippocampus, Wernicke' area, auditory cortex
auditory cortex
crucial in ability to perceive sound, such as pitch, where the sound orginates from, what is making the sound
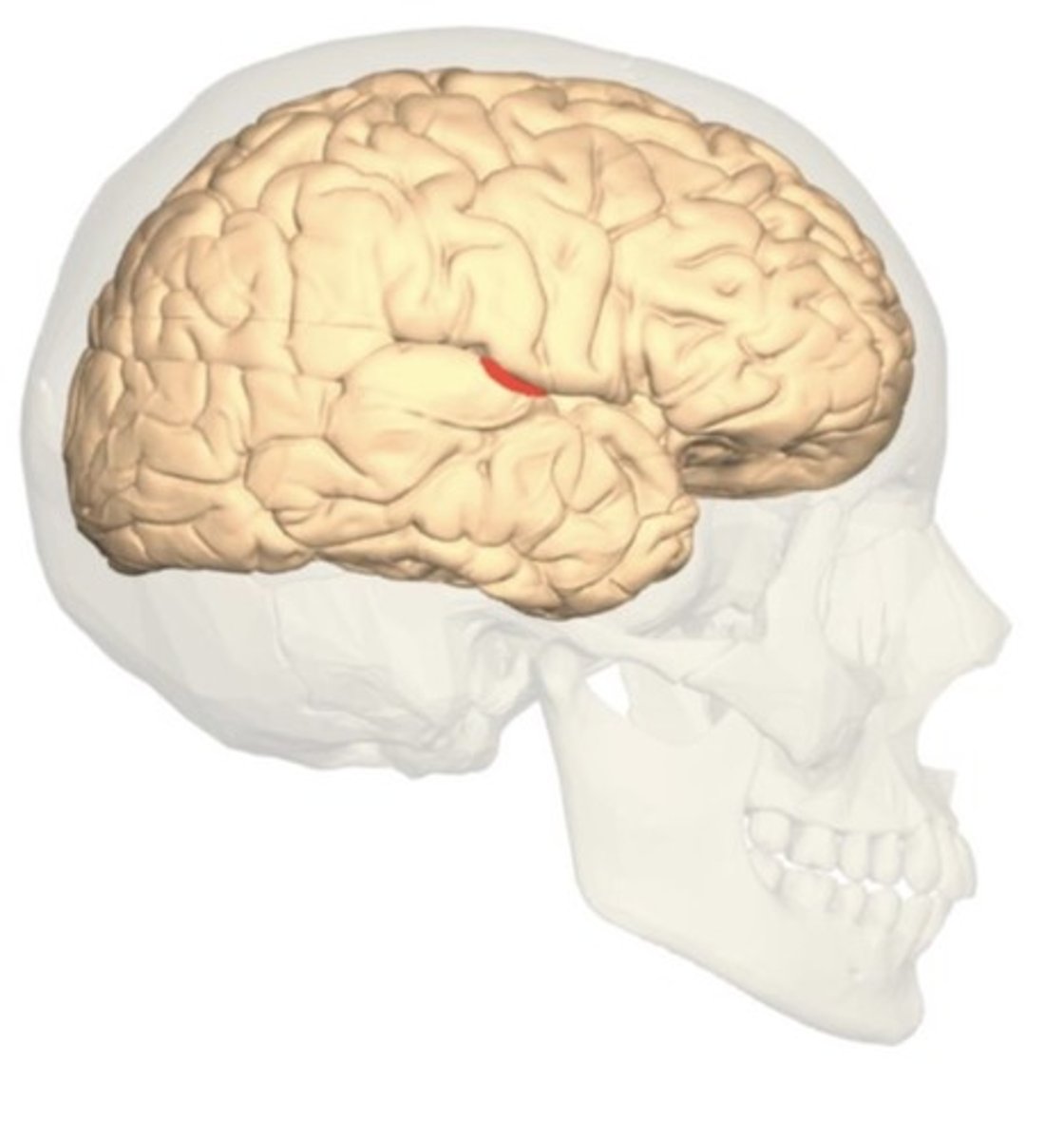
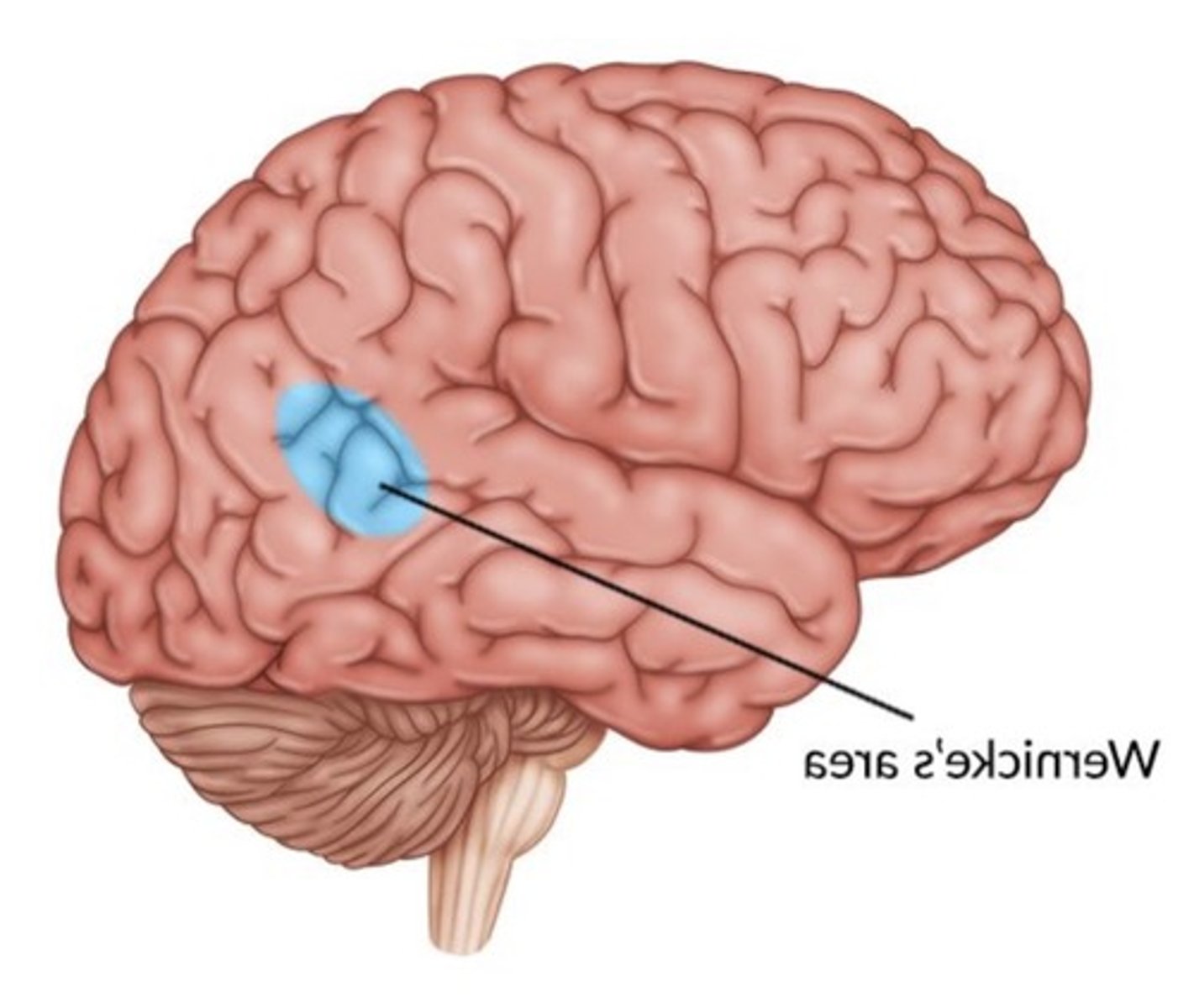
Wernicke's area
speech is normal, but language comprehension is impaired
damage to temporal lobe
disrupt auditory perception, deficits in ability to detect changes in pitch, localize sounds in space, or understand speech
2 parts of the human nervous system
central nervous system and peripheral nervous system
CNS components
brain and spinal cord
CNS function
processes info from outside the world through various senses and activates necessary actions. central to the way we think, feel, act
PNS components
spinal and cranial nerves, somatic and autonomic nervous system
PNS function
takes messages from the CNS to the rest of the body and from the sense organs to the CNS, on the edge of CNS
brain composition
millions of nerve cells, largest part of CNS
parts of PNS
somatic nervous system and autonomic nervous system
parts of the autonomic nervous system
sympathetic nervous system and parasympathetic nervous system
sympathetic nervous system
fight or flight, arouses body, when stressed active or in danger
ex. increased heart rate, pupil dilation
parasympathetic nervous system
bodily functions in day to day living, rest and digest; calms the body down and conserves energy
ex. digestion
somatic nervous system
network of nerves that communicate information from the sense organs to the CNS and motor messages from the CNS
to the muscles to move voluntarily
monitors bodily functions
autonomic nervous system
system of nerves connected to the heart, glands and smooth muscles such as the digestive and reproductive organs, and
tells the brain what is going on in these largely involuntary systems.
regulates involuntary functions
somatic nervous system examples
birds singing, light switched on = communicated to CNS through sense organs and spinal cord
typing = messages sent from CNS to spinal cord to muscles to do those things voluntarily
long term or extreme and heighted arousal in sympathetic nervous system
leads to impaired performace/mental problems such as anxiety
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging)
magnetic field of radio frequency pulses to measure sginal emitted from body tissues
detection of tumors and abnormalities
fMRI (functional magnetic resonance imaging)
MRI with color
measure activity in brain
oxygen blood levels in active parts show color on fMRI
look at brain structure and function (different types of behavior and place in brain used can be seen)
CAT vs MRI
CAT: quick, cheap, worse quality, 2D images, people with pacemakers can use
MRI: slow, expensive, high resolution images, 3D images, can't do pacemakers
EEG (electroencephalography)
detects and amplifies brain waves
electrodes fastened to scalp
different brain patterns can show problems with brain (epilepsy, tumors)
EEG limitation
cannot provide information from deep within the brain or detail about the parts of the brain activated
CAT scan (computerized axial tomography)
x-ray that sends narrow beams through head
scans slices of brain at each degree
detects tumors, strokes, injuries
shows atrophies (shrunken areas)
only show brain structure (2D)
phineas gage damage
Shooting the rod through his left cheek and out the top of his skull, causing major damage to his frontal lobes.
Recovered - able to talk sensibly and
regained full strength.
phineas gage changes
personality changed from polite, pleasant, and hardworking to loud, impulsive, dishonest
less capable of organizing himself
suffered strokes
phineas gage changes why
fronal lobe is responsible for planning, personality, and self-control
why do people have split brains
underwent surgery to reduce severe epileptic seizures
the corpus callosum is cut to stop brain activity associated with seizures from spreading from one hemisphere to the other
Who conducted split brain research?
Sperry and Gazzaniga
sperry split brain experiment results
if the picture was projected in the right visual field so the info went to the left hemisphere (the language hemisphere), she answered confidently and correctly
picture projected in left visual field=right hemisphere (non-verbal hemisphere) she could not say what she had seen, but could pick it up from under the screen with her left hand
Sperry split brain research procedure
split brain client at a table and hands fit under the screen so she could not see them
objects flashed to right or left visual field
asked what she saw
sperry conclusion
with a cut corpus callosum,
visual information could not be sent from the right to
the left hemisphere or vice versa.
lobotomy physician
walter jackson freeman II
what is the lobotomy based on
monkey received frontal lobe ablation (removal of tissue) and experienced reduced agitation when it got an answer wrong in a memory task (even though other monkeys experienced increased agitation)
why was freeman controversial/not trusted in the medical field
high fatality rate, attitude, and no interest to describe a scientific basis for the procedure
what did freeman develop
a lobotomy, a modified version of cutting sections of tissue in the prefrontal cortex, severing its' connections
used as a treatment for mental health issue
what kind of person did freeman conduct his first lobotomy on
63-year-old housewife who was suffering
from insomnia and agitated depression (mixed bipolar
disorder, in which manic and depressive symptoms
occur together).
spinal cord function
major thoroughfare for messages between the
brain and the rest of the body.
neurons in spinal cord that transmit info via impulses away from the brain
efferent or motor neurons
neurons in spinal cord that transmit info via impulses towards the brain
affarent or sensory neurons
spinal cord how many segments
31
where do sensory nerves lead to on the spinal cord
dorsal (back side) of each segment
where do motor nerves exit from on the spinal cord
ventral (abdominal) sides
what is between the dorsal and ventral sides of the spinal cord
grey matter
grey matter is composed of
nerve cells
concentration of them on the outer edges of the cerebral cortex
white matter
inside brain, composed of largely neural connections and called white matter because of a fatty coating
PNS cranial and spinal nerve functions
combine both sensory and motor functions, leading both to and from the brain, but there are functional differences in spinal nerves when they meet the cord.
what happens to the cranial and spinal nerves when they meet the spinal cord
they split into a dorsal root that has
sensory functions and a ventral root that has only
motor functions.
cranial nerves function
carry sensory input from the skin or motor output to the muscles of the head or face.
They also carry sensory information for vision,
hearing, smell and balance.
spinal cord injuries (paraplegia, quadriplegia)
paraplegia: lower part of the cord is
damaged, resulting in the lower limbs being
paralyzed
quadriplegia: upper part of the
spinal cord is damaged, resulting in the arms and
legs being paralyzed.