process improvement practice
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Achieve no more than 3.4 defects per million opportunities (DPMO) by reducing variation and eliminating process defects.
What is the goal of Six Sigma?
six sigma
A data-driven, statistically based approach that uses the DMAIC method to improve processes, eliminate defects, and produce measurable financial returns.
Motorola
Who pioneered and popularized Six Sigma?
key players in six sigma
champions
master black belts
black belts
green belts
yellow belts
yellow belts
entry-level
produce empirical results or effective information collectors
report issues to upper-level experts
beginners w/ some general six sigma knowledge
basic principles, fundamental quality tools
green belts
in less critical projects, they can be group leaders
trained in basic quality tools and work in teams
knowledgeable within the problem-solving model of DMAIC
obtain empirical results and make actual transformation
process mapping, hypothesis testing
black belts
full time project leaders on six sigma project
spend about two years as a black belt
significant and statistics training accomplished
project review measurement, multiple regression
master black belts
full-time, cross-functional, in-house six sigma
experts / consultants / coaches
identified by champions
experienced black belts serve as mentors and trainers
optimization experiments, advanced regression methods
champions
senior level or executive managers
establish six sigma vision
work with black belts to identify possible projects
provides continuing support for the project and validates the results at end of project
cultivate six sigma culture
DMAIC methodology
define
measure
analyze
improve
control
define
project selection
validate problem statement
business impact and goal statement with key metrics
measure
understand the current process status
measure current performance
assess process capability for baselines
analyze
analyze the process flow data and identify bottleneck points with problems
generate theories to explain potential causes, focusing on why defects, errors, or excessive variation occur
experimentation and verification of root causes
improve
generate potential solutions to address the root causes
evaluate solutions
develop a “to be” value stream map of the redesigned process
implement pilot solutions and compare results to baseline
develop and execute a full-scale implementation plan
control
complete the project and hand off the improved process to process owner
finalize the control system with revised procedures
maintain improvements
Maximize customer value by eliminating waste and improving process flow.
What is the goal of Lean?
Just-In-Time System (JIT)
Producing and delivering goods only when needed, in exact quantities, to reduce inventory and expose system problems.
T ransportation
I nventory
M otion
W aiting
O verproduction
O ver-processing
D efects
S kills (under-utilized talent)
What are the eight wastes (TIMWOODS) in Lean?
specify value in the eyes of the customer
identify the value stream and eliminate waste
use a pull system that is triggered by the customer
involve and empower employees
pursue continuously improve (Kaizen & 5S — short, straighten, stnadardize, and sustain)
Steps to Create a Lean Enterprise
Sort, Straighten, Shine, Standardize, Sustain
What is 5S in Lean?
kanban
Japanese word meaning “card” or “visible record” that refers to cards used to control the flow of production through a factory and to ensure just-in-time
Visual Management
The use of visual cues (colors, markings, charts) to monitor process status, manage flow, and ensure transparency.
Lean Vs. Six Sigma
Lean: Removes waste, improves flow, and shortens lead time
Six Sigma: Reduces variation and defects through data analysis
Lean Six Sigma
Combines Lean’s waste elimination with Six Sigma’s data-driven problem solving for a comprehensive improvement approach.
Lean: Visible process issues (inventory, flow, safety)
Six Sigma: invisible issues (variation, inconsistency)
What does Lean address vs Six Sigma?
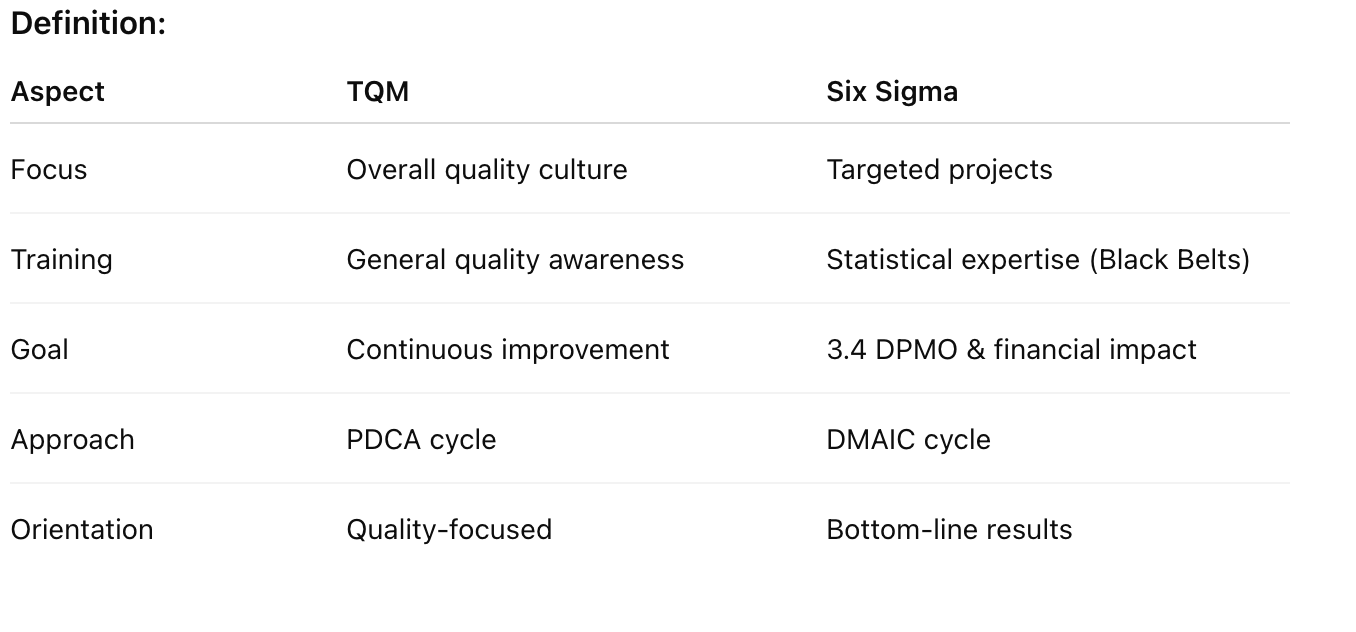
Lean: PDCA cycle, value-stream analysis, pull system
Six Sigma: DMAIC framework
What tool or philosophy guides each?
PDCA cycle
continuous improvement
more flexible and adaptable
faster and simpler
relies on trial and error
less data-driven
DMAIC
data-driven analysis and rigorous planning
more rigorous and structured
root-cause analysis
through and complex
require more resources and time
too complex for smaller-scale improvements