Biology Edexcel A-Level B Core Practical Paper 3
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
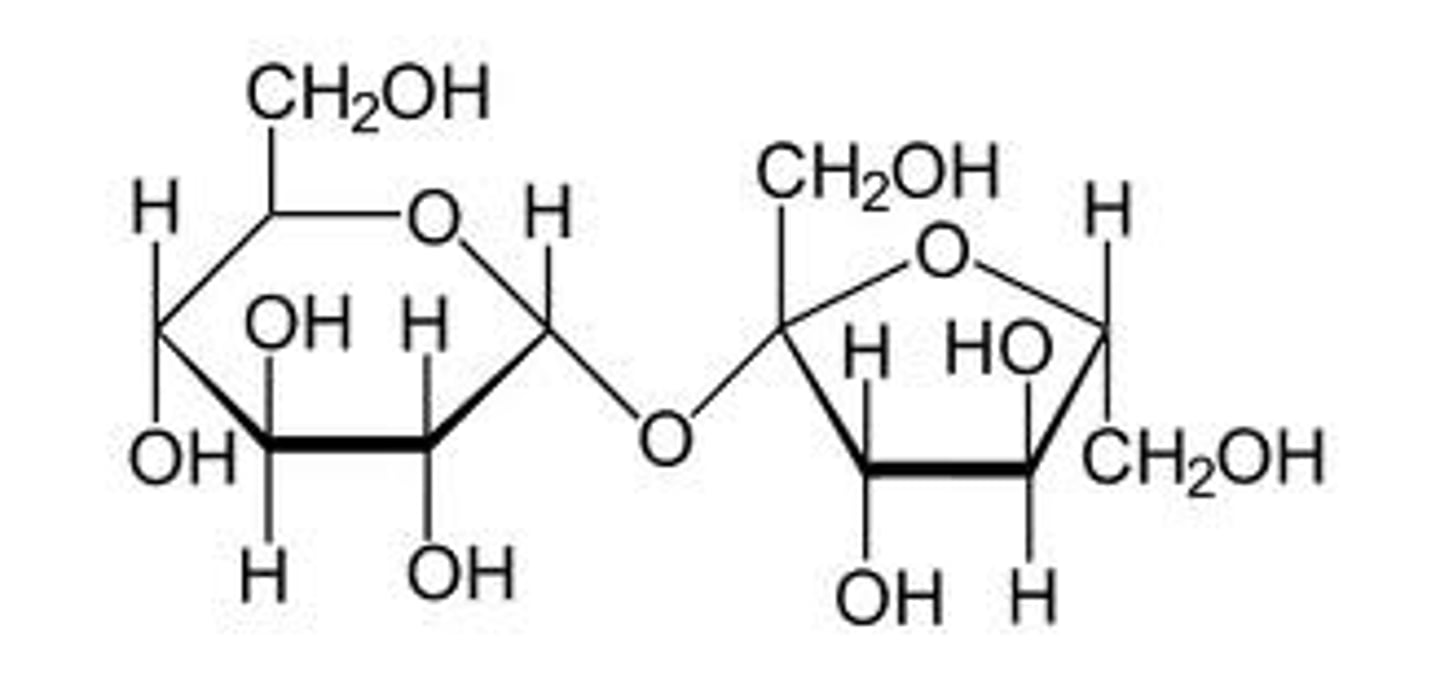
What type of carbohydrate is sucrose?
Disaccharide
What is sucrose composed of?
A glucose and fructose, combined in a condensation reaction
What is the formula for sucrose?
C12 H22 O11
What is a pollen grain?
The male gametophyte of the plant
How is a pollen grain formed?
1) Microspore mother cell divides by by meiosis
2) Creates 4 haploid cells (each develops into a pollen grain)
3) Each haploid cell divides once by mitosis
4) Forms the pollen grain
What does the whole pollen grain consist of?
1) Pollen tube nucleus
2) Generative nucleus
3) Cell membrane, wall and cytoplasm
What is the role of the generative nucleus?
Divides via mitosis to form two nuclei, one forms the embryo, the other fuses with polar nuceli to form the endosperm nucleus which is triploid
Role of endosperm nucleus
Provides the plant with food when it begins to germinate
What is the role of the pollen tube nucleus?
Produces hydrolytic enzymes that digest the tissue of the style
How does the pollen tube grow vertically down?
Via Positive chemotropism as the microphyle releases attractive chemicals
What is the Pollen culture medium
Range of materials such as Boric acid needed for growth. Without these salts and ions, key biological structures cannot form
Which two solutions do you need?
Pollen culture medium and the Sucrose solution which you mix
How is a sucrose solution created?
Via serial dilutions created using a stock solution.
Describe the Method
1) Mix the two named solutions
2) Use a perti dish and a moist filter
3) Take a clean slide and place a drop of this solution on
4) Then knock off pollen from the anther using a mounted needle onto the slide
5) Note time added
6) Repeat for each sucrose concentration
7) Record results at regular intervals (Every 3 mins)
What is the purpose of the petri dish?
Acts as a humid chamber where pollen slides will be placed to prevent drying out
Why is a cover slip not used?
Prevents anoxic conditions developing that could prevent growth
How do you actually measure pollen growth?
1) You only remove the slide from the dish when measuring
2) Place under x100 mag
3) Use a calibrated eyepiece graticule
4) Return to petri dish quickly
How long does it take for a tube to grow?
30 mins
What are you measuring?
The effect of sucrose on rate of pollen tube growth
Safety
1) Pollen can irritate lungs, bad for individuals with hay fever and asthma
2) Things that make up the pollen solution are hazards such as boric acid so wear eye protection.
Controlled Variables
1) Need all to be mature flowers
2) Use plant species that quickly germinate
3) Length of time allowed to grow
Why do you need to use mature flowers?
As these would shed pollen as they are ready to germinate
What do you display at the end of the experiment as your quantitative results?
The Average growth rate.
How do you calculate the average growth rate?
Total growth distance/time
Limitations
1) Hard to get pollen tubes to germinate as its random
2) Some don't grow straight,But graticule is straight, So our interpretation of length is subjective
3) May not be accurate
How does the pollen tube grow?
1) By extending the cell membrane via changes in their cytoskeleton
2) And by changes in water potential
3) When a pollen grain is released it has low WP and is dehydrated and when it reaches the stigma it becomes hydrated
4) Influx of water into pollen directs growth
What actually is the effect of sucrose on pollen tube growth?
Sucrose stimulates pollen growth on stigma, but then it lowers water potential, so the more sucrose, the less likley osmosis is to happen, which decrease the pollen tube length
What is the effect of too low sucrose concentration?
Water travels into the pollen, bursting the cell. Not hydrated enough to stimulate growth
What is the effect of too high sucrose concentration?
Pollen tubes growth is stunted as water travels out of the pollen by Osmosis due to the concentration gradient created. Pollen tube not hydrated.
How is a control set up during a practical measuring enzyme activity?
Replace enzyme with distilled water, or boiled enzyme solution
How can a colorimeter determine the rate of reaction between the enzyme trypsin and milk?
Tryspin is an enzyme that digests protein caesin in milk. As trypsin digests the milk, solution turns less and less cloudy towards colourless. Decrease in absorbance can be measured by the colorimeter
Outline the practical procedure of measuring the effect of enzyme concentration on enzyme activity, using trypsin and milk.
1. Dilute stock solution of trypsin with distilled water, to make solutions of concentrations of 0.2, 0.4, 0.6 and 0.8.
2. Calibrate colorimeter by filling cuvette with 2cm3 of trypsin solution, and 2cm3 of distilled water and set colorimeter absorbance to 0
3. Fill cuvette with 2cm3 of diluted trypsin solution with 2cm3 of milk solution
4. Measure absorbance at 15 second intervals for 5 minutes
5. Repeat at other trypsin concentrations
6. Plot rate of reaction against time graph
Effect of enzyme concentration on enzyme activity
As enzyme concentration increases, frequency of successful collisions per unit time to form enzyme substrate complexes will increase, so the rate of reaction increases until the optimum.
Past the optimum, rate of reaction plateau's as substrate concentration becomes the limiting factor.
How is the effect of pH on enzyme activity investigated?
1. Add fixed volumes of buffer solutions with different pH values to 1cm3 of trypsin solution and 2cm3 of milk
2. Measure absorbance immediately, and at 15 second intervals for 5 minutes
Effect of pH on enzyme activity
Enzyme activity is highest at optimum pH
Above or below the optimum, enzyme activity decreases as unsuitable pH disrupts active site, causing partial denaturation.
If pH values are too extreme, full denaturation may occur
How is effect of temperature on trypsin activity measured?
Prepare water baths at a range of different temperatures
Place 2cm3 of trypsin solution and 2cm3 of milk solution (not together in same contained) in each water bath
Leave solutions for 5 minutes to allow solutions to reach water bath temperatures
Mix together and measure absorbance every 15 seconds for 5 minutes
Effect of temperature on enzyme activity
Temperature increases rate of reaction up until optimum temperature. Increased temperature increases kinetic energy, therefore more frequent successful collisions per unit time forming more enzyme substrate complexes. Beyond this temperature, enzymes will begin to denature and disrupt the tertiary structure, and active sites change shape so that they can no longer bind to substrate.
What is the function of a stage micrometer?
Calibrate eyepiece graticule to determine length of structures
How is eyepiece graticule calibrated?
Line up scale of stage micrometer with divisions of eyepiece graticule.
Count the number of divisions present of eyepiece graticule equivalent to 1 division on stage micrometer.
Work out the length of 1 division of the eyepiece graticule.
Magnification formula
Size of image/Actual size of specimen
Outline the procedure to prepare a slide
Place stain on sample
Mount sample onto slide
Place coverslip on top (ensure there are no air bubbles as this can distort image)
Where in plants are cells undergoing mitosis found?
Meristem
What is mitotic index?
Ratio of cells undergoing mitosis in a tissue and total number of cells in that tissue
Outline procedure to prepare a root tip slide
1. Heat 1M HCl in 55degreesC water bath for 15 minutes
2. Cut a root tip from a garlic clove using a scalpel (5-10mm) and place in the HCl and leave for 5 minutes
3. Remove from the HCl and wash with cold distilled water
4. Dry lightly with tissue paper and place on a slide
5. Squash with a weighted needle to spread out cells
6. Add a few drops of stain (make the chromosomes visible)
Hazards and precautions for root tip mitosis experiment
HCl is corrosive -> avoid contact with eyes or skin
Blue Stain is corrosive -> Avoid contact with eyes or skin
Scalpel -> Can cut fingers
Why is the root tip placed in hot HCl
HCl dissolves the middle lamellae in order to break up the cellulose cell wall. This allows the stain to permeate and the tip to be squashed more easily.
Why is the sample squashed
Allows cells to be seen more easily
Describe how you could use chromatography to separate photosynthetic pigments found in leaves (3)
Add concentrated droplet of mixed pigments
Create a buildup of dots by drying and adding more on solvent line marked in pencil 2cm from bottom of paper
Place paper in ethanol (solvent) so paper is just touching solvent
Wait for 20 minutes and obtain solvent front