ANATOMY OF SENSES: EQUILIBIRUM (BALANCE)
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Static Equilibrium
associated with vestibule; when the head is motionless; elevates position of head relative to gravity
Macula
organ of static equilibrium
inside the utricle and saccule
specialized patches of epithelium surrounded by endolymph
contains thousands of hair cells
Otoliths
Hair cell cilia/microvilli are embedded in a gelatinous mass containing _________.
increase
FUNCTIONS OF OTOLITHS:
_________ the weight of the gelatinous mass
Make it more ________ to the force of gravity.
1 = ?
responsive
FUNCTIONS OF OTOLITHS:
_________ the weight of the gelatinous mass
Make it more ________ to the force of gravity.
2 = ?
Utricular mascula
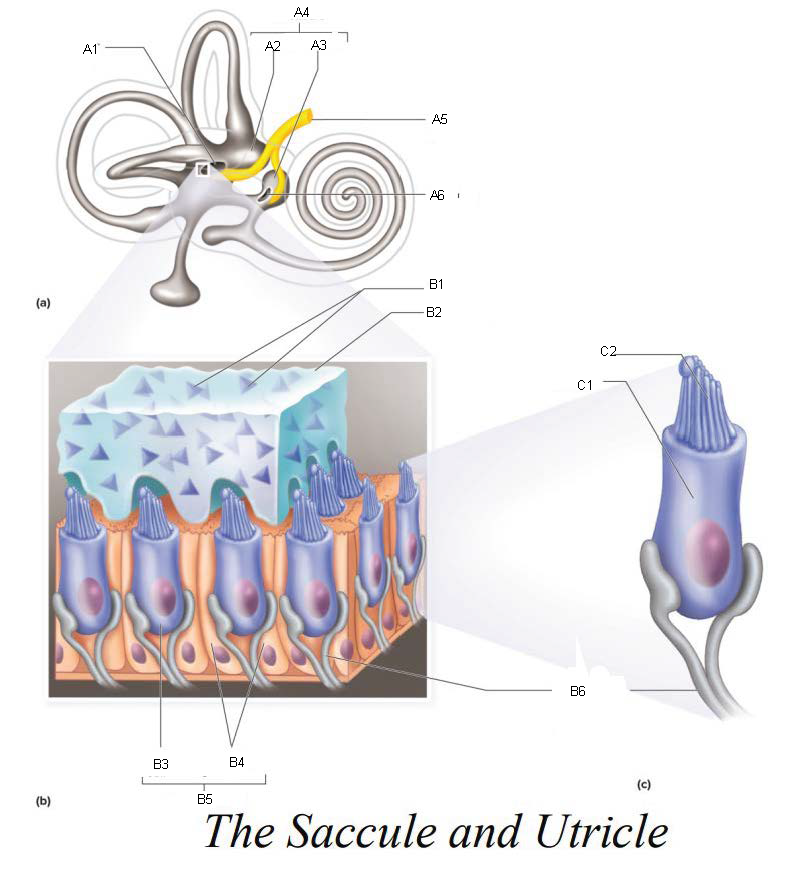
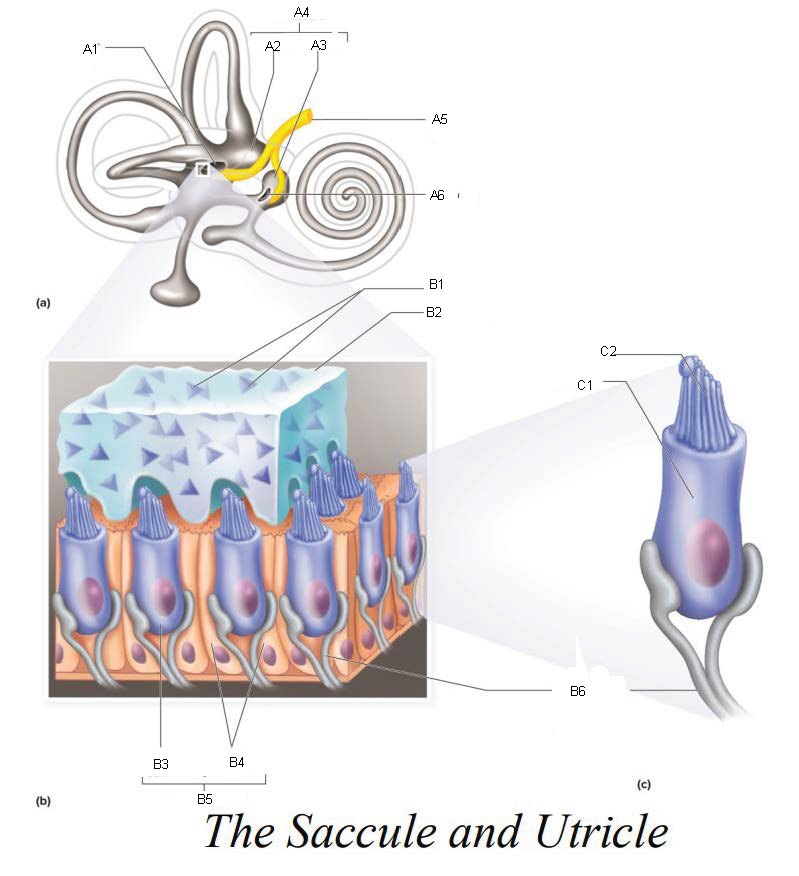
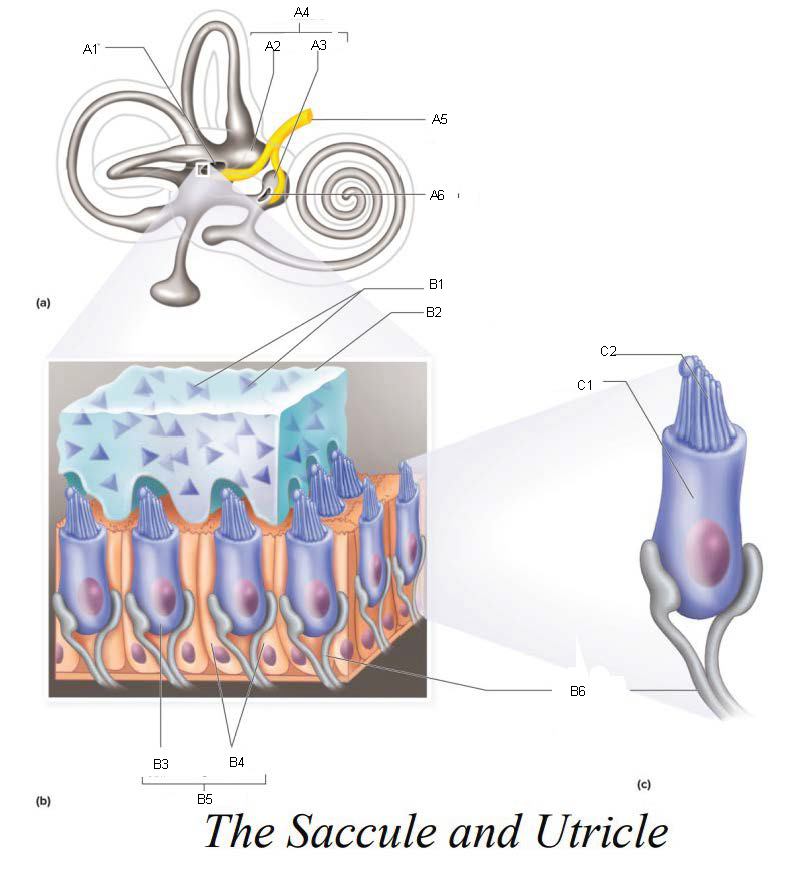
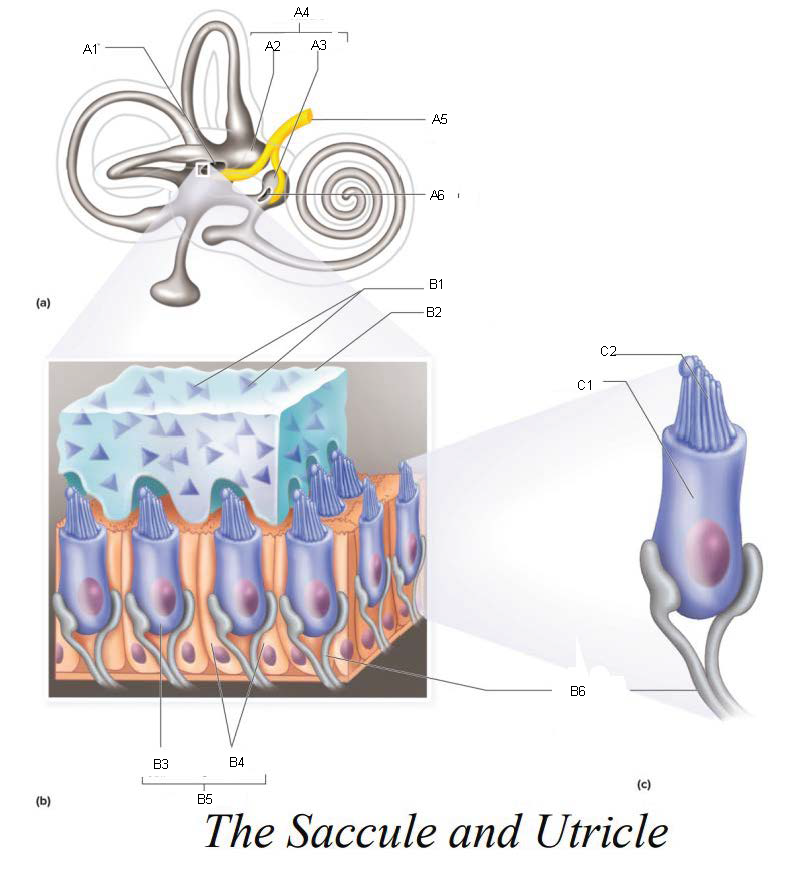
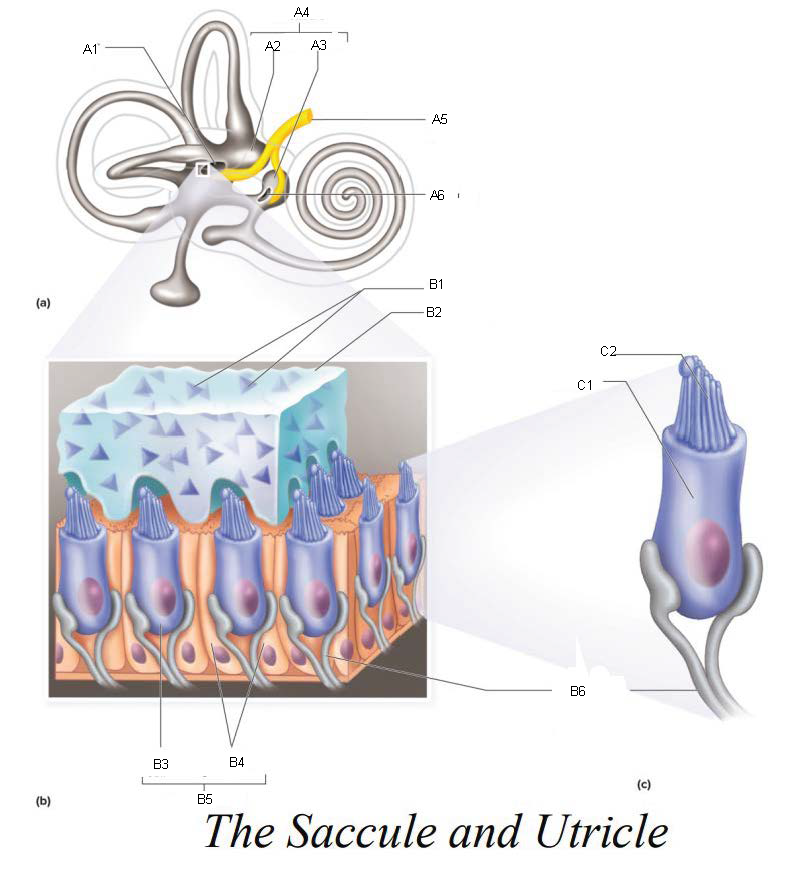
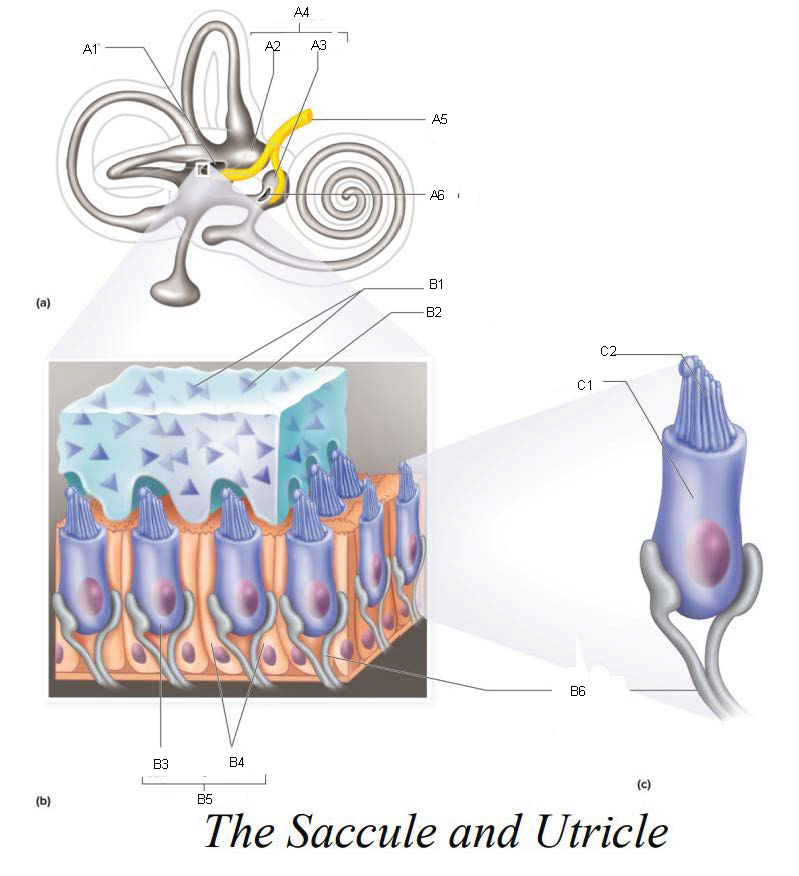
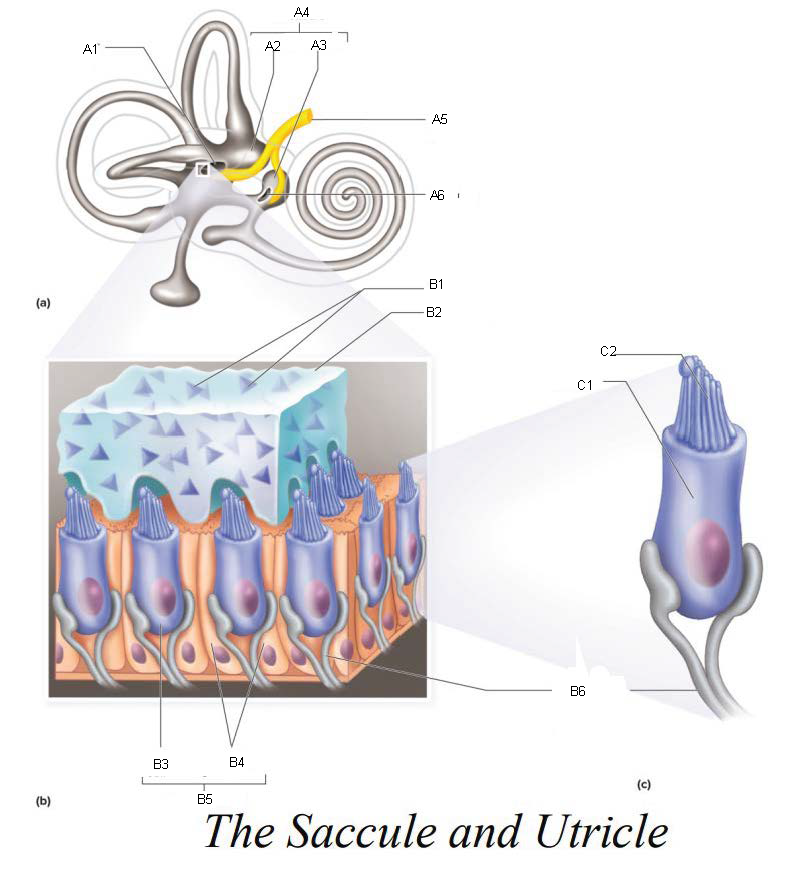
A1
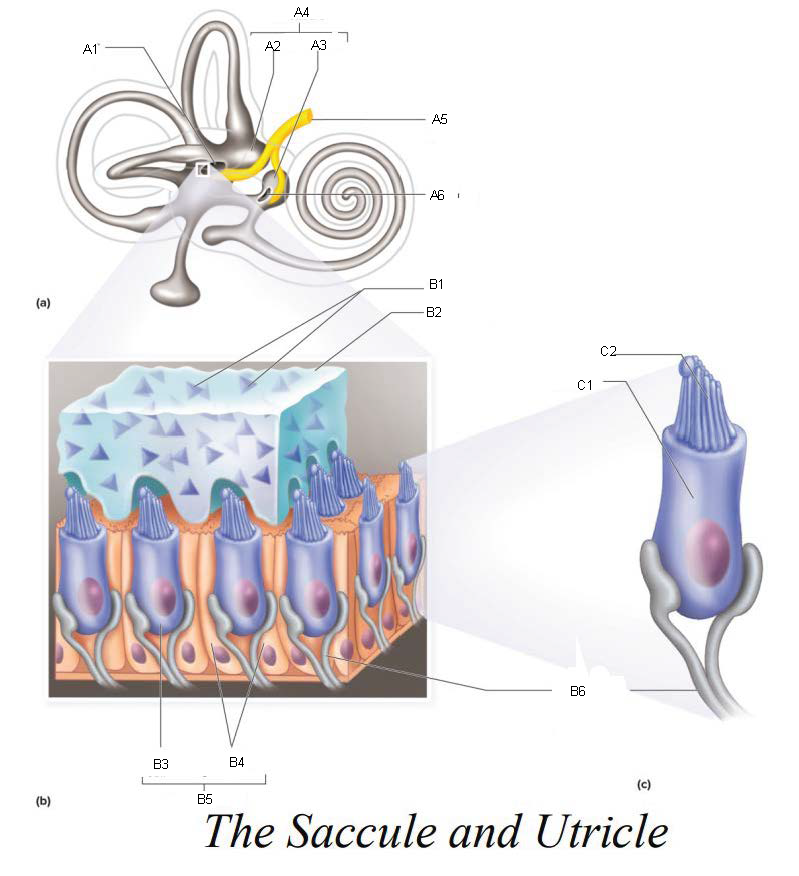
Utricle
A2
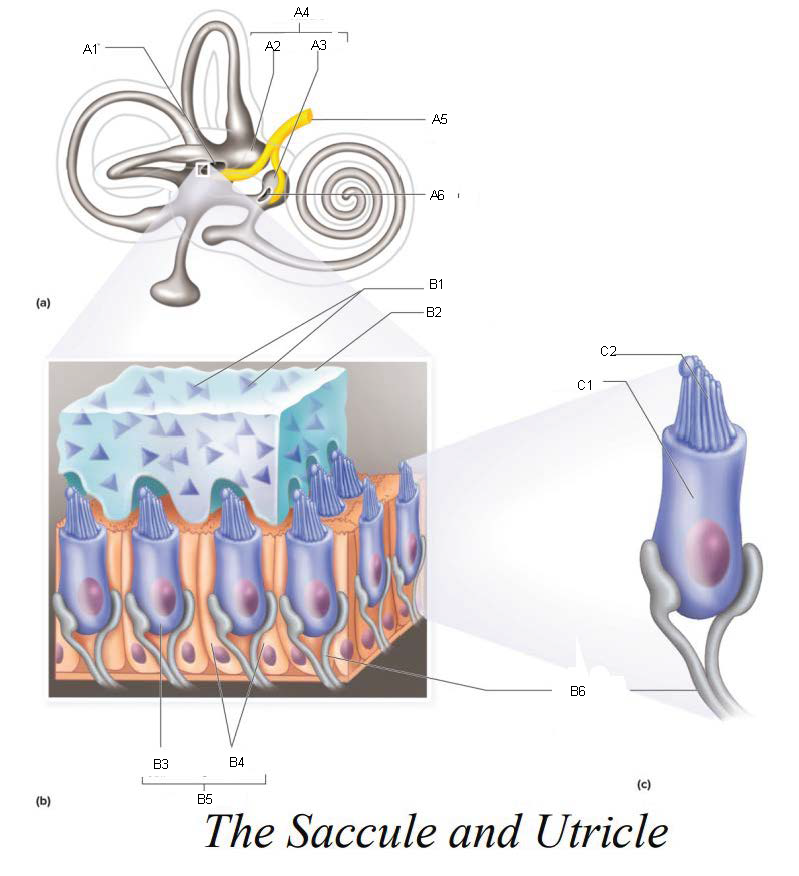
Saccule
A3
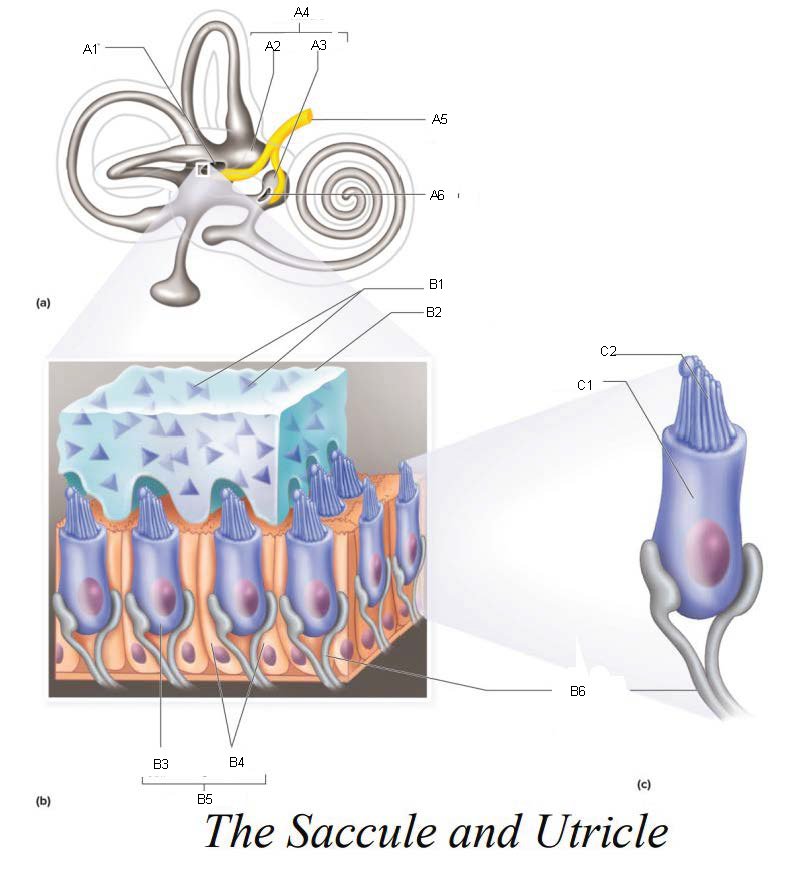
Vestibule
A4
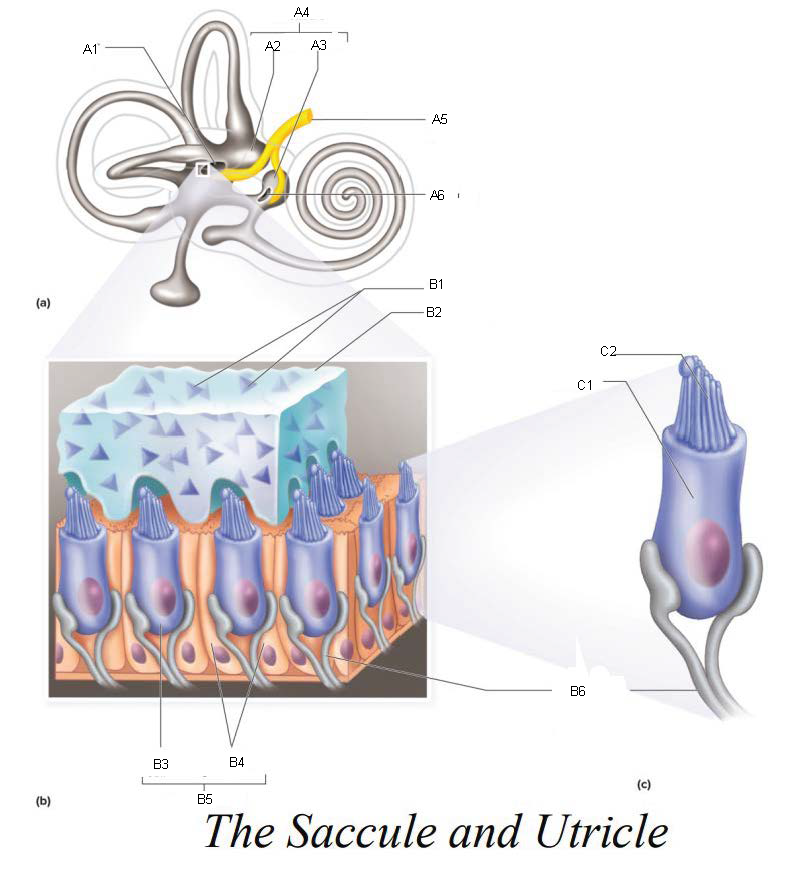
Vestibular Branch of the Auditory Nerve
A5
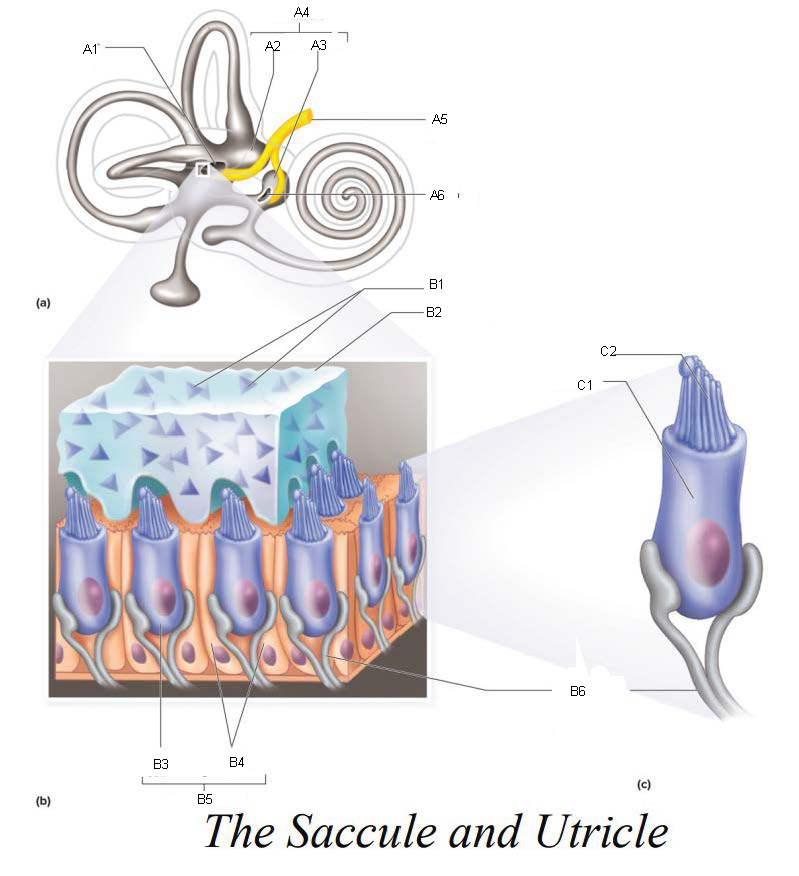
Saccular mascula
A6
Otoliths
B1
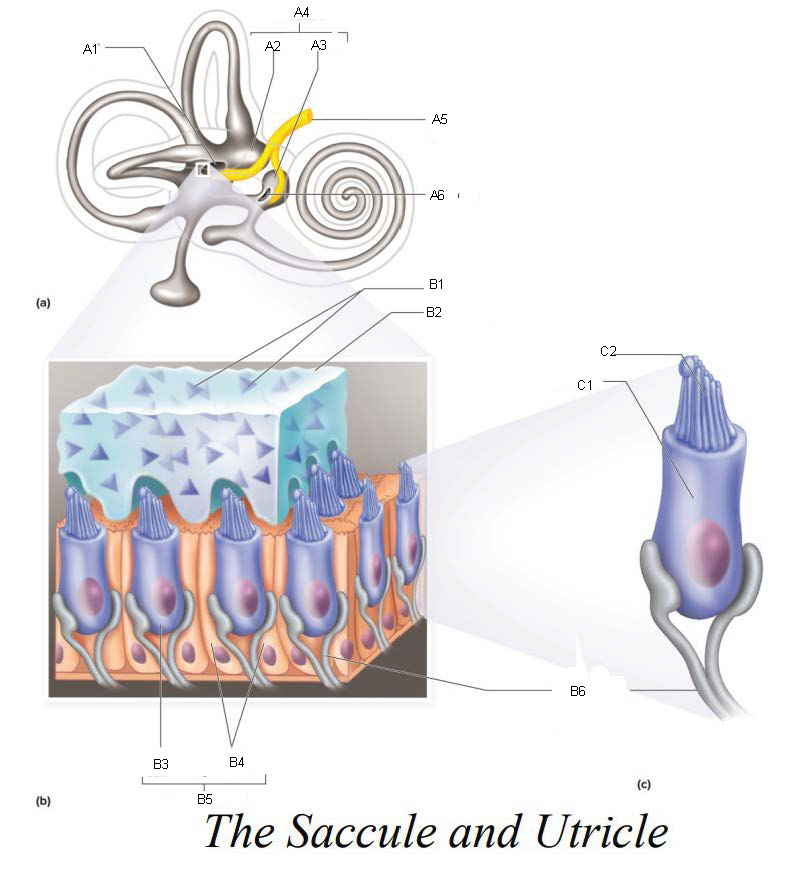
Otolithic membrane
B2
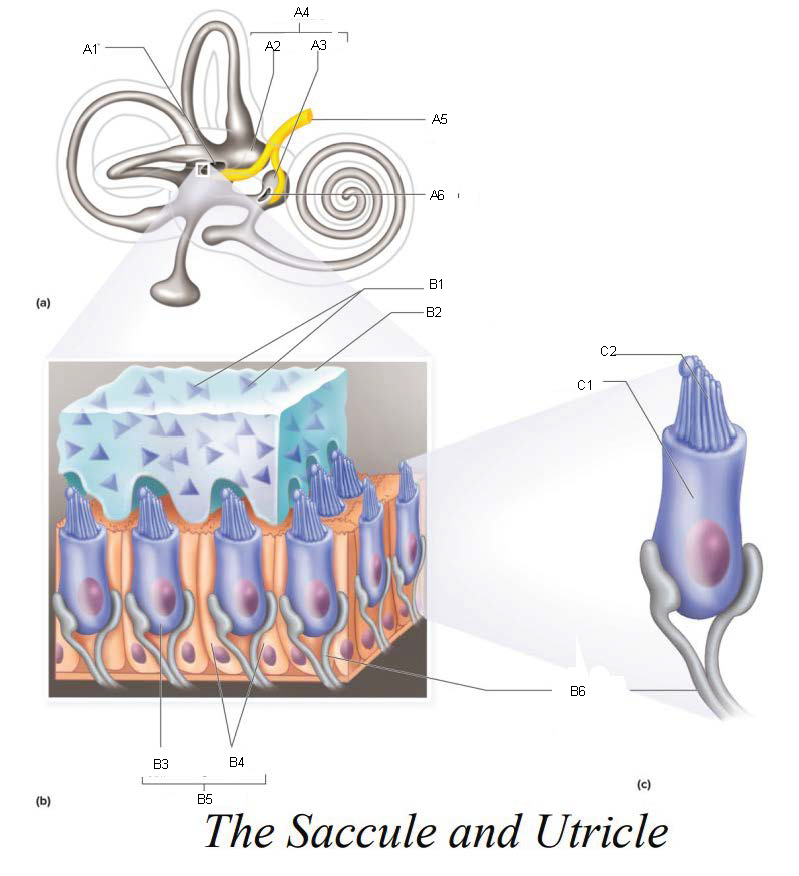
Hair cell
B3
Supporting cells
B4
Part of macula
B5
Nerve fibers of vestibular branch of the auditory nerve
B6
Hair Cell
C1
Microvilli
C2
Dynamic Equilibrium
associated with semicircular canals; when the head is moving; evaluates changes in direction and rate of head movement
Semicircular Canals
contain receptors that detect motion of the head; oriented at 90 degrees to each other
ampulla
attaches canal to utricle
Crista Ampullaris
part of ampulla; sensory organ for dynamic equilibrium; contains hair cells with processes extending into a cupula; connected to fibers from vestibulocochlear nerve
Ampullae
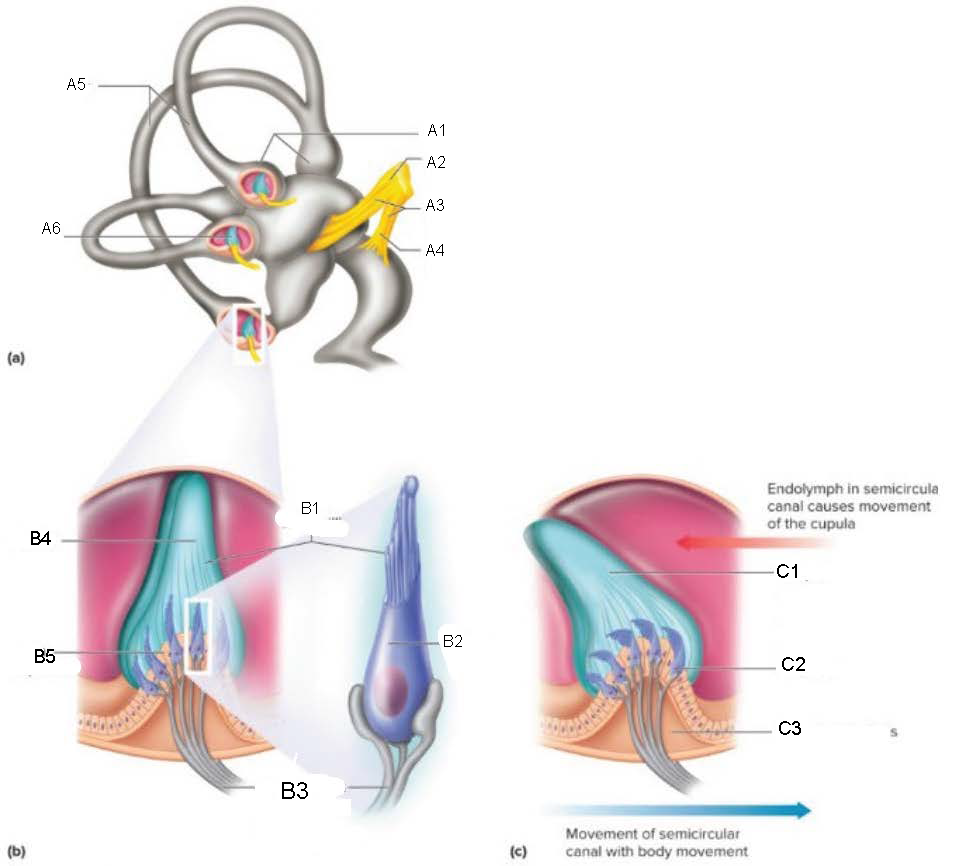
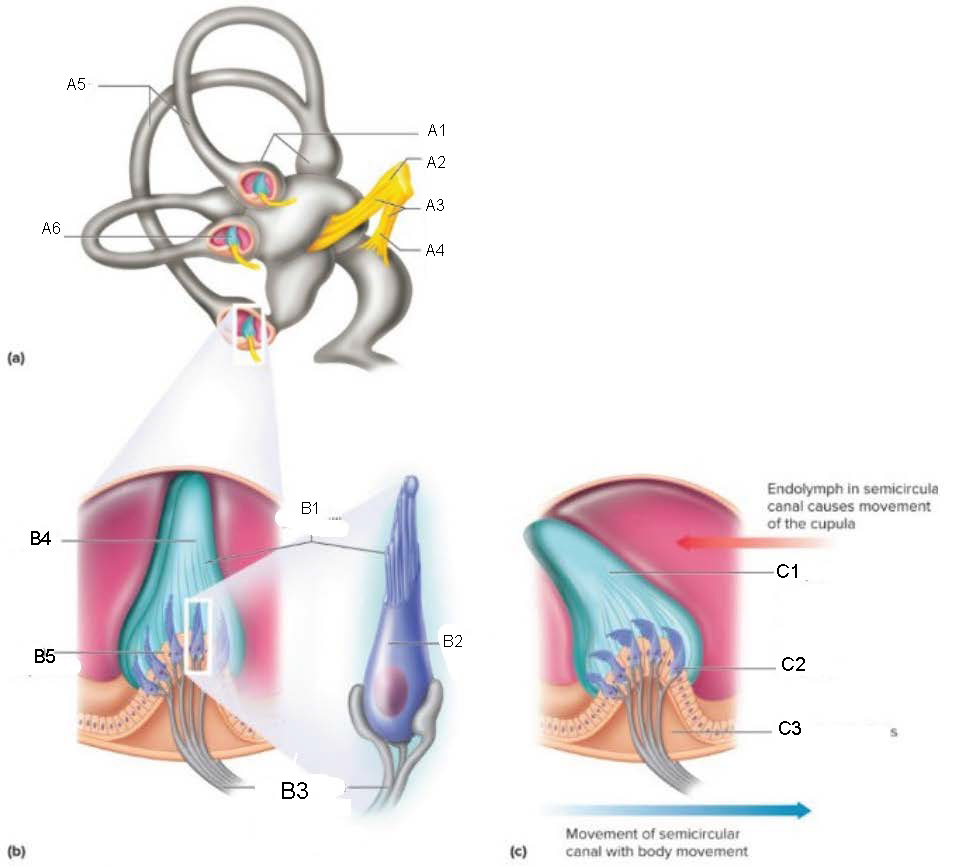
A1
Vestibular branch
A2
Auditory Nerve
A3
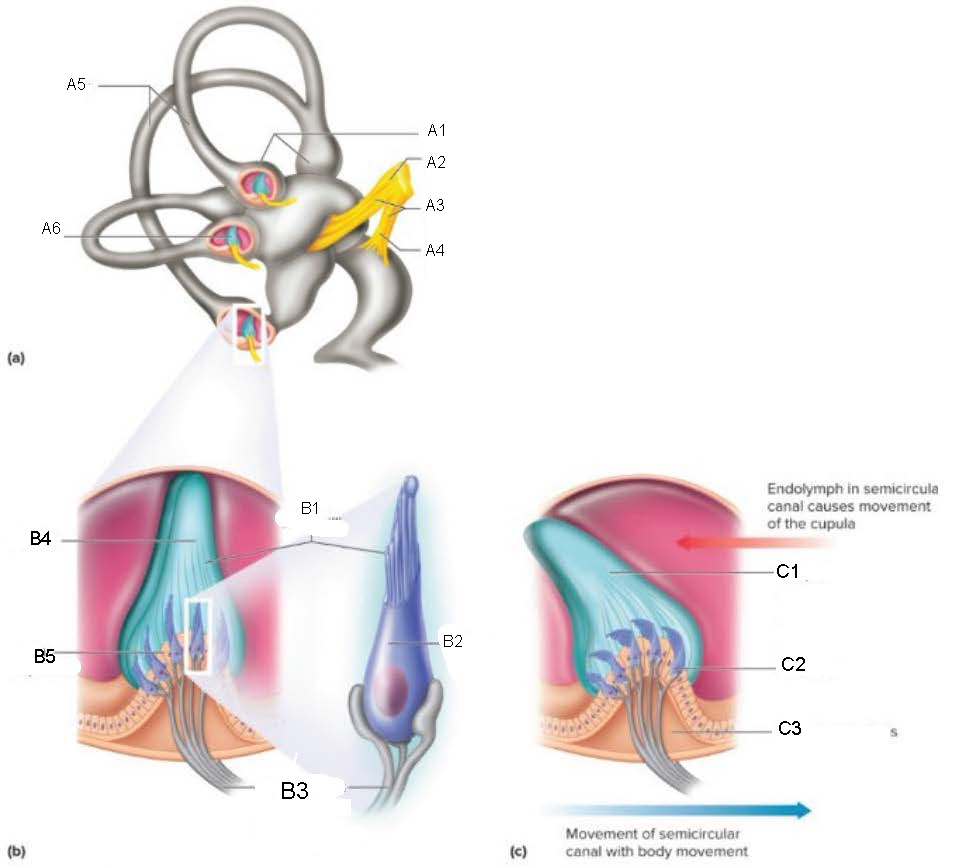
Cochlear branch
A4
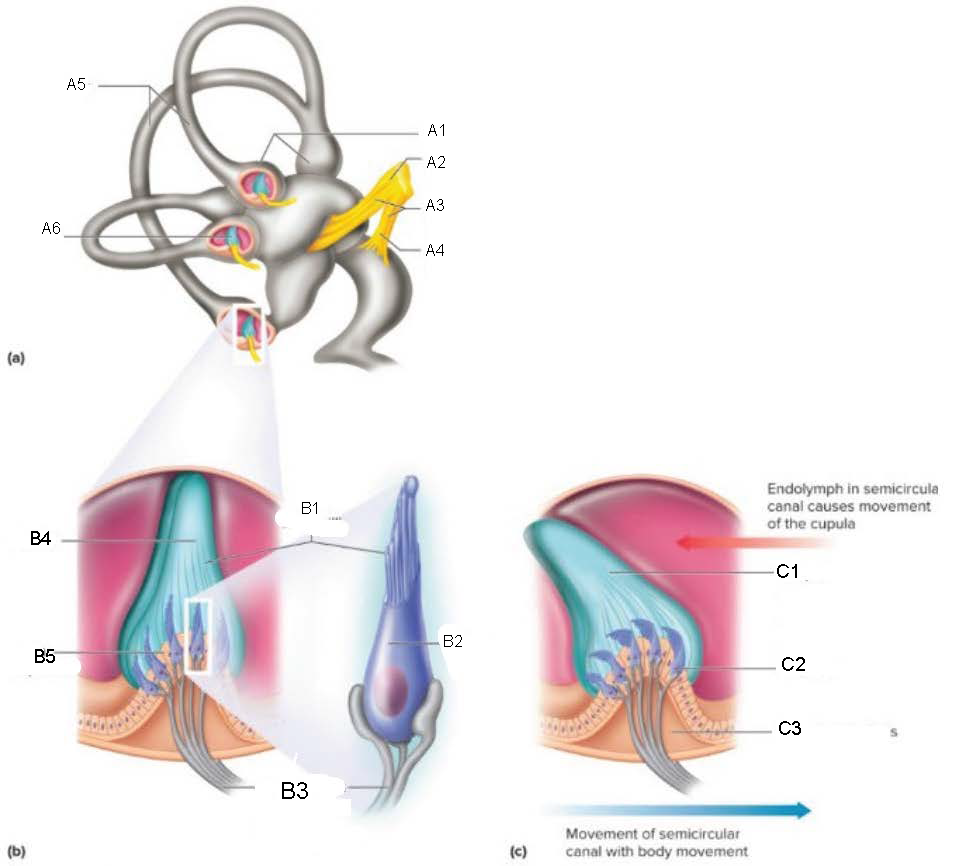
Semicircular canals
A5
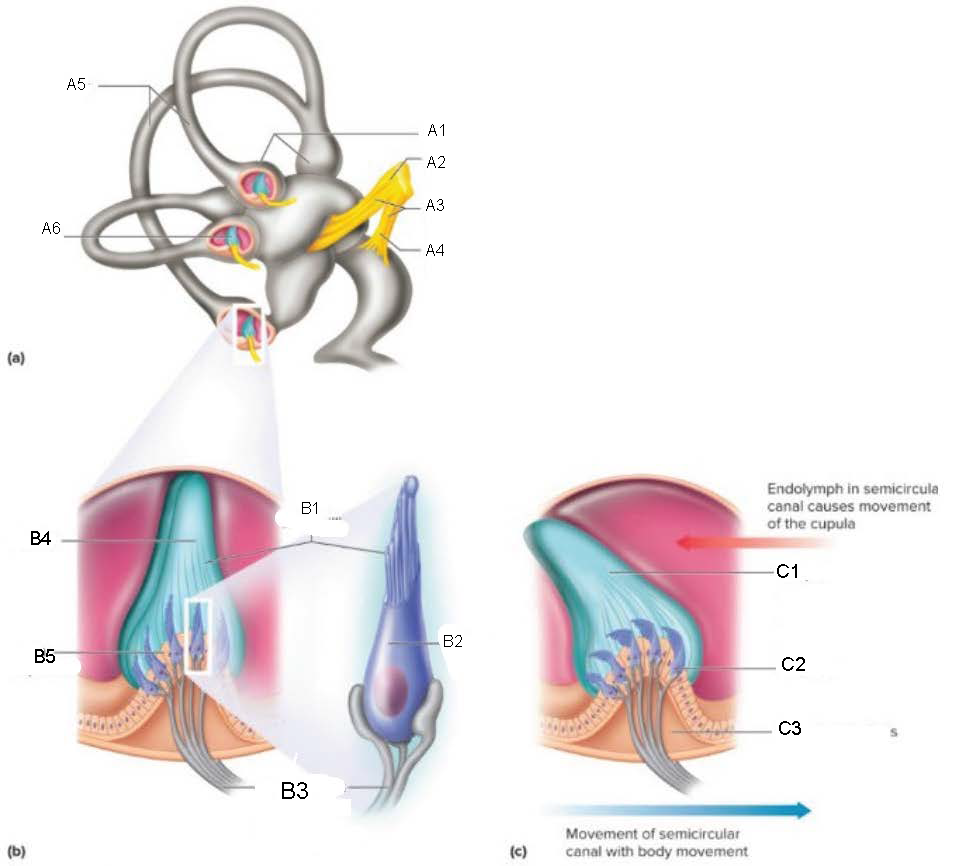
Cupula
A6
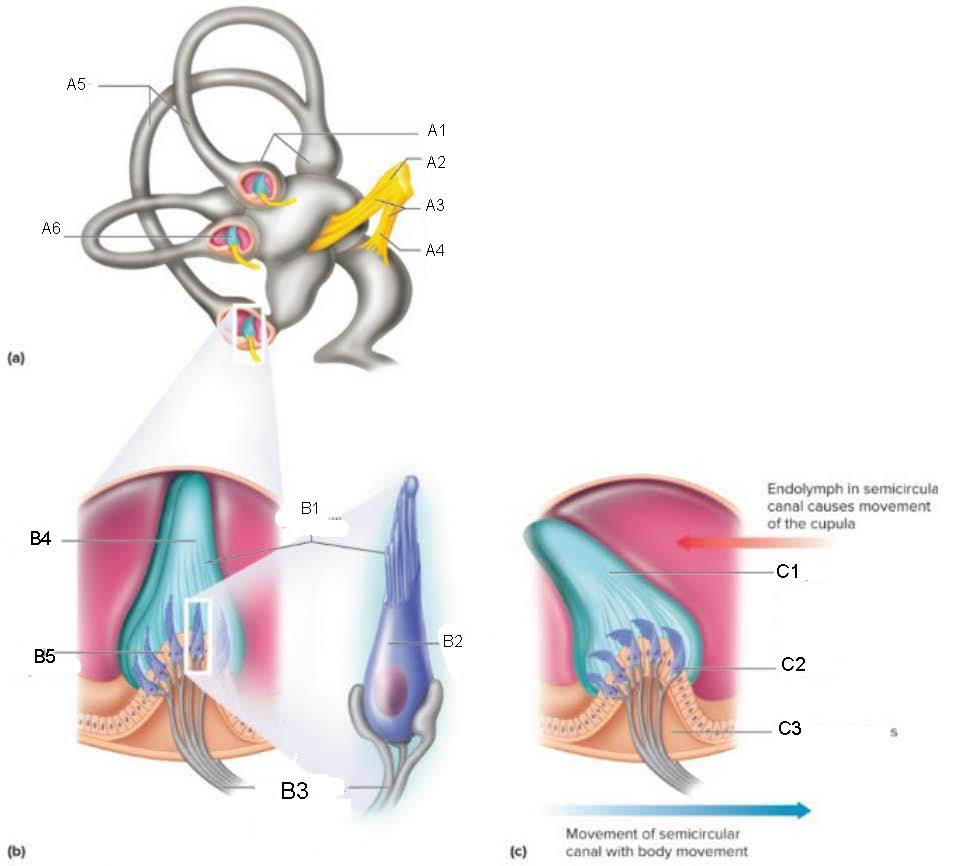
microvilli
B1
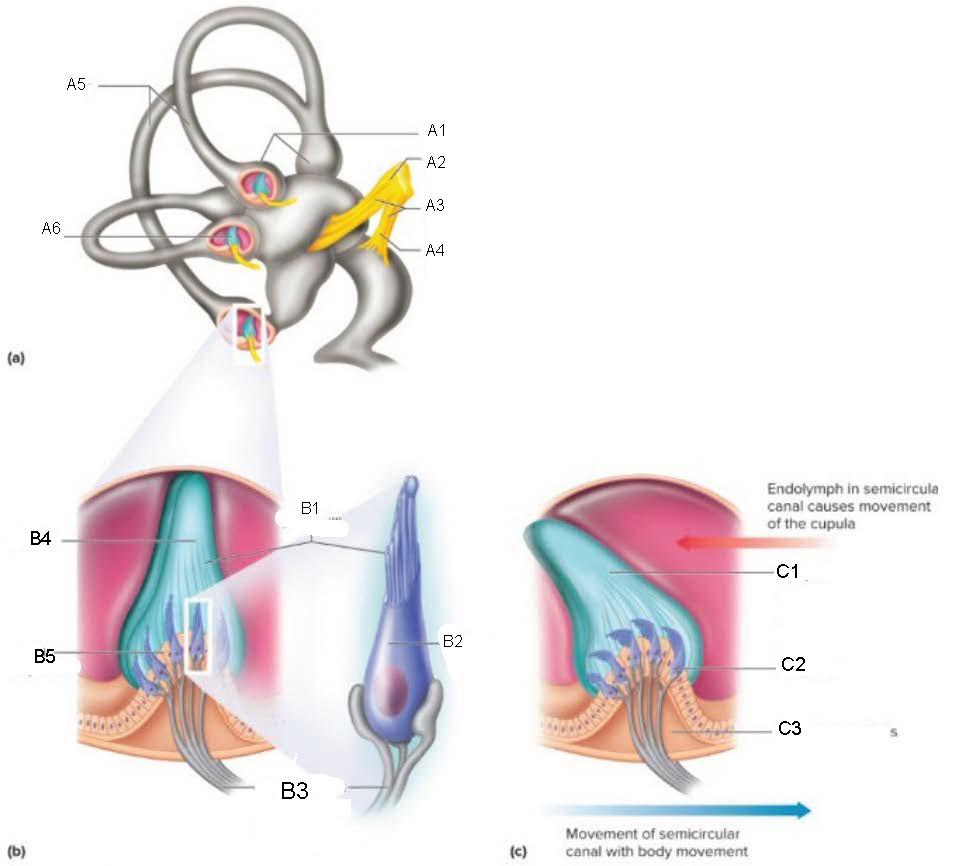
hair cell
B2
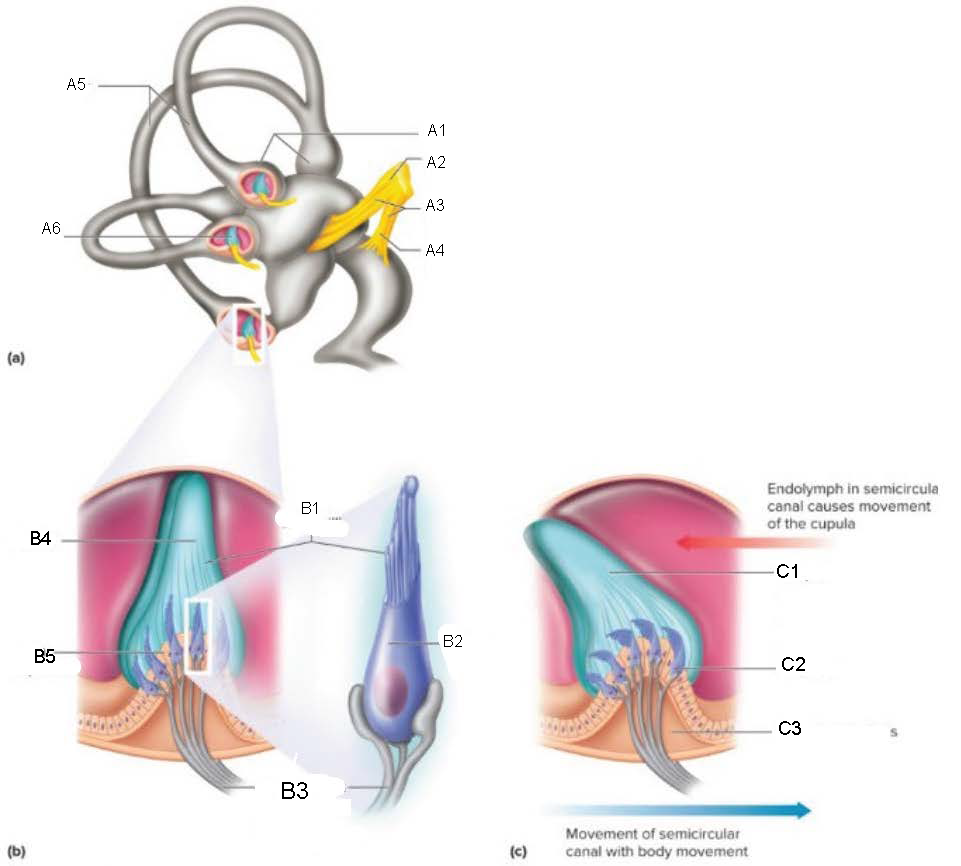
nerve fibers to vestibular branch of auditory nerve
B3
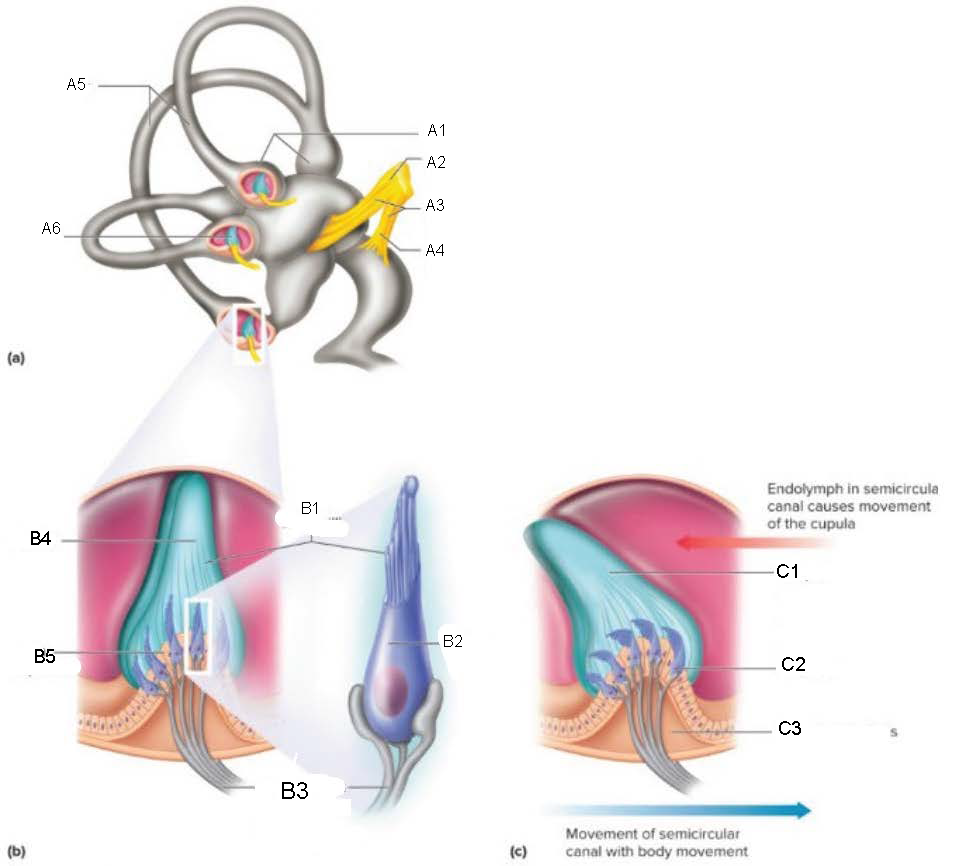
Cupula
B4
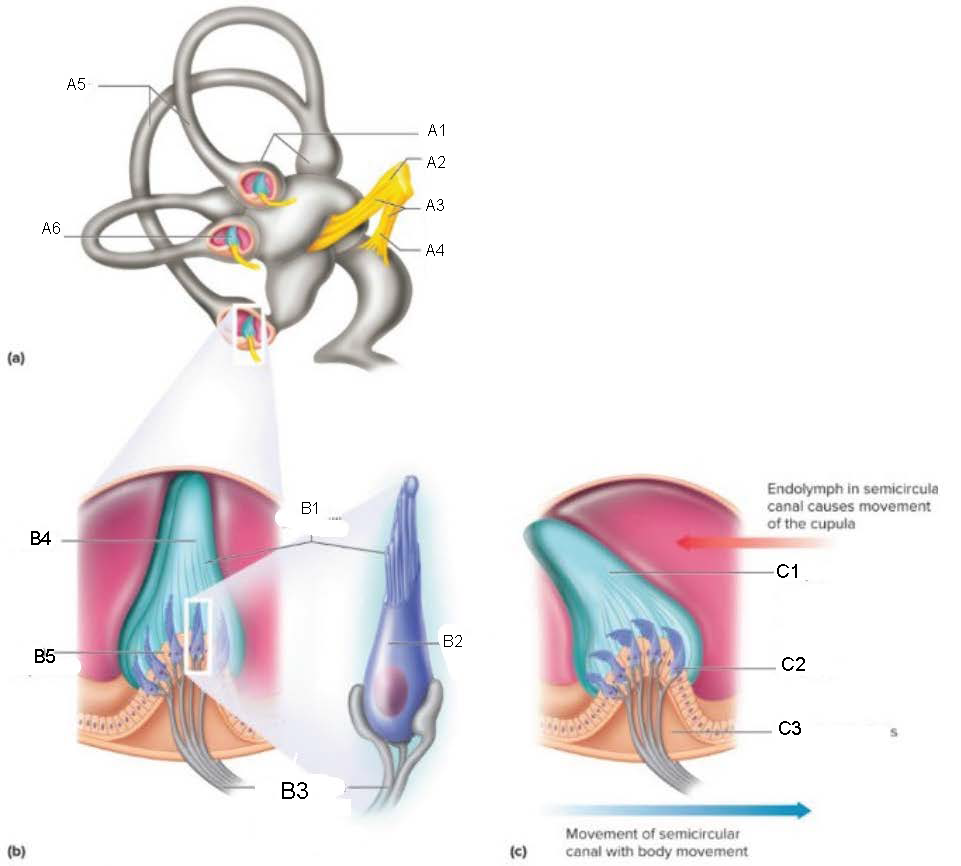
crista ampullaris
B5
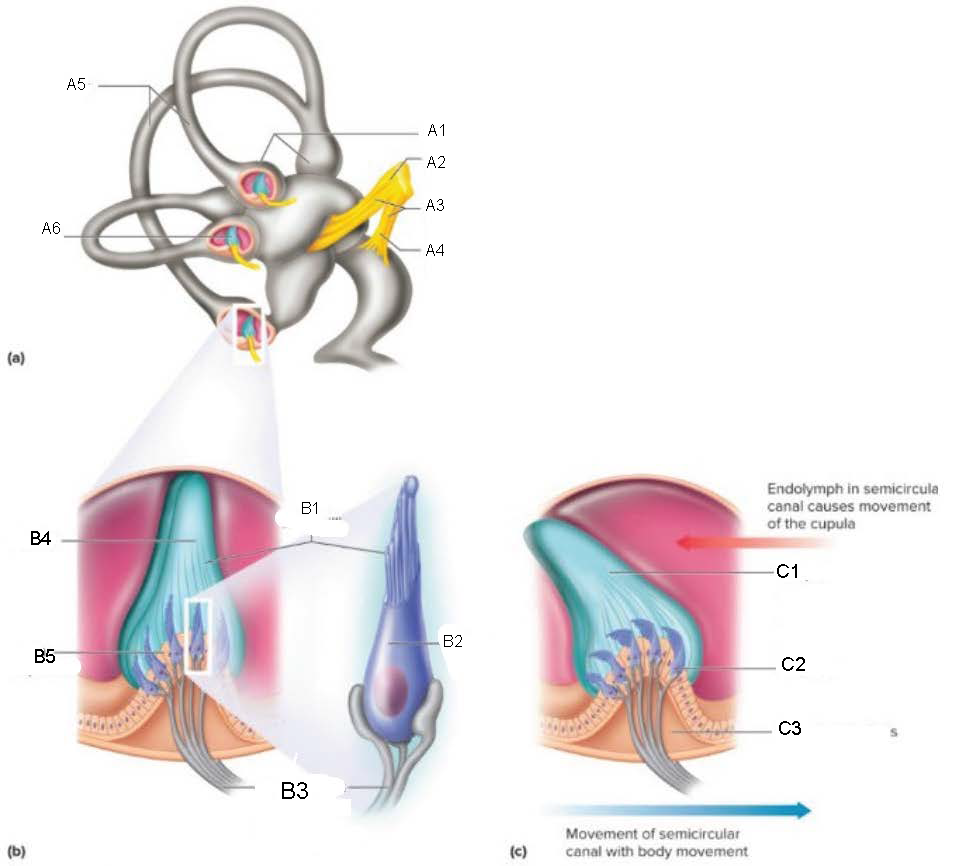
cupula
C1
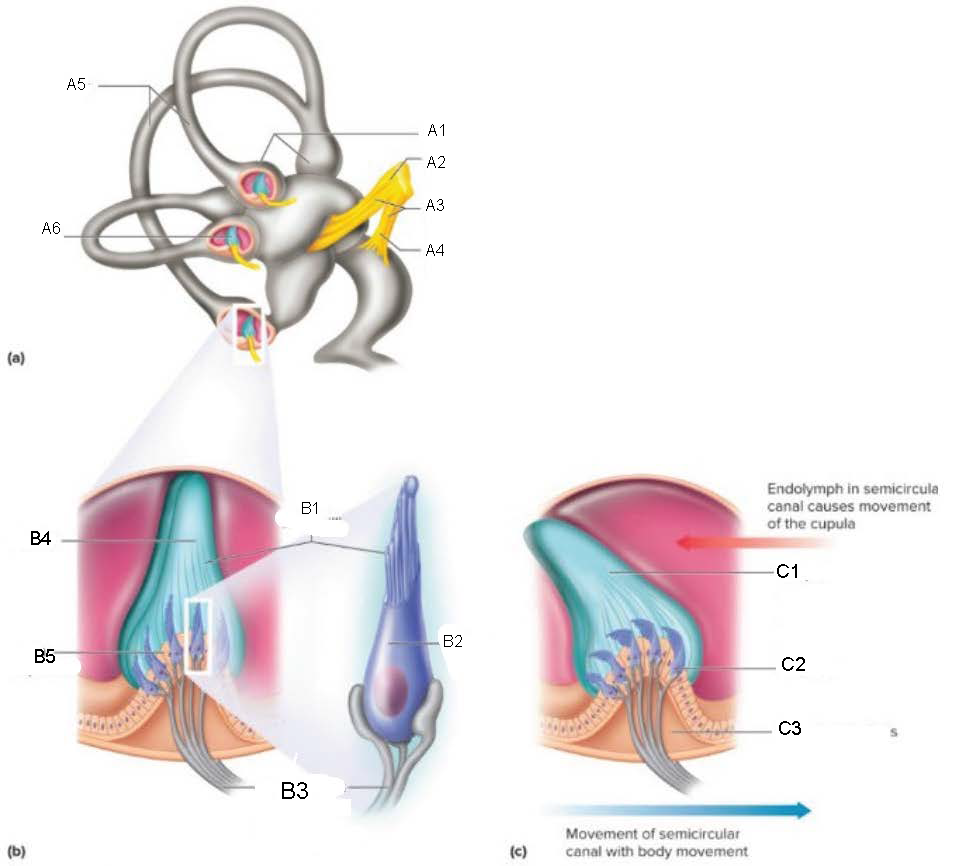
Hair cell
C2
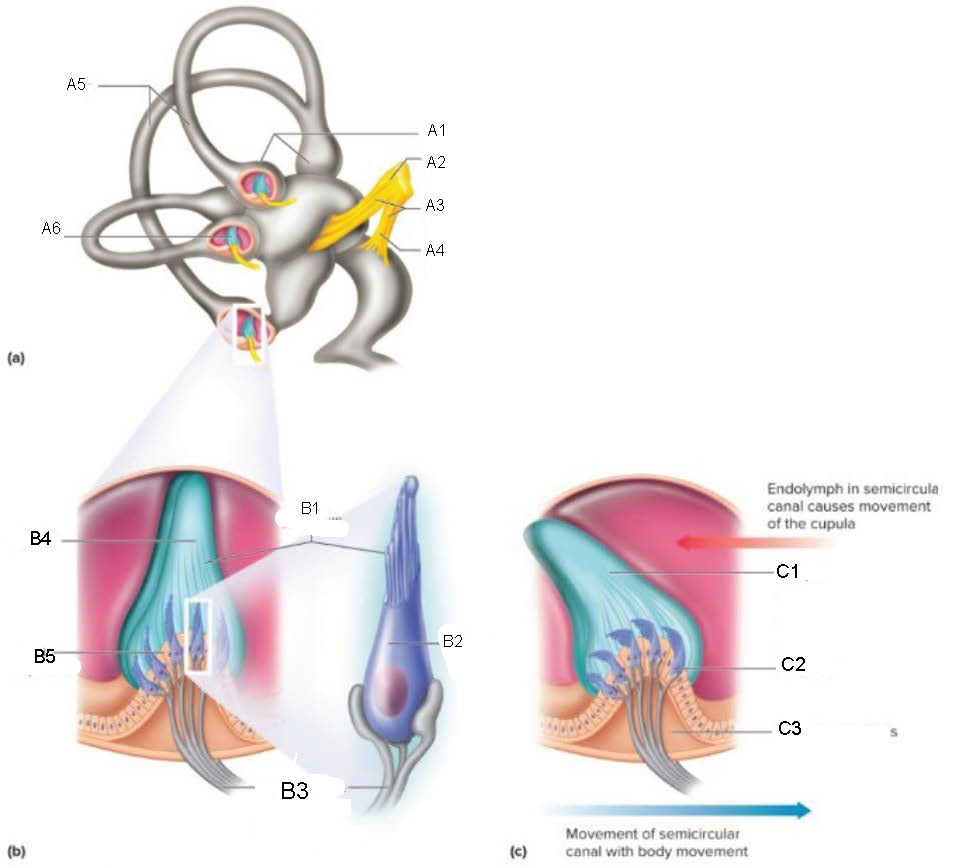
Crista ampullaris
C3
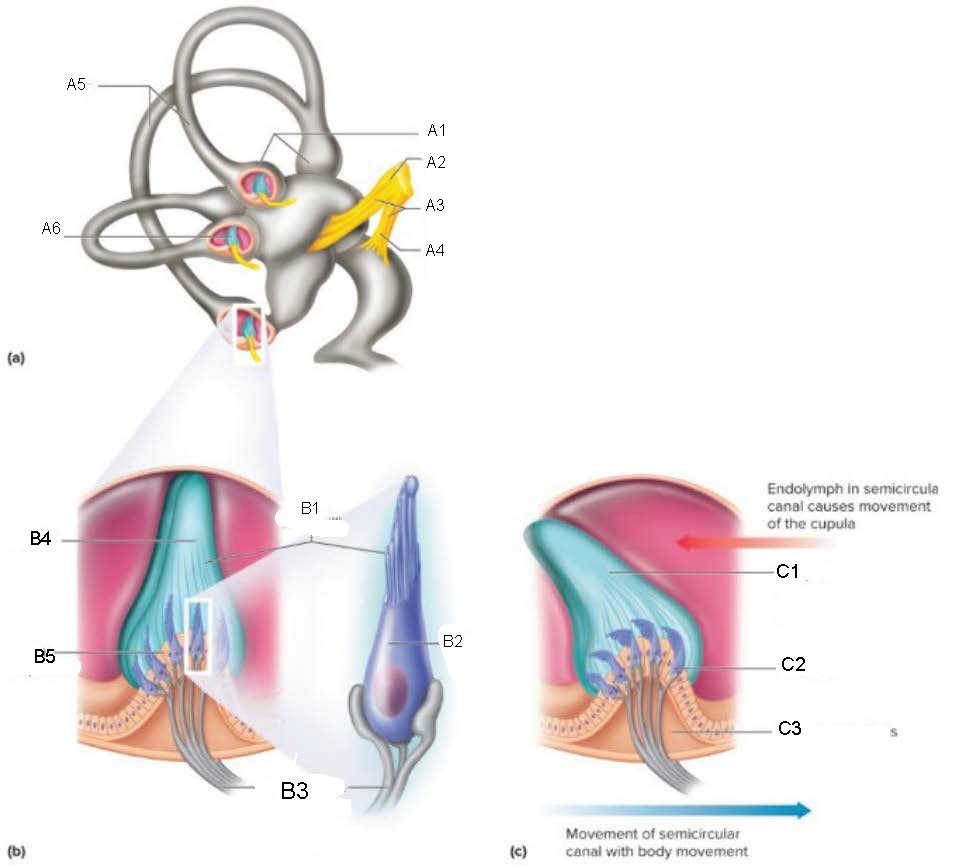
Mechanism of Static Equilibrium
pull of gravity on gelatinous mass causes hair cells to form impulses
Mechanism of Dynamic Equilibrium
when head turns, endolymph pushes on the cupula
hair cells bend, causing impulses to form