Joints wk9
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
116 Terms
What type of joint is a suture?
A fibrous joint.
Are sutures synarthrodial or diarthrodial?
Sutures are synarthrodial, meaning they are immovable.
Where are sutures typically found in the body?
Between the flat bones of the cranium.
Name an example of a suture in the skull.
The coronal suture.
What is another example of a suture besides the coronal suture?
The sagittal suture.
What is the third example of a suture mentioned?
The lambdoid suture.
What type of cartilage is found in a synchondrosis joint?
Hyaline cartilage.
Are synchondrosis joints synarthrodial or diarthrodial?
Synchondrosis joints are synarthrodial, meaning they are immovable.
Name an example of a synchondrosis joint.
The epiphyseal plates that join the epiphysis and diaphysis.
What is another example of a synchondrosis joint?
The sternocostal joint for costal pair #1.
What type of cartilage is found in a symphysis joint?
Fibrocartilage
Are symphysis joints synarthrodial or amphiarthrodial?
Symphysis joints are amphiarthrodial, meaning they are very slightly movable.
Name an example of a symphysis joint.
The pubic symphysis.
What is another example of a symphysis joint?
The joint between adjacent vertebral bodies (intervertebral disc).
What type of joint is a synovial joint?
Synovial joints are diarthrodial joints, meaning they are comparatively highly movable.
What is an example of a ball and socket joint?
The glenohumeral joint (shoulder joint) and the femoroacetabular joint (hip joint) are examples.
What is another example of a synovial joint?
The humeroradial joint, which is part of the elbow joint.
Why does the humeroradial joint lack the same freedom of movement as the shoulder and hip joints?
It lacks the freedom of movement due to the articulations between the radius and ulna.
Name an example of a hinge joint
The interphalangeal joints are examples of hinge joints.
What is another example of a hinge joint?
The tibiofemoral joint, which is part of the knee joint.
What is another example of a hinge joint in the body?
The humeroulnar joint, which is part of the elbow joint.
What type of joint is a hinge joint, and what are its characteristics?
A hinge joint is a type of synovial joint, which are all diarthrodial joints that are comparatively highly movable.
What type of joint is a condyloid joint?
A condyloid joint is also known as an ellipsoid joint.
Name an example of a condyloid joint.
The atlanto-occipital joint (between C1 and the occipital bone)
What are two more examples of condyloid joints?
Metacarpophalangeal joints and metatarsophalangeal joints.
What type of joints are condyloid joints classified as?
Condyloid joints are classified as synovial joints.
What type of joint is a pivot joint?
A pivot joint is a type of synovial joint.
Name an example of a pivot joint.
The atlantoaxial joint (between C1 and the dens of C2).
What are two more examples of pivot joints?
The proximal and distal radioulnar joints.
What type of joint is a saddle joint?
A saddle joint is a type of synovial joint.
Name an example of a saddle joint.
The carpometacarpal joint in the thumb.
What type of joint is a plane joint?
A plane joint is also known as a gliding joint and is a type of synovial joint.
Name an example of a plane joint.
Intercarpal joints and some intertarsal joints
What is another example of a plane joint?
Sternocostal joints (except for the first costal pair).
Name one more example of a plane joint.
Vertebrocostal joints.
What is another example of plane joints?
Intervertebral articulations between the superior and inferior articular facets.
What is flexion in terms of appendicular movement?
Flexion is the appendicular movement away from the mid-coronal plane.
What is extension in terms of appendicular movement?
Extension is the appendicular movement towards the mid-coronal plane.
Abduction
Movement of limbs away from the mid-sagittal plane
Movement of digits away from the midline of the lim
Adduction
Movement of limbs towards the mid-sagittal plane
Movement of digits towards the midline of the limb
What are rotational movements?
Rotational movements refer to the movement of a body part around its own axis.
What is rotation?
Rotation is the movement of a body part around its own axis.
What is the difference between medial and lateral rotation?
Medial rotation is when a body part turns inward toward the midline, while lateral rotation is when it turns outward away from the midline.
What is circumduction?
Circumduction is a circular movement that combines flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction.
Supine
when forearms are held with palms facing anteriorly
Prone
when forearms are held with palms facing posteriorly
to raise something up
Elevation
to lower something
Depression
flexion of the ankle so that the toes point up
Dorsiflexion
extension of the ankle so that the toes point down
Plantar flexion
to bring forward
Protraction
to pull backwards
Retraction
to move the thumb (digit 1, pollex) towards digit 5
Opposition
a return of the thumb to anatomical position
Reposition
Joints that articulate most of the bonesIn the skull
sutures
All sutures are ___
Synarthroses
Joints that hold the teeth in their alveoli in either the maxillae or the mandible
Gomphoses
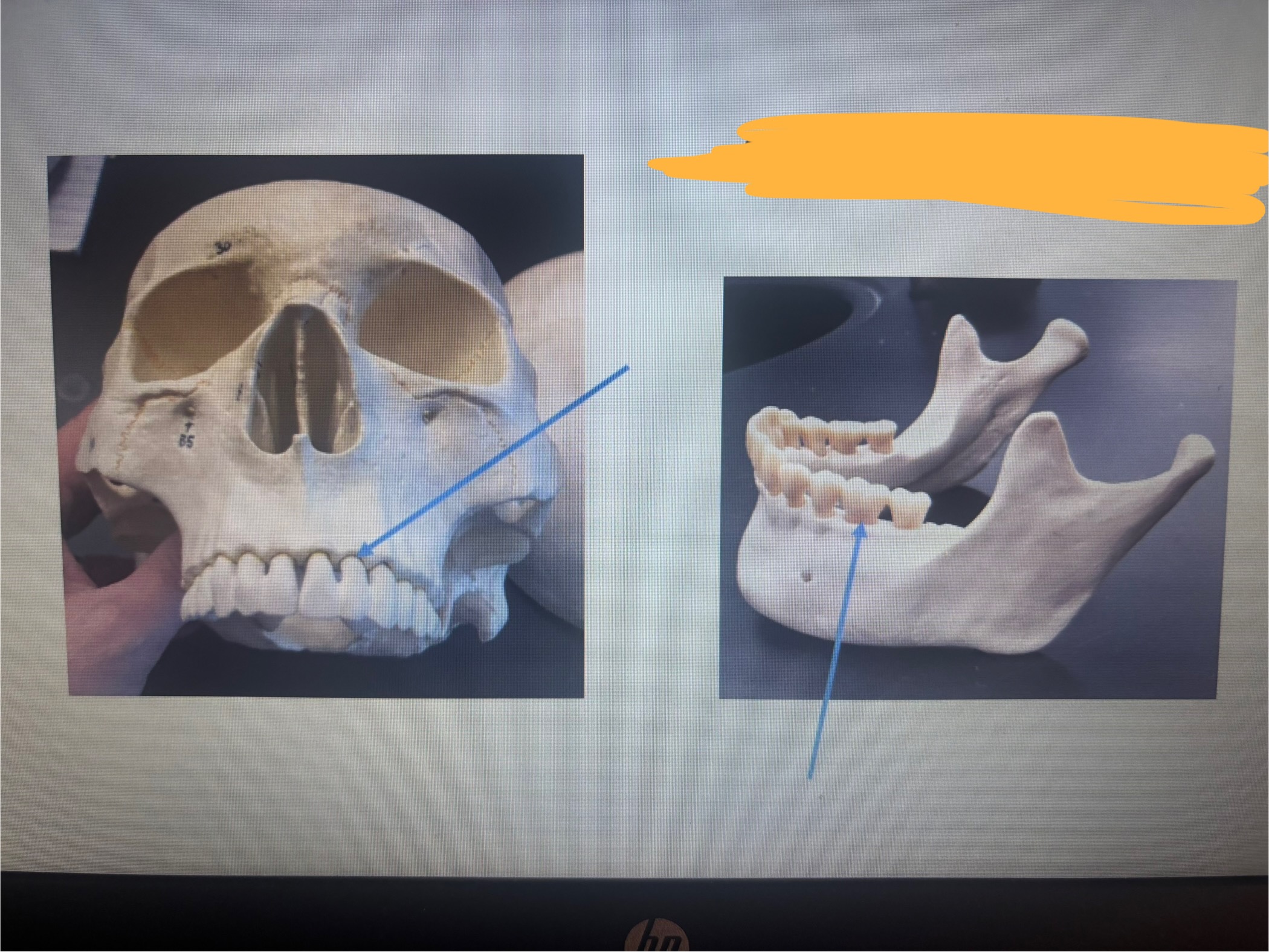
What is marked out?
All are synarthroses
Synchondroses
Use of hyaline cartilage as the principle anchorage to articulate structures and are all synarthroses
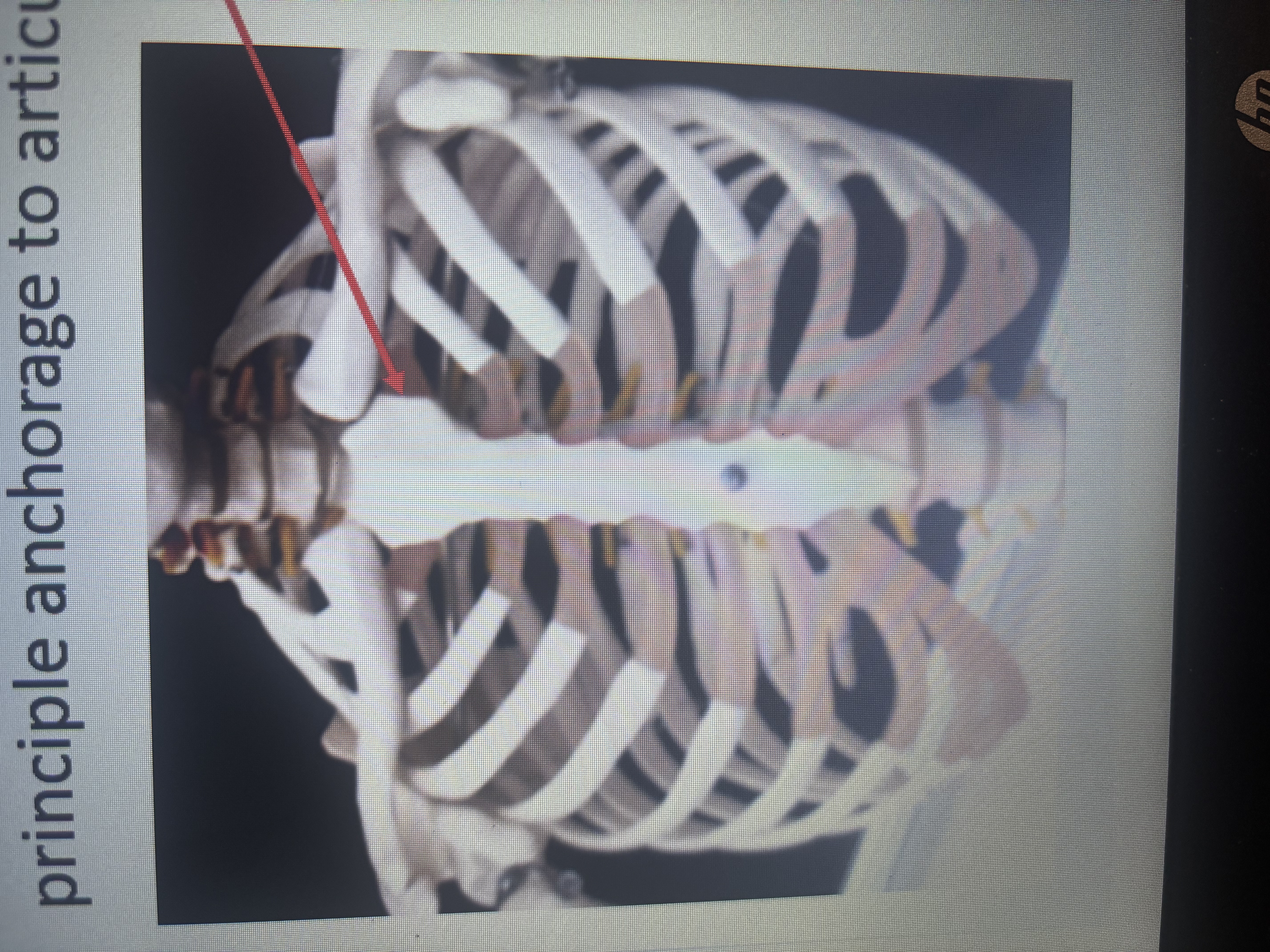
What is the arrow pointing at?
hyaline cartilage
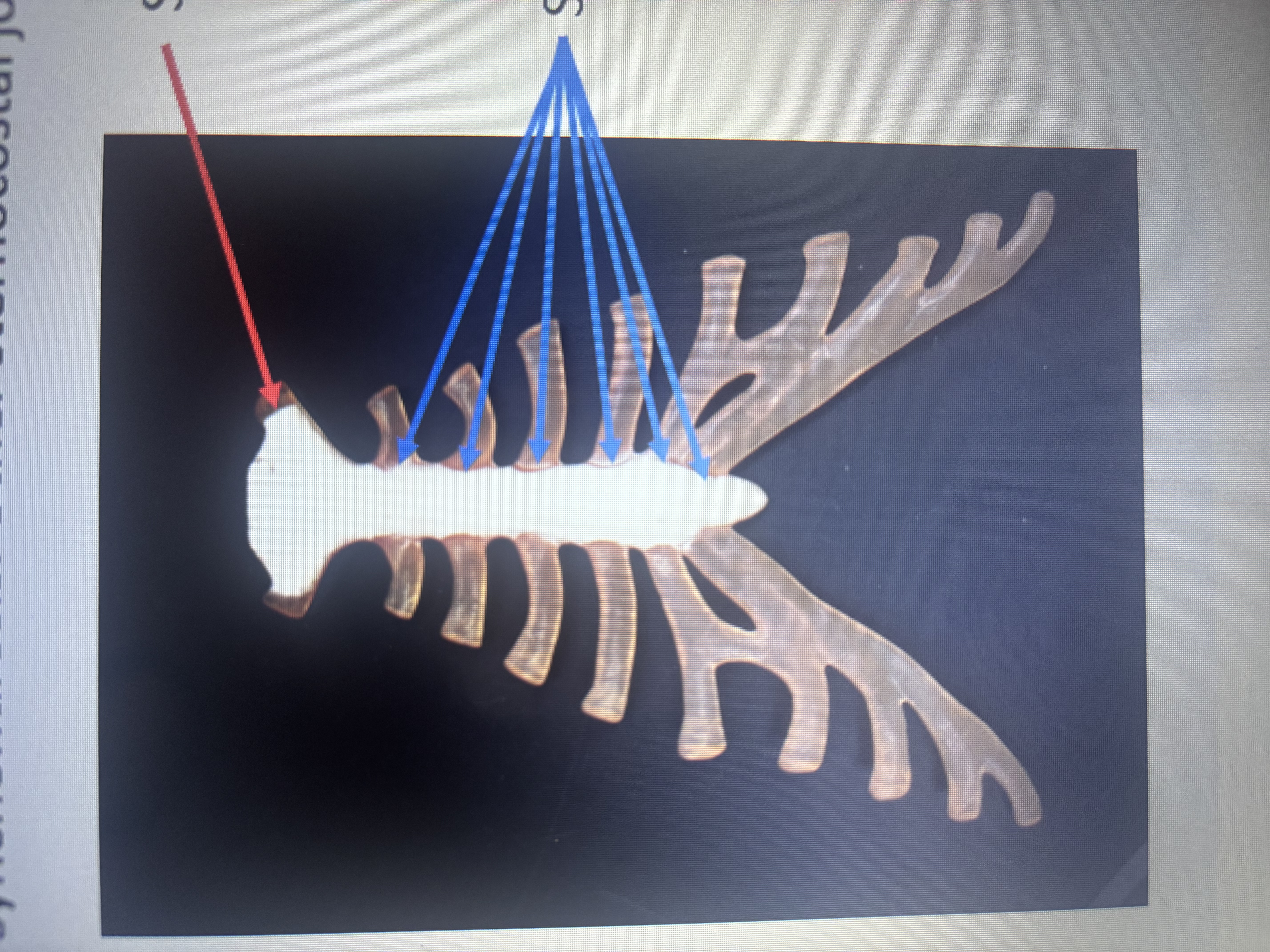
What is the red arrow pointing at?
Synchondrosis
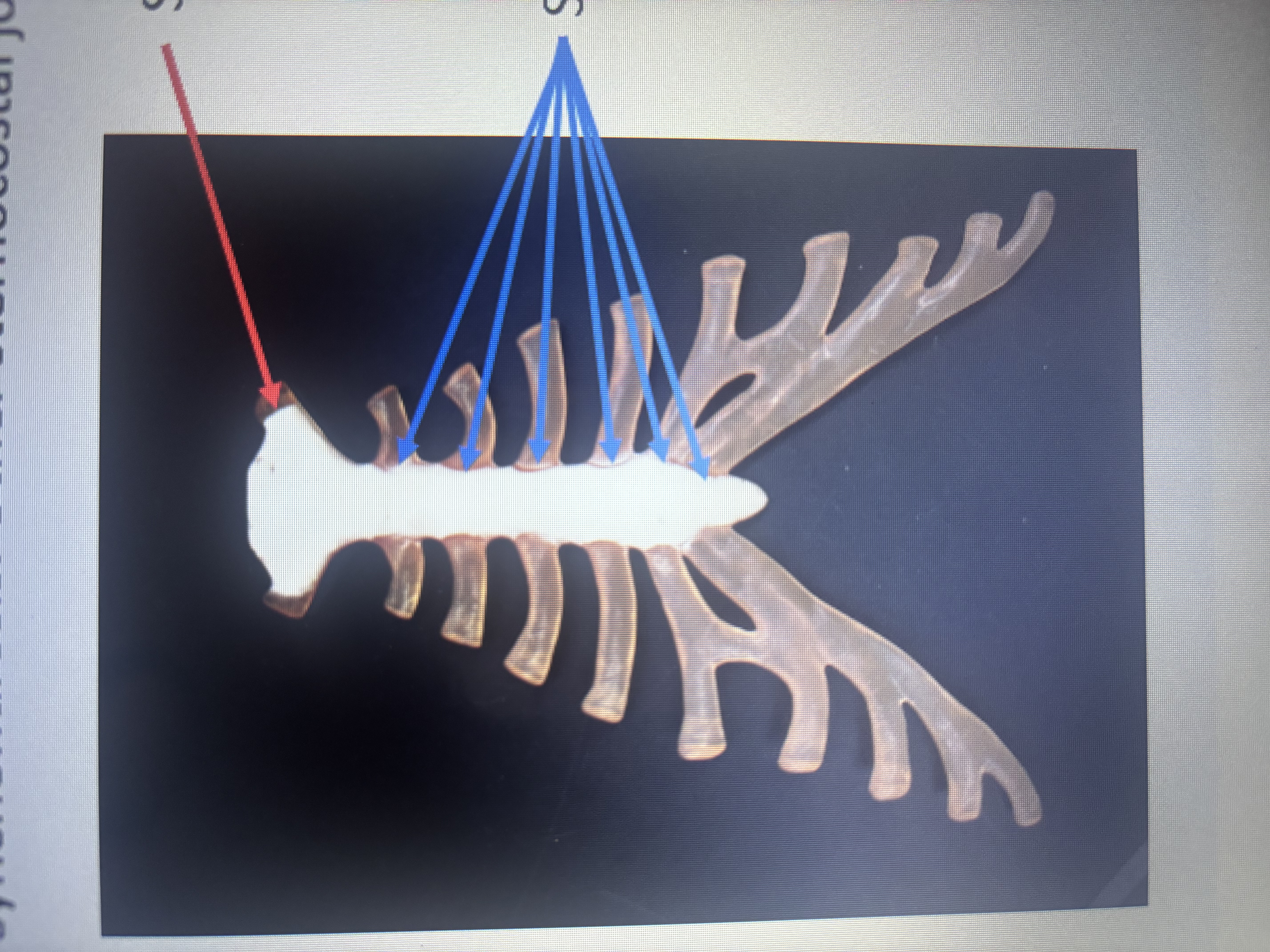
What is the blue arrow pointing at?
Synovial
Use of fibrocaritilage as the principle anchorage to articulate structures
Symphysis
What are the 1st arrow pointing at
pubic symphysis (amphiarthroses)
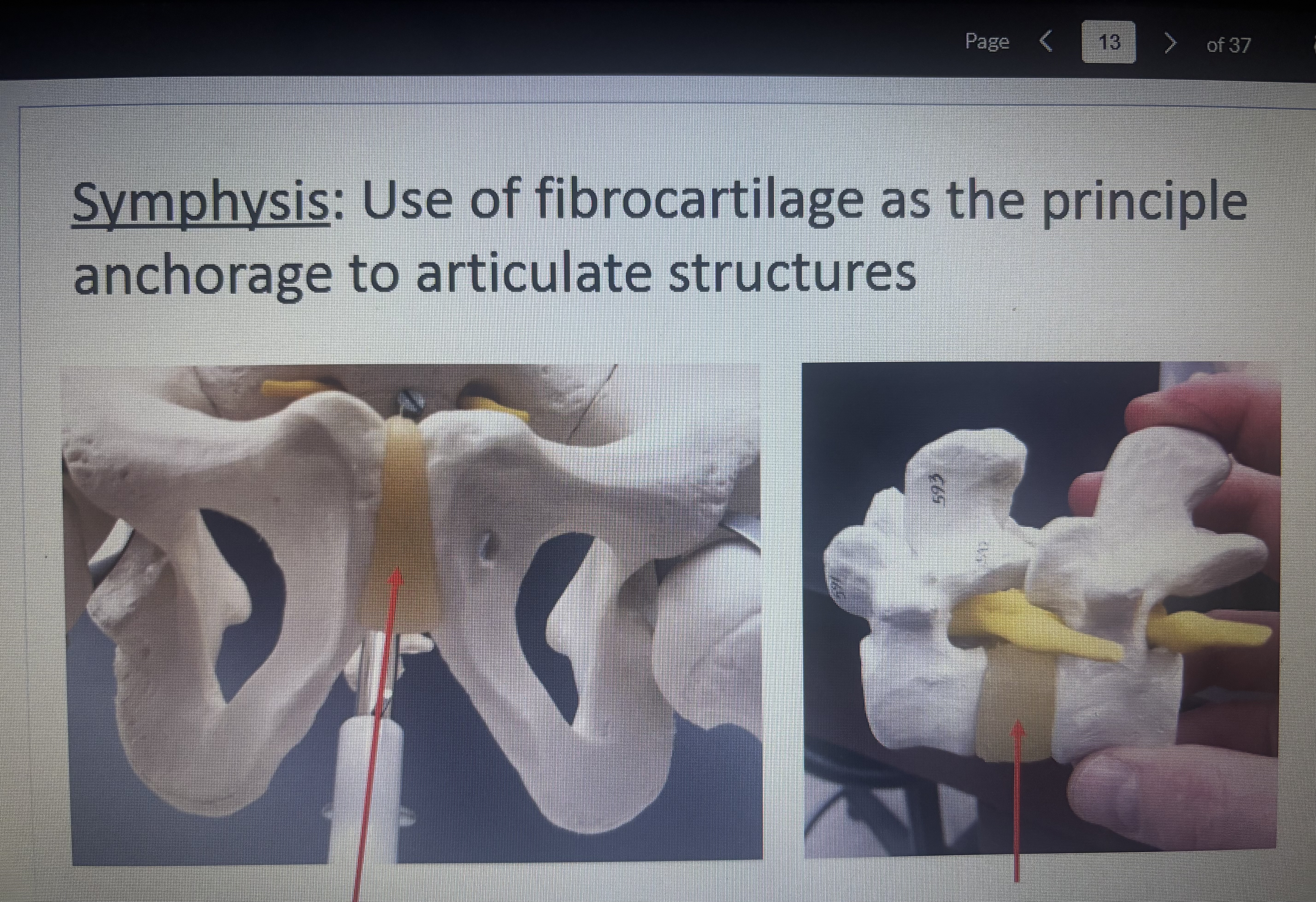
What is the 2nd arrow pointing at?
Intervertebral disk (amphiarthroses)
Fill in the blank
Diarthroses
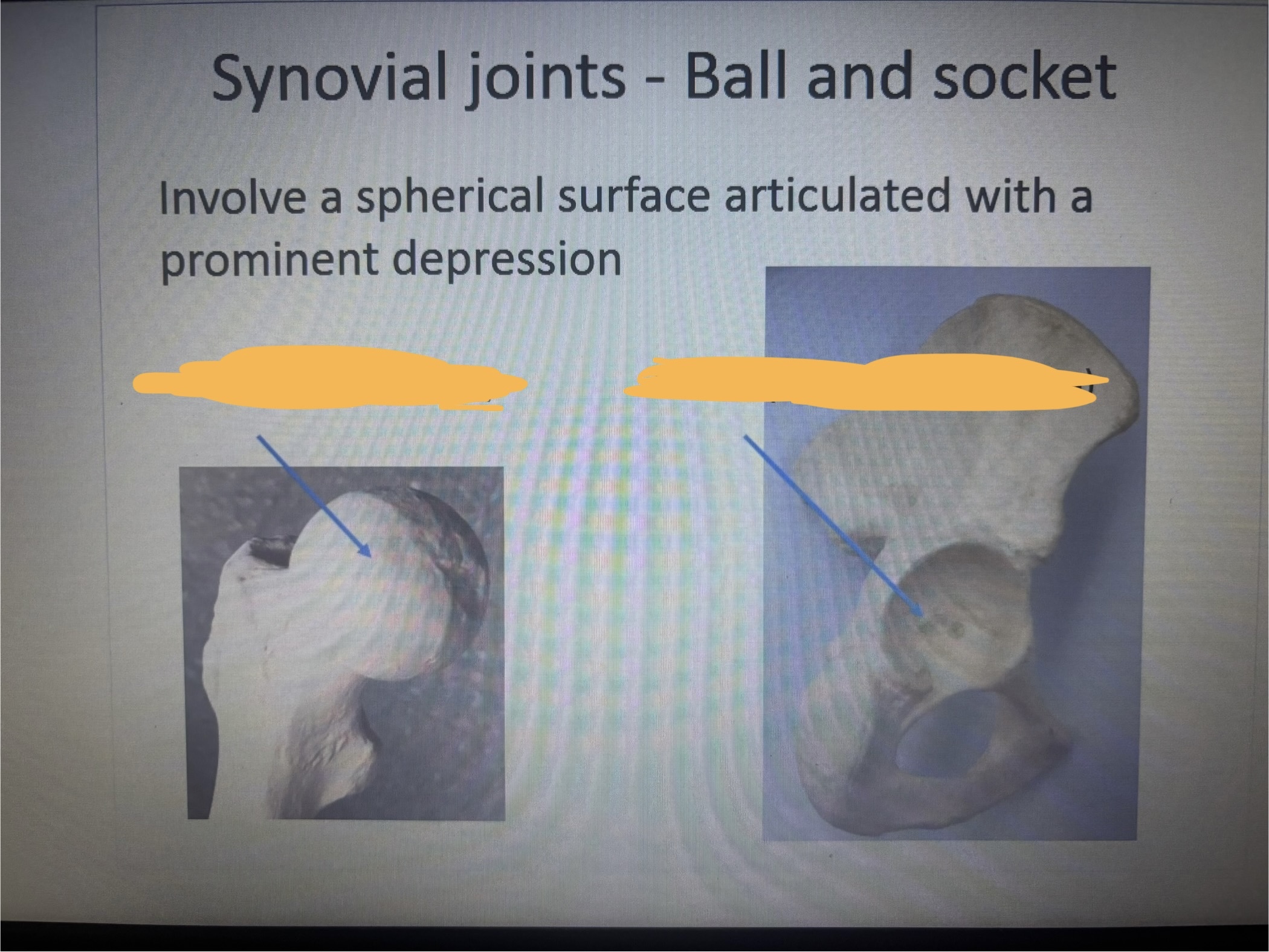
What is the 1st arrow pointing at?
Ball (head of femur)
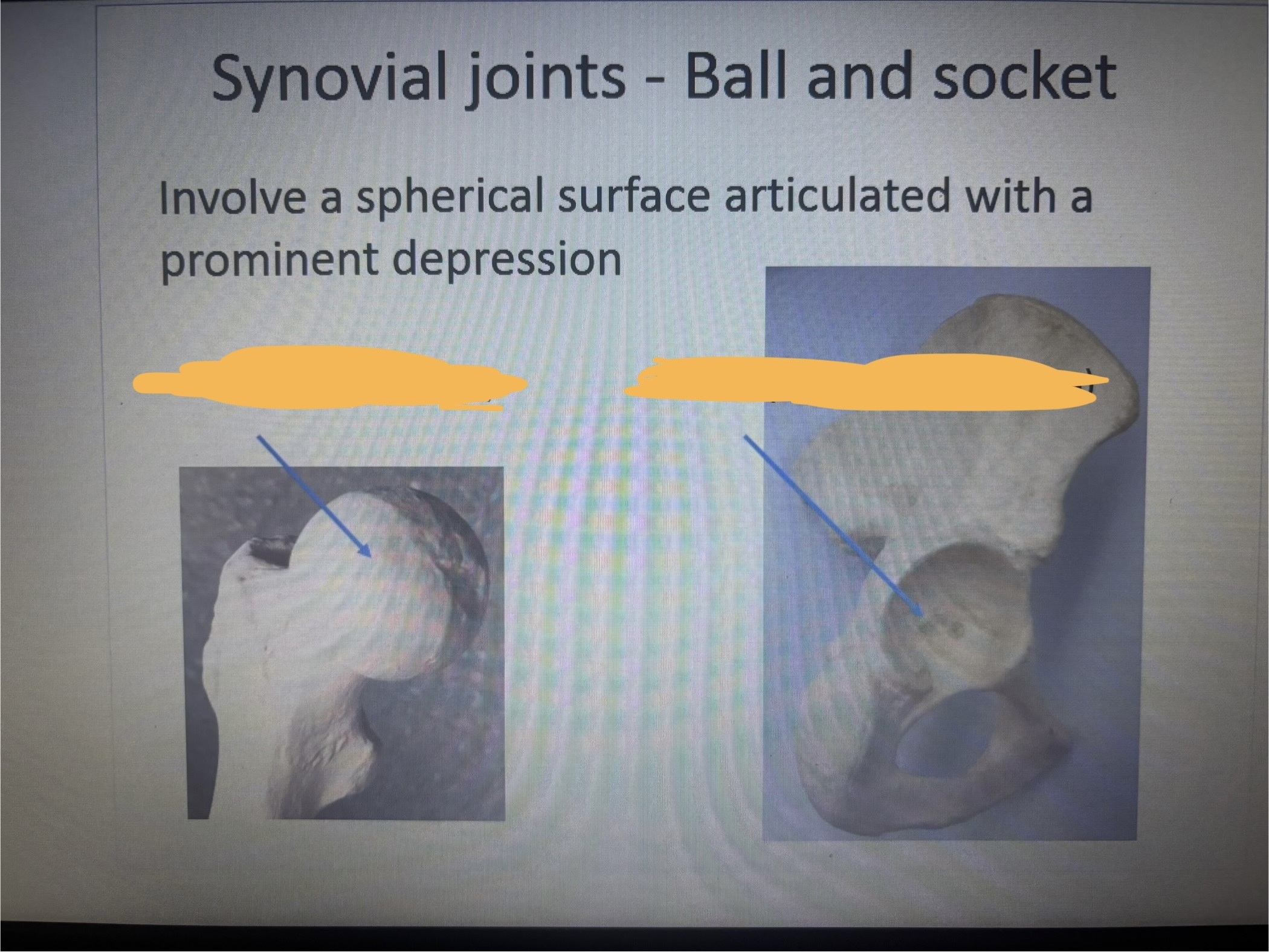
What is the 2nd arrow pointing at?
Socket (acerabulum of coxa)
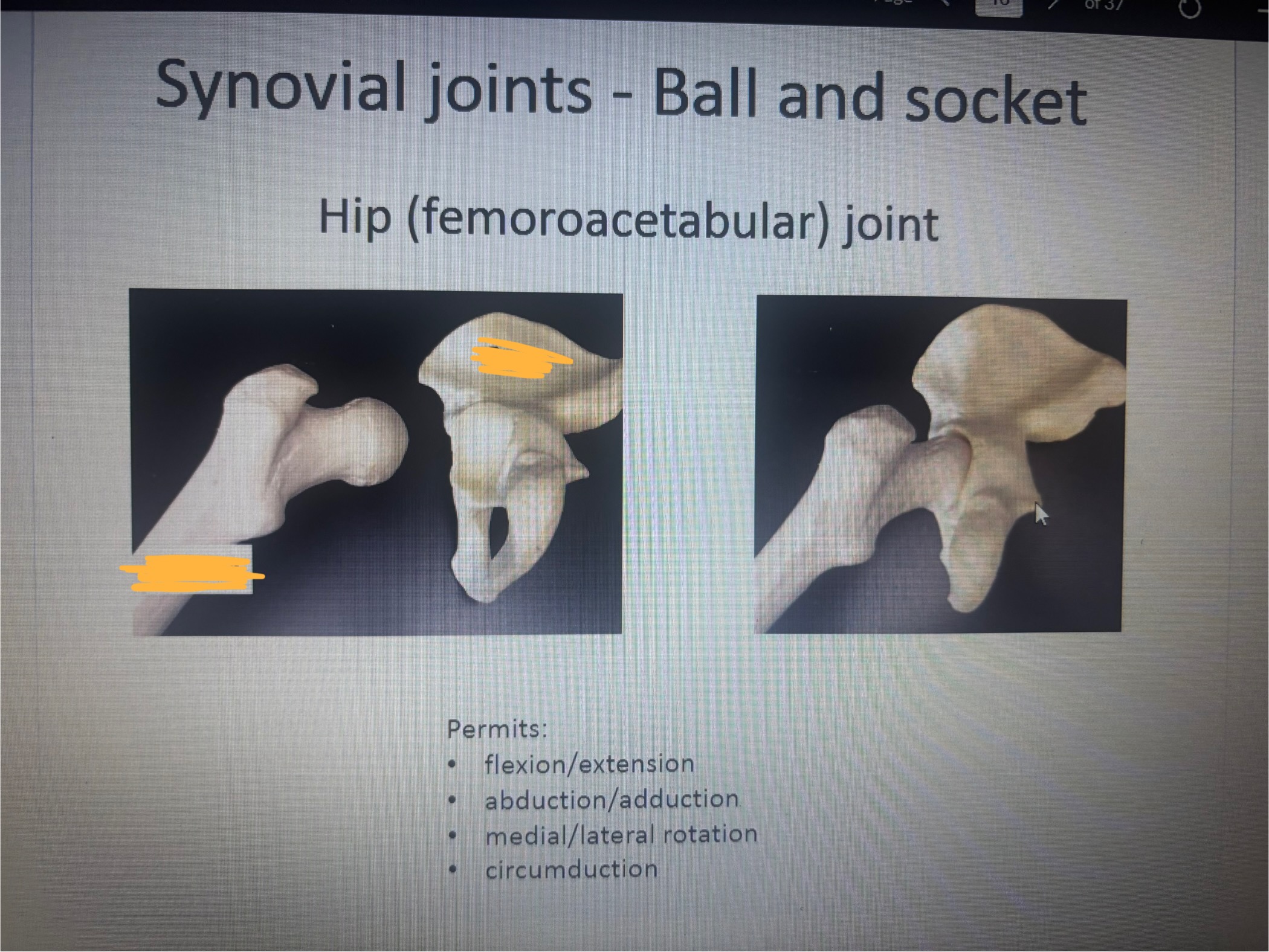
What is in the 1st blank
Femur hip (femoroacetabular) joint
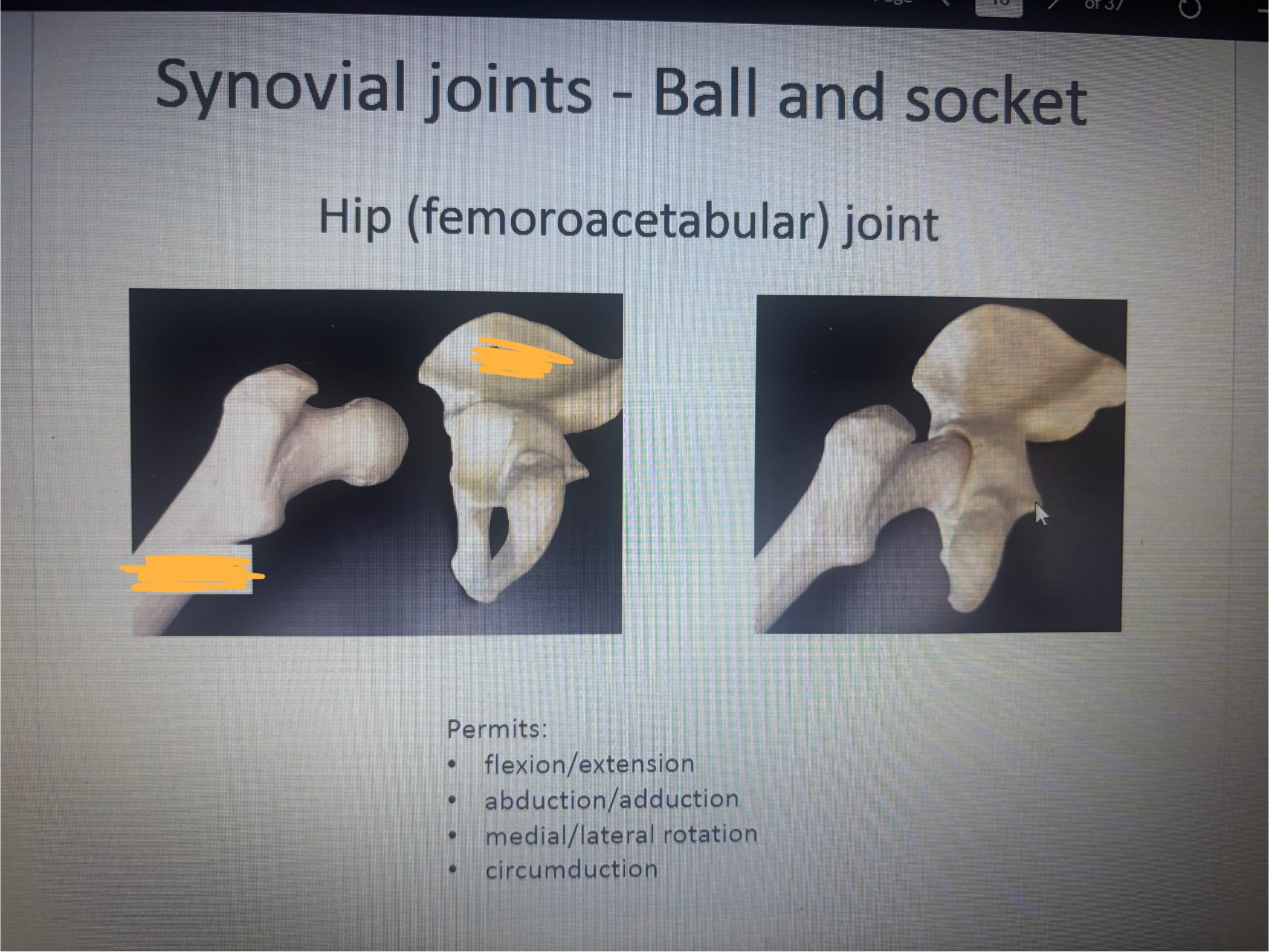
What is in the 2nd blank
Coxa hip femoroacetabular joint
The ball and socket hip femoracetabular joint permits
Permits:
flexion/extension
abduction/adduction
medial/lateral rotation
circumduction
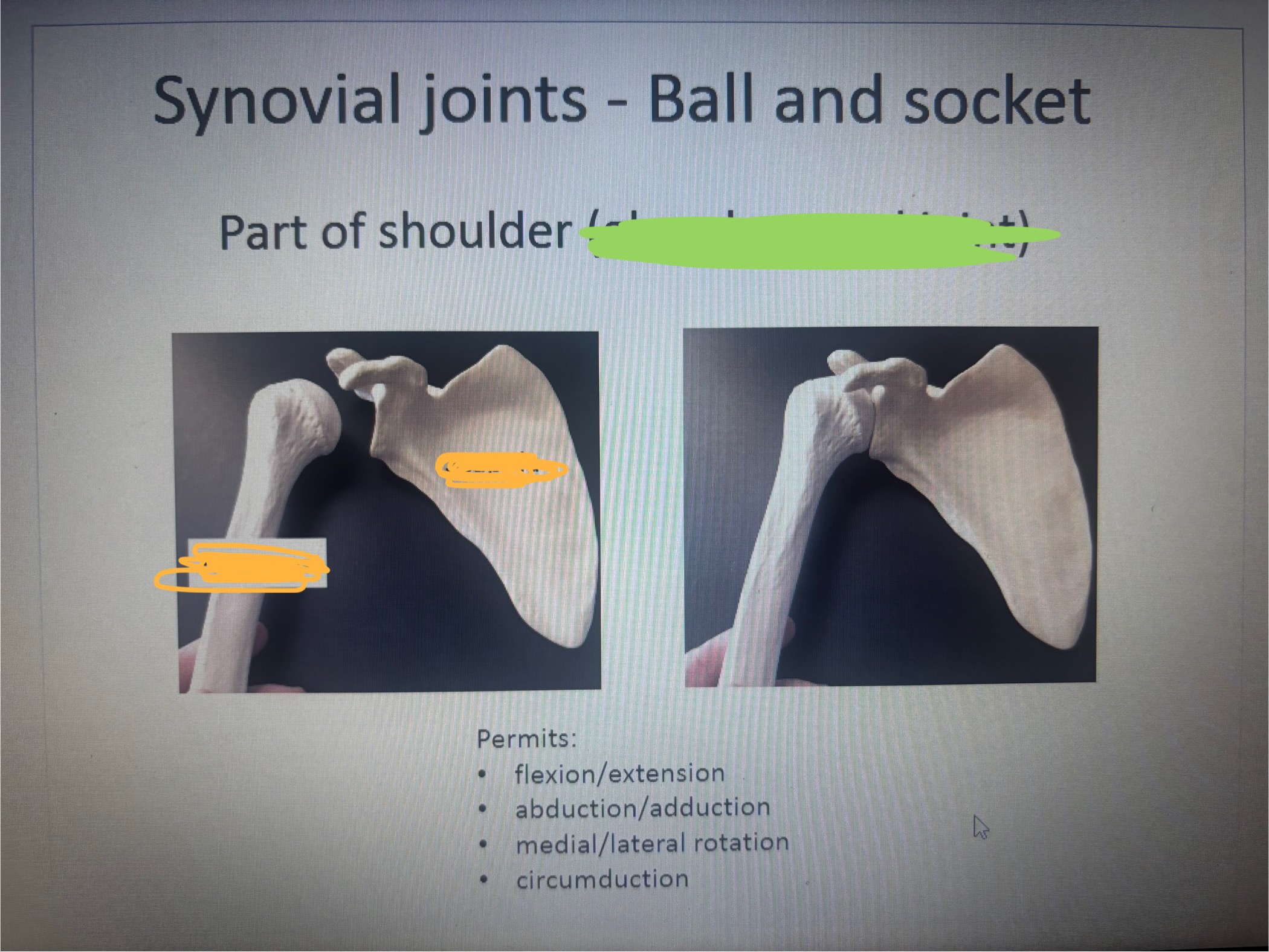
What is marked out in green
Glenohumeral joint
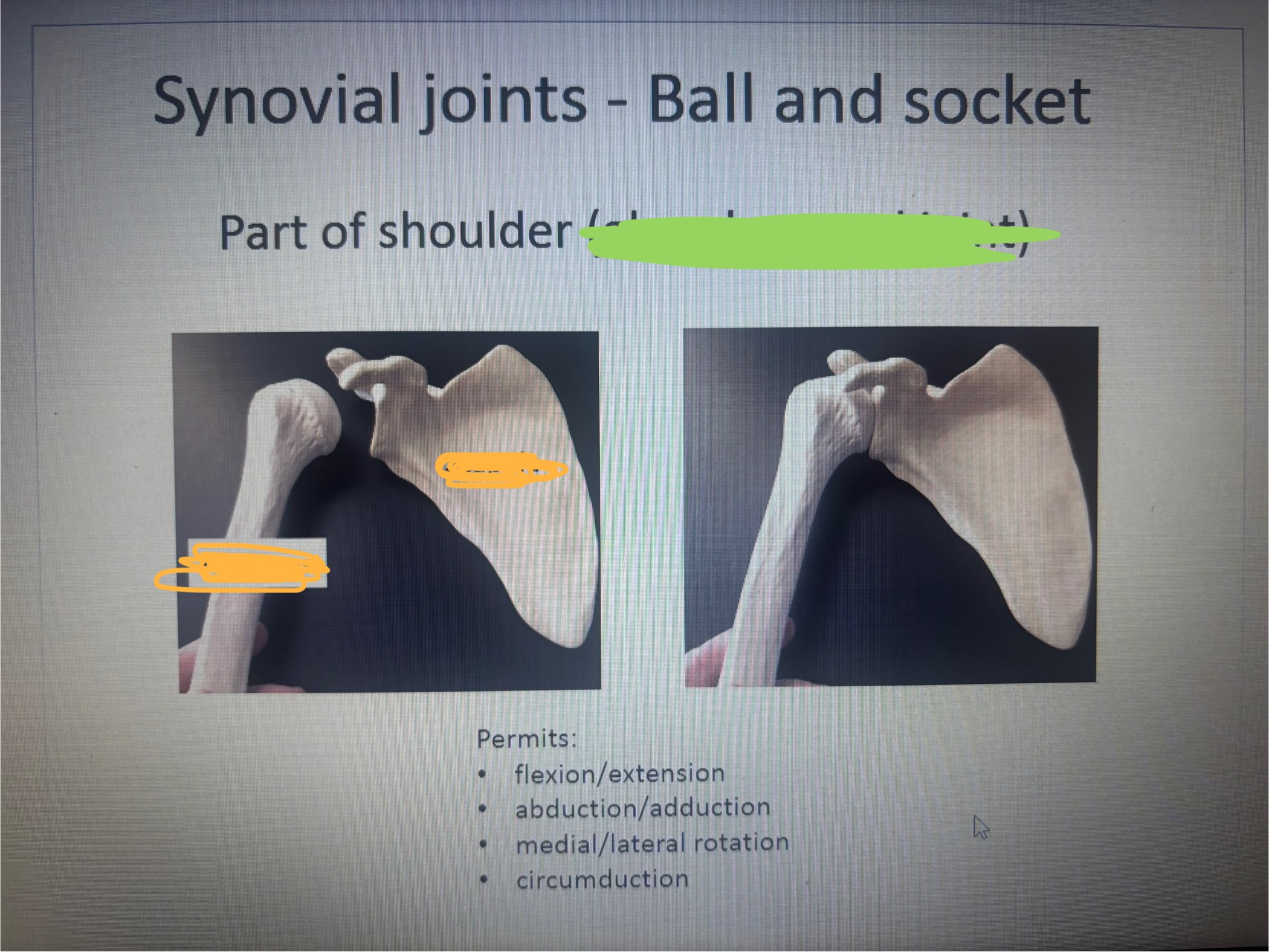
What is in the 1st blank
Humerus
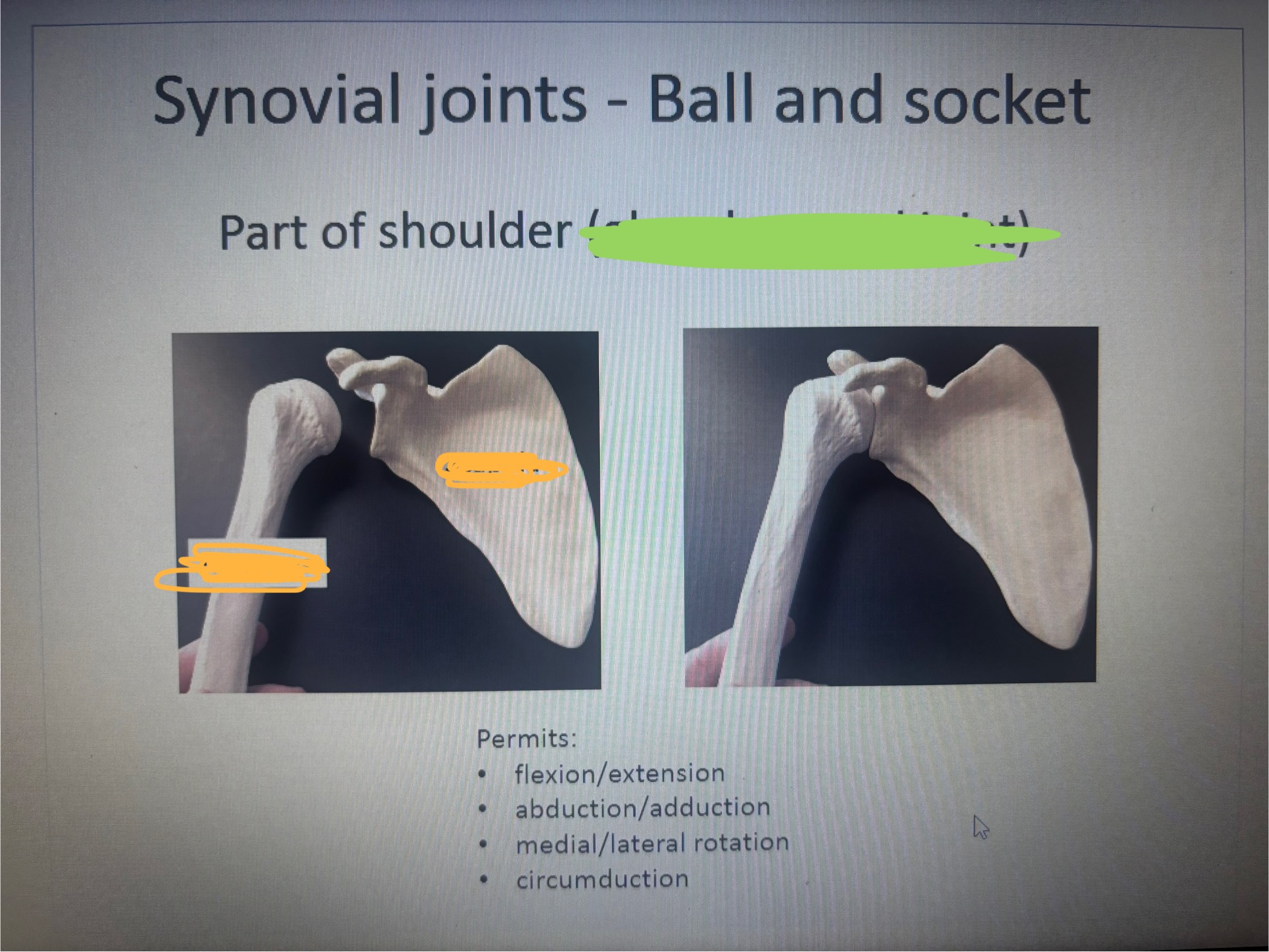
What is in the 2nd blank
Scapula
What movement does the part of shoulder (glenohumeral joint) allow
Permits:
flexion/extension
abduction/adduction
medial/lateral rotation
circumduction
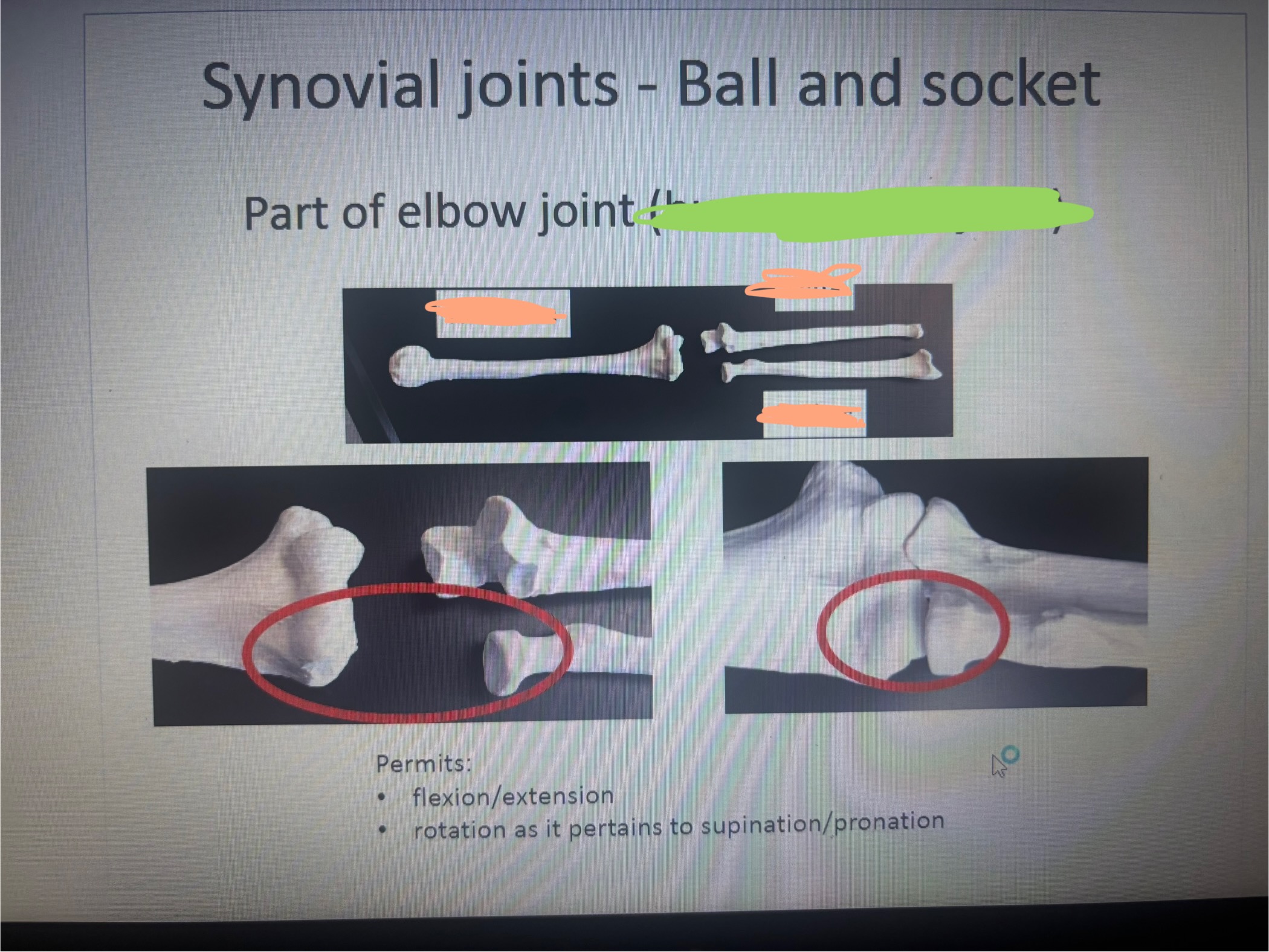
What is marked out in green humeroradial joint
humeroradial joint
What is the blank on the left?
Humerus
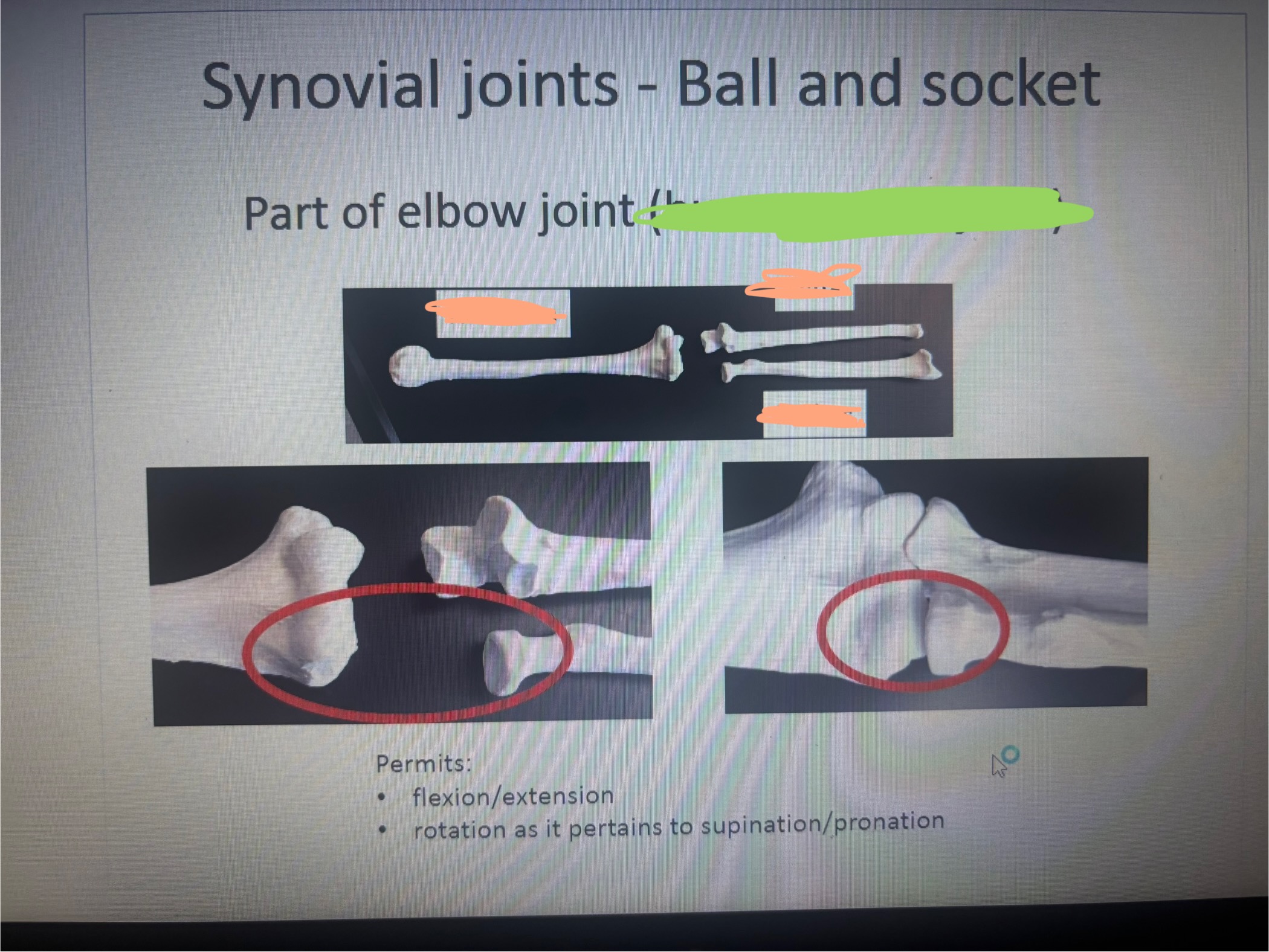
What is the blank on the top right?
Ulna?
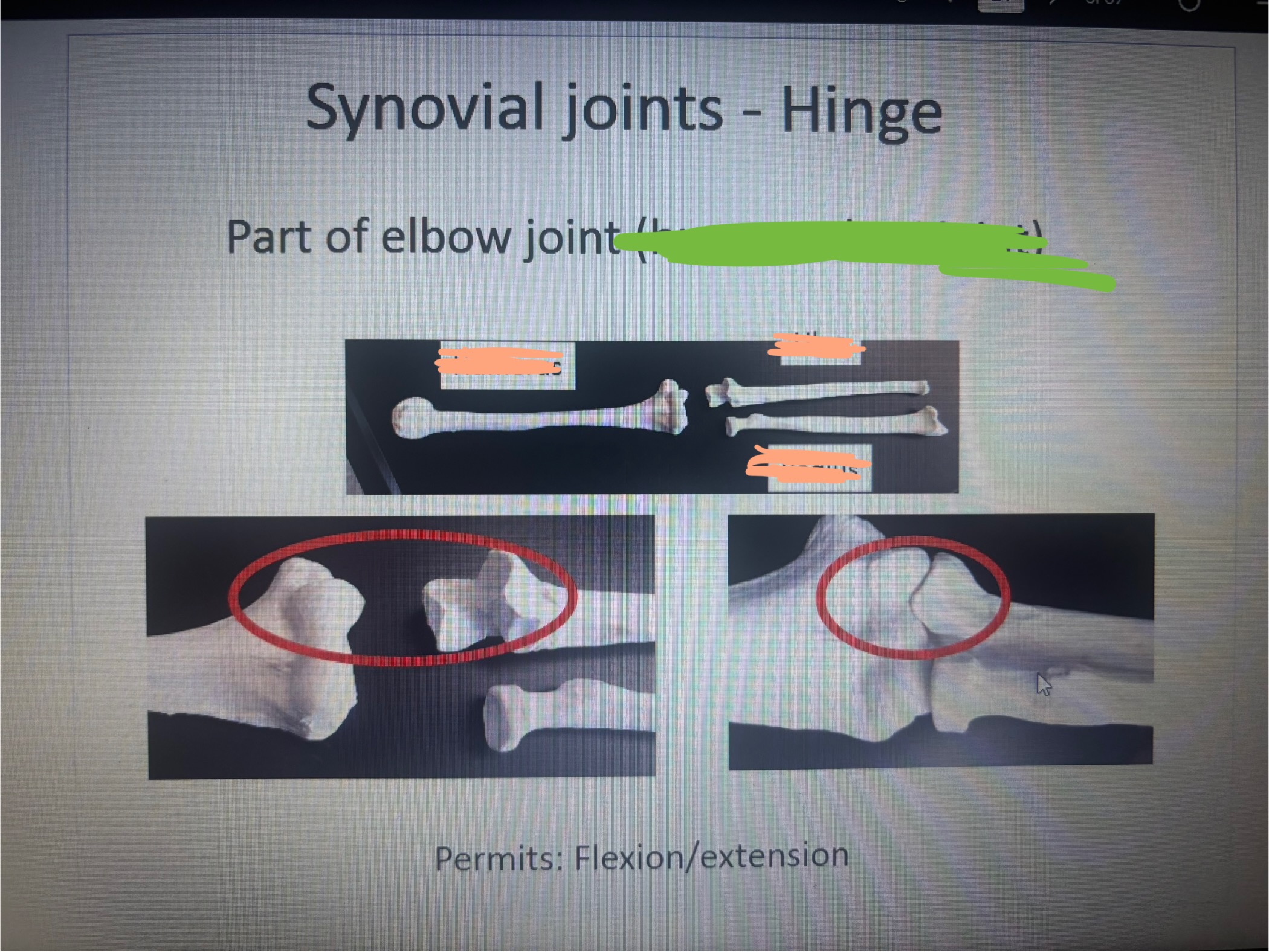
What is the blank on the bottom right
Radius
What movement does the humeroradial joint permit
Permits:
flexion/extension
rotation as it pertains to supination/pronation
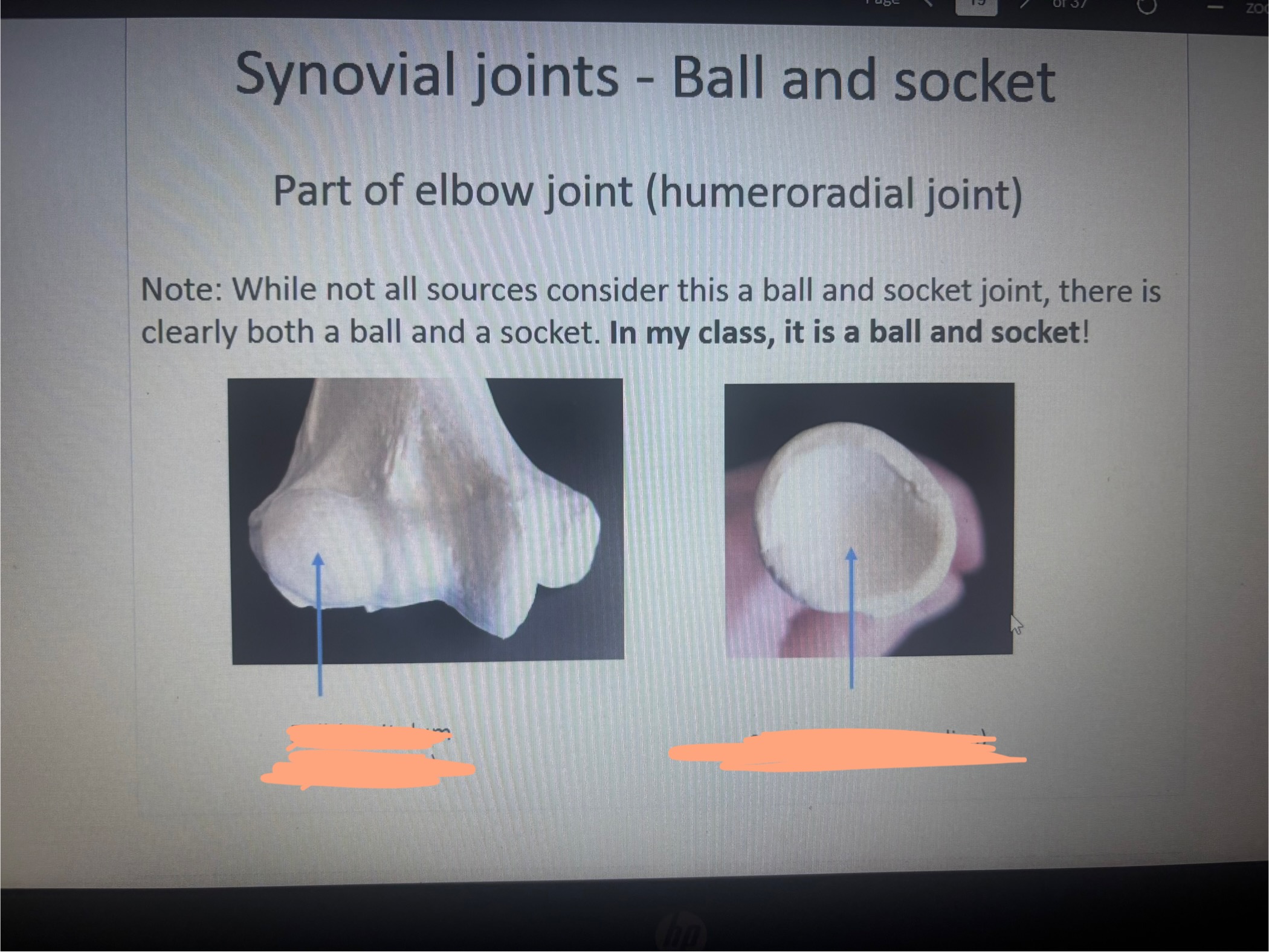
What is the 1st blank?
Ball (Capitulum of humerus)
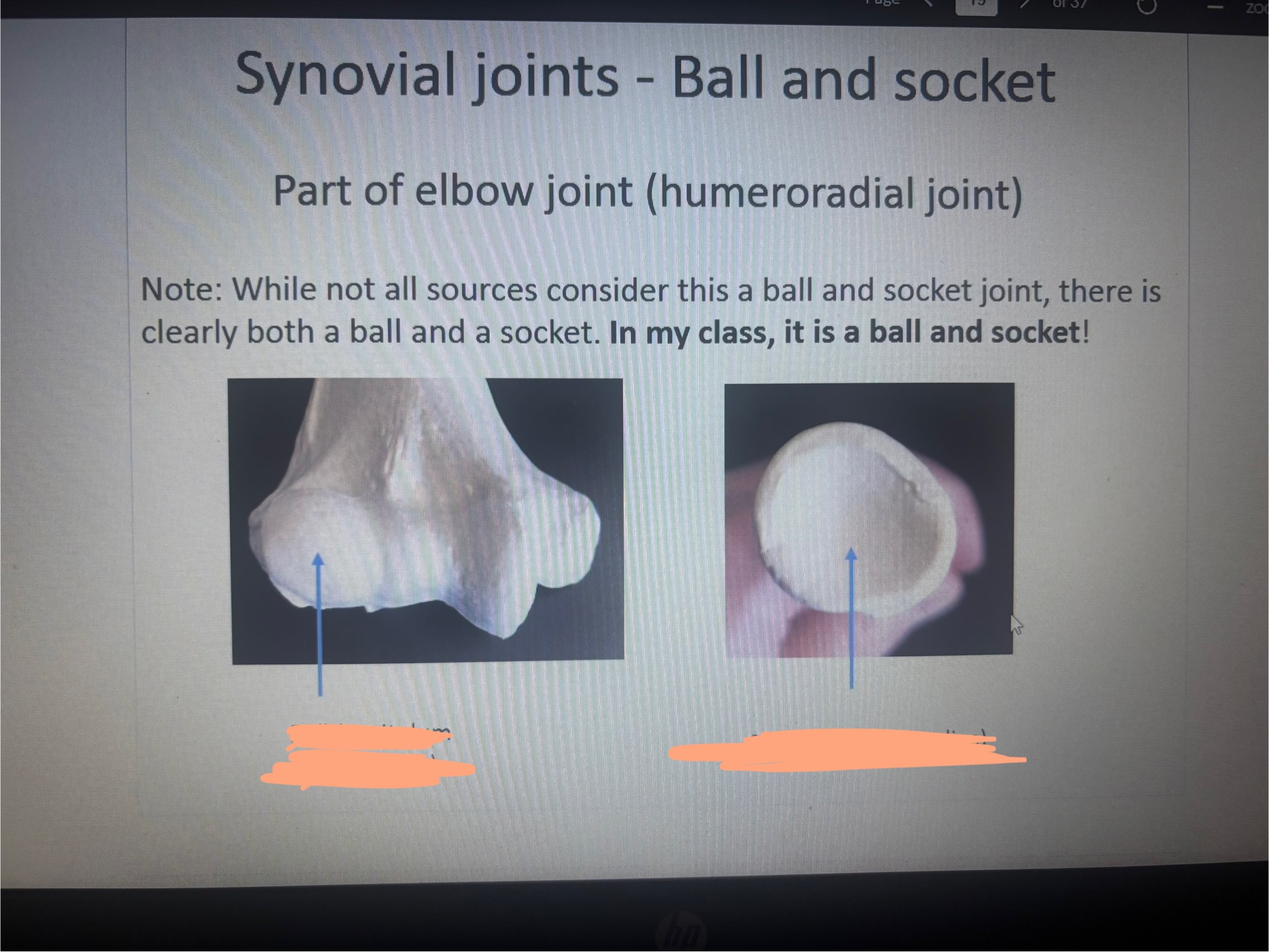
What is the 2nd blank?
Socket (head of radius)

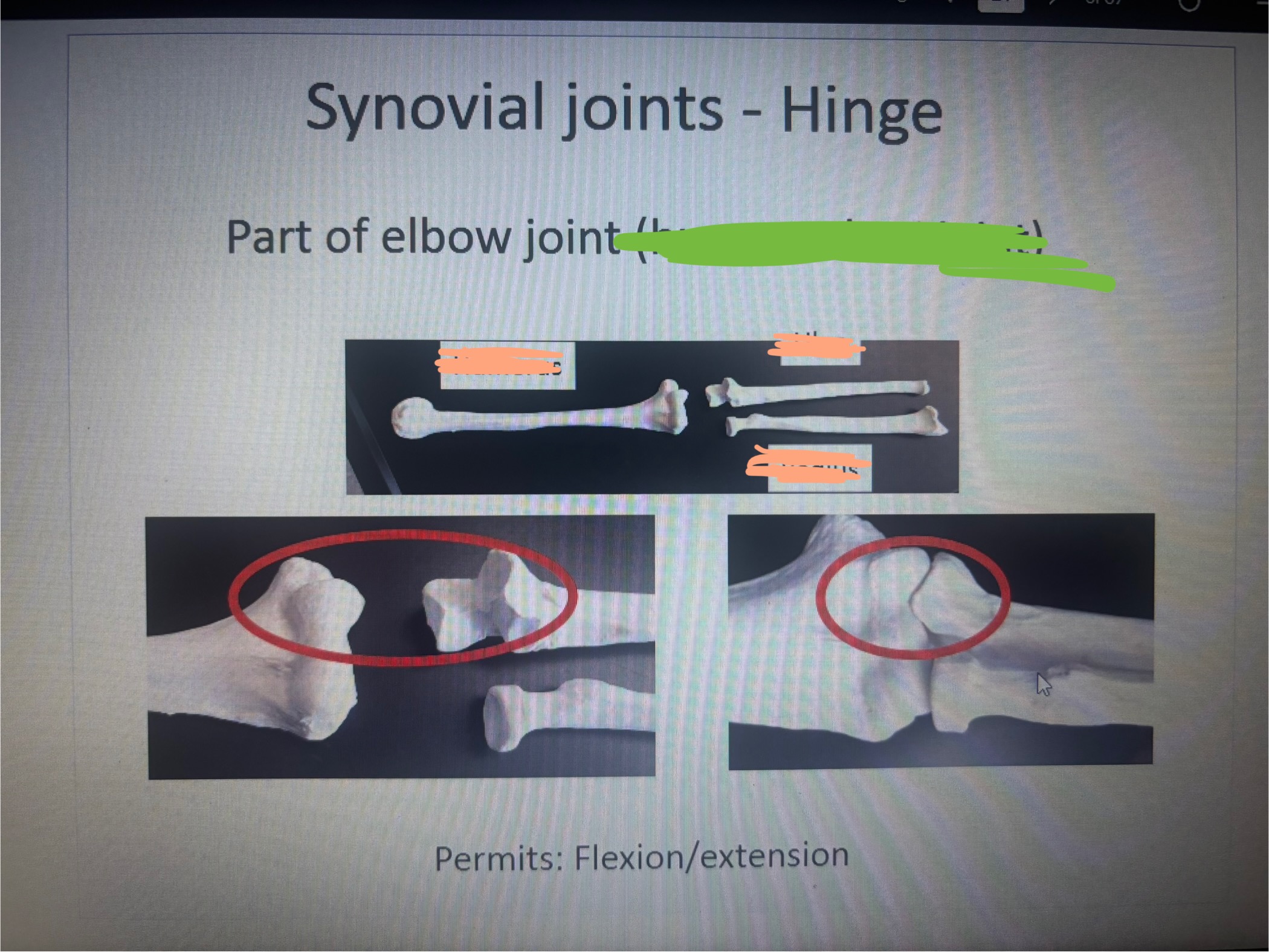
What is in the 1st blank
Trochlea (humerus)
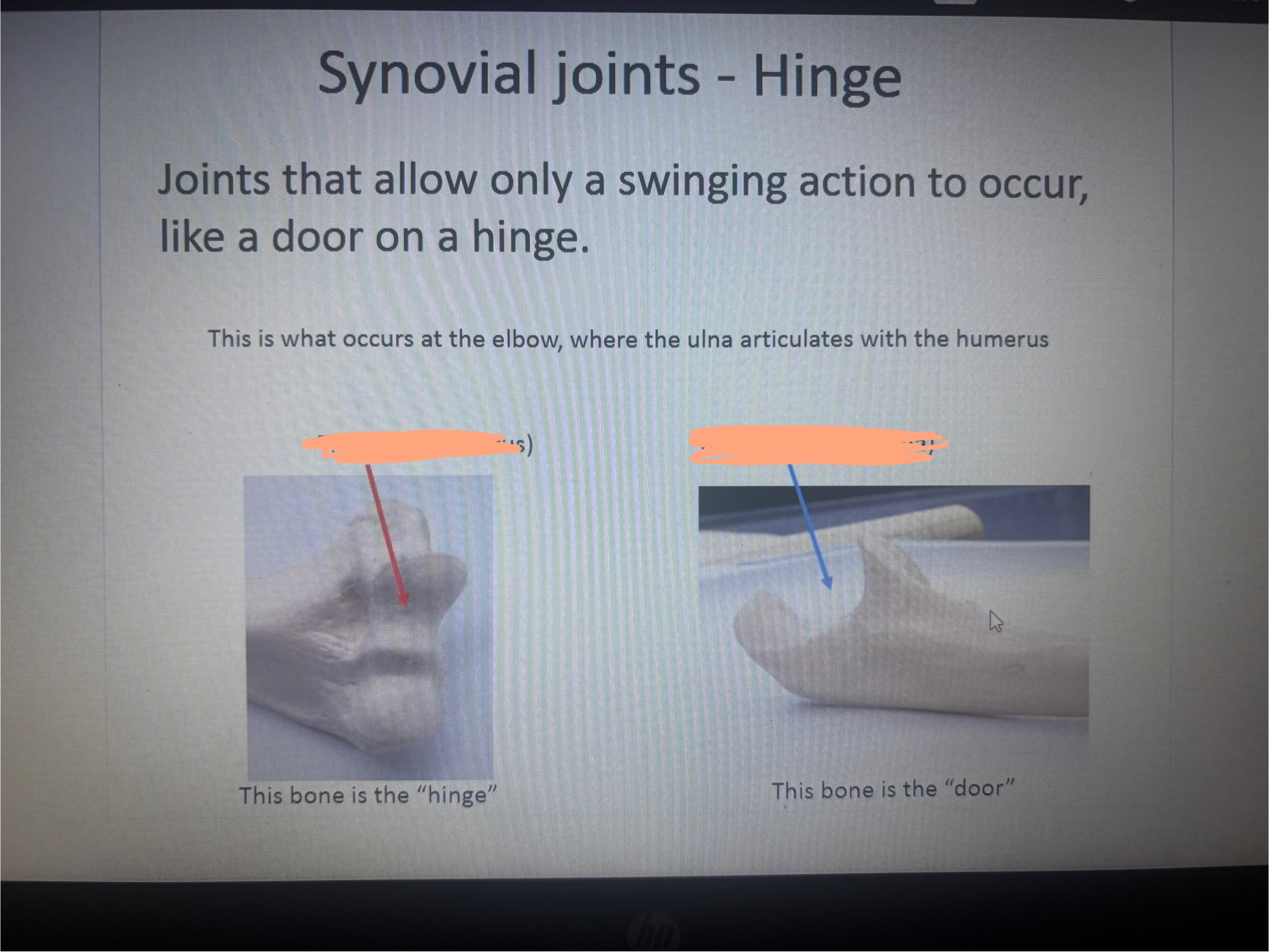
what is the 2nd blank
Trochlear notch (ulna)
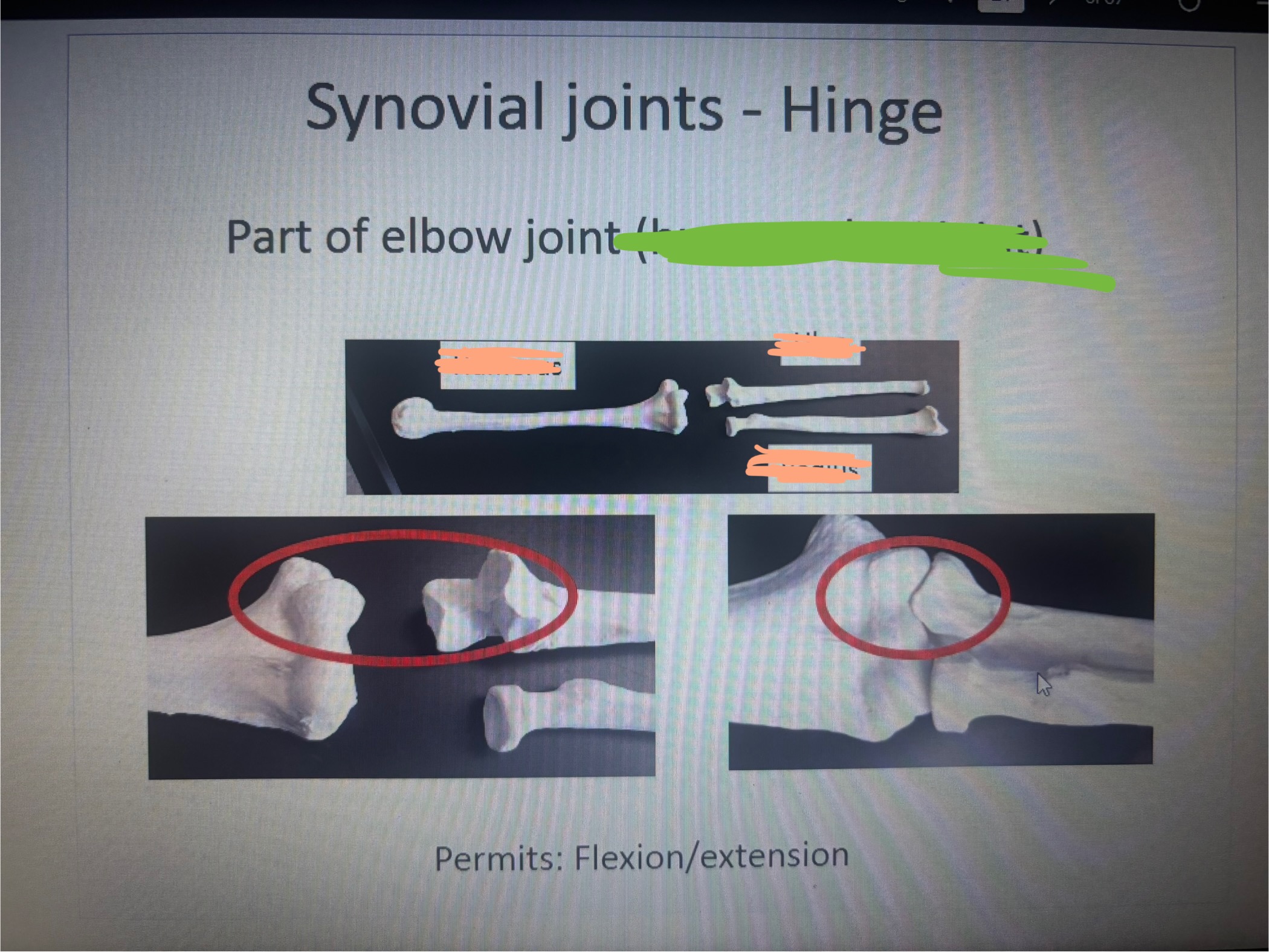
What is marked out?
Humerolunar joint
What movement does the humeroulnar permit
Flexion/ extension
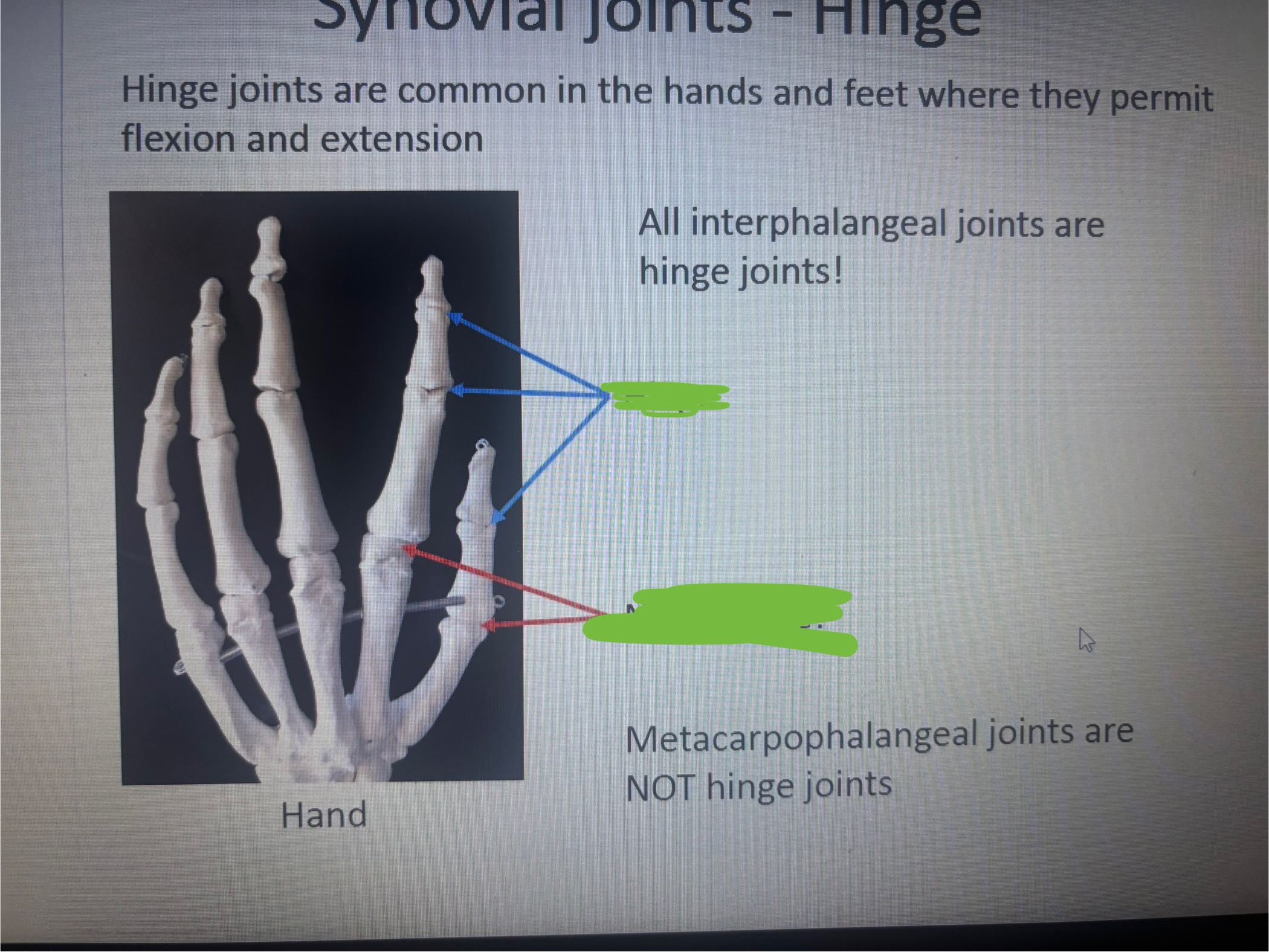
What is the 1st blank?
Hinge
What is the 2nd blank?
Not a hinge
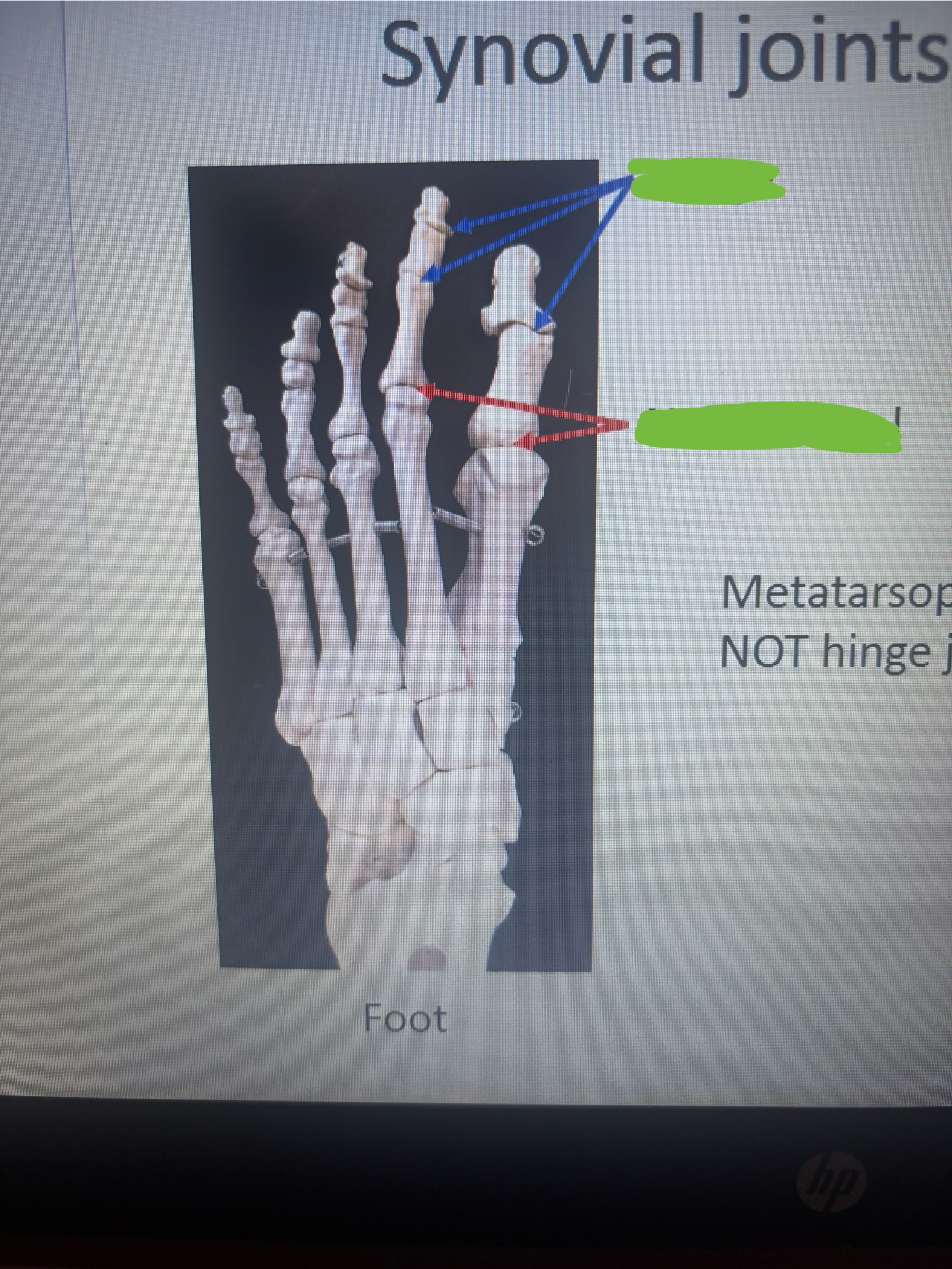
What is in the 1st blank?
Hinge
What is in the 2nd blank?
Not a hinge
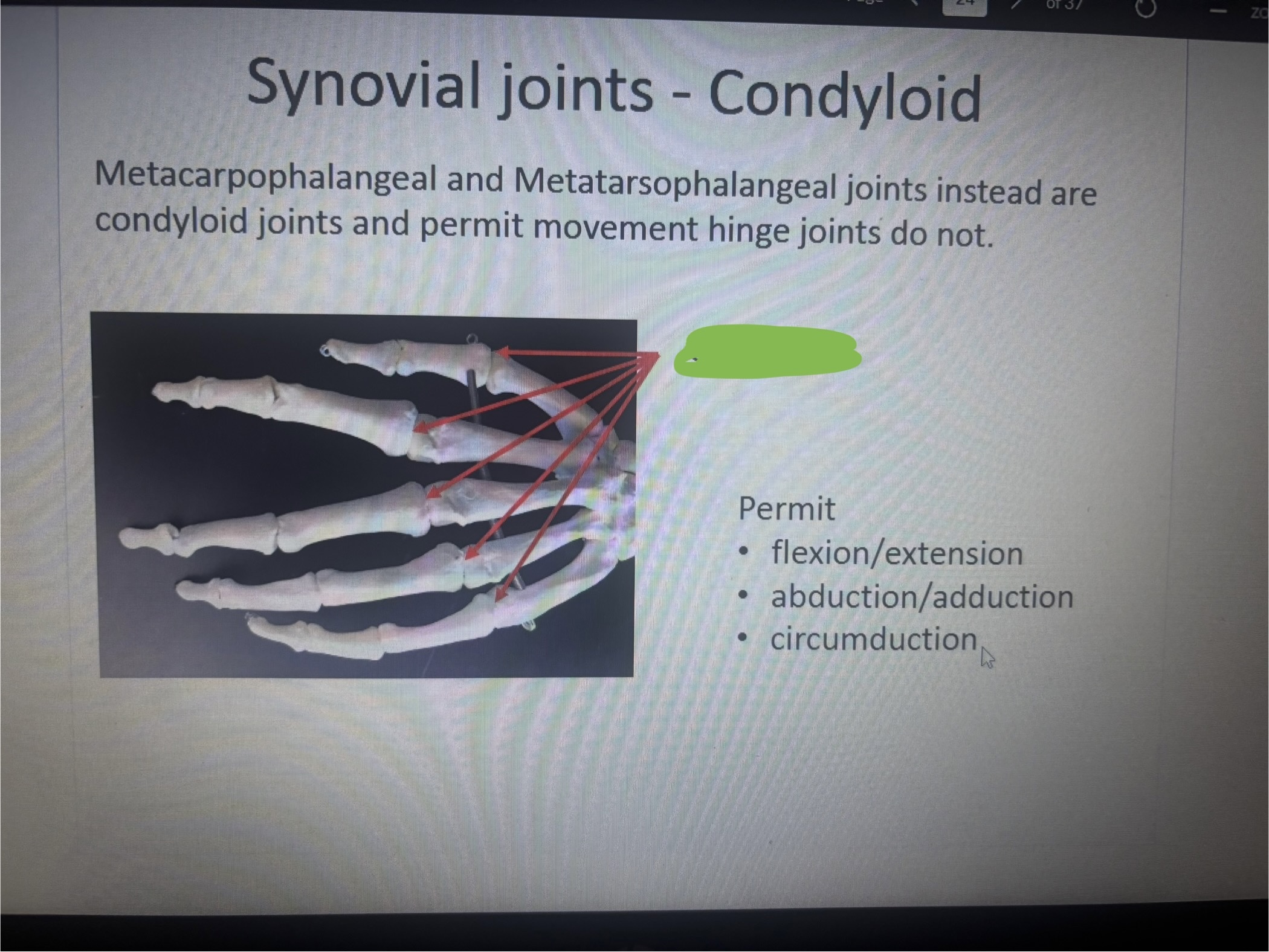
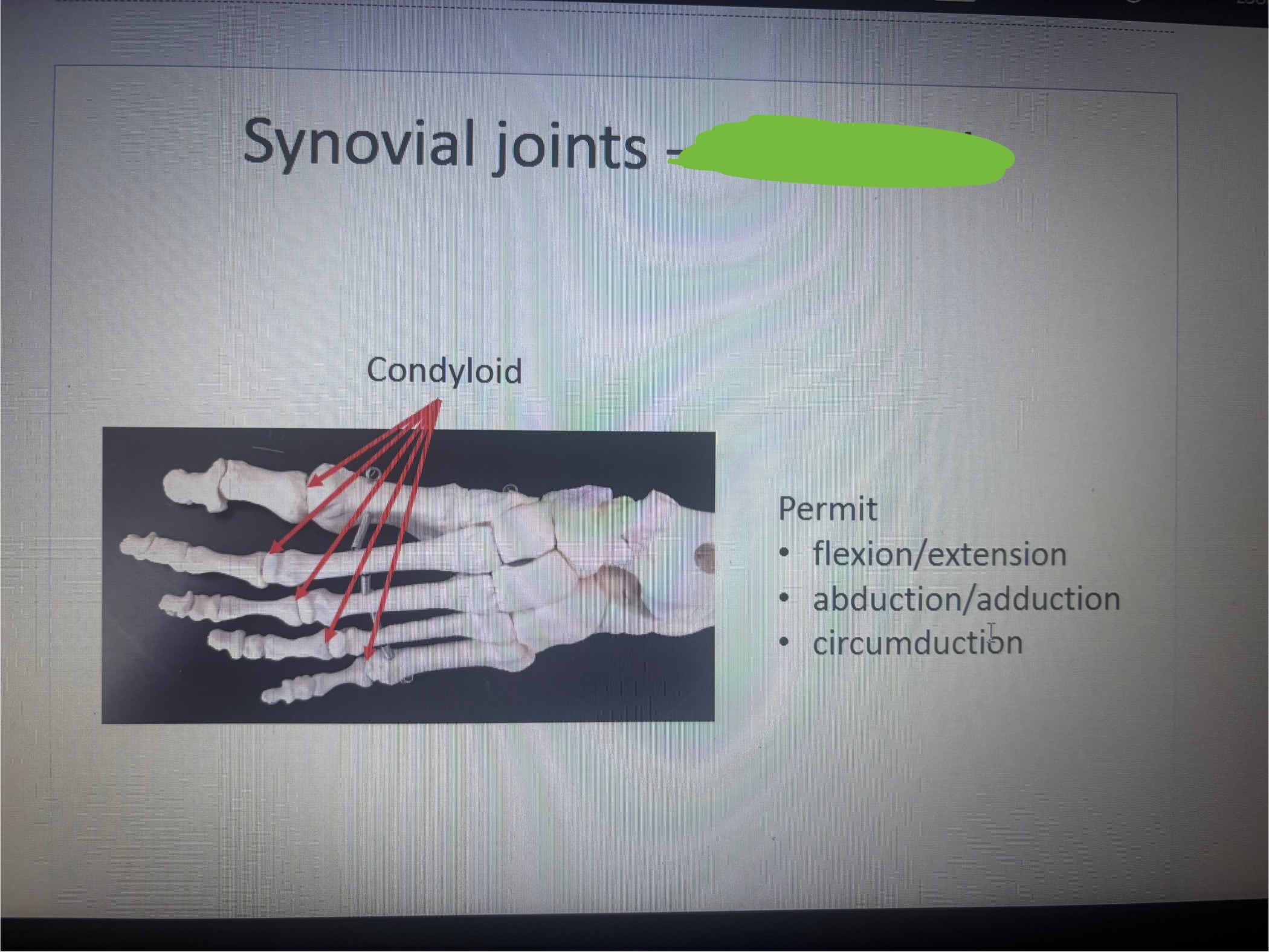
What is marked out
Condyloid
What movement does condyloid permit
Permit
• flexion/extension
• abduction/adduction
•
circumduction
What is marked out?
Condyloid
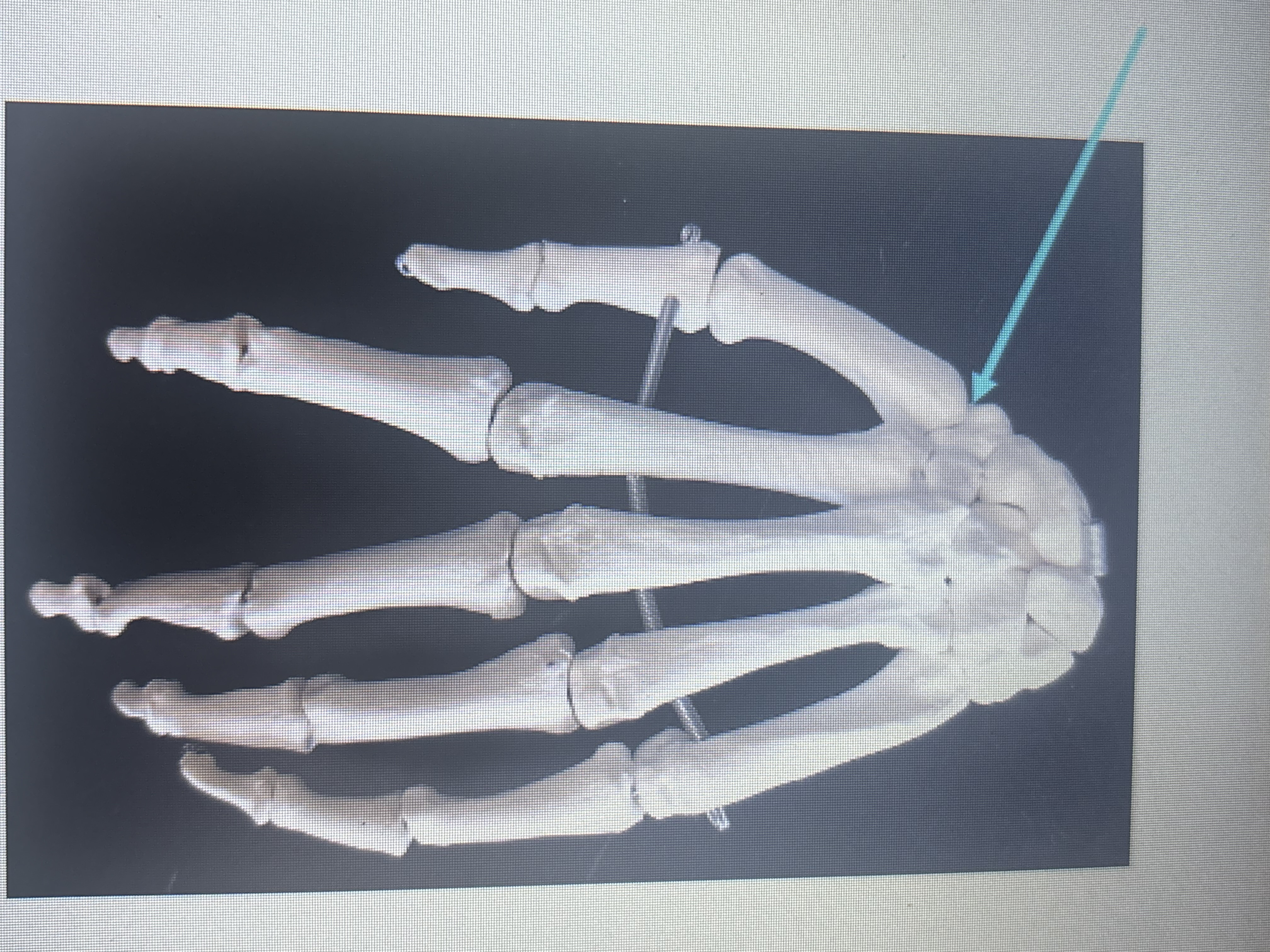
What is the arrow pointing at?
Saddle
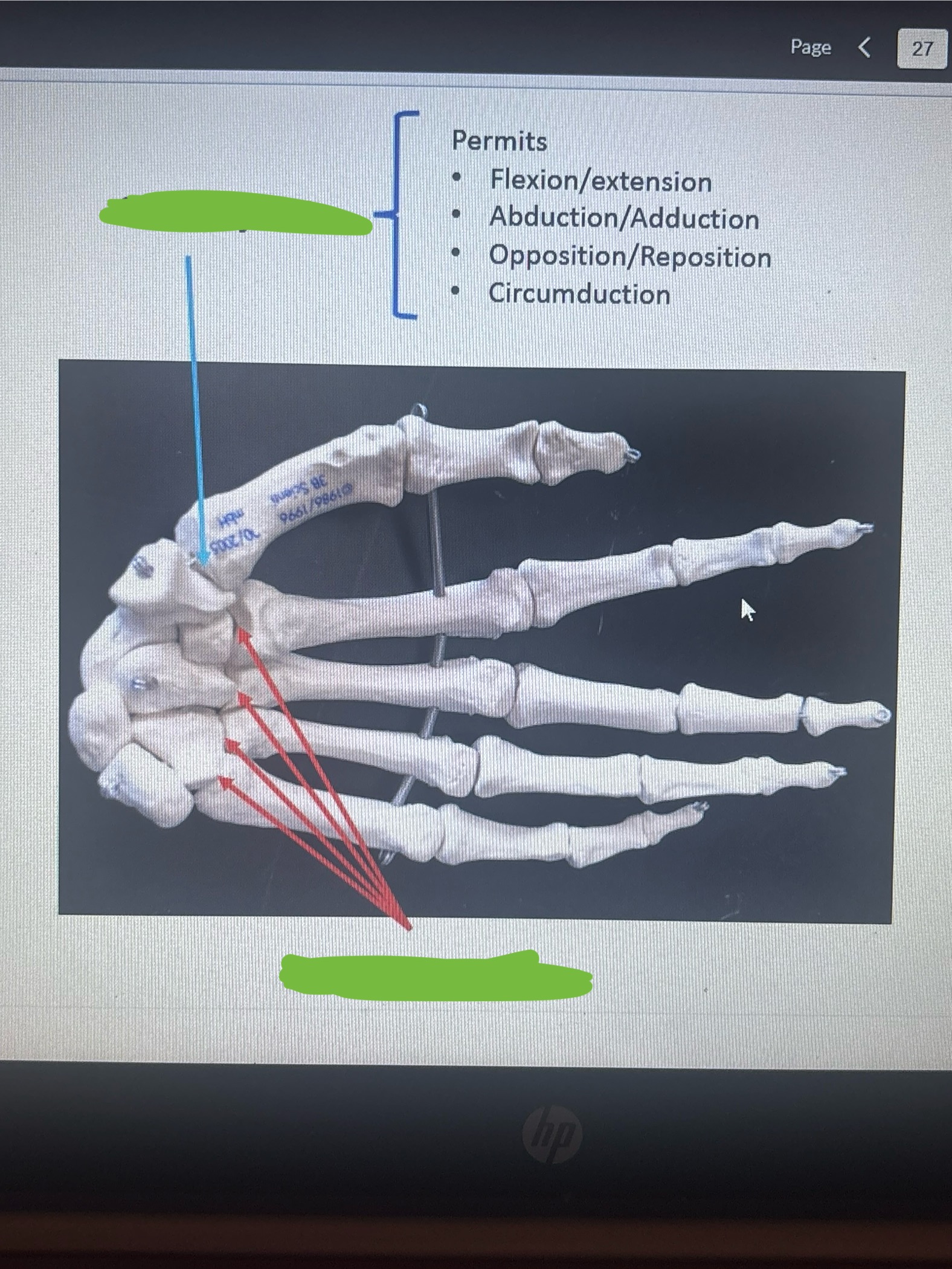
What is the top arrow pointing at?
Saddle joint
What are the bottom arrows pointing at?
Not saddle joints
What movement do saddle joints permit?
Permits
Flexion/extension
Abduction/Adduction
Opposition/Reposition
Circumduction
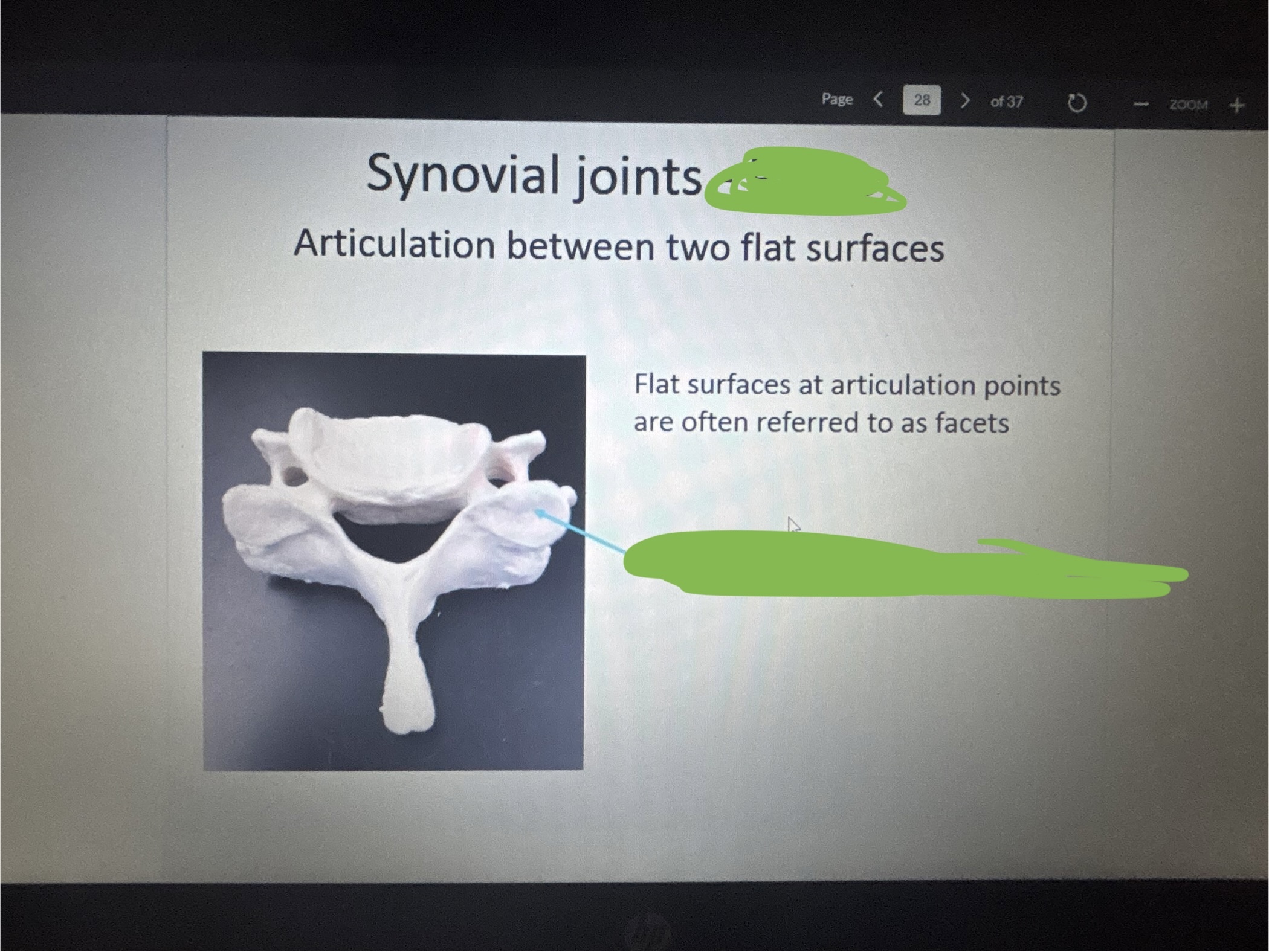
What is marked out on the top?
Plane
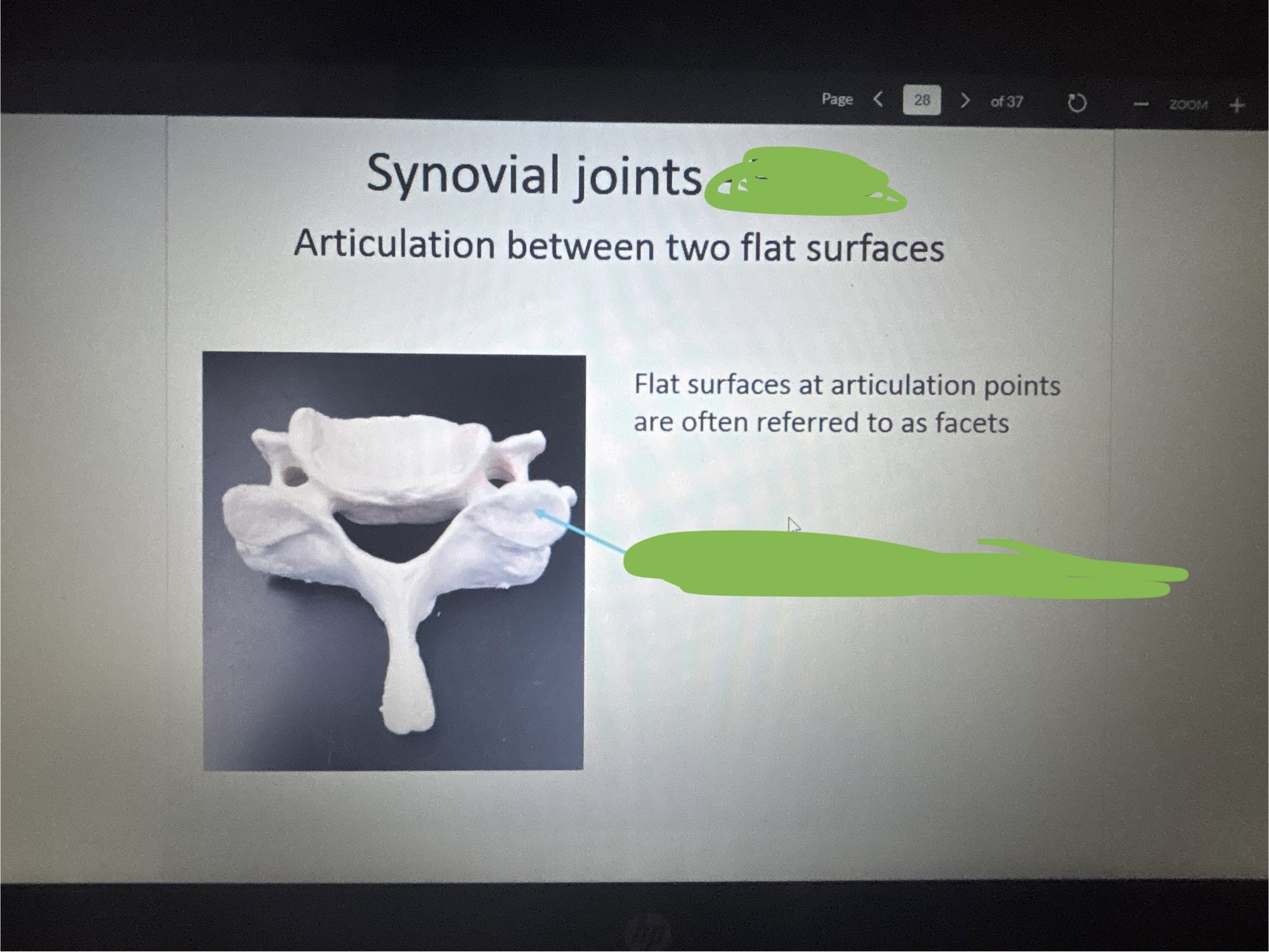
What is marked out on the bottom?
Superior articular facet
What is the arrow pointing at?
Plane joint