Proteins
1/7
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
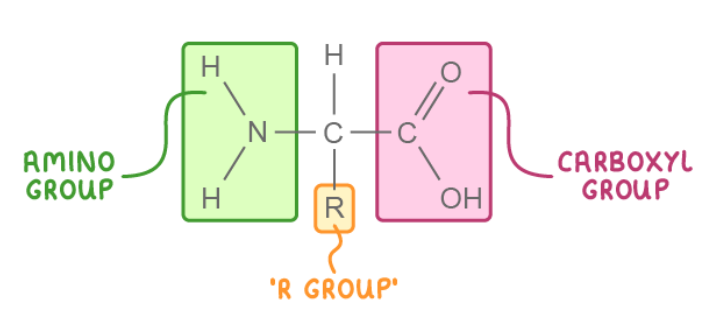
Draw an amino acid
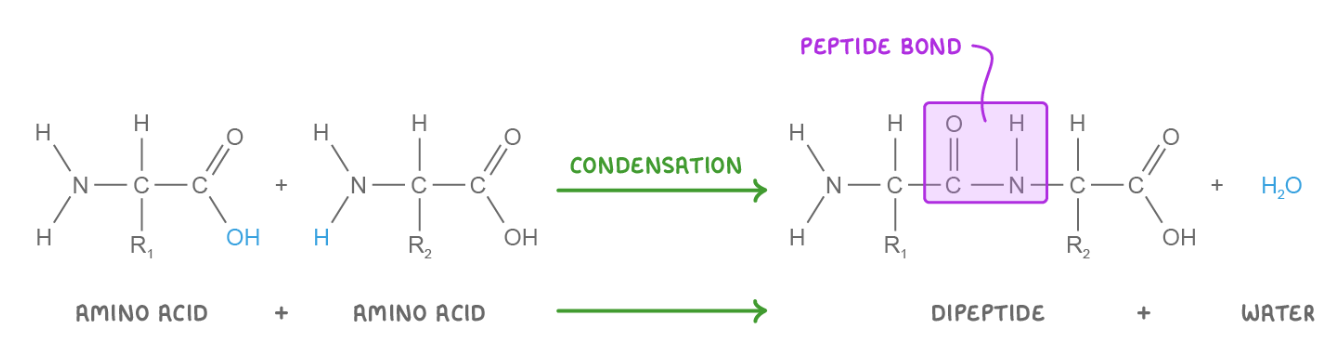
Describe the process of dipeptide condensation
When 2 amino acids join, the OH in the carboxyl group reacts with the H in the amine group of another amino acid. This releases water and forms a peptide bond (between the carbon of one amino acid and the nitrogen of another).
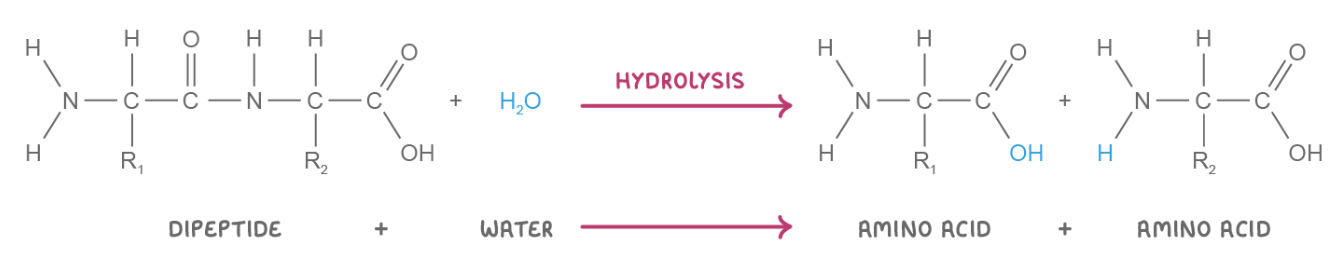
Describe the process of dipeptide hydrolysis
When a water molecule is added to a dipeptide, the peptide bond is broken, and 2 amino acids are released.
Test for proteins
Biuret test:
Add an equal volume of food sample and biuret solution to a test tube. Gently shake. If proteins are present, solution will turn from blue to lilac.
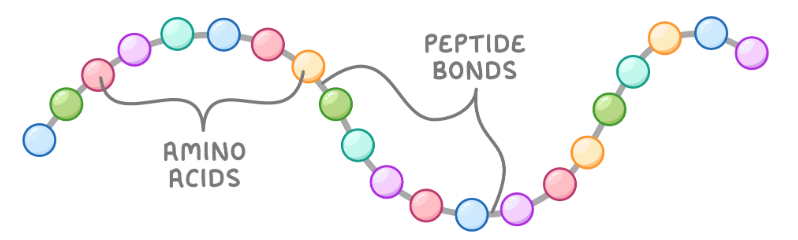
What is the primary structure of proteins?
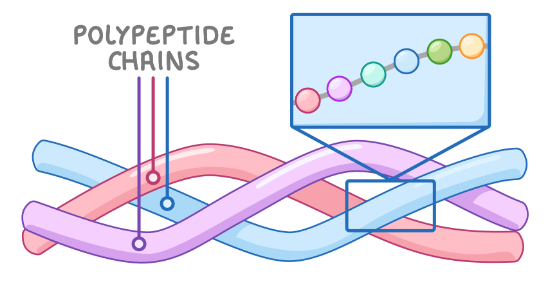
Primary structure is a sequence of amino acids in a chain, held together by peptide bonds.
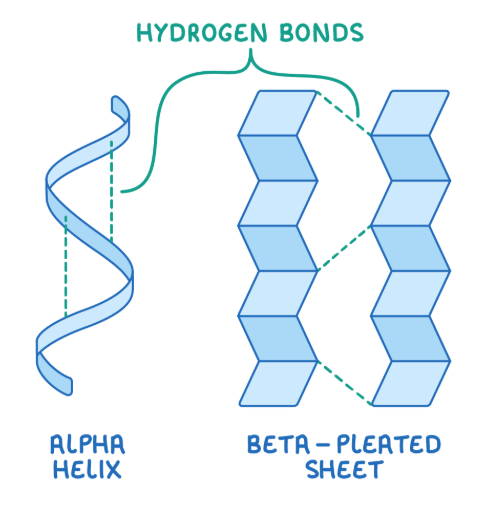
What is the secondary structure of proteins?
Secondary structure is when hydrogen bonds between the amino acids at different points on the chain cause the polypeptide chain to fold into either an alpha-helix, or a beta-pleated sheet.
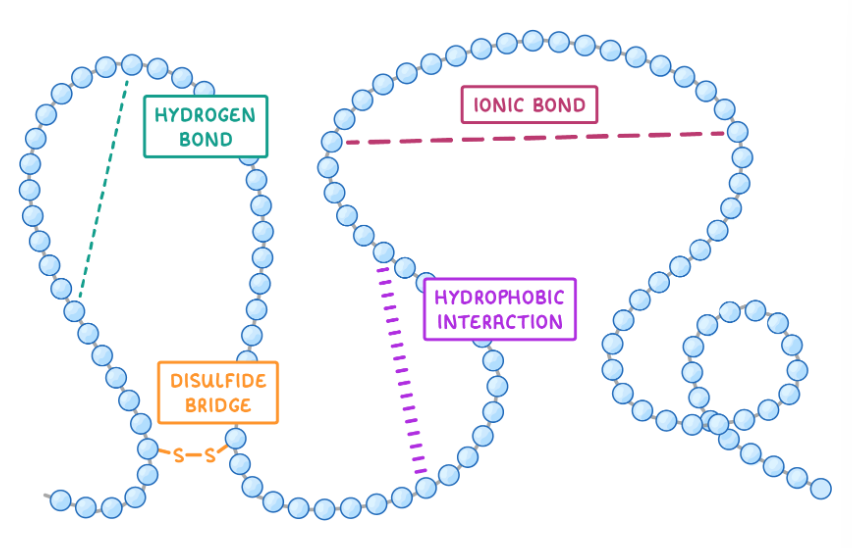
What is the tertiary structure of proteins?
Tertiary structure is when polypeptide chains fold further to create complex 3D structures. Held together with hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds (between R groups), disulphide bridges (very strong), and Van der Waal forces (hydrophobic and hydrophilic interactions between polar and non polar R groups).
What is the quaternary structure of proteins?
Quaternary structure involves 2 or more polypeptide chains held together with hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, disulphide bridges and hydrophobic and hydrophilic interactions.